SPP-SegNet and SE-DenseNet201: A Dual-Model Approach for Cervical Cell Segmentation and Classification
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Introduced SPP-SegNet, incorporating spatial pyramidal grouping and atrous convolutions to improve cervical cell segmentation performance.
- Developed SE-DenseNet201, integrating squeeze-and-excitation (SE) blocks to improve feature recalibration and boost classification accuracy.
2. Related Works
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Dataset and Preprocessing Technique
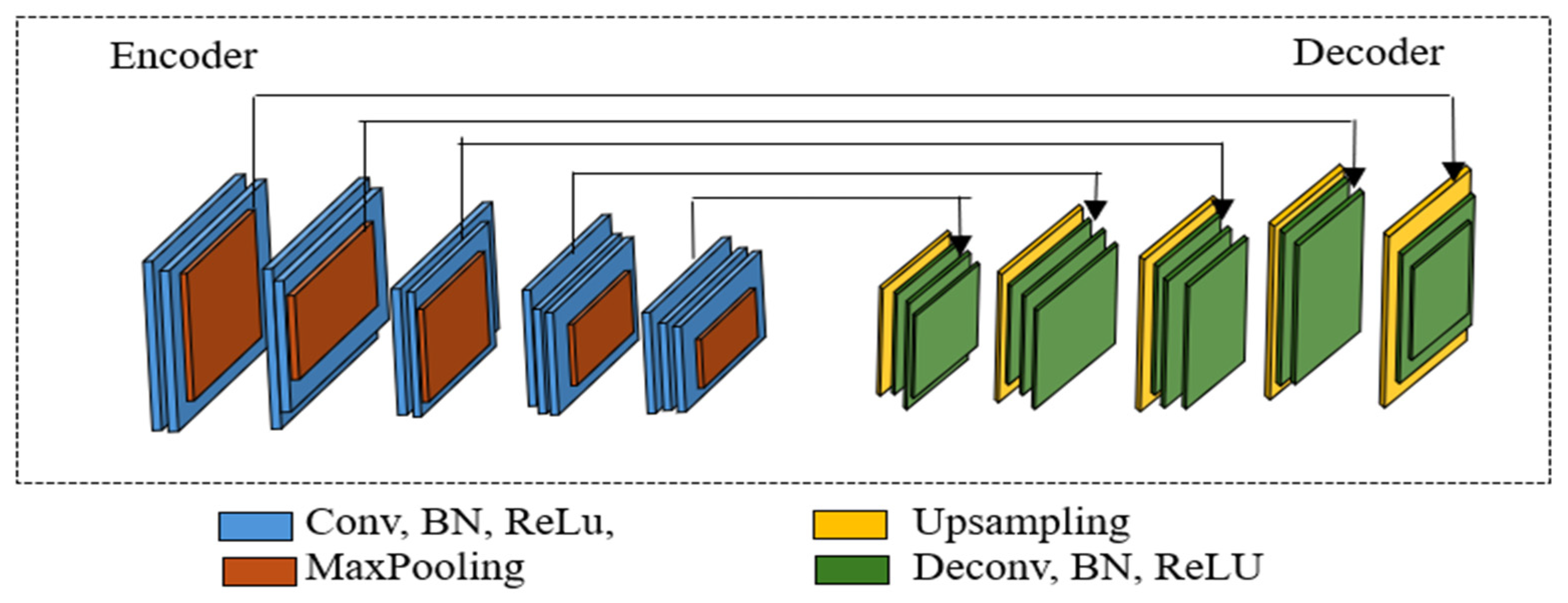
3.2. Proposed Method
3.3. Training Details and Performance Metrics
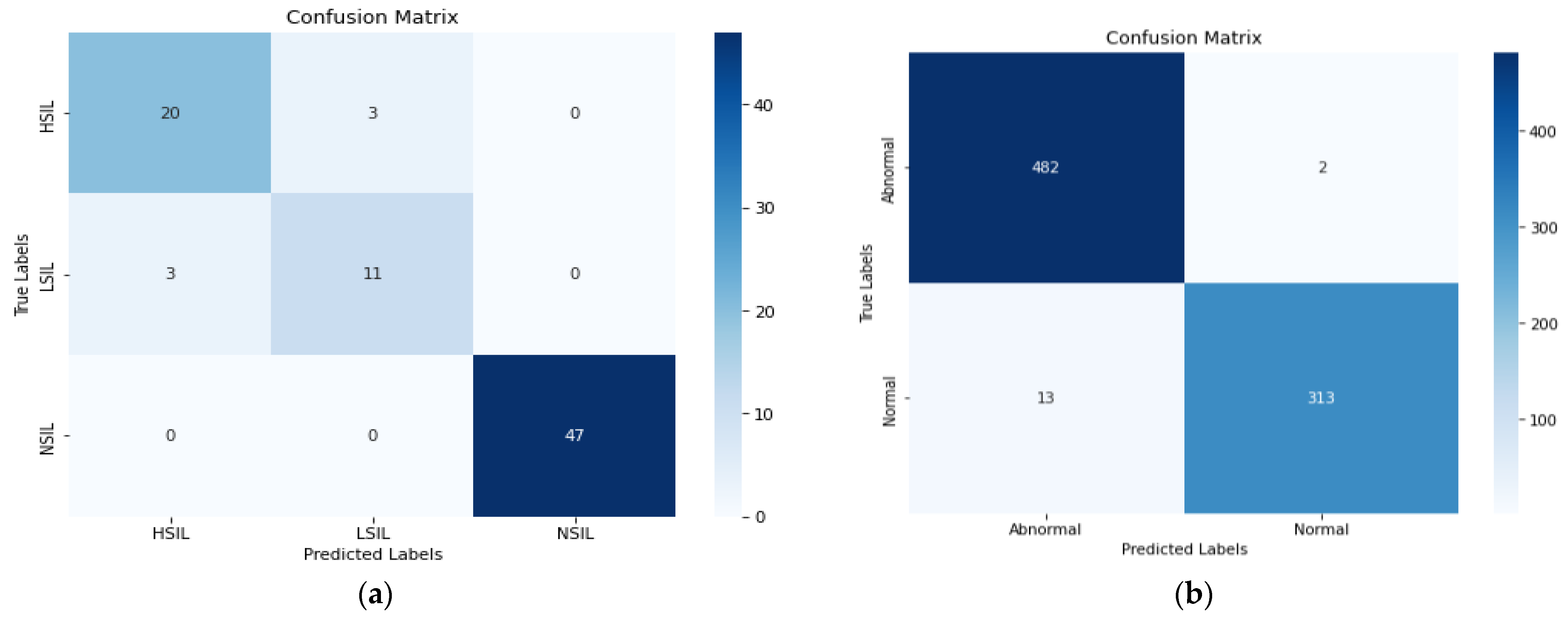
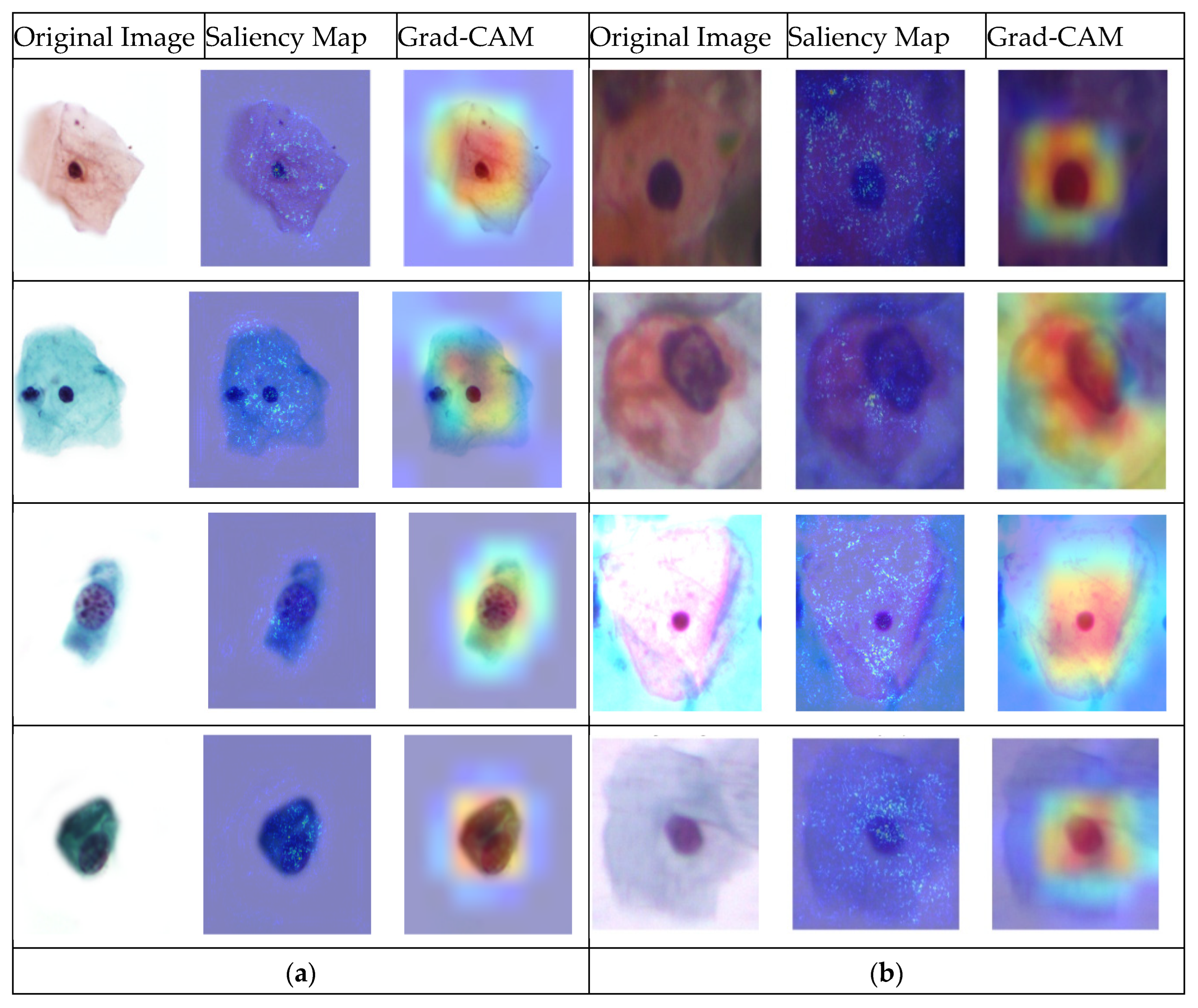
4. Results and Discussions
Ablation Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kurnianingsih; Allehaibi, K.H.S.; Nugroho, L.E.; Widyawan; Lazuardi, L.; Prabuwono, A.S.; Mantoro, T. Segmentation and classification of cervical cells using deep learning. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 116925–116941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Dou, Q.; Yang, H.; Liu, J.; Fu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, D. Cervical cell multi-classification algorithm using global context information and attention mechanism. Tissue Cell 2022, 74, 101677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chankong, T.; Theera-Umpon, N.; Auephanwiriyakul, S. Automatic cervical cell segmentation and classification in Pap smears. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2014, 113, 539–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, E.; Mahanta, L.B.; Das, C.R.; Choudhury, M.; Chowdhury, M. A shape context fully convolutional neural network for segmentation and classification of cervical nuclei in Pap smear images. Artif. Intell. Med. 2020, 107, 101897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, H.; Nasipuri, M. Segmentation of Pap Smear Images for Cervical Cancer Detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Calcutta Conference CALCON 2020, Kolkata, India, 28–29 February 2020; pp. 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desiani, A.; Suprihatin, B.; Yahdin, S.; Putri, A.I.; Husein, F.R. Bi-path Architecture of CNN Segmentation and Classification Method for Cervical Cancer Disorders Based on Pap-smear Images. IAENG Int. J. Comput. Sci. 2021, 48, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wubineh, B.Z.; Rusiecki, A.; Halawa, K. Classification of cervical cells from the Pap smear image using the RES_DCGAN data augmentation and ResNet50V2 with self-attention architecture. Neural Comput. Appl. 2024, 36, 21801–21815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wubineh, B.Z.; Rusiecki, A.; Halawa, K. Segmentation and Classification Techniques for Pap Smear Images in Detecting Cervical Cancer: A Systematic Review. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 118195–118213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wubineh, B.Z.; Rusiecki, A.; Halawa, K. Segmentation of Cytology Images to Detect Cervical Cancer Using Deep Learning Techniques. In International Conference on Computational Science; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 270–278. [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelmi, M.; Rusiecki, A. Simple CNN as an alternative for large pretrained models for medical image classification—MedMNIST case study. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2024, 239, 1298–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlap, P.; Min, H.; Vandenberg, N.; Dowling, J.; Holloway, L.; Haworth, A. A review of medical image data augmentation techniques for deep learning applications. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 65, 545–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wubineh, B.Z.; Rusiecki, A.; Halawa, K. Data Augmentation Techniques to Detect Cervical Cancer Using Deep Learning: A Systematic Review. In International Conference on Dependability of Computer Systems; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 325–336. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Lu, W.; Wu, J.; Ni, C.; Wang, H. SegNet Network Architecture for Deep Learning Image Segmentation and Its Integrated Applications and Prospects. Acad. J. Sci. Technol. 2024, 9, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afify, H.M.; Mohammed, K.K.; Hassanien, A.E. An improved framework for polyp image segmentation based on SegNet architecture. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2021, 31, 1741–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizar, E.; Zulkifley, M.A.; Muharar, R.; Zaman, M.H.M.; Mustaza, S.M. A Review on Multiscale-Deep-Learning Applications. Sensors 2022, 22, 7384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, L.; Chen, C.; Lin, Y.; Song, Z.; Su, J. A Three-Step Automated Segmentation Method for Early Cervical Cancer MRI Images Based on Deep Learning. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2024, 35, e23207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Du, H. Instance Segmentation of Overlapping Cervical Cells Based on Boundary Tracking. In Proceedings of the Chinese Automation Congress CAC 2021, Beijing, China, 22–24 October 2021; pp. 7600–7604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, J.B.A.; Rezende, M.T.; Diniz, D.N.; Carneiro, C.M.; Luz, E.J.d.S.; Souza, M.J.F.; Ushizima, D.M.; de Medeiros, F.N.S.; Bianchi, A.G.C. Segmentation of cervical nuclei using convolutional neural network for conventional cytology. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. Imaging Vis. 2023, 11, 1876–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, A.; Zhou, J.; Luo, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zhou, T. Overlapping cytoplasms segmentation via constrained multi-shape evolution for cervical cancer screening. Artif. Intell. Med. 2024, 148, 102756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vianna, P.; Farias, R.; Pereira, W.C.d.A. U-Net and SegNet performances on lesion segmentation of breast ultrasonography images. Res. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 37, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A Deep Convolutional Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmbhatt, P. Skin Lesion Segmentation Using SegNet. 2019, pp. 14–15. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/code/hashbanger/skin-lesion-segmentation-using-segnet#The-Model (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Göker, H. Detection of Cervical Cancer From Uterine Cervix Images Using Transfer Learning Architectures. Eskişehir Tech. Univ. J. Sci. Technol. A-Appl. Sci. Eng. 2024, 25, 222–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeleń, Ł.; Stankiewicz-Antosz, I.; Chosia, M.; Jeleń, M. Optimizing Cervical Cancer Diagnosis with Feature Selection and Deep Learning. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jing, S.; Dai, H.; Shi, A. High-resolution remote sensing images semantic segmentation using improved UNet and SegNet. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2023, 108, 108734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Li, C.; Du, T.; Jiang, H.; Ma, D.; Ma, Z.; Grzegorzek, M.; Jiang, T.; Sun, H. ECPC-IDS: A benchmark endometrial cancer PET/CT image dataset for evaluation of semantic segmentation and detection of hypermetabolic regions. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 171, 108217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.-Y.; Li, W. Explainable GeoAI: Can saliency maps help interpret artificial intelligence’s learning process? An empirical study on natural feature detection. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2023, 37, 963–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, C.; Akyıldız, B. Deep Learning Based Cervical Cells Classification from Pap Smear Images. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Information Technologies and Their Applications (ITTA 2024), Baku, Azerbaijan, 23–25 April 2024; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/386986535 (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Arya, M.; Yadav, P.K.; Jain, A.; Gupta, M.; Agarwal, S.; Rajpoot, A.S. Neural Network to detect Cervical Cancer early Using Pap smears Images. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Contemporary Computing and Informatics (IC3I-2024), Greater Noida, India, 18–20 September 2024; Volume 7, pp. 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Asbaily, S.A.; Almoshity, S.; Younus, S.; Bozed, K. Classification of Cervical Cancer using Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 4th International Maghreb Meeting of the Conference on Sciences and Techniques of Automatic Control and Computer Engineering (MI-STA), Tripoli city, Libya, 19–21 May 2024; pp. 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cömert, Z.; Efil, F.; Türkoğlu, M. Convolutional Block Attention Module and Parallel Branch Architectures for Cervical Cell Classification. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2025, 35, e70048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Dataset | Category | No. of Img | Categories | Image Size | Total Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pomeranian | HSIL | 124 | 1130 × 1130 | 419 | |
| LSIL | 61 | ||||
| NSIL | 234 | ||||
| SIPaKMeD | Dyskeratotic | 813 | Abnormal | different | 4049 |
| Koilocytotic | 825 | ||||
| Metaplastic | 793 | ||||
| Parabasal | 787 | Normal | |||
| Superficial–Intermediate | 831 |
| Dataset | Method | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | IoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pomeranian | Standard SegNet | 97.86% | 91.9% | 90.31% | 94.55% |
| SPP-SegNet | 98.53% | 96.41% | 91.32% | 95.75% | |
| SIPakMeD | Standard SegNet | 90.95% | 92.40% | 90.05% | 92.89% |
| SPP-SegNet | 94.15% | 93.87% | 94.94% | 95.08% | |
| Herlev | Standard SegNet | 86.74% | 91.05% | 90.35% | 90.33% |
| SPP-SegNet | 87.58% | 91.95% | 91.67% | 91.13% |
| Dataset | Method | Resent50V2 | Densenet121 | Densenet201 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acc | Pre | Rec | F1 | Acc | Pre | Rec | F1 | Acc | Pre | Rec | F1 | ||
| Pomeranian | Only classification | 81% | 77% | 81% | 79% | 87% | 87% | 87% | 85% | 90% | 90% | 90% | 90% |
| ROI | 83% | 87% | 83% | 84% | 85% | 84% | 85% | 84% | 86% | 86% | 86% | 83% | |
| BBox | 85% | 85% | 85% | 85% | 88% | 88% | 88% | 88% | 88% | 88% | 88% | 88% | |
| SIPaKMeD Multicell | Only classification | 90% | 91% | 90% | 90% | 92% | 91% | 91% | 91% | 91% | 91% | 91% | 91% |
| ROI | 87% | 86% | 87% | 86% | 90% | 90% | 90% | 90% | 90% | 90% | 90% | 90% | |
| BBox | 89% | 89% | 89% | 89% | 91% | 91% | 91% | 91% | 91% | 91% | 91% | 91% | |
| SIPaKMeD Binary | Only classification | 96% | 96% | 96% | 96% | 97% | 97% | 97% | 97% | 98% | 98% | 98% | 98% |
| ROI | 93% | 93% | 93% | 93% | 94% | 94% | 94% | 94% | 94% | 94% | 94% | 94% | |
| BBox | 94% | 94% | 94% | 94% | 96% | 96% | 96% | 96% | 96% | 96% | 96% | 96% | |
| Herlev Binary | Only classification | 87% | 88% | 87% | 87% | 88% | 88% | 88% | 88% | 88% | 88% | 88% | 88% |
| ROI | 84% | 84% | 84% | 84% | 85% | 85% | 85% | 85% | 86% | 86% | 86% | 86% | |
| BBox | 86% | 86% | 86% | 86% | 85% | 85% | 85% | 85% | 87% | 87% | 87% | 87% | |
| Dataset | Methods | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pomeranian | SE-DesneNet201 ROI | 87% | 87% | 87% | 87% |
| SE-DesneNet201 BBox | 93% | 93% | 93% | 93% | |
| SIPaKMeD Multiclass | SE-DesneNet201 ROI | 94% | 94% | 94% | 94% |
| SE-DesneNet201 BBox | 96% | 96% | 96% | 96% | |
| SIPaKMeD Binary | SE-DesneNet201 ROI | 97% | 97% | 97% | 97% |
| SE-DesneNet201 BBox | 99% | 99% | 99% | 99% | |
| Herlev Binary | SE-DesneNet201 ROI | 89% | 90% | 89% | 88% |
| SE-DesneNet201 BBox | 90% | 91% | 90% | 90% |
| Ref | Dataset | Task | Class | Methods | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score | IoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [3] | Herlev | Segmentation | - | FCM | - | 85% | - | - | - |
| [16] | Private data | Segmentation | - | SE-ATT-Unet | - | 92.32% | - | - | - |
| [17] | TCT image | Segmentation | - | U-Net | - | 95.04% | 96.19% | - | 91.60% |
| [28] | SIPaKMeD | Classification | 5 | ResNet50 | 95% | - | - | - | - |
| [29] | SIPaKMeD | Classification | 5 | CNN | 93% | - | - | - | - |
| [30] | SIPaKMeD | Classification | 5 | CNN + PCA | 94% | - | - | - | - |
| [31] | SIPaKMeD | Classification | 5 | CNN_CBAM | 92.8% | 93% | 92.8% | 92.8% | - |
| [7] | SIPaKMeD | Classification | 2 | DenseNet121 | 95% | 95% | 95% | 95% | - |
| Ours | SIPaKMeD | Classification | 5 | SE-DenseNet201 | 96% | 96% | 96% | 96% | - |
| Ours | SIPaKMeD | Classification | 2 | SE-DenseNet201 | 99% | 99% | 99% | 99% | - |
| Ours | Pomeranian | Segmentation | - | SPP-SegNet | 98.53% | 96.41% | 91.32% | - | 95.75% |
| Ours | SIPaKMeD | Segmentation | - | SPP-SegNet | 94.15% | 93.87% | 94.94% | - | 95.08% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wubineh, B.Z.; Rusiecki, A.; Halawa, K. SPP-SegNet and SE-DenseNet201: A Dual-Model Approach for Cervical Cell Segmentation and Classification. Cancers 2025, 17, 2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132177
Wubineh BZ, Rusiecki A, Halawa K. SPP-SegNet and SE-DenseNet201: A Dual-Model Approach for Cervical Cell Segmentation and Classification. Cancers. 2025; 17(13):2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132177
Chicago/Turabian StyleWubineh, Betelhem Zewdu, Andrzej Rusiecki, and Krzysztof Halawa. 2025. "SPP-SegNet and SE-DenseNet201: A Dual-Model Approach for Cervical Cell Segmentation and Classification" Cancers 17, no. 13: 2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132177
APA StyleWubineh, B. Z., Rusiecki, A., & Halawa, K. (2025). SPP-SegNet and SE-DenseNet201: A Dual-Model Approach for Cervical Cell Segmentation and Classification. Cancers, 17(13), 2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132177







