Stereotactic Radiotherapy to the Prostate and Pelvic Lymph Nodes for High-Risk and Very High-Risk Prostate Cancer in a Setting with a Hydrogel Spacer: A Toxicity Report
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Treatment
2.3. Statistical Analysis
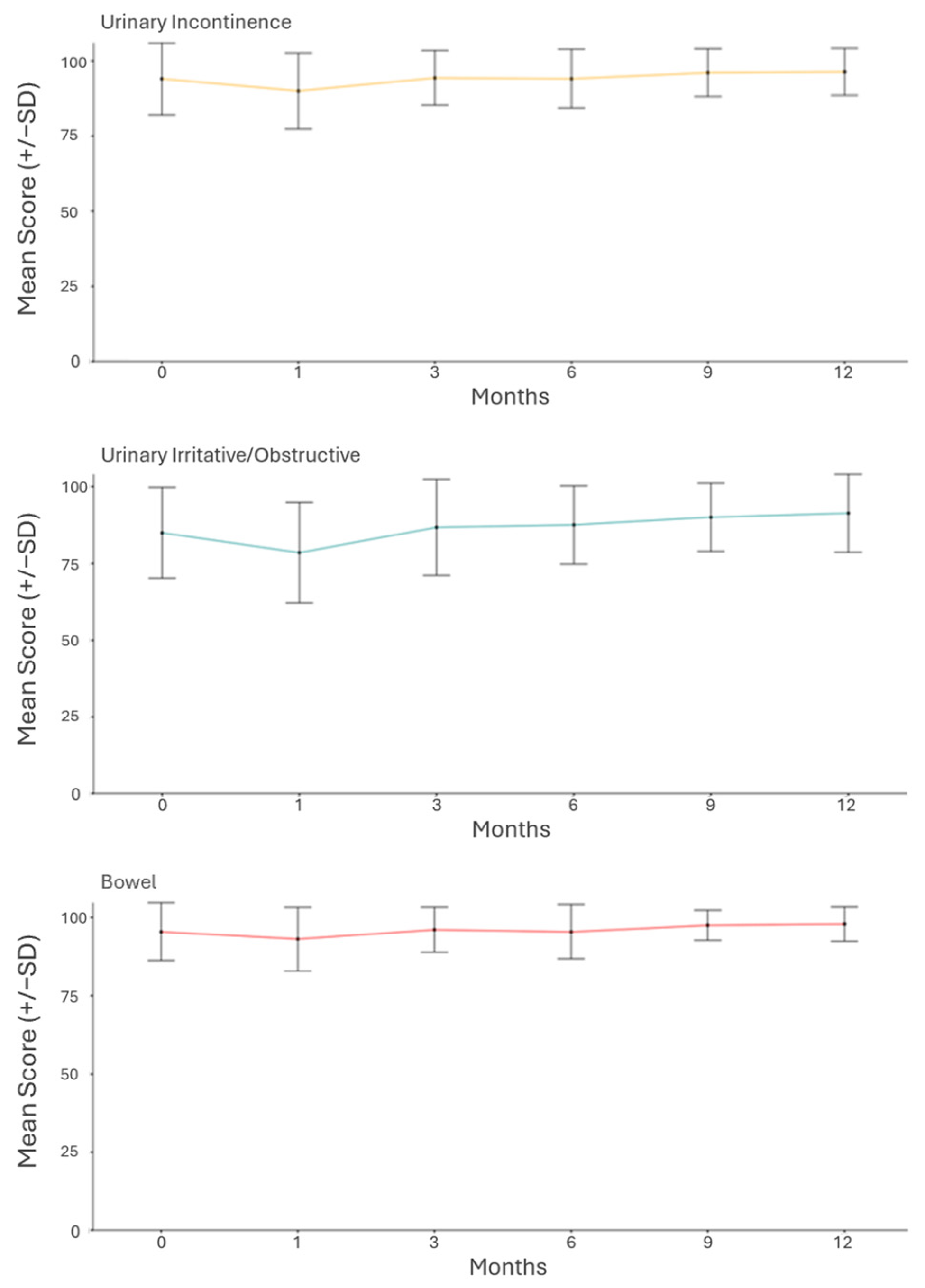
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SABR | Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy |
| ENI | Elective nodal irradiation |
| GU | Genitourinary |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| QoL | Quality of life |
| ADT | Androgen deprivation therapy |
| PEG | Polyethylene glycol |
| IPSS | International prostate symptom score |
| ECE | Extracapsular extension |
| CTV | Clinical target volume |
| PTV | Planning target volume |
| SIB | Simultaneous integrated boost |
| DIL | Dominant intraprostatic lesion |
| CTCAE | Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| MCIC | Minimally clinically important change |
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogelius, I.R.; Bentzen, S.M. Dose Response and Fractionation Sensitivity of Prostate Cancer After External Beam Radiation Therapy: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Trials. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 100, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dearnaley, D.; Syndikus, I.; Mossop, I.; Khoo, V.; Birtle, A.; Bloomfield, D.; Graham, J.; Kirkbride, P.; Logue, J.; Malik, Z.; et al. Conventional versus hypofractionated high-dose intensity-modulated radiotherapy for prostate cancer: 5-year outcomes of the randomised, non-inferiority, phase 3 CHHiP trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1047–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catton, C.N.; Lukka, H.; Gu, C.; Martin, J.M.; Supiot, S.; Chung, P.W.M.; Bauman, G.S.; Bahary, J.-P.; Ahmed, S.; Cheung, P.; et al. Randomized Trial of a Hypofractionated Radiation Regimen for the Treatment of Localized Prostate Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1884–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollack, A.; Walker, G.; Horwitz, E.M.; Price, R.; Feigenberg, S.; Konski, A.A.; Stoyanova, R.; Movsas, B.; Greenberg, R.E.; Uzzo, R.G.; et al. Randomized trial of hypofractionated external-beam radiotherapy for prostate cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3860–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmark, A.; Gunnlaugsson, A.; Beckman, L.; Thellenberg-Karlsson, C.; Hoyer, M.; Lagerlund, M.; Kindblom, J.; Ginman, C.; Johansson, B.; Björnlinger, K.; et al. Ultra-hypofractionated versus conventionally fractionated radiotherapy for prostate cancer: 5-year outcomes of the HYPO-RT-PC randomised, non-inferiority, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, D.H.; Tree, A.C.; Ostler, P.; Van Der Voet, H.; Loblaw, A.; Chu, W.; Ford, D.; Tolan, S.; Jain, S.; Martin, A.; et al. Intensity-modulated fractionated radiotherapy versus stereotactic body radiotherapy for prostate cancer (PACE-B): Acute toxicity findings from an international, randomised, open-label, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1531–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, V.; Maitre, P.; Kannan, S.; Panigrahi, G.; Krishnatry, R.; Bakshi, G.; Krishnatry, R.; Bakshi, G.; Prakash, G.; Pal, M.; et al. Prostate-Only Versus Whole-Pelvic Radiation Therapy in High-Risk and Very High-Risk Prostate Cancer (POP-RT): Outcomes From Phase III Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1234–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pommier, P.; Chabaud, S.; Lagrange, J.L.; Richaud, P.; Le Prise, E.; Wagner, J.P.; Azria, D.; Beckendorf, V.; Suchaud, J.-P.; Bernier, V.; et al. Is There a Role for Pelvic Irradiation in Localized Prostate Adenocarcinoma? Update of the Long-Term Survival Results of the GETUG-01 Randomized Study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 96, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, M., 3rd; DeSilvio, M.; Lawton, C.; Uhl, V.; Machtay, M.; Seider, M.J.; Rotman, M.; Jones, C.; Asbell, S.O.; Valicenti, R.K.; et al. Phase III trial comparing whole-pelvic versus prostate-only radiotherapy and neoadjuvant versus adjuvant combined androgen suppression: Radiation Therapy Oncology Group 9413. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 1904–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, V.; Mallick, I.; Maitre, P.; Mulye, G.; Arunsingh, M.; Valle, L.; Steinberg, M.; Kennedy, T.; Loblaw, A.; Kishan, A.U. Pelvic regional control with 25Gy in 5 fractions in SBRT for high risk prostate cancer: Pooled prospective outcomes from the SHARP consortium. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2025, 122, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshy, S.A.; Diven, M.A.; Ma, X.; Marciscano, A.E.; Hu, J.C.; McClure, T.D.; Barbieri, C.; Nagar, H. Differential Use of Radiotherapy Fractionation Regimens in Prostate Cancer. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2337165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houlihan, O.A.; Redmond, K.; Fairmichael, C.; Lyons, C.A.; McGarry, C.K.; Mitchell, D.; Deabreu, A.; Mamedov, A.; Zhang, L.; Cheung, P. A Randomized Feasibility Trial of Stereotactic Prostate Radiation Therapy With or Without Elective Nodal Irradiation in High-Risk Localized Prostate Cancer (SPORT Trial). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 117, 594–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glicksman, R.M.; Loblaw, A.; Morton, G.; Vesprini, D.; Szumacher, E.; Chung, H.T.; Chu, W.; Liu, S.K.; Tseng, C.-L.; Davidson, M.; et al. Elective pelvic nodal irradiation in the setting of ultrahypofractionated versus moderately hypofractionated and conventionally fractionated radiotherapy for prostate cancer: Outcomes from 3 prospective clinical trials. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 49, 100843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dams, R.; Jiang, N.Y.; Fuller, D.B.; Loblaw, A.; Jiang, T.; Katz, A.J.; Collins, S.P.; Aghdam, N.; Suy, S.; Stephans, K.L.; et al. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for High-Risk Localized Carcinoma of the Prostate (SHARP) Consortium: Analysis of 344 Prospectively Treated Patients. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 110, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamstra, D.A.; Mariados, N.; Sylvester, J.; Shah, D.; Karsh, L.; Hudes, R.; Beyer, D.; Kurtzman, S.; Bogart, J.; Hsi, R.A.; et al. Continued Benefit to Rectal Separation for Prostate Radiation Therapy: Final Results of a Phase III Trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 97, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.E.; Efstathiou, J.A.; Bhattacharyya, S.K.; Payne, H.A.; Woodward, E.; Pinkawa, M. Association of the Placement of a Perirectal Hydrogel Spacer with the Clinical Outcomes of Men Receiving Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e208221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, N.; Bahl, A.; Pinkawa, M.; Ryder, S.; Ahmadu, C.; Ross, J.; Binns, J.; Armstrong, N.; Woodward, E.; Ahmadu, C.; et al. SpaceOAR Hydrogel Spacer for Reducing Radiation Toxicity During Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer. A Systematic Review. Urology 2021, 156, e74–e85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariados, N.F.; Orio, P.F., 3rd; Schiffman, Z.; Van, T.J.; Engelman, A.; Nurani, R.; Kurtzman, S.M.; Lopez, E.; Chao, M.; Boike, T.P.; et al. Hyaluronic Acid Spacer for Hypofractionated Prostate Radiation Therapy: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2023, 9, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, P.; Vale, J.; Fonseca, G.; Costa, A.; Kos, M. Use of rectal balloon spacer in patients with localized prostate cancer receiving external beam radiotherapy. Tech. Innov. Patient Support Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 29, 100237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkert, M.R.; Zelefsky, M.J.; Hannan, R.; Desai, N.B.; Lotan, Y.; Laine, A.M. A Multi-Institutional Phase 2 Trial of High-Dose SAbR for Prostate Cancer Using Rectal Spacer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 111, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/prostate.pdf (accessed on 11 June 2024).
- Lawton, C.A.F.; Michalski, J.; El-Naqa, I.; Buyyounouski, M.K.; Lee, W.R.; Menard, C.; Michalski, J.; El-Naqa, I.; O’MEara, E. RTOG GU Radiation oncology specialists reach consensus on pelvic lymph node volumes for high-risk prostate cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2009, 74, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skolarus, T.A.; Dunn, R.L.; Sanda, M.G.; Chang, P.; Greenfield, T.K.; Litwin, M.S.; Wei, J.T.; PROSTQA Consortium. Minimally important difference for the Expanded Prostate Cancer Index Composite Short Form. Urology 2015, 85, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musunuru, H.B.; D’Alimonte, L.; Davidson, M.; Ho, L.; Cheung, P.; Vesprini, D.; Liu, S.; Chu, W.; Chung, H.; Ravi, A.; et al. Phase 1-2 Study of Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy Including Regional Lymph Node Irradiation in Patients With High-Risk Prostate Cancer (SATURN): Early Toxicity and Quality of Life. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 102, 1438–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tree, A.C.; Ostler, P.; van der Voet, H.; Chu, W.; Loblaw, A.; Ford, D.; Tolan, S.; Jain, S.; Martin, A.; Staffurth, J.; et al. Intensity-modulated radiotherapy versus stereotactic body radiotherapy for prostate cancer (PACE-B): 2-year toxicity results from an open-label, randomised, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 1308–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, W.L.; Cheung, P.; Chung, H.; Chu, W.; Detsky, J.; Liu, S.; Morton, G.; Szumacher, E.; Tseng, C.-L.; Vesprini, D.; et al. To Boost or Not to Boost: Pooled Analyses From 2-Fraction SABR Trials for Localized Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 117, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millot, J.C.; Arenas-Gallo, C.; Silver, E.; Goldman; Picciotto, S.; Jia, A.Y.; Zaorsky, N.G.; Spratt, D.E.; Fredman, E.T.; Shoag, J.E. Major Complications and Adverse Events Related to Use of SpaceOAR Hydrogel for Prostate Cancer Radiotherapy. Urology 2024, 188, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prada, P.J.; Fernández, J.; Martinez, A.A.; de la Rúa, A.; Gonzalez, J.M.; Fernandez, J.M.; Juan, G. Transperineal injection of hyaluronic acid in anterior perirectal fat to decrease rectal toxicity from radiation delivered with intensity modulated brachytherapy or EBRT for prostate cancer patients. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2007, 69, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björeland, U.; Notstam, K.; Fransson, P.; Söderkvist, K.; Beckman, L.; Jonsson, J.; Nyholm, T.; Widmark, A.; Karlsson, C.T. Hyaluronic acid spacer in prostate cancer radiotherapy: Dosimetric effects, spacer stability and long-term toxicity and PRO in a phase II study. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Dabkowski, M.; Costa, P.; Nurani, R.; Kos, M.; Vanneste, B.; Magel, D.; Sapir, E.; Zimberg, S.; Boychak, O.; et al. Prospective, Randomized Controlled Pivotal Trial of Biodegradable Balloon Rectal Spacer for Prostate Radiation Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 120, 1410–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkmeijer, L.G.W.; Groen, V.H.; Pos, F.J.; Haustermans, K.; Monninkhof, E.M.; Smeenk, R.J.; Kunze-Busch, M.; de Boer, J.C.J.; van der Voort van Zijp, J.; van Vulpen, M.; et al. Focal Boost to the Intraprostatic Tumor in External Beam Radiotherapy for Patients With Localized Prostate Cancer: Results From the FLAME Randomized Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cock, L.D.; Draulans, C.; Pos, F.J.; Isebaert, S.; Roover, R.D.; van der Heide, U.A. From once-weekly to semi-weekly whole prostate gland stereotactic radiotherapy with focal boosting: Primary endpoint analysis of the multicenter phase II hypo-FLAME 2.0 trial. Radiother. Oncol. 2023, 185, 109713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draulans, C.; Haustermans, K.; Pos, F.J.; van der Heide, U.A.; De Cock, L.; van der Voort van Zyp, J.; De Boer, H.; Smeenk, R.J.; Kunze-Busch, M.; Monninkhof, E.M.; et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy with a focal boost to the intraprostatic tumor for intermediate and high risk prostate cancer: 5-year efficacy and toxicity in the hypo-FLAME trial. Radiother. Oncol. 2024, 201, 110568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, V.; Mallick, I.; Gavarraju, A.; Sinha, S.; Krishnatry, R.; Telkhade, T.; Moses, A.; Kannan, S.; Prakash, G.; Pal, M.; et al. Study protocol of a randomised controlled trial of prostate radiotherapy in high-risk and node-positive disease comparing moderate and extreme hypofractionation (PRIME TRIAL). BMJ Open 2020, 10, e034623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, W.J.; Tyldesley, S.; Rodda, S.; Halperin, R.; Pai, H.; McKenzie, M.; Duncan, G.; Morton, G.; Hamm, J.; Murray, N. Androgen Suppression Combined with Elective Nodal and Dose Escalated Radiation Therapy (the ASCENDE-RT Trial): An Analysis of Survival Endpoints for a Randomized Trial Comparing a Low-Dose-Rate Brachytherapy Boost to a Dose-Escalated External Beam Boost for High- and Intermediate-risk Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 98, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodda, S.; Tyldesley, S.; Morris, W.J.; Keyes, M.; Halperin, R.; Pai, H.; McKenzie, M.; Duncan, G.; Morton, G.; Hamm, J.; et al. ASCENDE-RT: An Analysis of Treatment-Related Morbidity for a Randomized Trial Comparing a Low-Dose-Rate Brachytherapy Boost with a Dose-Escalated External Beam Boost for High- and Intermediate-Risk Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 98, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Target | Volume (%) | Dose (%) | Prescription |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTV of prostate | 95 | 99 | 36.25–40 Gy |
| CTV of prostate (gland) | 99 | 99 | 36.25–40 Gy |
| PTV of seminal vesicle | 95 | 99 | 35 Gy |
| PTV of nodes | 95 | 95 | 25 Gy |
| PTV of boost (optional) | 95 | 95 | 40–45 Gy |
| N = 100 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Age | ||
| Median (IQR) | 73 (69–77) | |
| Clinical stage | ||
| T1c | 40 | |
| T2c | 20 | |
| T3a | 25 | |
| T3b | 15 | |
| N1 (among above) | 7 | |
| PSA | ||
| Median (IQR) | 12.1 (7.4–21.8) | |
| ISUP grade group | ||
| GG1 | 3 | |
| GG2 | 15 | |
| GG3 | 13 | |
| GG4/5 | 69 | |
| Systemic staging | ||
| PET PSMA | 100 | |
| Stage group | ||
| IIB | 8 | |
| IIC | 20 | |
| IIIA | 14 | |
| IIIB | 40 | |
| IIIC | 29 | |
| IVA | 7 | |
| Risk group | ||
| High | 54 | |
| Very High | 46 | |
| Prostate volume (cc) | ||
| Median (IQR) | 39 (30–50) | |
| IPSS baseline score | ||
| Median (IQR) | 7 (5–11) | |
| SHIM baseline score | ||
| Median (IQR) | 12 (6–16) |
| GU Toxicity | |||||||||
| Grade 1 | Grade 2 | ||||||||
| Univariable | Multivariable | Univariable | Multivariable | ||||||
| 3 months | Variable | HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p |
| Age | 0.98 (0.92–1.05) | 0.62 | 0.98 (0.92–1.05) | 0.59 | 1.00 (0.94–1.08) | 0.92 | 0.99 (0.93–1.07) | 0.88 | |
| Prostate volume | 1.00 (0.98–1.03) | 0.73 | 1.01 (0.98–1.03) | 0.68 | 1.03 (0.99–1.06) | 0.06 | 1.03 (0.99–1.06) | 0.07 | |
| IPSS | 1.00 (0.88–1.14) | 0.96 | 0.99 (0.88–1.14) | 0.97 | 1.05 (0.91–1.20) | 0.49 | 1.03 (0.89–1.18) | 0.72 | |
| 12 months | Variable | HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p |
| Age | 0.89 (0.77–0.99) | 0.04 | 0.96 (0.82–1.13) | 0.61 | 0.89 (0.78–1.01) | 0.07 | 0.95 (0.81–1.13) | 0.59 | |
| Prostate volume | 0.96 (0.92–1.04) | 0.42 | 1.02 (0.96–1.09) | 0.58 | 0.96 (0.93–1.05) | 0.64 | 1.01 (0.95–1.08) | 0.69 | |
| IPSS | 1.03 (0.79–1.33) | 0.85 | 1.21 (0.85–1.73) | 0.29 | 1.00 (0.75–1.34) | 0.99 | 1.20 (0.83–1.73) | 0.34 | |
| GI Toxicity | |||||||||
| Grade 1 | |||||||||
| Univariable | Multivariable | ||||||||
| Variable | HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | |||||
| 3 months | SpaceOAR Yes vs. No | 0.09 (0.27–0.35) | 0.0004 | 0.08 (0.02–0.31) | 0.0003 | ||||
| Age | 1.01 (0.93–1.10) | 0.82 | 0.98 (0.89–1.08) | 0.68 | |||||
| Prostate volume | 1.01 (0.98–1.04) | 0.47 | 1.01 (0.97–1.04) | 0.62 | |||||
| IPSS | 1.06 (0.90–1.25) | 0.46 | 1.02 (0.85–1.23) | 0.80 | |||||
| 12 months | SpaceOAR Yes vs. No | NA | NA | NA | NA | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fredman, E.; Tschernichovsky, R.; Shemesh, D.; Weinstock-Sabbah, M.; Azuz, R.D.; Radus, R.; Moore, A.; Limon, D. Stereotactic Radiotherapy to the Prostate and Pelvic Lymph Nodes for High-Risk and Very High-Risk Prostate Cancer in a Setting with a Hydrogel Spacer: A Toxicity Report. Cancers 2025, 17, 1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17121970
Fredman E, Tschernichovsky R, Shemesh D, Weinstock-Sabbah M, Azuz RD, Radus R, Moore A, Limon D. Stereotactic Radiotherapy to the Prostate and Pelvic Lymph Nodes for High-Risk and Very High-Risk Prostate Cancer in a Setting with a Hydrogel Spacer: A Toxicity Report. Cancers. 2025; 17(12):1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17121970
Chicago/Turabian StyleFredman, Elisha, Roi Tschernichovsky, Danielle Shemesh, Miriam Weinstock-Sabbah, Ruth Dadush Azuz, Roman Radus, Assaf Moore, and Dror Limon. 2025. "Stereotactic Radiotherapy to the Prostate and Pelvic Lymph Nodes for High-Risk and Very High-Risk Prostate Cancer in a Setting with a Hydrogel Spacer: A Toxicity Report" Cancers 17, no. 12: 1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17121970
APA StyleFredman, E., Tschernichovsky, R., Shemesh, D., Weinstock-Sabbah, M., Azuz, R. D., Radus, R., Moore, A., & Limon, D. (2025). Stereotactic Radiotherapy to the Prostate and Pelvic Lymph Nodes for High-Risk and Very High-Risk Prostate Cancer in a Setting with a Hydrogel Spacer: A Toxicity Report. Cancers, 17(12), 1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17121970





