Anti-Neoplastic Activity of Estrogen Receptor Beta in Chemoresistant Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture
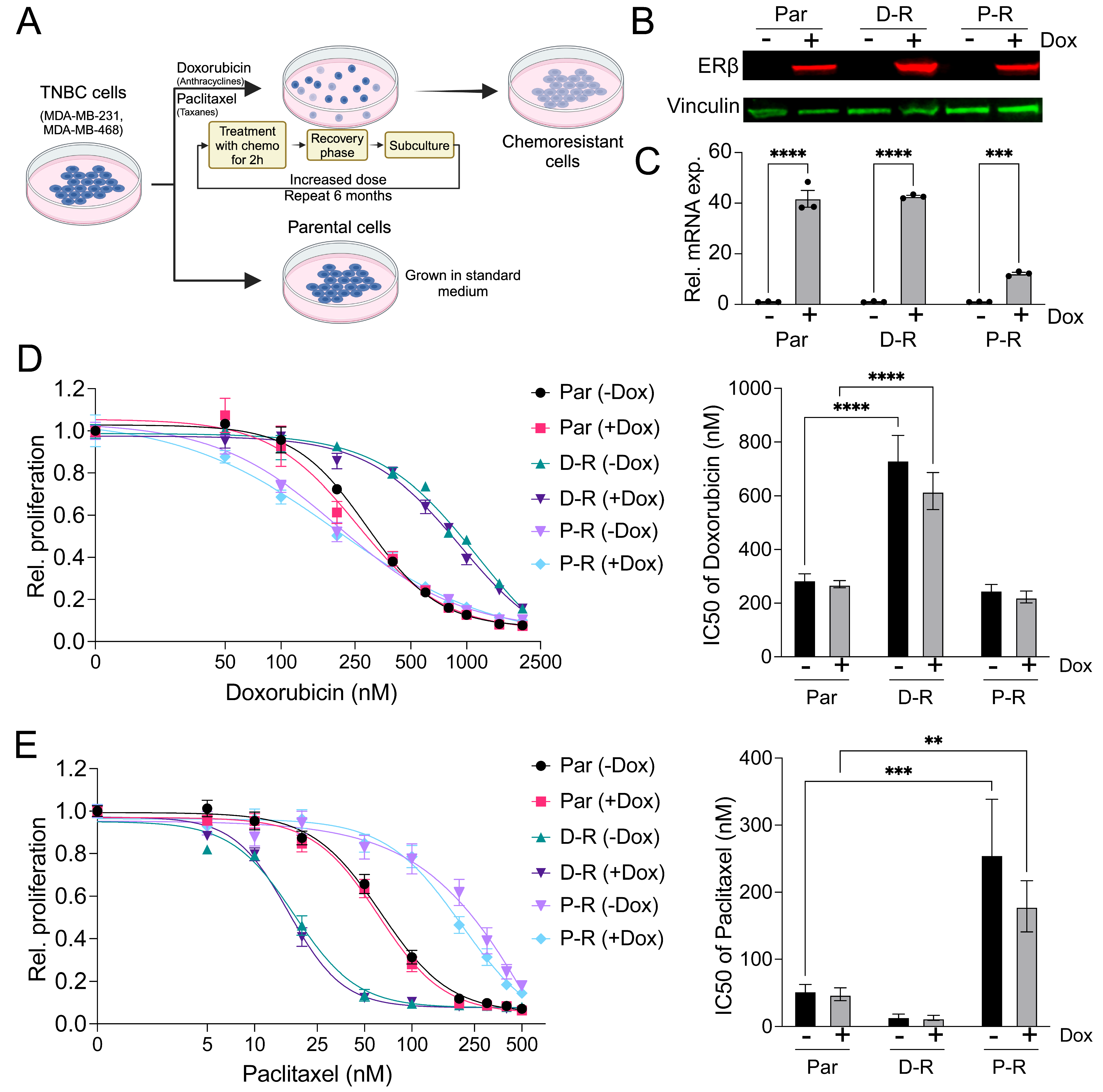
2.3. Generation of Chemotherapy-Resistant Lines
2.4. RT-PCR
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. Proliferation Assays
2.7. Karyotyping Analysis
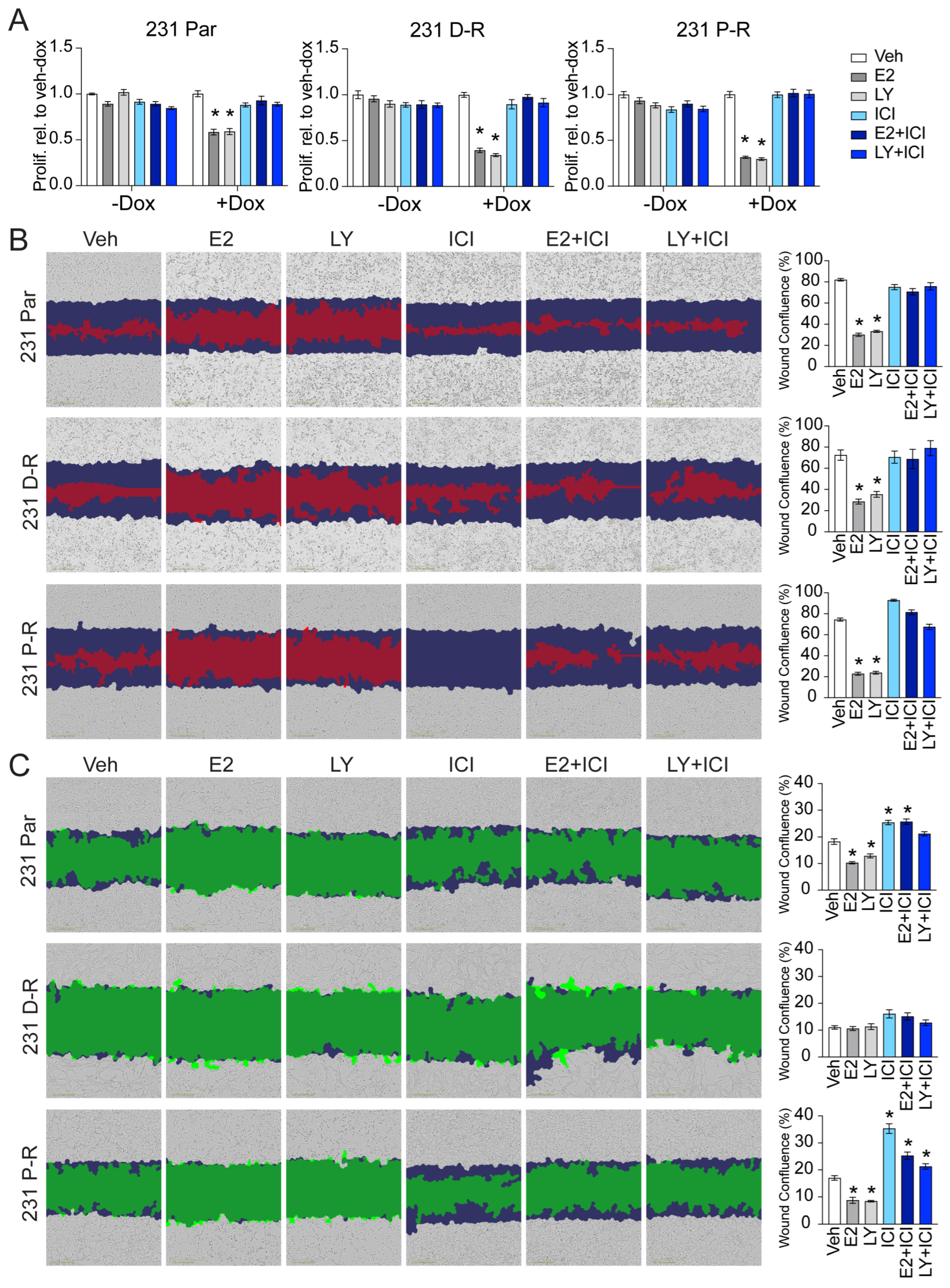
2.8. Migration Assays
2.9. Invasion Assays
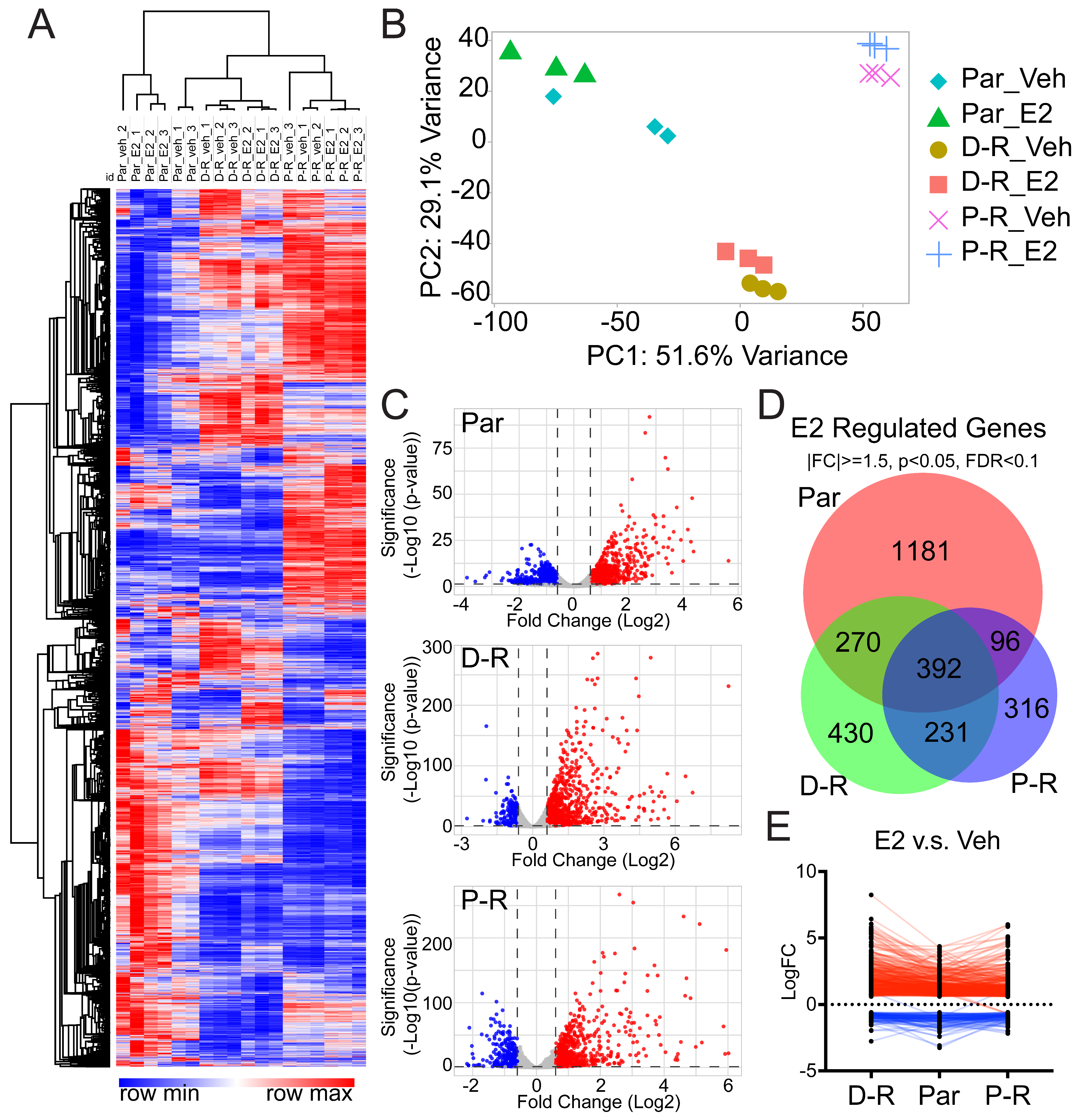
2.10. RNAseq
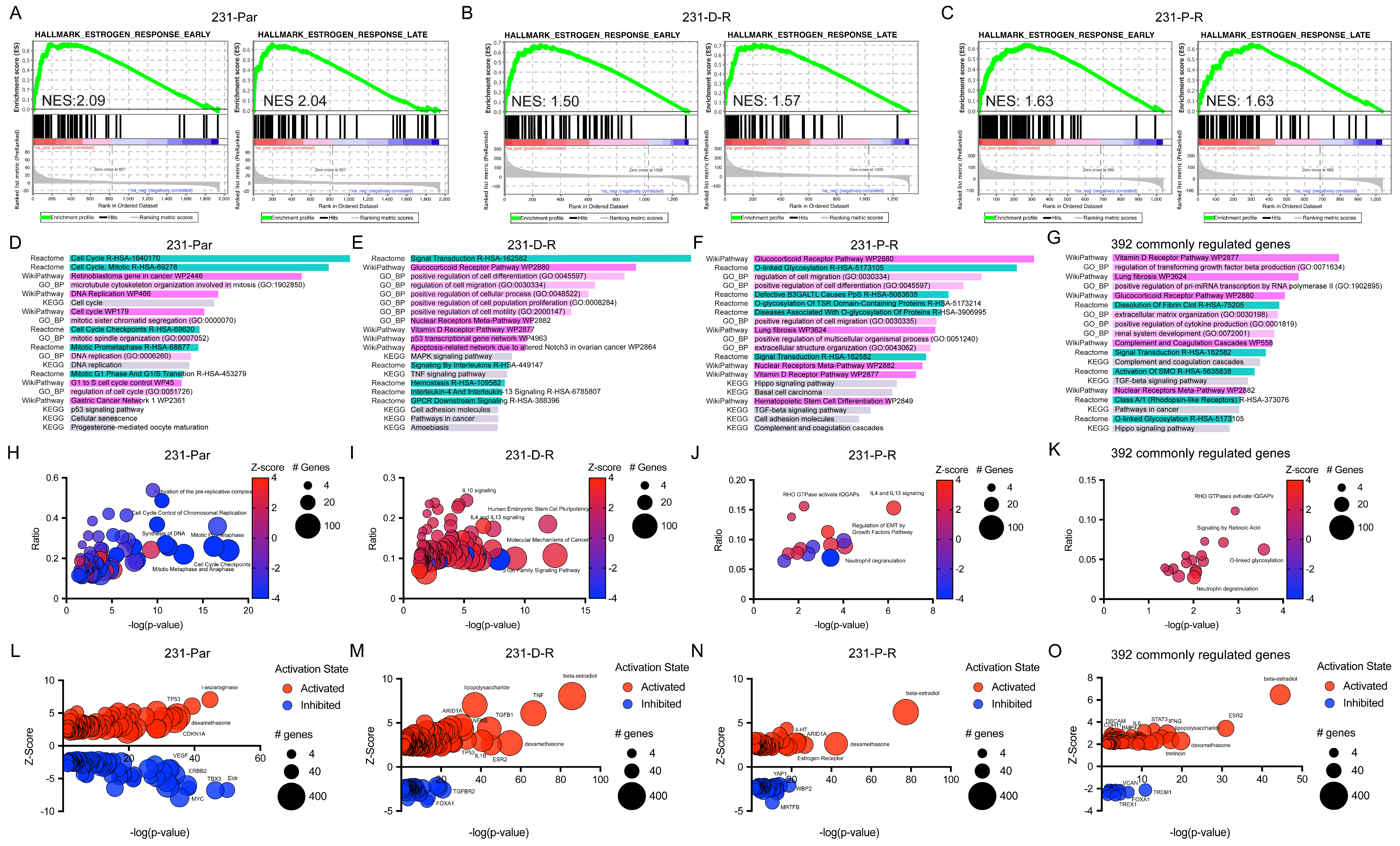
2.11. Pathway Analysis
2.12. Mergeomics Analysis
2.13. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Generation and Characterization of Chemotherapy-Resistant ERβ+ TNBC Cell Lines
3.2. Effect of Chemotherapy Resistance on Responsiveness to ERβ-Targeted Therapy
3.3. Transcriptomic Profiles of Chemotherapy-Resistant ERβ+ TNBC
3.4. Pathway Analysis of E2-Regulated Genes in Chemotherapy-Resistant ERβ+ TNBC Cells
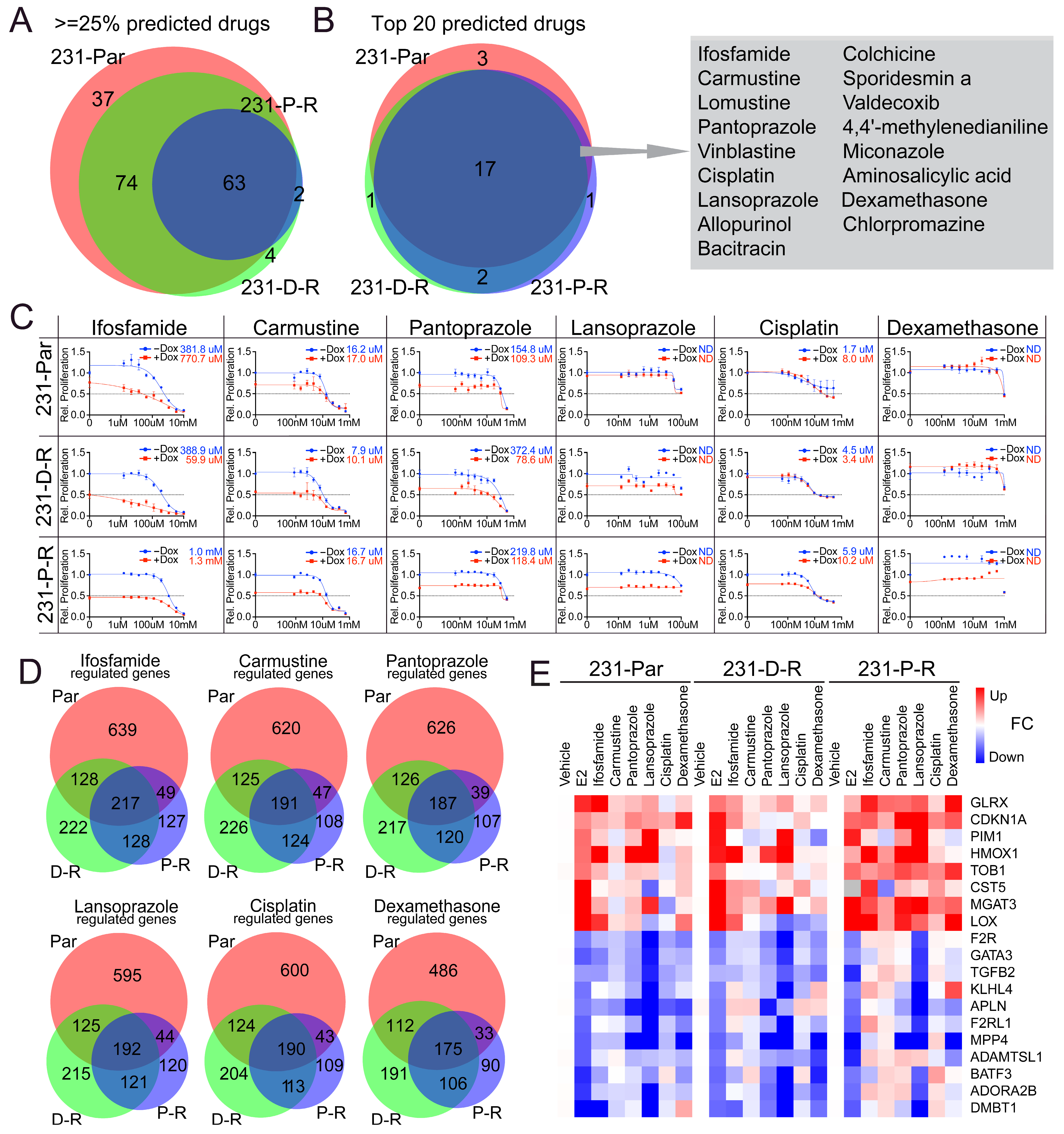
3.5. Identification and Validation of ERβ-Mimicking Compounds
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bianchini, G.; De Angelis, C.; Licata, L.; Gianni, L. Treatment landscape of triple-negative breast cancer—Expanded options, evolving needs. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 91–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Duan, J.J.; Bian, X.W.; Yu, S.C. Triple-negative breast cancer molecular subtyping and treatment progress. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loibl, S.; Poortmans, P.; Morrow, M.; Denkert, C.; Curigliano, G. Breast cancer. Lancet 2021, 397, 1750–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waks, A.G.; Winer, E.P. Breast Cancer Treatment: A Review. JAMA 2019, 321, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGowan, J.V.; Chung, R.; Maulik, A.; Piotrowska, I.; Walker, J.M.; Yellon, D.M. Anthracycline Chemotherapy and Cardiotoxicity. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2017, 31, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues-Ferreira, S.; Moindjie, H.; Haykal, M.M.; Nahmias, C. Predicting and Overcoming Taxane Chemoresistance. Trends Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prat, A.; Pineda, E.; Adamo, B.; Galvan, P.; Fernandez, A.; Gaba, L.; Diez, M.; Viladot, M.; Arance, A.; Munoz, M. Clinical implications of the intrinsic molecular subtypes of breast cancer. Breast 2015, 24 (Suppl. S2), S26–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liedtke, C.; Mazouni, C.; Hess, K.R.; Andre, F.; Tordai, A.; Mejia, J.A.; Symmans, W.F.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Hennessy, B.; Green, M.; et al. Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long-term survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longley, D.B.; Johnston, P.G. Molecular mechanisms of drug resistance. J. Pathol. 2005, 205, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedeljkovic, M.; Damjanovic, A. Mechanisms of Chemotherapy Resistance in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer-How We Can Rise to the Challenge. Cells 2019, 8, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawse, J.R.; Carter, J.M.; Aspros, K.G.M.; Bruinsma, E.S.; Koepplin, J.W.; Negron, V.; Subramaniam, M.; Ingle, J.N.; Rech, K.L.; Goetz, M.P. Optimized immunohistochemical detection of estrogen receptor beta using two validated monoclonal antibodies confirms its expression in normal and malignant breast tissues. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 179, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspros, K.G.M.; Carter, J.M.; Hoskin, T.L.; Suman, V.J.; Subramaniam, M.; Emch, M.J.; Ye, Z.; Sun, Z.; Sinnwell, J.P.; Thompson, K.J.; et al. Estrogen receptor beta repurposes EZH2 to suppress oncogenic NFkappaB/p65 signaling in triple negative breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2022, 8, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roger, P.; Sahla, M.E.; Makela, S.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Baldet, P.; Rochefort, H. Decreased expression of estrogen receptor beta protein in proliferative preinvasive mammary tumors. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 2537–2541. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Skliris, G.P.; Munot, K.; Bell, S.M.; Carder, P.J.; Lane, S.; Horgan, K.; Lansdown, M.R.; Parkes, A.T.; Hanby, A.M.; Markham, A.F.; et al. Reduced expression of oestrogen receptor beta in invasive breast cancer and its re-expression using DNA methyl transferase inhibitors in a cell line model. J. Pathol. 2003, 201, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, J.M.; Suman, V.J.; Subramaniam, M.; Wu, X.; Negron, V.; Gingery, A.; Pitel, K.S.; Shah, S.S.; Cunliffe, H.E.; McCullough, A.E.; et al. ERbeta1: Characterization, prognosis, and evaluation of treatment strategies in ERalpha-positive and -negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reese, J.M.; Bruinsma, E.S.; Monroe, D.G.; Negron, V.; Suman, V.J.; Ingle, J.N.; Goetz, M.P.; Hawse, J.R. ERbeta inhibits cyclin dependent kinases 1 and 7 in triple negative breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 96506–96521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, J.M.; Bruinsma, E.S.; Nelson, A.W.; Chernukhin, I.; Carroll, J.S.; Li, Y.; Subramaniam, M.; Suman, V.J.; Negron, V.; Monroe, D.G.; et al. ERbeta-mediated induction of cystatins results in suppression of TGFbeta signaling and inhibition of triple-negative breast cancer metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E9580–E9589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanle, E.K.; Zhao, Z.; Hawse, J.; Wisinski, K.; Keles, S.; Yuan, M.; Xu, W. Research resource: Global identification of estrogen receptor beta target genes in triple negative breast cancer cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 27, 1762–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.D.; Li, M.; Yuan, Y.; Mao, N.; Pan, L.Y. Biological comparison of ovarian cancer resistant cell lines to cisplatin and Taxol by two different administrations. Oncol. Rep. 2007, 17, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonego, M.; Pellizzari, I.; Dall’Acqua, A.; Pivetta, E.; Lorenzon, I.; Benevol, S.; Bomben, R.; Spessotto, P.; Sorio, R.; Gattei, V.; et al. Common biological phenotypes characterize the acquisition of platinum-resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnusamy, L.; Mahalingaiah, P.K.S.; Singh, K.P. Treatment schedule and estrogen receptor-status influence acquisition of doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 104, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; LaFramboise, T. CytoConverter: A web-based tool to convert karyotypes to genomic coordinates. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W.; Diamante, G.; Ding, J.; Nghiem, T.X.; Yang, J.; Ha, S.M.; Cohn, P.; Arneson, D.; Blencowe, M.; Garcia, J.; et al. PharmOmics: A species- and tissue-specific drug signature database and gene-network-based drug repositioning tool. iScience 2022, 25, 104052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, G.; Liu, L.; Yu, T.; Yu, L.; Feng, M.; Zhou, C.; Wang, X.; Teng, G.; Ma, Z.; Zhou, W.; et al. Genomic and transcriptomic analysis of breast cancer identifies novel signatures associated with response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Genome Med. 2024, 16, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Gao, R.; Sei, E.; Brandt, R.; Hartman, J.; Hatschek, T.; Crosetto, N.; Foukakis, T.; Navin, N.E. Chemoresistance Evolution in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Delineated by Single-Cell Sequencing. Cell 2018, 173, 879–893.e813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Kurt, Z.; Byars, S.G.; Tukiainen, T.; Kettunen, J.; Orozco, L.D.; Pellegrini, M.; Lusis, A.J.; Ripatti, S.; et al. Mergeomics: Multidimensional data integration to identify pathogenic perturbations to biological systems. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspros, K.G.M.; Emch, M.J.; Wang, X.; Subramaniam, M.; Hinkle, M.L.; Rodman, E.P.B.; Goetz, M.P.; Hawse, J.R. Disruption of estrogen receptor beta’s DNA binding domain impairs its tumor suppressive effects in triple negative breast cancer. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1047166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Nag, S.A.; Zhang, R. Targeting the NFkappaB signaling pathways for breast cancer prevention and therapy. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 264–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verzella, D.; Pescatore, A.; Capece, D.; Vecchiotti, D.; Ursini, M.V.; Franzoso, G.; Alesse, E.; Zazzeroni, F. Life, death, and autophagy in cancer: NF-kappaB turns up everywhere. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogston, N.; Harrison, A.J.; Cheung, H.F.; Ashton, B.A.; Hampson, G. Dexamethasone and retinoic acid differentially regulate growth and differentiation in an immortalised human clonal bone marrow stromal cell line with osteoblastic characteristics. Steroids 2002, 67, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, N.; Gans, E.H. Tretinoin: A Review of Its Anti-inflammatory Properties in the Treatment of Acne. J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2011, 4, 22–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; van Boxel-Dezaire, A.H.; Cheon, H.; Yang, J.; Stark, G.R. STAT3 activation in response to IL-6 is prolonged by the binding of IL-6 receptor to EGF receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16975–16980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, J.W.; McVicar, D.W. TREM and TREM-like receptors in inflammation and disease. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2009, 21, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munger, J.S.; Sheppard, D. Cross talk among TGF-beta signaling pathways, integrins, and the extracellular matrix. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a005017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsui, Y.; Shiina, H.; Kato, T.; Maekawa, S.; Hashimoto, Y.; Shiina, M.; Imai-Sumida, M.; Kulkarni, P.; Dasgupta, P.; Wong, R.K.; et al. Versican Promotes Tumor Progression, Metastasis and Predicts Poor Prognosis in Renal Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 884–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peran, I.; Dakshanamurthy, S.; McCoy, M.D.; Mavropoulos, A.; Allo, B.; Sebastian, A.; Hum, N.R.; Sprague, S.C.; Martin, K.A.; Pishvaian, M.J.; et al. Cadherin 11 Promotes Immunosuppression and Extracellular Matrix Deposition to Support Growth of Pancreatic Tumors and Resistance to Gemcitabine in Mice. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1359–1372.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.N.; Song, J.; Zhang, L.; LeMaire, S.A.; Hou, X.; Zhang, C.; Coselli, J.S.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Activation of the AMPK-FOXO3 pathway reduces fatty acid-induced increase in intracellular reactive oxygen species by upregulating thioredoxin. Diabetes 2009, 58, 2246–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Emch, M.J.; Goetz, M.P.; Hawse, J.R. Anti-Neoplastic Activity of Estrogen Receptor Beta in Chemoresistant Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers 2025, 17, 2132. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132132
Wang X, Emch MJ, Goetz MP, Hawse JR. Anti-Neoplastic Activity of Estrogen Receptor Beta in Chemoresistant Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2025; 17(13):2132. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132132
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiyin, Michael J. Emch, Matthew P. Goetz, and John R. Hawse. 2025. "Anti-Neoplastic Activity of Estrogen Receptor Beta in Chemoresistant Triple-Negative Breast Cancer" Cancers 17, no. 13: 2132. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132132
APA StyleWang, X., Emch, M. J., Goetz, M. P., & Hawse, J. R. (2025). Anti-Neoplastic Activity of Estrogen Receptor Beta in Chemoresistant Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers, 17(13), 2132. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132132






