Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment of Osteosarcoma
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Tissue Dissociation
2.2. Single-Cell Capture, Library Preparation and RNA-Seq
2.3. Single-Cell Data Processing and Quality Control
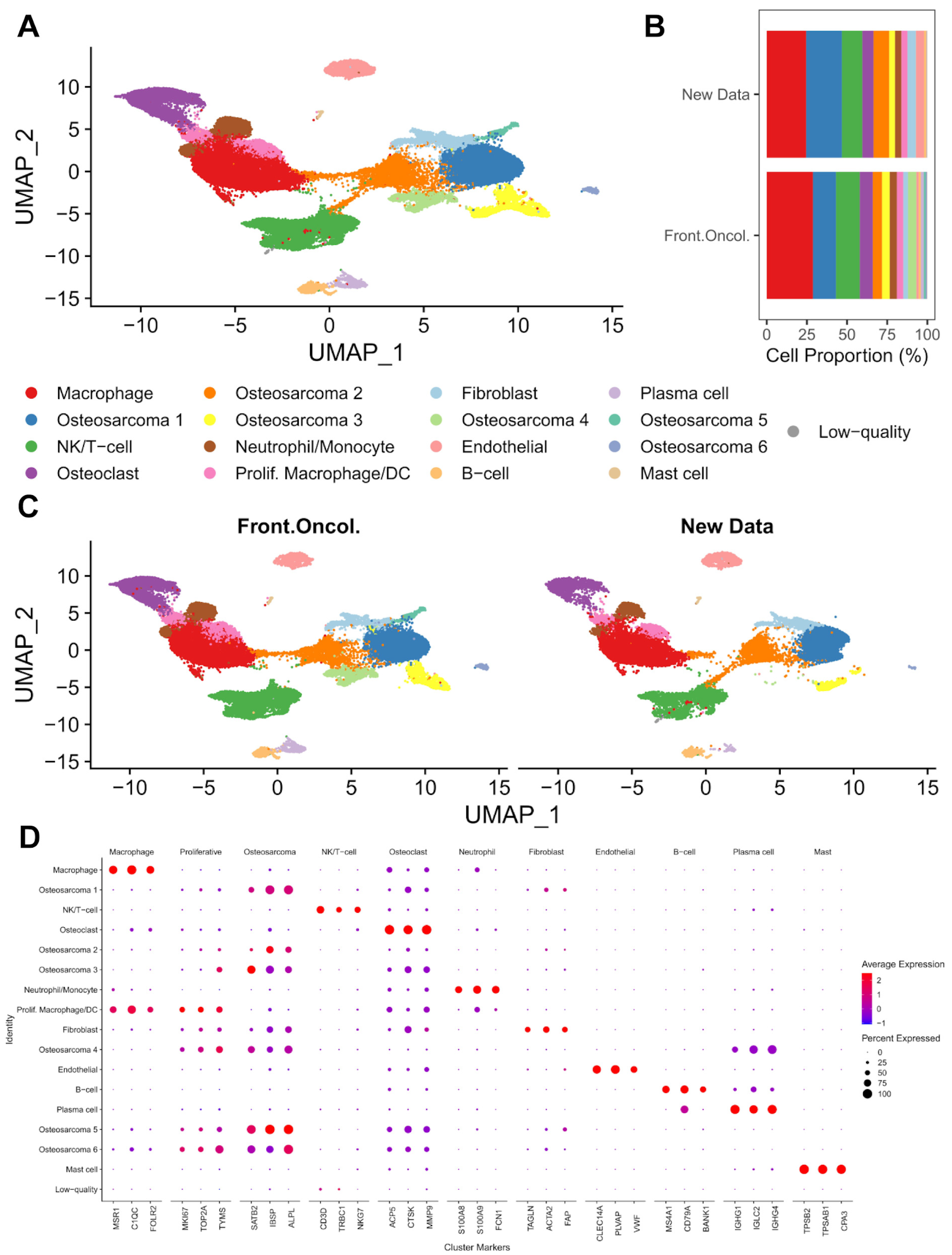
2.4. Clustering and Cell Type Determination
2.5. Copy Number Analysis
2.6. Cell–Cell Interactions
2.7. Visium Spatial Gene Expression Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Single-Cell Transcriptomic Analysis of Treatment-Naïve Osteosarcoma
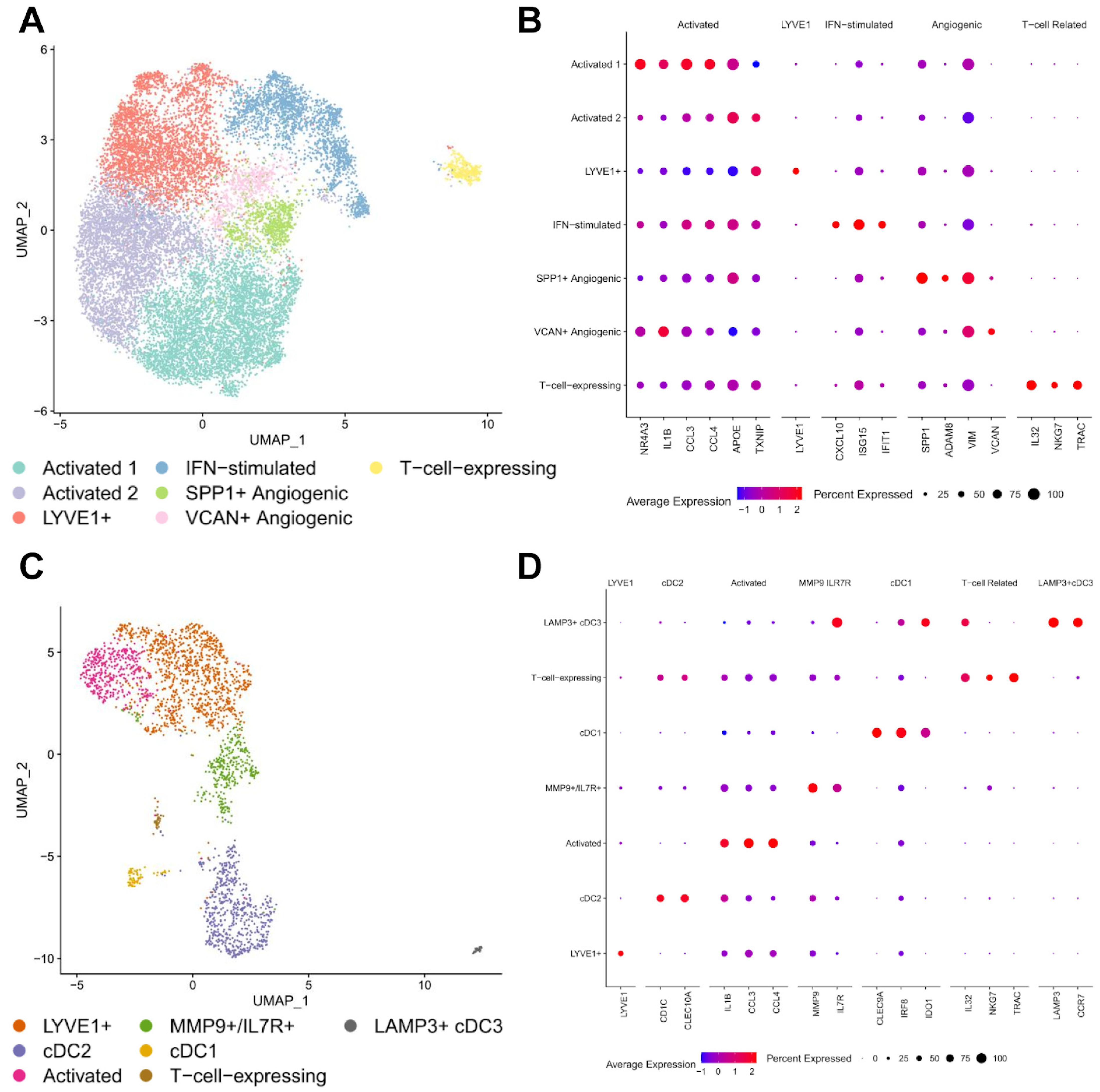
3.2. Macrophages and Dendritic Cells
3.3. Immunosuppressive Neutrophil/Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells (MDSCs)
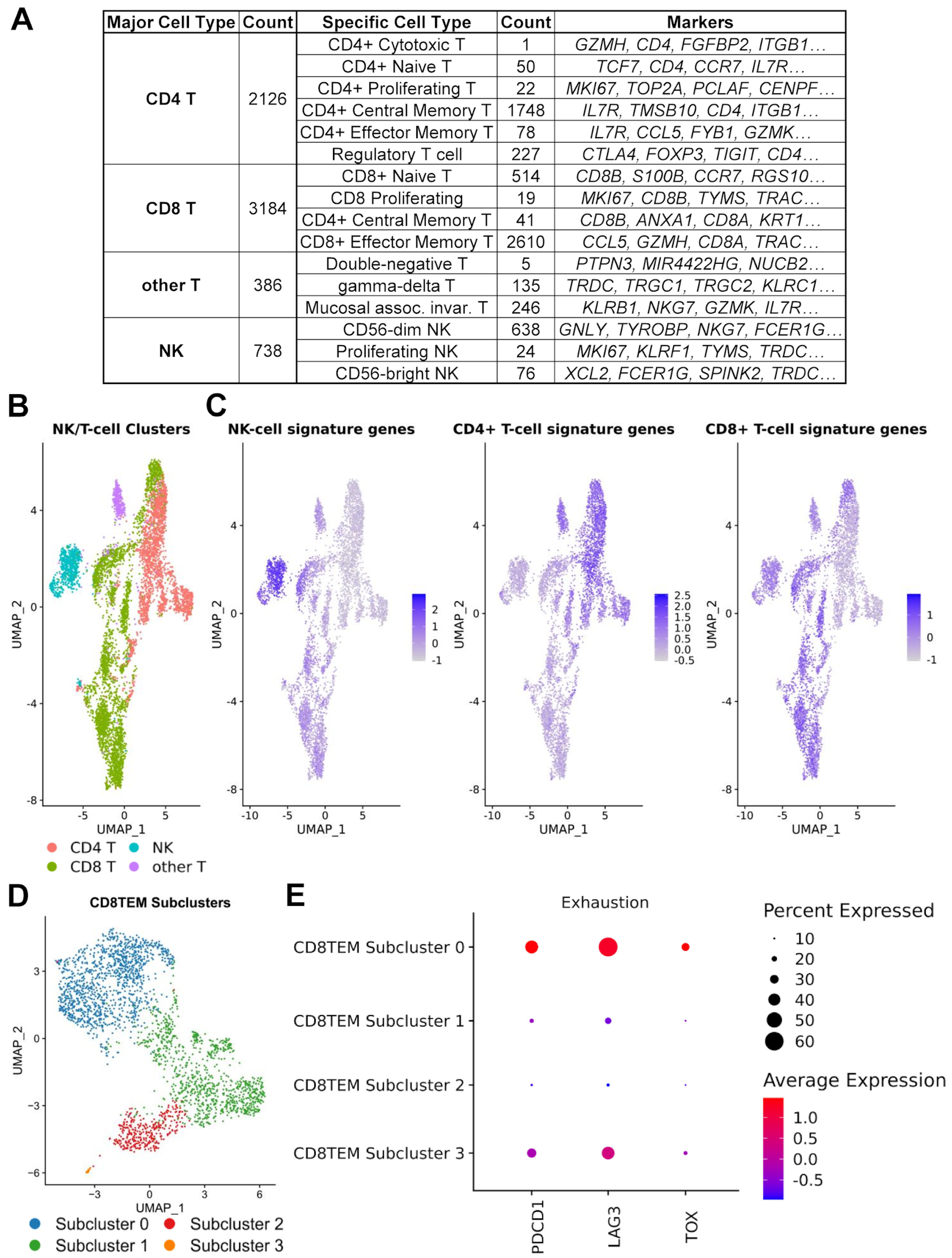
3.4. Regulatory and Exhausted T Cells
3.5. Osteosarcoma Cells
3.6. Cell–Cell Interactions
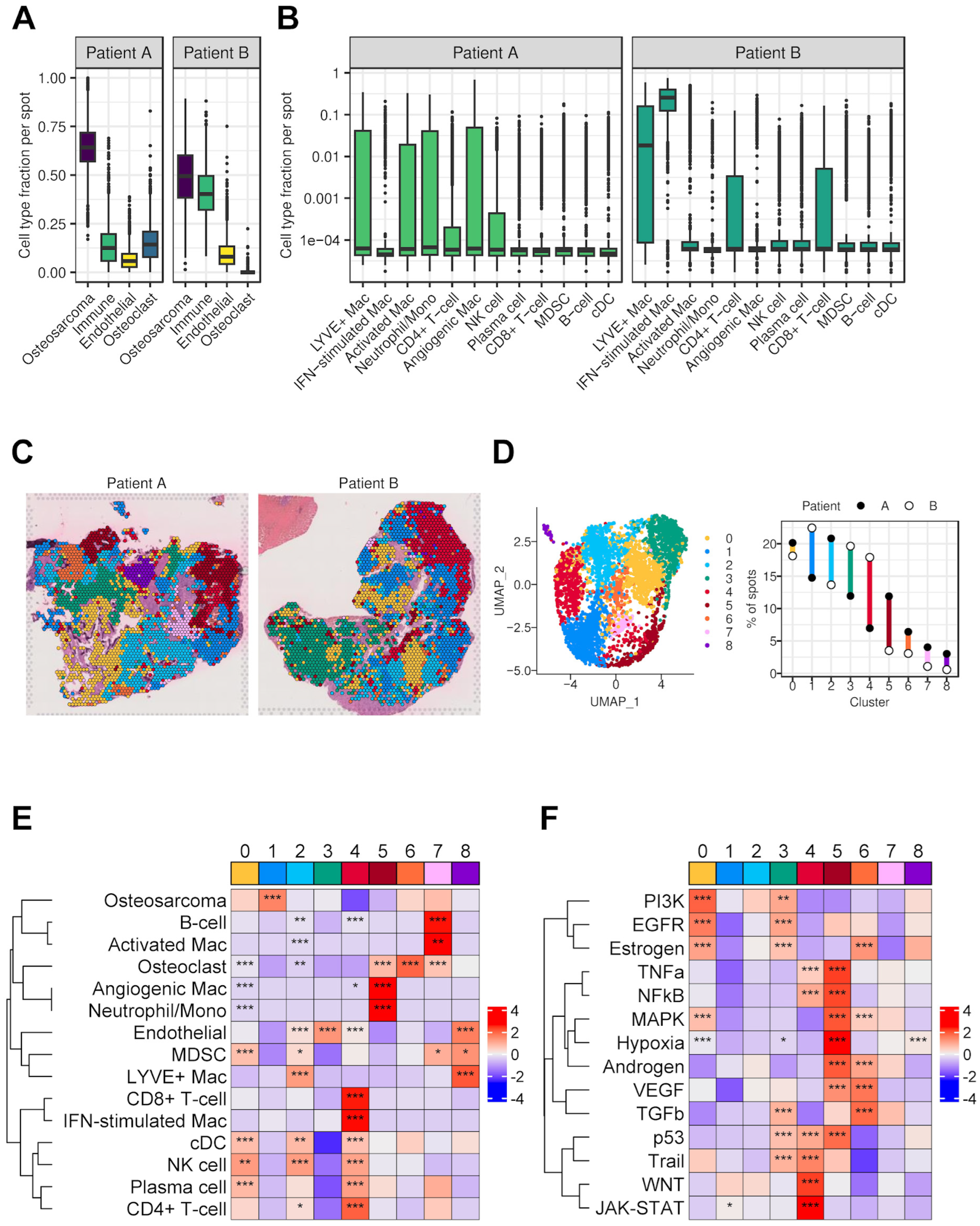
3.7. Spatial Transcriptomics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Preprint Statement
Abbreviations
| MDSCs | Myeloid-derived suppressor cells |
| OS | Osteosarcoma |
| IT | Immunotherapy |
| DC | Dendritic cells |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
| scRNA-seq | Single-cell RNA sequencing |
| CCMC | Connecticut Children’s Medical Center |
| CHCO | Children’s Hospital Colorado |
| PI | Propidium iodide |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| PBMC | Proliferating blood mononuclear cell |
| IPA | Ingenuity Pathway Analysis |
| FFPE | Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| RCTD | Robust Cell Type Decomposition |
| mregDCs | Mature regulatory dendritic cells |
| T-regs | Regulatory T cells |
| N-CM | Nonclassical monocyte |
| CD8TEM | CD8+ effector memory T cells |
References
- Meltzer, P.S.; Helman, L.J.; Longo, D.L. New Horizons in the Treatment of Osteosarcoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 2066–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Bahrami, A.; Pappo, A.; Easton, J.; Dalton, J.; Hedlund, E.; Ellison, D.; Shurtleff, S.; Wu, G.; Wei, L.; et al. Recurrent Somatic Structural Variations Contribute to Tumorigenesis in Pediatric Osteosarcoma. Cell Rep. 2014, 7, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koirala, P.; Roth, M.E.; Gill, J.; Piperdi, S.; Chinai, J.M.; Geller, D.S.; Hoang, B.H.; Park, A.; Fremed, M.A.; Zang, X.; et al. Immune Infiltration and Pd-L1 Expression in the Tumor Microenvironment Are Prognostic in Osteosarcoma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lussier, D.M.; Johnson, J.L.; Hingorani, P.; Blattman, J.N. Combination Immunotherapy with A-Ctla-4 and A-Pd-L1 Antibody Blockade Prevents Immune Escape and Leads to Complete Control of Metastatic Osteosarcoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2015, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, S.P.; Mahoney, M.R.; Van Tine, B.A.; Atkins, J.; Milhem, M.M.; Jahagirdar, B.N.; Antonescu, C.R.; Horvath, E.; Tap, W.D.; Schwartz, G.K.; et al. Nivolumab with or without Ipilimumab Treatment for Metastatic Sarcoma (Alliance A091401): Two Open-Label, Non-Comparative, Randomised, Phase 2 Trials. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawbi, H.A.; Burgess, M.; Bolejack, V.; Van Tine, B.A.; Schuetze, S.M.; Hu, J.; D’Angelo, S.; Attia, S.; Riedel, R.F.; Priebat, D.A.; et al. Pembrolizumab in Advanced Soft-Tissue Sarcoma and Bone Sarcoma (Sarc028): A Multicentre, Two-Cohort, Single-Arm, Open-Label, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1493–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnewies, M.; Roberts, E.W.; Kersten, K.; Chan, V.; Fearon, D.F.; Merad, M.; Coussens, L.M.; Gabrilovich, D.I.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S.; Hedrick, C.C.; et al. Understanding the Tumor Immune Microenvironment (Time) for Effective Therapy. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corre, I.; Verrecchia, F.; Crenn, V.; Redini, F.; Trichet, V. The Osteosarcoma Microenvironment: A Complex but Targetable Ecosystem. Cells 2020, 9, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Han, J.; Yang, L.; Cai, Z.; Sun, W.; Hua, Y.; Xu, J. Immune Microenvironment in Osteosarcoma: Components, Therapeutic Strategies and Clinical Applications. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 907550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Cao, J.; Li, B.; Nice, E.C.; Mao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, C. Managing the Immune Microenvironment of Osteosarcoma: The Outlook for Osteosarcoma Treatment. Bone Res. 2023, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Feng, W.; Dai, Y.; Bao, M.; Yuan, Z.; He, M.; Qin, Z.; Liao, S.; He, J.; Huang, Q.; et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomics Reveals the Complexity of the Tumor Microenvironment of Treatment-Naive Osteosarcoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 709210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, D.; Yang, Q.; Lv, X.; Huang, W.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, T.; Ding, X.; et al. Single-Cell Rna Landscape of Intratumoral Heterogeneity and Immunosuppressive Microenvironment in Advanced Osteosarcoma. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, W.; Yu, S. A Single-Cell and Spatially Resolved Atlas of Human Osteosarcomas. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 17, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; He, M.; Tang, H.; Xie, T.; Lin, Y.; Liu, S.; Liang, J.; Li, F.; Luo, K.; Yang, M.; et al. Single-Cell and Spatial Transcriptomics Reveal Metastasis Mechanism and Microenvironment Remodeling of Lymph Node in Osteosarcoma. BMC Med. 2024, 22, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.-Y.; Que, L.-Y.; Yang, F.; Feng, Y.; Ren, D.; Song, X. Single-Cell Transcriptional Profiling in Osteosarcoma and the Effect of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy on the Tumor Microenvironment. J. Bone Oncol. 2024, 46, 100604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hu, H.; Shao, Z.; Lv, X.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, X.; Song, Q.; Han, Y.; Guo, T.; Xiong, L.; et al. Characterizing the Tumor Microenvironment at the Single-Cell Level Reveals a Novel Immune Evasion Mechanism in Osteosarcoma. Bone Res. 2023, 11, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.X.Y.; Terry, J.M.; Belgrader, P.; Ryvkin, P.; Bent, Z.W.; Wilson, R.; Ziraldo, S.B.; Wheeler, T.D.; McDermott, G.P.; Zhu, J.; et al. Massively Parallel Digital Transcriptional Profiling of Single Cells. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Hao, S.; Andersen-Nissen, E.; Mauck, W.M.; Zheng, S.; Butler, A.; Lee, M.J.; Wilk, A.J.; Darby, C.; Zager, M.; et al. Integrated Analysis of Multimodal Single-Cell Data. Cell 2021, 184, 3573–3587.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- McGinnis, C.S.; Murrow, L.M.; Gartner, Z.J. Doubletfinder: Doublet Detection in Single-Cell Rna Sequencing Data Using Artificial Nearest Neighbors. Cell Syst. 2019, 8, 329–337.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsunsky, I.; Millard, N.; Fan, J.; Slowikowski, K.; Zhang, F.; Wei, K.; Baglaenko, Y.; Brenner, M.; Loh, P.-R.; Raychaudhuri, S. Fast, Sensitive and Accurate Integration of Single-Cell Data with Harmony. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDavid, A.; Finak, G.; Chattopadyay, P.K.; Dominguez, M.; Lamoreaux, L.; Ma, S.S.; Roederer, M.; Gottardo, R. Data Exploration, Quality Control and Testing in Single-Cell Qpcr-Based Gene Expression Experiments. Bioinformatics 2012, 29, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, T.; Butler, A.; Hoffman, P.; Hafemeister, C.; Papalexi, E.; Mauck, W.M.; Hao, Y.; Stoeckius, M.; Smibert, P.; Satija, R. Comprehensive Integration of Single-Cell Data. Cell 2019, 177, 1888–1902.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tickle, T.; Tirosh, I.; Georgescu, C.; Brown, M.; Haas, B. Infercnv of the Trinity Ctat Project; Klarman Cell Observatory, Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.; Sheng, J.; Gao, D.; Li, F.; Durrans, A.; Ryu, S.; Lee, S.B.; Narula, N.; Rafii, S.; Elemento, O.; et al. Transcriptome Analysis of Individual Stromal Cell Populations Identifies Stroma-Tumor Crosstalk in Mouse Lung Cancer Model. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 1187–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traag, V.A.; Waltman, L.; Van Eck, N.J. From Louvain to Leiden: Guaranteeing Well-Connected Communities. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cable, D.M.; Murray, E.; Zou, L.S.; Goeva, A.; Macosko, E.Z.; Chen, F.; Irizarry, R.A. Robust Decomposition of Cell Type Mixtures in Spatial Transcriptomics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 40, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcoxon, F. Individual Comparisons of Grouped Data by Ranking Methods. J. Econ. Èntomol. 1946, 39, 269–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, M.; Klinger, B.; Klünemann, M.; Sieber, A.; Uhlitz, F.; Sauer, S.; Garnett, M.J.; Blüthgen, N.; Saez-Rodriguez, J. Perturbation-Response Genes Reveal Signaling Footprints in Cancer Gene Expression. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wang, F.X.C.; Mu, J.; Li, J.; Yao, H.; Chen, K. Role of Tumor Microenvironment in Cancer Progression and Therapeutic Strategy. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 11149–11165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neophytou, C.M.; Panagi, M.; Stylianopoulos, T.; Papageorgis, P. The Role of Tumor Microenvironment in Cancer Metastasis: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cancers 2021, 13, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghban, R.; Roshangar, L.; Jahanban-Esfahlan, R.; Seidi, K.; Ebrahimi-Kalan, A.; Jaymand, M.; Kolahian, S.; Javaheri, T.; Zare, P. Tumor Microenvironment Complexity and Therapeutic Implications at a Glance. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakarov, S.; Lim, H.Y.; Tan, L.; Lim, S.Y.; See, P.; Lum, J.; Zhang, X.-M.; Foo, S.; Nakamizo, S.; Duan, K.; et al. Two Distinct Interstitial Macrophage Populations Coexist across Tissues in Specific Subtissular Niches. Science 2019, 363, eaau0964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.Y.; Lim, S.Y.; Tan, C.K.; Thiam, C.H.; Goh, C.C.; Carbajo, D.; Chew, S.H.S.; See, P.; Chakarov, S.; Wang, X.N.; et al. Hyaluronan Receptor Lyve-1-Expressing Macrophages Maintain Arterial Tone Through Hyaluronan-Mediated Regulation of Smooth Muscle Cell Collagen. Immunity 2018, 49, 326–341.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, C.H.; Jun Koh, Y.; Han, J.; Sung, H.K.; Jong Lee, H.; Morisada, T.; Schwendener, R.A.; Brekken, R.A.; Kang, G.; Oike, Y.; et al. Angiogenic Role of Lyve-1–Positive Macrophages in Adipose Tissue. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, e47–e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieu, T.Q.; Tazawa, K.; Kawashima, N.; Noda, S.; Fujii, M.; Nara, K.; Hashimoto, K.; Han, P.; Okiji, T. Kinetics of Lyve-1-Positive M2-Like Macrophages in Developing and Repairing Dental Pulp In Vivo and Their Pro-Angiogenic Activity In Vitro. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Flynn, W.F.; Sivajothi, S.; Luo, D.; Bozal, S.B.; Davé, M.; Luciano, A.A.; Robson, P.; Luciano, D.E.; Courtois, E.T.; et al. Single-Cell Analysis of Endometriosis Reveals a Coordinated Transcriptional Programme Driving Immunotolerance and Angiogenesis Across Eutopic and Ectopic Tissues. Nat. Cell Biol. 2022, 24, 1306–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opzoomer, J.W.; Anstee, J.E.; Dean, I.; Hill, E.J.; Bouybayoune, I.; Caron, J.; Muliaditan, T.; Gordon, P.; Sosnowska, D.; Nuamah, R. Macrophages Orchestrate the Expansion of a Proangiogenic Perivascular Niche During Cancer Progression. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg9518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Li, Z.; Gao, R.; Xing, B.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Qin, S.; Zhang, L.; Ouyang, H.; Du, P.; et al. A Pan-Cancer Single-Cell Transcriptional Atlas of Tumor Infiltrating Myeloid Cells. Cell 2021, 184, 792–809.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaluf, E.; Vokaer, B.; Detavernier, A.; Azouz, A.; Splittgerber, M.; Carrette, A.; Boon, L.; Libert, F.; Soares, M.P.; Le Moine, A.; et al. Heme Oxygenase-1 Orchestrates the Immunosuppressive Program of Tumor-Associated Macrophages. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 5, e133929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.-Y.; Xie, H.; Yuan, J.; Jiang, X.-Y.; Yong, J.-H.; Zeng, D.; Dou, Y.-Y.; Xiao, S.-S. M2-Like Tumor-Associated Macrophages-Secreted Egf Promotes Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Metastasis Via Activating Egfr-Erk Signaling and Suppressing Lncrna Limt Expression. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2019, 20, 956–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condamine, T.; Dominguez, G.A.; Youn, J.-I.; Kossenkov, A.V.; Mony, S.; Alicea-Torres, K.; Tcyganov, E.; Hashimoto, A.; Nefedova, Y.; Lin, C.; et al. Lectin-Type Oxidized Ldl Receptor-1 Distinguishes Population of Human Polymorphonuclear Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Cancer Patients. Sci. Immunol. 2016, 1, aaf8943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Tang, L.; Li, R.; Zhai, J.; Luo, S.; Peng, Y.; Chen, X.; Wei, L. Single-Cell Rna Sequencing Reveals Tcr(+) Macrophages in Hpv-Related Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1030222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, T.; Hahn, M.; Riabov, V.; Yin, S.; Kzhyshkowska, J.; Busch, S.; Püllmann, K.; Beham, A.W.; Neumaier, M.; Kaminski, W.E. A Combinatorial Alphabeta T Cell Receptor Expressed by Macrophages in the Tumor Microenvironment. Immunobiology 2017, 222, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedrick, C.C.; Malanchi, I. Neutrophils in Cancer: Heterogeneous and Multifaceted. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 22, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshetaiwi, H.; Pervolarakis, N.; McIntyre, L.L.; Ma, D.; Nguyen, Q.; Rath, J.A.; Nee, K.; Hernandez, G.; Evans, K.; Torosian, L.; et al. Defining the Emergence of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Breast Cancer Using Single-Cell Transcriptomics. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eaay6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastio, J.; Condamine, T.; Dominguez, G.; Kossenkov, A.V.; Donthireddy, L.; Veglia, F.; Lin, C.; Wang, F.; Fu, S.; Zhou, J.; et al. Identification of Monocyte-Like Precursors of Granulocytes in Cancer as a Mechanism for Accumulation of Pmn-Mdscs. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 216, 2150–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, D.N.; Smith, E.L.; Brentjens, R.J.; Wolchok, J.D. The Future of Cancer Treatment: Immunomodulation, Cars and Combination Immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 13, 273–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, A.; Wolchok, J.D. Cancer Immunotherapy Using Checkpoint Blockade. Science 2018, 359, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, A.; Perica, K.; Klebanoff, C.A.; Wolchok, J.D. Clinical Implications of T Cell Exhaustion for Cancer Immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 19, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielenska, M.; Bayani, J.; Pandita, A.; Toledo, S.; Marrano, P.; Andrade, J.; Petrilli, A.; Thorner, P.; Sorensen, P.; Squire, J.A. Comparative Genomic Hybridization Analysis Identifies Gains of 1p35 Approximately P36 and Chromosome 19 in Osteosarcoma. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2001, 130, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, T.; Schaefer, K.; Wai, D.; Buerger, H.; Flege, S.; Lindner, N.; Kevric, M.; Diallo, R.; Bankfalvi, A.; Brinkschmidt, C.; et al. Genetic Imbalances Revealed by Comparative Genomic Hybridization in Osteosarcomas. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 102, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forus, A.; Weghuis, D.O.; Smeets, D.; Fodstad, Ø.; Myklebost, O.; van Kessel, A.G. Comparative Genomic Hybridization Analysis of Human Sarcomas: Ii. Identification of Novel Amplicons at 6p and 17p in Osteosarcomas. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 1995, 14, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarkkanen, M.; Elomaa, I.; Blomqvist, C.; Kivioja, A.H.; Kellokumpu-Lehtinen, P.; Böhling, T.; Valle, J.; Knuutila, S. DNA Sequence Copy Number Increase at 8q: A Potential New Prognostic Marker in High-Grade Osteosarcoma. Int. J. Cancer 1999, 84, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Aguiar, S.; Zambaldi, L.D.J.G.; dos Santos, A.M.; Pinto, W., Jr.; Brandalise, S.R. Comparative Genomic Hybridization Analysis of Abnormalities in Chromosome 21 in Childhood Osteosarcoma. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2007, 175, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entz-Werle, N.; Lavaux, T.; Metzger, N.; Stoetzel, C.; Lasthaus, C.; Marec, P.; Kalita, C.; Brugieres, L.; Pacquement, H.; Schmitt, C.; et al. Involvement of Met/Twist/Apc Combination or the Potential Role of Ossification Factors in Pediatric High-Grade Osteosarcoma Oncogenesis. Neoplasia 2007, 9, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, S.H.; Ohnstad, H.O.; Paulsen, E.B.; Bjerkehagen, B.; Szuhai, K.; Serra, M.; Schaefer, K.; Myklebost, O.; Meza-Zepeda, L.A. Lsamp, a Novel Candidate Tumor Suppressor Gene in Human Osteosarcomas, Identified by Array Comparative Genomic Hybridization. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2009, 48, 679–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompetti, F.; Rizzo, P.; Simon, R.M.; Freidlin, B.; Mew, D.J.; Pass, H.I.; Picci, P.; Levine, A.S.; Carbone, M. Oncogene Alterations in Primary, Recurrent, and Metastatic Human Bone Tumors. J Cell Biochem. 1996, 63, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squire, J.A.; Pei, J.; Marrano, P.; Beheshti, B.; Bayani, J.; Lim, G.; Moldovan, L.; Zielenska, M. High-Resolution Mapping of Amplifications and Deletions in Pediatric Osteosarcoma by Use of Cgh Analysis of Cdna Microarrays. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2003, 38, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladanyi, M.; Park, C.K.; Lewis, R.; Jhanwar, S.C.; Healey, J.H.; Huvos, A.G. Sporadic Amplification of the Myc Gene in Human Osteosarcomas. Diagn. Mol. Pathol. 1993, 2, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maire, G.; Yoshimoto, M.; Chilton-MacNeill, S.; Thorner, P.S.; Zielenska, M.; Squire, J.A. Recurrent Recql4 Imbalance and Increased Gene Expression Levels Are Associated with Structural Chromosomal Instability in Sporadic Osteosarcoma. Neoplasia 2009, 11, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, C.; Kager, L.; Fink, F.M.; Gadner, H.; Ambros, P.F. Chromosomal Regions Involved in the Pathogenesis of Osteosarcomas. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2000, 28, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridge, J.A.; Nelson, M.; McComb, E.; McGuire, M.H.; Rosenthal, H.; Vergara, G.; Maale, G.E.; Spanier, S.; Neff, J.R. Cytogenetic Findings in 73 Osteosarcoma Specimens and a Review of the Literature. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 1997, 95, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertens, F.; Mandahl, N.; Örndal, C.; Baldetorp, B.; Bauer, H.C.F.; Rydholm, A.; Wiebe, T.; Willén, H.; Åkerman, M.; Heim, S.; et al. Cytogenetic Findings in 33 Osteosarcomas. Int. J. Cancer 1993, 55, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, A.M.; Sun, J.M.; Yu, A.; Voicu, H.; Shen, J.; Barkauskas, D.A.; Triche, T.J.; Gastier-Foster, J.M.; Man, T.-K.; Lau, C.C. Integrated DNA Copy Number and Expression Profiling Identifies Igf1r as a Prognostic Biomarker in Pediatric Osteosarcoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohata, N.; Ito, S.; Yoshida, A.; Kunisada, T.; Numoto, K.; Jitsumori, Y.; Kanzaki, H.; Ozaki, T.; Shimizu, K.; Ouchida, M. Highly Frequent Allelic Loss of Chromosome 6q16-23 in Osteosarcoma: Involvement of Cyclin C in Osteosarcoma. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2006, 18, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarkkanen, M.; Karhu, R.; Kallioniemi, A.; Elomaa, I.; Kivioja, A.H.; Nevalainen, J.; Böhling, T.; Karaharju, E.; Hyytinen, E.; Knuutila, S. Gains and Losses of DNA Sequences in Osteosarcomas by Comparative Genomic Hybridization. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 1334–1338. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, B.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Xiqiang, X.; Dong, J. The Nf-Kappab Pathway Is Critically Implicated in the Oncogenic Phenotype of Human Osteosarcoma Cells. J. Appl. Biomed. 2021, 19, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Gordon-Mitchell, S.; Sahu, S.; Bhagat, T.D.; Choudhary, G.; Aluri, S.; Pradhan, K.; Sahu, P.; et al. Innate Immune Mediator, Interleukin-1 Receptor Accessory Protein (Il1rap), Is Expressed and Pro-Tumorigenic in Pancreatic Cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauhari, S.; Jimeno, A.; Hreno, J.; Bauml, J.M.; Garcia-Ribas, I.; Öhman, M.W.; Rydberg-Millrud, C.; Cohen, R.B. Safety, Tolerability, and Preliminary Efficacy of Nadunolimab, a First-in-Class Monoclonal Antibody against Il1rap, in Combination with Pembrolizumab in Subjects with Solid Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, J.L.; Miatkowski, K.; Sizing, I.; Griffiths, D.; Zafari, M.; Benjamin, C.D.; Meier, W.; Mackay, F. Signaling through the Lymphotoxin Beta Receptor Induces the Death of Some Adenocarcinoma Tumor Lines. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 183, 867–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Cheng, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, R.; Saleh, A.; Si, H.; Lee, S.; Guven-Maiorov, E.; Keskin, O.; Gursoy, A. Head and Neck Cancers Promote an Inflammatory Transcriptome through Coactivation of Classic and Alternative Nf-Κb Pathways. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 1760–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, J.A. Colony-Stimulating Factors in Inflammation and Autoimmunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, T.; Yakoub, M.A.; Chandler, A.; Christ, A.B.; Yang, G.; Ouerfelli, O.; Rajasekhar, V.K.; Yoshida, A.; Kondo, H.; Hata, T. Csf1/Csf1r Signaling Inhibitor Pexidartinib (Plx3397) Reprograms Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Stimulates T-Cell Infiltration in the Sarcoma Microenvironment. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 1388–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyraud, F.; Cousin, S.; Italiano, A. Csf-1r Inhibitor Development: Current Clinical Status. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 19, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, J.L.; Mohamadzadeh, M. Macrophages and Chemokines as Mediators of Angiogenesis. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergadi, E.; Ieronymaki, E.; Lyroni, K.; Vaporidi, K.; Tsatsanis, C. Akt Signaling Pathway in Macrophage Activation and M1/M2 Polarization. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Semba, T.; Manyam, G.C.; Wang, J.; Shao, S.; Bertucci, F.; Finetti, P.; Krishnamurthy, S.; Phi, L.T.H.; Pearson, T.; et al. Egfr Is a Master Switch between Immunosuppressive and Immunoactive Tumor Microenvironment in Inflammatory Breast Cancer. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabn7983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Soliman, A.; Joehlin-Price, A.; Rose, P.G.; Vlad, A.; Edwards, R.P.; Mahdi, H. High Tgf-Beta Signature Predicts Immunotherapy Resistance in Gynecologic Cancer Patients Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibition. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2021, 5, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauken, K.E.; Wherry, E.J. Overcoming T Cell Exhaustion in Infection and Cancer. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumber, D.; Wang, L.D. Improving Car-T Immunotherapy: Overcoming the Challenges of T Cell Exhaustion. EBioMedicine 2022, 77, 103941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yi, M.; Niu, M.; Mei, Q.; Wu, K. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells: An Emerging Target for Anticancer Immunotherapy. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlanda, C.; Mantovani, A. Interleukin-1 in Tumor Progression, Therapy, and Prevention. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1023–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Zheng, X. Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist: An Alternative Therapy for Cancer Treatment. Life Sci. 2023, 335, 122276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villatoro, A.; Cuminetti, V.; Bernal, A.; Torroja, C.; Cossío, I.; Benguría, A.; Ferré, M.; Konieczny, J.; Vázquez, E.; Rubio, A.; et al. Endogenous Il-1 Receptor Antagonist Restricts Healthy and Malignant Myeloproliferation. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeester, B.A.; Slipek, N.J.; Pomeroy, E.J.; Laoharawee, K.; Osum, S.H.; Larsson, A.T.; Williams, K.B.; Stratton, N.; Yamamoto, K.; Peterson, J.J. Plx3397 Treatment Inhibits Constitutive Csf1r-Induced Oncogenic Erk Signaling, Reduces Tumor Growth, and Metastatic Burden in Osteosarcoma. Bone 2020, 136, 115353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boye, K.; Longhi, A.; Guren, T.; Lorenz, S.; Næss, S.; Pierini, M.; Taksdal, I.; Lobmaier, I.; Cesari, M.; Paioli, A. Pembrolizumab in Advanced Osteosarcoma: Results of a Single-Arm, Open-Label, Phase 2 Trial. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2021, 70, 2617–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglio, S.R.; Lagerweij, T.; Pérez-Lanzón, M.; Ho, X.D.; Léveillé, N.; Melo, S.A.; Cleton-Jansen, A.-M.; Jordanova, E.S.; Roncuzzi, L.; Greco, M. Blocking Tumor-Educated Msc Paracrine Activity Halts Osteosarcoma Progression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3721–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, B.H.; Koks, S. The Whole Transcriptome Analysis Using Ffpe and Fresh Tissue Samples Identifies the Molecular Fingerprint of Osteosarcoma. Exp. Biol. Med. 2024, 249, 10161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, X.D.; Nguyen, H.G.; Trinh, L.H.; Reimann, E.; Prans, E.; Kõks, G.; Maasalu, K.; Le, V.Q.; Nguyen, V.H.; Le, N.T.N.; et al. Analysis of the Expression of Repetitive DNA Elements in Osteosarcoma. Front. Genet. 2017, 8, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, X.D.; Phung, P.; Le, V.Q.; Nguyen, V.H.; Reimann, E.; Prans, E.; Kõks, G.; Maasalu, K.; Le, N.T.; Trinh, L.H.; et al. Whole Transcriptome Analysis Identifies Differentially Regulated Networks between Osteosarcoma and Normal Bone Samples. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 1802–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taylor, A.M.; Sheng, J.; Ng, P.K.S.; Harder, J.M.; Kumar, P.; Ahn, J.Y.; Cao, Y.; Dzis, A.M.; Jillette, N.L.; Goodspeed, A.; et al. Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment of Osteosarcoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 2117. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132117
Taylor AM, Sheng J, Ng PKS, Harder JM, Kumar P, Ahn JY, Cao Y, Dzis AM, Jillette NL, Goodspeed A, et al. Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment of Osteosarcoma. Cancers. 2025; 17(13):2117. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132117
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaylor, Aaron Michael, Jianting Sheng, Patrick Kwok Shing Ng, Jeffrey M. Harder, Parveen Kumar, Ju Young Ahn, Yuliang Cao, Alissa M. Dzis, Nathaniel L. Jillette, Andrew Goodspeed, and et al. 2025. "Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment of Osteosarcoma" Cancers 17, no. 13: 2117. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132117
APA StyleTaylor, A. M., Sheng, J., Ng, P. K. S., Harder, J. M., Kumar, P., Ahn, J. Y., Cao, Y., Dzis, A. M., Jillette, N. L., Goodspeed, A., Bodlak, A., Wu, Q., Isakoff, M. S., George, J., Grassmann, J. D. S., Luo, D., Flynn, W. F., Courtois, E. T., Robson, P., ... Lau, C. C. (2025). Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment of Osteosarcoma. Cancers, 17(13), 2117. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17132117






