Simple Summary
Lung cancer is a very serious disease, and it becomes worse when combined with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [COPD], another chronic lung illness. Both are linked to smoking and long-term lung inflammation. Scientists are now focusing on tiny particles called small extracellular vesicles (sEVs), which are released by cells and carry important molecules. In lung cancer, sEVs often carry cancer-related signals, while in COPD, they carry inflammation-related ones. These signals could help doctors to diagnose and monitor the diseases more accurately. However, collecting and studying sEVs is still difficult, which limits their use in clinics. This review looks at the potential of sEVs as helpful tools in treating lung cancer and COPD and highlights the need for more research.
Abstract
Lung cancer is one of the deadliest forms of cancer. Its prognosis becomes even worse when it co-occurs with other diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Both illnesses have numerous shared risk factors, including the use of tobacco smoke, and have similar underlying mechanisms like long-term inflammation. There are some other less studied but equally important molecules, like small extracellular vesicles (sEVs), that have been shown to mediate effective communication at the cellular level and may affect the progression of a disease or cause resistance to therapies. In sEVs from lung cancer tumors, there are onco-proteins (e.g., tumor initiator EGFR mutations, onco-miR, miR-21), while in sEVs from patients with COPD, there are pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-6 and TNF-α that enhance airway inflammation. These potential biomarkers of sEVs from chronic lung disease have great value in defense against emerging health problems; however, limitations in sample extraction and analysis are obstacles that hinder clinical enhanced applicability. This review focuses on sEV-derived biomarkers in lung cancer and COPD for diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic monitoring purposes. To make these molecules more useful in real-life therapy and determine their signature’s role, further investigation with a high-scale study is necessary.
1. Introduction
As time elapses, the list of people dying from lung cancer continues to increase, owing to its rank as the second most fatal cancer type across the globe, with 2.5 million new cases and 1.8 million deaths annually. The development of lung cancer in conjunction with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) differs by gender, age, and geographical location. The risk is approximately twofold for male COPD patients as opposed to females (5.09% versus 2.52%). However, the risk continues to grow with age, with more than 10% of younger lung cancer patients also having COPD. Geographically, the Western Pacific has the highest prevalence of COPD at 7.78%, followed by 3.25% in the Americas and 3.21% in Europe [1]. Smoking is the primary risk factor, alongside pollution and pre-existing lung conditions like COPD, which also contribute to high mortality rates. Late-stage diagnosis significantly affects survival, with 77% of cases being diagnosed at advanced stages [2]. Diagnosis involves using imaging techniques and biopsies to classify lung cancer into non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) (Figure 1). Treatment varies by type and stage, including surgery [2], radiation, chemotherapy [3], and targeted therapies [4,5] based on genetic mutations. Recent advances in medicine, particularly using the immune system in treatment through immunotherapy [6], have shown immense possibility, especially concerning severe NSCLC cases. To improve the condition of the afflicted, the expansion of screening with the employment of new innovative biomarkers that aid in improving diagnosis and screening approaches is required. Efforts towards early detection screening have emerged to help lung cancer patients immensely. This is important in ensuring better outcomes for managing affected individuals. Scientists are searching for new biomarkers to aid in early lung cancer diagnosis and determine outcome prediction with or without other respiratory disease comorbidity [4,7,8,9,10]. The goal of this narrative review is to identify the roles, functions, and diagnostic or prognostic value of small EVs released from lung cancer or COPD patients using different original articles from peer-reviewed publishers such as Elsevier, Science Direct, PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar. It also analyzes the potential difficulties in distinguishing accurate small extracellular vesicle biomarkers considering the presence of comorbidities. We address the issues of interpreting biomarkers with concurrent pathologies and highlight important factors needed to refine accuracy in multi-faceted clinical situations.
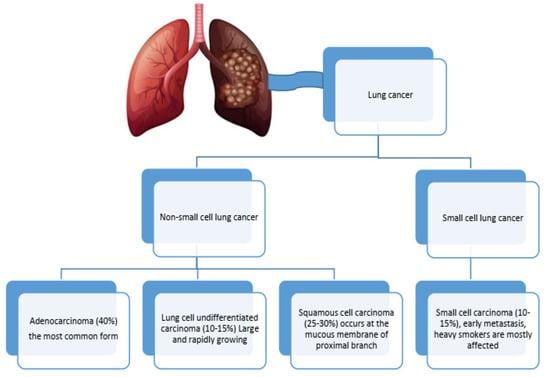
Figure 1.
The most common types of lung cancer.
Dual Battles: Immune Dynamics in COPD and Lung Cancer Progression
The immune system, which includes T cells, B cells, NK cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells, is essential in defending the body from cancerous cells. With lung cancer, the tumor microenvironment (TME) is a complex ecosystem that not only fosters tumor development but also shields it from immune response [11]. Cancer cells commonly use tactics to escape immune surveillance and strike, for instance, the downregulation of molecules responsible for antigen presentation [12], immunosuppressive cytokine secretion, inhibitory receptor expression, and recruitment of immunosuppressive cell types [13].
Furthermore, COPD is defined by persistent inflammation and constriction of the airways following the inhalation of harmful particulates or gases, especially cigarette smoke [14]. The response of the immune system is quite complicated and often overlaps with non-small-cell lung cancer, which is associated with a higher likelihood of lung cancer. Pro-inflammatory cytokines are released by macrophages and neutrophils in COPD, leading to tissue damage and mucus hypersecretion [15]. The cells that include Th1 and Th17 subsets activate macrophages and worsen inflammation. On the other hand, plasma cells differentiated from B cells are also active in inflammation [16]. The increased levels of inflammatory proteins and chemokines critically damage airway, cause inflammation and modify the environment. Tissue damage from oxidative balance in COPD is detrimental to the cells and increases inflammation. There are often such changes with persistent inflammation to the structure of the airways, which leads to further issues with the limitation of airflow and respiratory problems. This means that the region is subject to hyperinflammation, which may lead to a more persistent infection.
A combination of these two diseases can severely suppress immunity in the affected individual [17], making them experience elevated systemic oxidative stress and diminished levels of antioxidants and inflammatory cells [18]. Sustained lung inflammation due to irritants like cigarette smoke or neoplastic cells can be the cause of the priming of the immune system, shifting to the inflammatory state alongside tissue damage and further inflammation. COPD coupled with lung cancer can also increase the incidence and severity of infection due to impaired lung function and immunity while enhancing the chances of altering treatment selection and changing treatment response towards lung cancer. These two diseases can also lead to the compromising of the immune system, causing a shift towards a pro-inflammatory response and favoring tumor cell evasion [19]. The coexistence of these two conditions can also affect the selection and efficacy of lung cancer treatments, as well as increase susceptibility to respiratory infections due to compromised lung function and weakened immune response [20].
Therefore, early diagnosis and prognosis of treatment and its efficacy biomarkers is significant, as these biomolecules are expected to be accurate and precise. Recently, attention has shifted to extracellular vesicles (EVs) such as small EVs for their potential use in diagnostic and monitoring treatment purposes [10]. These biomolecules are noteworthy due to their small dimensions and originate from a unique process of production, namely an endocytic process, where they are substantially produced from parent cells. In the diseases of lung cancer and COPD, small EVs are known to participate in progression, immune modulation, and tissue remodeling, which goes beyond the activities of cells and includes tissue repair and fibrosis [21].
2. Small EVs as a Hidden Language
EVs are membrane-bound structures released by cells into bodily fluids that facilitate intercellular communication by transporting proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and metabolites [22]. Varieties of these messengers are further explained in Table 1 and include small EVs (30–150 nm, located in multivesicular bodies) [23], microvesicles (100–1000 nm, from plasma membrane budding), and apoptotic bodies (500–2000 nm, released during cell death). EVs mediate development, physiological processes, and the regulation of immunity and have future potential in scientific investigation and medicine delivery. There are a few other subdivisions of EVs that are known, but for their indefinite overlap in size and biogenesis pathways, they are mostly included in one of the three main EV categories, as mentioned above. Certain EVs, however, enclose distinct molecular identities or functional roles in living systems, but within the context of current understanding, their classification will remain primarily based on their size. More studies must be conducted on the biogenesis, molecular composition, and functional attributes for EVs to aid in determining applicable classification strategies.

Table 1.
Classifications of EVs.
3. From Cells to Circulation
Small EVs facilitate intercellular communication, maintaining cellular balance and immune function [27]. They are secreted ubiquitously across cell types including γδ T lymphocytes, which demonstrate potential as cancer immune-therapeutics. Tumor-derived EVs function as antigen carriers, while immune cell-derived vesicles exhibit intrinsic antineoplastic activity via bioactive molecular cargo [28]. They promote cancer progression through angiogenesis [29], oncogenic molecule transfer, and metastatic site preparation [30]. EVs originate from tumor cells (promoting growth, angiogenesis, metastasis, immune evasion), immune cells (modulating anti-cancer responses), and respiratory cells. In lung cancer, tumor-derived EVs facilitate progression and metastasis [31]. During COPD, inflammation causes the immune system to be over activated and release pro-inflammatory mediators that damage tissues and remodel airways [32], while cigarette smoke-damaged epithelial cells release inflammatory EVs [14,33,34]. sEVs from patients suffering from COPD exhibited significantly higher levels of IL-1β, TNF-α, MMPs [35], and dysregulated miRNAs like miR-21 [34]. In a clinical setting, sEVs can be used as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for the detection of the disease in its early stages [36,37], disease monitoring [38,39], and even as therapeutic agents through the modulation of the sEV-mediated routes [40].
EV autoantibodies have been also identified as potential biomarkers in lung cancer, complementing their previously established role of EVs in biomarker identification. This finding expands the repertoire of molecular signatures that may facilitate the early detection and characterization of lung malignancies. The presence of these autoantibodies in patient serum provides an additional dimension to the multi-faceted approach of cancer diagnostics, potentially enhancing sensitivity and specificity when used in conjunction with EV-derived biomarkers [41].
4. From Sample to Signal: The Challenge of Isolation and Characterization
There is a significant lack of consensus regarding standardized protocols for EV isolation and characterization among researchers, representing a critical bottleneck in comparative studies of EVs with other molecular entities (Table 2). Despite numerous techniques being available, including ultracentrifugation [42], density gradient approaches [43], polymer-based precipitation [44], and size exclusion chromatography [45], methodological variations yield heterogeneous EV populations with differing purity profiles.
Similarly, characterization methods ranging from NTA [46], TEM [47], and flow cytometry to advanced techniques like fluorescence NTA [48] and ExoArc-SEC coupling [49] produce inconsistent results across laboratories. This methodological inconsistency impedes biomarker discovery efforts in lung cancer and COPD, where protein analysis workflows encompassing extraction, quantification [23], and profiling require rigorous standardization to establish clinically relevant markers [50].
Additional characterization includes lipid assays [51], functional assays, RNA expression analysis via qPCR [52], and Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) for binding kinetics [53]. On the other hand, most peripheral EVs are platelet-derived, creating significant challenges in developing EV-based diagnostic and prognostic markers. Platelets release abundant EVs during both normal physiology and sample processing, generating background noise that masks disease-specific signals. For reliable EV biomarker research, effective platelet removal protocols must be implemented [54]. Consequently, the field urgently requires guidelines establishing reproducible isolation and characterization protocols to facilitate meaningful cross-study comparisons and accelerate EV-based clinical applications.

Table 2.
EV isolation and characterization methods.
Table 2.
EV isolation and characterization methods.
| Method | Advantage | Disadvantage | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isolation | Ultracentrifugation | Large volumes processing | Time-consuming, costly equipment, non-EV contamination risk | [42] |
| Density graident centrifugatin | Higher purity | Labor and time intensive | [43] | |
| Immunoaffinity capture | High specificity | Potentia.antibody carryover, expensive | [44] | |
| Polymer precipitation | Simple | Contaminants, co-precipitation | ||
| Size exclusion chromatography | Gentle on EVs | Limited sample volume, EV dilution | [45] | |
| Microfluidic device | Rapid | Device.fabrication complexity; potential for clogging | [49] | |
| Characterization | NTA | Provides size distribution and concentration, relatively quick | Limited sensitivity for small EVs, affected by sample purity | [46] |
| Western blotting | Confirms presence of EVs marker | Labor and time consuming | [50] | |
| Flowcytometry | Multiparametric analysis | Limited sensitivity for small EVs | [50] | |
| TEM | Detailed, structural information visually | potential artifacts, not quantitative | [47] | |
| Dynamic light scattering | Quick | Less accurate for polydisperse samples | [55] | |
| SPR | Measures EV binding affinity | Complex data interpretation | [53] |
EVs—extracellular vesicles; NTA—nano-particle tracking analysis; TEM—transmission electron microscope.
5. Unlocking Cargos
Herein, we define small EVs possessing unique bioactive characteristics that allow the modulation of several cellular activities. The comprehensive protein composition of small EVs involves an array of proteins related to membrane transport, antigen capturing, and cell communication. Additionally, small EVs carry different species of RNAs such as messenger RNA (mRNA), microRNA (miRNA), and long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) that alter the expression of genes in each target cell. Furthermore, the small EVs comprise lipids to improve their structural stability due to their ability to bind with the cells of interest [56].
The identified biomarkers listed in Table 3 are diagnostically noted to be present in the context of lung cancer. However, the coexistence of these biomarkers may allow us to reasonably assume alterations to the downregulation or overexpression modifier. Their expression will be based on their relationship with lung cancer pathology; however, there is room for, and need for, further examination.

Table 3.
Genetic, protein, and lipid biomarkers of small EVs that were identified during lung cancer infection.
6. Bridging the Dual Treats: Expression Role in Comorbid Lung Cancer and COPD
While identifying disease-specific sEV markers in comorbid conditions remains difficult, some markers have been identified for various pathological states. The dominant pan-EV markers are tetraspanins (CD9, CD63, CD81), endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCR) components (TSG101, ALIX), and membrane proteins (flotillin-1, annexins). Furthermore, the conserved cargos across diverse cell-derived EVs are heat shock proteins (HSP70, HSP90) and cytoskeletal components (actin, tubulin), as demonstrated by the comparative analysis presented in Table 4. The presence of these markers facilitates the isolation and characterization of EVs, but their widespread presence is counterproductive when attempting to identify disease-specific vesicle populations. This highlights the need for further refined approaches to analyze the EV signatures of distinct diseases, especially with more complex pathological cases that have comorbidities [90].

Table 4.
Common EV markers during lung cancer and COPD.
7. Concluding the Promise of sEVs
The field of lung cancer sEV markers is developing quickly and has considerable prognostic and therapeutic prospects. The discovery of sEV-associated proteins, microRNA (miRNA), and DNA mutations elements enable non-invasive early diagnosis and treatment decisions. Yet, the application of these strategies in clinical practice needs to address standardization, secure large clinical studies, and resolve ethical issues.
The integration of sEV markers into general medical practice may improve the prognosis and quality of life of patients suffering both from lung cancer and COPD. We suggest the study of sEV markers during co-infections of COPD, allergies, and other inflammatory diseases to gain better insights and formulate new diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. To conclude, though the sEV markers in question are extremely promising, their clinical application is bound by the need for extensive proof of concept with supporting data. Their adoption and integration will reshape lung cancer management and care alongside other related diseases, ultimately improving patients’ health and quality of life.
Author Contributions
Y.A. conceptualized the review and drafted the manuscript. F.B. contributed to the literature review and critically revised the text. U.S. and F.B. provided insights on extracellular vesicle biology and contributed to review editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a PhD scholarship from the German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD).
Data Availability Statement
This article is a review and does not report any original data. All data referenced in this work are available through the cited sources.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- Luo, G.; Zhang, Y.; Rumgay, H.; Morgan, E.; Langselius, O.; Vignat, J.; Vignat, J.; Colombet, M.; Bray, F. Estimated worldwide variation and trends in incidence of lung cancer by histological subtype in 2022 and over time: A population-based study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2025, 13, 348–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Qin, Y.; Zhao, W.; Liang, Z.; Li, M.; Liu, D.; Bai, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, Y.; et al. International expert consensus on diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer complicated by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2023, 12, 1661–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessner, P.; Tessema, B.; Scholz, M.; Sack, U.; Boldt, A.; Kühnapfel, A.; Gessner, C. The influence of anti-cancer therapies on lymphocyte subpopulations of lung cancer patients. Front Immunol. 2023, 14, 1239097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figarol, S.; Delahaye, C.; Gence, R.; Doussine, A.; Cerapio, J.P.; Brachais, M.; Tardy, C.; Béry, N.; Asslan, R.; Colinge, J.; et al. Farnesyltransferase inhibition overcomes cancer adaptive resistance to targeted therapies. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Noia, V.; D’Aveni, A.; D’Argento, E.; Rossi, S.; Ghirardelli, P.; Bortolotti, L.; Vavassori, V.; Bria, E.; Ceresoli, G.L. Treating disease progression with osimertinib in EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer: Novel targeted agents and combination strategies. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Lu, L.; Deng, S.; Meng, J.; Wan, C.; Huang, J.; Sun, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wu, B.; Wu, G.; et al. USP7 targeting modulates anti-tumor immune response by reprogramming Tumor-associated Macrophages in Lung Cancer. Theranostics 2020, 10, 9332–9347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, F.; Li, K.; Jiao, K.; Hu, J.; Song, H.; Ma, Q.Y.; Wang, J. A new immune signature for survival prediction and immune checkpoint molecules in non-small cell lung cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1095313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaga, M.; Chorostowska-Wynimko, J.; Horváth, I.; Tammemagi, M.C.; Shitrit, D.; Eisenberg, V.H.; Liang, H.; Stav, D.; Levy Faber, D.; Jansen, M.; et al. Validation of Lung EpiCheck, a novel methylation-based blood assay, for the detection of lung cancer in European and Chinese high-risk individuals. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2002682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Liao, Z.; Deng, L.; Xu, L.; Tan, Y.; Liu, K.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y. High diagnostic value of miRNAs for NSCLC: Quantitative analysis for both single and combined miRNAs in lung cancer. Ann. Med. 2021, 53, 2178–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huda, M.N.; Nafiujjaman, M.; Deaguero, I.G.; Okonkwo, J.; Hill, M.L.; Kim, T.; Nurunnabi, M. Potential Use of Exosomes as Diagnostic Biomarkers and in Targeted Drug Delivery: Progress in Clinical and Preclinical Applications. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 2106–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnewies, M.; Roberts, E.W.; Kersten, K.; Chan, V.; Fearon, D.F.; Merad, M.; Coussens, L.M.; Gabrilovich, D.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S.; Hedrick, C.C.; et al. Understanding the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) for effective therapy. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, M.; Wang, W.; Gao, X.; Wu, L.; Jin, P.; Wu, H.; Yu, J.; Meng, X. Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Patients With EGFR Mutated NSCLC and Potential Risk Factors Associated With Prognosis: A Single Institution Experience. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 832419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.S.; Mellman, I. Elements of cancer immunity and the cancer-immune set point. Nature 2017, 541, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manevski, M.; Devadoss, D.; Long, C.; Singh, S.P.; Nasser, M.W.; Borchert, G.M.; Nair, M.N.; Rahman, I.; Sopori, M.; Chand, H.S. Increased Expression of LASI lncRNA Regulates the Cigarette Smoke and COPD Associated Airway Inflammation and Mucous Cell Hyperplasia. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 803362. [Google Scholar]
- Guiedem, E.; Ikomey, G.M.; Nkenfou, C.; Walter, P.Y.E.; Mesembe, M.; Chegou, N.N.; Jacobs, G.B.; Okomo Assoumou, M.C. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): Neutrophils, macrophages and lymphocytes in patients with anterior tuberculosis compared to tobacco related COPD. BMC Res. Notes 2018, 11, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyraud, E.; Maurat, E.; Sac-Epée, J.M.; Henrot, P.; Zysman, M.; Esteves, P.; Trian, T.; Dupuy, J.W.; Leipold, A.; Saliba, A.E.; et al. Short-range interactions between fibrocytes and CD8+ T cells in COPD bronchial inflammatory response. Elife 2023, 12, RP85875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Sun, S.W.; Xiong, X.Z. From COPD to Lung Cancer: Mechanisms Linking, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prognosis. Int. J. COPD 2022, 17, 2603–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shaughnessy, M.; Sheils, O.; Baird, A.M. The Lung Microbiome in COPD and Lung Cancer: Exploring the Potential of Metal-Based Drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazourian, L.; Regis, S.M.; Pagura, E.J.; Price, L.L.; Gawlik, M.; Lamb, C.; Rieger-Christ, K.M.; Thedinger, W.B.; Sanayei, A.M.; Sanayei, A.M.; et al. Qualitative coronary artery calcification scores and risk of all cause, COPD and pneumonia hospital admission in a large CT lung cancer screening cohort. Respir. Med. 2021, 186, 106540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, H.H.; Niemann, D.; Munson-McGee, S.H. Association between asthma, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and lung cancer in the US population. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 20147–20158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, H.; Sohal, I.S.; Soto-Vargas, Z.; Byappanhalli, A.M.; Humphrey, S.E.; Kubo, H.; Kitdumrongthum, S.; Copeland, S.; Tian, F.; Chairoungdua, A.; et al. Extracellular vesicles released by non-small cell lung cancer cells drive invasion and permeability in non-tumorigenic lung epithelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 972. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, S.; Zheng, S.; Lu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Xu, H.; Huang, J.; Lei, Y.; Liu, C.; et al. Exosomal miR-375-3p breaks vascular barrier and promotes small cell lung cancer metastasis by targeting claudin-1. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 3155–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescitelli, R.; Lässer, C.; Jang, S.C.; Cvjetkovic, A.; Malmhäll, C.; Karimi, N.; Höög, J.L.; Johansson, I.; Fuchs, J.; Thorsell, A.; et al. Subpopulations of extracellular vesicles from human metastatic melanoma tissue identified by quantitative proteomics after optimized isolation. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 9, 1722433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolova, V.; Ludwig, A.K.; Hornung, S.; Rotan, O.; Horn, P.A.; Epple, M.; Giebel, B. Characterisation of exosomes derived from human cells by nanoparticle tracking analysis and scanning electron microscopy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 87, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzan, E.; Radu, C.M.; Tine, M.; Neri, T.; Biondini, D.; Semenzato, U.; Casara, A.; Balestro, E.; Simioni, P.; Celi, A.; et al. Microvesicles in bronchoalveolar lavage as a potential biomarker of COPD. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2021, 320, L241–L245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsergent, E.; Grisard, E.; Buchrieser, J.; Schwartz, O.; Théry, C.; Lavieu, G. Quantitative characterization of extracellular vesicle uptake and content delivery within mammalian cells. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Song, X.; Wang, N.; Xue, L.; Song, X.; Xie, L. Tumor-derived exosomal proteins as diagnostic biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chung, Y.; Tu, C.R.; Zhang, W.; Mu, X.; Wang, M.; Chan, G.C.; Leung, W.H.; Lau, Y.L.; et al. Tumor vaccine based on extracellular vesicles derived from γδ-T cells exerts dual antitumor activities. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2023, 12, e12360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Lu, M.; Ding, Q.; Chen, A.F.; Xiang, M.; Chen, S. iPSC-derived exosomes promote angiogenesis in naturally aged mice. Aging 2023, 15, 5854–5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, M.; Rajeswari, V.D. Critical Review on the Different Roles of Exosomes in TNBC and Exosomal-Mediated Delivery of microRNA/siRNA/lncRNA and Drug Targeting Signalling Pathways in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Molecules 2023, 28, 1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, T.; Liao, R. Exosomal Non-Coding RNAs: Novel Regulators of Macrophage-Linked Intercellular Communication in Lung Cancer and Inflammatory Lung Diseases. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koba, T.; Takeda, Y.; Narumi, R.; Shiromizu, T.; Nojima, Y.; Ito, M.; Kuroyama, M.; Futami, Y.; Takimoto, T.; Matsuki, T.; et al. Proteomics of serum extracellular vesicles identifies a novel copd biomarker, fibulin-3 from elastic fibres. ERJ Open Res. 2021, 7, 00658-2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.B.A.; Armitage, J.; Teo, T.H.; Ong, N.E.; Shin, H.; Moodley, Y.P. Elevated levels of circulating exosome in COPD patients are associated with systemic inflammation. Respir. Med. 2017, 132, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Ling, M.; Xue, J.; Dai, X.; Sun, Q.; Chen, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Liu, J.; Luo, F.; et al. Exosomal microRNA-21 derived from bronchial epithelial cells is involved in aberrant epithelium-fibroblast cross-talk in COPD induced by cigarette smoking. Theranostics 2018, 8, 5419–5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Farrell, H.E.; Bowman, R.V.; Fong, K.M.; Yang, I.A. Plasma extracellular vesicle mirnas can identify lung cancer, current smoking status, and stable copd. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, L.; Wu, Y.; Ou, Y.; Lu, H.; Yao, X. A novel diagnostic signature based on three circulating exosomal mircoRNAs for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, J.; Su, W.; Liu, L.; Rao, B.; Lin, M.; Feng, Y.; Qiu, F.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Identification of Three Circular RNA Cargoes in Serum Exosomes as Diagnostic Biomarkers of Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer in the Chinese Population. J. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 22, 1096–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Sun, W.; Shen, K.; Lv, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zhan, P.; Lv, T.; et al. Elevated exosome-derived miRNAs predict osimertinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisakane, K.; Seike, M.; Sugano, T.; Yoshikawa, A.; Matsuda, K.; Takano, N.; Takahashi, S.; Noro, R.; Gemma, A. Exosome-derived miR-210 involved in resistance to osimertinib and epithelial–mesenchymal transition in EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer cells. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 1690–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Puranik, N.; Yadav, D.; Lee, P.C.W. Lipid nanocarrier-based drug delivery systems: Therapeutic advances in the treatment of lung cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 2659–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuya, W.L.; Peyper, J.M.; Myen, T.T.; Anuar, N.D.; Anwar, A.; Gudimella, R.; Rutt, N.H.; Rosli, N.S.M.; Badri, N.H.; Rahman, T.N.A.; et al. Exosome autoantibody biomarkers for detection of lung cancer. Mil. Med. Res. 2024, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helwa, I.; Cai, J.; Drewry, M.D.; Zimmerman, A.; Dinkins, M.B.; Khaled, M.L.; Seremwe, M.; Dismuke, W.M.; Bieberich, E.; Stamer, W.D.; et al. A comparative study of serum exosome isolation using differential ultracentrifugation and three commercial reagents. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, S.L.; Allen, C.L.; Benjamin-Davalos, S.; Koroleva, M.; MacFarland, D.; Minderman, H.; Ernstoff, M.S. A Rapid Exosome Isolation Using Ultrafiltration and Size Exclusion Chromatography (REIUS) Method for Exosome Isolation from Melanoma Cell Lines. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2265, 289–304. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Bautista, A.; Torres-Acosta, M.A.; González-Valdez, J. Characterization and optimization of polymer-polymer aqueous two-phase systems for the isolation and purification of CaCo2 cell-derived exosomes. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0273243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, M.; Wu, J.; Zhu, J.; Lubman, D.M. Comparison of an Optimized Ultracentrifugation Method versus Size-Exclusion Chromatography for Isolation of Exosomes from Human Serum. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 3599–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auger, C.; Brunel, A.; Darbas, T.; Akil, H.; Perraud, A.; Bégaud, G.; Bessette, B.; Christou, N.; Verdier, M. Extracellular Vesicle Measurements with Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis: A Different Appreciation of Up and Down Secretion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Xue, H.; Chen, Q.; Yang, G. A method for extraction of exosomes from breast tumour cells and characterisation by transmission electron microscopy. J. Microsc. 2023, 292, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desgeorges, A.; Hollerweger, J.; Lassacher, T.; Rohde, E.; Helmbrecht, C.; Gimona, M. Differential fluorescence nanoparticle tracking analysis for enumeration of the extracellular vesicle content in mixed particulate solutions. Methods 2020, 177, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, S.Y.; Lok, W.W.; Goh, K.Y.; Ong, H.B.; Tay, H.M.; Su, C.; Kong, F.; Upadya, M.; Wang, W.; Radnaa, E.; et al. High-Throughput Microfluidic Extraction of Platelet-free Plasma for MicroRNA and Extracellular Vesicle Analysis. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 6623–6637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J.A.; Goberdhan, D.C.I.; O’Driscoll, L.; Buzas, E.I.; Blenkiron, C.; Bussolati, B.; Cai, H.; Di Vizio, D.; Driedonks, T.A.P.; Erdbrügger, U.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biadglegne, F.; Schmidt, J.R.; Engel, K.M.; Lehmann, J.; Lehmann, R.T.; Reinert, A.; König, B.; Schiller, J.; Kalkhof, S.; Sack, U. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Affects Protein and Lipid Content of Circulating Exosomes in Infected Patients Depending on Tuberculosis Disease State. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, H.; Yang, W.; Li, J. Exosomal Circular RNA RNA-seq Profiling and the Carcinogenic Role of Exosomal circ-CYP24A1 in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 675842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalczyk, A.; Gajda-Walczak, A.; Ruzycka-Ayoush, M.; Targonska, A.; Mosieniak, G.; Glogowski, M.; Cieckiewicz, A.S.; Prochorec-Sobieszek, M.; Bamburowicz-Klimkowska, M.; Nowicka, A.M.; et al. Parallel SPR and QCM-D Quantitative Analysis of CD9, CD63, and CD81 Tetraspanins: A Simple and Sensitive Way to Determine the Concentration of Extracellular Vesicles Isolated from Human Lung Cancer Cells. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 9520–9530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracht, J.W.P.; Los, M.; van Eijndhoven, M.A.J.; Bettin, B.; van der Pol, E.; Pegtel, D.M.; Nieuwland, R. Platelet removal from human blood plasma improves detection of extracellular vesicle-associated miRNA. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2023, 12, e12302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, T.S.; Ahn, Y.; Im, Y.J.; Kim, S.S.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, J.; Choi, Y.; Lee, D.; Kang, E.; Jin, G.; et al. The characterization of exosomes from fibrosarcoma cell and the useful usage of Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) for their evaluation. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0231994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginini, L.; Billan, S.; Fridman, E.; Gil, Z. Insight into Extracellular Vesicle-Cell Communication: From Cell Recognition to Intracellular Fate. Cells. 2022, 11, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yu, Z.; Yuan, S.; Xie, W.; Li, C.; Hu, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Wu, N.; Wu, L.; Bai, L.; et al. Circulating exosomal microRNAs as prognostic biomarkers for non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 13048–13058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanin, A.A.I.; Ramos, K.S. Circulating Exosomal miRNA Profiles in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers. Cells 2024, 13, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdipourbozorgbaghi, M.; Vancura, A.; Radpour, R.; Haefliger, S. Circulating miRNA panels as a novel non-invasive diagnostic, prognostic, and potential predictive biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Br. J. Cancer 2024, 131, 1350–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontis, F.; Roz, L.; Mensah, M.; Segale, M.; Moro, M.; Bertolini, G.; Petraroia, I.; Centonze, G.; Ferretti, A.M.; Suatoni, P.; et al. Circulating extracellular vesicles from individuals at high-risk of lung cancer induce pro-tumorigenic conversion of stromal cells through transfer of miR-126 and miR-320. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Park, H.; Choi, Y.J.; Im, K.; Lee, C.W.; Kim, D.S.; Pack, C.G.; Kim, H.Y.; Choi, C.M.; Lee, J.C.; et al. Identification of exosomal microRNA panel as diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for small cell lung cancer. Biomark. Res. 2023, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Liu, B.; Li, R.; Wang, F.; Wang, N.; Zhang, M.; Bai, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, L.; Han, D.; et al. miR-146a-5p Plays an Oncogenic Role in NSCLC via Suppression of TRAF6. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chen, J.; Fan, M. Plasma Exosomal miRNAs as Response Biomarkers of Immunotherapy in Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2023, 117, e70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Xin, X.; Cao, X.; Nasifu, L.; Nie, Z.; He, B. The diagnostic and prognostic value of exosomal microRNAs in lung cancer: A systematic review. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2024, 26, 1921–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yin, Z.; Lu, P.; Ma, Y.; Luo, B.; Xiang, L.; Zhang, W.; He, Y.; Liang, X. Lung carcinoma cells secrete exosomal malat1 to inhibit dendritic cell phagocytosis, inflammatory response, costimulatory molecule expression and promote dendritic cell autophagy via AKT/MTOR pathway. Onco. Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 10693–10705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, L.; Deng, G.; Ding, Y.; Bi, K.; Jin, H.; Shu, J.; Yang, J.; Deng, H.; Wang, Z.; et al. Exosomal HOTAIR promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of lung cancer by sponging miR-203. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 1265–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, L.; Zhu, T.; Lv, B.; An, T.; Zhang, Q.; Shang, Y.; Shang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Q. Exosomal LncRNA RP5-977B1 as a novel minimally invasive biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 27, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, D.; Wang, C.; Yang, Z.; Han, F.; Zhan, H. Clinical Significance of Serum-Derived Exosomal LINC00917 in Patients With Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 728763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiller, C.; Viktorsson, K.; Gomero, E.P.; Hååg, P.; Arapi, V.; Kaminskyy, V.O.; Kamali, C.; De Petris, L.; Ekman, S.; Lewensohn, R.; et al. Detection of tumor-associated membrane receptors on extracellular vesicles from non-small cell lung cancer patients via immuno-pcr. Cancers 2021, 13, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Yin, Z.; Yang, L.; Fan, J.; Xu, J.; Jin, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhang, D.; Yang, G. Smoking induced extracellular vesicles release and their distinct properties in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 3435–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöne, N.; Kemper, M.; Menck, K.; Evers, G.; Krekeler, C.; Schulze, A.B.; Carter-Cooper, B.A.; Lapidus, R.; Peleg, A.; Arroyo-Hernández, M.; et al. PD-L1 on large extracellular vesicles is a predictive biomarker for therapy response in tissue PD-L1-low and -negative patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Abudula, M.; Li, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y. Icotinib-resistant HCC827 cells produce exosomes with mRNA MET oncogenes and mediate the migration and invasion of NSCLC. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanteloup, G.; Cordonnier, M.; Isambert, N.; Bertaut, A.; Hervieu, A.; Hennequin, A.; Luu, M.; Zanetta, S.; Coudert, B.; Bengrine, L.; et al. Monitoring HSP70 exosomes in cancer patients’ follow up: A clinical prospective pilot study. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 9, 1766192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, X.; Guo, C.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, K.; Luo, Y.; An, M.; Lin, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Gao, X.; et al. SUMOylation-triggered ALIX activation modulates extracellular vesicles circTLCD4-RWDD3 to promote lymphatic metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, K.; Siampour, H.; Allahverdi, A.; Moshaii, A.; Naderi-Manesh, H. Lung Cancer Cell-Derived Exosome Detection Using Electrochemical Approach towards Early Cancer Screening. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, H.M.; An, H.J.; Jung, J.J.; Song, D.H. The prognostic significance of cd63 expression in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Pol. J. Pathol. 2019, 70, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Li, T.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Y. Label-Free Multiplex Profiling of Exosomal Proteins with a Deep Learning-Driven 3D Surround-Enhancing SERS Platform for Early Cancer Diagnosis. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 6794–6801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, X.; Li, N.; Lou, C.; Huang, Y.; Tian, D.; Shen, Y.; et al. Evaluation of EpCAM-specific exosomal lncRNAs as potential diagnostic biomarkers for lung cancer using droplet digital PCR. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 100, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, K.R.; Paulsen, B.S.; Bæk, R.; Varming, K.; Sorensen, B.S.; Jørgensen, M.M. Exosomal proteins as potential diagnostic markers in advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 26659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Chen, J.; Feng, C.; Wu, W.; Wang, Y.; Tong, J.; Zhou, D. Preferential localization of MUC1 glycoprotein in exosomes secreted by non-small cell lung carcinoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikova, S.E.; Soloveva, N.A.; Farafonova, T.E.; Tikhonova, O.V.; Liao, P.C.; Zgoda, V.G. Proteomic signature of extracellular vesicles for lung cancer recognition. Molecules 2021, 26, 6145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.S.; Faruque, H.; Al Kim, J.H.; Kim, K.J.; Choi, J.E.; Kim, B.A.; Kim, B.; Kim, Y.J.; Woo, M.H.; Park, J.Y.; et al. Cd5l as an extracellular vesicle-derived biomarker for liquid biopsy of lung cancer. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, S.; Zhu, R.; Li, H.; Han, Q.; Zhao, R.C. Lung tumor exosomes induce a pro-inflammatory phenotype in mesenchymal stem cells via NFκB-TLR signaling pathway. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.W.M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y.; Kang, W.Y.; Arnold, S.; Higashi, R.M.; Liu, J.; Lane, A.N. Exosomal lipids for classifying early and late stage non-small cell lung cancer. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1037, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolarz, M.; Kurczyk, A.; Jelonek, K.; Żyła, J.; Mielańczyk, Ł.; Sitkiewicz, M.; Pietrowska, M.; Polańska, J.; Rzyman, W.; Widłak, P. The lipid composition of serum-derived small extracellular vesicles in participants of a lung cancer screening study. Cancers 2021, 13, 3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machala, M.; Slavík, J.; Kováč, O.; Procházková, J.; Pěnčíková, K.; Pařenicová, M.; Straková, N.; Kotouček, J.; Kulich, P.; Mollerup, S.; et al. Changes in sphingolipid profile of benzo[a]pyrene-transformed human bronchial epithelial cells are reflected in the altered composition of sphingolipids in their exosomes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, M.; Shenoy, G.N.; Loyall, J.L.; Gray, B.D.; Bapardekar, M.; Conway, A.; Minderman, H.; Kelleher, R.J., Jr.; Carreno, B.M.; Linette, G.; et al. Novel phosphatidylserine-binding molecule enhances antitumor T-cell responses by targeting immunosuppressive exosomes in human tumor microenvironments. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e003148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.M.; Zou, Y.Q.; Lin, J.; Huang, B.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, W.M.; Min, Q.H.; et al. Identification of differential expressed PE exosomal miRNA in lung adenocarcinoma, tuberculosis, and other benign lesions. Medicine 2017, 96, e8361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Kang, M.H.; Jeyaraj, M.; Kim, J.H. Platinum nanoparticles enhance exosome release in human lung epithelial adenocarcinoma cancer cells (A549): Oxidative stress and the ceramide pathway are key players. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 515–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; Gan, J.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Song, T.; Yang, Y.; Ji, G.; Li, W. Proteomic Analysis of Plasma Exosomes Enables the Identification of Lung Cancer in Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Thorac. Cancer 2025, 16, e15517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petraroia, I.; Ghidotti, P.; Bertolini, G.; Pontis, F.; Roz, L.; Balsamo, M.; Suatoni, P.; Pastorino, U.; Ferretti, A.M.; Sozzi, G.; et al. Extracellular vesicles from subjects with COPD modulate cancer initiating cells phenotype through HIF-1α shuttling. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).