“Seeing Is Believing”: Additive Utility of 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. PET/CT Imaging
2.2. MRI
2.3. Histopathology
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fütterer, J.J.; Briganti, A.; De Visschere, P.; Emberton, M.; Giannarini, G.; Kirkham, A.; Taneja, S.S.; Thoeny, H.; Villeirs, G.; Villers, A. Can Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer Be Detected with Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging? A Systematic Review of the Literature. Eur. Urol. 2015, 68, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, H.U.; Bosaily, A.E.-S.; Brown, L.C.; Gabe, R.; Kaplan, R.; Parmar, M.K.; Collaco-Moraes, Y.; Ward, K.; Hindley, R.G.; Freeman, A.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of multi-parametric MRI and TRUS biopsy in prostate cancer (PROMIS): A paired validating confirmatory study. Lancet 2017, 389, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasivisvanathan, V.; Rannikko, A.S.; Borghi, M.; Panebianco, V.; Mynderse, L.A.; Vaarala, M.H.; Briganti, A.; Budäus, L.; Hellawell, G.; Hindley, R.G.; et al. MRI-Targeted or Standard Biopsy for Prostate-Cancer Diagnosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1767–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woythal, N.; Arsenic, R.; Kempkensteffen, C.; Miller, K.; Janssen, J.-C.; Huang, K.; Makowski, M.R.; Brenner, W.; Prasad, V. Immunohistochemical Validation of PSMA Expression Measured by 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT in Primary Prostate Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afshar-Oromieh, A.; Malcher, A.; Eder, M.; Eisenhut, M.; Linhart, H.G.; Hadaschik, B.A.; Holland-Letz, T.; Giesel, F.L.; Kratochwil, C.; Haufe, S.; et al. PET imaging with a [68Ga]gallium-labelled PSMA ligand for the diagnosis of prostate cancer: Biodistribution in humans and first evaluation of tumour lesions. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2013, 40, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, K.M.; So, W.Z.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, A.; Yap DW, T.; Takwoingi, Y.; Tay, K.J.; Tuan, J.; Thang, S.P.; Lam, W.; et al. Head-to-head Comparison of the Diagnostic Accuracy of Prostate-specific Membrane Antigen Positron Emission Tomography and Conventional Imaging Modalities for Initial Staging of Intermediate- to High-risk Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Eur. Urol. 2023, 84, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fendler, W.P.; Eiber, M.; Beheshti, M.; Bomanji, J.; Ceci, F.; Cho, S.; Giesel, F.; Haberkorn, U.; Hope, T.A.; Kopka, K.; et al. 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT: Joint EANM and SNMMI procedure guideline for prostate cancer imaging: Version 1.0. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 44, 1014–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmett, L.; Buteau, J.; Papa, N.; Moon, D.; Thompson, J.; Roberts, M.J.; Rasiah, K.; Pattison, D.A.; Yaxley, J.; Thomas, P.; et al. The Additive Diagnostic Value of Prostate-specific Membrane Antigen Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography to Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging Triage in the Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer (PRIMARY): A Prospective Multicentre Study. Eur. Urol. 2021, 80, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
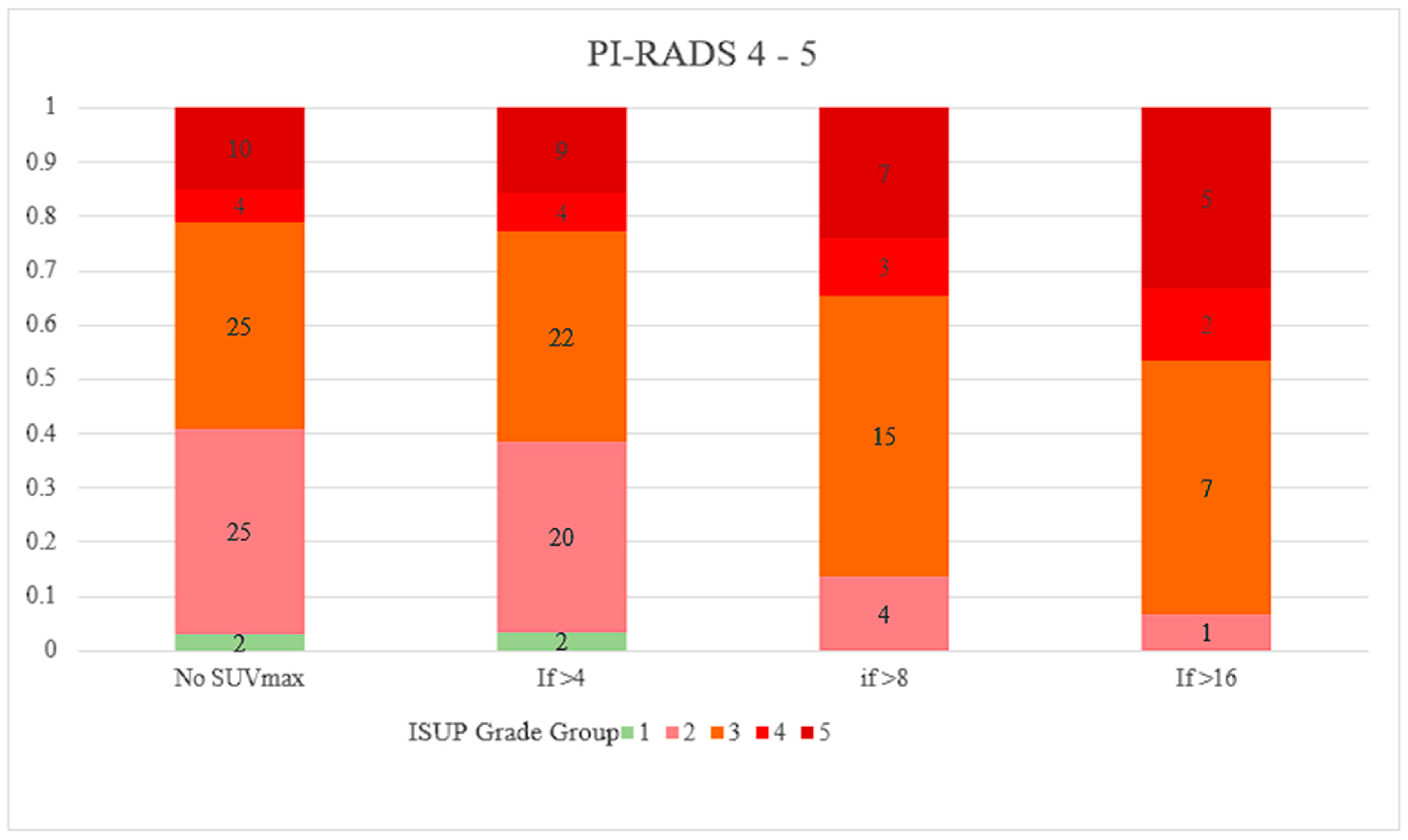
- Ptasznik, G.; Papa, N.; Kelly, B.D.; Thompson, J.; Stricker, P.; Roberts, M.J.; Hofman, M.S.; Buteau, J.; Murphy, D.G.; Emmett, L.; et al. High prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) positron emission tomography (PET) maximum standardized uptake value in men with PI-RADS score 4 or 5 confers a high probability of significant prostate cancer. BJU Int. 2022, 130, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, J.M.; Wiegand, B.; Hadaschik, B.; Herrmann, K.; Kleesiek, J. Virtual Biopsy: Just an AI Software or a Medical Procedure? J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 511–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasivisvanathan, V.; Emberton, M.; Moore, C.M. There Is No Longer a Role for Systematic Biopsies in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis. Eur. Urol. Open Sci. 2022, 38, 12–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljungberg, B.; Albiges, L.; Abu-Ghanem, Y.; Bedke, J.; Capitanio, U.; Dabestani, S.; Fernández-Pello, S.; Giles, R.H.; Hofmann, F.; Hora, M.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma: The 2022 Update. Eur. Urol. 2022, 82, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.L.; Papa, N.; Hanegbi, U.; Snow, R.; Grummet, J.; Mann, S.; Cuthbertson, A.; Frydenberg, M.; Moon, D. Predictors of erectile dysfunction after transperineal template prostate biopsy. Investig. Clin. Urol. 2021, 62, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.S.H.; Goh, C.X.Y.; Koh, Y.S.; Li, Y.; Tuan, J.K.L.; Chua, E.T.; Tan, T.W.K.; Wang, M.L.C.; Lee, L.S.; Tay, K.J.; et al. 68Gallium-labelled PSMA-PET/CT as a diagnostic and clinical decision-making tool in Asian prostate cancer patients following prostatectomy. Cancer Biol. Med. 2019, 16, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Lee, A.; Yang, X.Y.; Law, Y.M.; Huang, H.H.; Lau, W.K.; Lee, L.S.; Ho, H.S.; Cheng, C.W.; Yuen, J.S.; et al. External validation and comparison of magnetic resonance imaging-based predictive models for clinically significant prostate cancer. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2021, 39, e1–e783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barentsz, J.O.; Weinreb, J.C.; Verma, S.; Thoeny, H.C.; Tempany, C.M.; Shtern, F.; Padhani, A.R.; Margolis, D.; Macura, K.J.; Haider, M.A.; et al. Synopsis of the PI-RADS v2 Guidelines for Multiparametric Prostate Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Recommendations for Use. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paner, G.P.; Srigley, J.R.; Pettus, J.; Giannico, G.A.; Sirintrapun, J.; Harik, L.R. Protocol for the Examination of Radical Prostatectomy Specimens From Patients with Carcinoma of the Prostate Gland. Coll. Am. Pathol. 2021, 8–10. Available online: https://documents.cap.org/protocols/Prostate_4.2.0.1.REL_CAPCP.pdf (accessed on 31 July 2023).
- Scheltema, M.J.; Tay, K.J.; Postema, A.W.; de Bruin, D.M.; Feller, J.; Futterer, J.J.; George, A.K.; Gupta, R.T.; Kahmann, F.; Kastner, C.; et al. Utilization of multiparametric prostate magnetic resonance imaging in clinical practice and focal therapy: Report from a Delphi consensus project. World J. Urol. 2017, 35, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, P.J.; Emmett, L.; Ho, B.; Delprado, W.; Ting, F.; Nguyen, Q.; Stricker, P.D. Prospective evaluation of 68Gallium-prostate-specific membrane antigen positron emission tomography/computed tomography for preoperative lymph node staging in prostate cancer. BJU Int. 2017, 119, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottet, N.; van den Bergh, R.C.N.; Briers, E.; Van den Broeck, T.; Cumberbatch, M.G.; De Santis, M.; Fanti, S.; Fossati, N.; Gandaglia, G.; Gillessen, S.; et al. EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer-2020 Update. Part 1: Screening, Diagnosis, and Local Treatment with Curative Intent. Eur. Urol. 2021, 79, 243–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, B.; Parry, M.G.; Sujenthiran, A.; Nossiter, J.; Cowling, T.E.; Aggarwal, A.; Cathcart, P.; Payne, H.; van der Meulen, J.; Clarke, N. Comparison of complications after transrectal and transperineal prostate biopsy: A national population-based study. BJU Int. 2020, 126, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doblhammer, S.; Kinger, P.; Starmuehler, M.; Muschitz, C.; Schima, W.; Susani, M.; Baierl, A.; Broessner, C. A comprehensive comparison between mpMRI of the prostate, MR-US fusion biopsy and whole mount histopathology. World J. Urol. 2023, 41, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzgreve, A.; Unterrainer, M.; Calais, J.; Adams, T.; Oprea-Lager, D.E.; Goffin, K.; Lopci, E.; Unterrainer, L.M.; Kramer KK, M.; Schmidt-Hegemann, N.-S.; et al. Is PSMA PET/CT cost-effective for the primary staging in prostate cancer? First results for European countries and the USA based on the proPSMA trial. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2023, 50, 3750–3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, R.; Jeet, V.; Sharma, R.; Hoyle, M.; Parkinson, B. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA) Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography (PET/CT) for the Primary Staging of Prostate Cancer in Australia. Pharmacoeconomics 2022, 40, 807–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Sar, E.C.A.; Keusters, W.R.; van Kalmthout, L.W.M.; Braat, A.J.A.T.; de Keizer, B.; Frederix, G.W.J.; Kooistra, A.; Lavalaye, J.; Lam, M.G.E.H.; van Melick, H.H.E. Cost-effectiveness of the implementation of [68Ga]Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT at initial prostate cancer staging. Insights Imaging 2022, 13, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ménard, C.; Young, S.; Zukotynski, K.; Hamilton, R.J.; Bénard, F.; Yip, S.; McCabe, C.; Saad, F.; Brundage, M.; Nitulescu, R.; et al. PSMA PET/CT guided intensification of therapy in patients at risk of advanced prostate cancer (PATRON): A pragmatic phase III randomized controlled trial. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, L.G.; Elliott, T.M.; Joshi, A.; Williams, E.D.; Vela, I. Exploratory cost-effectiveness analysis of 68Gallium-PSMA PET/MRI-based imaging in patients with biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2020, 37, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouvière, O.; Crouzet, S. Prostate Cancer Diagnosis Without Histological Proof: Is Treating Images Reasonable? Eur. Urol. Open Sci. 2022, 46, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmett, L.; Papa, N.; Buteau, J.; Ho, B.; Liu, V.; Roberts, M.; Thompson, J.; Moon, D.; Sheehan-Dare, G.; Alghazo, O.; et al. The PRIMARY Score: Using Intraprostatic 68Ga-PSMA PET/CT Patterns to Optimize Prostate Cancer Diagnosis. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 1644–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmett, L.; Papa, N.; Counter, W.; Calais, J.; Barbato, F.; Burger, I.; Eiber, M.; Roberts, M.J.; Agrawal, S.; Franklin, A.; et al. Reproducibility and Accuracy of the PRIMARY Score on PSMA PET and of PI-RADS on Multiparametric MRI for Prostate Cancer Diagnosis Within a Real-World Database. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 2024, 65, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Overall | ISUP Grade Group ≥ 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Patients | 42 | 42 | |
| Age, year (IQR) | 69 (65.8–71.3) | " | |
| PSA, ng/mL (IQR) | 12.0 (6.08–24.3) | " | |
| PV, mL (IQR) | 46 (31.9–58.0) | " | |
| PSA Density, ng/mL/mL (IQR) | 0.253 (0.170–0.670) | " | |
| Number of Lesions | 122 | 92 | |
| mpMRI, n (%) | 122 | 92 | |
| Negative | 3 (2.5) | 2 (2.2) | |
| PI-RADS 3 | 18 (14.8) | 7 (7.6) | |
| PI-RADS 4 | 65 (53.3) | 48 (52.2) | |
| PI-RADS 5 | 36 (29.5) | 35 (38.0) | |
| 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT, n (%) | 122 | 92 | |
| Negative | 42 (34.4) | 20 (21.7) | |
| Positive | 80 (65.6) | 72 (78.3) | |
| SUVmax | 4.45 (1.88–8.28) | 5.75 (2.50–11.2) | |
| Histology, n (%) | 122 | 92 | |
| Nil cancer | 22 (18.0) | " | |
| 3 + 3 | 8 (6.6) | " | |
| 3 + 4 | 45 (36.9) | 45 (48.9) | |
| 4 + 3 | 28 (23.0) | 28 (30.4) | |
| ≥4 + 4 | 19 (15.6) | 19 (20.7) | |
| mpMRI 4–5 | 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT | mpMRI 4–5 + 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity, % | 90.2 (83.1–95.2) | 78.5 (69.4–86.0) | 74.2 (64.7–82.4) |
| Specificity, % | 40.0 (23.8–57.8) | 73.3 (56.0–86.8) | 83.3 (67.5–93.7) |
| PPV, % | 82.2 (74.0–88.8) | 90.1 (82.4–95.4) | 93.2 (86.0–97.5) |
| NPV, % | 57.1 (36.1–76.6) | 52.4 (37.5–67.0) | 51.0 (37.2–64.7) |
| AUC | 0.65 | 0.76 | 0.79 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chin, J.; Tan, Y.G.; Lee, A.; Ng, T.K.; Shi, R.; Tang, C.Y.L.; Thang, S.P.; Tuan, J.K.L.; Cheng, C.W.S.; Tay, K.J.; et al. “Seeing Is Believing”: Additive Utility of 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis. Cancers 2024, 16, 1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091777
Chin J, Tan YG, Lee A, Ng TK, Shi R, Tang CYL, Thang SP, Tuan JKL, Cheng CWS, Tay KJ, et al. “Seeing Is Believing”: Additive Utility of 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis. Cancers. 2024; 16(9):1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091777
Chicago/Turabian StyleChin, Joel, Yu Guang Tan, Alvin Lee, Tze Kiat Ng, Ruoyu Shi, Charlene Yu Lin Tang, Sue Ping Thang, Jeffrey Kit Loong Tuan, Christopher Wai Sam Cheng, Kae Jack Tay, and et al. 2024. "“Seeing Is Believing”: Additive Utility of 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis" Cancers 16, no. 9: 1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091777
APA StyleChin, J., Tan, Y. G., Lee, A., Ng, T. K., Shi, R., Tang, C. Y. L., Thang, S. P., Tuan, J. K. L., Cheng, C. W. S., Tay, K. J., Ho, H. S. S., Wang, H.-J., Chiu, P. K.-F., Teoh, J. Y.-C., Lam, W. W.-C., Law, Y. M., Yuen, J. S. P., & Chen, K. (2024). “Seeing Is Believing”: Additive Utility of 68Ga-PSMA-11 PET/CT in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis. Cancers, 16(9), 1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091777







