Radiation Dose Reduction in Cancer Imaging with New-Model CT Scanners: A Quality of Care Evaluation
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
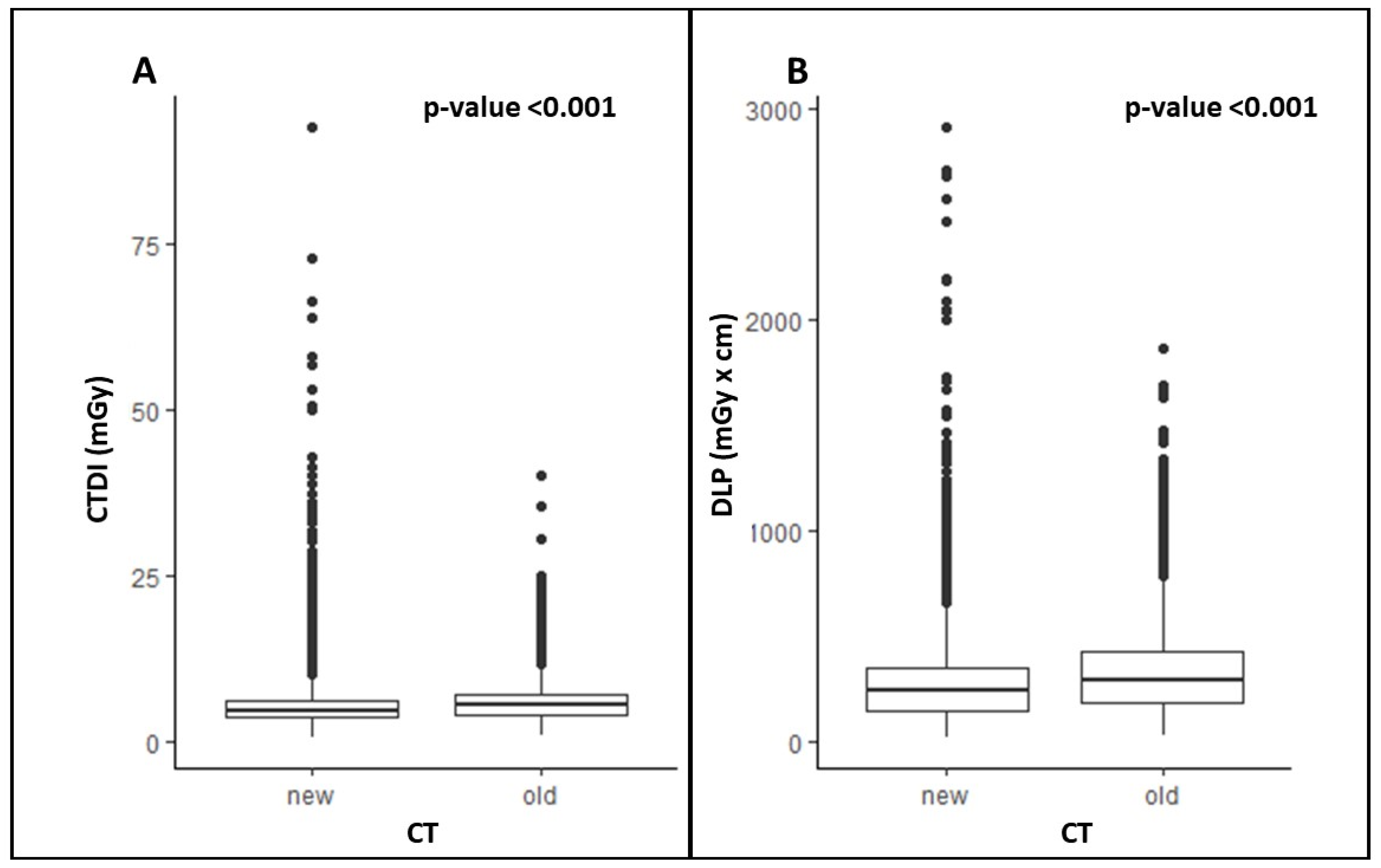
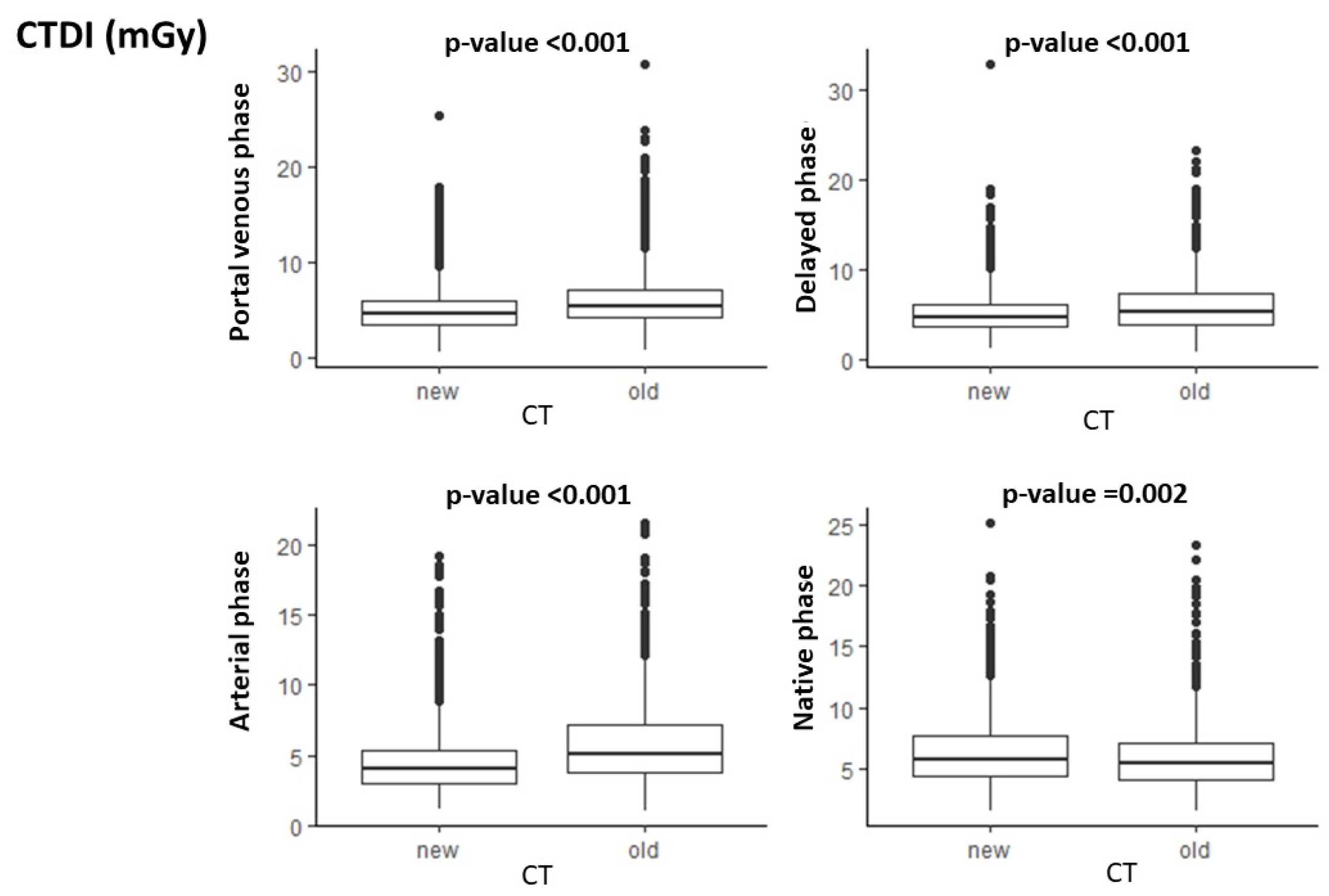
3.1. CTDI
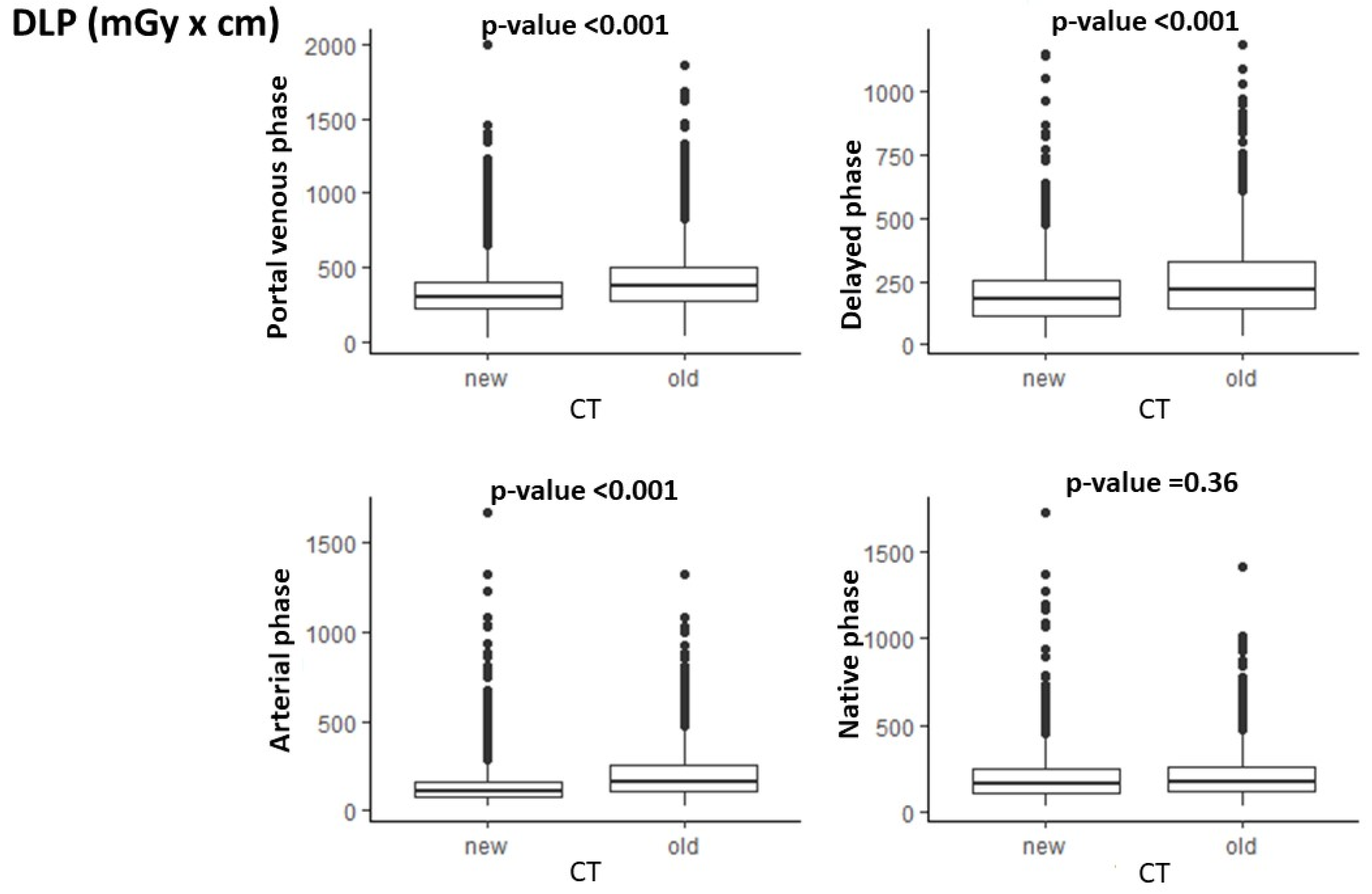
3.2. DLP
3.3. SNR
3.4. CNR
4. Discussion
4.1. Radiation Dose
4.1.1. Radiation Dose Reduction
4.1.2. CT Technology Updates Contributing to Radiation Dose Reduction
4.2. Objective Image Quality
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNR | Contrast-to-Noise Ratio |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| CTDI | Computed Tomography Dose Index |
| DLP | Dose Length Product |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| PACS | Picture Archive and Communication System |
| SNR | Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
References
- Lee, T.-Y.; Chhem, R.K. Impact of new technologies on dose reduction in CT. Eur. J. Radiol. 2010, 76, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahesh, M.; Ansari, A.J.; Mettler, F.A. Patient Exposure from Radiologic and Nuclear Medicine Procedures in the United States and Worldwide: 2009–2018. Radiology 2023, 307, e221263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milano, M.T.; Mahesh, M.; Mettler, F.A.; Elee, J.; Vetter, R.J. Patient Radiation Exposure: Imaging During Radiation Oncology Procedures: Executive Summary of NCRP Report No. 184. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2020, 17, 1176–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCollough, C.H. Computed Tomography Technology-and Dose-in the 21st Century. Health Phys. 2019, 116, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamat, M.I. Strategies and Scientific Basis of Dose Reduction on State-of-the-Art Multirow Detector X-Ray CT Systems. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 43, 33–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, S.M.R.; Kalra, M.K.; Schmidt, B.; Raupach, R.; Maher, M.M.; Blake, M.A.; Saini, S. CT images of abdomen and pelvis: Effect of nonlinear three-dimensional optimized reconstruction algorithm on image quality and lesion characteristics. Radiology 2005, 237, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lell, M.; Kachelrieß, M. Computed Tomography 2.0: New Detector Technology, AI, and Other Developments. Investig. Radiol. 2023, 58, 587–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrixon, A.D. New ICRP recommendations. J. Radiol. Prot. 2008, 28, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICRP. The 2007 Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. ICRP publication 103. Ann. ICRP 2007, 37, 9–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, S.; Bellesi, L.; D’ermo, A.; Bonomo, L.; D’ecclesiis, O.; Magoga, F.; Presilla, S.; Spanò, A.; Minzolini, V.; Piccolo, F.L.; et al. Body CT examinations in oncologic patients: The impact of subspecialty radiology on radiation exposure in the clinical practice. A quality care study. Radiol. Medica 2024, 129, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lell, M.M.; Kachelrieß, M. Recent and Upcoming Technological Developments in Computed Tomography: High Speed, Low Dose, Deep Learning, Multienergy. Investig. Radiol. 2019, 55, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalal, T.; Kalra, M.K.; Rizzo, S.M.R.; Schmidt, B.; Suess, C.; Flohr, T.; Blake, M.A.; Saini, S. Metallic prosthesis: Technique to avoid increase in CT radiation dose with automatic tube current modulation in a phantom and patients. Radiology 2005, 236, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arapakis, I.; Efstathopoulos, E.; Tsitsia, V.; Kordolaimi, S.; Economopoulos, N.; Argentos, S.; Ploussi, A.; Alexopoulou, E. Using “iDose4” iterative reconstruction algorithm in adults’ chest-abdomen-pelvis CT examinations: Effect on image quality in relation to patient radiation exposure. Br. J. Radiol. 2014, 87, 20130613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazel, R.; Krumholz, H.M.; Wang, Y.; Ross, J.S.; Chen, J.; Ting, H.H.; Shah, N.D.; Nasir, K.; Einstein, A.J.; Nallamothu, B.K. exposure to low-dose ionizing radiation from medical imaging procedures. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remedios, D. Cumulative radiation dose from multiple CT examinations: Stronger justification, fewer repeats, or dose reduction technology needed? Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 1837–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantarcı, M.; Aydın, S.; Oğul, H.; Kızılgöz, V. New imaging techniques and trends in radiology. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2025; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderer, S. CT Scans Linked to More Cancer Cases Than Previously Estimated. JAMA, 2025; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.B.; Zhang, S.; Erkanli, A.; Frush, D.P.; Samei, E. Variability in image quality and radiation dose within and across 97 medical facilities. J. Med. Imaging 2021, 8, 052105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, M.M.; Kalra, M.K.; Rizzo, S.; Mueller, P.R.; Saini, S. Multidetector CT urography in imaging of the urinary tract in patients with hematuria. Korean J. Radiol. 2004, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, J.G.; Yu, L.; Fidler, J.L.; Levin, D.L.; DeLone, D.R.; Hough, D.M.; Takahashi, N.; Venkatesh, S.K.; Sykes, A.G.; White, D.; et al. Estimation of observer performance for reduced radiation dose levels in CT: Eliminating reduced dose levels that are too low is the first step. Acad. Radiol. 2017, 24, 876–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, M.K.; Maher, M.M.; Toth, T.L.; Hamberg, L.M.; Blake, M.A.; Shepard, J.-A.; Saini, S. Strategies for CT radiation dose optimization. Radiology 2004, 230, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillon, M.; Si-Mohamed, S.; Coulon, P.; Vuillod, A.; Klahr, P.; Boussel, L. Reduction of patient radiation dose with a new organ based dose modulation technique for thoraco-abdominopelvic computed tomography (CT) (Liver dose right index). Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2018, 99, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollough, C.H.; Primak, A.N.; Braun, N.; Kofler, J.; Yu, L.; Christner, J. Strategies for reducing radiation dose in CT. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 47, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Goo, J.M.; Ye, H.J.; Ye, S.-J.; Park, C.M.; Chun, E.J.; Im, J.-G. Radiation dose modulation techniques in the multidetector CT era: From basics to practice. RadioGraphics 2008, 28, 1451–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, S.P.; Johnson, P.T.; Deshmukh, S.; Mahesh, M.; Grant, K.L.; Fishman, E.K. CT Dose reduction applications: Available tools on the latest generation of CT scanners. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2013, 10, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L. Model-based Iterative Reconstruction: A Promising Algorithm for Today’s Computed Tomography Imaging. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Sci. 2014, 45, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltybaeva, N.; Alkadhi, H. Vertical off-centering affects organ dose in chest CT: Evidence from Monte Carlo simulations in anthropomorphic phantoms. Med. Phys. 2017, 44, 5697–5704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollough, C.H.; Chen, G.H.; Kalender, W.; Leng, S.; Samei, E.; Taguchi, K.; Wang, G.; Yu, L.; Pettigrew, R.I. Achieving routine submillisievert CT scanning: Report from the summit on management of radiation dose in CT. Radiology 2012, 264, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffary, A.; Trabzonlu, T.A.; Kim, D.; Yaghmai, V. Comparison of Tin Filter–Based Spectral Shaping CT and Low-Dose Protocol for Detection of Urinary Calculi. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 212, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, G.; Herts, B.; Primak, A.; Segars, P.; Li, X. Effect of tin spectral filtration on organ and effective dose in CT colonography and CT lung cancer screening. Med. Phys. 2023, 51, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyendecker, P.; Faucher, V.; Labani, A.; Noblet, V.; Lefebvre, F.; Magotteaux, P.; Ohana, M.; Roy, C. Prospective evaluation of ultra-low-dose contrast-enhanced 100-kV abdominal computed tomography with tin filter: Effect on radiation dose reduction and image quality with a third-generation dual-source CT system. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 29, 2107–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Qurashi, A.; A Rainford, L.; Alshamrani, K.M.; Foley, S.J. The Impact of Obesity on Abdominal CT Radiation Dose and Image Quality. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2018, 185, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, C.; Meyer, M.; Fink, C.; Schmidt, B.; Sedlmair, M.; Schoenberg, S.O.; Henzler, T. Potential for radiation dose savings in abdominal and chest CT using automatic tube voltage selection in combination with automatic tube current modulation. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 203, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.H.; Lee, J.M.; Moon, S.K.; Baek, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Flohr, T.G.; Kim, K.W.; Kim, S.J.; Han, J.K.; Choi, B.I. Attenuation-based automatic tube voltage selection and tube current modulation for dose reduction at contrast-enhanced liver CT. Radiology 2012, 265, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogalla, P.; Paravasthu, M.; Farrell, C.; Kandel, S. Helical CT with variable target noise levels for dose reduction in chest, abdomen and pelvis CT. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 3922–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.B.; Kim, S.M.; Yoon, J.-T.; Ahn, Y.; Do, K.-H. Radiation dose reduction and image quality enhancement for patients unable to elevate their arms in chest CT: A comparative study. Eur. J. Radiol. 2025, 188, 112120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhard, M.; Blüthgen, C.; Barth, B.K.; Frauenfelder, T.; Saltybaeva, N.; Martini, K. Vertical Off-Centering in Reduced Dose Chest-CT: Impact on Effective Dose and Image Noise Values. Acad. Radiol. 2020, 27, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibzadeh, M.; Ay, M.; Asl, A.K.; Ghadiri, H.; Zaidi, H. Impact of miscentering on patient dose and image noise in x-ray CT imaging: Phantom and clinical studies. Phys. Medica 2012, 28, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postmus, P.E.; Kerr, K.M.; Oudkerk, M.; Senan, S.; Waller, D.A.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Escriu, C.; Peters, S.; ESMO Guidelines Committee. Early and locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28 (Suppl. S4), iv1–iv21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Cervantes, A.; Adam, R.; Sobrero, A.; van Krieken, J.H.; Aderka, D.; Aguilar, E.A.; Bardelli, A.; Benson, A.; Bodoky, G.; et al. ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1386–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrella, F.; Rizzo, S.; Attili, I.; Passaro, A.; Zilli, T.; Martucci, F.; Bonomo, L.; Del Grande, F.; Casiraghi, M.; De Marinis, F.; et al. Stage III Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: An Overview of Treatment Options. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 3160–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, C.; Castro, E.; Fizazi, K.; Heidenreich, A.; Ost, P.; Procopio, G.; Tombal, B.; Gillessen, S.; ESMO Guidelines Committee. Prostate cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1119–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, S.; Avesani, G.; Panico, C.; Manganaro, L.; Gui, B.; Lakhman, Y.; Andrieu, P.C.; Bharwani, N.; Rockall, A.; Thomassin-Naggara, I.; et al. Ovarian cancer staging and follow-up: Updated guidelines from the European Society of Urogenital Radiology female pelvic imaging working group. Eur. Radiol. 2025; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waarts, M.R.; Stonestrom, A.J.; Park, Y.C.; Levine, R.L. Targeting mutations in cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e154943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, S.; Yu, Z.; Halaweish, A.; Kappler, S.; Hahn, K.; Henning, A.; Li, Z.; Lane, J.; Levin, D.L.; Jorgensen, S.; et al. Dose-efficient ultrahigh-resolution scan mode using a photon counting detector computed tomography system. J. Med. Imaging 2016, 3, 043504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Leng, S.; Li, Z.; Halaweish, A.F.; Kappler, S.; Ritman, E.L.; McCollough, C.H. How Low Can We Go in Radiation Dose for the Data-Completion Scan on a Research Whole-Body Photon-Counting Computed Tomography System. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2016, 40, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| CT Phases | ||
|---|---|---|
| Old CT Scanners N (%) | New CT Scanners N (%) | |
| Unenhanced | 1254 (64.7) | 683 (35.3) |
| Arterial | 1869 (63.8) | 1059 (36.2) |
| Venous | 5002 (60.6) | 3254 (39.4) |
| Delayed | 888 (60.0) | 592 (40.0) |
| Old CT Scanners Median (IQR) | New CT Scanners Median (IQR) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CTDI | |||
| Overall | 5.40 (4.08–7.14) | 4.63 (3.55–6.20) | <0.001 |
| Phase | |||
| Unenhanced | 5.42 (4.07–7.13) | 5.72 (4.34–7.67) | 0.002 |
| Arterial | 5.13 (3.75–7.10) | 4.01 (3.00–5.32) | <0.001 |
| Venous | 5.40 (4.17–7.09) | 4.56 (3.57–5.97) | <0.001 |
| Delayed | 5.30 (3.95–7.34) | 4.72 (3.65–6.21) | <0.001 |
| DLP | |||
| Overall | 288.6 (180.6–423.0) | 244.0 (148.0–352.0) | <0.001 |
| Phase | |||
| Unenhanced | 177.6 (119.6–262.9) | 168.0 (116.0–250.0) | 0.36 |
| Arterial | 164.9 (107.1–256.0) | 112.0 (77.8–163.0) | <0.001 |
| Venous | 370.2 (277.2–497.8) | 297.0 (228.0–399.0) | <0.001 |
| Delayed | 215.7 (144.0–329.4) | 177.5 (112.8–257.5) | <0.001 |
| Median (IQR) | p-Value for Difference | |
|---|---|---|
| Liver | 0.72 | |
| Old CT scanners | 8.59 (7.29–9.63) | |
| New CT scanners | 8.47 (7.40–9.39) | |
| Aorta | 0.51 | |
| Old CT scanners | 10.9 (9.81–11.9) | |
| New CT scanners | 10.5 (8.90–12.57) |
| Median (IQR) | p-Value for Difference | |
|---|---|---|
| Liver | 0.24 | |
| Old CT scanners | 2.55 (2.22–3.19) | |
| New CT scanners | 2.86 (2.28–3.42) | |
| Aorta | 0.03 | |
| Old CT scanners | 4.67 (3.91–5.52) | |
| New CT scanners | 5.23 (4.17–6.38) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rizzo, S.; Bellesi, L.; Khalifa, E.B.; Presilla, S.; D’Ermo, A.; Magoga, F.; Merli, M.; Rezzonico, E.; D’Ecclesiis, O.; Del Grande, F. Radiation Dose Reduction in Cancer Imaging with New-Model CT Scanners: A Quality of Care Evaluation. Cancers 2025, 17, 1815. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111815
Rizzo S, Bellesi L, Khalifa EB, Presilla S, D’Ermo A, Magoga F, Merli M, Rezzonico E, D’Ecclesiis O, Del Grande F. Radiation Dose Reduction in Cancer Imaging with New-Model CT Scanners: A Quality of Care Evaluation. Cancers. 2025; 17(11):1815. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111815
Chicago/Turabian StyleRizzo, Stefania, Luca Bellesi, Ebticem Ben Khalifa, Stefano Presilla, Andrea D’Ermo, Francesco Magoga, Matteo Merli, Ermidio Rezzonico, Oriana D’Ecclesiis, and Filippo Del Grande. 2025. "Radiation Dose Reduction in Cancer Imaging with New-Model CT Scanners: A Quality of Care Evaluation" Cancers 17, no. 11: 1815. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111815
APA StyleRizzo, S., Bellesi, L., Khalifa, E. B., Presilla, S., D’Ermo, A., Magoga, F., Merli, M., Rezzonico, E., D’Ecclesiis, O., & Del Grande, F. (2025). Radiation Dose Reduction in Cancer Imaging with New-Model CT Scanners: A Quality of Care Evaluation. Cancers, 17(11), 1815. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111815








