Endocrine Immune-Related Adverse Events Are Independent Predictors of Survival in Patients with Lung Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
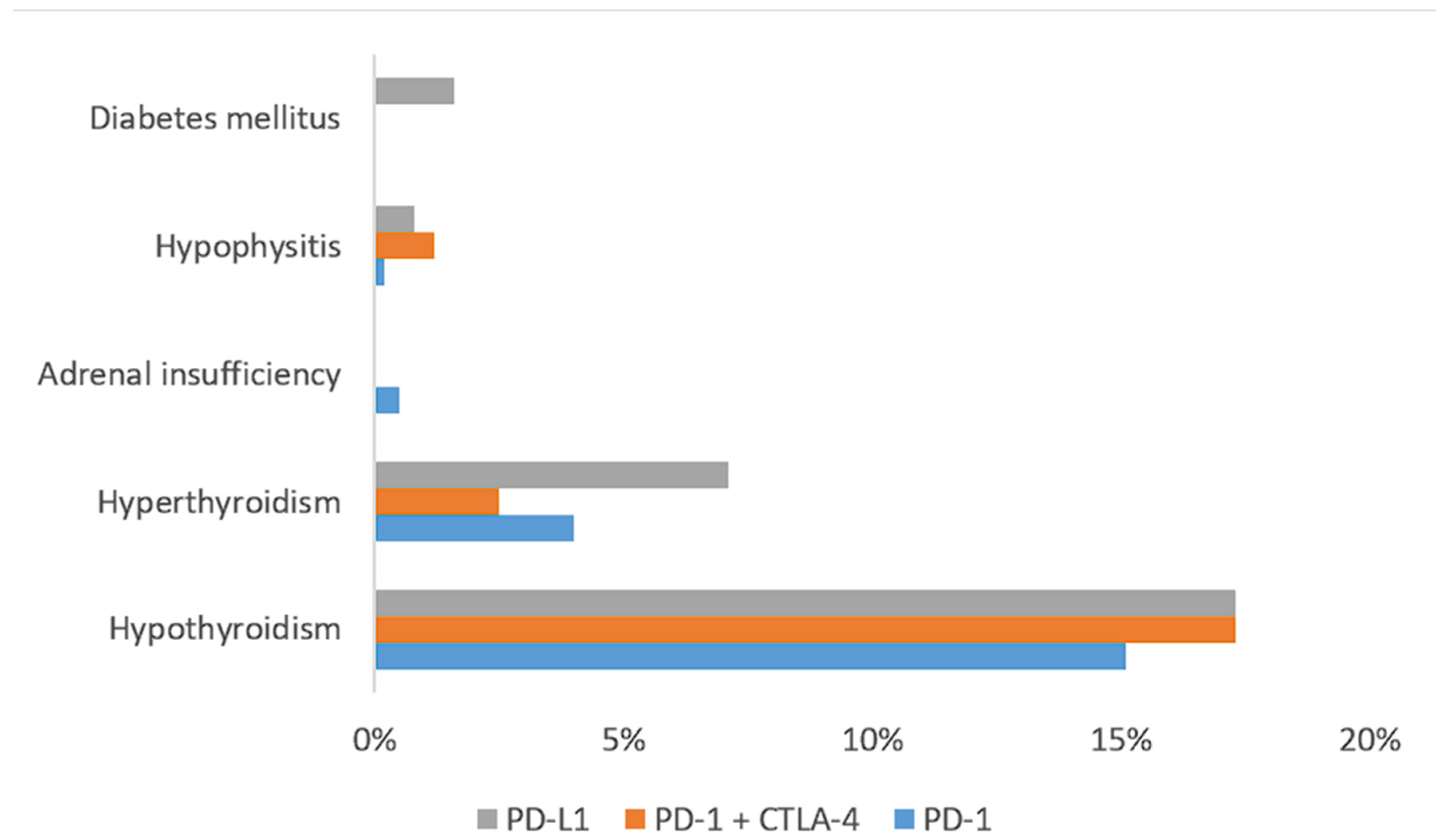
4.1. irAEs
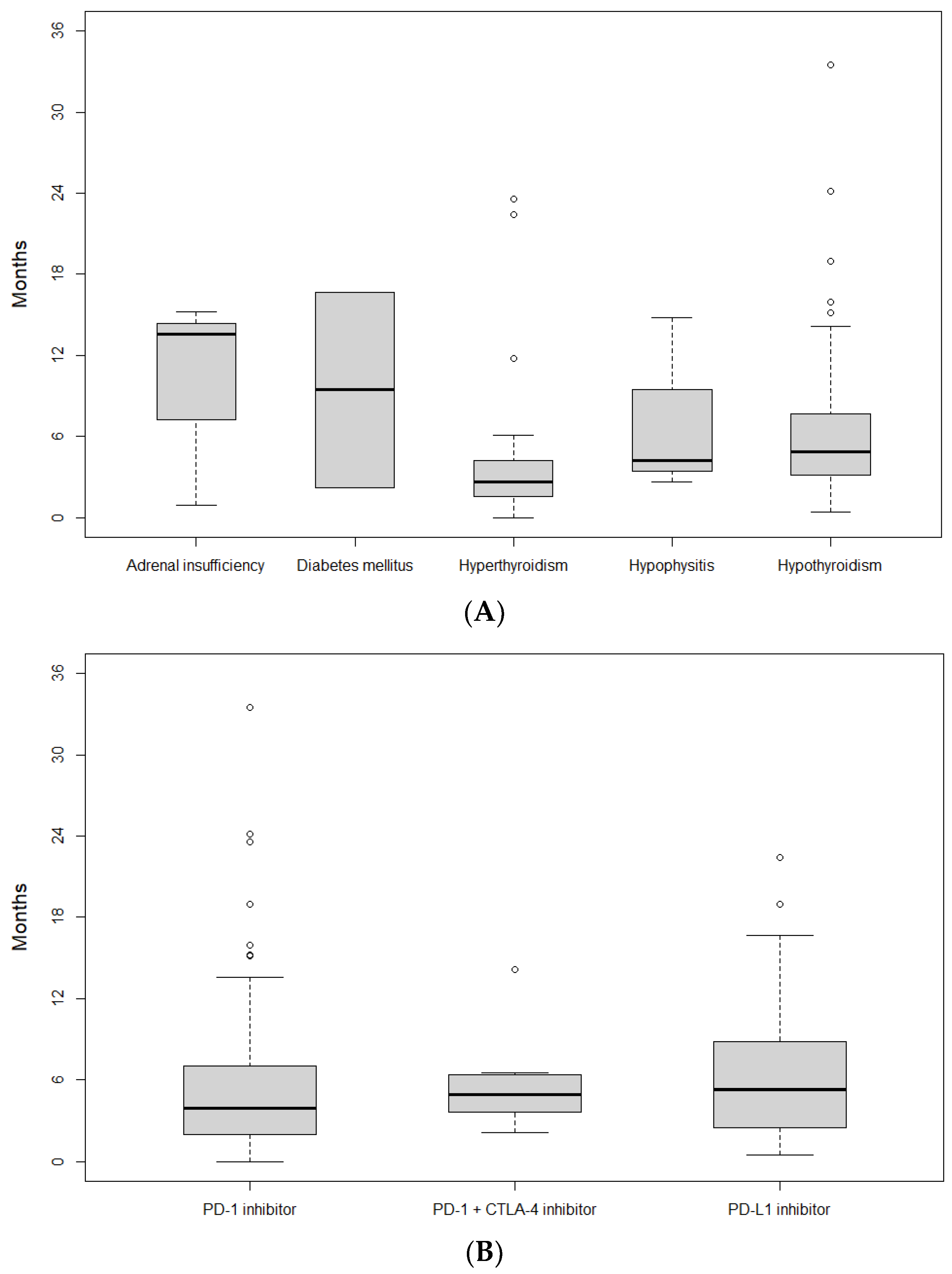
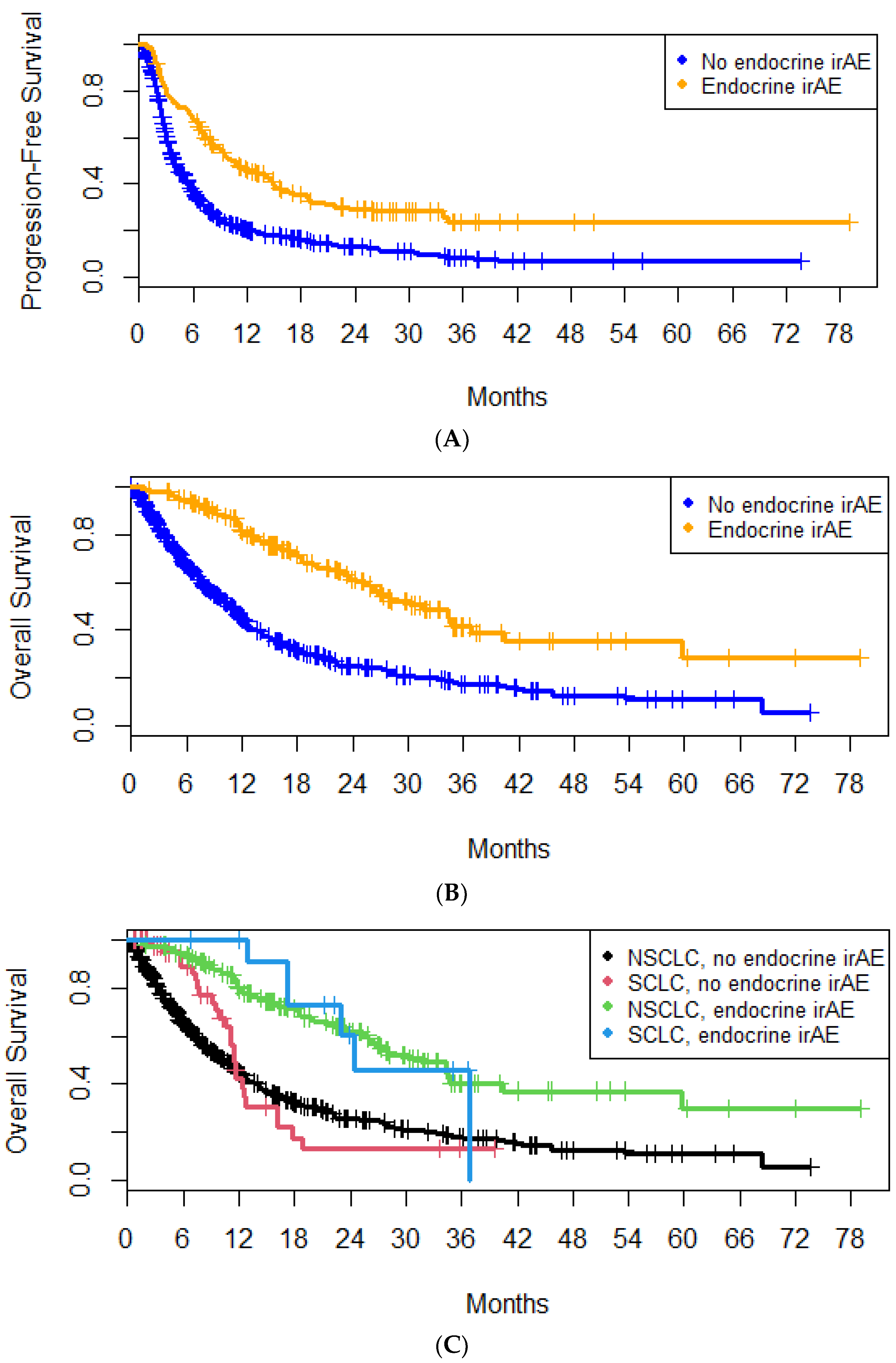
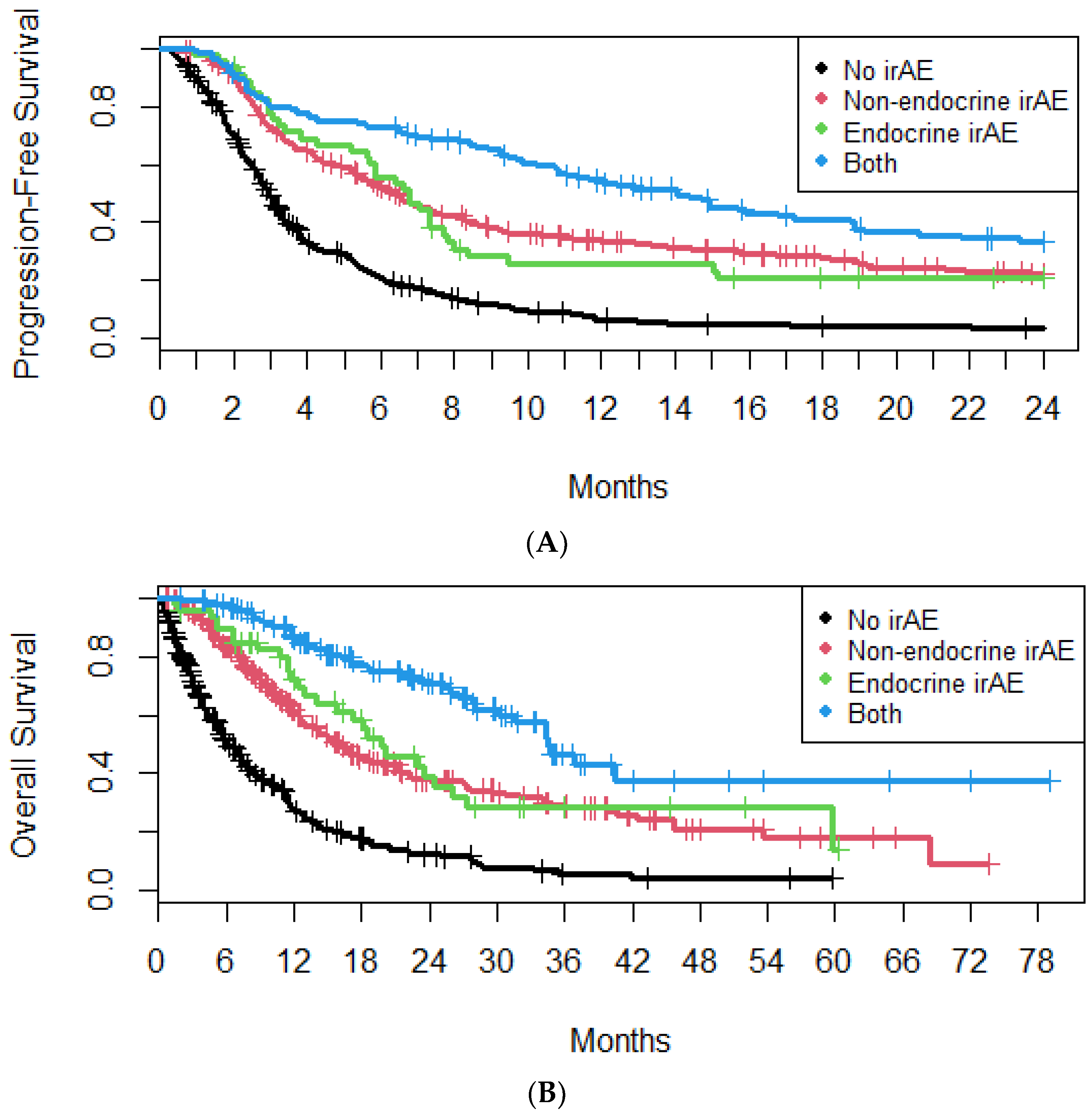
4.2. E-irAEs
4.3. Non-Endocrine irAEs
4.4. Corticosteroids
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamdani, H.; Matosevic, S.; Khalid, A.B.; Durm, G.; Jalal, S.I. Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer: Current Landscape and Future Directions. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 823618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumeh, P.C.; Harview, C.L.; Yearley, J.H.; Shintaku, I.P.; Taylor, E.J.M.; Robert, L.; Chmielowski, B.; Spasic, M.; Henry, G.; Ciobanu, V.; et al. PD-1 Blockade Induces Responses by Inhibiting Adaptive Immune Resistance. Nature 2014, 515, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, L.B.; Salama, A.K.S. A Review of Cancer Immunotherapy Toxicity. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 86–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; Brahmer, J.R.; Callahan, M.K.; Flores-Chávez, A.; Keegan, N.; Khamashta, M.A.; Lambotte, O.; Mariette, X.; Prat, A.; Suárez-Almazor, M.E. Immune-Related Adverse Events of Checkpoint Inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso-Sousa, R.; Barry, W.T.; Garrido-Castro, A.C.; Hodi, F.S.; Min, L.; Krop, I.E.; Tolaney, S.M. Incidence of Endocrine Dysfunction Following the Use of Different Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Regimens: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, F.; Sofiya, L.; Sykiotis, G.P.; Lamine, F.; Maillard, M.; Fraga, M.; Shabafrouz, K.; Ribi, C.; Cairoli, A.; Guex-Crosier, Y.; et al. Adverse Effects of Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors: Epidemiology, Management and Surveillance. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 563–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.J.; Powers, A.C.; Johnson, D.B. Endocrine Toxicities of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.M.; Fallahi, P.; Elia, G.; Ragusa, F.; Ruffilli, I.; Patrizio, A.; Galdiero, M.R.; Baldini, E.; Ulisse, S.; Marone, G.; et al. Autoimmune Endocrine Dysfunctions Associated with Cancer Immunotherapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Xie, W.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Geng, Y.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, Z. Association of Immune Related Adverse Events with Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Overall Survival in Cancers: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 633032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, Y.-M.M.; Wang, W.; McGregor, B.; Hamnvik, O.-P.R. Associations between Immune-Related Thyroid Dysfunction and Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2022, 71, 1795–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoja, L.; Day, D.; Wei-Wu Chen, T.; Siu, L.L.; Hansen, A.R. Tumour- and Class-Specific Patterns of Immune-Related Adverse Events of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 2377–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, E.; Newsom-Davis, T.; Morganstein, D.L. Immunotherapy-Induced Endocrinopathies: Assessment, Management and Monitoring. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 10, 2042018819896182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, R.; Marini, A.; Roviello, G.; Presotto, E.M.; Desideri, I.; Ciardetti, I.; Brugia, M.; Pimpinelli, N.; Antonuzzo, L.; Mini, E.; et al. Endocrine-Related Adverse Events in a Large Series of Cancer Patients Treated with Anti-PD1 Therapy. Endocrine 2021, 74, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, A.; Saito, Y.; Okamoto, K.; Narumi, K.; Furugen, A.; Takekuma, Y.; Sugawara, M.; Kobayashi, M. Preexisting Autoimmune Disease Is a Risk Factor for Immune-Related Adverse Events: A Meta-Analysis. Support. Care Cancer 2021, 29, 7747–7753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chennamadhavuni, A.; Abushahin, L.; Jin, N.; Presley, C.J.; Manne, A. Risk Factors and Biomarkers for Immune-Related Adverse Events: A Practical Guide to Identifying High-Risk Patients and Rechallenging Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 779691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelmachowska-Banaś, M.; Czajka-Oraniec, I. Management of Endocrine Immune-Related Adverse Events of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: An Updated Review. Endocr. Connect. 2020, 9, R207–R228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkotou, E.; Anagnostakis, M.; Evangelou, G.; Syrigos, N.K.; Gkiozos, I. Real-World Data and Evidence in Lung Cancer: A Review of Recent Developments. Cancers 2024, 16, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, B.J.; Naidoo, J.; Santomasso, B.D.; Lacchetti, C.; Adkins, S.; Anadkat, M.; Atkins, M.B.; Brassil, K.J.; Caterino, J.M.; Chau, I.; et al. Management of Immune-Related Adverse Events in Patients Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy: ASCO Guideline Update. JCO 2021, 39, 4073–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Buren, I.; Madison, C.; Kohn, A.; Berry, E.; Kulkarni, R.P.; Thompson, R.F. Survival Among Veterans Receiving Steroids for Immune-Related Adverse Events After Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2340695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsukane, R.; Suetsugu, K.; Hata, K.; Matsuda, K.; Nakao, S.; Minami, H.; Watanabe, H.; Hirota, T.; Egashira, N.; Ieiri, I. Systematic Surveillance of Immune-Related Adverse Events in Clinical Practice and Impact of Subsequent Steroid Medication on Survival Outcomes. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 28, 860–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Hu, J.; Betof Warner, A.; Quach, H.T.; Cann, C.G.; Zhang, M.Z.; Si, L.; Tang, B.; Cui, C.; Yang, X.; et al. Early Use of High-Dose Glucocorticoid for the Management of irAE Is Associated with Poorer Survival in Patients with Advanced Melanoma Treated with Anti–PD-1 Monotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 5993–6000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomura, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Oya, Y.; Uchida, K.; Murotani, K. Impact of Corticosteroids for IrAEs on the Clinical Outcome of Immunotherapy in Patients With NSCLC. Anticancer Res. 2022, 42, 5961–5969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaucher, L.; Adda, L.; Séjourné, A.; Joachim, C.; Chaby, G.; Poulet, C.; Liabeuf, S.; Gras-Champel, V.; Masmoudi, K.; Moreira, A.; et al. Impact of the Corticosteroid Indication and Administration Route on Overall Survival and the Tumor Response after Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Initiation. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2021, 13, 1758835921996656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciuti, B.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Adeni, A.; Sholl, L.M.; Nishino, M.; Awad, M.M. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Outcomes for Patients with Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Receiving Baseline Corticosteroids for Palliative Versus Nonpalliative Indications. JCO 2019, 37, 1927–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Johnson, D.B. Immune-Related Adverse Events and Anti-Tumor Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Chen, C.; Gu, Y.; Lu, W.; Zhan, P.; Liu, H.; Lv, T.; Song, Y.; Zhang, F. Immune-Related Adverse Events Predict the Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Lung Cancer Patients: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 631949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.; Quandt, Z.; Bluestone, J.A. The Balancing Act between Cancer Immunity and Autoimmunity in Response to Immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postow, M.A.; Sidlow, R.; Hellmann, M.D. Immune-Related Adverse Events Associated with Immune Checkpoint Blockade. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.K.; Bass, A.R. Autoimmune Complications of Immunotherapy: Pathophysiology and Management. BMJ 2020, 369, m736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giobbie-Hurder, A.; Gelber, R.D.; Regan, M.M. Challenges of Guarantee-Time Bias. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 2963–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Hu, C.; Zhang, A.; Wang, X.; Zeng, D.; Long, T.; Zhu, B.; Wang, Z. A Real-World Retrospective Study of Incidence and Associated Factors of Endocrine Adverse Events Related to PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors. Ann. Transl. Med. 2023, 11, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, G.; Gasper, H.; Man, J.; Lord, S.; Marschner, I.; Friedlander, M.; Lee, C.K. Defining the Most Appropriate Primary End Point in Phase 2 Trials of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Advanced Solid Cancers. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoroso, V.; Gallo, F.; Alberti, A.; Paloschi, D.; Ferrari Bravo, W.; Esposito, A.; Cosentini, D.; Grisanti, S.; Pedersini, R.; Petrelli, F.; et al. Immune-Related Adverse Events as Potential Surrogates of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors’ Efficacy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Studies. ESMO Open 2023, 8, 100787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Subgroup | N (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Female | 245 (24.9%) | |
| Male | 738 (75.1%) | |
| Age | ≥65 | 570 (58%) |
| <65 | 413 (42%) | |
| Smoking status | ||
| Current | 595 (67.1%) | |
| Former | 265 (29.9%) | |
| Never | 27 (3%) | |
| Comorbidity | ||
| Cardiac | 642 (67.9%) | |
| Endocrine | 322 (34%) | |
| Pulmonary | 255 (27%) | |
| Gastrointestinal | 88 (9.4%) | |
| Renal | 53 (5.6%) | |
| Rheumatologic | 20 (2.1%) | |
| ECOG PS | ||
| 0 | 198 (20.8%) | |
| 1 | 498 (52.4%) | |
| 2 | 211 (22.2%) | |
| ≥3 | 44 (4.6%) | |
| Prior treatments | ||
| Surgery | 166 (17%) | |
| Radiotherapy | 427 (44.3%) | |
| Chemotherapy | 472 (48.6%) | |
| Treatment line | ||
| Consolidation | 61 (6.3%) | |
| 1 | 549 (56.4%) | |
| 2 | 272 (27.9%) | |
| ≥3 | 92 (9.4%) |
| Subgroup | N (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Tumor specimen | ||
| Tissue | 912 (92.9%) | |
| Cytology | 70 (7.1%) | |
| Histologic subtype | ||
| Adenocarcinoma | 474 (48.3%) | |
| Squamous | 280 (28.5%) | |
| SCLC | 142 (14.5%) | |
| NSCLC NOS | 31 (3.2%) | |
| LCNEC | 17 (1.7%) | |
| Other | 37 (3.8%) | |
| PD-L1 | ||
| <1% | 180 (27.1%) | |
| 1–49% | 247 (37.2%) | |
| ≥50% | 237 (35.7%) | |
| Driver mutations | ||
| No | 368 (71.8%) | |
| Yes | 144 (28.2%) | |
| Stage at treatment initiation | ||
| II | 2 (0.2%) | |
| IIIA | 36 (3.7%) | |
| IIIB | 62 (6.3%) | |
| IIIC | 17 (1.7%) | |
| IVA | 357 (36.4%) | |
| IVB | 508 (51.7%) | |
| Metastatic sites | ||
| Contralateral Lung | 383 (39%) | |
| Pleura | 348 (35.4%) | |
| Brain | 188 (19.1%) | |
| Bone | 310 (31.5%) | |
| Liver | 194 (19.7%) | |
| Adrenal gland | 182 (18.5%) | |
| Other | 309 (31.5%) | |
| Checkpoint inhibitor | ||
| PD-1 inhibitor | 670 (68.1%) | |
| PD-L1 inhibitor | 221 (22.5%) | |
| PD-1 + CTLA-4 inhibitor | 92 (9.4%) | |
| Concurrent chemotherapy | ||
| No | 499 (50.8%) | |
| Platinum-pemetrexed | 211 (21.5%) | |
| Platinum-etoposide | 157 (16%) | |
| Platinum-taxane | 103 (10.5%) | |
| Single-agent chemotherapy | 12 (1.2%) | |
| Concurrent radiotherapy | 193 (19.8%) | |
| Objective Response | ||
| Complete response (CR) | 6 (0.7%) | |
| Partial response (PR) | 200 (22.1%) | |
| Stable disease (SD) | 249 (27.5%) | |
| Progressive disease (PD) | 450 (49.7%) | |
| Subsequent therapy | ||
| Chemotherapy | 345 (89.8%) | |
| Targeted therapy | 17 (4.4%) | |
| Chemoimmunotherapy | 14 (3.7%) | |
| Radiotherapy | 5 (1.3%) | |
| Immunotherapy | 3 (0.8%) |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subgroup | p-Value | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | |
| Age | <65 | 0.021 | 0.0012 | 0.54 (0.37–0.78) |
| BMI | Normal | (ref) | ||
| Overweight | 0.023 | |||
| Obese | ||||
| ECOG PS | 0 | (ref) | ||
| 1 | 8.07 × 10−8 | |||
| 2 | 1.18 × 10−22 | 0.016 | 2.46 (1.18–5.09) | |
| 3 | 3.24 × 10−16 | 0.014 | 3.43 (1.28–9.18) | |
| 4 | 0.0007 | |||
| Pulmonary comorbidity | 0.063 | 0.042 | 1.52 (1.02–2.27) | |
| Endocrine comorbidity | 0.094 | |||
| Histologic subtype | Adenocarcinoma | (ref) | ||
| Squamous | 0.00019 | |||
| SCLC | ||||
| Pleomorphic | ||||
| NOS | ||||
| LCNEC | ||||
| Stage at diagnosis | I | (ref) | ||
| II | ||||
| IIIA | 0.056 | |||
| IIIB | ||||
| IIIC | 0.037 | |||
| IVA | ||||
| IVB | 0.029 | |||
| Metastases | Lung | 0.002 | ||
| Pleura | 4.67 × 10−8 | 0.010 | 1.64 (1.13–2.38) | |
| Liver | 1.07 × 10−10 | |||
| Brain | 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.067 | 1.61 (0.97–2.67) | |
| Bone | 2.20 × 10−7 | |||
| Adrenal gland | 0.027 | 0.012 | 1.88 (1.15–3.07) | |
| Other | 0.029 | |||
| PD-L1 | <1% | (ref) | ||
| 1–49% | 0.011 | |||
| ≥50% | 0.040 | 0.001 | 0.44 (0.27–0.71) | |
| Prior surgery | 0.0002 | |||
| Prior radiotherapy | 0.024 | |||
| Prior chemotherapy | 4.33 × 10−7 | |||
| Treatment line | 1 | (ref) | ||
| 2 | 2.72 × 10−10 | |||
| 3 | 1.70 × 10−9 | |||
| 4 | 4.12 × 10−5 | |||
| 5 | ||||
| Consolidation | 0.0039 | |||
| Checkpoint inhibitor | PD-1 inhibitor | (ref) | ||
| PD-L1 inhibitor | 5.97 × 10−4 | |||
| PD-1 + CTLA-4 inhibitor | 0.025 | 0.053 | 0.49 (0.24–1.01) | |
| Concurrent radiotherapy | 0.0012 | 0.018 | 0.57 (0.36–0.91) | |
| Endocrine irAE | 1.56 × 10−15 | 0.005 | 0.48 (0.28–0.80) | |
| Non-endocrine irAE | 2.92 × 10−28 | 2.88 × 10−8 | 0.34 (0.23–0.50) | |
| White blood cell count | 7.72 × 10−6 | 0.0008 | 0.9993 (0.99889–0.9997) | |
| Platelets | 0.033 | |||
| Neutrophils | 2.21 × 10−8 | 0.0006 | 1.001 (1.00032–1.0012) | |
| Lymphocytes | 0.087 | 0.009 | 1.001 (1.00018–1.0013) | |
| NLR | <2 | (ref) | ||
| 2–3 | ||||
| >3 | 9.94 × 10−9 | |||
| LDH | >ULN | 1.96 × 10−6 | 0.034 | 1.6 (1.04–2.48) |
| Hemoglobin | ≥12 mg/dL | 1.94 × 10−6 | ||
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subgroup | p-Value | p-Value | OR (95% CI) | |
| Sex | Male | 0.091 | ||
| ECOG PS | 0 | (ref) | ||
| 1 | ||||
| 2 | 0.0014 | 0.0955 | 0.42 (0.15–1.16) | |
| 3 | 0.0648 | |||
| 4 | ||||
| Endocrine comorbidity | 0.0168 | 0.0061 | 2.10 (1.24–3.58) | |
| Histology | Adenocarcinoma | (ref) | ||
| Adenosquamous | 0.0144 | |||
| SCLC | ||||
| LCNEC | 0.0948 | |||
| NOS | ||||
| Pleomorphic | 0.0145 | |||
| Squamous | ||||
| Bone metastases | 0.0998 | |||
| Liver metastases | 0.0002 | 0.0383 | 0.33 (0.11–0.94) | |
| PD-L1 TPS | <1% | (ref) | ||
| 1–49% | 0.074 | |||
| ≥50% | ||||
| Prior surgery | 0.004 | 0.0619 | 1.80 (0.97–3.35) | |
| Treatment line | 1 | (ref) | ||
| 2 | ||||
| 3 | ||||
| 4 | ||||
| 5 | ||||
| Consolidation | 0.0978 | |||
| Checkpoint inhibitor | PD-1 inhibitor | (ref) | ||
| PD-L1 inhibitor | ||||
| PD-1 + CTLA-4 inhibitor | 0.0702 | |||
| Concurrent radiotherapy | 0.0741 | |||
| Concurrent chemotherapy | No | (ref) | ||
| Platinum-etoposide | ||||
| Platinum-pemetrexed | ||||
| Platinum-taxane | 0.0381 | |||
| Single-agent | ||||
| Objective response | SD/PD | (ref) | ||
| CR/PR | 3.59 × 10−6 | 0.0455 | 1.84 (1.01–3.34) | |
| Dermatologic irAE | 3.03 × 10−8 | 0.051 | 1.76 (1.00–3.10) | |
| Pulmonary irAE | 0.045 | |||
| Liver irAE | 0.0049 | |||
| Other irAE | 4.13 × 10−7 | |||
| Neutrophils | 0.0527 | |||
| NLR | <2 | (ref) | ||
| 2–3 | ||||
| >3 | 0.009 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panagiotou, E.; Ntouraki, S.; Vathiotis, I.A.; Livanou, M.E.; Trimis, A.; Evangelou, G.; Charpidou, A.; Syrigos, K.; Peppa, M. Endocrine Immune-Related Adverse Events Are Independent Predictors of Survival in Patients with Lung Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091764
Panagiotou E, Ntouraki S, Vathiotis IA, Livanou ME, Trimis A, Evangelou G, Charpidou A, Syrigos K, Peppa M. Endocrine Immune-Related Adverse Events Are Independent Predictors of Survival in Patients with Lung Cancer. Cancers. 2024; 16(9):1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091764
Chicago/Turabian StylePanagiotou, Emmanouil, Sofia Ntouraki, Ioannis A. Vathiotis, Maria Effrosyni Livanou, Athanasios Trimis, Georgios Evangelou, Andriani Charpidou, Konstantinos Syrigos, and Melpomeni Peppa. 2024. "Endocrine Immune-Related Adverse Events Are Independent Predictors of Survival in Patients with Lung Cancer" Cancers 16, no. 9: 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091764
APA StylePanagiotou, E., Ntouraki, S., Vathiotis, I. A., Livanou, M. E., Trimis, A., Evangelou, G., Charpidou, A., Syrigos, K., & Peppa, M. (2024). Endocrine Immune-Related Adverse Events Are Independent Predictors of Survival in Patients with Lung Cancer. Cancers, 16(9), 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091764








