CD300a: An Innate Immune Checkpoint Shaping Tumor Immunity and Therapeutic Opportunity
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Expression and Function of the Inhibitory Receptor CD300a
1.2. CD300a: Genomic Localization, Structure, and Expression Regulation
1.3. Distinct Roles of SHP-1 and SHP-2 in CD300a-Mediated Inhibition
1.4. Activating Members of the CD300 Family
| Receptor | Expressing Cells | Structural Features | Recruited Molecules | Functional Type | Notes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD300a | Eosinophils, neutrophils, basophils, macrophages, and mast cells | Typical ITIM motifs | SHP-1, SHP-2 | Inhibitory receptor | Binds phosphatidylserine (PS) and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), negative regulation | [2,7,43,44,45,46] |
| CD300b | Neutrophils, macrophages, and mast cells | No ITIM, requires DAP12 | DAP12 (activating adaptor) | Activating receptor | Enhances cells survival and activation | [22] |
| CD300c | Basophils, mast cells, B cells, monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells | No ITIM, requires DAP12 | DAP12 | Activating receptor | Enhances allergic responses and activation | [23,24,25] |
| CD300d | Monocytes and granulocytes | Activating type (prominent ITAM-like motif) | DAP12 | Activating receptor | Participates in inflammation regulation | [26] |
| CD300e | Monocytes and myeloid dendritic cells | No ITIM, requires DAP12 | DAP12 | Activating receptor | Promotes production of inflammatory cytokines | [27] |
| CD300f | Monocytes, macrophages dendritic cells, mast cells and granulocytes | Multiple ITIM motifs (including non-classical ITIM) | SHP-1, SHP-2, PI3K (p85) | Inhibitory receptor | Promotes clearance of apoptotic cells, prevents autoimmunity | [12,29,30,31,32] |
| CD300g | Vascular endothelial cells | Mucin-like extracellular domain | Cell adhesion | Facilitates lymphocyte rolling and transmigration across the endothelium | [33] |
2. Immunoregulatory Roles of CD300a Across Innate Immune Cell Subsets
2.1. Expression and Functional Regulation of CD300a in Monocytes and Macrophages
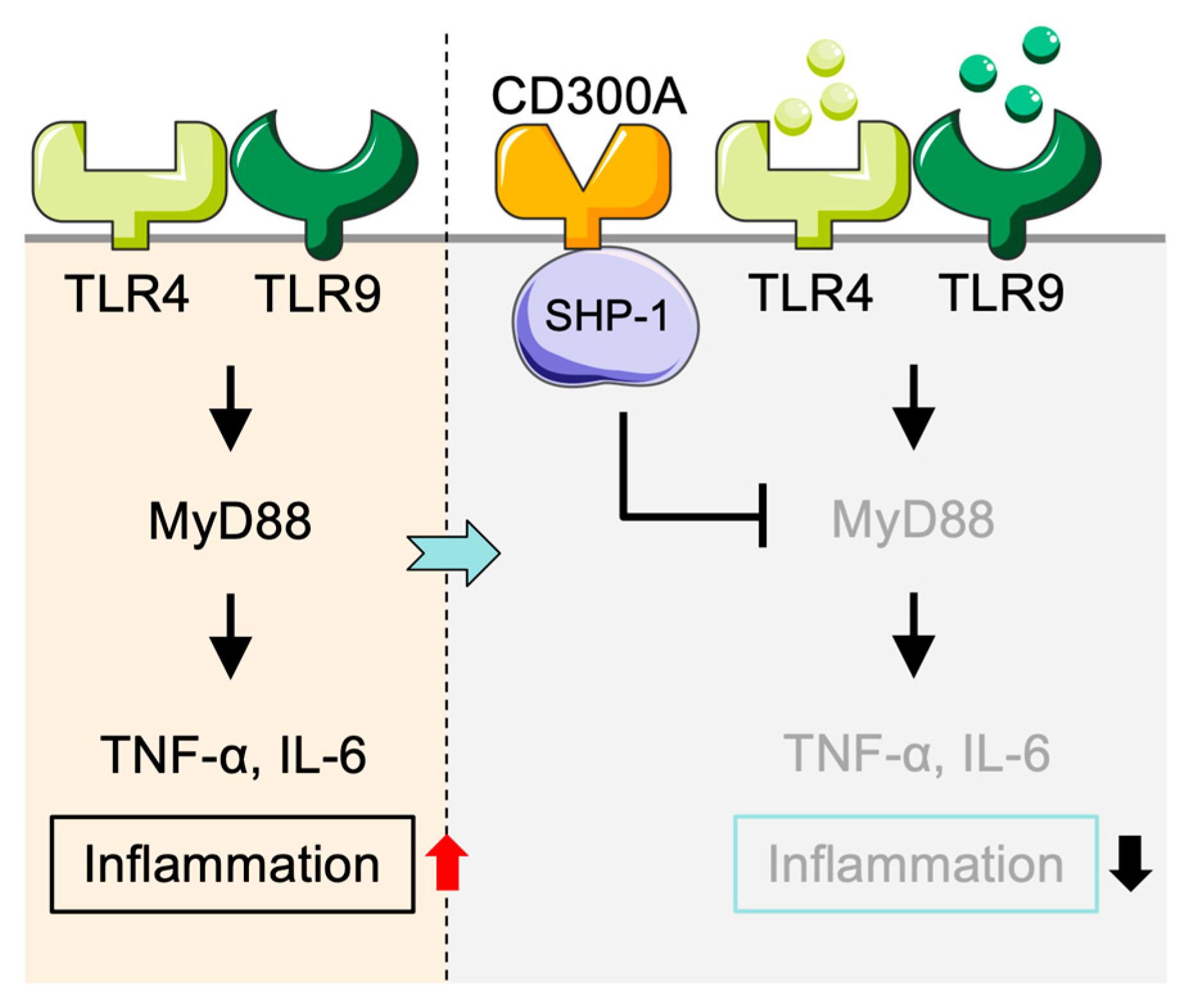
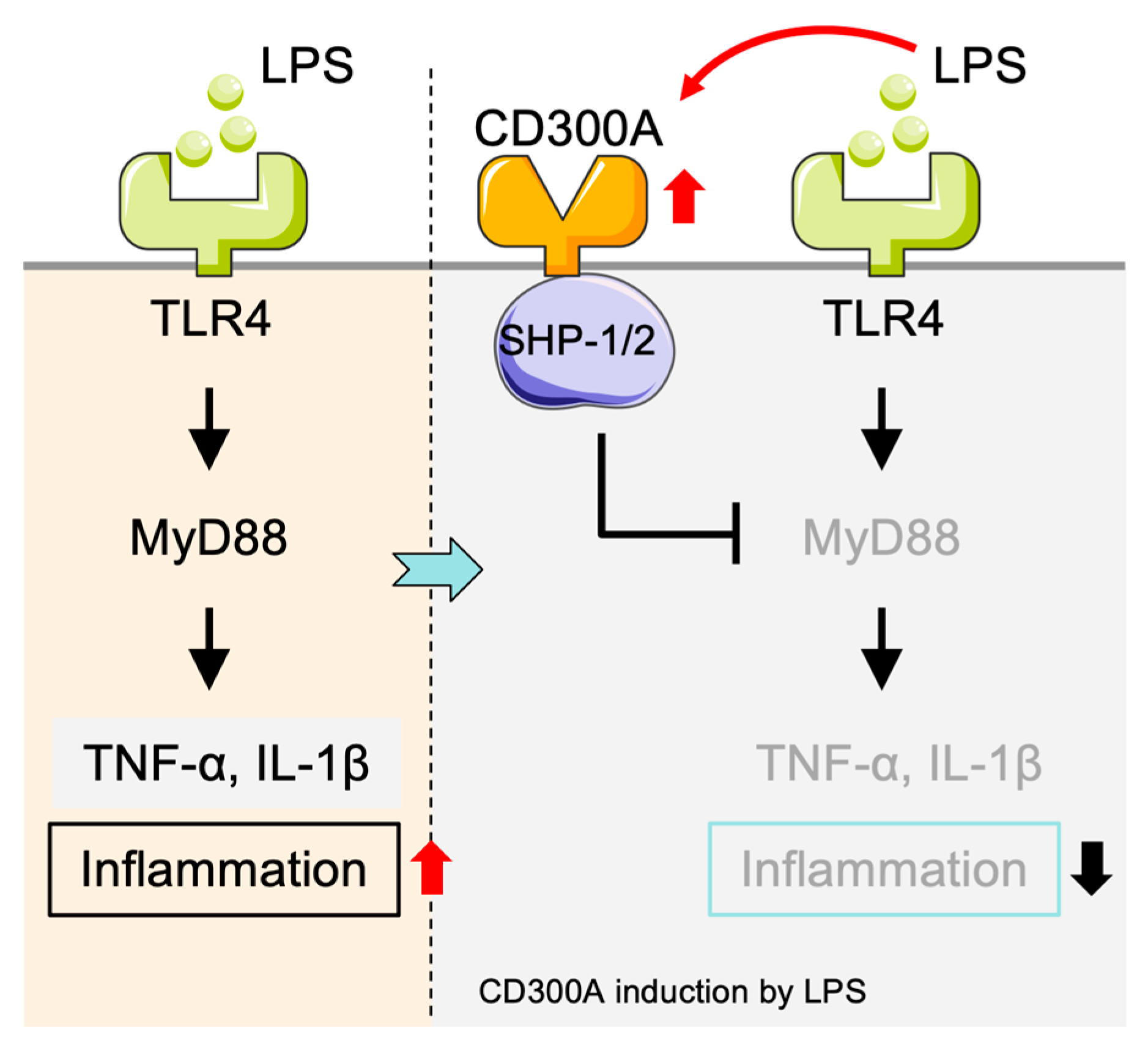
2.1.1. Inhibitory Function of CD300a in TLR Signaling in Monocytes
2.1.2. Effects of CD300a Deficiency or Knockdown on Function
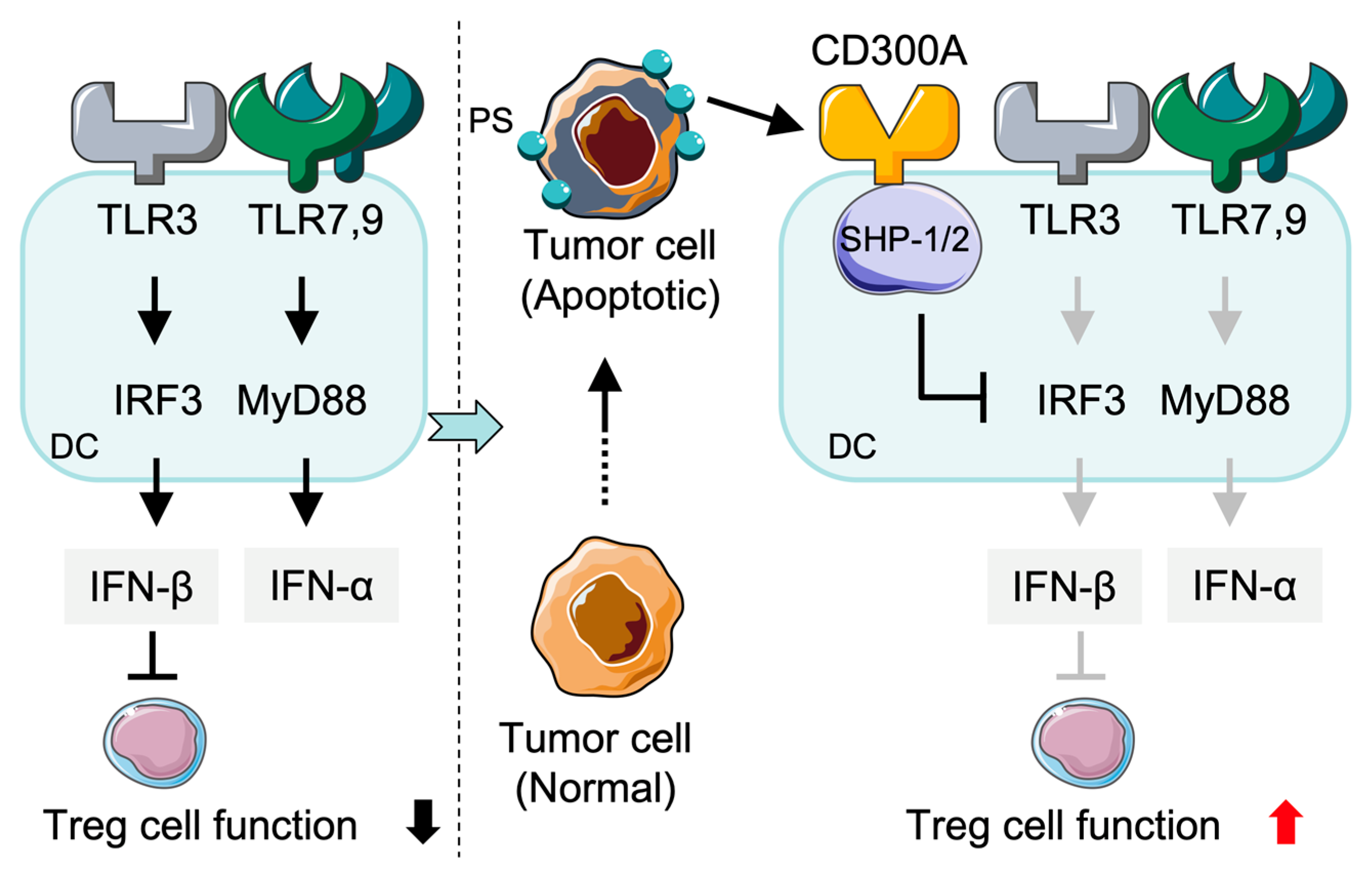
2.2. Expression and Function of CD300a in DCs
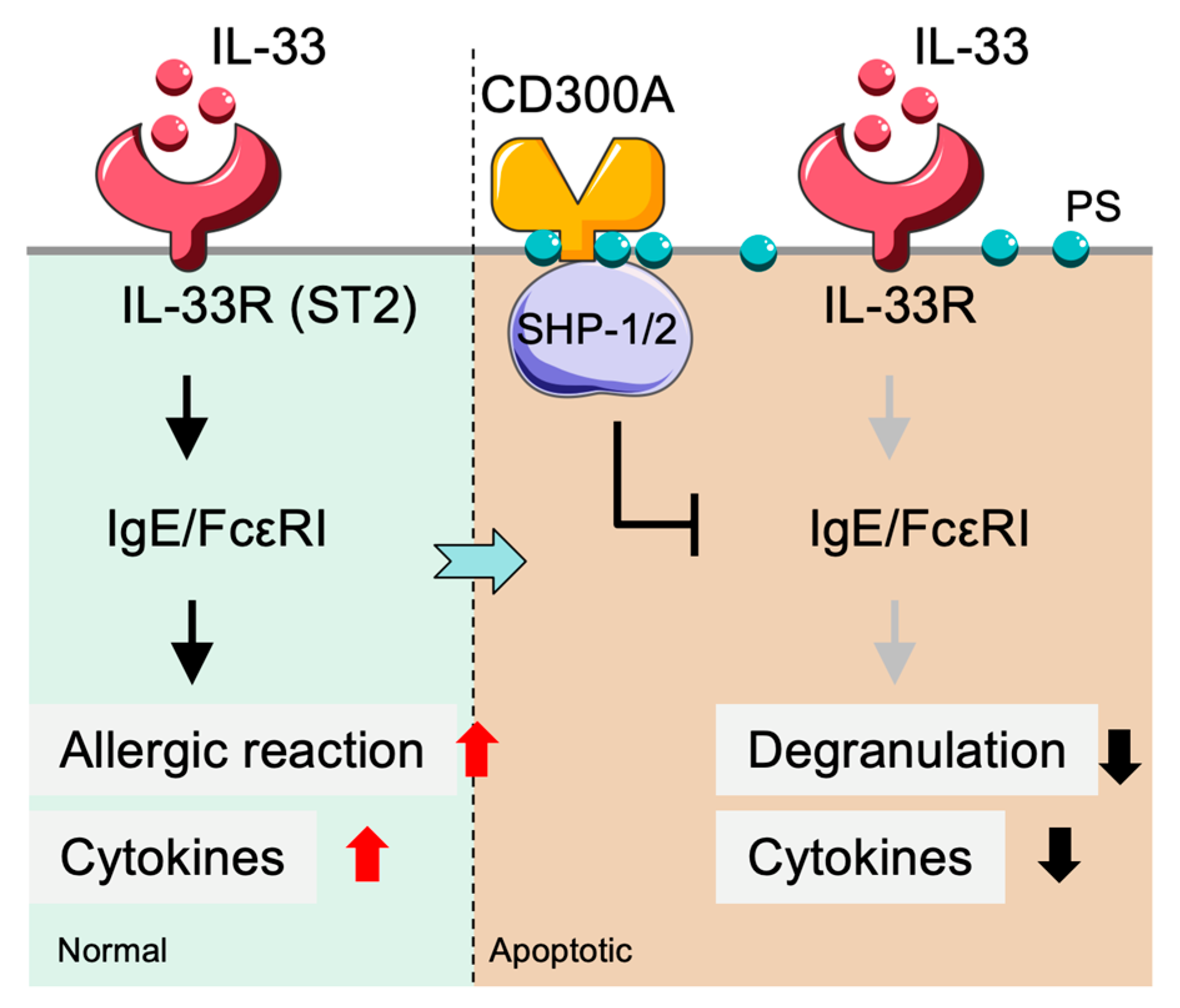
2.3. CD300a-Mediated Inhibition of Mast Cell Activation in Allergic Responses
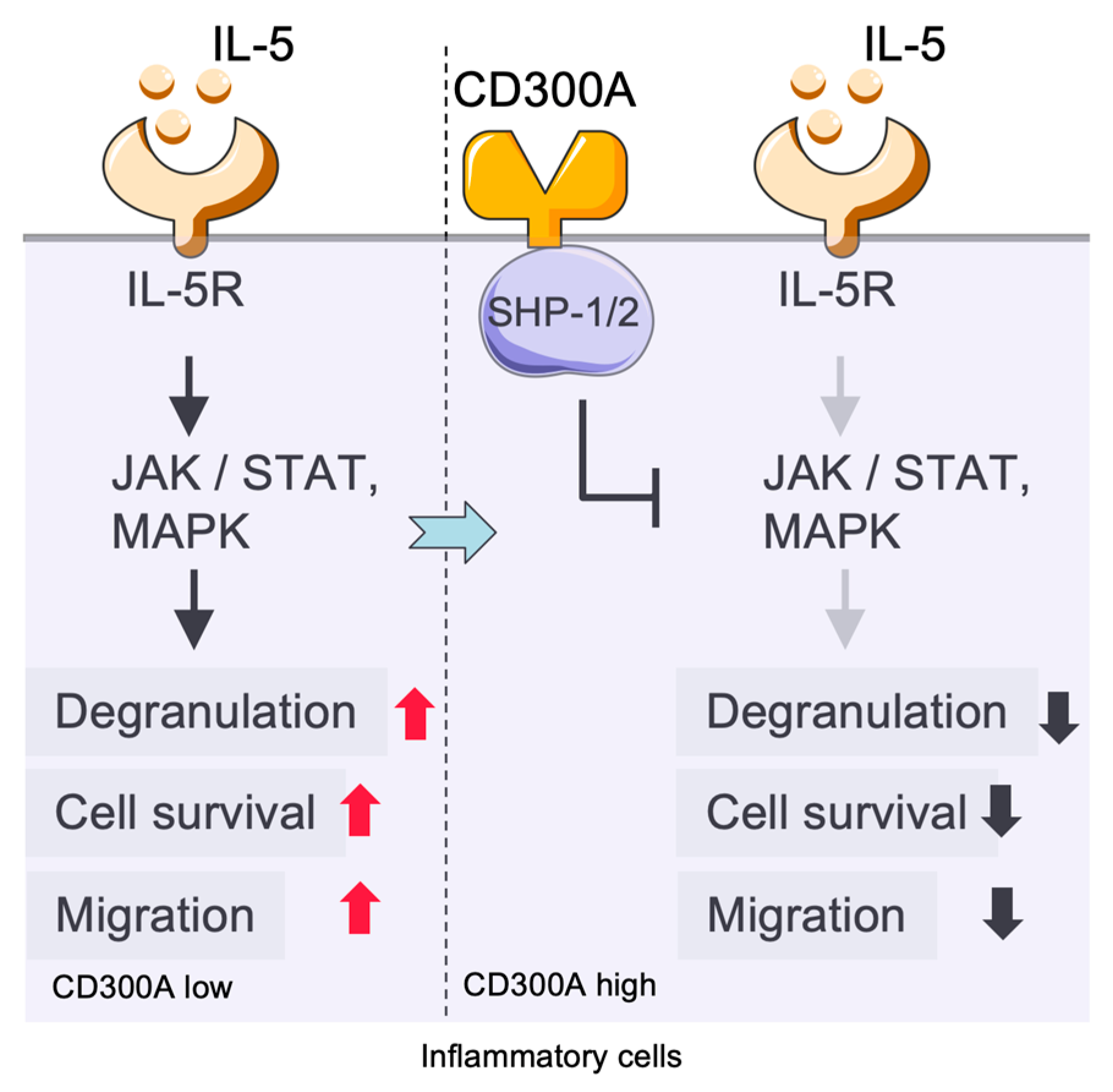
2.4. Immunoregulatory Role of CD300a in Eosinophils and Interaction with the TLR/MyD88 Pathway
2.5. CD300a in Neutrophils
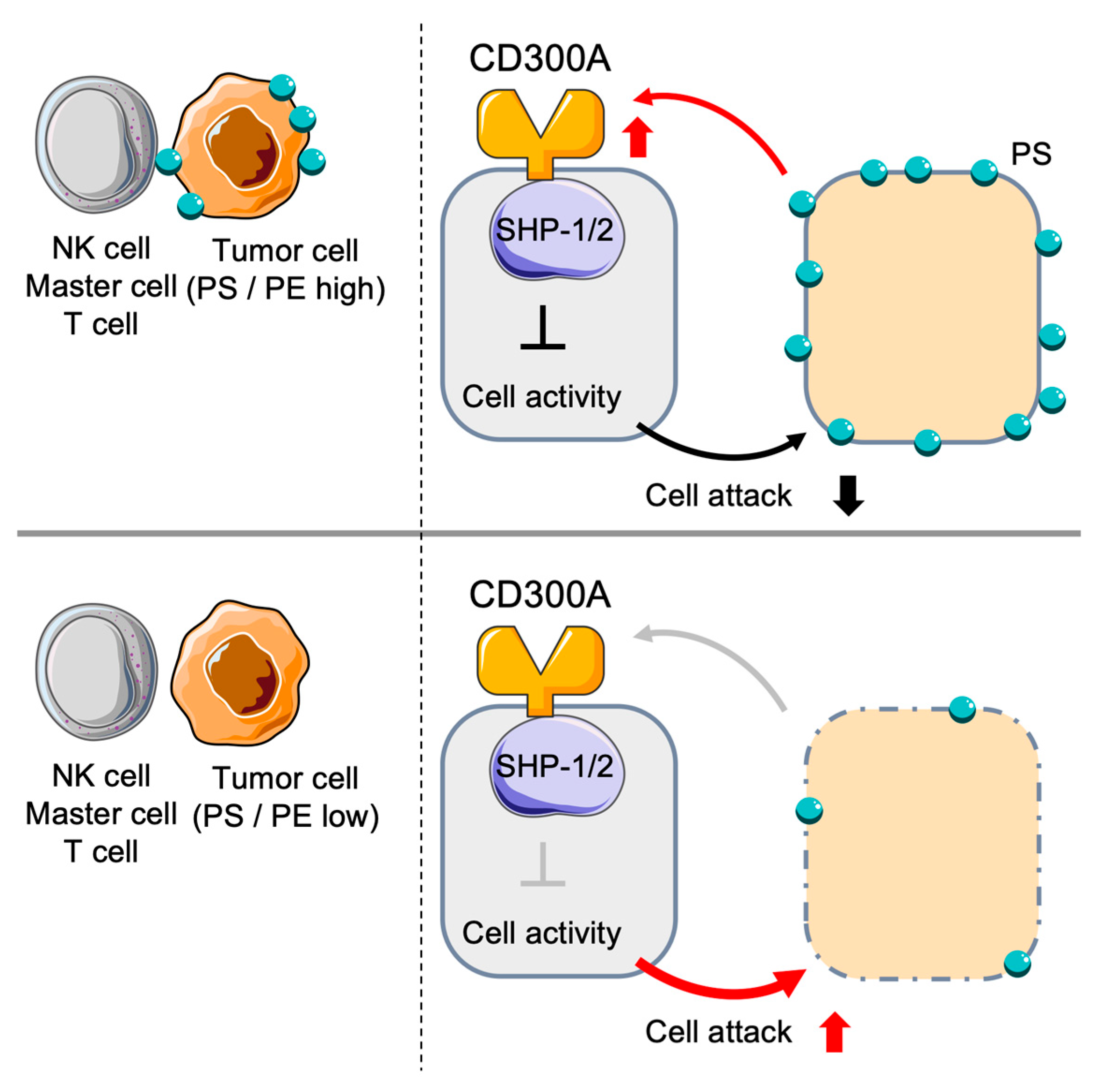
2.6. Inhibitory Function of CD300a in NK Cells
3. CD300a in Tumor Immunology
3.1. CD300a-Mediated Signaling in Hematologic Malignancies
3.2. Possible Roles of CD300a in Solid Tumors
4. Cross-Talk: Linking Immune Modulation to Tumor Progression
4.1. CD300a-Mediated Modulation in TME
4.1.1. CD300a and TME
4.1.2. CD300a and Pathological Neutrophil Activation
4.2. CD300a and NK Cells in Cancer
4.3. CD300a and Mast Cells in Cancer
5. Therapeutic Implications
5.1. CD300a Blockade as Monotherapy
5.2. CD300 Molecules in the Regulation of TLR-Mediated Immune Signaling and Inflammation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, Y.; Ao, T.; Wang, X.; Wei, W.; Fan, J.; Tian, X. CD300a and CD300f Molecules Regulate the Function of Leukocytes. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 93, 107373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitallé, J.; Terrén, I.; Orrantia, A.; Bilbao, A.; Gamboa, P.M.; Borrego, F.; Zenarruzabeitia, O. The Expression and Function of CD300 Molecules in the Main Players of Allergic Responses: Mast Cells, Basophils and Eosinophils. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrego, F. The CD300 Molecules: An Emerging Family of Regulators of the Immune System. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2013, 121, 1951–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Barriocanal, A.; Comas-Casellas, E.; Schwartz, S.; Martín, M.; Sayos, J. CD300 Heterocomplexes, a New and Family-Restricted Mechanism for Myeloid Cell Signaling Regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 41781–41794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabato, V.; Verweij, M.M.; Bridts, C.H.; Levi-Schaffer, F.; Gibbs, B.F.; De Clerck, L.S.; Schiavino, D.; Ebo, D.G. CD300a Is Expressed on Human Basophils and Seems to Inhibit IgE/FcεRI-dependent Anaphylactic Degranulation. Cytometry B Clin. Cytom. 2012, 82, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachelet, I.; Munitz, A.; Moretta, A.; Moretta, L.; Levi-Schaffer, F. The Inhibitory Receptor IRp60 (CD300a) Is Expressed and Functional on Human Mast Cells. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 7989–7995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munitz, A.; Bachelet, I.; Eliashar, R.; Moretta, A.; Moretta, L.; Levi-Schaffer, F. The Inhibitory Receptor IRp60 (CD300a) Suppresses the Effects of IL-5, GM-CSF, and Eotaxin on Human Peripheral Blood Eosinophils. Blood 2006, 107, 1996–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simhadri, V.R.; Andersen, J.F.; Calvo, E.; Choi, S.-C.; Coligan, J.E.; Borrego, F. Human CD300a Binds to Phosphatidylethanolamine and Phosphatidylserine, and Modulates the Phagocytosis of Dead Cells. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2012, 119, 2799–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, S.; Pal, P.; Lal, G. Key Activating and Inhibitory Ligands Involved in the Mobilization of Natural Killer Cells for Cancer Immunotherapies. ImmunoTargets Ther. 2021, 10, 387–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Tarquini, F.; Romero, R.; Kim, C.J.; Tarca, A.L.; Bhatti, G.; Lee, J.; Sundell, I.B.; Mittal, P.; Kusanovic, J.P. Peripheral CD300a+ CD8+ T Lymphocytes with a Distinct Cytotoxic Molecular Signature Increase in Pregnant Women with Chronic Chorioamnionitis. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2012, 67, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lankry, D.; Simic, H.; Klieger, Y.; Levi-Schaffer, F.; Jonjic, S.; Mandelboim, O. Expression and Function of CD300 in NK Cells. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 2877–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, G.J.; Ju, X.; Tate, C.; Hart, D.N. The CD300 Family of Molecules Are Evolutionarily Significant Regulators of Leukocyte Functions. Trends Immunol. 2009, 30, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasiorowski, R.E.; Ju, X.; Hart, D.N.; Clark, G.J. CD300 Molecule Regulation of Human Dendritic Cell Functions. Immunol. Lett. 2013, 149, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, G.J.; Ju, X.; Azlan, M.; Tate, C.; Ding, Y.; Hart, D.N. The CD300 Molecules Regulate Monocyte and Dendritic Cell Functions. Immunobiology 2009, 214, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Pai, T.; Ross, A.C. All-Trans-Retinoic Acid and Erk1/2 Signaling Synergistically Regulate the Expression of CD300B in Human Monocytic Cells. Cell. Immunol. 2011, 268, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitallé, J.; Terrén, I.; Gamboa-Urquijo, L.; Orrantia, A.; Tarancón-Díez, L.; Genebat, M.; Zenarruzabeitia, O. Polyfunctional HIV-1 Specific Response by CD8⁺ T Lymphocytes Expressing High Levels of CD300a. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formentini, M.; Navas, A.; Hassouneh, F.; Lopez-Sejas, N.; Alonso, C.; Tarazona, R.; Solana, R.; Pera, A. Impact of Cytomegalovirus and Age on T-Cell Subsets Defined by CD161, CD300a, and/or CD57 Expression in Healthy Andalusians. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2021, 76, 1946–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsvetkova, I.; Tsvetankova, R.; Todorova, K.; Hayrabedyan, S. The Effect of CD300A Receptor on Caspase-1 Activity in the Context of Cell Death and on Its Activators Nlrp3 and Asc in Sertoli Cells. Proc. Bulg. Acad. Sci. 2022, 75, 1830–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBell, K.E.; Simhadri, V.R.; Mariano, J.L.; Borrego, F. Functional Requirements for Inhibitory Signal Transmission by the Immunomodulatory Receptor CD300a. BMC Immunol. 2012, 13, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-J.; Lee, S.-M.; Suk, K.; Lee, W.-H. CD300a and CD300f Differentially Regulate the MyD88 and TRIF-mediated TLR Signalling Pathways through Activation of SHP-1 and/or SHP-2 in Human Monocytic Cell Lines. Immunology 2012, 135, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahashi-Oda, C.; Tahara-Hanaoka, S.; Shoji, M.; Okoshi, Y.; Nakano-Yokomizo, T.; Ohkohchi, N.; Yasui, T.; Kikutani, H.; Honda, S.; Shibuya, K. Apoptotic Cells Suppress Mast Cell Inflammatory Responses via the CD300a Immunoreceptor. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1493–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Tian, L.; Voss, O.H.; Margulies, D.H.; Krzewski, K.; Coligan, J.E. CD300b Regulates the Phagocytosis of Apoptotic Cells via Phosphatidylserine Recognition. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 1746–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenarruzabeitia, O.; Vitallé, J.; Terrén, I.; Orrantia, A.; Astigarraga, I.; Dopazo, L.; Gonzalez, C.; Santos-Díez, L.; Tutau, C.; Gamboa, P.M. CD300c Costimulates IgE-Mediated Basophil Activation, and Its Expression Is Increased in Patients with Cow’s Milk Allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 700–711.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Su, M.; Lin, Y.; Lai, L. A CD300c-Fc Fusion Protein Inhibits t Cell Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simhadri, V.R.; Mariano, J.L.; Gil-Krzewska, A.; Zhou, Q.; Borrego, F. CD300c Is an Activating Receptor Expressed on Human Monocytes. J. Innate Immun. 2013, 5, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comas-Casellas, E.; Martínez-Barriocanal, Á.; Miró, F.; Ejarque-Ortiz, A.; Schwartz, S.; Martín, M.; Sayós, J. Cloning and Characterization of CD300d, a Novel Member of the Human CD300 Family of Immune Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 9682–9693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brckalo, T.; Calzetti, F.; Pérez-Cabezas, B.; Borràs, F.E.; Cassatella, M.A.; López-Botet, M. Functional Analysis of the CD300e Receptor in Human Monocytes and Myeloid Dendritic Cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isobe, M.; Izawa, K.; Sugiuchi, M.; Sakanishi, T.; Kaitani, A.; Takamori, A.; Maehara, A.; Matsukawa, T.; Takahashi, M.; Yamanishi, Y. The CD300e Molecule in Mice Is an Immune-Activating Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 3793–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Errico, D.; Aguilar, H.; Kitzig, F.; Brckalo, T.; Sayós, J.; López-Botet, M. IREM-1 Is a Novel Inhibitory Receptor Expressed by Myeloid Cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2004, 34, 3690–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, I.; Tahara-Hanaoka, S.; Hitomi, K.; Nakano, T.; Nakahashi-Oda, C.; Kurita, N.; Honda, S.; Shibuya, K.; Shibuya, A. Caspase-Independent Cell Death by CD300LF (MAIR-V), an Inhibitory Immunoglobulin-like Receptor on Myeloid Cells. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izawa, K.; Kitaura, J.; Yamanishi, Y.; Matsuoka, T.; Kaitani, A.; Sugiuchi, M.; Takahashi, M.; Maehara, A.; Enomoto, Y.; Oki, T. An Activating and Inhibitory Signal from an Inhibitory Receptor LMIR3/CLM-1: LMIR3 Augments Lipopolysaccharide Response through Association with FcRγ in Mast Cells. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izawa, K.; Maehara, A.; Isobe, M.; Yasuda, Y.; Urai, M.; Hoshino, Y.; Ueno, K.; Matsukawa, T.; Takahashi, M.; Kaitani, A. Disrupting Ceramide-CD300f Interaction Prevents Septic Peritonitis by Stimulating Neutrophil Recruitment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, S.I.; Ju, X.; Silveira, P.A.; Kupresanin, F.; Horvath, L.G.; Clark, G.J. CD300f Signalling Induces Inhibitory Human Monocytes/Macrophages. Cell. Immunol. 2023, 390, 104731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izawa, K.; Isobe, M.; Matsukawa, T.; Ito, S.; Maehara, A.; Takahashi, M.; Yamanishi, Y.; Kaitani, A.; Oki, T.; Okumura, K. Sphingomyelin and Ceramide Are Physiological Ligands for Human LMIR3/CD300f, Inhibiting FcεRI-Mediated Mast Cell Activation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 270–273.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsukawa, T.; Izawa, K.; Isobe, M.; Takahashi, M.; Maehara, A.; Yamanishi, Y.; Kaitani, A.; Okumura, K.; Teshima, T.; Kitamura, T. Ceramide-CD300f Binding Suppresses Experimental Colitis by Inhibiting ATP-Mediated Mast Cell Activation. Gut 2016, 65, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, K.; Urai, M.; Izawa, K.; Otani, Y.; Yanagihara, N.; Kataoka, M.; Takatsuka, S.; Abe, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Shimizu, K. Mouse LIMR3/CD300f Is a Negative Regulator of the Antimicrobial Activity of Neutrophils. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papareddy, P.; Rossnagel, M.; Doreen Hollwedel, F.; Kilic, G.; Veerla, S.; Naudin, C.; Smeds, E.; Westman, J.; Martinez-Martinez, I.; Egesten, A. A Human Antithrombin Isoform Dampens Inflammatory Responses and Protects from Organ Damage during Bacterial Infection. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 2442–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-C.; Simhadri, V.R.; Tian, L.; Gil-Krzewska, A.; Krzewski, K.; Borrego, F.; Coligan, J.E. Cutting Edge: Mouse CD300f (CMRF-35–like Molecule-1) Recognizes Outer Membrane-Exposed Phosphatidylserine and Can Promote Phagocytosis. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 3483–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Choi, S.C.; Lee, H.N.; Murakami, Y.; Qi, C.F.; Sengottuvelu, M.; Voss, O.; Krzewski, K.; Coligan, J.E. Enhanced Efferocytosis by Dendritic Cells Underlies Memory T-Cell Expansion and Susceptibility to Autoimmune Disease in CD300f-Deficient Mice. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 1086–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatsu, H.; Hase, K.; Ohmae, M.; Ohshima, S.; Hashimoto, K.; Taniura, N.; Yamamoto, A.; Ohno, H. CD300 Antigen like Family Member G: A Novel Ig Receptor like Protein Exclusively Expressed on Capillary Endothelium. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 348, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umemoto, E.; Tanaka, T.; Kanda, H.; Jin, S.; Tohya, K.; Otani, K.; Matsutani, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Ebisuno, Y.; Jang, M.H. Nepmucin, a Novel HEV Sialomucin, Mediates L-Selectin–Dependent Lymphocyte Rolling and Promotes Lymphocyte Adhesion under Flow. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 1603–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Umemoto, E.; Tanaka, T.; Shimomura, Y.; Tohya, K.; Kunizawa, K.; Yang, B.-G.; Jang, M.H.; Hirata, T.; Miyasaka, M. Nepmucin/CLM-9, an Ig Domain-Containing Sialomucin in Vascular Endothelial Cells, Promotes Lymphocyte Transendothelial Migration in Vitro. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 3018–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitallé, J.; Terrén, I.; Orrantia, A.; Zenarruzabeitia, O.; Borrego, F. CD300 Receptor Family in Viral Infections. Eur. J. Immunol. 2019, 49, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaacson, B.; Baron, M.; Yamin, R.; Bachrach, G.; Levi-Schaffer, F.; Granot, Z.; Mandelboim, O. The Inhibitory Receptor CD300a Is Essential for Neutrophil-mediated Clearance of Urinary Tract Infection in Mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2021, 51, 2218–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yotsumoto, K.; Okoshi, Y.; Shibuya, K.; Yamazaki, S.; Tahara-Hanaoka, S.; Honda, S.; Osawa, M.; Kuroiwa, A.; Matsuda, Y.; Tenen, D.G. Paired Activating and Inhibitory Immunoglobulin-like Receptors, MAIR-I and MAIR-II, Regulate Mast Cell and Macrophage Activation. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenarruzabeitia, O.; Vitallé, J.; Eguizabal, C.; Simhadri, V.R.; Borrego, F. The Biology and Disease Relevance of CD300a, an Inhibitory Receptor for Phosphatidylserine and Phosphatidylethanolamine. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 5053–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozenberg, P.; Reichman, H.; Moshkovits, I.; Munitz, A. CD300 Family Receptors Regulate Eosinophil Survival, Chemotaxis, and Effector Functions. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018, 104, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Nakahashi-Oda, C.; Okayama, Y.; Shibuya, A. Autonomous Regulation of IgE-Mediated Mast Cell Degranulation and Immediate Hypersensitivity Reaction by an Inhibitory Receptor CD300a. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 323–327.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Xu, Y.; Zeng, X.; Fang, J.; Morse III, H.C.; Zhou, J.X. Suppression of CD300A Inhibits the Growth of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 31191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitallé, J.; Terrén, I.; Orrantia, A.; Pérez-Garay, R.; Vidal, F.; Iribarren, J.A.; Rodríguez, C.; Lirola, A.M.L.; Bernal, E.; Zenarruzabeitia, O. CD300a Inhibits CD16-Mediated NK Cell Effector Functions in HIV-1-Infected Patients. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 16, 940–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Cai, H.; Wang, R.; Cui, Y. Overexpression of CD300A Inhibits Progression of NSCLC through Downregulating Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 8875–8883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raggi, F.; Blengio, F.; Eva, A.; Pende, D.; Varesio, L.; Bosco, M.C. Identification of CD300a as a New Hypoxia-Inducible Gene and a Regulator of CCL20 and VEGF Production by Human Monocytes and Macrophages. Innate Immun. 2014, 20, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosco, M.C.; Puppo, M.; Santangelo, C.; Anfosso, L.; Pfeffer, U.; Fardin, P.; Battaglia, F.; Varesio, L. Hypoxia Modifies the Transcriptome of Primary Human Monocytes: Modulation of Novel Immune-Related Genes and Identification of CC-Chemokine Ligand 20 as a New Hypoxia-Inducible Gene. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 1941–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, K.A.; Rowe, D.C.; Barnes, B.J.; Caffrey, D.R.; Visintin, A.; Latz, E.; Monks, B.; Pitha, P.M.; Golenbock, D.T. LPS-TLR4 Signaling to IRF-3/7 and NF-κB Involves the Toll Adapters TRAM and TRIF. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Takeda, K.; Akira, S. TIR Domain-Containing Adaptors Define the Specificity of TLR Signaling. Mol. Immunol. 2004, 40, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Nakahashi-Oda, C.; Lyu, W.; Tanaka, M.; Rai, A.; Muramoto, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mizuno, S.; Shibuya, K.; Shibuya, A. Inhibitory Immunoreceptors CD300a and CD300lf Cooperate to Regulate Mast Cell Activation. J. Immunol. 2025, 214, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.; Zenke, M.; Hart, D.N.; Clark, G.J. CD300a/c Regulate Type I Interferon and TNF-α Secretion by Human Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells Stimulated with TLR7 and TLR9 Ligands. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2008, 112, 1184–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangaplara, A.; Martens, C.; Dahlstrom, E.; Metidji, A.; Gokhale, A.S.; Glass, D.D.; Lopez-Ocasio, M.; Baur, R.; Kanakabandi, K.; Porcella, S.F.; et al. Type I Interferon Signaling Attenuates Regulatory T Cell Function in Viral Infection and in the Tumor Microenvironment. PLOS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-N.; Tian, L.; Bouladoux, N.; Davis, J.; Quinones, M.; Belkaid, Y.; Coligan, J.E.; Krzewski, K. Dendritic Cells Expressing Immunoreceptor CD300f Are Critical for Controlling Chronic Gut Inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 1905–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, Y.; Nishiyama, N.; Koizumi, H.; Kanemaru, K.; Nakahashi-Oda, C.; Shibuya, A. Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Regulate Tumor-Infiltrating Regulatory T Cells via the Inhibitory Immunoreceptor CD300a. eLife 2021, 10, e61999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, Y.; Tang, X.; Coligan, J.E.; Borrego, F. The CD300a (IRp60) Inhibitory Receptor Is Rapidly up-Regulated on Human Neutrophils in Response to Inflammatory Stimuli and Modulates CD32a (FcγRIIa) Mediated Signaling. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shik, D.; Moshkovits, I.; Karo-Atar, D.; Reichman, H.; Munitz, A. Interleukin-33 Requires CMRF 35-like Molecule-1 Expression for Induction of Myeloid Cell Activation. Allergy 2014, 69, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lankry, D.; Rovis, T.L.; Jonjic, S.; Mandelboim, O. The Interaction between CD 300a and Phosphatidylserine Inhibits Tumor Cell Killing by NK Cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 2151–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabato, V.; Boita, M.; Shubber, S.; Bridts, C.H.; Shibuya, A.; De Clerck, L.S.; Falcone, F.H.; Ebo, D.G. Mechanism of Phosphatidylserine Inhibition of IgE/FcεRI-Dependent Anaphylactic Human Basophil Degranulation via CD300a. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 734–737.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlomovitz, I.; Speir, M.; Gerlic, M. Flipping the Dogma–Phosphatidylserine in Non-Apoptotic Cell Death. Cell Commun. Signal. 2019, 17, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachelet, I.; Munitz, A.; Levi-Schaffer, F. Abrogation of Allergic Reactions by a Bispecific Antibody Fragment Linking IgE to CD300a. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 117, 1314–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitlock, J.M.; Chernomordik, L.V. Flagging Fusion: Phosphatidylserine Signaling in Cell–Cell Fusion. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, E.; Yan, T.; Xu, Z.; Shang, Z. Tumor Microenvironment and Cell Fusion. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 5013592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Huang, X.; Lynn, K.D.; Thorpe, P.E. Phosphatidylserine-Targeting Antibody Induces M1 Macrophage Polarization and Promotes Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell Differentiation. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2013, 1, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, H.; Okugawa, S.; Ota, Y.; Yamaguchi, M.; Tomizawa, H.; Matsushima, K.; Ohta, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Hirai, K. Expression and Function of Toll-like Receptors in Eosinophils: Activation by Toll-like Receptor 7 Ligand. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 3977–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissim Ben Efraim, A.H.; Karra, L.; Ben-Zimra, M.; Levi-Schaffer, F. The Inhibitory Receptor CD 300a Is Up-regulated by Hypoxia and GM-CSF in Human Peripheral Blood Eosinophils. Allergy 2013, 68, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karra, L.; Singh Gangwar, R.; Shamri, R.; Puzzovio, P.G.; Cohen-Mor, S.; Levy, B.D.; Levi-Schaffer, F. Leukocyte CD300a Contributes to the Resolution of Murine Allergic Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 2998–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimasi, N.; Roessle, M.; Moran, O.; Candiano, G.; Svergun, D.I.; Biassoni, R. Molecular Analysis and Solution Structure from Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering of the Human Natural Killer Inhibitory Receptor IRp60 (CD300a). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2007, 40, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raulet, D.H. Missing Self Recognition and Self Tolerance of Natural Killer (NK) Cells. Semin. Immunol. 2006, 18, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretta, A.; Bottino, C.; Vitale, M.; Pende, D.; Cantoni, C.; Mingari, M.C.; Biassoni, R.; Moretta, L. Activating Receptors and Coreceptors Involved in Human Natural Killer Cell-Mediated Cytolysis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 19, 197–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, S.; Groh, V.; Wu, J.; Steinle, A.; Phillips, J.H.; Lanier, L.L.; Spies, T. Activation of NK Cells and T Cells by NKG2D, a Receptor for Stress-Inducible MICA. Science 1999, 285, 727–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakahashi-Oda, C.; Tahara-Hanaoka, S.; Honda, S.; Shibuya, K.; Shibuya, A. Identification of Phosphatidylserine as a Ligand for the CD300a Immunoreceptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 417, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantoni, C.; Bottino, C.; Augugliaro, R.; Morelli, L.; Marcenaro, E.; Castriconi, R.; Vitale, M.; Pende, D.; Sivori, S.; Millo, R. Molecular and Functional Characterization of IRp60, a Member of the Immunoglobulin Superfamily That Functions as an Inhibitory Receptor in Human NK Cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 1999, 29, 3148–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, O.H.; Tian, L.; Murakami, Y.; Coligan, J.E.; Krzewski, K. Emerging Role of CD300 Receptors in Regulating Myeloid Cell Efferocytosis. Mol. Cell. Oncol. 2015, 2, e964625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Liu, B.; Ding, Q.; He, D.; Zhang, R.; Yang, F.; Fan, H.; Teng, L.; Xin, T. CD300A Inhibits Tumor Cell Growth by Downregulating AKT Phosphorylation in Human Glioblastoma Multiforme. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 3471. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Zimra, M.; Levi-Schaffer, F. The Inhibitory Receptor CD300a Functions as an Immune Checkpoint in a 4T1 Breast Cancer Model. Ann. Allergy. Asthma. Immunol. 2024, 133, S82–S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woehlecke, H.; Pohl, A.; Alder-Baerens, N.; Lage, H.; Herrmann, A. Enhanced Exposure of Phosphatidylserine in Human Gastric Carcinoma Cells Overexpressing the Half-Size ABC Transporter BCRP (ABCG2). Biochem. J. 2003, 376, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.P.; Holth, A.; Kleinberg, L.; Ruud, M.G.; Elstrand, M.B.; Tropé, C.G.; Davidson, B.; Risberg, B. Evaluation of Cell Surface Expression of Phosphatidylserine in Ovarian Carcinoma Effusions Using the Annexin-V/7-AAD Assay: Clinical Relevance and Comparison with Other Apoptosis Parameters. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 132, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirszberg, C.; Lima, L.G.; de Oliveira, A.D.S.; Pickering, W.; Gray, E.; Barrowcliffe, T.W.; Rumjanek, V.M.; Monteiro, R.Q. Simultaneous Tissue Factor Expression and Phosphatidylserine Exposure Account for the Highly Procoagulant Pattern of Melanoma Cell Lines. Melanoma Res. 2009, 19, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xia, P.; Wen, X.; Ma, J.; Lin, J.; Qian, J. Pan-cancer Analysis Identifies CD300 Molecules as Potential Immune Regulators and Promising Therapeutic Targets in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 789–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal Rojas, I.M.; Mok, W.-H.; Pearson, F.E.; Minoda, Y.; Kenna, T.J.; Barnard, R.T.; Radford, K.J. Human Blood CD1c+ Dendritic Cells Promote Th1 and Th17 Effector Function in Memory CD4+ T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizzoli, G.; Krietsch, J.; Weick, A.; Steinfelder, S.; Facciotti, F.; Gruarin, P.; Bianco, A.; Steckel, B.; Moro, M.; Crosti, M. Human CD1c+ Dendritic Cells Secrete High Levels of IL-12 and Potently Prime Cytotoxic T-Cell Responses. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2013, 122, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haist, M.; Stege, H.; Grabbe, S.; Bros, M. The Functional Crosstalk between Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Regulatory T Cells within the Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers 2021, 13, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnewies, M.; Roberts, E.W.; Kersten, K.; Chan, V.; Fearon, D.F.; Merad, M.; Coussens, L.M.; Gabrilovich, D.I.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S.; Hedrick, C.C. Understanding the Tumor Immune Microenvironment (TIME) for Effective Therapy. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Feng, C.; Li, J.; Jiang, E.; Shang, Z. Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Crosstalk in Tumor Microenvironment Dominates Tumor Fate. Trends Cell Biol. 2024, 35, 230–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Tahara-Hanaoka, S.; Nabekura, T.; Ikeda, K.; Jiang, S.; Tsutsumi, S.; Inagaki, T.; Magoori, K.; Higurashi, T.; Takahashi, H. PPARβ/δ Activation of CD300a Controls Intestinal Immunity. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, X.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Shen, G.; Peng, J.; Zheng, P. CD300ld on Neutrophils Is Required for Tumour-Driven Immune Suppression. Nature 2023, 621, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wang, T.; Xiao, X.; Zheng, X.; Sun, H.; Sun, R.; Ma, H.; Tian, Z.; Zheng, X. Blockade of CD300A Enhances the Ability of Human NK Cells to Lyse Hematologic Malignancies. Cancer Biol. Med. 2024, 21, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munitz, A.; Bachelet, I.; Levi-Schaffer, F. A Novel CCR3-CD300a Bispecific Antibody Fragment Reverses Airway Inflammation and Tissue Remodeling in a Model of Established-Chronic Experimental Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 117, S328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabato, V.; Beyens, M.; Toscano, A.; Van Gasse, A.; Ebo, D.G. Mast Cell–Targeting Therapies in Mast Cell Activation Syndromes. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2024, 24, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallegos, V.A.M. Multifaceted Approaches to Tumor Microenvironment Modulation and Immune Checkpoint Targeting. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichterman, J.N.; Reddy, S.M. Mast Cells: A New Frontier for Cancer Immunotherapy. Cells 2021, 10, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Dong, Y.; Cao, Y.; Luo, Y. Correlation between TLR 2, TLR 3, TLR 4, and TLR 9 Polymorphisms and Susceptibility to and Prognosis of Severe Hepatitis among the Newborns. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2018, 32, e22292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartey, S.; Takeuchi, O. Pathogen Recognition and Toll-like Receptor Targeted Therapeutics in Innate Immune Cells. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 36, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.; Moir, S.; Kardava, L.; Debell, K.; Simhadri, V.R.; Ferrando-Martínez, S.; Leal, M.; Peña, J.; Coligan, J.E.; Borrego, F. CD300a Is Expressed on Human B Cells, Modulates BCR-Mediated Signaling, and Its Expression Is down-Regulated in HIV Infection. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2011, 117, 5870–5880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinidou, A.; Alifieris, C.; Trafalis, D.T. Targeting Programmed Cell Death-1 (PD-1) and Ligand (PD-L1): A New Era in Cancer Active Immunotherapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 194, 84–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez, N.G.; Berner, F.; Friebel, E.; Unger, S.; Wyss, N.; Gomez, J.M.; Purde, M.-T.; Niederer, R.; Porsch, M.; Lichtensteiger, C.; et al. Immune Signatures Predict Development of Autoimmune Toxicity in Patients with Cancer Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Med 2023, 4, 113–129.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhukova, N.; Orlova, R.; Malkova, A.; Kaledina, E.; Demchenkova, A.; Naimushina, P.; Nazarov, V.; Mazing, A.; Lapin, S.; Belyak, N.; et al. The Novel Diagnostic Index Based on HLA-DRB1 Genotype and PD-L1 Expression Can Predict Severe irAEs in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma Taking Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. The Results of the Pilot Study. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 42, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Ma, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Yu, Z.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, M.; Zhuang, G.; Jing, Y. Divergent Tumor and Immune Cell Reprogramming Underlying Immunotherapy Response and Immune-Related Adverse Events in Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e007305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochigneux, P.; Bertucci, A.; Loir, E.; Mattei, A.; Robert, D.; Dassa, M.; Chanez, B.; Ebbo, M.; Gaigne, L.; Chretien, A.S.; et al. Case Report: A Severe Myositis Mimicking Bulbar Palsy after Administration of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1496427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolladille, C.; Ederhy, S.; Sassier, M.; Cautela, J.; Thuny, F.; Cohen, A.A.; Fedrizzi, S.; Chrétien, B.; Da-Silva, A.; Plane, A.-F.; et al. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Rechallenge After Immune-Related Adverse Events in Patients with Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, R.; Põder, J.; LaPorte, K.M.; Malek, T.R. Engineering IL-2 for Immunotherapy of Autoimmunity and Cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 614–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, S.N.; Kue, C.S. A Combination Therapy of Cyclophosphamide and Immunomodulating Agents in Cancer. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2024, 25, e15680096314791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, J.-M.; Liu, H.-Y. CD300a: An Innate Immune Checkpoint Shaping Tumor Immunity and Therapeutic Opportunity. Cancers 2025, 17, 1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111786
Peng J-M, Liu H-Y. CD300a: An Innate Immune Checkpoint Shaping Tumor Immunity and Therapeutic Opportunity. Cancers. 2025; 17(11):1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111786
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Jei-Ming, and Hui-Ying Liu. 2025. "CD300a: An Innate Immune Checkpoint Shaping Tumor Immunity and Therapeutic Opportunity" Cancers 17, no. 11: 1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111786
APA StylePeng, J.-M., & Liu, H.-Y. (2025). CD300a: An Innate Immune Checkpoint Shaping Tumor Immunity and Therapeutic Opportunity. Cancers, 17(11), 1786. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111786





