Next-Generation Therapies in Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL): The Evolving Landscape in Treatment of Relapse/Refractory After CAR-T Cells
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Prognostic Factors
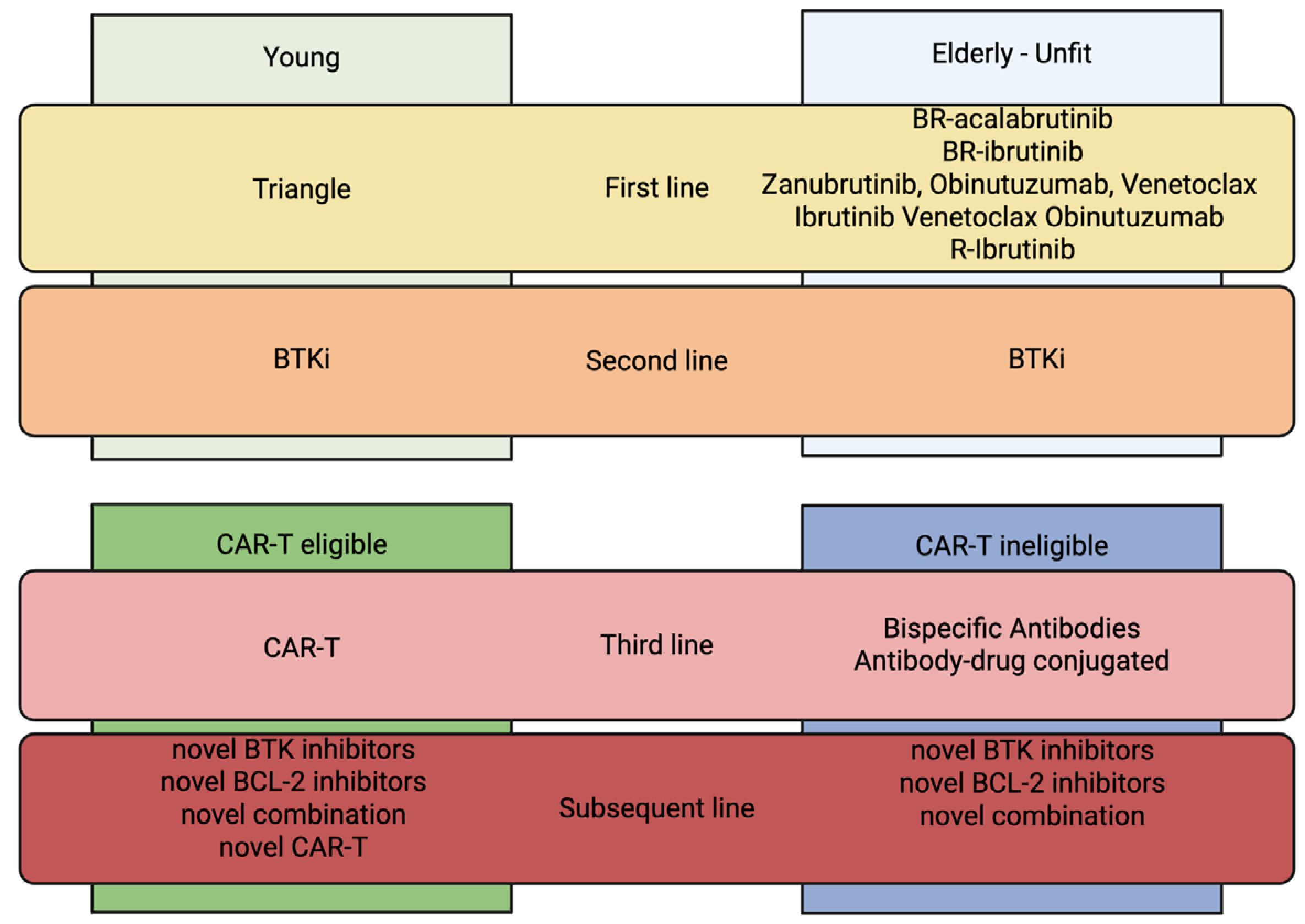
3. New Milestones in MCL Treatment
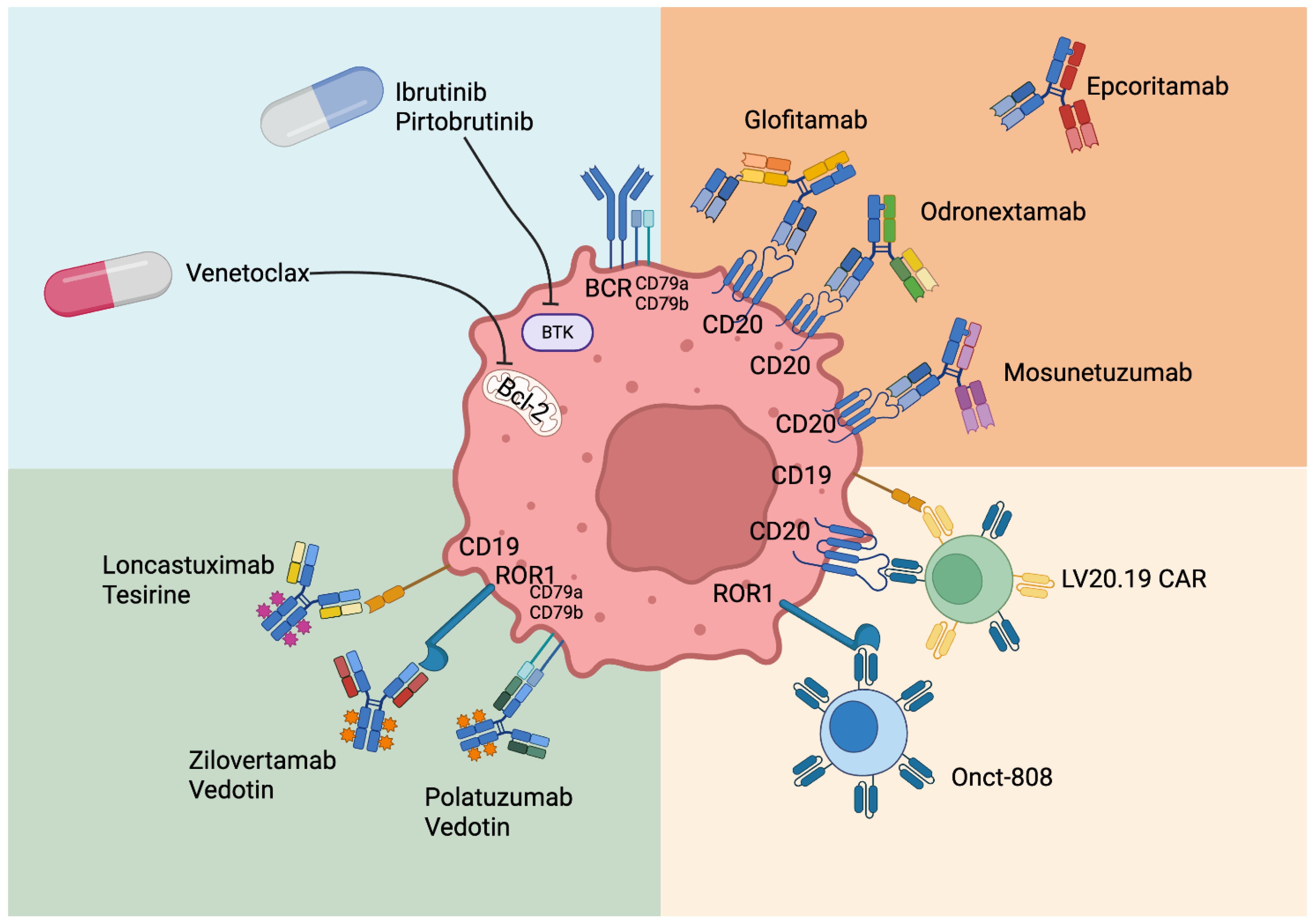
4. Role of New Drugs in Relapsed/Refractory MCL After CAR-T Cells or Not Eligible for CAR-T-Cell Therapy
4.1. Currently Available Treatments
- Ibrutinib + Venetoclax
- Trial Sympatico
4.2. Treatment Under Investigation but Not Currently Available
- Novel Antibodies
- Antibody–drug conjugate
- Zilovertamab Vedotin
- Loncastuximab-tesirine
- Bispecific Antibodies
- Glofitamab
- Epcoritamab
- Mosunetuzumab single agent
- Mosunetuzumab combinations
- Odronextamab
- Allogeneic stem cell transplantation
- Horizon Scanning and Future Perspectives
- BTK degraders
- Novel Tyrosine Kinase (TK) inhibitors
- Novel BCL-2 inhibitors
- AKT-inhibitors
- Novel CAR-T cells
- Exploratory trials
5. Conclusions
6. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MCL | mantle cell lymphoma |
| CAR-T cells | chimeric antigen receptor-T cells |
| BTKi | Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| MAB | monoclonal antibody |
| ICD | immunoconjugated drug |
| TCE | T-cell engaging |
| R/R | relapsed/refractory |
| NHL | non-Hodgkin lymphoma |
| COO | cell of origin |
| MIPI | MCL international prognostic index |
| MRD | minimal residual disease |
| ASCT | autologous stem cell transplantation |
| ORR | overall response rate |
| CR | complete remission |
| PFS | progression-free survival |
| OS | overall survival |
| DOR | duration of response |
| BR | Bendamustine-rituximab |
| BAC | Bendamustine-cytarabine-rituximab |
| R-CHOP | rituximab-prednisone-doxorubicin-vincristine-cyclophosphamide |
| MTD | maximum tolerated dose |
| Brexu-cel | Brexucabtagene autoleucel |
| Liso-cel | Lisocabtagene maraleucel |
| CLL | chronic lymphocytic leukemia |
| TLS | tumor lysis syndrome |
| CRS | cytokine release syndrome |
| ICANS | immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome |
| ROR1 | retinoic acid receptor 1 |
| PD-L1 | programmed death-ligand 1 |
| DLBCL | diffuse large B-cell lymphoma |
| FL | follicular lymphoma |
References
- Dreyling, M.; Campo, E.; Hermine, O.; Jerkeman, M.; Le Gouill, S.; Rule, S.; Shpilberg, O.; Walewski, J.; Ladetto, M. Newly diagnosed and relapsed mantle cell lymphoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28 (Suppl. 4), iv62–iv71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romaguera, J.E.; Medeiros, L.J.; Hagemeister, F.B.; Fayad, L.E.; Rodriguez, M.A.; Pro, B.; Younes, A.; McLaughlin, P.; Goy, A.; Sarris, A.H.; et al. Frequency of gastrointestinal involvement and its clinical significance in mantle cell lymphoma. Cancer 2003, 97, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silkenstedt, E.; Dreyling, M. Mantle cell lymphoma-Update on molecular biology, prognostication and treatment approaches. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 41 (Suppl. 1), 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo, E.; Jaffe, E.S.; Cook, J.R.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Anderson, K.C.; Brousset, P.; Cerroni, L.; de Leval, L.; Dirnhofer, S.; et al. The International Consensus Classification of Mature Lymphoid Neoplasms: A report from the Clinical Advisory Committee. Blood 2022, 140, 1229–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puente, X.S.; Jares, P.; Campo, E. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia and mantle cell lymphoma: Crossroads of genetic and microenvironment interactions. Blood 2018, 131, 2283–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaggio, R.; Amador, C.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Attygalle, A.D.; Araujo, I.B.O.; Berti, E.; Bhagat, G.; Borges, A.M.; Boyer, D.; Calaminici, M.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1720–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoster, E.; Rosenwald, A.; Berger, F.; Bernd, H.W.; Hartmann, S.; Loddenkemper, C.; Barth, T.F.; Brousse, N.; Pileri, S.; Rymkiewicz, G.; et al. Prognostic Value of Ki-67 Index, Cytology, and Growth Pattern in Mantle-Cell Lymphoma: Results From Randomized Trials of the European Mantle Cell Lymphoma Network. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1386–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoster, E.; Dreyling, M.; Klapper, W.; Gisselbrecht, C.; van Hoof, A.; Kluin-Nelemans, H.C.; Pfreundschuh, M.; Reiser, M.; Metzner, B.; Einsele, H.; et al. A new prognostic index (MIPI) for patients with advanced-stage mantle cell lymphoma. Blood 2008, 111, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aukema, S.M.; Hoster, E.; Rosenwald, A.; Canoni, D.; Delfau-Larue, M.H.; Rymkiewicz, G.; Thorns, C.; Hartmann, S.; Kluin-Nelemans, H.; Hermine, O.; et al. Expression of TP53 is associated with the outcome of MCL independent of MIPI and Ki-67 in trials of the European MCL Network. Blood 2018, 131, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskelund, C.W.; Dahl, C.; Hansen, J.W.; Westman, M.; Kolstad, A.; Pedersen, L.B.; Montano-Almendras, C.P.; Husby, S.; Freiburghaus, C.; Ek, S.; et al. TP53 mutations identify younger mantle cell lymphoma patients who do not benefit from intensive chemoimmunotherapy. Blood 2017, 130, 1903–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermine, O.; Jiang, L.; Walewski, J.; Bosly, A.; Thieblemont, C.; Szymczyk, M.; Pott, C.; Salles, G.; Feugier, P.; Hübel, K.; et al. High-Dose Cytarabine and Autologous Stem-Cell Transplantation in Mantle Cell Lymphoma: Long-Term Follow-Up of the Randomized Mantle Cell Lymphoma Younger Trial of the European Mantle Cell Lymphoma Network. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pott, C.; Hoster, E.; Delfau-Larue, M.H.; Beldjord, K.; Böttcher, S.; Asnafi, V.; Plonquet, A.; Siebert, R.; Callet-Bauchu, E.; Andersen, N.; et al. Molecular remission is an independent predictor of clinical outcome in patients with mantle cell lymphoma after combined immunochemotherapy: A European MCL intergroup study. Blood 2010, 115, 3215–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, S.; Yan, Y.; Jin, M.; Bhattacharya, S.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yang, L.; Gine, E.; Clot, G.; Chen, L.; et al. Genomic and transcriptomic profiling reveals distinct molecular subsets associated with outcomes in mantle cell lymphoma. J. Clin. Invest. 2022, 132, e153283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.; Jain, P.; Hu, S.; Ok, C.Y.; Wang, W.J.; Quesada, A.E.; Wei, Q.; Li, S.; Xu, J.; Loghavi, S.; et al. Optical genome mapping reveals diverse mechanisms of cyclin activation in mantle cell lymphomas lacking IGH::CCND1. Hum. Pathol. 2025, 159, 105793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarian, G.; Chemali, L.; Bensalah, M.; Zindel, C.; Lefebvre, V.; Thieblemont, C.; Martin, A.; Tueur, G.; Letestu, R.; Fleury, C.; et al. TP53 Mutations Detected by NGS Are a Major Clinical Risk Factor for Stratifying Mantle Cell Lymphoma. Am. J. Hematol. 2025, 100, 933–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoellner, A.K.; Unterhalt, M.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Hübel, K.; Thieblemont, C.; Metzner, B.; Topp, M.; Truemper, L.; Schmidt, C.; Bouabdallah, K.; et al. Long-term survival of patients with mantle cell lymphoma after autologous haematopoietic stem-cell transplantation in first remission: A post-hoc analysis of an open-label, multicentre, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2021, 8, e648–e657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gouill, S.; Thieblemont, C.; Oberic, L.; Moreau, A.; Bouabdallah, K.; Dartigeas, C.; Damaj, G.; Gastinne, T.; Ribrag, V.; Feugier, P.; et al. Rituximab after Autologous Stem-Cell Transplantation in Mantle-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1250–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rummel, M.J.; Niederle, N.; Maschmeyer, G.; Banat, G.A.; von Grünhagen, U.; Losem, C.; Kofahl-Krause, D.; Heil, G.; Welslau, M.; Balser, C.; et al. Bendamustine plus rituximab versus CHOP plus rituximab as first-line treatment for patients with indolent and mantle-cell lymphomas: An open-label, multicentre, randomised, phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisi, M.C.; Moia, R.; Patti, C.; Evangelista, A.; Ferrero, S.; Spina, M.; Tani, M.; Botto, B.; Celli, M.; Puccini, B.; et al. Long-term follow-up of rituximab plus bendamustine and cytarabine in older patients with newly diagnosed MCL. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 3916–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robak, T.; Jin, J.; Pylypenko, H.; Verhoef, G.; Siritanaratkul, N.; Drach, J.; Raderer, M.; Mayer, J.; Pereira, J.; Tumyan, G.; et al. Frontline bortezomib, rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (VR-CAP) versus rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) in transplantation-ineligible patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma: Final overall survival results of a randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visco, C.; Di Rocco, A.; Evangelista, A.; Quaglia, F.M.; Tisi, M.C.; Morello, L.; Zilioli, V.R.; Rusconi, C.; Hohaus, S.; Sciarra, R.; et al. Outcomes in first relapsed-refractory younger patients with mantle cell lymphoma: Results from the MANTLE-FIRST study. Leukemia 2021, 35, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.L.; Rule, S.; Martin, P.; Goy, A.; Auer, R.; Kahl, B.S.; Jurczak, W.; Advani, R.H.; Romaguera, J.E.; Williams, M.E.; et al. Targeting BTK with ibrutinib in relapsed or refractory mantle-cell lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreyling, M.; Jurczak, W.; Jerkeman, M.; Silva, R.S.; Rusconi, C.; Trneny, M.; Offner, F.; Caballero, D.; Joao, C.; Witzens-Harig, M.; et al. Ibrutinib versus temsirolimus in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle-cell lymphoma: An international, randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet 2016, 387, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Rule, S.; Zinzani, P.L.; Goy, A.; Casasnovas, O.; Smith, S.D.; Damaj, G.; Doorduijn, J.; Lamy, T.; Morschhauser, F.; et al. Acalabrutinib in relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (ACE-LY-004): A single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gouill, S.; Długosz-Danecka, M.; Rule, S.; Zinzani, P.L.; Goy, A.; Smith, S.D.; Doorduijn, J.K.; Panizo, C.; Shah, B.D.; Davies, A.J.; et al. Final results and overall survival data from a phase II study of acalabrutinib monotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma, including those with poor prognostic factors. Haematologica 2024, 109, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinzani, P.L.; Mauro, F.R.; Tedeschi, A.; Varettoni, M.; Zaja, F.; Barosi, G. Unmet clinical needs in the use of zanubrutinib in malignant lymphomas (Waldenström macroglobulinemia, marginal zone lymphoma and mantle cell lymphoma): A consensus-based position paper from an ad hoc expert panel. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 41, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.S.; Opat, S.; Simpson, D.; Cull, G.; Munoz, J.; Phillips, T.J.; Kim, W.S.; Rule, S.; Atwal, S.K.; Wei, R.; et al. Zanubrutinib for the treatment of relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 2577–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhou, K.; Zou, D.; Zhou, J.; Hu, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, H.; Ji, J.; Xu, W.; Jin, J.; et al. Treatment of Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Mantle-Cell Lymphoma with Zanubrutinib, a Selective Inhibitor of Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 4216–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flinsenberg, T.W.H.; Tromedjo, C.C.; Hu, N.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Thia, K.Y.T.; Noori, T.; Song, X.; Aw Yeang, H.X.; Tantalo, D.G.; et al. Differential effects of BTK inhibitors ibrutinib and zanubrutinib on NK-cell effector function in patients with mantle cell lymphoma. Haematologica 2020, 105, e76–e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhou, K.; Zou, D.; Zhou, J.; Hu, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, H.; Ji, J.; Xu, W.; Jin, J.; et al. Zanubrutinib in relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma: Long-term efficacy and safety results from a phase 2 study. Blood 2022, 139, 3148–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.L.; Jurczak, W.; Jerkeman, M.; Trotman, J.; Zinzani, P.L.; Belada, D.; Boccomini, C.; Flinn, I.W.; Giri, P.; Goy, A.; et al. Ibrutinib plus Bendamustine and Rituximab in Untreated Mantle-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 2482–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, T.; Wang, M.; Robak, T.; Gallinson, D.; Stevens, D.; Patel, K.; Ramadan, S.; Wun, C.C.; Jurczak, W.; Smith, S.D. Safety and efficacy of acalabrutinib plus bendamustine and rituximab in patients with treatment-naïve or relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma: Phase Ib trial. Haematologica 2025, 110, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreyling, M.; Mayer, J.; Belada, D.; Song, Y.; Jurczak, W.; Paludo, J.; Chu, M.P.; Kryachok, I.; Fogliatto, L.M.; Cheah, C.Y.; et al. High-Risk Subgroups and MRD: An Updated Analysis of the Phase 3 ECHO Trial of Acalabrutinib with Bendamustine/Rituximab in Previously Untreated Mantle Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2024, 144 (Suppl. 1), 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visco, C.; Tabanelli, V.; Sacchi, M.V.; Evangelista, A.; Ferrarini, I.; Tisi, M.C.; Merli, A.; Fiori, S.; Zilioli, V.R.; Re, A.; et al. Rituximab, Bendamustine and Cytarabine Followed By Venetoclax (V-RBAC) in High-Risk Older Patients with Mantle Cell Lymphoma: A Phase 2 Study By the Fondazione Italiana Linfomi (FIL). Blood 2023, 142 (Suppl. 1), 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacoboni, G.; Navarro, V.; Martín-López, A.; Rejeski, K.; Kwon, M.; Jalowiec, K.A.; Amat, P.; Reguera-Ortega, J.L.; Gallur, L.; Blumenberg, V.; et al. Recent Bendamustine Treatment Before Apheresis Has a Negative Impact on Outcomes in Patients With Large B-Cell Lymphoma Receiving Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyling, M.; Doorduijn, J.; Giné, E.; Jerkeman, M.; Walewski, J.; Hutchings, M.; Mey, U.; Riise, J.; Trneny, M.; Vergote, V.; et al. Ibrutinib combined with immunochemotherapy with or without autologous stem-cell transplantation versus immunochemotherapy and autologous stem-cell transplantation in previously untreated patients with mantle cell lymphoma (TRIANGLE): A three-arm, randomised, open-label, phase 3 superiority trial of the European Mantle Cell Lymphoma Network. Lancet 2024, 403, 2293–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladetto, M.; Gutmair, K.; Doorduijn, J.K.; Gine, E.; Jerkeman, M.; Walewski, J.; Hutchings, M.; Mey, U.; Riise, J.; Trneny, M.; et al. Impact of Rituximab Maintenance Added to Ibrutinib-Containing Regimens with and without ASCT in Younger, Previously Untreated MCL Patients: An Analysis of the Triangle Data Embedded in the Multiply Project. Blood 2024, 144 (Suppl. 1), 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.J.; Jerkeman, M.; Sorrell, L.; Wright, D.; Glimelius, I.; Pasanen, A.; Christensen, J.H.; Wader, K.F.; Davies, A.J.; Morley, N.; et al. Ibrutinib-Rituximab Is Superior to Rituximab-Chemotherapy in Previously Untreated Older Mantle Cell Lymphoma Patients: Results from the International Randomised Controlled Trial, Enrich. Blood 2024, 144 (Suppl. 1), 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Soumerai, J.; Abramson, J.S.; Barnes, J.A.; Caron, P.; Chhabra, S.; Chabowska, M.; Dogan, A.; Falchi, L.; Grieve, C.; et al. Zanubrutinib, obinutuzumab, and venetoclax for first-line treatment of mantle cell lymphoma with a TP53 mutation. Blood 2025, 145, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gouill, S.; Morschhauser, F.; Chiron, D.; Bouabdallah, K.; Cartron, G.; Casasnovas, O.; Bodet-Milin, C.; Ragot, S.; Bossard, C.; Nadal, N.; et al. Ibrutinib, obinutuzumab, and venetoclax in relapsed and untreated patients with mantle cell lymphoma: A phase 1/2 trial. Blood 2021, 137, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, A.R.; Shah, N.N.; Jurczak, W.; Cheah, C.Y.; Pagel, J.M.; Woyach, J.A.; Fakhri, B.; Eyre, T.A.; Lamanna, N.; Patel, M.R.; et al. Pirtobrutinib in relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies (BRUIN): A phase 1/2 study. Lancet 2021, 397, 892–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davids, M.S.; Roberts, A.W.; Seymour, J.F.; Pagel, J.M.; Kahl, B.S.; Wierda, W.G.; Puvvada, S.; Kipps, T.J.; Anderson, M.A.; Salem, A.H.; et al. Phase I First-in-Human Study of Venetoclax in Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchings, M.; Morschhauser, F.; Iacoboni, G.; Carlo-Stella, C.; Offner, F.C.; Sureda, A.; Salles, G.; Martínez-Lopez, J.; Crump, M.; Thomas, D.N.; et al. Glofitamab, a Novel, Bivalent CD20-Targeting T-Cell-Engaging Bispecific Antibody, Induces Durable Complete Remissions in Relapsed or Refractory B-Cell Lymphoma: A Phase I Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1959–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glimelius, I.; Kim, W.S.; Paszkiewicz-Kozik, E.; Ernst, D.; Merryman, R.W.; Moreira, C.; Tu, S.; Ren, Y.; Ryland, K.; Ogbu, U.C.; et al. Zilovertamab Vedotin Monotherapy for Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Mantle Cell Lymphoma: Cohort a of the Multicenter, Open-Label, Phase 2 Waveline-006 Study. Blood 2024, 144 (Suppl. 1), 4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budde, L.E.; Matasar, M.; Sehn, L.H.; Assouline, S.E.; Kuruvilla, J.; Flinn, I.W.; Yoon, S.-S.; Bosch, F.; Greenwald, D.; Gutierrez, N.C.; et al. Mosunetuzumab Monotherapy Demonstrates Encouraging Activity and a Manageable Safety Profile in Patients with Heavily Pre-Treated Relapsed or Refractory Mantle Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2024, 144 (Suppl. 1), 1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budde, L.E.; Olszewski, A.J.; Assouline, S.; Lossos, I.S.; Diefenbach, C.; Kamdar, M.; Ghosh, N.; Modi, D.; Sabry, W.; Naik, S.; et al. Mosunetuzumab with polatuzumab vedotin in relapsed or refractory aggressive large B cell lymphoma: A phase 1b/2 trial. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannerji, R.; Arnason, J.E.; Advani, R.H.; Brown, J.R.; Allan, J.N.; Ansell, S.M.; Barnes, J.A.; O’Brien, S.M.; Chávez, J.C.; Duell, J.; et al. Odronextamab, a human CD20×CD3 bispecific antibody in patients with CD20-positive B-cell malignancies (ELM-1): Results from the relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma cohort in a single-arm, multicentre, phase 1 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2022, 9, e327–e339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamadani, M.; Radford, J.; Carlo-Stella, C.; Caimi, P.F.; Reid, E.; O’Connor, O.A.; Feingold, J.M.; Ardeshna, K.M.; Townsend, W.; Solh, M.; et al. Final results of a phase 1 study of loncastuximab tesirine in relapsed/refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2021, 137, 2634–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Munoz, J.; Goy, A.; Locke, F.L.; Jacobson, C.A.; Hill, B.T.; Timmerman, J.M.; Holmes, H.; Jaglowski, S.; Flinn, I.W.; et al. KTE-X19 CAR T-Cell Therapy in Relapsed or Refractory Mantle-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1331–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Munoz, J.; Goy, A.; Locke, F.L.; Jacobson, C.A.; Hill, B.T.; Timmerman, J.M.; Holmes, H.; Jaglowski, S.; Flinn, I.W.; et al. Three-Year Follow-Up of KTE-X19 in Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Mantle Cell Lymphoma, Including High-Risk Subgroups, in the ZUMA-2 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jain, P.; Locke, F.L.; Maurer, M.J.; Frank, M.J.; Munoz, J.L.; Dahiya, S.; Beitinjaneh, A.M.; Jacobs, M.T.; McGuirk, J.P.; et al. Brexucabtagene Autoleucel for Relapsed or Refractory Mantle Cell Lymphoma in Standard-of-Care Practice: Results From the US Lymphoma CAR T Consortium. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 2594–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Siddiqi, T.; Gordon, L.I.; Kamdar, M.; Lunning, M.; Hirayama, A.V.; Abramson, J.S.; Arnason, J.; Ghosh, N.; Mehta, A.; et al. Lisocabtagene Maraleucel in Relapsed/Refractory Mantle Cell Lymphoma: Primary Analysis of the Mantle Cell Lymphoma Cohort From TRANSCEND NHL 001, a Phase I Multicenter Seamless Design Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 1146–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacoboni, G.; Rejeski, K.; Villacampa, G.; van Doesum, J.A.; Chiappella, A.; Bonifazi, F.; Lopez-Corral, L.; van Aalderen, M.; Kwon, M.; Martínez-Cibrian, N.; et al. Real-world evidence of brexucabtagene autoleucel for the treatment of relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 3606–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, G.; Dreyling, M.; Oberic, L.; Gine, E.; Zinzani, P.L.; Linton, K.; Vilmar, A.; Jerkeman, M.; Chen, J.M.H.; Ohler, A.; et al. Indirect treatment comparison of brexucabtagene autoleucel (ZUMA-2) versus standard of care (SCHOLAR-2) in relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2024, 65, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.; Martin, P.; Christos, P.; Cerchietti, L.; Tam, W.; Shah, B.; Schuster, S.J.; Rodriguez, A.; Hyman, D.; Calvo-Vidal, M.N.; et al. Five-year follow-up of lenalidomide plus rituximab as initial treatment of mantle cell lymphoma. Blood 2018, 132, 2016–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcaini, L.; Lamy, T.; Walewski, J.; Belada, D.; Mayer, J.; Radford, J.; Jurczak, W.; Morschhauser, F.; Alexeeva, J.; Rule, S.; et al. Prospective subgroup analyses of the randomized MCL-002 (SPRINT) study: Lenalidomide versus investigator’s choice in relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 180, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eve, H.E.; Carey, S.; Richardson, S.J.; Heise, C.C.; Mamidipudi, V.; Shi, T.; Radford, J.A.; Auer, R.L.; Bullard, S.H.; Rule, S.A. Single-agent lenalidomide in relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma: Results from a UK phase II study suggest activity and possible gender differences. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 159, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.; Martin, P.; Shah, B.; Schuster, S.J.; Smith, S.M.; Furman, R.R.; Christos, P.; Rodriguez, A.; Svoboda, J.; Lewis, J.; et al. Lenalidomide plus Rituximab as Initial Treatment for Mantle-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1835–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhoda, S.; Vistarop, A.; Wang, Y.L. Resistance to Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibition in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2023, 200, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Wang, J.; Hong, J. Next-generation Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) Inhibitors Potentially Targeting BTK C481S Mutation- Recent Developments and Perspectives. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 1674–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, A.R.; Flinn, I.W.; Pagel, J.M.; Brown, J.R.; Cheah, C.Y.; Coombs, C.C.; Patel, M.R.; Rothenberg, S.M.; Tsai, D.E.; Ku, N.C.; et al. Results from a First-in-Human, Proof-of-Concept Phase 1 Trial in Pretreated B-Cell Malignancies for Loxo-305, a Next-Generation, Highly Selective, Non-Covalent BTK Inhibitor. Blood 2019, 134 (Suppl. 1), 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telaraja, D.; Kasamon, Y.L.; Collazo, J.S.; Leong, R.; Wang, K.; Li, P.; Dahmane, E.; Yang, Y.; Earp, J.; Grimstein, M.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Pirtobrutinib for Relapsed or Refractory Mantle Cell Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyre, T.A.; Shah, N.N.; Dreyling, M.; Jurczak, W.; Wang, Y.; Cheah, C.Y.; Song, Y.; Gandhi, M.; Chay, C.; Sharman, J.; et al. BRUIN MCL-321: Phase III study of pirtobrutinib versus investigator choice of BTK inhibitor in BTK inhibitor naive mantle cell lymphoma. Future Oncol. 2022, 18, 3961–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VENCLEXTA (Venetoclax) [Prescribing Information]; AbbVie Inc.: North Chicago, IL, USA,, 2019.
- Haselager, M.V.; Kielbassa, K.; Ter Burg, J.; Bax, D.J.C.; Fernandes, S.M.; Borst, J.; Tam, C.; Forconi, F.; Chiodin, G.; Brown, J.R.; et al. Changes in Bcl-2 members after ibrutinib or venetoclax uncover functional hierarchy in determining resistance to venetoclax in CLL. Blood 2020, 136, 2918–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Ramchandren, R.; Chen, R.; Karlin, L.; Chong, G.; Jurczak, W.; Wu, K.L.; Bishton, M.; Collins, G.P.; Eliadis, P.; et al. Concurrent ibrutinib plus venetoclax in relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma: The safety run-in of the phase 3 SYMPATICO study. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Jurczak, W.; Trněný, M.; Belada, D.; Wrobel, T.; Ghosh, N.; Keating, M.-M.; van Meerten, T.; Fernandez Alvarez, R.; von Keudell, G.; et al. Ibrutinib Combined with Venetoclax in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Mantle Cell Lymphoma: Primary Analysis Results from the Randomized Phase 3 Sympatico Study. Blood 2023, 142 (Suppl. 2), LBA-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Jurczak, W.; Trneny, M.; Belada, D.; Wrobel, T.; Ghosh, N.; Keating, M.M.; van Meerten, T.; Alvarez, R.F.; von Keudell, G.; et al. Ibrutinib plus venetoclax in relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (SYMPATICO): A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2025, 26, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurgeon, S.; Mei, M.; Barr, P.; Barrientos, J.; Vos, S.; Furman, R.; Patel, K.; Thompson, P.; Choi, M.; Kallam, A.; et al. Waveline-001: Updated Results from a Phase 1 Dose Escalation and Cohort Expansion Study of Zilovertamab Vedotin (MK-2140) in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood 2022, 140, 6640–6641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.L.; Barrientos, J.C.; Furman, R.R.; Mei, M.; Barr, P.M.; Choi, M.Y.; de Vos, S.; Kallam, A.; Patel, K.; Kipps, T.J.; et al. Zilovertamab Vedotin Targeting of ROR1 as Therapy for Lymphoid Cancers. NEJM Evid. 2022, 1, EVIDoa2100001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabretta, E.; Hamadani, M.; Zinzani, P.L.; Caimi, P.; Carlo-Stella, C. The antibody-drug conjugate loncastuximab tesirine for the treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2022, 140, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D. Cancer biomarkers for targeted therapy. Biomark. Res. 2019, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caimi, P.F.; Ai, W.; Alderuccio, J.P.; Ardeshna, K.M.; Hamadani, M.; Hess, B.; Kahl, B.S.; Radford, J.; Solh, M.; Stathis, A.; et al. Loncastuximab tesirine in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (LOTIS-2): A multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consolidation With Loncastuximab Tesirine After a Short Course of Immunochemotherapy in BTKi-Treated (or Intolerant) Relapsed/Refractory Mantle Cell Lymphoma Patients. (FIL_COLUMN) ClinicalTrials.gov ID NCT05249959. Available online: https://inclinicaltrials.com/refractory-mantle-cell-lymphoma/NCT05249959/ (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- Depaus, J.; Bryan, L.; Ungar, D.; Dautaj, I.; Wagner-Johnston, N. Safety and Anti-Tumor Activity Study of Loncastuximab Tesirine and Ibrutinib in Diffuse Large B-Cell or Mantle Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2019, 134, 5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskowitz, C.H.; Bastos-Oreiro, M.; Ungar, D.; Dautaj, I.; Kalac, M. Safety and Anti-Tumor Activity Study of Loncastuximab Tesirine and Durvalumab in Diffuse Large B-Cell, Mantle Cell, or Follicular Lymphoma. Blood 2019, 134 (Suppl. 1), 2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacac, M.; Colombetti, S.; Herter, S.; Sam, J.; Perro, M.; Chen, S.; Bianchi, R.; Richard, M.; Schoenle, A.; Nicolini, V.; et al. CD20-TCB with Obinutuzumab Pretreatment as Next-Generation Treatment of Hematologic Malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 4785–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COLUMVI Prescribing Information. Available online: https://www.gene.com/download/pdf/columvi_prescribing.pdf (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Phillips, T.J.; Carlo-Stella, C.; Morschhauser, F.; Bachy, E.; Crump, M.; Trněný, M.; Bartlett, N.L.; Zaucha, J.; Wrobel, T.; Offner, F.; et al. Glofitamab in Relapsed/Refractory Mantle Cell Lymphoma: Results From a Phase I/II Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bröske, A.E.; Korfi, K.; Belousov, A.; Wilson, S.; Ooi, C.H.; Bolen, C.R.; Canamero, M.; Alcaide, E.G.; James, I.; Piccione, E.C.; et al. Pharmacodynamics and molecular correlates of response to glofitamab in relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 1025–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, T.J.; Matasar, M.; Eyre, T.A.; Gine, E.; Filézac De L’Étang, A.; Byrne, B.; Lundberg, L.; Padovani, A.; Boetsch, C.; Bottos, A.; et al. GLOBRYTE: A Phase III, Open-Label, Multicenter, Randomized Trial Evaluating Glofitamab Monotherapy in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Mantle Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2023, 142 (Suppl. 1), 3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelberts, P.J.; Hiemstra, I.H.; de Jong, B.; Schuurhuis, D.H.; Meesters, J.; Beltran Hernandez, I.; Oostindie, S.C.; Neijssen, J.; van den Brink, E.N.; Horbach, G.J.; et al. DuoBody-CD3xCD20 induces potent T-cell-mediated killing of malignant B cells in preclinical models and provides opportunities for subcutaneous dosing. EBioMedicine 2020, 52, 102625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrijn, A.F.; Meesters, J.I.; de Goeij, B.E.; van den Bremer, E.T.; Neijssen, J.; van Kampen, M.D.; Strumane, K.; Verploegen, S.; Kundu, A.; Gramer, M.J.; et al. Efficient generation of stable bispecific IgG1 by controlled Fab-arm exchange. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 5145–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrijn, A.F.; Meesters, J.I.; Priem, P.; de Jong, R.N.; van den Bremer, E.T.; van Kampen, M.D.; Gerritsen, A.F.; Schuurman, J.; Parren, P.W. Controlled Fab-arm exchange for the generation of stable bispecific IgG1. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 2450–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchings, M.; Mous, R.; Clausen, M.R.; Johnson, P.; Linton, K.M.; Chamuleau, M.E.D.; Lewis, D.J.; Sureda Balari, A.; Cunningham, D.; Oliveri, R.S.; et al. Dose escalation of subcutaneous epcoritamab in patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma: An open-label, phase 1/2 study. Lancet 2021, 398, 1157–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budde, L.E.; Assouline, S.; Sehn, L.H.; Schuster, S.J.; Yoon, S.S.; Yoon, D.H.; Matasar, M.J.; Bosch, F.; Kim, W.S.; Nastoupil, L.J.; et al. Durable Responses With Mosunetuzumab in Relapsed/Refractory Indolent and Aggressive B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas: Extended Follow-Up of a Phase I/II Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 2250–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, S.J.; Sehn, L.H.; Bartlett, N.L.; Matasar, M.; Assouline, S.; Giri, P.; Kuruvilla, J.; Shadman, M.; Cheah, C.Y.; Dietrich, S.; et al. Mosunetuzumab Monotherapy Continues to Demonstrate Durable Responses in Patients with Relapsed and/or Refractory Follicular Lymphoma after ≥2 Prior Therapies: 3-Year Follow-up from a Pivotal Phase II Study. Blood 2023, 142 (Suppl. 1), 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budde, L.E.; Sehn, L.H.; Matasar, M.; Schuster, S.J.; Assouline, S.; Giri, P.; Kuruvilla, J.; Canales, M.; Dietrich, S.; Fay, K.; et al. Safety and efficacy of mosunetuzumab, a bispecific antibody, in patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma: A single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 1055–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budde, E.L.; Bartlett, N.L.; Giri, P.; Schuster, S.J.; Assouline, S.; Yoon, S.-S.; Fay, K.; Matasar, M.J.; Gutierrez, N.C.; Marlton, P.; et al. Subcutaneous Mosunetuzumab Is Active with a Manageable Safety Profile in Patients (pts) with Relapsed/Refractory (R/R) B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas (B-NHLs): Updated Results from a Phase I/II Study. Blood 2022, 140 (Suppl. 1), 3753–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/lunsumio#authorisation-details (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- Budde, L.E.; Assouline, S.; Sehn, L.H.; Schuster, S.J.; Yoon, S.S.; Yoon, D.H.; Matasar, M.J.; Bosch, F.; Kim, W.S.; Nastoupil, L.J.; et al. Single-Agent Mosunetuzumab Shows Durable Complete Responses in Patients With Relapsed or Refractory B-Cell Lymphomas: Phase I Dose-Escalation Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, N.L.; Assouline, S.; Giri, P.; Schuster, S.J.; Cheah, C.Y.; Matasar, M.; Gregory, G.P.; Yoon, D.H.; Shadman, M.; Fay, K.; et al. Mosunetuzumab monotherapy is active and tolerable in patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 4926–4935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, R.C.; Poh, C.; Shadman, M.; Till, B.G.; Smith, S.D.; Ujjani, C.S.; Ottemiller, S.; Fessel, M.M.; Joy, B.; DeBell, J.; et al. Early Complete Responses with Mosunetuzumab Monotherapy in Treatment-Naïve Follicular and Marginal Zone Lymphomas with Only Low-Grade Cytokine Release Syndrome. Blood 2023, 142 (Suppl. 1), 4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, C.Y.; Assouline, S.; Baker, R.; Bartlett, N.L.; El-Sharkawi, D.; Giri, P.; Ku, M.; Schuster, S.J.; Matasar, M.; Radford, J.; et al. Mosunetuzumab Monotherapy Demonstrates Activity and a Manageable Safety Profile in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Richter’s Transformation. Blood 2023, 142 (Suppl. 1), 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.L.; Assouline, S.; Kamdar, M.; Ghosh, N.; Naik, S.; Nakhoda, S.K.; Chavez, J.C.; Jia, T.; Pham, S.; Huw, L.-Y.; et al. Fixed Duration Mosunetuzumab Plus Polatuzumab Vedotin Has Promising Efficacy and a Manageable Safety Profile in Patients with BTKi Relapsed/Refractory Mantle Cell Lymphoma: Initial Results from a Phase Ib/II Study. Blood 2023, 142 (Suppl. 1), 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.S.; Kim, T.M.; Cho, S.G.; Jarque, I.; Iskierka-Jażdżewska, E.; Poon, L.M.; Prince, H.M.; Zhang, H.; Cao, J.; Zhang, M.; et al. Odronextamab monotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma: Primary efficacy and safety analysis in phase 2 ELM-2 trial. Nat. Cancer 2025, 6, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayyappan, S.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, T.M.; Walewski, J.; Cho, S.-G.; Jarque, I.; Iskierka-Jazdzewska, E.; Poon, M.; Oh, S.Y.; Inng Lim, F.L.W.; et al. Final Analysis of the Phase 2 ELM-2 Study: Odronextamab in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory (R/R) Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL). Blood 2023, 142, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer-Visser, J.; Fiaschi, N.; Deering, R.P.; Cygan, K.J.; Scott, D.; Jeong, S.; Boucher, L.; Gupta, N.T.; Gupta, S.; Adler, C.; et al. Molecular assessment of intratumoral immune cell subsets and potential mechanisms of resistance to odronextamab, a CD20×CD3 bispecific antibody, in patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2024, 12, e008338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, M.; Canale, F.A.; Naso, V.; Porto, G.; Gerace, D.; Allegra, A. Do CAR-T and Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant Both Have a Place in Lymphoid Neoplasms? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, A.; Bento, L.; Novelli, S.; Martin, A.; Gutierrez, G.; Queralt Salas, M.; Bastos-Oreiro, M.; Perez, A.; Hernani, R.; Cruz Viguria, M.; et al. Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation in Mantle Cell Lymphoma; Insights into Its Potential Role in the Era of New Immunotherapeutic and Targeted Therapies: The GETH/GELTAMO Experience. Cancers 2022, 14, 2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Blasi, R.; Le Gouill, S.; Bachy, E.; Cartron, G.; Beauvais, D.; Le Bras, F.; Gros, F.X.; Choquet, S.; Bories, P.; Feugier, P.; et al. Outcomes of patients with aggressive B-cell lymphoma after failure of anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy: A DESCAR-T analysis. Blood 2022, 140, 2584–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebers, N.; Boumendil, A.; Finel, H.; Edelmann, D.; Kobbe, G.; Baermann, B.N.; Serroukh, Y.; Blaise, D.; Beelen, D.W.; Solano, C.; et al. Brexucabtagene autoleucel versus allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in relapsed and refractory mantle cell lymphoma. Blood Cancer Discov. 2025, 6, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurko, J.; Nizamuddin, I.; Epperla, N.; David, K.; Cohen, J.B.; Moyo, T.K.; Ollila, T.; Hess, B.; Roy, I.; Ferdman, R.; et al. Peri-CAR-T practice patterns and survival predictors for all CAR-T patients and post-CAR-T failure in aggressive B-NHL. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 2657–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, S.; Shouval, R.; Walji, M.; Flynn, J.R.; Yerushalmi, R.; Shem-Tov, N.; Danylesko, I.; Tomas, A.A.; Fein, J.A.; Devlin, S.M.; et al. Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation after Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy in Large B Cell Lymphoma. Transplant. Cell Ther. 2023, 29, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacoboni, G.; Iraola-Truchuelo, J.; O’Reilly, M.; Navarro, V.; Menne, T.; Kwon, M.; Martín-López, A.; Chaganti, S.; Delgado, J.; Roddie, C.; et al. Treatment outcomes in patients with large B-cell lymphoma after progression to chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy. Hemasphere 2024, 8, e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya, S.; Bourcier, J.; Noviski, M.; Lu, H.; Thompson, M.C.; Chirino, A.; Jahn, J.; Sondhi, A.K.; Gajewski, S.; Tan, Y.S.M.; et al. Kinase-impaired BTK mutations are susceptible to clinical-stage BTK and IKZF1/3 degrader NX-2127. Science 2024, 383, eadi5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danilov, A.; Tees, M.; Patel, K.; Wierda, W.; Patel, M.; Flinn, I.; Latif, T.; Ai, W.; Thompson, M.; Wang, M.; et al. A First-in-Human Phase 1 Trial of NX-2127, a First-in-Class Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) Dual-Targeted Protein Degrader with Immunomodulatory Activity, in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory B Cell Malignancies. Blood 2023, 142, 4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.N.; Omer, Z.; Collins, G.P.; Forconi, F.; Danilov, A.; Byrd, J.C.; El-Sharkawi, D.; Searle, E.; Alencar, A.J.; Ma, S.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) Degrader NX-5948 in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory (R/R) Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): Updated Results from an Ongoing Phase 1a/b Study. Blood 2024, 144 (Suppl. 1), 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Profitos-Peleja, N. The Multikinase CDK4/6 Inhibitor Narazaciclib Overcomes Btki Resistance in Mantle Cell Lymphoma by Targeting USP24-P53. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/371455714_Prolonged_cell_cycle_arrest_by_the_CDK46_antagonist_narazaciclib_restores_ibrutinib_response_in_preclinical_models_of_BTKi-resistant_mantle_cell_lymphoma (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- Parra, J.R.M.; et al. (Eds.) Hemasphere, 2024; Volume 8. (Suppl. 1), 1272.
- Lantermans, H.C.; Ma, F.; Kuil, A.; van Kesteren, S.; Yasinoglu, S.; Yang, G.; Buhrlage, S.J.; Wang, J.; Gray, N.S.; Kersten, M.J.; et al. The dual HCK/BTK inhibitor KIN-8194 impairs growth and integrin-mediated adhesion of BTKi-resistant mantle cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2024, 38, 1570–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, R.; Bellanger, C.; Kervoëlen, C.; Tessoulin, B.; Dousset, C.; Menoret, E.; Asnagli, H.; Parker, A.; Beer, P.; Pellat-Deceunynck, C.; et al. Selective pharmacologic targeting of CTPS1 shows single-agent activity and synergizes with BCL2 inhibition in aggressive mantle cell lymphoma. Haematologica 2024, 109, 2574–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thus, Y.J.; Eldering, E.; Kater, A.P.; Spaargaren, M. Tipping the balance: Toward rational combination therapies to overcome venetoclax resistance in mantle cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2022, 36, 2165–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolnikova, A.; Kazantsev, D.; Klanova, M.; Pokorna, E.; Sovilj, D.; Kelemen, C.D.; Tuskova, L.; Hoferkova, E.; Mraz, M.; Helman, K.; et al. Blockage of BCL-XL overcomes venetoclax resistance across BCL2+ lymphoid malignancies irrespective of BIM status. Blood Adv. 2024, 8, 3532–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goy, A.; Hernandez-Ilzaliturri, F.J.; Kahl, B.; Ford, P.; Protomastro, E.; Berger, M. A phase I/II study of the pan Bcl-2 inhibitor obatoclax mesylate plus bortezomib for relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2014, 55, 2761–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, C.; Tam, C.; Lasica, M.; Verner, E.; Browett, P.; Anderson, M.A.; Hilger, J.; Fang, Y.; Simpson, D.; Opat, S. A Phase 1 Study with the Novel B-Cell Lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) Inhibitor Bgb-11417 As Monotherapy or in Combination with Zanubrutinib (ZANU) in Patients (Pts) with CLL/SLL: Preliminary Data. Blood 2022, 140, 2321–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumerai, J.; Lasica, M.; Opat, S.; Cheah, C.; Chan, H.; Verner, E.; Barca, E.; Tedeschi, A.; Hilger, J.; Fang, Y.; et al. A Phase 1 Study with the Novel B-Cell Lymphoma 2 (Bcl-2) Inhibitor Bgb-11417 As Monotherapy or in Combination with Zanubrutinib (ZANU) in Patients (Pts) with Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL) or Waldenström Macroglobulinemia (WM): Preliminary Data. Blood 2022, 140, 9325–9327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodson, D.; Shouse, G.; Shin, H.J.; Salar Silvestre, A.; Bobillo Varela, S.; Ribrag, V.; Macpherson, N.; Cordoba, R.; Seok Kim, J.; Radford, J.; et al. P1098: A Phase II, Open-Label, Multicenter Study of Capivasertib, A Potent, Oral Pan-AKT Inhibitor, in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (Capital). Hemasphere 2023, 7, e5749555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Johnson, P.; Yazji, S.; Katz, Y.; Pietrofeso, A.; Robinson, J.; Mei, M.; Frigault, M.; Breitmeyer, J.; Jacobson, C. A Phase 1/2 Study of a ROR1-Targeting CAR T Cell Therapy (ONCT-808) in Adult Patients with Relapsed/Refractory (R/R) Aggressive B Cell Lymphomas (BCL). Blood 2024, 144, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.N.; Fenske, T.; Johnson, B.; Szabo, A.; Devata, S.; Longo, W.; Kearl, T.; Zamora, A.; Hari, P.; Schneider, D.; et al. P1082: Results from a Phase 1/2 Study of Tandem, Bispecific Anti-CD20/Anti-CD19 (LV20.19) CAR T-Cells for Mantle Cell Lymphoma. Hemasphere 2023, 7, e207658e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.K.; Williams, J.; Sorathia, K.; Pray, B.; Abusaleh, K.; Bian, Z.; Sharma, A.; Hout, I.; Nishat, S.; Hanel, W.; et al. A novel CAR-T cell product targeting CD74 is an effective therapeutic approach in preclinical mantle cell lymphoma models. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 12, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Drug | Study | Patient Number | Post-ASCT | Post-CAR-T | ORR | CR | OS | mPFS | mDOR | mFU | AEs ≥ G3 | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ibrutinib | NCT01236391 | 111 | 12 (11%) | - | 68% | 21% | N.R. | 13.9 | 17.5 | 15.3 | [22] | |
| Ibrutinib | NCT01646021 | 280 | - | - | 72% | 19% | N.R. | 14.6 | N.R. | 20 | 94 (68%) | [23] |
| Acalabrutinib | NCT02213926 | 124 | 22 (18%) | - | 81% | 40% | N.R. | N.R. | N.R. | 15.2 | 48 (39%) | [24] |
| Zanubrutinib | NCT03206970 | 86 | - | - | 83.7% | 77.9% | N.R. | 33 | N.R. | 35.3 | [30] |
| Study | Patient Number | Post-ASCT | Post-CAR-T | ORR | CR | OS | mPFS | mDOR | mFU | AEs ≥ G3 | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pirtobrutinib | NCT03740529 | 127 | 81% | 43% | NR 62% at 18 months | NR 74% at 18 months | 18 | (20.5%) | [41] | |||
| Venetoclax + ibrutinib | NCT03112174 | 267 | 39 (29%) | 75% | 21% | 36.7 | 31.9 | (84%) | [42] | |||
| Glofitamab | NCT03075696 | 61 | 2 (3.3%) | 16 (26.7%) | 74% | 71% | 29.9 | 16.8 | 16.2 | 19.6 | (65%) | [43] |
| Zilovertamab vedotin | NCT03833180 | 40 | 11 (28%) | 6 (15%) | 40% | 13% | 9 | 3.4 | 3 | 32 (80%) | [44] | |
| Mosunetuzumab | NCT02500407 | 25 | (33%) | 44% | 24% | 7.3 | 3.7 | 10.3 | 54.5 | 19 (76%) | [45] | |
| Mosunetuzumab + polatuzumab | NCT03671018 | 20 | 15 (12.5%) | 42 (35%) | 75% | 70% | 23.3 | 11.4 | NR at mFU of 45 months | 45 | (56.7%) | [46] |
| Odronextamab | NCT02290951 | 12 | 3 (25%) | 50% | 33% | 7.6 | 26.2 | [47] | ||||
| Loncastuximab-tesirine | NCT02669017 | 15 | 46.7% | 33% | N.R. | 4.8 | [48] |
| NCT Number | Name | Phase | State | Drug |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04939272 | I–II | Not recruiting | Copanlisib Hydrochloride, Venetoclax | |
| NCT03891355 | FIL_KLIMT | II | Not recruiting | Carfilzomib, Lenalidomide, Dexamethasone |
| NCT04047797 | II | Not recruiting | Ixazomib, Ixazomib Citrate, Rituximab | |
| NCT02558816 | OAsls | I–II | Not recruiting | Ibrutinib, Obinutuzumab, GDC-0199 (Venetoclax) |
| NCT02446236 | Ib | Not recruiting | Lenalidomide, Ibrutinib, Rituximab | |
| NCT01695941 | I | Not recruiting | Alisertib, Bortezomib, Rituximab | |
| NCT03440567 | I | Not recruiting | Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation, Avelumab, Carboplatin, Etoposide Phosphate, Ibrutinib, Ifosfamide, Rituximab, Utomilumab | |
| NCT04659044 | II | Not recruiting | Polatuzumab Vedotin, Rituximab, Rituximab and Hyaluronidase Human, Venetoclax | |
| NCT01996865 | MAGNIFY | IIIb | Not recruiting | Lenalidomide, Rituximab |
| NCT04703686 | II | Not recruiting | Obinutuzumab, RO7082859 (Glofitamab) | |
| NCT03162536 | I–II | Not recruiting | Nemtabrutinib | |
| NCT03015896 | I–II | Not recruiting | Lenalidomide, Nivolumab | |
| NCT04578600 | I/Ib | Not recruiting | Lenalidomide, Obinutuzumab, Oral Azacitidine | |
| NCT03277729 | I/II | Not recruiting | Chimeric Antigen Receptor-T-Cell Therapy, Cyclophosphamide, Fludarabine Phosphate | |
| NCT04205409 | II | Not recruiting | Nivolumab | |
| NCT02568553 | I | Not recruiting | Blinatumomab, Lenalidomide | |
| NCT03997968 | I/II | Not recruiting | CYT-0851, CYT-0851 + gemcitabine/capecitabine/rituximab and bendamustine | |
| NCT05131022 | Ia/Ib | Recruiting | NX5948 | |
| NCT06252675 | II | Recruiting | Obinutuzumab, Glofitamab, Pirtobrutinib | |
| NCT05471843 | I/II | Not recruiting | BGB-11417 | |
| NCT05868395 | II | Recruiting | Polatuzumab, Bendamustine, Rituximab | |
| NCT06324994 | II | Not yet recruiting | Linperlisib + Obinutuzumab and Venetoclax | |
| NCT06106841 | Ib/II | Recruiting | TQB3909 | |
| NCT04484012 | II | Recruiting | Acalabrutinib, CD19CAR-CD28-CD3zeta-EGFRt-expressing Tn/mem-enriched T lymphocytes | |
| NCT04186520 | I/II | Recruiting | LV20.19 CAR-T | |
| NCT05910801 | II | Recruiting | Lenalidomide, Tafasitamab, Venetoclax | |
| NCT05716087 | II | Not recruiting | LP-168 (Rocbrutinib) | |
| NCT06192888 | I | Recruiting | Glofitamab, Obinutuzumab, Lenalidomide | |
| NCT06558604 | GLOASIS | II | Recruiting | Obinutuzumab, Glofitamab, Venetoclax, Zanubrutinib |
| NCT05249959 | COLUMN | II | Recruiting | ADCT-402 (loncastuximab tesirine), Rituximab-Bendamustine, Ara-C |
| NCT05529069 | II | Recruiting | Pirtobrutinib, Venetoclax | |
| NCT05444322 | I | Recruiting | RD14-01 cell infusion (anti ROR1 CAR-T) | |
| NCT06300528 | II | Recruiting | Pemigatinib | |
| NCT05990465 | I | Recruiting | Pirtobrutinib, LV20.19 CAR-T | |
| NCT06208735 | I | Recruiting | CLIC-2201 | |
| NCT04763083 | I | Recruiting | NVG-111 | |
| NCT05370430 | I | Recruiting | BAFFR-CAR-T cells | |
| NCT06464861 | I | Recruiting | CD19-CAR-NK/T | |
| NCT06544265 | I | Recruiting | SynKIR-310 (Autologous T Cells Transduced with CD19 KIR-CAR) | |
| NCT03676504 | I/II | Recruiting | CD19.CAR-T Cells, Fludarabine, Cyclophosphamide | |
| NCT04775745 | I | Recruiting | LP-168 (Rocbrutinib) | |
| NCT05643742 | I/II | Recruiting | CTX112 (Allogeneic CRISPR-Cas9 Engineered CD19 CAR-T) | |
| NCT05453396 | II | Recruiting | Loncastuximab Tesirine | |
| NCT06285422 | I | Recruiting | SC262 | |
| NCT05887167 | I | Recruiting | Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation, CAR-T | |
| NCT04830137 | Ia/Ib | Recruiting | NX-2127 | |
| NCT02952508 | CLOVER-1 | II | Not recruiting | CLR 131 (Iopofosine I 131) |
| NCT06191887 | Ia/Ib | Recruiting | Autologous BAFFR-targeting CAR-T Cells, Bendamustine, Cyclophosphamide, Fludarabine | |
| NCT06561425 | I/II | Recruiting | GLPG5101 | |
| NCT03888105 | II | Recruiting | Odronextamab | |
| NCT03547115 | I | Recruiting | Voruciclib | |
| NCT06256484 | I | Recruiting | ATA3219 | |
| NCT04223765 | I | Recruiting | CAR.k.28, Fludarabine, Cyclophosphamide, Bendamustine | |
| NCT05780034 | I | Recruiting | AC676 | |
| NCT06542250 | TITANium | I/II | Recruiting | AZD5492 |
| NCT05665530 | I | Not recruiting | PRT2527, Zanubrutinib, Venetoclax |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boccellato, E.; Comba, L.; Tavarozzi, R.; Castellino, C.; Foglietta, M.; Mattei, D.; Ladetto, M.; Massaia, M.; Castellino, A. Next-Generation Therapies in Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL): The Evolving Landscape in Treatment of Relapse/Refractory After CAR-T Cells. Cancers 2025, 17, 2239. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132239
Boccellato E, Comba L, Tavarozzi R, Castellino C, Foglietta M, Mattei D, Ladetto M, Massaia M, Castellino A. Next-Generation Therapies in Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL): The Evolving Landscape in Treatment of Relapse/Refractory After CAR-T Cells. Cancers. 2025; 17(13):2239. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132239
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoccellato, Elia, Lorenzo Comba, Rita Tavarozzi, Claudia Castellino, Myriam Foglietta, Daniele Mattei, Marco Ladetto, Massimo Massaia, and Alessia Castellino. 2025. "Next-Generation Therapies in Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL): The Evolving Landscape in Treatment of Relapse/Refractory After CAR-T Cells" Cancers 17, no. 13: 2239. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132239
APA StyleBoccellato, E., Comba, L., Tavarozzi, R., Castellino, C., Foglietta, M., Mattei, D., Ladetto, M., Massaia, M., & Castellino, A. (2025). Next-Generation Therapies in Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL): The Evolving Landscape in Treatment of Relapse/Refractory After CAR-T Cells. Cancers, 17(13), 2239. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132239






