Splenectomy in Onco-Hematologic Patients: A Retrospective Study of Early Complications and 1-Year Mortality
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
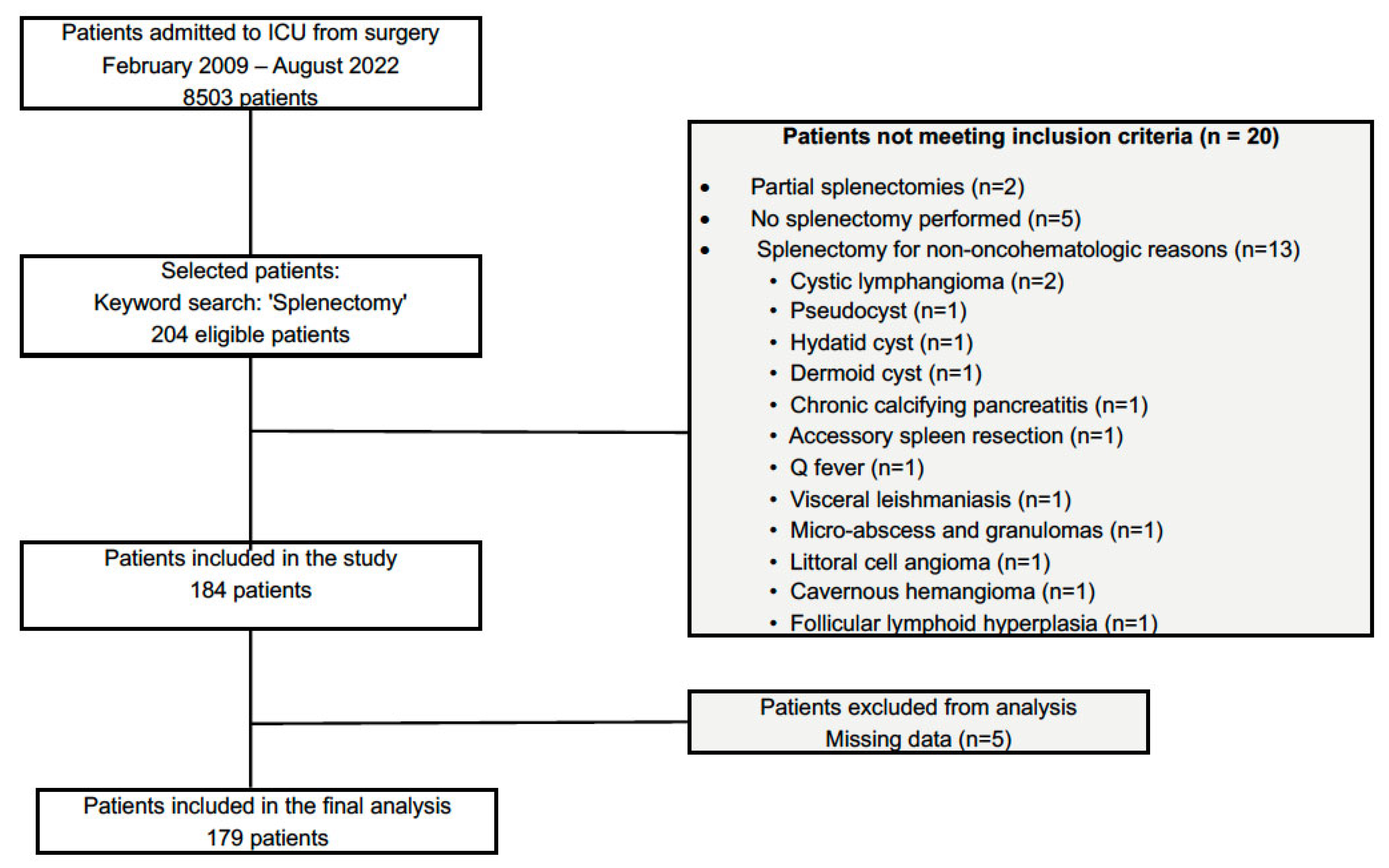
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics (Table 1)
| Patient Characteristics | Total Population (n = 179) | No Complication (n = 93) | Severe Complication (n = 86) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 64 [55–71] | 63 [54–71] | 65 [58–70] | 0.400 |
| Sex—Female | 100 (55.9) | 61 (65.6) | 39 (45.3) | 0.010 |
| Sex—Male | 79 (44.1) | 32 (34.4) | 47 (54.7) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.9 [21.7–27.1] | 23.6 [21.3–27.1] | 23.9 [22.3–27.1] | 0.284 |
| Obesity (BMI > 30) | 25 (14.0) | 13 (14.0) | 12 (14.0) | 1.000 |
| Weight loss | 69 (38.6) | 27 (29.0) | 42 (48.8) | 0.010 |
| ASA score > 2 | 62 (34.6) | 23 (24.7) | 39 (45.3) | 0.006 |
| MET < 4 | 14 (7.8) | 1 (1.1) | 13 (15.1) | 0.001 |
| ECOG-PS > 1 | 26 (14.5) | 7 (7.5) | 19 (22.1) | 0.011 |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index | 5 [3–7] | 6 [4–8] | 5 [3–7] | 0.106 |
| Solid vs. Hematology Cancer | 103 (57.5) | 57 (61.3) | 46 (53.5) | 0.366 |
| Pancreas | 31 (17.3) | 12 (12.9) | 19 (22.1) | 0.154 |
| Ovarian | 24 (13.4) | 17 (18.3) | 7 (8.1) | 0.077 |
| Uterus | 11 (6.1) | 7 (7.5) | 4 (4.7) | 0.625 |
| Gastric | 11 (6.1) | 6 (6.5) | 5 (5.8) | 1.000 |
| Colon | 7 (3.9) | 4 (4.3) | 3 (3.5) | 1.000 |
| Peritoneal disease | 8 (4.5) | 4 (4.3) | 4 (4.7) | 1.000 |
| Other solid | 15 (8.4) | 7 (7.5) | 8 (9.3) | 0.874 |
| Lymphomas | 48 (26.8) | 28 (30.1) | 20 (23.3) | 0.301 |
| Leukemias | 13 (7.3) | 4 (4.3) | 9 (10.5) | 0.112 |
| Myelofibrosis | 17 (9.5) | 5 (4.4) | 12 (14.0) | 0.051 |
| Preoperative Anticancer Treatments | ||||
| Chemotherapy | 109 (60.9) | 58 (62.4) | 51 (59.3) | 0.790 |
| Radiotherapy | 15 (8.4) | 9 (9.7) | 6 (7.0) | 0.703 |
| Corticosteroids | 25 (14.0) | 7 (7.5) | 18 (20.9) | 0.018 |
| Preoperative hemoglobin (g/dL) | 11.8 [10.0–13.0] | 12.0 [10.6–13.0] | 11.0 [9.3–12.6] | 0.010 |
| Splenomegaly | 96 (53.6) | 44 (47.3) | 52 (60.5) | 0.107 |
| Spleen length (cm) | 13 [11–23] | 12 [11–18] | 14 [11–25] | 0.051 |
| Antibiotic prophylaxis | 175 (97.8) | 93 (100.0) | 82 (95.3) | 0.107 |
| Penicillins | 161 (90.0) | 84 (90.3) | 77 (95.1) | 0.370 |
| Others | 14 (8.4) | 10 (10.8) | 4 (4.9) | 0.260 |
| Vaccination | 165 (92.2) | 92 (98.9) | 73 (84.9) | 0.012 |
| Intraoperative Period | ||||
| Laparotomy | 154 (86.0) | 75 (80.6) | 79 (91.9) | 0.052 |
| Laparoscopy | 37 (20.7) | 24 (25.8) | 13 (15.1) | 0.114 |
| Elective surgery | 162 (90.5) | 93 (100.0) | 69 (80.2) | <0.001 |
| Emergency surgery | 17 (9.5) | 0 (0.0) | 17 (19.8) | <0.001 |
| Metastasectomy | 54 (30.2) | 39 (41.9) | 15 (17.4) | 0.001 |
| Surgical Indication | ||||
| Invasion | 42 (23.5) | 19 (20.4) | 23 (26.7) | 0.388 |
| Symptomatic splenomegaly | 40 (22.4) | 16 (17.2) | 24 (27.9) | 0.124 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 38 (21.2) | 18 (19.4) | 20 (23.3) | 0.649 |
| Diagnosis | 30 (16.8) | 13 (14.0) | 17 (19.8) | 0.403 |
| Bleeding | 18 (10.1) | 5 (5.4) | 13 (15.1) | 0.052 |
| Duration of surgery (hours) | 3.5 [2.4–5.5] | 3.4 [2.6–5.5] | 4.0 [2.1–5.8] | 0.932 |
| Use of vasopressors | 37 (20.7) | 11 (11.8) | 26 (30.2) | 0.003 |
| Blood loss (mL) | 300 [150–675] | 300 [100–500] | 400 [200–850] | 0.013 |
3.2. Causal Disease Leading to Splenectomy (Table 1)
3.3. Intraoperative Period (Table 1)
3.4. Postoperative Period (Table 2)
| Outcomes | Total Population (n = 179) | No Complication (n = 93) | Severe Complication (n = 86) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Postoperative Period | ||||
| SAPS II score | 27 [21–35] | 26 [21–30] | 30 [23–39] | 0.003 |
| SOFA at ICU admission | 2 [1–5] | 1 [1–2] | 3 [2–7] | <0.001 |
| Surgical complications | 68 (38.0) | 21 (22.6) | 47 (54.7) | <0.001 |
| Clavien–Dindo grade > 2 | 44 (24.6) | 0 (0.0) | 44 (51.2) | <0.001 |
| Reoperation | 23 (12.9) | 0 (0.0) | 23 (26.7) | <0.001 |
| Medical complications | 96 (53.6) | 29 (31.2) | 67 (77.9) | <0.001 |
| Sepsis at day 30 | 54 (30.2) | 0 (0.0) | 54 (62.8) | <0.001 |
| Sepsis at day 90 | 71 (39.7) | 0 (0.0) | 71 (82.6) | <0.001 |
| Thromboembolic event at Day 90 | 12 (6.7) | 0 (0.0) | 12 (15.6) | 0.001 |
| DVT | 7 (3.9) | 0 (0.0) | 7 (9.1) | 0.020 |
| PE | 4 (2.2) | 0 (0.0) | 4 (5.2) | 0.086 |
| Myocardial infarction | 2 (1.1) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (2.6) | 0.395 |
| Stroke | 1 (0.6) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.3) | 0.924 |
| Arterial thrombosis | 1 (0.6) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.3) | 0.924 |
| Preventive anticoagulation | 140 (78.2) | 78 (90.7) | 62 (84.9) | 0.383 |
| Organ Failure at Day 90 | ||||
| Vasopressors | 24 (13.4) | 0 (0.0) | 24 (27.9) | <0.001 |
| Renal replacement therapy | 8 (4.5) | 0 (0.0) | 8 (9.3) | 0.015 |
| O2 > 5 L/min | 21 (11.7) | 0 (0.0) | 21 (24.4) | <0.001 |
| High-flow oxygen | 9 (5.0) | 0 (0.0) | 9 (10.5) | 0.008 |
| Non-invasive ventilation | 11 (6.1) | 0 (0.0) | 11 (12.8) | 0.001 |
| Invasive mechanical ventilation | 12 (6.7) | 0 (0.0) | 12 (14.0) | 0.001 |
| Time to severe complication (days) | 2 [0–12] | NA | 2 [0–12] | NA |
| IMC/ICU length of stay (days) | 5 [3–7] | 3 [0–5] | 6 [3–8] | <0.001 |
| Hospital length of stay (days) | 11 [8–16] | 9 [7–12] | 16 [11–26] | <0.001 |
| Death at day 90 | 12 (6.7) | 0 (0.0) | 12 (14.0) | 0.001 |
3.5. Prophylaxis and Supportive Care (Table 2)
3.6. Sepsis and Microbiological Documentation (Table 2)
3.7. Organ Failures by Day 90 (Table 2)
3.8. Thromboembolic Events (Table 2)
3.9. 30- and 90-Day Mortality (Table 2)
3.10. Major Complications at Day 90 (Table 2)
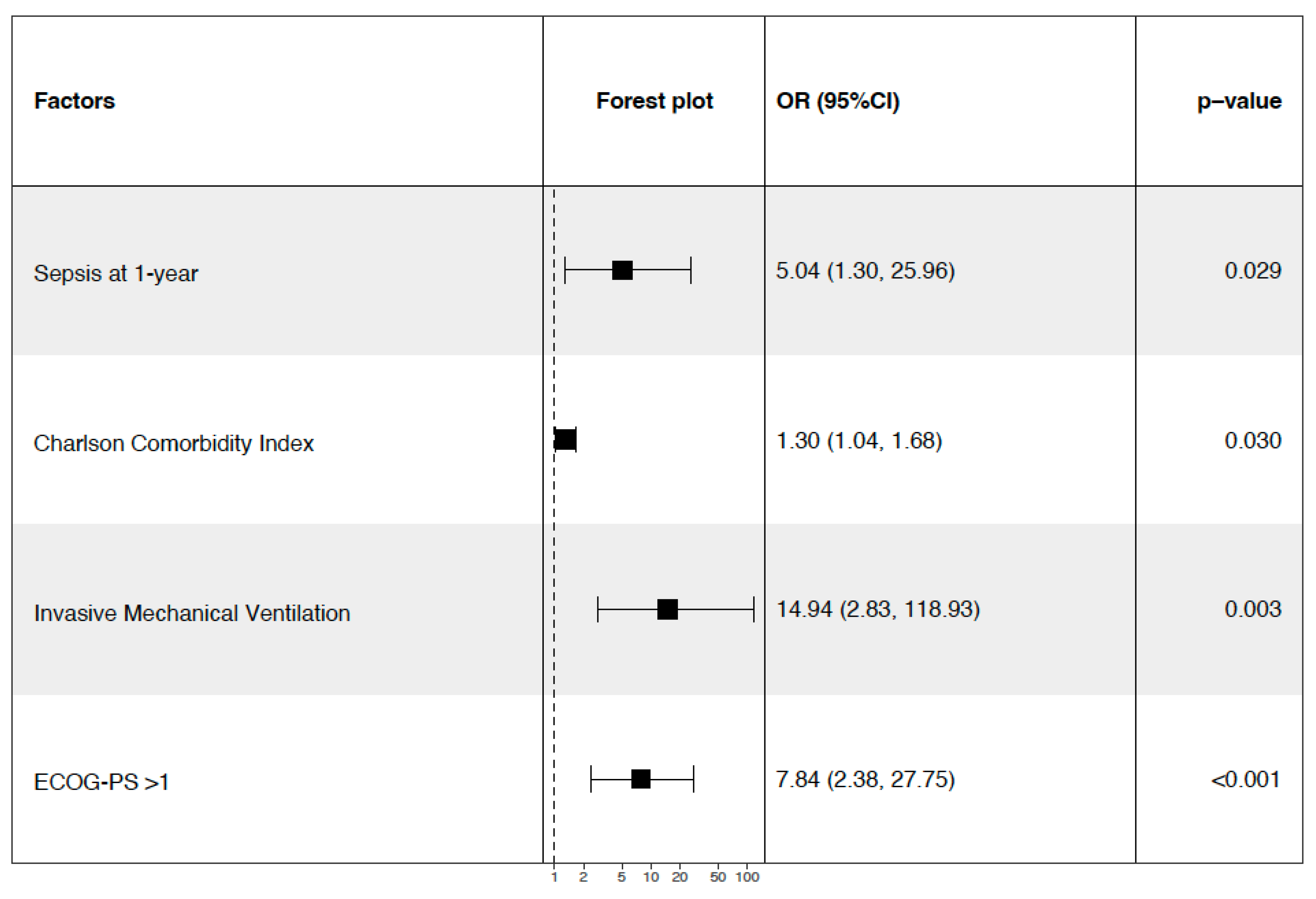
3.11. 1-Year Mortality and Follow-Up (Table 3)
| Patient Characteristics | Total Population (n = 179) | Alive at 1 Year (n = 139) | Death at 1 Year (n = 40) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 64 [55–71] | 64 [55–70] | 66 [59–73] | 0.077 |
| Sex—Female | 100 (55.9) | 80 (57.6) | 20 (50.0) | 0.505 |
| Sex—Male | 79 (44.1) | 59 (42.4) | 20 (50.0) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.9 [21.7–27.1] | 24.2 [21.9–27.4] | 23.2 [21.1–24.3] | 0.111 |
| Obesity (BMI > 30) | 25 (14) | 19 (13.7) | 6 (15) | 1.000 |
| Weight loss | 69 (38.6) | 49 (35.3) | 20 (50.0) | 0.132 |
| ASA score > 2 | 62 (34.6) | 38 (27.3) | 24 (60.0) | <0.001 |
| MET < 4 | 14 (7.8) | 5 (3.6) | 9 (22.5) | <0.001 |
| ECOG-PS > 1 | 26 (14.5) | 13 (9.4) | 13 (32.5) | 0.001 |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index | 5 [3–7] | 5 [3–7] | 6 [4–7] | 0.093 |
| Solid vs. Hematology Cancer | 103 (57.5) | 80 (57.6) | 23 (57.5) | 1.000 |
| Pancreas | 31 (17.3) | 23 (16.5) | 8 (20.0) | 0.786 |
| Ovarian | 24 (13.4) | 20 (14.4) | 4 (10.0) | 0.649 |
| Uterus | 11 (6.1) | 10 (7.2) | 1 (2.5) | 0.474 |
| Gastric | 11 (6.1) | 7 (5.0) | 4 (10.0) | 0.436 |
| Colon | 7 (3.9) | 7 (5.0) | 0 | 0.325 |
| Peritoneal disease | 8 (4.5) | 7 (5.0) | 1 (2.5) | 0.803 |
| Other solid | 15 (8.4) | 9 (6.5) | 6 (15.0) | 0.164 |
| Lymphomas | 48 (26.8) | 37 (26.6) | 11 (27.5) | 0.903 |
| Leukemias | 13 (7.3) | 9 (6.5) | 4 (10) | 0.681 |
| Myelofibrosis | 17 (9.5) | 14 (10.1) | 3 (7.5) | 0.855 |
| Preoperative Anticancer Treatments | ||||
| Chemotherapy | 109 (60.9) | 84 (60.4) | 25 (62.5) | 0.958 |
| Radiotherapy | 15 (8.4) | 12 (8.6) | 3 (7.5) | 1.000 |
| Corticosteroids | 25 (14.0) | 15 (10.8) | 10 (25.0) | 0.043 |
| Preoperative hemoglobin (g/dL) | 11.8 [10.2–13] | 12 [10.5–13] | 10.4 [9–12.2] | 0.001 |
| Splenomegaly | 96 (53.6) | 44 (47.3) | 52 (60.5) | 0.107 |
| Spleen length (cm) | 13 [11–23] | 13 [11–21] | 13 [11–25] | 0.590 |
| Antibiotic prophylaxis | 175 (97.8) | 139 (100.0) | 36 (90.0) | 0.001 |
| Penicillins | 161 (90.0) | 129 (92.8) | 32 (80.0) | 1.000 |
| Others | 14 (8.4) | 10 (7.2) | 4 (10.0) | 1.000 |
| Vaccination | 165 (92.2) | 135 (97.1) | 30 (75.0) | <0.001 |
| Intraoperative Period | ||||
| Laparotomy | 154 (86.0) | 115 (82.7) | 39 (97.5) | 0.034 |
| Laparoscopy | 37 (20.7) | 30 (21.6) | 7 (17.5) | 0.734 |
| Elective surgery | 162 (90.5) | 131 (94.2) | 31 (77.5) | 0.004 |
| Emergency surgery | 17 (9.5) | 8 (5.8) | 9 (22.5) | 0.004 |
| Metastasectomy | 54 (30.2) | 49 (35.3) | 5 (12.5) | 0.010 |
| Surgical Indication | ||||
| Invasion | 42 (23.5) | 29 (20.9) | 13 (32.5) | 0.159 |
| Symptomatic splenomegaly | 40 (22.4) | 27 (19.4) | 13 (32.5) | 0.125 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 38 (21.2) | 27 (19.4) | 11 (27.5) | 0.378 |
| Diagnosis | 30 (16.8) | 25 (18.0) | 5 (12.5) | 0.563 |
| Bleeding | 18 (10.1) | 10 (7.2) | 8 (20.0) | 0.033 |
| Duration of surgery (hours) | 3.5 [2.4–5.5] | 3.5 [2.5–5.3] | 4.2 [2.4–6.5] | 0.143 |
| Use of vasopressors | 37 (20.7) | 24 (17.3) | 13 (32.5) | 0.043 |
| Bleeding (mL) | 300 [150–675] | 300 [125–500] | 500 [225–950] | 0.017 |
| Intraoperative transfusion | 42 (23.5) | 24 (17.3) | 18 (45.0) | <0.001 |
| SAPS II score | 27 [21–35] | 26 [21–32] | 34.5 [21–43] | 0.032 |
| SOFA score at ICU admission | 2 [1–5] | 2 [1–3] | 5 [2–9] | 0.001 |
| Surgical complications | 68 (38.0) | 46 (33.1) | 22 (55.0) | 0.029 |
| Clavien–Dindo grade > 2 | 44 (24.6) | 25 (18.0) | 19 (47.5) | <0.001 |
| Reoperation | 23 (12.9) | 14 (10.1) | 9 (22.5) | 0.062 |
| Medical complications | 96 (53.6) | 64 (46.0) | 32 (80.0) | <0.001 |
| Sepsis at 1 year | 94 (52.5) | 65 (46.8) | 29 (72.5) | <0.001 |
| Thromboembolic event at 1 year | 21 (11.7) | 17 (12.2) | 4 (10.0) | 0.085 |
| DVT—n (%) | 14 (7.8) | 12 (8.6) | 2 (5.0) | 1.000 |
| PE—n (%) | 4 (2.2) | 2 (1.4) | 2 (5.0) | 0.002 |
| Myocardial infarction | 4 (2.2) | 3 (2.2) | 1 (2.5) | 0.468 |
| Stroke | 1 (0.6) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.5) | 0.034 |
| Arterial thrombosis | 1 (0.6) | 1 (0.7) | 0 (0.0) | 1.000 |
| Preventive anticoagulation | 140 (78.2) | 112 (80.6) | 28 (70.0) | 0.900 |
| Organ Failure at Day 90 | ||||
| Vasopressors | 24 (13.4) | 11 (7.9) | 13 (32.5) | <0.001 |
| Renal replacement therapy | 8 (4.5) | 1 (0.7) | 7 (17.5) | <0.001 |
| Oxygen > 5 L/min | 21 (11.7) | 7 (5.0) | 14 (35.0) | 0.003 |
| High-flow oxygen | 9 (5.0) | 5 (3.6) | 4 (10.0) | 0.786 |
| Non-invasive ventilation | 11 (6.1) | 4 (2.9) | 7 (17.5) | 0.002 |
| Invasive mechanical ventilation | 12 (6.7) | 2 (1.4) | 10 (25.0) | <0.001 |
| IMC/ICU length of stay (days) | 5 [3–7] | 4 [1.5–6] | 7 [3–8] | 0.001 |
| Hospital length of stay (days) | 11 [8–16] | 1 [8– 14] | 17 [10–26] | <0.001 |
3.12. Hematology Malignancy vs. Solid Tumor (Table 4)
| Patient Characteristics | Total Population (n = 179) | Hematology (n = 76) | Solid Tumors (n = 103) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 64 [55–71] | 64 [56–70] | 64 [55–71] | 0.550 |
| Sex—Female | 100 (55.9) | 37 (48.7) | 63 (61.2) | 0.131 |
| Sex—Male | 79 (44.1) | 39 (51.3) | 40 (38.8) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.9 [21.7–27.1] | 23.9 [21.5–26.7] | 23.9 [21.8–27.8] | 0.557 |
| Obesity (BMI > 30) | 25 (14.0) | 3 (3.9) | 22 (21.4) | 0.002 |
| Weight loss | 69 (38.6) | 23 (30.3) | 46 (44.7) | 0.072 |
| ASA score > 2 | 62 (34.6) | 36 (47.4) | 26 (25.2) | 0.004 |
| MET < 4 | 14 (7.8) | 11 (14.5) | 3 (2.9) | 0.010 |
| ECOG-PS > 1 | 26 (14.5) | 19 (25.0) | 7 (6.8) | 0.001 |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index | 5 [3–7] | 24 [18–29] | 11 [10–13] | <0.001 |
| Preoperative Anticancer Treatments | ||||
| Chemotherapy | 109 (60.9) | 49 (64.5) | 60 (58.3) | 0.491 |
| Radiotherapy | 15 (8.4) | 8 (10.5) | 7 (6.8) | 0.537 |
| Corticosteroids | 25 (14.0) | 24 (31.6) | 1 (1.0) | <0.001 |
| Preoperative hemoglobin (g/dL) | 11.8 [10–13.0] | 10.4 [9.0–12.2] | 12.2 [11–13.3] | <0.001 |
| Splenomegaly | 96 (53.6) | 68 (89.5) | 28 (27.2) | <0.001 |
| Spleen length (cm) | 13 [11–23] | 12 [11–18] | 14 [11–25] | 0.051 |
| Antibiotic prophylaxis | 175 (97.8) | 75 (98.7) | 100 (97.1) | 0.849 |
| Penicillins | 161 (90.0) | 68 (94.4) | 97 (97.0) | 0.571 |
| Others | 14 (8.4) | 8 (10.8) | 6 (6.0) | 0.383 |
| Vaccination | 165 (92.2) | 92 (98.9) | 73 (84.9) | 0.656 |
| Intraoperative Period | ||||
| Laparotomy | 154 (86.0) | 54 (71.1) | 100 (97.1) | <0.001 |
| Laparoscopy | 37 (20.7) | 29 (38.2) | 8 (7.8) | <0.001 |
| Elective surgery | 162 (90.5) | 69 (90.8) | 92 (89.3) | 0.943 |
| Emergency surgery | 17 (9.5) | 6 (7.9) | 11 (10.7) | 0.711 |
| Metastasectomy | 54 (30.2) | 7 (9.2) | 47 (45.6) | <0.001 |
| Surgical Indication | ||||
| Invasion | 42 (23.5) | 0 (0.0) | 42 (40.8) | <0.001 |
| Symptomatic splenomegaly | 40 (22.4) | 16 (17.2) | 24 (27.9) | 0.124 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 38 (21.2) | 38 (50.0) | 0 (0.0) | <0.001 |
| Diagnosis | 30 (16.8) | 28 (36.8) | 2 (1.9) | <0.001 |
| Bleeding | 18 (10.1) | 4 (5.3) | 14 (13.6) | 0.120 |
| Duration of surgery (hours) | 3.5 [2.4–5.5] | 2.5 [2.0–3.2] | 5.0 [3.3–6.5] | <0.001 |
| Use of vasopressors | 37 (20.7) | 4 (5.3) | 33 (32.0) | <0.001 |
| Blood loss (mL) | 300 [150–675] | 300 [100–800] | 350 [162–575] | 0.868 |
| Intraoperative transfusion | 42 (23.5) | 23 (30.7) | 19 (18.4) | 0.086 |
| Postoperative Period | ||||
| SAPS II score | 27 [21–35] | 29 [24–39] | 26 [20–33] | 0.081 |
| SOFA at ICU admission | 2 [1–5] | 3 [2–5] | 2 [1–3] | 0.025 |
| Severe complications | 86 (48) | 40 (52.6) | 46 (44.7) | 0.291 |
| Surgical complications | 68 (38.0) | 25 (32.0) | 43 (41.7) | 0.242 |
| Clavien–Dindo grade > 2 | 44 (24.6) | 16 (21.1) | 28 (27.2) | 0.444 |
| Reoperation | 23 (12.9) | 7 (9.3) | 16 (15.5) | 0.321 |
| Medical complications | 96 (53.6) | 42 (54.7) | 54 (52.4) | 0.886 |
| Sepsis at day 30 | 54 (30.2) | 21 (28.0) | 32 (31.1) | 0.783 |
| Sepsis at day 90 | 71 (39.7) | 32 (43.8) | 29 (28.4) | 0.051 |
| Sepsis at 1 year | 91 (51%) | 48 (66.7) | 43 (44.3) | 0.006 |
| Thromboembolic event at day 90 | 12 (6.7) | 5 (6.5) | 7 (7.0) | 1 |
| DVT | 7 (3.9) | 4 (4.4) | 3 (3.0) | 0.952 |
| PE | 4 (2.2) | 2 (2.9) | 2 (2.0) | 1.000 |
| Myocardial infarction | 2 (1.1) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (2.0) | 0.654 |
| Stroke | 1 (0.6) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.0) | 1.000 |
| Arterial thrombosis | 1 (0.6) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.0) | 1.000 |
| Thromboembolic event at 1 year | 21 (11.7) | 7 (9.8) | 14 (16.7) | 0.350 |
| Preventive anticoagulation | 140 (78.2) | 58 (95.1) | 82 (83.7) | 0.057 |
| Organ Failure at Day 90 | ||||
| Vasopressors | 24 (13.4) | 7 (9.2) | 17 (16.5) | 0.095 |
| Renal replacement therapy | 8 (4.5) | 2 (2.7) | 5 (4.9) | 0.726 |
| O2 > 5 L/min | 21 (11.7) | 7 (9.2) | 14 (13.6) | 0.506 |
| High-flow oxygen | 9 (5.0) | 5 (6.5) | 4 (3.9) | 0.940 |
| Non-invasive ventilation | 11 (6.1) | 3 (4.0) | 8 (7.8) | 0.474 |
| Invasive mechanical ventilation | 12 (6.7) | 4 (4.4) | 8 (7.8) | 0.474 |
| Time to severe complication (days) | 2 [0–12] | 2 [0–15] | 2 [0–8] | 0.980 |
| IMC/ICU length of stay (days) | 5 [3–7] | 2 [0–4] | 5 [3–7] | <0.001 |
| Hospital length of stay (days) | 11 [8–16] | 9 [6–12] | 14 [9–18] | <0.001 |
| Death at day 90 | 12 (6.7) | 9 (11.8) | 3 (2.9) | 0.040 |
| Death at 1 year | 40 (22.3) | 17 (22.4) | 23 (22.3) | 1 |
4. Discussion
4.1. Nutritional Status and Prehabilitation
4.2. Surgical Approach and Disease Context
4.3. Immediate Postoperative Severity
4.4. Immunity, Sepsis, and Long-Term Mortality
4.5. Comorbidity Burden and Performance Status
4.6. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mebius, R.E.; Kraal, G. Structure and Function of the Spleen. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 606–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Sabatino, A.; Carsetti, R.; Corazza, G.R. Post-Splenectomy and Hyposplenic States. Lancet 2011, 378, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuter, D.J.; Ghanima, W.; Cooper, N.; Liebman, H.A.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Y.; Miyakawa, Y.; Homenda, W.; Morales Galindo, L.E.E.; Basquiera, A.L.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Rilzabrutinib vs Placebo in Adults with Immune Thrombocytopenia: The Phase 3 LUNA3 Study. Blood 2025, 145, 2914–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokart, D.; Giaoui, E.; Barbier, L.; Lambert, J.; Sannini, A.; Chow-Chine, L.; Brun, J.-P.; Faucher, M.; Guiramand, J.; Ewald, J.; et al. Postoperative Sepsis in Cancer Patients Undergoing Major Elective Digestive Surgery Is Associated with Increased Long-Term Mortality. J. Crit. Care 2016, 31, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, K.; Kurokawa, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Hirota, M.; Kawabata, R.; Mikami, J.; Masuzawa, T.; Takiguchi, S.; Mori, M.; Doki, Y. Risk Factors for Poor Compliance with Adjuvant S-1 Chemotherapy for Gastric Cancer: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 24, 2639–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokart, D.; Penalver, M.; Chow-Chine, L.; Ewald, J.; Sannini, A.; Brun, J.P.; Bisbal, M.; Lelong, B.; Delpero, J.R.; Faucher, M.; et al. Surgical Treatment of Acute Abdominal Complications in Hematology Patients: Outcomes and Prognostic Factors. Leuk. Lymphoma 2017, 58, 2395–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristinsson, S.Y.; Gridley, G.; Hoover, R.N.; Check, D.; Landgren, O. Long-Term Risks after Splenectomy among 8,149 Cancer-Free American Veterans: A Cohort Study with up to 27 Years Follow-Up. Haematologica 2014, 99, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinwar, P.D. Overwhelming Post Splenectomy Infection Syndrome—Review Study. Int. J. Surg. 2014, 12, 1314–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canac, J.; Faucher, M.; Depeyre, F.; Tourret, M.; Tezier, M.; Cambon, S.; Ettori, F.; Servan, L.; Alisauskaite, J.; Pouliquen, C.; et al. Factors Associated with 1-Year Mortality in Elderly Patients (Age ≥ 80 Years) with Cancer Undergoing Major Abdominal Surgery: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 30, 8083–8093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah, J.; Olszewski, A.J. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Splenectomy for Splenic Lymphomas: Analysis of the National Cancer Data Base. Hematology 2019, 24, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippova, O.T.; Kim, S.W.; Cowan, R.A.; Chi, A.J.; Iasonos, A.; Zhou, Q.C.; Broach, V.; Zivanovic, O.; Long Roche, K.; Sonoda, Y.; et al. Hematologic Changes after Splenectomy for Ovarian Cancer Debulking Surgery, and Association with Infection and Venous Thromboembolism. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2020, 30, 1183–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faucher, M.; Dahan, S.; Morel, B.; de Guibert, J.M.; Chow-Chine, L.; Gonzalez, F.; Bisbal, M.; Servan, L.; Sannini, A.; Tezier, M.; et al. The Effect of Postoperative Sepsis on 1-Year Mortality and Cancer Recurrence Following Transhiatal Esophagectomy for Esophageal-Gastric Junction Adenocarcinomas: A Retrospective Observational Study. Cancers 2025, 17, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farid, S.G.; Aldouri, A.; Morris-Stiff, G.; Khan, A.Z.; Toogood, G.J.; Lodge, J.P.A.; Prasad, K.R. Correlation Between Postoperative Infective Complications and Long-Term Outcomes After Hepatic Resection for Colorectal Liver Metastasis. Ann. Surg. 2010, 251, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederholm, T.; Jensen, G.L.; Correia, M.I.T.D.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Fukushima, R.; Higashiguchi, T.; Baptista, G.; Barazzoni, R.; Blaauw, R.; Coats, A.; et al. GLIM Criteria for the Diagnosis of Malnutrition—A Consensus Report from the Global Clinical Nutrition Community. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GlobalSurg Collaborative and NIHR Global Health Unit on Global Surgery. Impact of Malnutrition on Early Outcomes after Cancer Surgery: An International, Multicentre, Prospective Cohort Study. Lancet Glob. Health 2023, 11, e341–e349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettori, F.; Henin, A.; Zemmour, C.; Chow-Chine, L.; Sannini, A.; Bisbal, M.; Gonzalez, F.; Servan, L.; de Guibert, J.M.; Faucher, M.; et al. Impact of a Computer-Assisted Decision Support System (CDSS) on Nutrition Management in Critically Ill Hematology Patients: The NUTCHOCO Study (Nutritional Care in Hematology Oncologic Patients and Critical Outcome). Ann. Intensive Care 2019, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.N.; Kufeldt, J.; Kisser, U.; Hornung, H.-M.; Hoffmann, J.; Andraschko, M.; Werner, J.; Rittler, P. Effects of Malnutrition on Complication Rates, Length of Hospital Stay, and Revenue in Elective Surgical Patients in the G-DRG-System. Nutrition 2016, 32, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ely, E.W. The ABCDEF Bundle: Science and Philosophy of How ICU Liberation Serves Patients and Families. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 45, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindle, M.; Nelson, G.; Lobo, D.N.; Ljungqvist, O.; Gustafsson, U.O. Recommendations from the ERAS® Society for Standards for the Development of Enhanced Recovery after Surgery Guidelines. BJS Open 2020, 4, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balan, N.; deVirgilio, C.M.; Ozao-Choy, J.; Moazzez, A. Association of Laparoscopic Approach With Improved Short-Term Outcomes in Patients With Hematologic Malignancy Undergoing Splenectomy. Am. Surg. 2023, 89, 4160–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez Monclova, J.; Targarona Soler, E.; Peraza Solis, Y.; Vidal Gonzalez, P.; Balague Ponz, C.; Rodriguez Luppi, C.; Trias Folch, M. Laparoscopic Approach for Isolated Splenic Metastasis: Comprehensive Literature Review and Report of 6 Cases. Surg. Laparosc. Endosc. Percutan Tech. 2013, 23, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, E.; Vorobii, O.; Silins, I.; Sundström Poromaa, I.; Stålberg, K.; Lomnytska, M. Splenectomy as an Indicator for Ovarian Cancer Spread and Complete Cytoreduction. Gynecol. Oncol. 2025, 197, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAneny, D.; LaMorte, W.W.; Scott, T.E.; Weintraub, L.R.; Beazley, R.M. Is Splenectomy More Dangerous for Massive Spleens? Am. J. Surg. 1998, 175, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Ren, S.; Li, C.; Qian, S.; Liu, P. Management of Postoperative Complications Following Splenectomy. Int. Surg. 2013, 98, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Alfy, M.S.; El-Sayed, M.H. Overwhelming Postsplenectomy Infection: Is Quality of Patient Knowledge Enough for Prevention? Hematol. J. 2004, 5, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, F.; Ahmed, J.; Malik, F. Post-Splenectomy Sepsis: A Review of the Literature. Cureus 2020, 12, e6898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azoulay, E.; Mokart, D.; Kouatchet, A.; Demoule, A.; Lemiale, V. Acute Respiratory Failure in Immunocompromised Adults. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalpadakis, C.; Pangalis, G.A.; Angelopoulou, M.K.; Sachanas, S.; Vassilakopoulos, T.P. Should Rituximab Replace Splenectomy in the Management of Splenic Marginal Zone Lymphoma? Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2018, 31, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, P.; Pardanani, A.D.; Starlinger, P.; Tefferi, A.; Gangat, N. Outcome of Splenectomy in JAK2 Inhibitor Treated Patients with Myelofibrosis: A Mayo Clinic Experience in 34 Consecutive Cases. Blood 2024, 144, 6662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucchini, E.; Zaja, F.; Bussel, J. Rituximab in the Treatment of Immune Thrombocytopenia: What Is the Role of This Agent in 2019? Haematologica 2019, 104, 1124–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assi, R.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Cortes, J.E.; Pemmaraju, N.; Wang, X.; Nogueras-Gonzalez, G.; Jabbour, E.; Bose, P.; Kadia, T.; et al. A Phase II Trial of Ruxolitinib in Combination with Azacytidine in Myelodysplastic Syndrome/Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Ananin, S.; Novelli, S.; Cambeiro Cabré, L.; Vila Riera, C.; Ballester Vàzquez, E.; Julià Verdaguer, E.; Targarona, E.M. Elective Splenectomy for Hematological Diseases: A Vanishing Indication. Surg. Endosc. 2024, 38, 6332–6337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Effect of Exercise and Nutrition Prehabilitation on Functional Capacity in Esophagogastric Cancer Surgery: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Surg. 2018, 153, 1081–1089. [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.J.; Hackney, R.J.; Lamb, P.J.; Wigmore, S.J.; Christopher Deans, D.A.; Skipworth, R.J.E. Prehabilitation Before Major Abdominal Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World J. Surg. 2019, 43, 1661–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faucher, M.; Ravot, S.; Barthes, L.; de Guibert, J.M.; Chow-Chine, L.; Gonzalez, F.; Bisbal, M.; Servan, L.; Tezier, M.; Tourret, M.; et al. Splenectomy in Onco-Hematologic Patients: A Retrospective Study of Early Complications and 1-Year Mortality. Cancers 2025, 17, 2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132241
Faucher M, Ravot S, Barthes L, de Guibert JM, Chow-Chine L, Gonzalez F, Bisbal M, Servan L, Tezier M, Tourret M, et al. Splenectomy in Onco-Hematologic Patients: A Retrospective Study of Early Complications and 1-Year Mortality. Cancers. 2025; 17(13):2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132241
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaucher, Marion, Stanislas Ravot, Loïc Barthes, Jean Manuel de Guibert, Laurent Chow-Chine, Frédéric Gonzalez, Magali Bisbal, Luca Servan, Marie Tezier, Maxime Tourret, and et al. 2025. "Splenectomy in Onco-Hematologic Patients: A Retrospective Study of Early Complications and 1-Year Mortality" Cancers 17, no. 13: 2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132241
APA StyleFaucher, M., Ravot, S., Barthes, L., de Guibert, J. M., Chow-Chine, L., Gonzalez, F., Bisbal, M., Servan, L., Tezier, M., Tourret, M., Cambon, S., Pouliquen, C., Mallet, D., Nguyen Duong, L., Ettori, F., Ewald, J., Léone, M., Sannini, A., Garnier, J., & Mokart, D. (2025). Splenectomy in Onco-Hematologic Patients: A Retrospective Study of Early Complications and 1-Year Mortality. Cancers, 17(13), 2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132241






