Pediatric Versus Adult Nasopharyngeal Cancer in Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. MRI Scanning
2.3. Evaluation of Imaging Data
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HNC | Head and neck |
| RMS | Rhabdomyosarcomas |
| NPC | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma |
| SCC | Squamous cell carcinoma |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| EBV | Epstein–Barr virus |
| RT | Radiotherapy |
| OS | Overall survival |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| 18 FDG PET-CT | 18F-fluoro-deoxy-glucose positron emission tomography |
| DWI | Diffusion-weighted imaging |
| ADC | Apparent diffusion coefficient |
| AFNI | Analysis of Functional NeuroImages |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| ICC | Intraclass correlation coefficient |
| CI | Confidence intervals |
| PET | Positron emission tomography |
References
- Grønhøj, C.; Hjalgrim, L.; Jakobsen, K.K.; Charabi, B.; Mirian, C.; Laier, G.H.; Kiss, K.; Rechnitzer, C.; Friborg, J.; Von Buchwald, C.; et al. Incidence of Head and Neck Cancer in Children: A Danish Nationwide Study from 1978 to 2014. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2018, 65, e27037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qaisi, M.; Eid, I. Pediatric Head and Neck Malignancies. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 28, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, J.; Tufaro, A.P. Head and Neck Malignancies in Children. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2024, 36, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Ami, T. Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in Children, Current Treatment Approach. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 46, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claude, L.; Jouglar, E.; Duverge, L.; Orbach, D. Update in Pediatric Nasopharyngeal Undifferentiated Carcinoma. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20190107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnaoui, M.; Lahmar, R.; Ben Mabrouk, A.; Masmoudi, M.; Mighri, K.; Driss, N. Predictive Epidemiological and Clinical Factors of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Diagnosis: Adult versus Pediatric Population. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 137, 110203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.T.; Ye, W.; Zeng, Y.-X.; Adami, H.-O. The Evolving Epidemiology of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2021, 30, 1035–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, I.; Casanova, M.; Ferrari, A.; Rihani, R.; Rodriguez-Galindo, C. Differential Features of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in Children and Adults: A SEER Study. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2010, 55, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-P.; Chan, A.T.C.; Le, Q.-T.; Blanchard, P.; Sun, Y.; Ma, J. Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Lancet 2019, 394, 64–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayan, I.; Kaytan, E.; Ayan, N. Childhood Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: From Biology to Treatment. Lancet Oncol. 2003, 4, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Ami, T.; Kontny, U.; Surun, A.; Brecht, I.B.; Almaraz, R.L.; Dragomir, M.; Pourtsidis, A.; Casanova, M.; Fresneau, B.; Bisogno, G.; et al. Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in Children and Adolescents: The EXPeRT/PARTNER Diagnostic and Therapeutic Recommendations. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2021, 68, e29018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Li, W.-F.; Chen, N.-Y.; Zhang, N.; Hu, G.-Q.; Xie, F.-Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, X.-Z.; Li, J.-G.; Zhu, X.-D.; et al. Induction Chemotherapy plus Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy versus Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy Alone in Locoregionally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Phase 3, Multicentre, Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1509–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Galindo, C.; Krailo, M.D.; Krasin, M.J.; Huang, L.; McCarville, M.B.; Hicks, J.; Pashankar, F.; Pappo, A.S. Treatment of Childhood Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma With Induction Chemotherapy and Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy: Results of the Children’s Oncology Group ARAR0331 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 3369–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Luo, J.; He, X.; Zhu, C. Evaluation of Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography (CT) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) in the Detection of Retropharyngeal Lymph Node Metastases in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Patients. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 1733–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartuccio, N.; Pulizzi, S.; Modica, D.M.; Nicolosi, S.; D’Oppido, D.; Moreci, A.M.; Ialuna, S. Head-to-Head Comparison of [18F]FDG PET Imaging and MRI for the Detection of Recurrence or Residual Tumor in Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2024, 16, 3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Vardhanabhuti, V. PET/CT. PET Clin. 2022, 17, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mui, A.W.L.; Lee, A.W.M.; Lee, V.H.F.; Ng, W.T.; Vardhanabhuti, V.; Man, S.S.Y.; Chua, D.T.T.; Law, S.C.K.; Guan, X.Y. Prognostic and Therapeutic Evaluation of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma by Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced (DCE), Diffusion-Weighted (DW) Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS). Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 83, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.D. MR Imaging of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. N. Am. 2022, 30, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orman, G.; Tran, B.H.; Desai, N.; Meoded, A.; Kralik, S.; Smith, V.; Hicks, J.; Kirsch, C.; Huisman, T.A.G.M. Neuroimaging Characteristics of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in Children. J. Neuroimaging 2021, 31, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, S.C.; Giger, R.; Bojaxhiu, B.; Sachpekidis, C.; Dammann, F.; Dettmer, M.S.; Arnold, A.; Wartenberg, J.; Nisa, L. Multimodal Imaging With Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Detect Extracapsular Extension in Head and Neck Cancer. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, E163–E169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohandas, A.; Marcus, C.; Kang, H.; Truong, M.-T.; Subramaniam, R.M. FDG PET/CT in the Management of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 203, W146–W157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Mao, Y.-P.; Tang, L.-L.; Chen, L.; Sun, Y.; Ma, J. The Evolution of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Staging. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20190244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel Razek, A.A.K.; Gaballa, G.; Elhawarey, G.; Megahed, A.S.; Hafez, M.; Nada, N. Characterization of Pediatric Head and Neck Masses with Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging. Eur. Radiol. 2009, 19, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.D.; Vlantis, A.C.; Yuen, T.W.C.; Law, B.K.H.; Bhatia, K.S.; Zee, B.C.Y.; Woo, J.K.S.; Chan, A.T.C.; Chan, K.C.A.; Ahuja, A.T. Detection of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma by MR Imaging: Diagnostic Accuracy of MRI Compared with Endoscopy and Endoscopic Biopsy Based on Long-Term Follow-Up. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, 2380–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.-F.; Chen, L.; Mao, Y.-P.; Shen, J.-X.; Zhang, F.; Peng, H.; Liu, Q.; et al. Prognostic Value of the Primary Lesion Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Retrospective Study of 541 Cases. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, V.; Li, X.; Lee, V.H.F.; Lam, K.O.; Chan, Q.; Khong, P.L. Intravoxel Incoherent Motion MR Imaging: Comparison of Diffusion and Perfusion Characteristics between Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma and Post-Chemoradiation Fibrosis. Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 2793–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://afni.nimh.nih.gov (accessed on 29 November 2024).
- IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows SPSS, version 26; IBM Corporation: Armonk, NY, USA, 2018.
- JASP, version 0.19.0; JASP—JASP Team: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024.
- Stelow, E.B.; Wenig, B.M. Update from The 4th Edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Head and Neck Tumours: Nasopharynx. Head Neck Pathol. 2017, 11, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.-L.; Chen, Y.-P.; Mao, Y.-P.; Wang, Z.-X.; Guo, R.; Chen, L.; Tian, L.; Lin, A.-H.; Li, L.; Sun, Y.; et al. Validation of the 8th Edition of the UICC/AJCC Staging System for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma From Endemic Areas in the Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy Era. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2017, 15, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, B.K.H.; King, A.D.; Bhatia, K.S.; Ahuja, A.T.; Kam, M.K.M.; Ma, B.B.; Ai, Q.Y.; Mo, F.K.F.; Yuan, J.; Yeung, D.K.W. Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Can Pretreatment DWI Predict Local Failure Based on Long-Term Outcome? AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 1706–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Bhalla, A.S.; Sharma, R.; Kumar, A.; Thakar, A.; Vishnubhatla, S.M.; Sharma, M.C.; Sharma, S.C. Can Diffusion Weighted Imaging Aid in Differentiating Benign from Malignant Sinonasal Masses?: A Useful Adjunct. Pol. J. Radiol. 2017, 82, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, D.; Xu, L.; Hong, L.; Xu, Y.; Pan, J. Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Early Response Assessment of Chemoradiotherapy in Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 32, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.-Y.; Wang, Y.-J.; Liu, J.-P.; Zhou, X.-H.; Xu, Z.-F.; Chen, X.-P.; Xu, T.; Wei, W.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y. Pretreatment Diffusion-Weighted MRI Can Predict the Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 307943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.-P.; Hou, J.; Li, F.-P.; Wang, H.; Hu, P.-S.; Bi, F.; Wang, W. Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Differentiation Between Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma and Lymphoma at the Primary Site. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2016, 40, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Lu, N.; Lian, S.; Li, H.; Yin, S.; Geng, Z.; Xie, C. The Primary Lesion Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Is a Prognostic Factor for Locoregionally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Retrospective Study. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.-F.; Zhang, W.-B.; Ke, S.-B.; Zhao, F.; Yan, S.-X.; Wang, Q.-D.; Teng, L.-S. The Prognostic Value of Pretreatment Tumor Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Values in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.-T.; Guo, S.-S.; Li, H.; Lin, C.; Sun, R.; Chen, Q.-Y.; Liang, Y.-J.; Tang, Q.-N.; Sun, X.-S.; Tang, L.-Q.; et al. Percent Change in Apparent Diffusion Coefficient and Plasma EBV DNA after Induction Chemotherapy Identifies Distinct Prognostic Response Phenotypes in Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Winters, R.; Gajra, A. Nasopharyngeal Cancer. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Tang, Y.; Gao, L.; Huang, X.; Luo, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, K.; Qu, Y.; Xiao, J.; Xu, G.; et al. Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in Children and Adolescents—A Single Institution Experience of 158 Patients. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 9, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.B.; Greene, F.L.; Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Brookland, R.K.; Meyer, L.; Gress, D.M.; Byrd, D.R.; Winchester, D.P. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to Build a Bridge from a Population-based to a More “Personalized” Approach to Cancer Staging. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.W.M.; Ng, W.T.; Chan, J.Y.W.; Corry, J.; Mäkitie, A.; Mendenhall, W.M.; Rinaldo, A.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Saba, N.F.; Strojan, P.; et al. Management of Locally Recurrent Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2019, 79, 101890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karray, H.; Ayadi, W.; Fki, L.; Hammami, A.; Daoud, J.; Drira, M.M.; Frikha, M.; Jlidi, R.; Middeldorp, J.M. Comparison of Three Different Serological Techniques for Primary Diagnosis and Monitoring of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in Two Age Groups from Tunisia. J. Med. Virol. 2005, 75, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baujat, B.; Audry, H.; Bourhis, J.; Chan, A.T.C.; Onat, H.; Chua, D.T.T.; Kwong, D.L.W.; al-Sarraf, M.; Chi, K.-H.; Hareyama, M.; et al. Chemotherapy in Locally Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: An Individual Patient Data Meta-Analysis of Eight Randomized Trials and 1753 Patients. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 64, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casanova, M.; Bisogno, G.; Gandola, L.; Cecchetto, G.; Di Cataldo, A.; Basso, E.; Indolfi, P.; D’Angelo, P.; Favini, F.; Collini, P.; et al. A Prospective Protocol for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in Children and Adolescents: The Italian Rare Tumors in Pediatric Age (TREP) Project. Cancer 2012, 118, 2718–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Galindo, C.; Wofford, M.; Castleberry, R.P.; Swanson, G.P.; London, W.B.; Fontanesi, J.; Pappo, A.S.; Douglass, E.C. Preradiation Chemotherapy with Methotrexate, Cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil, and Leucovorin for Pediatric Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Results of Pediatric Oncology Group (Now Children’s Oncology Group) Study 9486. Cancer 2005, 103, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatakenaka, M.; Nakamura, K.; Yabuuchi, H.; Shioyama, Y.; Matsuo, Y.; Ohnishi, K.; Sunami, S.; Kamitani, T.; Setoguchi, T.; Yoshiura, T.; et al. Pretreatment Apparent Diffusion Coefficient of the Primary Lesion Correlates With Local Failure in Head-and-Neck Cancer Treated with Chemoradiotherapy or Radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 81, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltzschig, H.K.; Carmeliet, P. Hypoxia and Inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, R.; Sugahara, T.; Nakamura, H.; Hirai, T.; Kitajima, M.; Hayashida, Y.; Baba, Y.; Oya, N.; Kuratsu, J.; Yamashita, Y. Malignant Supratentorial Astrocytoma Treated with Postoperative Radiation Therapy: Prognostic Value of Pretreatment Quantitative Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging. Radiology 2007, 243, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizel, D.M.; Sibley, G.S.; Prosnitz, L.R.; Scher, R.L.; Dewhirst, M.W. Tumor Hypoxia Adversely Affects the Prognosis of Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1997, 38, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakenaka, M.; Shioyama, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Yabuuchi, H.; Matsuo, Y.; Sunami, S.; Kamitani, T.; Yoshiura, T.; Nakashima, T.; Nishikawa, K.; et al. Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Calculated with Relatively High B-Values Correlates with Local Failure of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated with Radiotherapy. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 32, 1904–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, F.L.; Pang, R.T.K.; Ma, B.B.Y.; Lee, M.M.L.; Chow, S.M.; Poon, T.C.W.; Chan, A.T.C. Pharmacoproteomics Study of Cetuximab in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. J. Proteome Res. 2006, 5, 3260–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandecaveye, V.; De Keyzer, F.; Vander Poorten, V.; Dirix, P.; Verbeken, E.; Nuyts, S.; Hermans, R. Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Value of Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging for Nodal Staging. Radiology 2009, 251, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.-M.; Chen, X.-X.; Li, Y.-L.; Hua, J.; Chen, J.; Hu, J.; Xu, J.-R. On the Utility of Quantitative Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging as a Tool in Differentiation between Malignant and Benign Thyroid Nodules. Acad. Radiol. 2014, 21, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoeny, H.C.; De Keyzer, F.; King, A.D. Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in the Head and Neck. Radiology 2012, 263, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
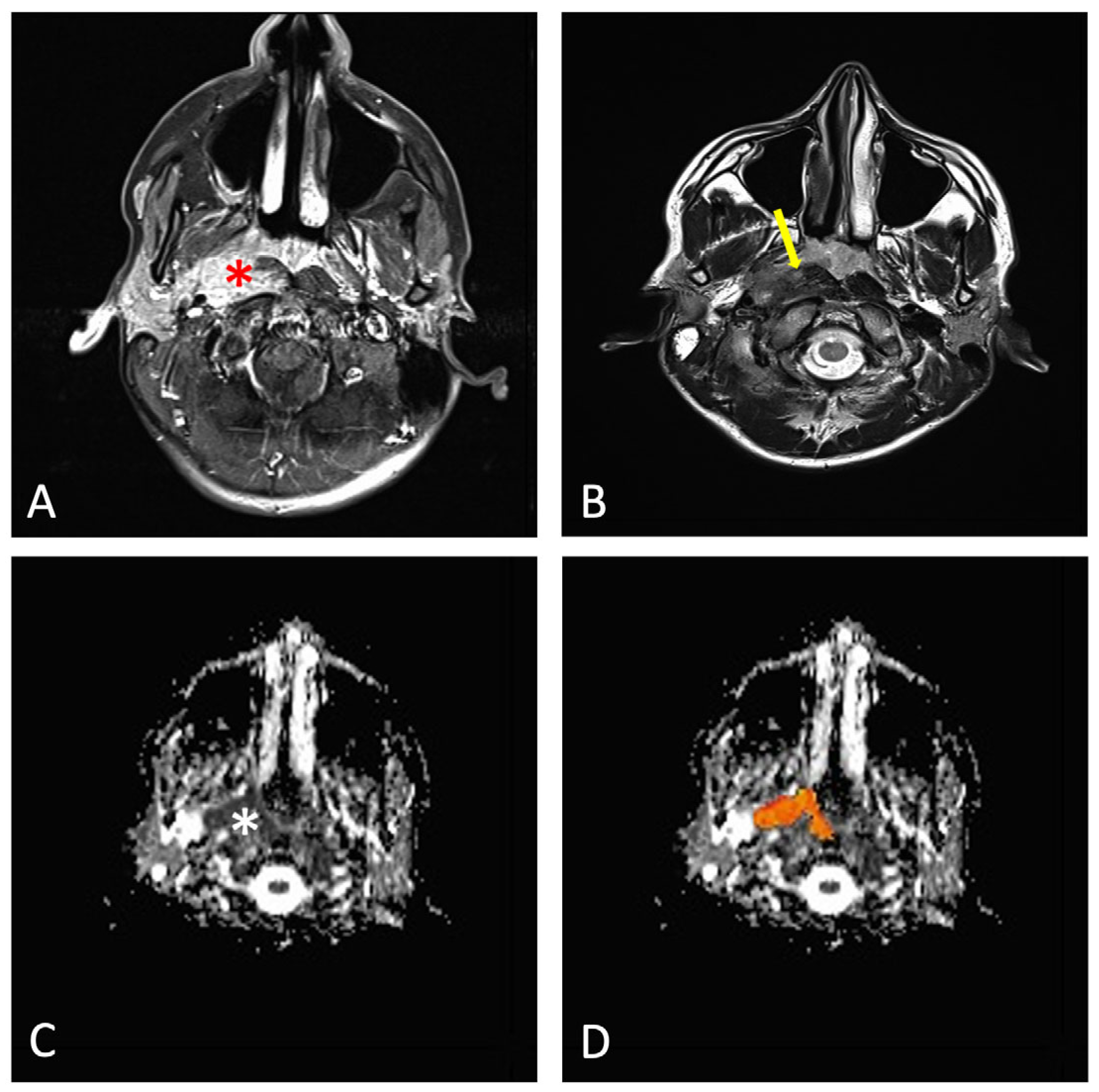
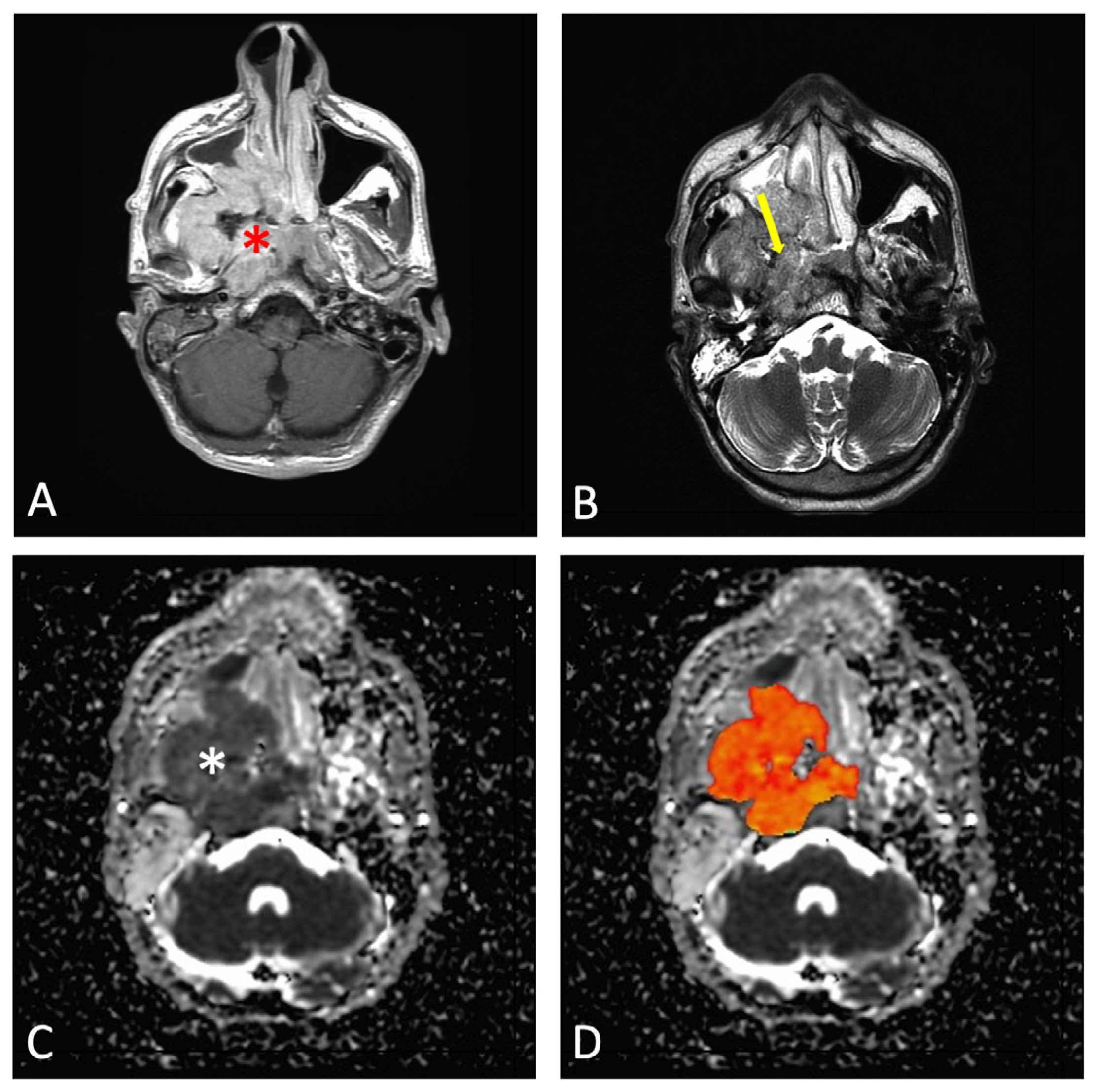
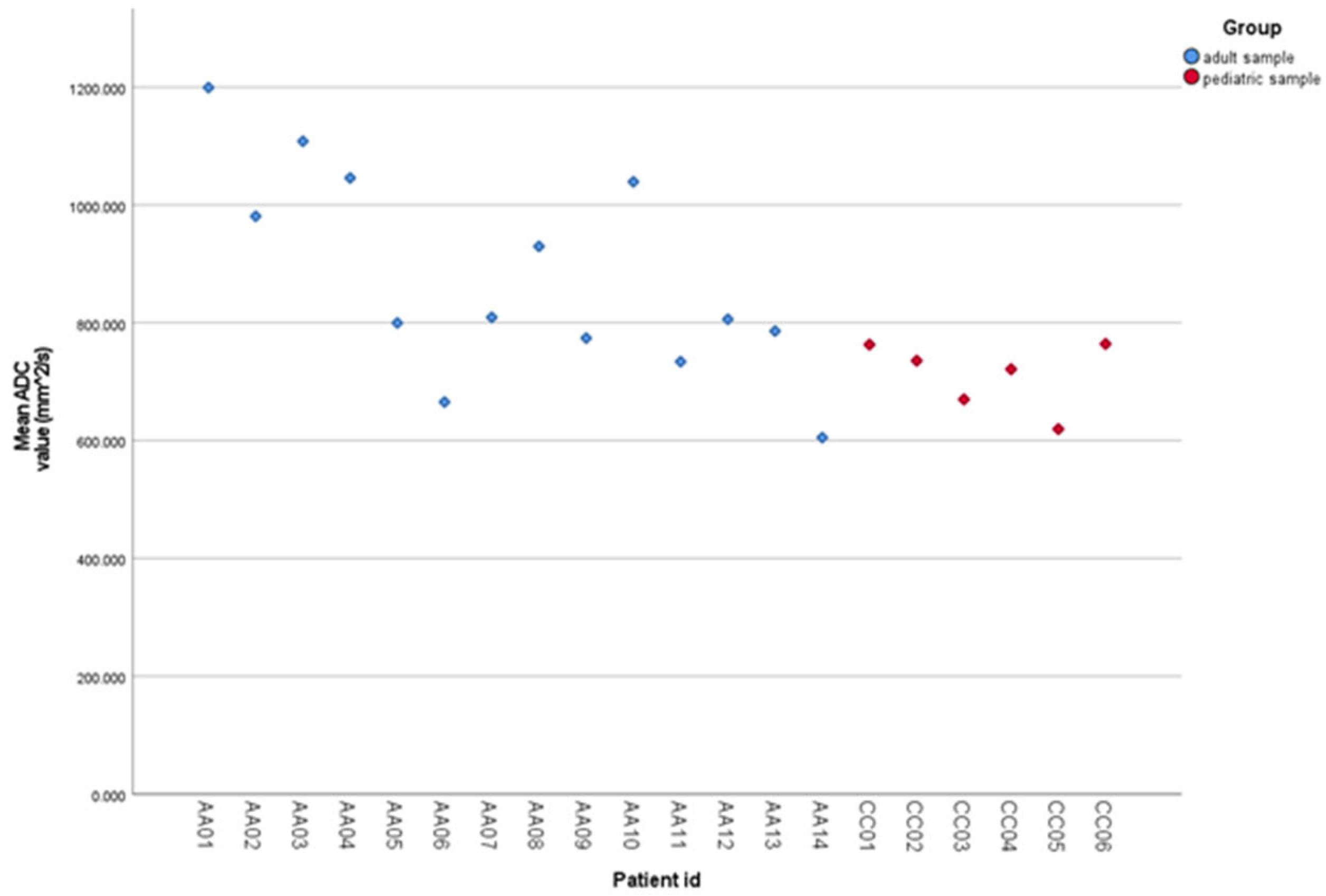
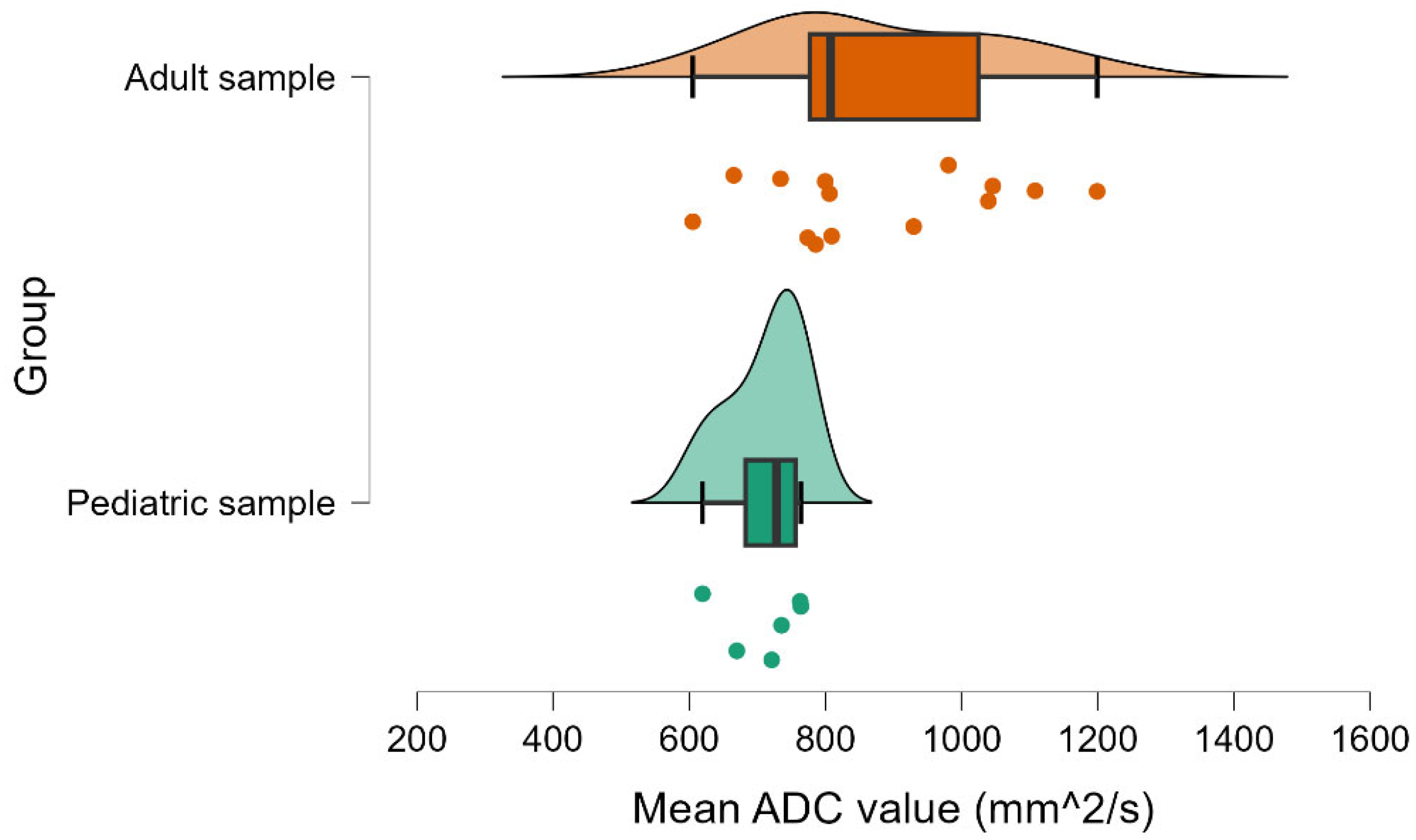
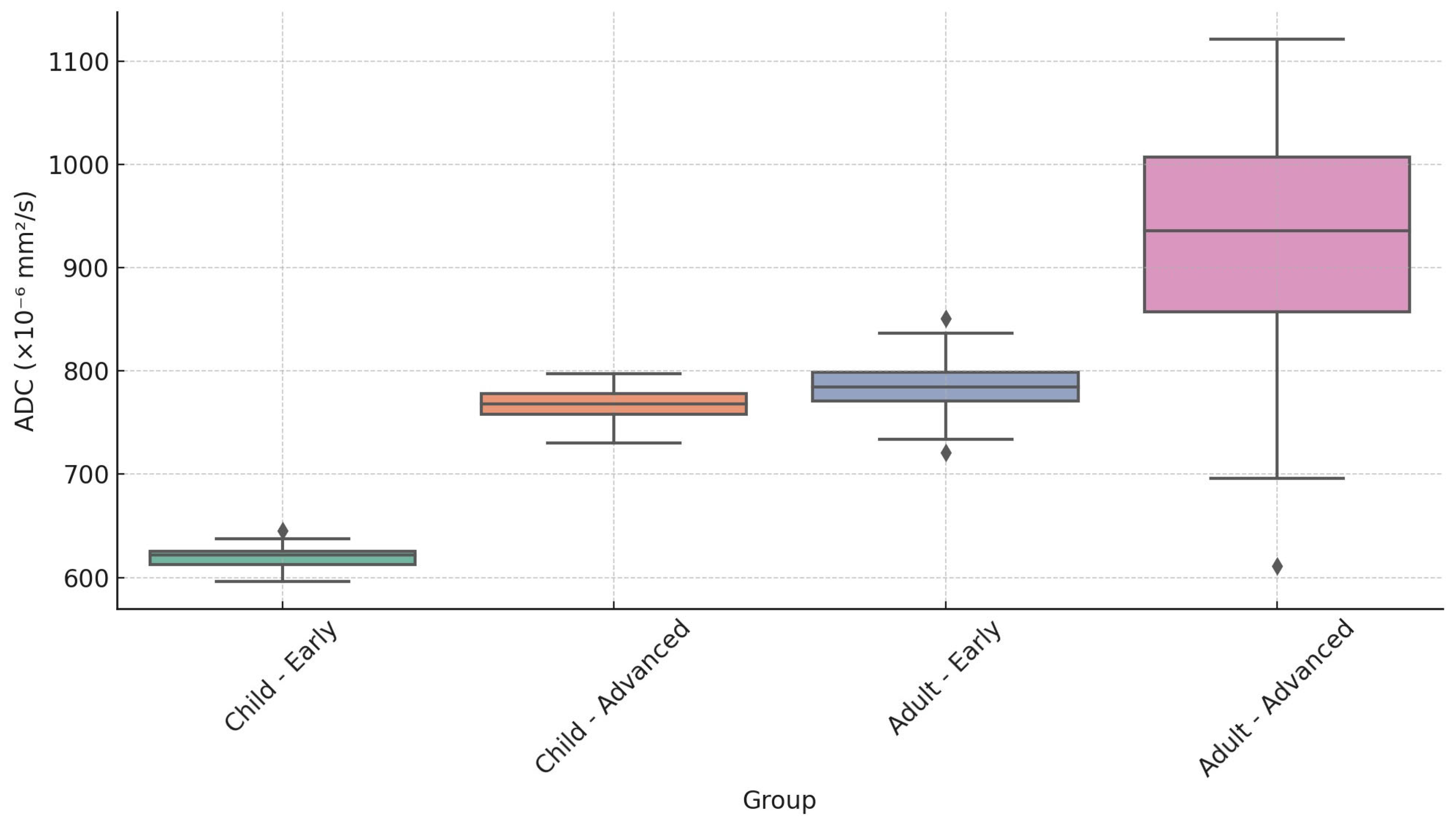
| Age Group | Tumor Stage | Minimum | Median | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Child | Early (T1–T2) | 590 | 620 | 650 |
| Child | Advanced (T3–T4) | 730 | 770 | 810 |
| Adult | Early (T1–T2) | 665 | 785 | 806 |
| Adult | Advanced (T3–T4) | 605 | 930 | 1200 |
| Characteristic | No. of Children n = 6 (%) | No. of Adults n = 14 (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | ||
| Median | 16 | 58 |
| Range | 12–17 | 34–70 |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 3 (50) | 10 (71.4) |
| Female | 3 (50) | 4 (28.6) |
| Pathologic Type 1 | ||
| keratinizing squamous carcinoma | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| differentiated/undifferentiated non-keratinizing carcinoma | 6 (100.0) | 14 (100.0) |
| basaloid squamous carcinoma | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| T Category 2 | ||
| T1 | 1 (16.7) | 0 (0.0) |
| T2 | 1 (16.7) | 4 (28.6) |
| T3 | 1 (16.7) | 4 (28.6) |
| T4 | 3 (50.0) | 6 (42.9) |
| N Category 2 | ||
| N0 | 0 (0.0) | 3 (21.4) |
| N1 | 2 (33.3) | 0 (0.0) |
| N2 | 3 (50.0) | 6 (42.9) |
| N3 | 1 (16.7) | 5 (35.7) |
| Stage 2 | ||
| I | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| II | 1 (16.7) | 1 (7.1) |
| III | 0 (0.0) | 3 (21.4) |
| IV A/B | 5 (83.3) | 10 (71.4) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Crasnean, E.; Nechifor, R.E.; Fodor, L.; Almășan, O.; Sollmann, N.; Ban, A.; Roman, R.; Mitre, I.; Bran, S.; Onișor, F.; et al. Pediatric Versus Adult Nasopharyngeal Cancer in Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Cancers 2025, 17, 2237. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132237
Crasnean E, Nechifor RE, Fodor L, Almășan O, Sollmann N, Ban A, Roman R, Mitre I, Bran S, Onișor F, et al. Pediatric Versus Adult Nasopharyngeal Cancer in Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Cancers. 2025; 17(13):2237. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132237
Chicago/Turabian StyleCrasnean, Emil, Ruben Emanuel Nechifor, Liviu Fodor, Oana Almășan, Nico Sollmann, Alina Ban, Raluca Roman, Ileana Mitre, Simion Bran, Florin Onișor, and et al. 2025. "Pediatric Versus Adult Nasopharyngeal Cancer in Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging" Cancers 17, no. 13: 2237. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132237
APA StyleCrasnean, E., Nechifor, R. E., Fodor, L., Almășan, O., Sollmann, N., Ban, A., Roman, R., Mitre, I., Bran, S., Onișor, F., Dinu, C., Băciuț, M., & Hedeșiu, M. (2025). Pediatric Versus Adult Nasopharyngeal Cancer in Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Cancers, 17(13), 2237. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132237











