A Tumor-Specific Molecular Network Promotes Tumor Growth in Drosophila by Enforcing a Jun N-Terminal Kinase–Yorkie Feedforward Loop
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fly Stocks
2.2. Generation of Somatic Clones
2.3. Immunohistochemistry and Image Acquisition
2.4. Statistical Analyses
2.5. qRT-PCR
3. Results
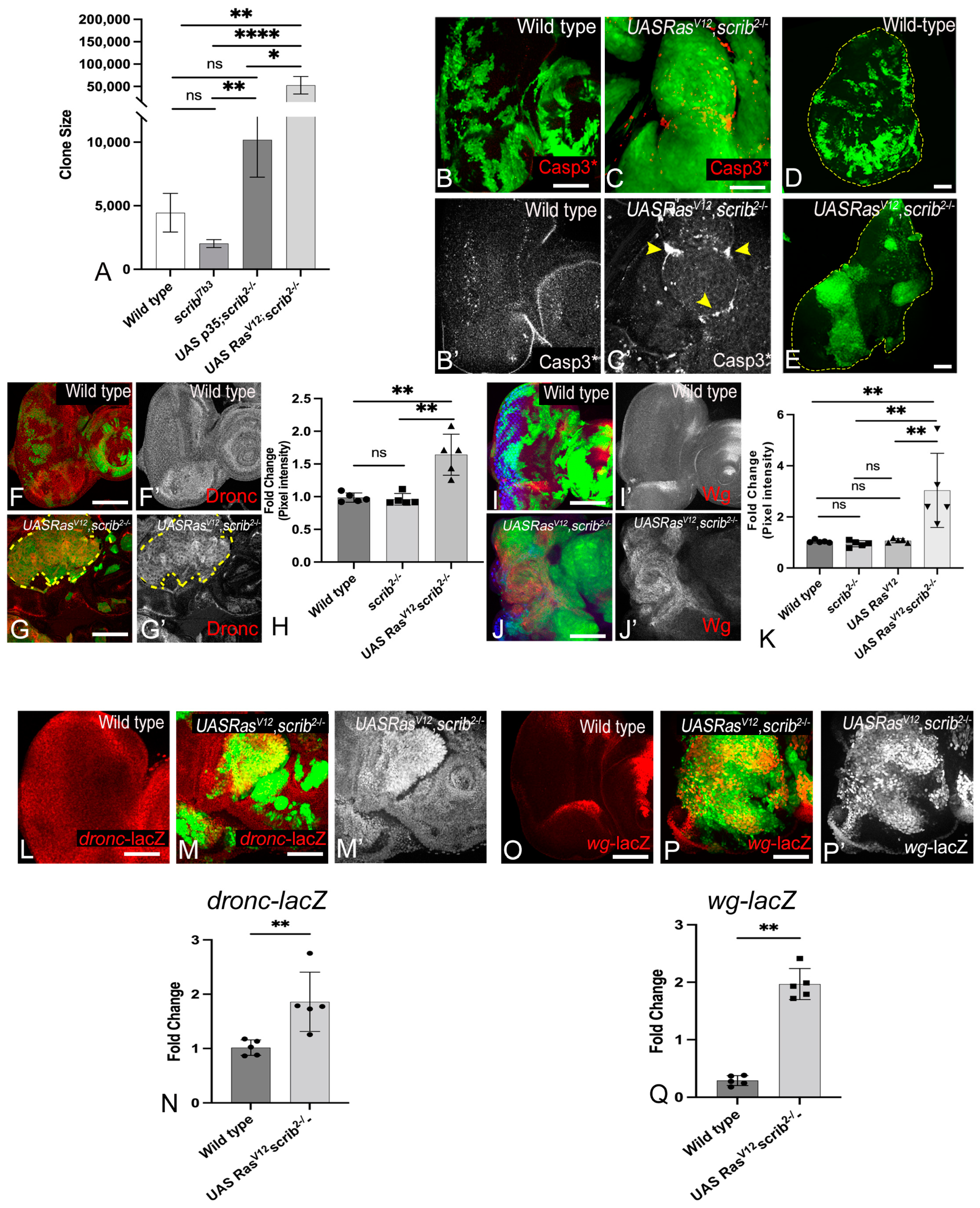
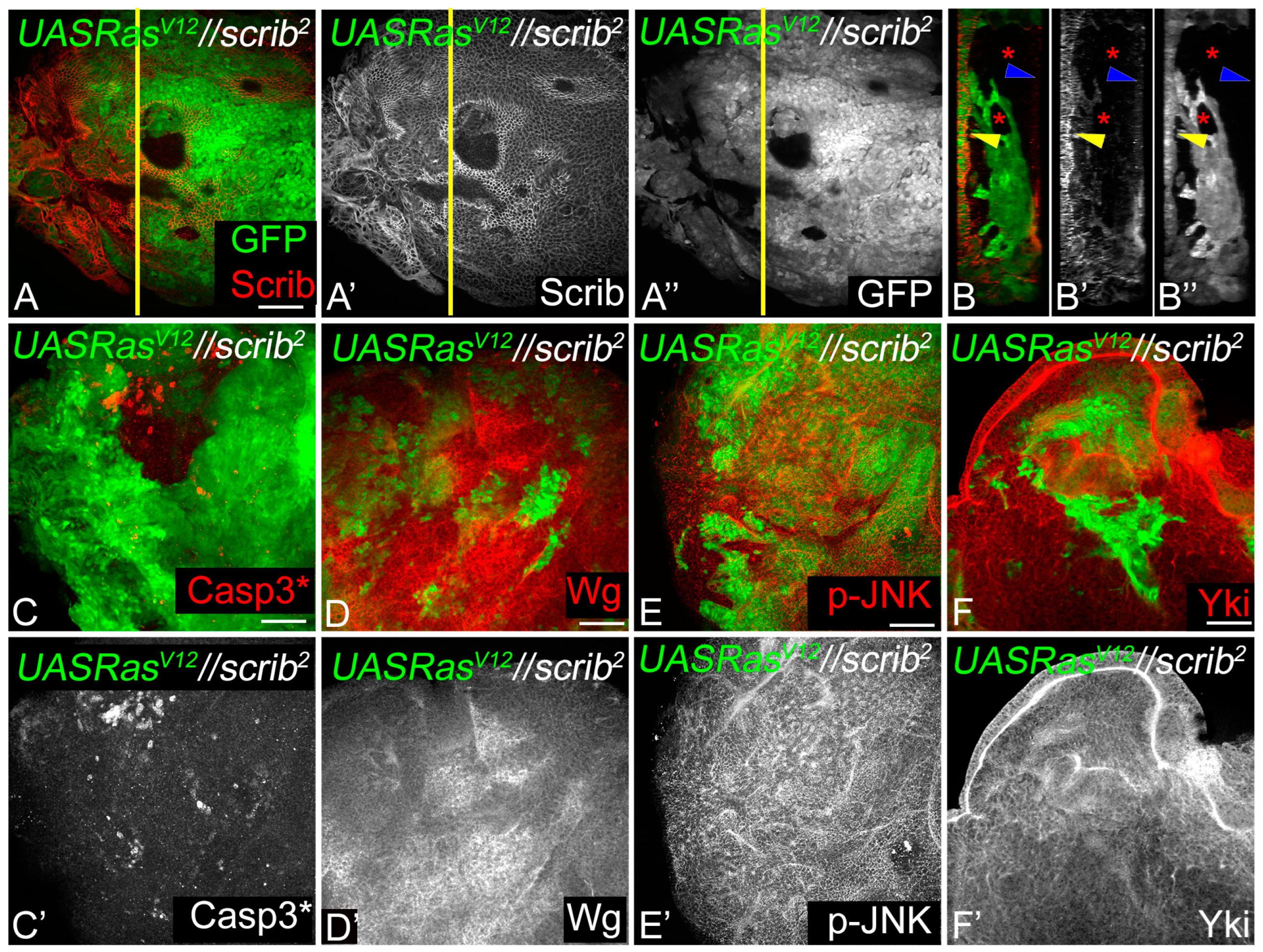
3.1. RasV12,scrib− Cells Grow Robustly and Induce JNK, Yki, Dronc, and Wg
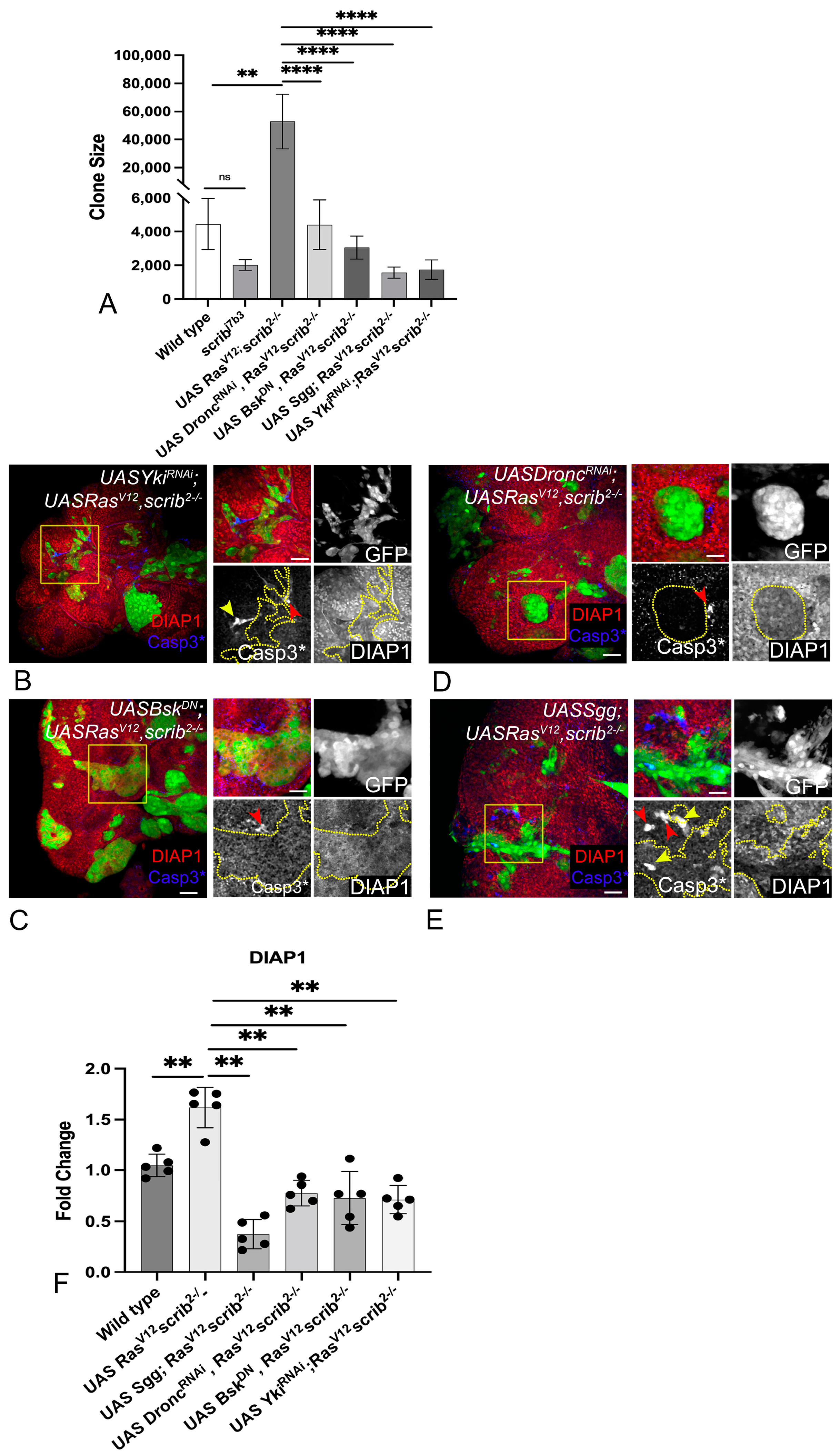
3.2. RasV12,scrib− Tumors Require JNK, Yki, Dronc, and Wg for Growth
3.3. Downregulation of JNK, Yki, Dronc, and Wg Impairs Cellular Fitness
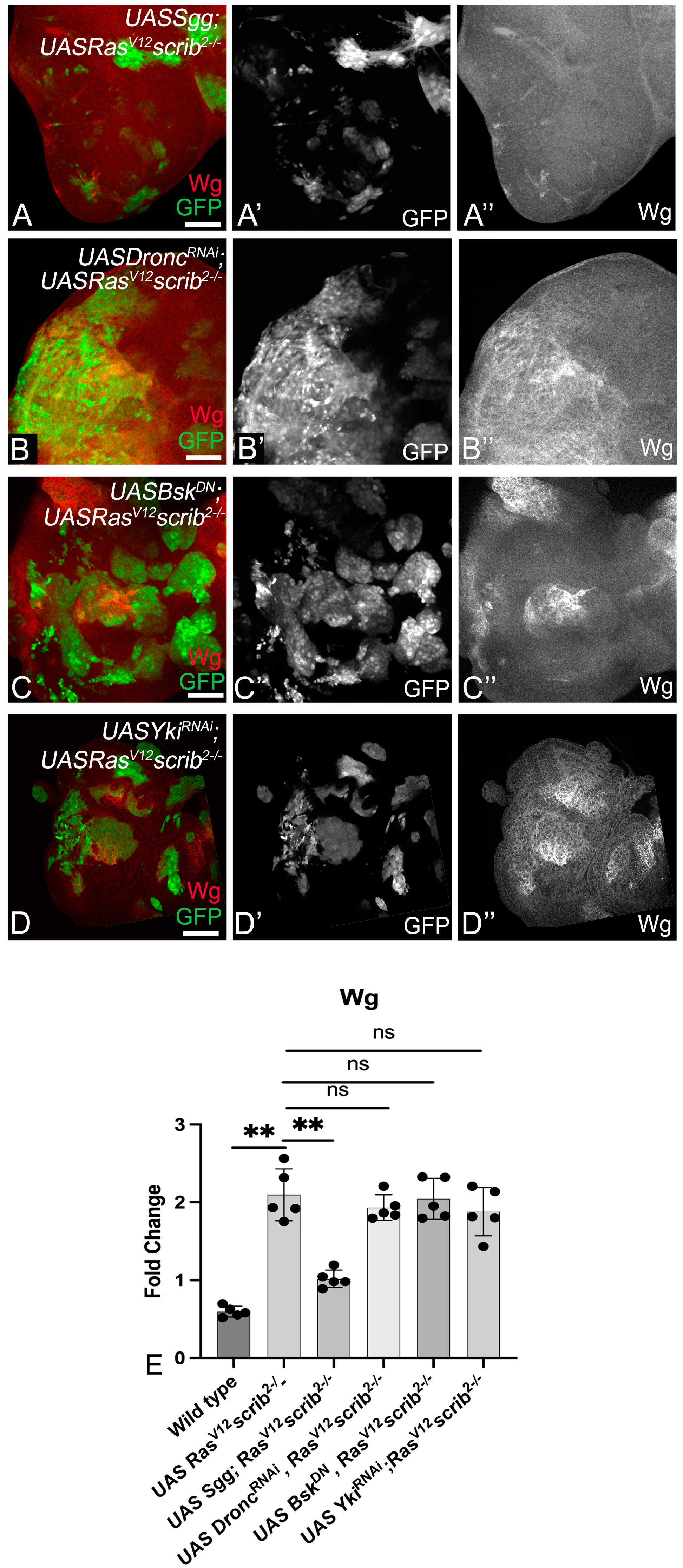
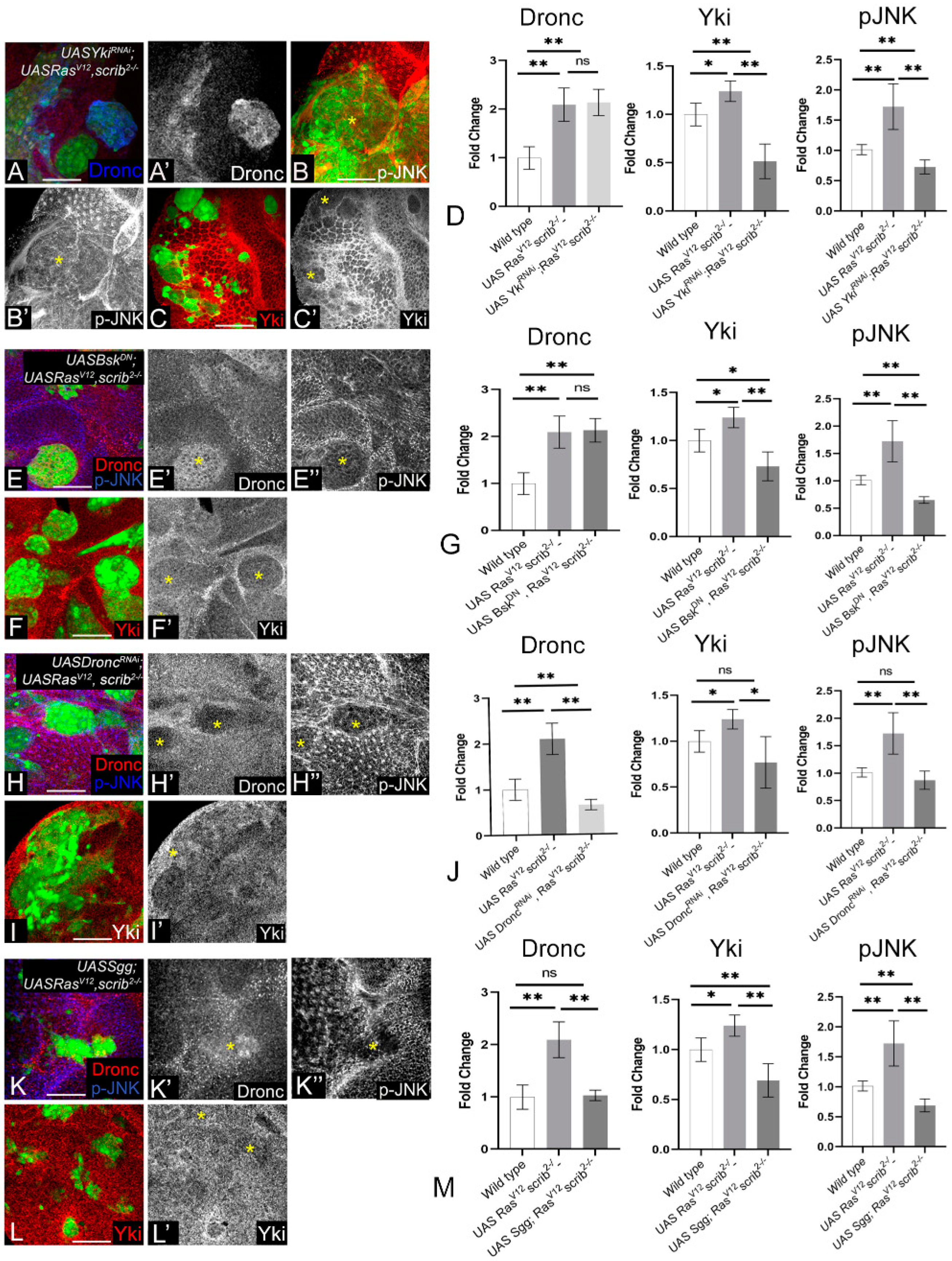
3.4. Wg, Dronc, JNK, and Yki Form a Molecular Network in RasV12,scrib− Tumors
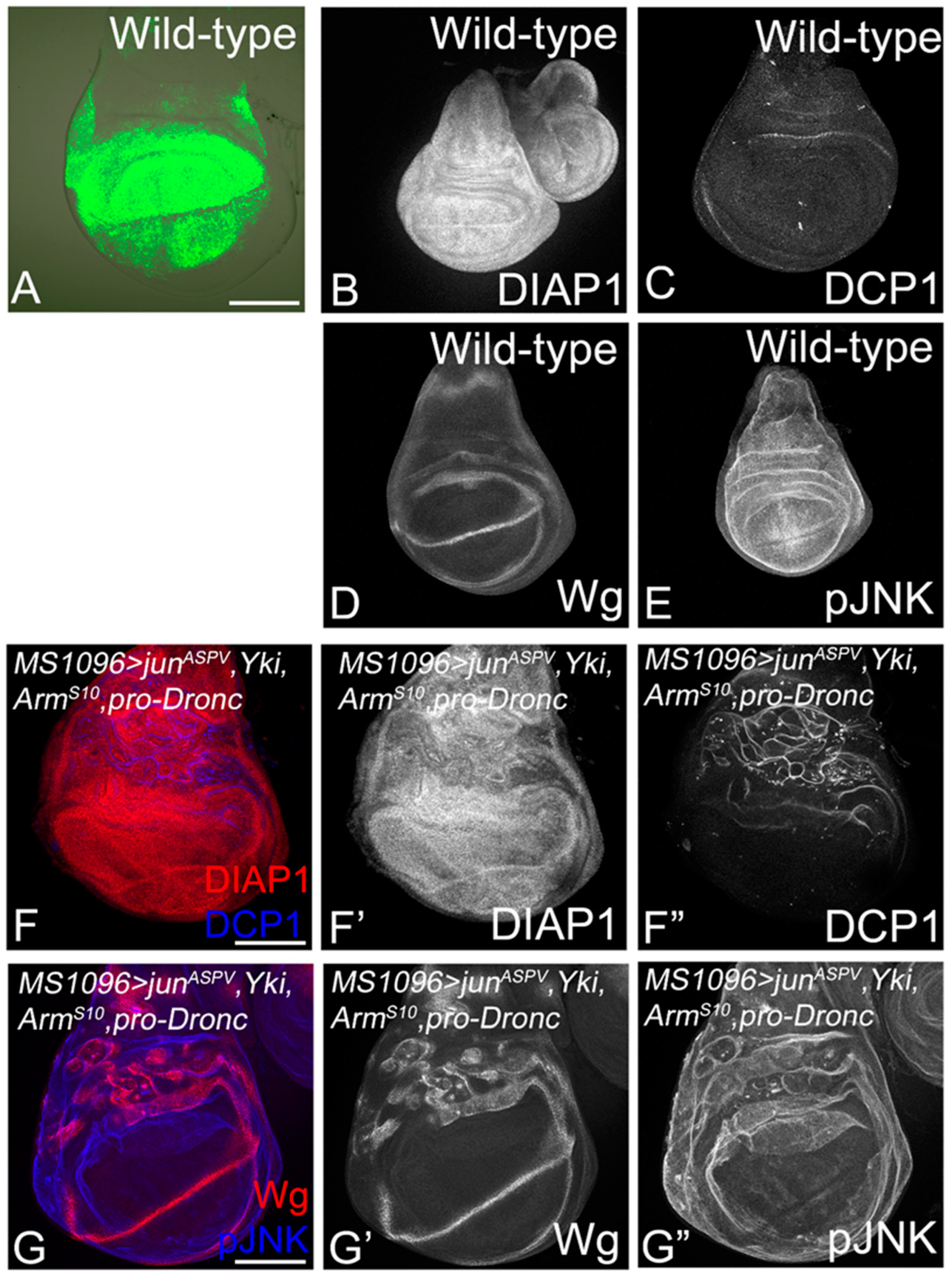
3.5. Cooperative Interactions Stimulate the Molecular Network and Tumor Growth
3.6. The Role of Apical–Basal Polarity in the Establishment of Tumor-Specific Molecular Networks
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blum, A.; Wang, P.; Zenklusen, J.C. SnapShot: TCGA-Analyzed Tumors. Cell 2018, 173, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertins, P.; Tang, L.C.; Krug, K.; Clark, D.J.; Gritsenko, M.A.; Chen, L.; Clauser, K.R.; Clauss, T.R.; Shah, P.; Gillette, M.A.; et al. Reproducible workflow for multiplexed deep-scale proteome and phosphoproteome analysis of tumor tissues by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 1632–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Vega, F.; Mina, M.; Armenia, J.; Chatila, W.K.; Luna, A.; La, K.C.; Dimitriadoy, S.; Liu, D.L.; Kantheti, H.S.; Saghafinia, S.; et al. Oncogenic Signaling Pathways in The Cancer Genome Atlas. Cell 2018, 173, 321–337.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, J.N.; Collisson, E.A.; Mills, G.B.; Shaw, K.R.M.; Ozenberger, B.A.; Ellrott, K.; Shmulevich, I.; Sander, C.; Stuart, J.M. The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, The Cancer Genome Atlas Pan-Cancer analysis project. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vreede, G.; Gerlach, S.U.; Bilder, D. Epithelial monitoring through ligand-receptor segregation ensures malignant cell elimination. Science 2022, 376, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelstein, B.; Papadopoulos, N.; Velculescu, V.E.; Zhou, S.; Diaz, L.A.; Kinzler, K.W. Cancer Genome Landscapes. Science 2013, 339, 1546–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torkamani, A.; Verkhivker, G.; Schork, N.J. Cancer driver mutations in protein kinase genes. Cancer Lett. 2009, 281, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagliarini, R.A.; Xu, T. A Genetic Screen in Drosophila for Metastatic Behavior. Science 2003, 302, 1227–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumby, A.M. Scribble mutants cooperate with oncogenic Ras or Notch to cause neoplastic overgrowth in Drosophila. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 5769–5779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Pastor-Pareja, J.C.; Xu, T. Interaction between RasV12 and scribbled clones induces tumour growth and invasion. Nature 2010, 463, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillard, C.; Reis, J.G.T.; Rusten, T.E. RasV12; scrib−/− Tumors: A Cooperative Oncogenesis Model Fueled by Tumor/Host Interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-L.; Schroeder, M.C.; Kango-Singh, M.; Tao, C.; Halder, G. Tumor suppression by cell competition through regulation of the Hippo pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Irvine, K.D. Ajuba Family Proteins Link JNK to Hippo Signaling. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, ra81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Irvine, K.D. Regulation of Hippo signaling by Jun kinase signaling during compensatory cell proliferation and regeneration, and in neoplastic tumors. Dev. Biol. 2011, 350, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerlach, S.U.; Eichenlaub, T.; Herranz, H. Yorkie and JNK Control Tumorigenesis in Drosophila Cells with Cytokinesis Failure. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 1491–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Wang, H.; Ji, J.; Xu, W.; Sun, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Xue, L. Hippo signaling promotes JNK-dependent cell migration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1934–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bejsovec, A. Wingless Signaling: A Genetic Journey from Morphogenesis to Metastasis. Genetics 2018, 208, 1311–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, K.D.; Harvey, K.F. Control of Organ Growth by Patterning and Hippo Signaling in Drosophila. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a019224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kockel, L.; Homsy, J.G.; Bohmann, D. Drosophila AP-1: Lessons from an invertebrate. Oncogene 2001, 20, 2347–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalini, S.; Dorstyn, L.; Dawar, S.; Kumar, S. Old, new and emerging functions of caspases. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 526–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzanne, M.; Steller, H. Shaping organisms with apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichenlaub, T.; Cohen, S.M.; Herranz, H. Cell competition drives the formation of metastatic tumors in a drosophila model of epithelial tumor formation. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morata, G.; Ballesteros-Arias, L. Cell competition, apoptosis and tumour development. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2015, 59, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baillon, L.; Basler, K. Reflections on cell competition. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 32, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Bergmann, A. Apoptosis-induced compensatory proliferation. The Cell is dead. Long live the Cell! Trends Cell Biol. 2008, 18, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajra, K.M.; Liu, J.R. Apoptosome dysfunction in human cancer. Apoptosis 2004, 9, 691–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, B.S.; Yoshida, E.; Johnston, L.A. Compensatory Proliferation in Drosophila Imaginal Discs Requires Dronc-Dependent p53 Activity. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, 1606–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, J.R.; Guo, M.; Hay, B.A. Compensatory proliferation induced by cell death in the Drosophila wing disc requires activity of the apical cell death caspase dronc in a nonapoptotic role. Curr. Biol. 2004, 14, 1262–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilder, D.; Perrimon, N. Localization of apical epithelial determinants by the basolateral PDZ protein Scribble. Nature 2000, 403, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakouros, D.; Daish, T.J.; Kumar, S. Ecdysone receptor directly binds the promoter of the Drosophila caspase dronc, regulating its expression in specific tissues. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 165, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boedigheimer, M.; Bryant, P.; Laughon, A. Expanded, a negative regulator of cell proliferation in drosophila, shows homology to the NF2 tumor suppressor. Mech. Dev. 1993, 44, 83–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Moses, K. Wingless and patched are negative regulators of the morphogenetic furrow and can affect tissue polarity in the developing Drosophila compound eye. Development 1995, 121, 2279–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, K.; Awano, W.; Suzuki, K.; Hiromi, Y.; Yamamoto, D. The Drosophila mushroom body is a quadruple structure of clonal units each of which contains a virtually identical set of neurones and glial cells. Development 1997, 124, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ren, F.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; Jiang, J. The TEAD/TEF family of transcription factor Scalloped mediates Hippo signaling in organ size control. Dev. Cell 2008, 14, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treier, M.; Bohmann, D.; Mlodzik, M. JUN cooperates with the ETS domain protein pointed to induce photoreceptor R7 fate in the Drosophila eye. Cell 1995, 83, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Wu, S.; Barrera, J.; Matthews, K.; Pan, D. The Hippo Signaling Pathway Coordinately Regulates Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis by Inactivating Yorkie, the Drosophila Homolog of YAP. Cell 2005, 122, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kango-Singh, M.; Nolo, R.; Tao, C.; Verstreken, P.; Hiesinger, P.R.; Bellen, H.J.; Halder, G. Shar-pei mediates cell proliferation arrest during imaginal disc growth in Drosophila. Development 2002, 129, 5719–5730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igaki, T.; Pagliarini, R.A.; Xu, T. Loss of Cell Polarity Drives Tumor Growth and Invasion through JNK Activation in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, B.A.; Wolff, T.; Rubin, G.M. Expression of baculovirus P35 prevents cell death in Drosophila. Development 1994, 120, 2121–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.-P.; Fletcher, A.G.; Baena-Lopez, L.A. Mechanisms and mechanics of cell competition in epithelia. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto, M.; Kizawa, D.; Ohsawa, S.; Igaki, T. JNK signaling is converted from anti- to pro-tumor pathway by Ras-mediated switch of Warts activity. Dev. Biol. 2015, 403, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snigdha, K.; Singh, A.; Kango-Singh, M. Yorkie-Cactus (IκBα)-JNK axis promotes tumor growth and progression in Drosophila. Oncogene 2021, 40, 4124–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziosi, M.; Baena-López, L.A.; Grifoni, D.; Froldi, F.; Pession, A.; Garoia, F.; Trotta, V.; Bellosta, P.; Cavicchi, S.; Pession, A. dMyc functions downstream of yorkie to promote the supercompetitive behavior of hippo pathway mutant Cells. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1001140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlirova, M.; Bohmann, D. JNK- and Fos-regulated Mmp1 expression cooperates with Ras to induce invasive tumors in Drosophila. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 5294–5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doggett, K.; Grusche, F.A.; Richardson, H.E.; Brumby, A.M. Loss of the Drosophila cell polarity regulator Scribbled promotes epithelial tissue overgrowth and cooperation with oncogenic Ras-Raf through impaired Hippo pathway signaling. BMC Dev. Biol. 2011, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igaki, T.; Pastor-Pareja, J.C.; Aonuma, H.; Miura, M.; Xu, T. Intrinsic Tumor Suppression and Epithelial Maintenance by Endocytic Activation of Eiger/TNF Signaling in Drosophila. Dev. Cell 2009, 16, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Arias, J.M.; Pinal, N.; Cristobal-Vargas, S.; Estella, C.; Morata, G. Lack of apoptosis leads to cellular senescence and tumorigenesis in Drosophila epithelial cells. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Marca, J.E.; Richardson, H.E. Two-Faced: Roles of JNK Signalling During Tumourigenesis in the Drosophila Model. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senoo-Matsuda, N.; Johnston, L.A. Soluble factors mediate competitive and cooperative interactions between cells expressing different levels of Drosophila Myc. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18543–18548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Bergmann, A. Distinct mechanisms of apoptosis-induced compensatory proliferation in proliferating and differentiating tissues in the Drosophila eye. Dev. Cell 2008, 14, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryoo, H.D.; Gorenc, T.; Steller, H. Apoptotic Cells Can Induce Compensatory Cell Proliferation through the JNK and the Wingless Signaling Pathways. Dev. Cell 2004, 7, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verghese, S.; Bedi, S.; Kango-Singh, M. Hippo signalling controls Dronc activity to regulate organ size in Drosophila. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 19, 1664–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, E.; Feng, Y.; Rauskolb, C.; Maitra, S.; Fehon, R.; Irvine, K.D. Delineation of a Fat tumor suppressor pathway. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazelett, D.J.; Bourouis, M.; Walldorf, U.; Treisman, J.E. Decapentaplegic and wingless are regulated by eyes absent and eyegone and interact to direct the pattern of retinal differentiation in the eye disc. Development 1998, 125, 3741–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.L.; Hawkins, C.J.; Yoo, S.J.; Müller, H.-A.J.; Hay, B.A. The Drosophila Caspase Inhibitor DIAP1 Is Essential for Cell Survival and Is Negatively Regulated by HID. Cell 1999, 98, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingham, P.W.; Hidalgo, A. Regulation of wingless transcription in the Drososphila embryo. Development 1993, 117, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoffe, K.B.; Manoukian, A.S.; Wilder, E.L.; Brand, A.H.; Perrimon, N. Evidence for engrailed-Independent wingless Autoregulation in Drosophila. Dev. Biol. 1995, 170, 636–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Manoukian, A.S.; Yoffe, K.B.; Wilder, E.L.; Perrimon, N. The porcupine gene is required for wingless autoregulation in Drosophila. Development 1995, 121, 4037–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dow, L.E.; Elsum, I.A.; King, C.L.; Kinross, K.M.; Richardson, H.E.; Humbert, P.O. Loss of human Scribble cooperates with H-Ras to promote cell invasion through deregulation of MAPK signalling. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5988–6001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gödde, N.J.; Pearson, H.B.; Smith, L.K.; Humbert, P.O. Dissecting the role of polarity regulators in cancer through the use of mouse models. Exp. Cell Res. 2014, 328, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, H.B.; McGlinn, E.; Phesse, T.J.; Schlüter, H.; Srikumar, A.; Gödde, N.J.; Woelwer, C.B.; Ryan, A.; Phillips, W.A.; Ernst, M.; et al. The polarity protein Scrib mediates epidermal development and exerts a tumor suppressive function during skin carcinogenesis. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsum, I.; Yates, L.; Humbert, P.O.; Richardson, H.E. The Scribble–Dlg–Lgl polarity module in development and cancer: From flies to man. Essays Biochem. 2012, 53, 141–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, Y.; Kimura, R.; Hirade, K.; Yanase, S.; Nishioka, Y.; Kasuga, N.; Yamaguchi, R.; Ebi, H. Scribble mis-localization induces adaptive resistance to KRAS G12C inhibitors through feedback activation of MAPK signaling mediated by YAP-induced MRAS. Nat. Cancer 2023, 4, 829–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floc’Hlay, S.; Balaji, R.; Stanković, D.; Christiaens, V.M.; González-Blas, C.B.; De Winter, S.; Hulselmans, G.J.; De Waegeneer, M.; Quan, X.; Koldere, D.; et al. Shared enhancer gene regulatory networks between wound and oncogenic programs. eLife 2023, 12, e81173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, M.; Potier, D.; Romanelli, L.; Jacobs, J.; Mach, J.; Hamaratoglu, F.; Aerts, S.; Halder, G. An Ectopic Network of Transcription Factors Regulated by Hippo Signaling Drives Growth and Invasion of a Malignant Tumor Model. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 2101–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Külshammer, E.; Mundorf, J.; Kilinc, M.; Frommolt, P.; Wagle, P.; Uhlirova, M. Interplay among transcription factors Ets21c, Fos and Ftz-F1 drives JNK-mediated tumor malignancy. Dis. Models Mech. 2015, 8, dmm.020719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunker, B.D.; Nellimoottil, T.T.; Boileau, R.M.; Classen, A.K.; Bilder, D. The transcriptional response to tumorigenic polarity loss in Drosophila. eLife 2015, 4, e03189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, T.; Zhang, L.; Deng, M.; Huang, S.; Wang, Y.; Pham, T.T.; Smith, A.A.; Sridhar, V.; Cabernard, C.; Wang, J.; et al. Dynamic MAPK signaling activity underlies a transition from growth arrest to proliferation in Drosophila scribble mutant tumors. Dis. Models Mech. 2019, 12, dmm.040147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verghese, S.; Waghmare, I.; Kwon, H.; Hanes, K.; Kango-Singh, M. Scribble Acts in the Drosophila Fat-Hippo Pathway to Regulate Warts Activity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waghmare, I.; Kango-Singh, M. Loss of Cell Adhesion Increases Tumorigenic Potential of Polarity Deficient Scribble Mutant Cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, E.; Lindblad, J.L.; Bergmann, A. Tumor-promoting function of apoptotic caspases by an amplification loop involving ROS, macrophages and JNK in Drosophila. eLife 2017, 6, e26747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Garijo, A.; Martín, F.A.; Morata, G. Caspase inhibition during apoptosis causes abnormal signalling and developmental aberrations in Drosophila. Development 2004, 131, 5591–5598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith-Bolton, R.K.; Worley, M.I.; Kanda, H.; Hariharan, I.K. Regenerative Growth in Drosophila Imaginal Discs Is Regulated by Wingless and Myc. Dev. Cell 2009, 16, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zecca, M.; Struhl, G. A Feed-Forward Circuit Linking Wingless, Fat-Dachsous Signaling, and the Warts-Hippo Pathway to Drosophila Wing Growth. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konsavage, W.M.; Yochum, G.S. Intersection of Hippo/YAP and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2013, 45, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittkorn, E.; Sarkar, A.; Garcia, K.; Kango-Singh, M.; Singh, A. The Hippo pathway effector Yki downregulates Wg signaling to promote retinal differentiation in the Drosophila eye. Development 2015, 142, 2002–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, M.A.; Huang, Q.; Li, F.; Liu, X.; Li, C.-Y. Cell Death–Stimulated Cell Proliferation: A Tissue Regeneration Mechanism Usurped by Tumors During Radiotherapy. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 23, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Li, F.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Shi, W.; Liu, F.-F.; O’Sullivan, B.; He, Z.; Peng, Y.; Tan, A.-C.; et al. Caspase 3–mediated stimulation of tumor cell repopulation during cancer radiotherapy. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.C.; Wang, L.; Yamada, K.M.; Baena-Lopez, L.A. Non-apoptotic activation of Drosophila caspase-2/9 modulates JNK signaling, the tumor microenvironment, and growth of wound-like tumors. Cell Rep. 2022, 39, 110718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sun, J.; Wang, D.; Pflugfelder, G.O.; Shen, J. Fold formation at the compartment boundary of Drosophila wing requires Yki signaling to suppress JNK dependent apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Chen, Y.; Xu, W.; Wu, N.; Li, M.; Cao, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, Q.; Xue, L. Impaired Hippo signaling promotes Rho1–JNK-dependent growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 1065–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, F.; Ege, N.; Grande-Garcia, A.; Hooper, S.; Jenkins, R.P.; Chaudhry, S.I.; Harrington, K.; Williamson, P.; Moeendarbary, E.; Charras, G.; et al. Mechanotransduction and YAP-dependent matrix remodelling is required for the generation and maintenance of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, X.; Nguyen, H.T.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, R.; Hagman, Z.; Voorhoeve, P.M.; Cohen, S.M. Opposing activities of the R as and H ippo pathways converge on regulation of YAP protein turnover. EMBO J. 2014, 33, 2447–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, E.R.; Camargo, F.D. The Hippo superhighway: Signaling crossroads converging on the Hippo/Yap pathway in stem cells and development. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2013, 25, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Moroishi, T.; Guan, K.-L. Mechanisms of Hippo pathway regulation. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenbluh, J.; Nijhawan, D.; Cox, A.G.; Li, X.; Neal, J.T.; Schafer, E.J.; Zack, T.I.; Wang, X.; Tsherniak, A.; Schinzel, A.C.; et al. β-Catenin-Driven Cancers Require a YAP1 Transcriptional Complex for Survival and Tumorigenesis. Cell 2012, 151, 1457–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, G.G.; Carrara, M.; Yuan, W.-C.; Valdes-Quezada, C.; Gurung, B.; Pepe-Mooney, B.; Zhang, T.; Geeven, G.; Gray, N.S.; de Laat, W.; et al. YAP Drives Growth by Controlling Transcriptional Pause Release from Dynamic Enhancers. Mol. Cell 2015, 60, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, C.; Bardet, A.F.; Roma, G.; Bergling, S.; Clay, I.; Ruchti, A.; Agarinis, C.; Schmelzle, T.; Bouwmeester, T.; Schübeler, D.; et al. YAP1 Exerts Its Transcriptional Control via TEAD-Mediated Activation of Enhancers. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanconato, F.; Forcato, M.; Battilana, G.; Azzolin, L.; Quaranta, E.; Bodega, B.; Rosato, A.; Bicciato, S.; Cordenonsi, M.; Piccolo, S. Genome-wide association between YAP/TAZ/TEAD and AP-1 at enhancers drives oncogenic growth. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 1218–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.; Slattery, M.; Ma, L.; Crofts, A.; White, K.P.; Mann, R.S.; Irvine, K.D. Genome-wide Association of Yorkie with Chromatin and Chromatin-Remodeling Complexes. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Robinson, B.S.; Xu, W.; Yang, L.; Yao, B.; Zhao, H.; Byun, P.K.; Jin, P.; Veraksa, A.; Moberg, K.H. The Ecdysone Receptor Coactivator Taiman Links Yorkie to Transcriptional Control of Germline Stem Cell Factors in Somatic Tissue. Dev. Cell 2015, 34, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Waghmare, I.; Gangwani, K.; Rai, A.; Singh, A.; Kango-Singh, M. A Tumor-Specific Molecular Network Promotes Tumor Growth in Drosophila by Enforcing a Jun N-Terminal Kinase–Yorkie Feedforward Loop. Cancers 2024, 16, 1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091768
Waghmare I, Gangwani K, Rai A, Singh A, Kango-Singh M. A Tumor-Specific Molecular Network Promotes Tumor Growth in Drosophila by Enforcing a Jun N-Terminal Kinase–Yorkie Feedforward Loop. Cancers. 2024; 16(9):1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091768
Chicago/Turabian StyleWaghmare, Indrayani, Karishma Gangwani, Arushi Rai, Amit Singh, and Madhuri Kango-Singh. 2024. "A Tumor-Specific Molecular Network Promotes Tumor Growth in Drosophila by Enforcing a Jun N-Terminal Kinase–Yorkie Feedforward Loop" Cancers 16, no. 9: 1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091768
APA StyleWaghmare, I., Gangwani, K., Rai, A., Singh, A., & Kango-Singh, M. (2024). A Tumor-Specific Molecular Network Promotes Tumor Growth in Drosophila by Enforcing a Jun N-Terminal Kinase–Yorkie Feedforward Loop. Cancers, 16(9), 1768. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091768







