Dysregulated miRNA Expression and Its Association with Immune Checkpoints in Head and Neck Cancer
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification and Survival Analysis of Differentially Expressed miRNAs in HNC
2.2. Immune Regulation Analysis of miRNAs
2.3. Protein–Protein Interaction Analysis and Hub Gene Identification
2.4. Expression Validation of miRNAs from GSE Datasets
2.5. Regulatory miRNA–mRNA Correlation and Immune Cell Infiltration Analysis in HNC
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Upregulated miRNA Expression and Its Inverse Correlation with Survival in HNC
3.2. Top Downregulated miRNAs and Their Prognostic Potential in HNC
3.3. Enrichment of Candidate miRNAs in Immune Evasion
3.4. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Analysis and Hub Gene Identification in Immune Evasion
3.5. Expression Validation of Leading miRNAs Using GSE Dataset
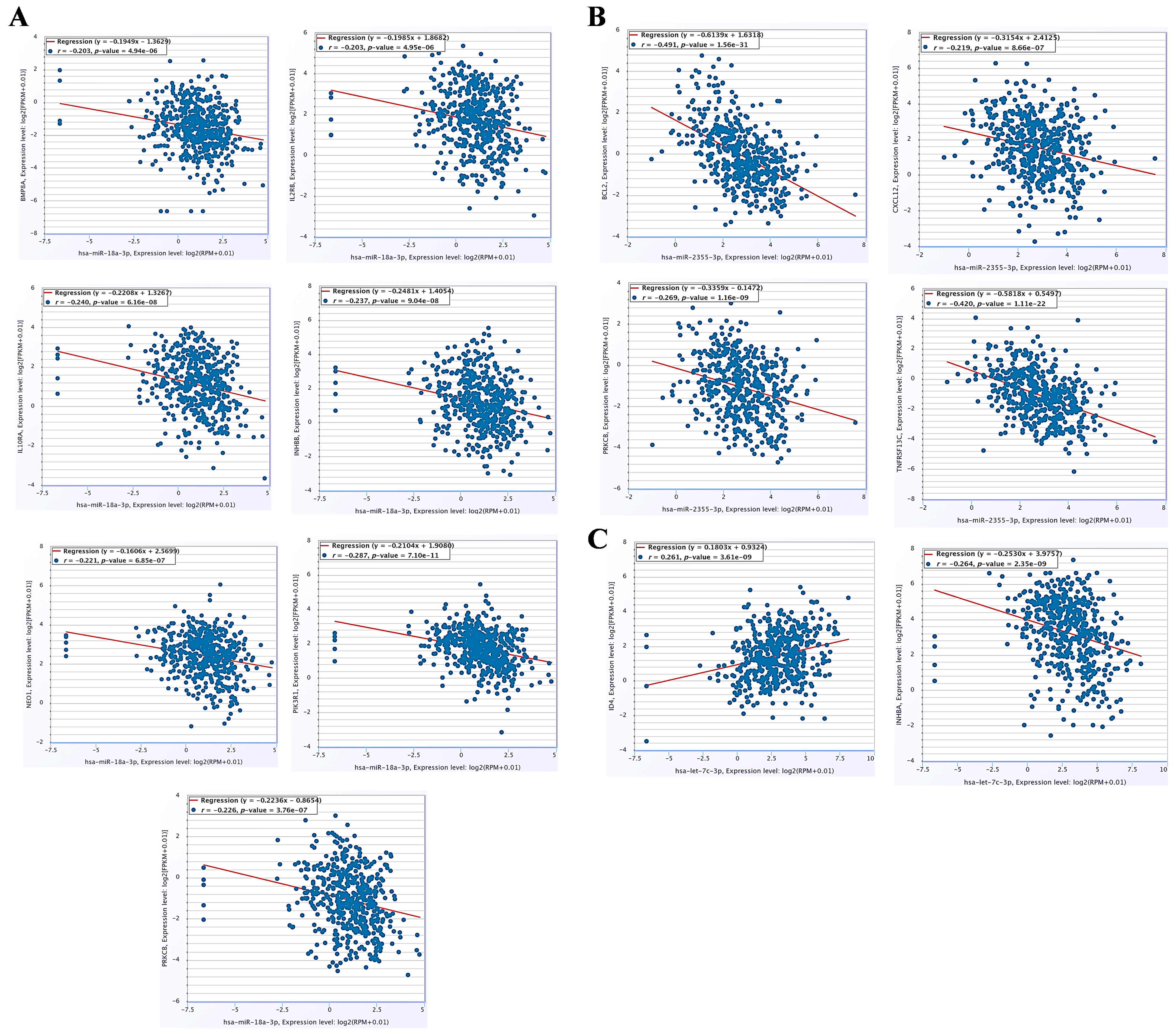
3.6. The miRNA–mRNA Co-Expression Analysis and Immune Cell Infiltration Patterns in HNC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cohen, N.; Fedewa, S.; Chen, A.Y. Epidemiology and Demographics of the Head and Neck Cancer Population. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 30, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Y.; Gong, M.; Deng, Y.; Wang, H.; Ye, D. T cell effects and mechanisms in immunotherapy of head and neck tumors. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, S.; Behrooz, A.B.; Whichelo, R.; Fernandes, A.; Emwas, A.H.; Jaremko, M.; Markowski, J.; Los, M.J.; Ghavami, S.; Vitorino, R. Progress in Precision Medicine for Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, J.A.; Otsuka, A.; Kabashima, K. Anti-PD-1 and Anti-CTLA-4 Therapies in Cancer: Mechanisms of Action, Efficacy, and Limitations. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobday, S.B.; Brody, R.M.; Kriegsman, B.; Basu, D.; Newman, J.; Cohen, R.B.; Lukens, J.N.; Singh, A.; D’Avella, C.A.; Sun, L. Outcomes Among Patients with Mucosal Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated with Checkpoint Inhibitors. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2022, 148, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali Syeda, Z.; Langden, S.S.S.; Munkhzul, C.; Lee, M.; Song, S.J. Regulatory Mechanism of MicroRNA Expression in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuaib, M.; Kumar, S. Induced expression of miR-1250-5p exerts tumor suppressive role in triple-negative breast cancer cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2023, 124, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doghish, A.S.; El-Husseiny, A.A.; Khidr, E.G.; Elrebehy, M.A.; Elballal, M.S.; Abdel-Reheim, M.A.; Abdel Mageed, S.S.; Zaki, M.B.; Mohammed, O.A.; Khaled, R.; et al. Decoding the role of miRNAs in oral cancer pathogenesis: A focus on signaling pathways. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2023, 252, 154949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mahdy, H.A.; Mohamadin, A.M.; Abulsoud, A.I.; Khidr, E.G.; El-Husseiny, A.A.; Ismail, A.; Elsakka, E.G.E.; Mokhlis, H.A.; El-Husseiny, H.M.; Doghish, A.S. miRNAs as potential game-changers in head and neck cancer: Future clinical and medicinal uses. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2023, 245, 154457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Tai, S.K.; Yang, M.H. Snail-overexpressing Cancer Cells Promote M2-Like Polarization of Tumor-Associated Macrophages by Delivering MiR-21-Abundant Exosomes. Neoplasia 2018, 20, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.Y.; Choi, S.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Seog, K.J.; Hong, S.H.; Lee, H.J. Transcriptome Analysis of HNSCC by Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Extracellular Vesicles. Oral Dis. 2024, 13, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Shi, J.; Wu, K.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J. HCV-induced miR-21 contributes to evasion of host immune system by targeting MyD88 and IRAK1. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gao, Y. Pancreatic cancer cell-derived microRNA-155-5p-containing extracellular vesicles promote immune evasion by triggering EHF-dependent activation of Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 100, 107990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Matthen, M.; Yoon, A.; Schwartz, G.K.; Bala, S.; Taylor, A.M.; Momen-Heravi, F. Down-regulation of the tumor suppressor miR-34a contributes to head and neck cancer by up-regulating the MET oncogene and modulating tumor immune evasion. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekar, D.S.; Karthikeyan, S.K.; Korla, P.K.; Patel, H.; Shovon, A.R.; Athar, M.; Netto, G.J.; Qin, Z.S.; Kumar, S.; Manne, U.; et al. UALCAN: An update to the integrated cancer data analysis platform. Neoplasia 2022, 25, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Győrffy, B. Integrated analysis of public datasets for the discovery and validation of survival-associated genes in solid tumors. Innovation 2024, 5, 100625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, V.; Bell, G.W.; Nam, J.W.; Bartel, D.P. Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. Elife 2015, 4, e05005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, B.T.; Hao, M.; Qiu, J.; Jiao, X.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Imamichi, T.; Chang, W. DAVID: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation of gene lists (2021 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W216–W221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, Z.; Asl Aminabadi, N.; Attaran, R.; Pournagiazar, F.; Ghertasi Oskouei, S.; Ahmadpour, F. MicroRNAs as prognostic molecular signatures in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oral. Oncol. 2015, 51, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.L.; Jiang, Y.H.; Feng, J.G.; Su, D.; Chen, P.C.; Mao, W.M. MicroRNA-17, microRNA-18a, and microRNA-19a are prognostic indicators in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2014, 97, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, S.; Xiao, R.; Shi, L.; Zhou, X.; Yang, T.; Zhang, M.; Weng, N.; Zhao, X.; Wang, R.; Liu, J.; et al. MicroRNA-18a promotes cancer progression through SMG1 suppression and mTOR pathway activation in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Q.; Nie, Q.; Wu, R.; Huang, Y. Exosomal miR-18a-5p promotes EMT and metastasis of NPC cells via targeting BTG3 and activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cell Cycle 2023, 22, 1544–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Guan, F.; Fan, T.; Li, S.; Ma, S.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, W.; Liu, H. LncRNA WDFY3-AS2 suppresses proliferation and invasion in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating miR-2355-5p/SOCS2 axis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 8206–8220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Cai, Q.; Deng, L.; Ouyang, Q.; Zhang, X.H.; Zheng, J. Invasion and metastasis in cancer: Molecular insights and therapeutic targets. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Long, X.; Chao, C.; Yan, C.; Wu, Q.; Hua, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, A.; Fang, W. Knocking down CDK4 mediates the elevation of let-7c suppressing cell growth in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Dai, F.; Lu, Y.; Dai, L.; Niu, M.; Guo, H.; Li, W.; Xue, X.; et al. Circular RNA circCORO1C promotes laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma progression by modulating the let-7c-5p/PBX3 axis. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Tang, Y.L.; Liang, X.H. Transforming growth factor-β signaling in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Insights into cellular responses. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 4799–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.Y.; Johnson, F.M. Defining the role of the JAK-STAT pathway in head and neck and thoracic malignancies: Implications for future therapeutic approaches. Drug Resist. Updat. 2010, 13, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Z.; Huang, J.; Qiao, B.; Lam, A.K. Immune checkpoint pathways in immunotherapy for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oral. Sci. 2020, 12, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Cheng, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, R.; Saleh, A.; Si, H.; Lee, S.; Guven-Maiorov, E.; Keskin, O.; Gursoy, A.; et al. Head and Neck Cancers Promote an Inflammatory Transcriptome through Coactivation of Classic and Alternative NF-κB Pathways. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 1760–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selimovic, D.; Wahl, R.U.; Ruiz, E.; Aslam, R.; Flanagan, T.W.; Hassan, S.Y.; Santourlidis, S.; Haikel, Y.; Friedlander, P.; Megahed, M.; et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α triggers opposing signals in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and induces apoptosis via mitochondrial- and non-mitochondrial-dependent pathways. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 55, 1324–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Wang, S. Preclinical development and clinical studies of targeted JAK/STAT combined Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 130, 111717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damasio, M.P.S.; Nascimento, C.S.; Andrade, L.M.; de Oliveira, V.L.; Calzavara-Silva, C.E. The role of T-cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: From immunity to immunotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1021609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Soliman, A.; Joehlin-Price, A.; Rose, P.G.; Vlad, A.; Edwards, R.P.; Mahdi, H. High TGF-β signature predicts immunotherapy resistance in gynecologic cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibition. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2021, 5, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forster, M.D.; Devlin, M.J. Immune Checkpoint Inhibition in Head and Neck Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betzler, A.C.; Theodoraki, M.N.; Schuler, P.J.; Döscher, J.; Laban, S.; Hoffmann, T.K.; Brunner, C. NF-κB and Its Role in Checkpoint Control. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, A.; Li, F.; Chen, F.; Zuo, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Xiao, B.; Tao, Z. PD-L1 promotes head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell growth through mTOR signaling. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 41, 2833–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastwika, K.J.; Wilson, W., 3rd; Li, Q.K.; Norris, J.; Xu, H.; Ghazarian, S.R.; Kitagawa, H.; Kawabata, S.; Taube, J.M.; Yao, S.; et al. Control of PD-L1 Expression by Oncogenic Activation of the AKT-mTOR Pathway in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, L.L.; Yu, G.T.; Deng, W.W.; Mao, L.; Liu, J.F.; Ma, S.R.; Fan, T.F.; Hall, B.; Kulkarni, A.B.; Zhang, W.F.; et al. Targeting STAT3 signaling reduces immunosuppressive myeloid cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1130206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Tong, Q.; Liu, B.; Huang, W.; Tian, Y.; Fu, X. Targeting STAT3 in Cancer Immunotherapy. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepanski, M.J.; Czystowska, M.; Szajnik, M.; Harasymczuk, M.; Boyiadzis, M.; Kruk-Zagajewska, A.; Szyfter, W.; Zeromski, J.; Whiteside, T.L. Triggering of Toll-like receptor 4 expressed on human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma promotes tumor development and protects the tumor from immune attack. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 3105–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veigas, F.; Mahmoud, Y.D.; Merlo, J.; Rinflerch, A.; Rabinovich, G.A.; Girotti, M.R. Immune Checkpoints Pathways in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, H.B.; Schuler, P.J.; Lee, S.C.; Srivastava, R.M.; Argiris, A.; Ferrone, S.; Whiteside, T.L.; Ferris, R.L. CTLA-4+ Regulatory T Cells Increased in Cetuximab-Treated Head and Neck Cancer Patients Suppress NK Cell Cytotoxicity and Correlate with Poor Prognosis. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2200–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, A.K.; Müer, A.; Mairinger, F.D.; Weichert, W.; Stenzinger, A.; Hummel, M.; Budach, V.; Tinhofer, I. MiR-200b and miR-155 as predictive biomarkers for the efficacy of chemoradiation in locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 77, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okkenhaug, K.; Vanhaesebroeck, B. PI3K in Lymphocyte Development, Differentiation and Activation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Cheng, X.; Yang, H.; Lian, S.; Jiang, Y.; Liang, J.; Chen, X.; Mo, S.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, S.; et al. BCL-2 Expression Promotes Immunosuppression in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia by Enhancing Regulatory T Cell Differentiation and Cytotoxic T Cell Exhaustion. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.M.; Lam, H.Y.P.; Hsu, H.J.; Jiang, S.J. Interleukin-10: A Double-Edged Sword in Breast Cancer. Tzu Chi Med. J. 2021, 33, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
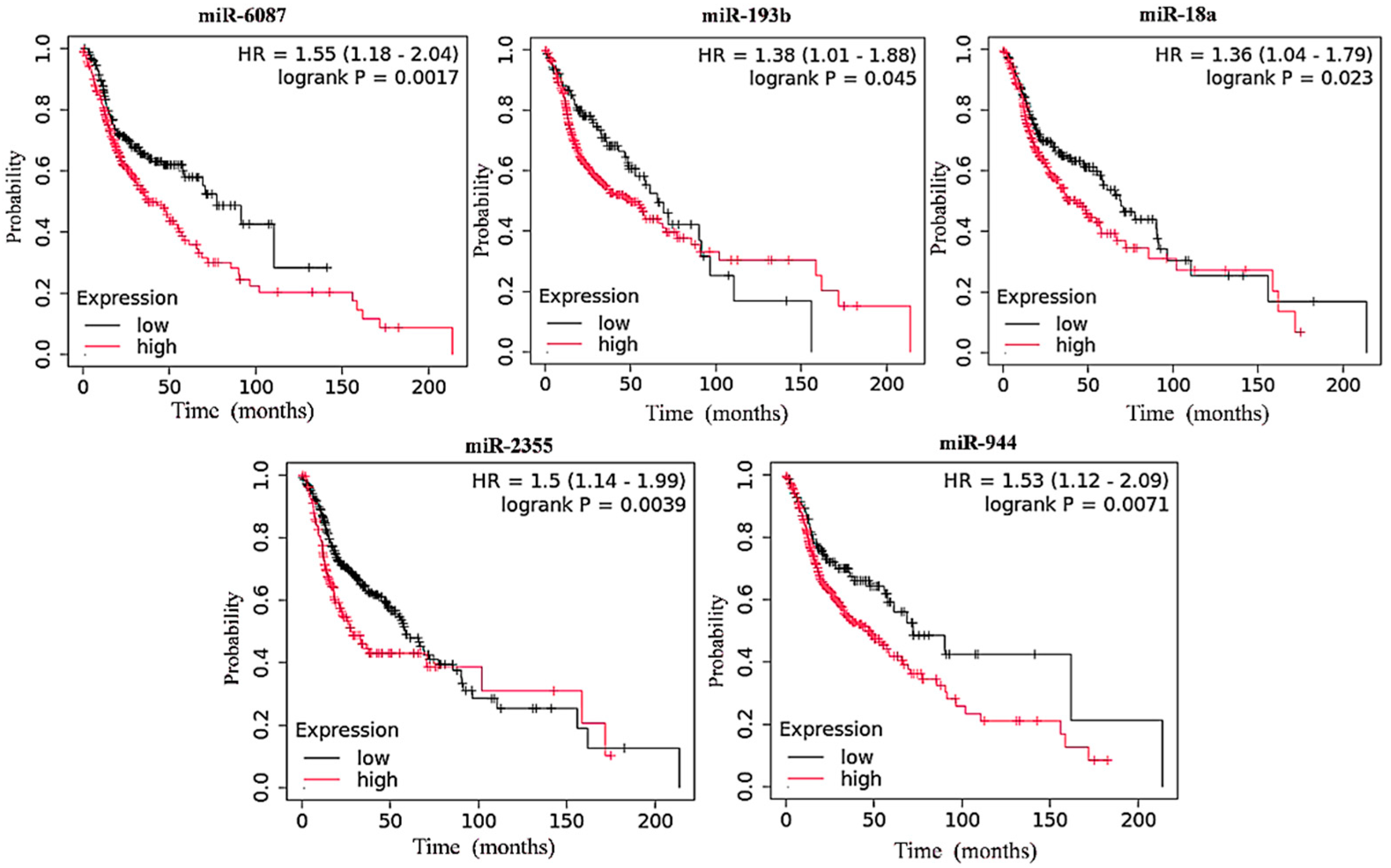
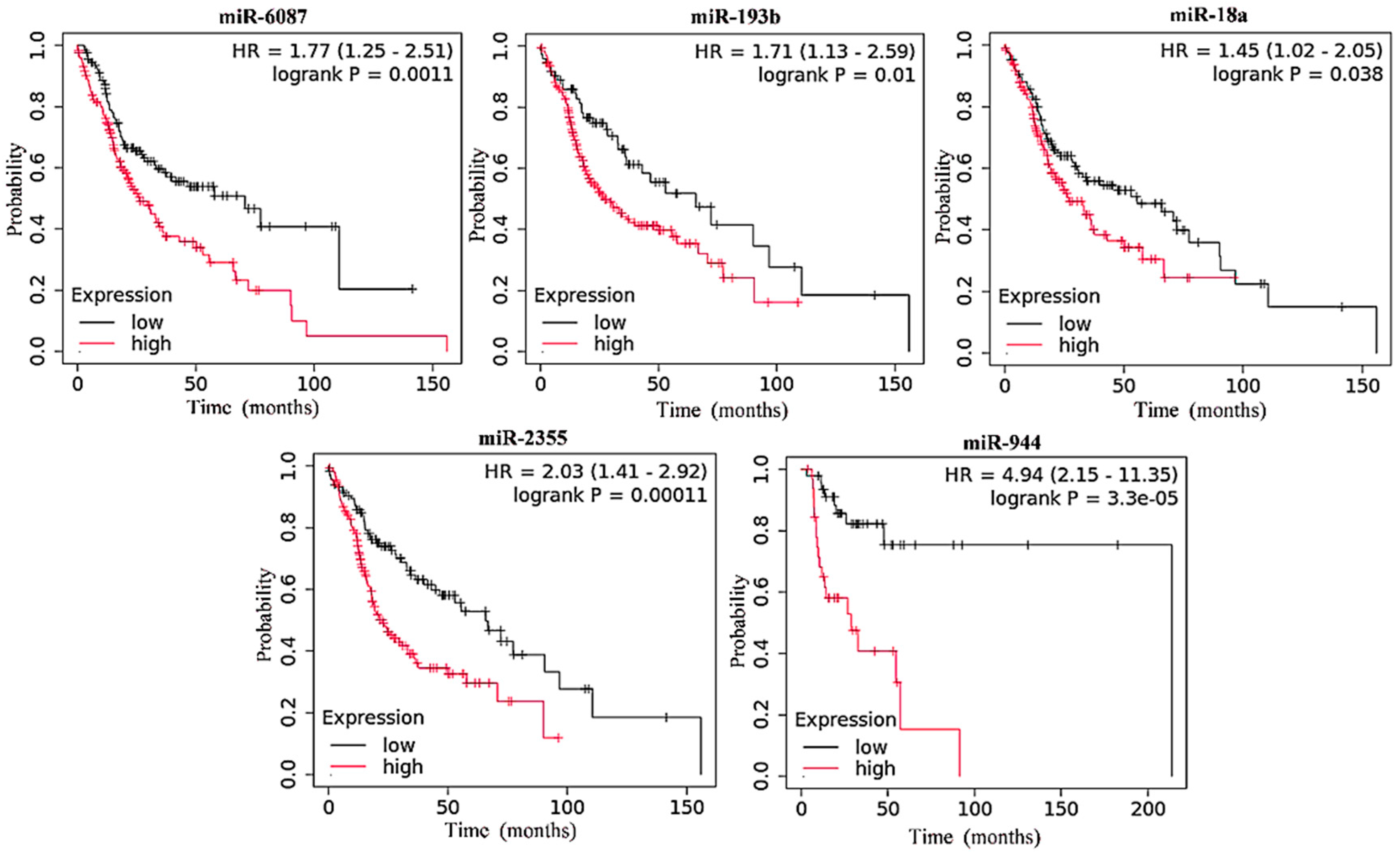
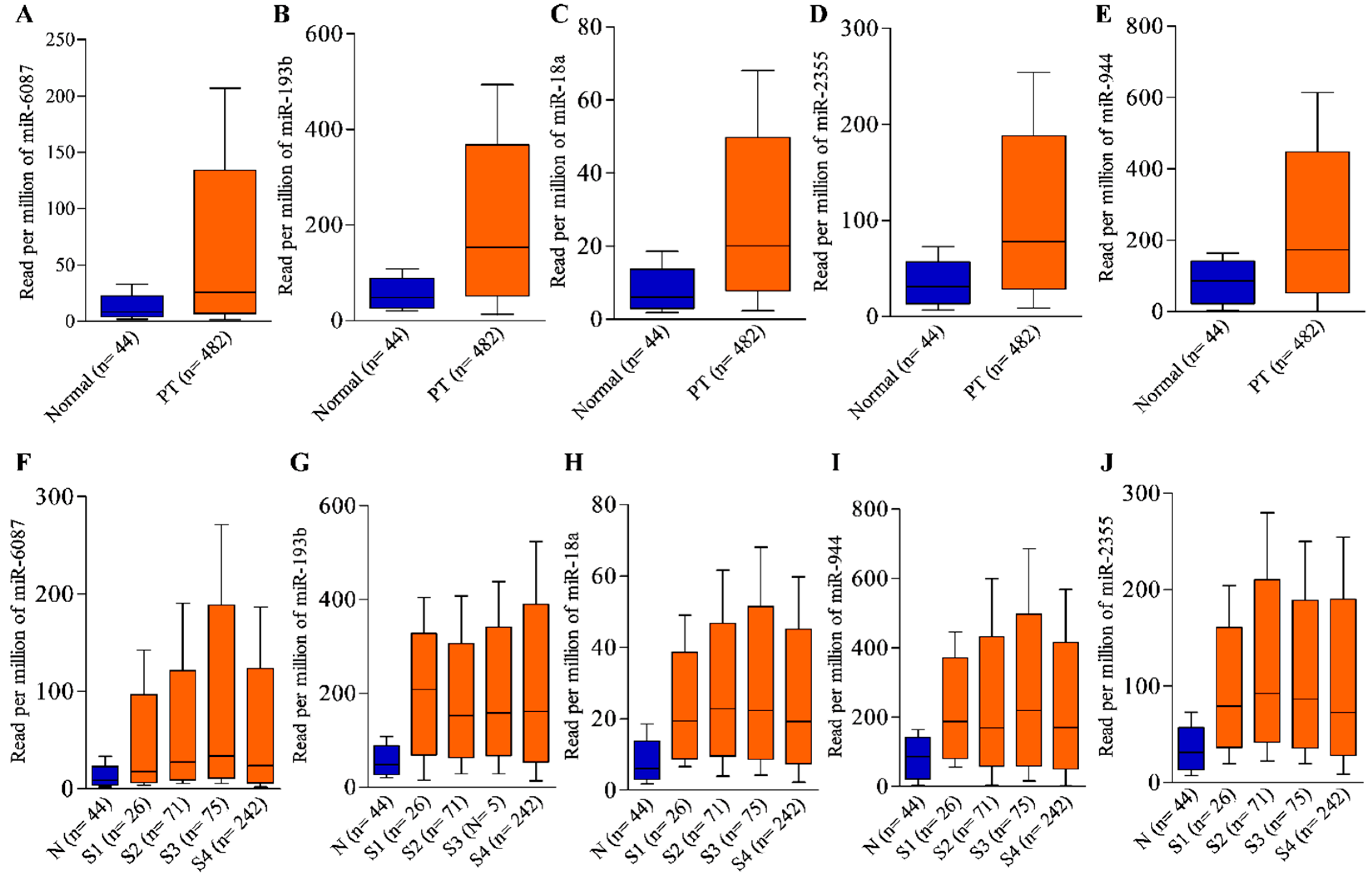


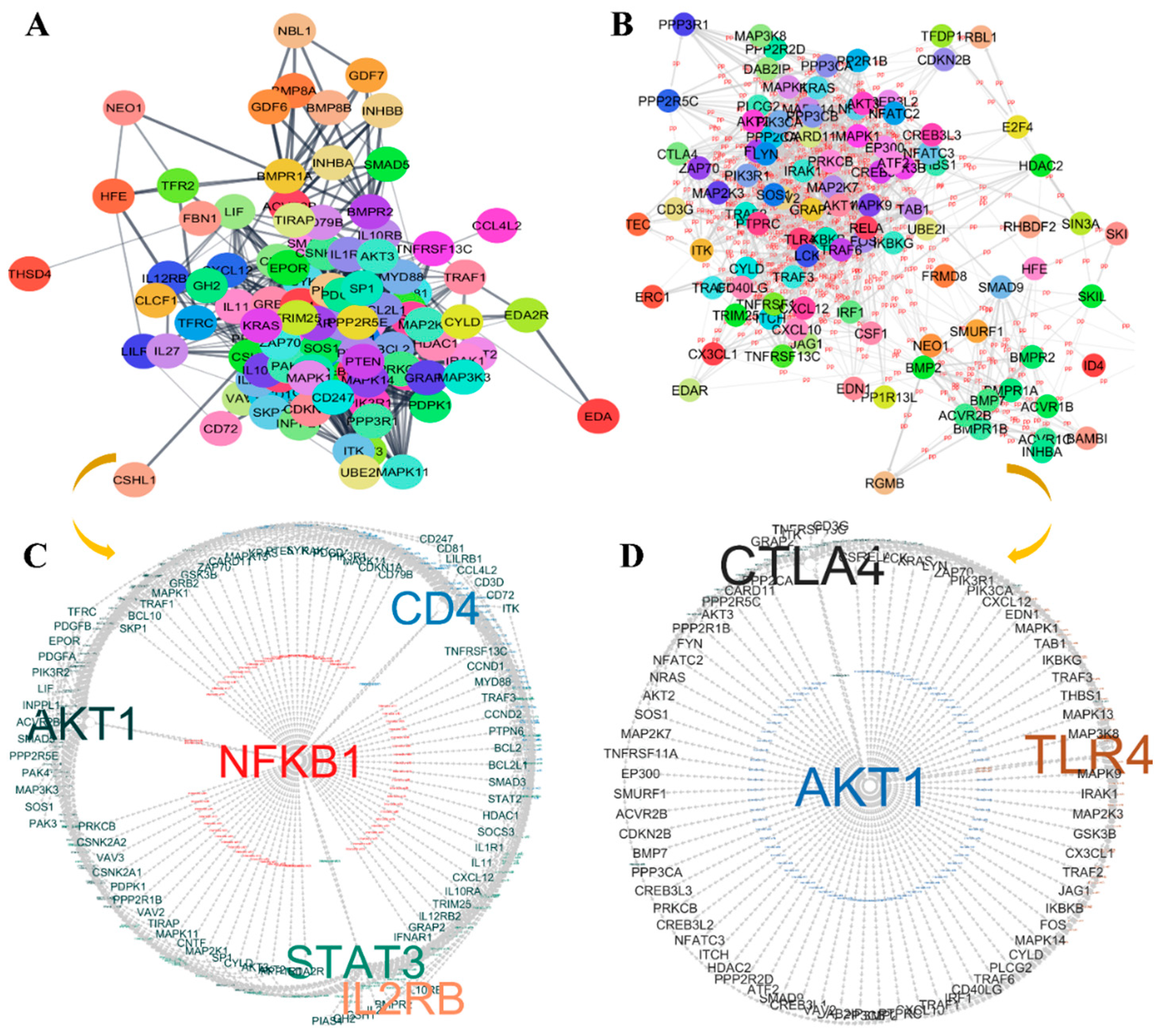
| miRNA | Low-Expression Cohort (Months) | High-Expression Cohort (Months) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Combined Stages | Advance Stages | All Combined Stages | Advance Stages | |
| Overexpressed | ||||
| hsa-miR-6087 | 77.30 | 70.67 | 37.77 | 26.30 |
| hsa-miR-193b | 65.73 | 65.73 | 50.13 | 26.87 |
| hsa-miR-18a | 69.43 | 55.70 | 42.97 | 26.87 |
| hsa-miR-2355 | 58.73 | 65.73 | 27.87 | 22.67 |
| hsa-miR-944 | 72.20 | 57.73 | 46.60 | 32.67 |
| Underexpressed | ||||
| hsa-miR-99a | 36.03 | 18.20 | 69.43 | 53.03 |
| hsa-miR-29c | 47.67 | 27.97 | 58.73 | 57.73 |
| hsa-let-7c | 40.07 | 19.23 | 65.73 | 53.03 |
| hsa-miR-6510 | 50.13 | 26.87 | 65.73 | 65.73 |
| Regulatory miRNA | Immune Signaling Pathways | Gene Count | p-Value | Genes Involved |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upregulated miRNAs’ signaling pathways | ||||
| miR-18a-3p | hsa04630:JAK-STAT signaling pathway | 33 | 0.023954886 | CDKN1A, CNTF, CSH1, PDGFB, PDGFA, PIK3R2, IL27, PIK3R1, SOCS3, CCND2, CCND1, AKT2, AKT3, AKT1, IL12RB2, PIAS4, IL11, IL10RB, IL10RA, STAT2, STAT3, LIF, CSHL1, EPOR, GH2, CLCF1, IL2RB, BCL2, GRB2, PTPN6, SOS1, BCL2L1, IFNAR1 |
| hsa04660:T cell receptor signaling pathway | 30 | 0.001266955 | GSK3B, ITK, PIK3R2, PIK3R1, CD3D, PPP3R1, PPP2R1B, PPP2R5E, AKT2, GRAP2, AKT3, AKT1, MAPK1, PAK3, PAK4, VAV3, MAP2K1, PDPK1, MAPK14, MAPK13, VAV2, MAPK11, CD4, GRB2, KRAS, PTPN6, PDCD1, CD247, SOS1, CARD11 | |
| hsa04350:TGF-beta signaling pathway | 23 | 0.0279178 | BMPR2, SMAD3, TFRC, HDAC1, HFE, BMP8A, BMP8B, INHBB, INHBA, GDF6, SMAD5, ACVR2B, THSD4, GDF7, PPP2R1B, SP1, TFR2, MAPK1, NBL1, NEO1, SKP1, BMPR1A, FBN1 | |
| hsa05235:PD-L1 expression and PD-1 checkpoint pathway in cancer | 22 | 0.008014647 | MAP3K3, MAP2K1, CSNK2A2, STAT3, PTEN, PIK3R2, PIK3R1, MAPK14, CD3D, MAPK13, MAPK11, CD4, PPP3R1, AKT2, AKT3, AKT1, MAPK1, KRAS, PTPN6, PDCD1, CD247, MYD88 | |
| hsa04662:B cell receptor signaling pathway | 22 | 0.007028352 | VAV3, GSK3B, MAP2K1, CD72, PRKCB, CD81, INPPL1, LILRB1, PIK3R2, PIK3R1, VAV2, CD79B, PPP3R1, AKT2, AKT3, AKT1, MAPK1, GRB2, KRAS, PTPN6, SOS1, CARD11 | |
| miR-2335-3p | hsa04064:NF-kappa B signaling pathway | 25 | 0.014080501 | EDA, CCL4L1, TNFRSF13C, BCL10, EDA2R, IRAK1, PPP1R13L, TRIM25, PIAS4, EDA, RADD, UBE2I, SYK, CSNK2A1, PRKCB, IL1R1, TRAF1, TIRAP, NFKB1, CYLD, ZAP70, CXCL12, TRAF3, BCL2, MYD88, CARD11 |
| Downregulated miRNAs’ signaling pathways | ||||
| Let-7c | hsa04350:TGF-beta signaling pathway | 29 | 1.37E-04 | HDAC2, BMPR2, ZFYVE9, HFE, ACVR1B, THBS1, PPP2CA, ACVR1C, PPP2R1B, SIN3A, EP300, E2F4, NEO1, SKIL, CDKN2B, SMURF1, SMAD9, INHBA, RGMB, BMP7, ACVR2B, SKI, BMP2, RBL1, TFDP1, BAMBI, ID4, BMPR1B, BMPR1A |
| hsa04660:T cell receptor signaling pathway | 29 | 0.001149086 | GSK3B, ITK, CD3G, PIK3R1, PPP2CA, PPP3CA, MAPK9, PPP3CB, NRAS, PPP3R1, PPP2R1B, GRAP2, AKT3, CTLA4, FYN, MAP3K8, NFATC3, NFATC2, PPP2R5C, FOS, MAPK14, VAV2, PTPRC, TEC, PIK3CA, LCK, PPP2R2D, KRAS, SOS1 | |
| miR-6510 | hsa04668:TNF signaling pathway | 28 | 0.02621548 | ATF2, CSF1, RELA, CX3CL1, IKBKB, CREB3L3, AKT2, CREB3L1, CREB3L2, AKT1, MAPK1, IKBKG, MAP2K7, MAP2K3, EDN1, JAG1, RHBDF2, DAB2IP, TRAF2, TRAF1, MAPK13, CYLD, CXCL10, ITCH, FRMD8, TRAF3, IRF1, TAB1 |
| hsa04064:NF-kappaB signaling pathway | 25 | 0.031971598 | TNFRSF13C, TNFRSF11A, RELA, IKBKB, IRAK1, PPP1R13L, PLCG2, TRIM25, IKBKG, ERC1, LYN, UBE2I, PRKCB, TRAF2, TRAF1, EDAR, CYLD, ZAP70, CXCL12, CD40LG, TRAF3, TRAF6, TAB1, TLR4, CARD11 | |
| Gene Node | Identifier | Node Degree | Betweenness | Closeness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upregulated miRNAs hub genes in immune evasion | ||||
| AKT1 | 9606.ENSP00000451828 | 65 | 1151.233 | 83.83333 |
| STAT3 | 9606.ENSP00000264657 | 60 | 970.7170 | 81.50000 |
| NFKB1 | 9606.ENSP00000226574 | 58 | 777.0496 | 79.25000 |
| CD4 | 9606.ENSP00000011653 | 53 | 1003.502 | 77.66667 |
| BCL2 | 9606.ENSP00000381185 | 45 | 473.0872 | 73.50000 |
| PIK3R1 | 9606.ENSP00000428056 | 43 | 622.3602 | 73.00000 |
| PTEN | 9606.ENSP00000361021 | 43 | 229.4419 | 71.58333 |
| KRAS | 9606.ENSP00000256078 | 39 | 228.9372 | 69.83333 |
| MAPK1 | 9606.ENSP00000215832 | 39 | 176.7926 | 69.75000 |
| MYD88 | 9606.ENSP00000498321 | 38 | 224.4583 | 68.91667 |
| SYK | 9606.ENSP00000364898 | 38 | 151.3794 | 69.08333 |
| GRB2 | 9606.ENSP00000376345 | 37 | 130.7906 | 68.58333 |
| GSK3B | 9606.ENSP00000324806 | 35 | 143.0187 | 67.58333 |
| MAPK14 | 9606.ENSP00000229795 | 34 | 117.3630 | 66.91667 |
| PTPN6 | 9606.ENSP00000391592 | 32 | 155.2973 | 66.08333 |
| BCL2L1 | 9606.ENSP00000365230 | 31 | 140.8044 | 65.16667 |
| CCND1 | 9606.ENSP00000227507 | 31 | 45.69035 | 65.41667 |
| IL2RB | 9606.ENSP00000216223 | 31 | 63.51949 | 65.58333 |
| ZAP70 | 9606.ENSP00000264972 | 30 | 96.13023 | 64.66667 |
| Downregulated miRNAs hub genes in immune evasion | ||||
| AKT1 | 9606.ENSP00000451828 | 69 | 83.50000 | 1719.840 |
| RELA | 9606.ENSP00000384273 | 45 | 71.00000 | 620.9879 |
| TRAF6 | 9606.ENSP00000433623 | 43 | 70.00000 | 383.0736 |
| GSK3B | 9606.ENSP00000324806 | 42 | 69.33333 | 395.8324 |
| MAPK1 | 9606.ENSP00000215832 | 40 | 68.50000 | 324.4336 |
| FOS | 9606.ENSP00000306245 | 38 | 67.00000 | 235.4975 |
| LCK | 9606.ENSP00000477713 | 37 | 66.00000 | 164.1376 |
| TLR4 | 9606.ENSP00000363089 | 37 | 66.00000 | 144.1318 |
| FYN | 9606.ENSP00000346671 | 36 | 66.33333 | 248.3050 |
| EP300 | 9606.ENSP00000263253 | 35 | 65.83333 | 292.4875 |
| KRAS | 9606.ENSP00000256078 | 35 | 64.66667 | 155.6484 |
| LYN | 9606.ENSP00000428924 | 35 | 64.83333 | 139.4930 |
| PIK3CA | 9606.ENSP00000263967 | 35 | 66.16667 | 498.1811 |
| IKBKB | 9606.ENSP00000430684 | 32 | 63.66667 | 127.1822 |
| PTPRC | 9606.ENSP00000411355 | 31 | 63.50000 | 139.3552 |
| CTLA4 | 9606.ENSP00000497102 | 30 | 62.50000 | 93.57661 |
| IKBKG | 9606.ENSP00000483825 | 30 | 61.83333 | 127.4694 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shuaib, M.; Saini, D.; Sharma, G.; Singh, I.; Gupta, S.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, P. Dysregulated miRNA Expression and Its Association with Immune Checkpoints in Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers 2025, 17, 2169. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132169
Shuaib M, Saini D, Sharma G, Singh I, Gupta S, Kumar S, Kumar P. Dysregulated miRNA Expression and Its Association with Immune Checkpoints in Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers. 2025; 17(13):2169. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132169
Chicago/Turabian StyleShuaib, Mohd, Diksha Saini, Gargi Sharma, Ishwar Singh, Sanjay Gupta, Shashank Kumar, and Pramod Kumar. 2025. "Dysregulated miRNA Expression and Its Association with Immune Checkpoints in Head and Neck Cancer" Cancers 17, no. 13: 2169. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132169
APA StyleShuaib, M., Saini, D., Sharma, G., Singh, I., Gupta, S., Kumar, S., & Kumar, P. (2025). Dysregulated miRNA Expression and Its Association with Immune Checkpoints in Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers, 17(13), 2169. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132169








