Peri-Implant Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC): Clinicopathological Features and Staging Issues
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inclusion Criteria and Participants
2.2. Clinical Workflow
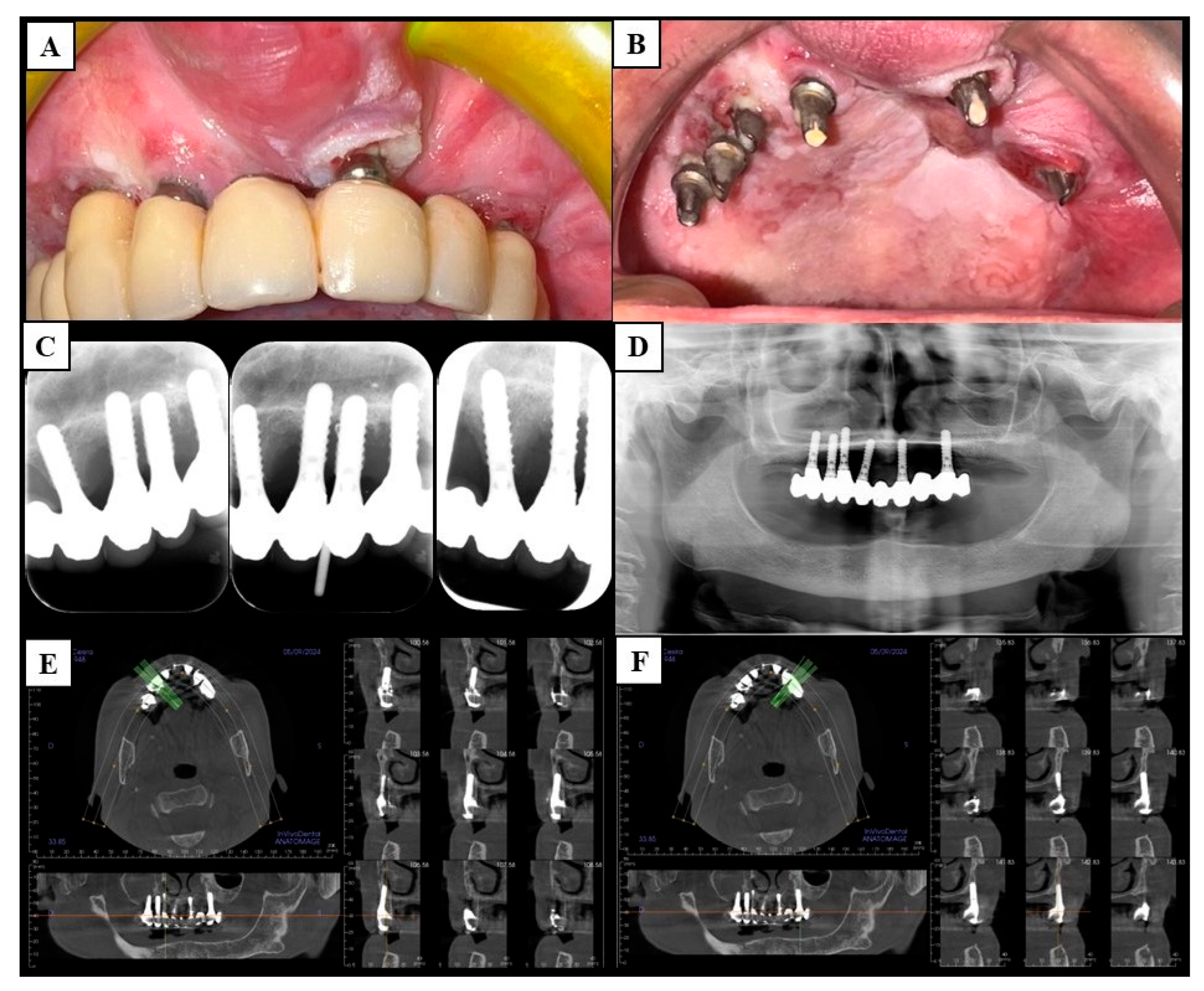
2.2.1. Diagnostic Phase and Clinical Staging
2.2.2. Surgical Phase and Pathological Staging
2.2.3. Follow-Up
2.3. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Preoperative Outcomes
3.2. Histological and Postoperative Outcomes
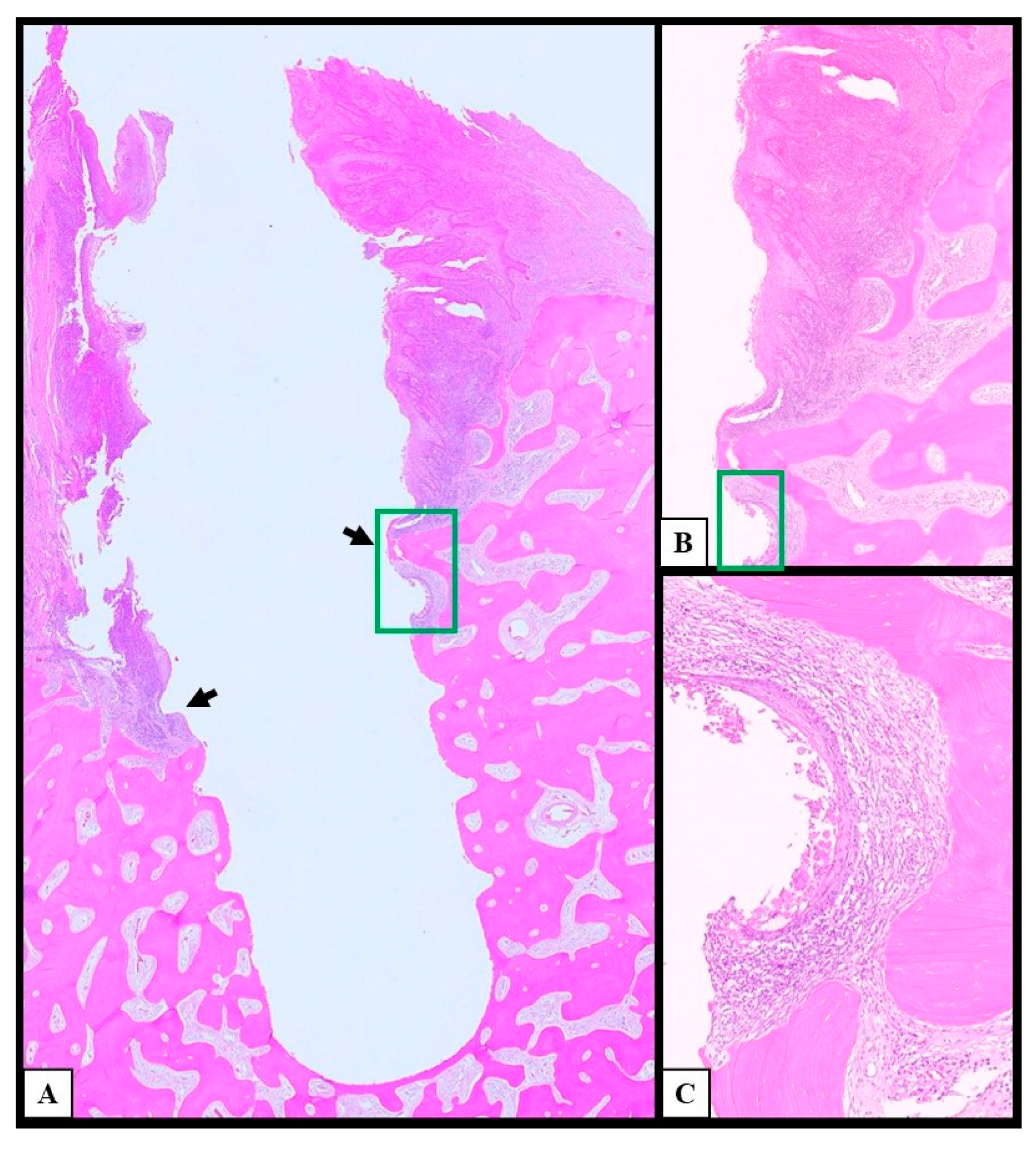
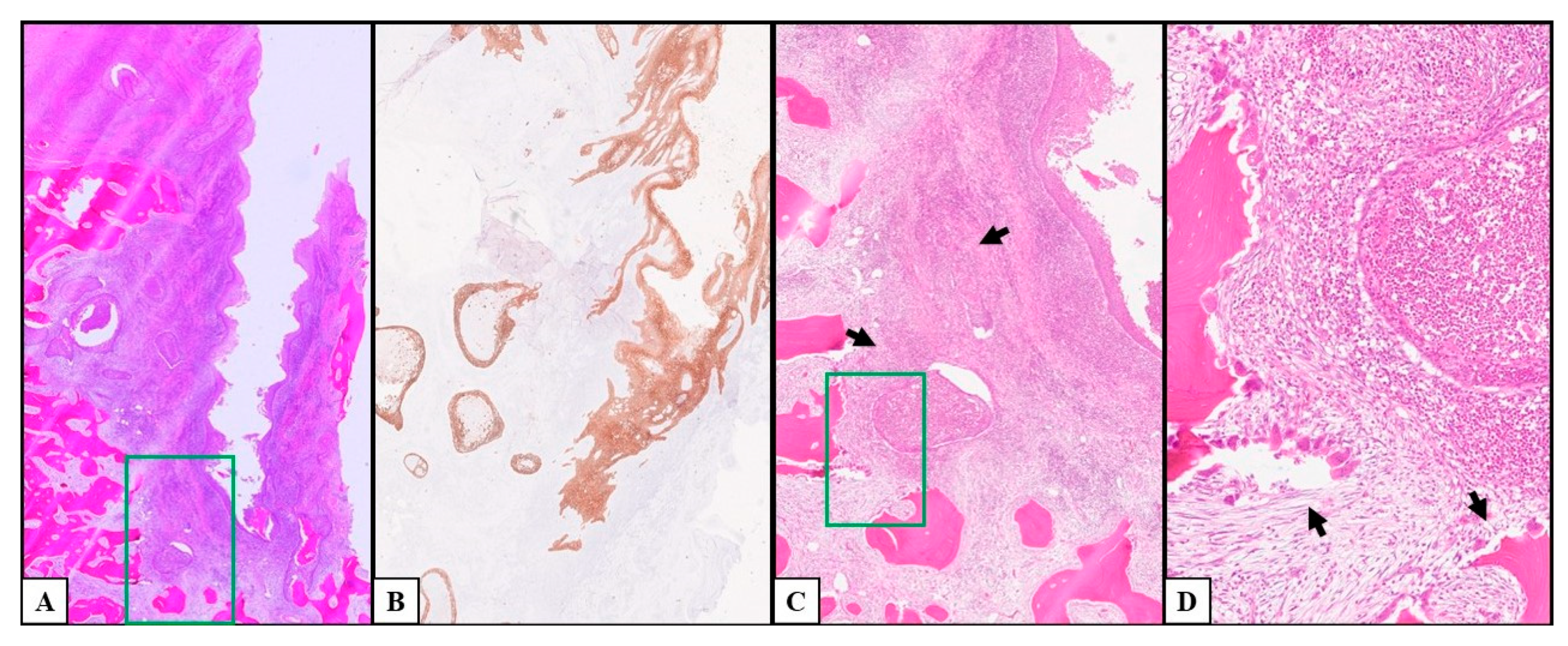
4. Discussion
4.1. Peri-Implant Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Peri-Implantitis: The Diagnostic Challenge
4.2. Risk Factors for Peri-Implant Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
4.3. Oral Carcinogenesis and Dental Implants
4.4. Histological Examination of Peri-Implant Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
4.5. Limitations and Implications for Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jané-Salas, E.; López-López, J.; Roselló-Llabrés, X.; Rodríguez-Argueta, O.-F.; Chimenos-Küstner, E. Relationship between Oral Cancer and Implants: Clinical Cases and Systematic Literature Review. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2012, 17, e23–e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, M.; Tsuno, H.; Ishizaka, R.; Fujiwara, K.; Imaue, S.; Tomihara, K.; Minamisaka, T. Primary Peri-Implant Oral Intra-Epithelial Neoplasia/Carcinoma in Situ: A Case Report Considering Risk Factors for Carcinogenesis. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2017, 3, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado-Peralvo, A.O.; Arriba-Fuente, L.; Mateos-Moreno, M.V.; Salgado-García, A. Is there an Association between Dental Implants and Squamous Cell Carcinoma? Br. Dent. J. 2016, 221, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiser, V.; Abu-El Naaj, I.; Shlomi, B.; Fliss, D.M.; Kaplan, I. Primary Oral Malignancy Imitating Peri-Implantitis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 74, 1383–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, S.; Tilakaratne, W.M. Update from the 5th Edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Head and Neck Tumors: Tumours of the Oral Cavity and Mobile Tongue. Head Neck Pathol. 2022, 16, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, M.; Tostes Oliveira, D.; Landman, G.; Kowalski, L. Histologic Subtypes of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Prognostic Relevance. J. (Can. Dent. Assoc.) 2007, 73, 339–344. [Google Scholar]
- Roi, A.; Roi, C.I.; Andreescu, N.I.; Riviş, M.; Badea, I.D.; Meszaros, N.; Rusu, L.C.; Iurciuc, S. Oral Cancer Histopathological Subtypes in Association with Risk Factors: A 5-Year Retrospective Study. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2020, 61, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.H.; Eo, M.Y.; Park, M.W.; Myoung, H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.M. Clinical Retrospective Analysis of Peri-Implant Oral Malignancies. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2024, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chainani-Wu, N.; Chang, C.; Sim, C.; Wu, T.C.; Cox, D.; Sirjani, D.; Silverman, S. Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Mimicking Peri-Implantitis. Clin. Adv. Periodontics 2016, 6, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, E.; Spink, M.J.; Messina, A.M. Peri-Implant Primary Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case Report with 5 Years’ Follow-Up. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 71, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, T.; Kawahara, D.; Inoue, R.; Kato, T.; Ishihara, N.; Kamiya, H.; Bessho, K. Squamous Cell Carcinoma around a Subperiosteal Implant in the Maxilla and the Association of Chronic MECHANICAL irritation and Peri-Implantitis: A Case Report. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2022, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglundh, T.; Armitage, G.; Araujo, M.G.; Avila-Ortiz, G.; Blanco, J.; Camargo, P.M.; Chen, S.; Cochran, D.; Derks, J.; Figuero, E.; et al. Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions: Consensus Report of Workgroup 4 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. 1), S313–S318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokaya, D.; Srimaneepong, V.; Wisitrasameewon, W.; Humagain, M.; Thunyakitpisal, P. Peri-Implantitis Update: Risk Indicators, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Eur. J. Dent. 2020, 14, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, I.; Zeevi, I.; Tal, H.; Rosenfeld, E.; Chaushu, G. Clinicopathologic Evaluation of malignancy Adjacent to Dental Implants. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2017, 123, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstraeten, J.; Slootweg, P.J.; Cuijpers, V.M.; Meijer, G.J. Do Dental Implants Facilitate Bone Invasion in Patients with Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma? A Case Series. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 52, 413–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, A.; Puthussery, F.J.; Downie, I.P.; Flood, T.R. Squamous Cell Carcinoma Presenting as Peri-Implantitis: A Case Report. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2009, 91, W8–W10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sotorra-Figuerola, D.; Lafuente-Ibáñez de Mendoza, I.; Parra-Pérez, C.; Aguirre-Urizar, J.M. Histopathological Analysis of Biopsies of “Peri-Implant Inflammatory Lesions.” Everything Is Not What It Seems. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2020, 22, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limongelli, L.; Capodiferro, S.; Tempesta, A.; Sportelli, P.; Dell’Olio, F.; Angelelli, G.; Maiorano, E.; Favia, G. Early Tongue Carcinomas (Clinical Stage I and II): Echo-Guided Three-Dimensional Diode Laser Mini-Invasive Surgery with Evaluation of Histological Prognostic Parameters. A Study of 85 Cases with Prolonged Follow-Up. Lasers Med. Sci. 2020, 35, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, A.M. Perform a death-defying act: The 90-Second Oral Cancer Examination. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2001, 132, S36–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempesta, A.; Capodiferro, S.; Mauceri, R.; Lauritano, D.; Maiorano, E.; Favia, G.; Limongelli, L. Peri-Implantitis-Like Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw: Clinical Considerations and Histological Evaluation with Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope. Oral Dis. 2022, 28, 1603–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olander, J.; Barkarmo, S.; Hammarström Johansson, P.; Wennerberg, A.; Stenport, V.F. Inflammatory Gene Profile and Particle Presence in Peri-Implant Mucosa: A Pilot Study on 9 Patients. J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2023, 14, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, N.-A.; Gorolay, V.V.; Wu, X. Differentiating Post-Treatment Changes from Tumor Recurrence in the Oral Cavity and Oropharynx. Semin. Roentgenol. 2023, 58, 272–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Takahashi, K.; Eda, T.; Kondoh, T.; Goss, A. Peri-Implant Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Aust. Dent. J. 2018, 63, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Gupta, R.; Gill, S.; Narula, V. Malignancy around Implants in Patients with a History of a Potentially Malignant or Malignant Lesion: A Systematic Review. Gen. Dent. 2024, 72, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Warnakulasuriya, S.; Kujan, O.; Aguirre-Urizar, J.M.; Bagan, J.V.; González-Moles, M.Á.; Kerr, A.R.; Lodi, G.; Mello, F.W.; Monteiro, L.; Ogden, G.R.; et al. Oral potentially malignant disorders: A Consensus Report from an International Seminar on Nomenclature and Classification, Convened by the WHO Collaborating Centre for Oral Cancer. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 1862–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinchasov, G.; Haimov, H.; Druseikaite, M.; Pinchasov, D.; Astramskaite, I.; Sarikov, R.; Juodzbalys, G. Oral Cancer around Dental Implants Appearing in Patients With\without a History of Oral or Systemic Malignancy: A Systematic Review. J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2017, 8, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Miranda-Galvis, M.; Rumayor Piña, A.; Sales de Sá, R.; Almeida Leite, A.; Agustin Vargas, P.; Calsavara, V.F.; Lópes Pinto, C.A.; Teng, Y.; Kowalski, L.P. PD-L1 Expression Patterns in Oral Cancer as an Integrated Approach for Further Prognostic Classification. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 1699–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocini, R.; Vianini, M.; Girolami, I.; Calabrese, L.; Scarpa, A.; Martini, M.; Morbini, P.; Marletta, S.; Brunelli, M.; Molteni, G.; et al. PD-L1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma: A Key Biomarker from the Laboratory to the Bedside. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2022, 8, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkerk, K.; Geurts, B.S.; Zeverijn, L.J.; van der Noort, V.; Verheul, H.M.W.; Haanen, J.B.A.G.; van der Veldt, A.A.M.; Eskens, F.A.L.M.; Aarts, M.J.B.; van Herpen, C.M.L.; et al. Cemiplimab in Locally Advanced or Metastatic Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Prospective Real-World Data from the DRUG Access Protocol. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2024, 39, 100875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Outcomes | Results | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample Size (n) | 21 | |||||
| Female/Male (n/n; Ratio) | 13/8; 1.6 | |||||
| Age (Mean ± SD) | 70.6 ± 11.7 years | |||||
| Number of OSCCs | 24 | |||||
| Number of Implants Involved | 50 | |||||
| Clinical Presentation (n; %) | Erythroplakia-like | Exophytic mixed | ||||
| 14; 58.3% | 10; 41.7% | |||||
| cTNM Staging (n; %) | Stage I | Stage II | Stage III | Stage IVa | Stage IVb | Stage IVc |
| 9; 37.5% | 12; 50.0% | 1; 4.2% | 2; 8.3% | 0; 0.0% | 0; 0.0% | |
| pTNM Staging (n; %) | Stage I | Stage II | Stage III | Stage IVa | Stage IVb | Stage IVc |
| 5; 20.8% | 1; 4.2% | 2; 8.3% | 10; 41.7% | 6; 25.0% | 0; 0.0% | |
| Grading (n; %) | G1 | G2 | G3 | |||
| 10; 41.7% | 8; 33.3% | 6; 25.0% | ||||
| Presence of PI-Like Inflammation (n; %) | 22; 91.6% | |||||
| Follow-Up (Mean ± SD) | 3.4 ± 1.0 years | |||||
| Disease-Free Survival (Mean ± SD) | 30.1 ± 17.9 months | |||||
| Medical History | n | % |
|---|---|---|
| Previous oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) and former smokers | 3 | 14.3% |
| Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia (PVL) | 4 | 19.0% |
| Oral lichen planus (OLP) | 3 | 14.3% |
| Oral lichen planus (OLP) AND smoking habit | 2 | 9.5% |
| Lichenoid dysplasia | 1 | 4.8% |
| Lichenoid dysplasia AND smoking habit | 1 | 4.8% |
| Smoking habit | 3 | 14.3% |
| Negative medical history for risk factors | 4 | 19.0% |
| PHASE | RECOMMENDATIONS |
|---|---|
| Medical History | Check for previous oral cancers, oral potentially malignant disorders, and smoking habits. |
| Clinical Examination | Use vital stainings (toluidine blue and Lugol’s solution) to study erythroplakia-like and exophytic mixed lesions of peri-implant mucosa. |
| Consider as suspicious all lesions persisting after two weeks from the decontamination of peri-implant pockets. | |
| Check for multiple synchronous suspicious lesions. | |
| For an optimal clinical examination, study the suspicious lesions after removing the dental prosthesis. | |
| Imaging | Use scattering-free methods, such as intraoral radiograms and magnetic resonance imaging, to study the bone associated with suspicious peri-implant lesions. |
| Diagnostic Interventions | Gather mucosal samples for histological examination in case of surgery for treatment of peri-implantitis. |
| Perform biopsy and histological examination of suspicious peri-implant lesions; the most experienced operators can perform peri-implant sulcus sampling for cytologic examination. | |
| Surgical Excision | The demolitive approach is more recommendable than the conservative. |
| Follow-Up | The worse the histological grading of cancer, the stricter the follow-up should be. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Limongelli, L.; Dell’Olio, F.; D’Amati, A.; Cascardi, E.; Forte, M.; Siciliani, R.A.; Manfuso, A.; Maiorano, E.; Favia, G.; Copelli, C.; et al. Peri-Implant Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC): Clinicopathological Features and Staging Issues. Cancers 2025, 17, 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132149
Limongelli L, Dell’Olio F, D’Amati A, Cascardi E, Forte M, Siciliani RA, Manfuso A, Maiorano E, Favia G, Copelli C, et al. Peri-Implant Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC): Clinicopathological Features and Staging Issues. Cancers. 2025; 17(13):2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132149
Chicago/Turabian StyleLimongelli, Luisa, Fabio Dell’Olio, Antonio D’Amati, Eliano Cascardi, Marta Forte, Rosaria Arianna Siciliani, Alfonso Manfuso, Eugenio Maiorano, Gianfranco Favia, Chiara Copelli, and et al. 2025. "Peri-Implant Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC): Clinicopathological Features and Staging Issues" Cancers 17, no. 13: 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132149
APA StyleLimongelli, L., Dell’Olio, F., D’Amati, A., Cascardi, E., Forte, M., Siciliani, R. A., Manfuso, A., Maiorano, E., Favia, G., Copelli, C., & Capodiferro, S. (2025). Peri-Implant Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma (OSCC): Clinicopathological Features and Staging Issues. Cancers, 17(13), 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132149












