The Molecular Landscape of Primary CNS Lymphomas (PCNSLs) in Children and Young Adults
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Immunohistochemisty
2.3. Next-Generation Sequencing
2.4. Target Panel Sequencing
2.5. Sanger Sequencing
2.6. FISH Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of This Study Cohort
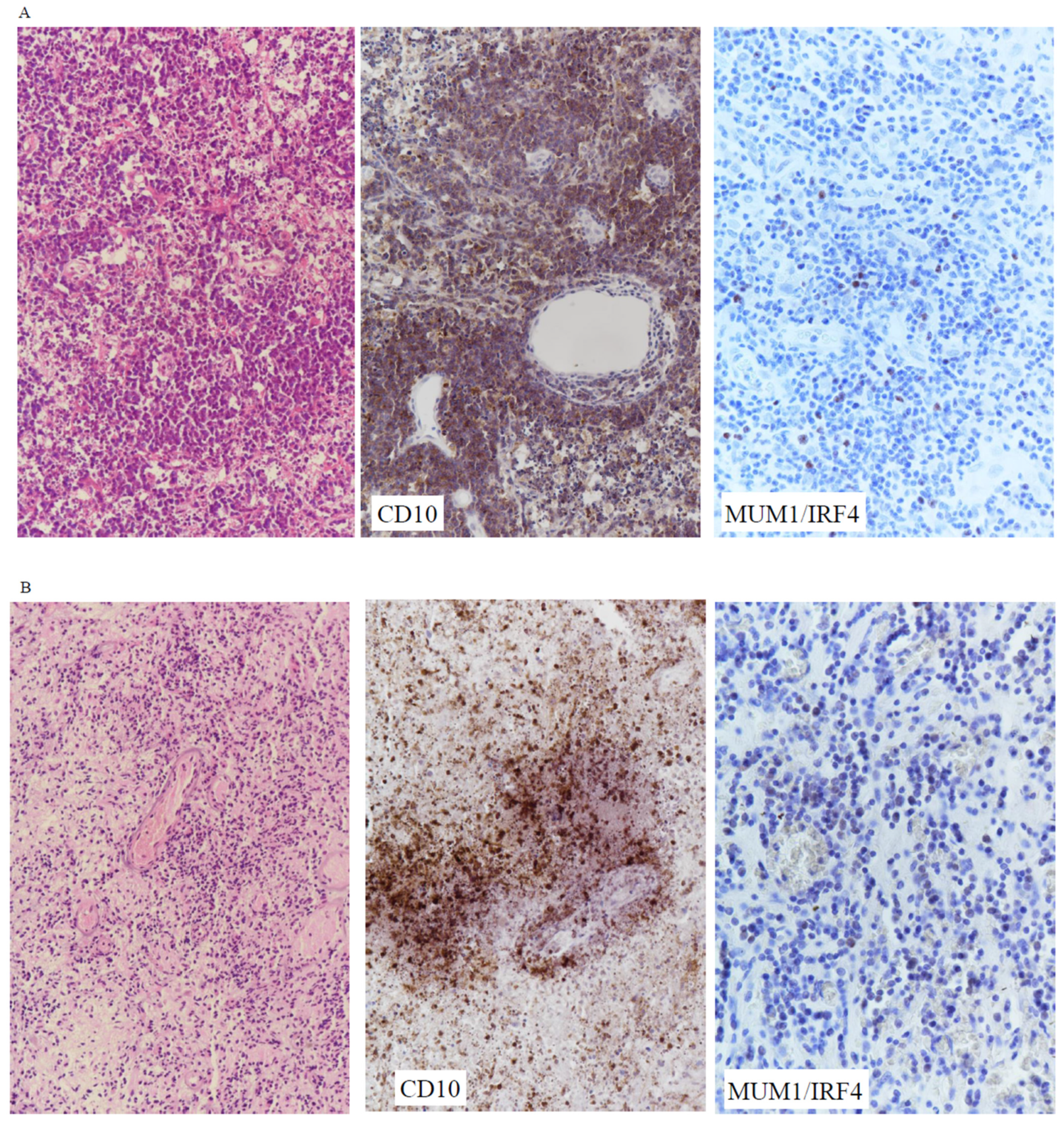
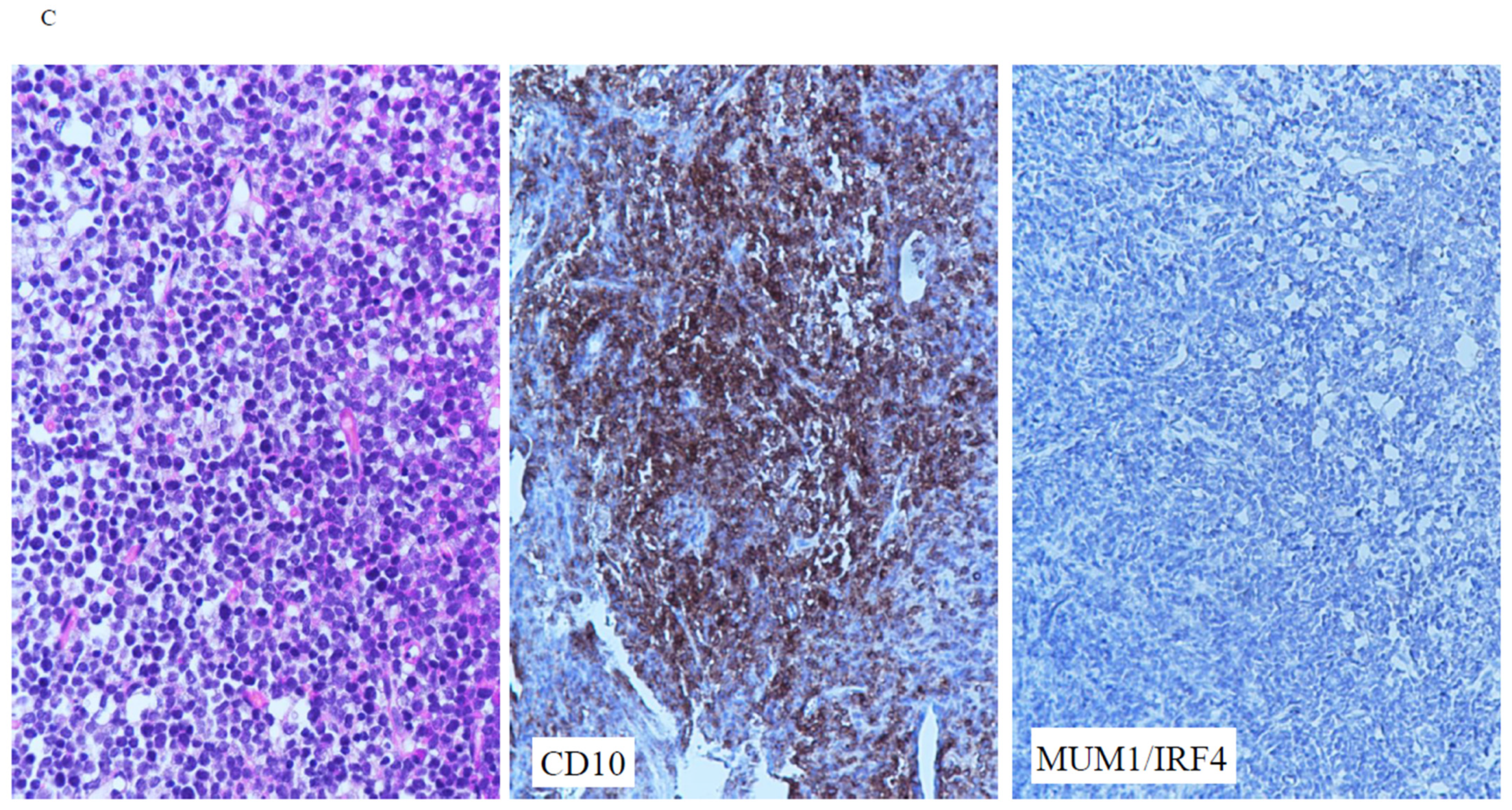
3.2. Immunophenotype
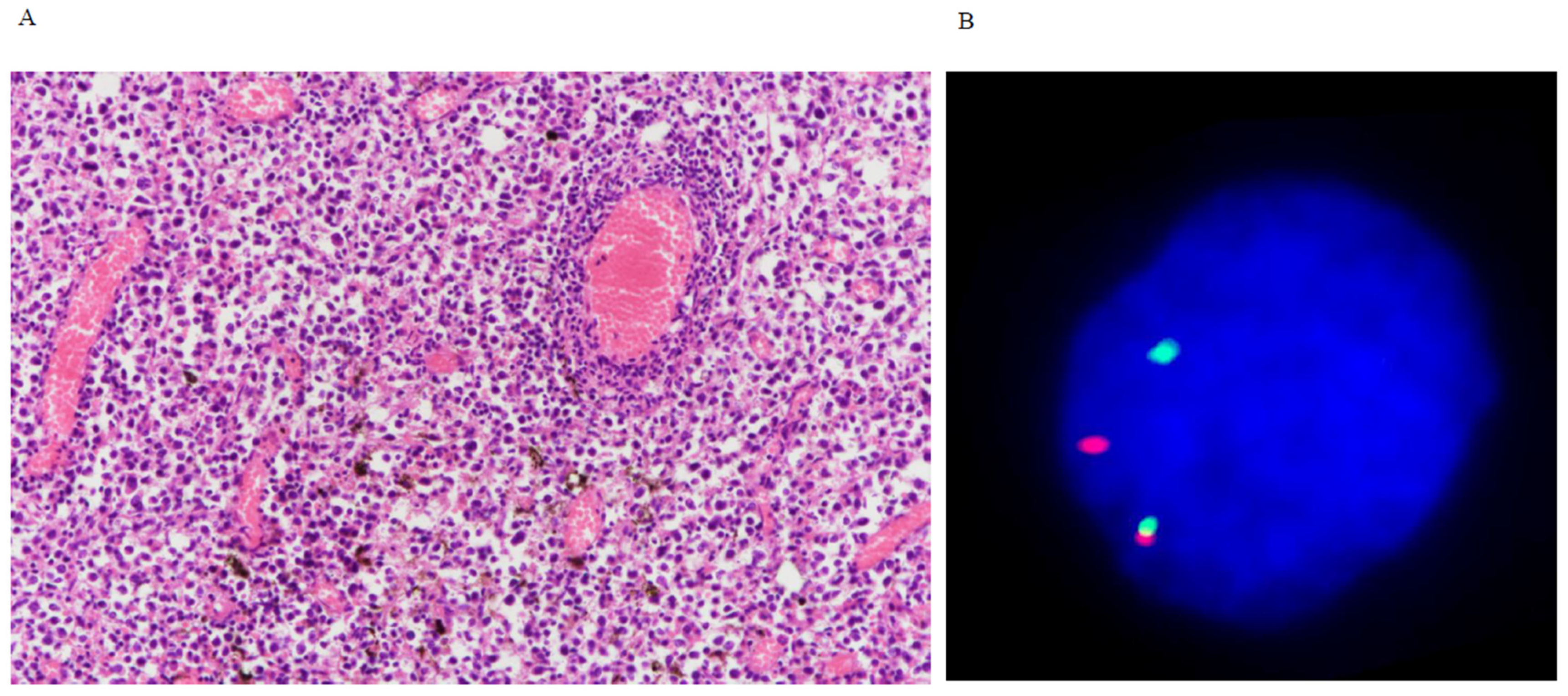
3.3. Breakapart FISH
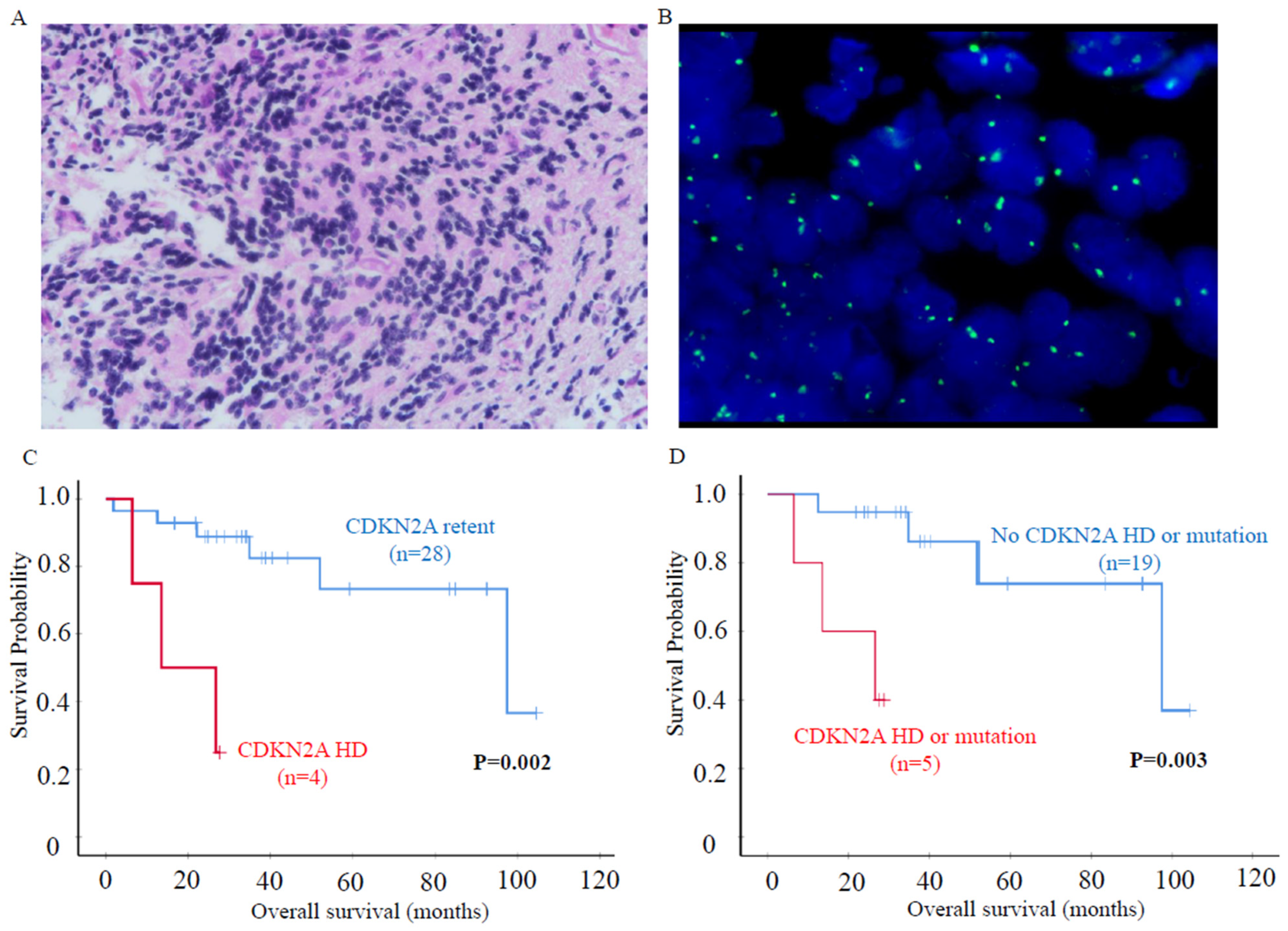
3.4. CDKN2A Homozygous Deletion
3.5. HLA Homozygous Deletion
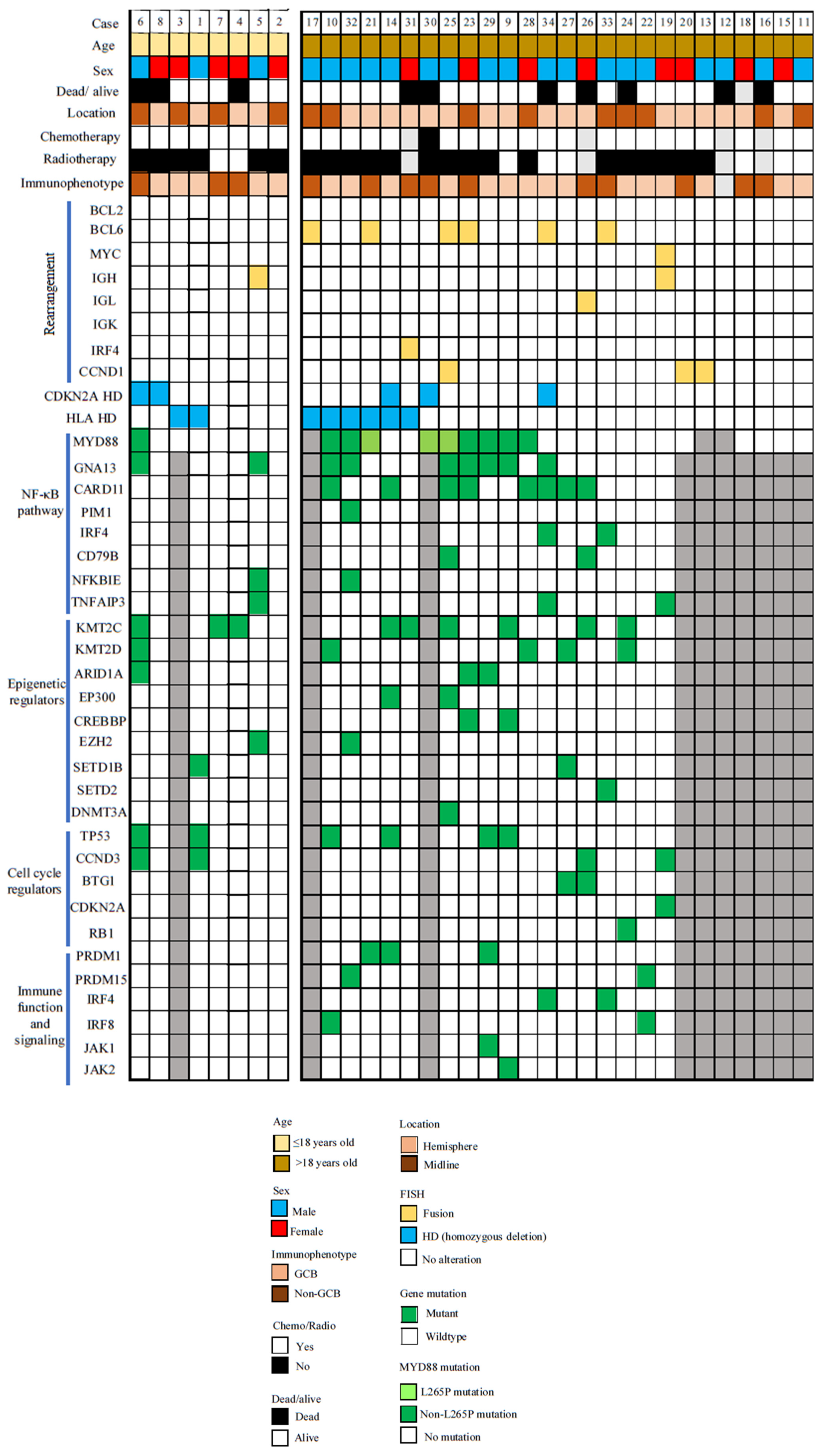
3.6. Mutation Profiling
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deckert, M.; Batchelor, T.; Ferry, J.A.; Hoang-Xuan, K.; Nagane, M.; Paulus, M.; Weller, M. Primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the CNS. In WHO Classification of Tumours, Central Nervous System Tumours, the WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board, 5th ed.; IRAC: Lyon, France, 2021; Chapter 10; pp. 351–355. [Google Scholar]
- Guney, E.; Lucas, C.G.; Qi, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhang, R.; Ohgami, R.S.; Rubenstein, J.L.; Boue, D.R.; Schafernak, K.; Wertheim, G.B.; et al. A genetically distinct pediatric subtype of primary CNS large B-cell lymphoma is associated with favorable clinical outcome. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 3189–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Verdin, I.; Kirasic, E.; Wienand, K.; Mokhtari, K.; Eimer, S.; Loiseau, H.; Rousseau, A.; Paillassa, J.; Ahle, G.; Lerintiu, F.; et al. Molecular and clinical diversity in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abla, O.; Weitzman, S. Primary central nervous system lymphoma in children. Neurosurg. Focus 2006, 21, E8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vater, I.; Montesinos-Rongen, M.; Schlesner, M.; Haake, A.; Purschke, F.; Sprute, R.; Mettenmeyer, N.; Nazzal, I.; Nagel, I.; Gutwein, J.; et al. The mutational pattern of primary lymphoma of the central nervous system determined by whole-exome sequencing. Leukemia 2015, 29, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilleri-Broet, S.; Criniere, E.; Broet, P.; Delwail, V.; Mokhtari, K.; Moreau, A.; Kujas, M.; Raphael, M.; Iraqi, W.; Sautes-Fridman, C.; et al. A uniform activated B-cell-like immunophenotype might explain the poor prognosis of primary central nervous system lymphomas: Analysis of 83 cases. Blood 2006, 107, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montesinos-Rongen, M.; Brunn, A.; Bentink, S.; Basso, K.; Lim, W.K.; Klapper, W.; Schaller, C.; Reifenberger, G.; Rubenstein, J.; Wiestler, O.D.; et al. Gene expression profiling suggests primary central nervous system lymphomas to be derived from a late germinal center B cell. Leukemia 2008, 22, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deckert, M.; Montesinos-Rongen, M.; Brunn, A.; Siebert, R. Systems biology of primary CNS lymphoma: From genetic aberrations to modeling in mice. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 127, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos-Rongen, M.; Godlewska, E.; Brunn, A.; Wiestler, O.D.; Siebert, R.; Deckert, M. Activating L265P mutations of the MYD88 gene are common in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Acta Neuropathol. 2011, 122, 791–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos-Rongen, M.; Schmitz, R.; Brunn, A.; Gesk, S.; Richter, J.; Hong, K.; Wiestler, O.D.; Siebert, R.; Kuppers, R.; Deckert, M. Mutations of CARD11 but not TNFAIP3 may activate the NF-kappaB pathway in primary CNS lymphoma. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 120, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodor, C.; Alpar, D.; Marosvari, D.; Galik, B.; Rajnai, H.; Batai, B.; Nagy, A.; Kajtar, B.; Burjan, A.; Deak, B.; et al. Molecular Subtypes and Genomic Profile of Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 79, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos-Rongen, M.; Schafer, E.; Siebert, R.; Deckert, M. Genes regulating the B cell receptor pathway are recurrently mutated in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 124, 905–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapuy, B.; Roemer, M.G.; Stewart, C.; Tan, Y.; Abo, R.P.; Zhang, L.; Dunford, A.J.; Meredith, D.M.; Thorner, A.R.; Jordanova, E.S.; et al. Targetable genetic features of primary testicular and primary central nervous system lymphomas. Blood 2016, 127, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayyar, N.; White, M.D.; Gill, C.M.; Lastrapes, M.; Bertalan, M.; Kaplan, A.; D’Andrea, M.R.; Bihun, I.; Kaneb, A.; Dietrich, J.; et al. MYD88 L265P mutation and CDKN2A loss are early mutational events in primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chukwueke, U.; Grommes, C.; Nayak, L. Primary Central Nervous System Lymphomas. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 36, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deckert, M.; Engert, A.; Bruck, W.; Ferreri, A.J.; Finke, J.; Illerhaus, G.; Klapper, W.; Korfel, A.; Kuppers, R.; Maarouf, M.; et al. Modern concepts in the biology, diagnosis, differential diagnosis and treatment of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Leukemia 2011, 25, 1797–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braggio, E.; Van Wier, S.; Ojha, J.; McPhail, E.; Asmann, Y.W.; Egan, J.; da Silva, J.A.; Schiff, D.; Lopes, M.B.; Decker, P.A.; et al. Genome-Wide Analysis Uncovers Novel Recurrent Alterations in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3986–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Aguilar, A.; Idbaih, A.; Boisselier, B.; Habbita, N.; Rossetto, M.; Laurenge, A.; Bruno, A.; Jouvet, A.; Polivka, M.; Adam, C.; et al. Recurrent mutations of MYD88 and TBL1XR1 in primary central nervous system lymphomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 5203–5211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreher, S.; Johrens, K.; Strehlow, F.; Martus, P.; Borowiec, K.; Radke, J.; Heppner, F.; Roth, P.; Thiel, E.; Pietsch, T.; et al. Prognostic impact of B-cell lymphoma 6 in primary CNS lymphoma. Neuro-Oncology 2015, 17, 1016–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riemersma, S.A.; Oudejans, J.J.; Vonk, M.J.; Dreef, E.J.; Prins, F.A.; Jansen, P.M.; Vermeer, M.H.; Blok, P.; Kibbelaar, R.E.; Muris, J.J.; et al. High numbers of tumour-infiltrating activated cytotoxic T lymphocytes, and frequent loss of HLA class I and II expression, are features of aggressive B cell lymphomas of the brain and testis. J. Pathol. 2005, 206, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapuy, B.; Stewart, C.; Dunford, A.J.; Kim, J.; Kamburov, A.; Redd, R.A.; Lawrence, M.S.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Li, A.J.; Ziepert, M.; et al. Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma are associated with distinct pathogenic mechanisms and outcomes. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, R.; Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Johnson, C.A.; Phelan, J.D.; Wang, J.Q.; Roulland, S.; Kasbekar, M.; Young, R.M.; Shaffer, A.L.; et al. Genetics and Pathogenesis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Phelan, J.D.; Coulibaly, Z.A.; Roulland, S.; Young, R.M.; Wang, J.Q.; Schmitz, R.; Morin, R.D.; Tang, J.; et al. A Probabilistic Classification Tool for Genetic Subtypes of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma with Therapeutic Implications. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 551–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venturutti, L.; Melnick, A.M. The dangers of deja vu: Memory B cells as the cells of origin of ABC-DLBCLs. Blood 2020, 136, 2263–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturutti, L.; Teater, M.; Zhai, A.; Chadburn, A.; Babiker, L.; Kim, D.; Beguelin, W.; Lee, T.C.; Kim, Y.; Chin, C.R.; et al. TBL1XR1 Mutations Drive Extranodal Lymphoma by Inducing a Pro-tumorigenic Memory Fate. Cell 2020, 182, 297–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubschmann, D.; Kleinheinz, K.; Wagener, R.; Bernhart, S.H.; Lopez, C.; Toprak, U.H.; Sungalee, S.; Ishaque, N.; Kretzmer, H.; Kreuz, M.; et al. Mutational mechanisms shaping the coding and noncoding genome of germinal center derived B-cell lymphomas. Leukemia 2021, 35, 2002–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacy, S.E.; Barrans, S.L.; Beer, P.A.; Painter, D.; Smith, A.G.; Roman, E.; Cooke, S.L.; Ruiz, C.; Glover, P.; Van Hoppe, S.J.L.; et al. Targeted sequencing in DLBCL, molecular subtypes, and outcomes: A Haematological Malignancy Research Network report. Blood 2020, 135, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papageorgiou, G.I.; Razis, E.D. CNS Tumors in Adolescents and Young Adults: The Need for a Holistic Specialized Approach. JCO Oncol. Pract. 2020, 16, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.F.; Li, K.K.; Huang, Q.J.; Wang, W.W.; Kwan, J.S.; Chen, H.; Liu, X.Z.; Li, W.C.; Chan, D.T.; Zhang, Z.Y.; et al. Molecular landscape of IDH-wild-type, H3-wild-type glioblastomas of adolescents and young adults. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2022, 48, e12802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attarbaschi, A.; Abla, O.; Ronceray, L.; Bansil, S.; Bomken, S.; Burkhardt, B.; Ceppi, F.; Chiang, A.K.S.; Dave, H.; Fedorova, A.; et al. Primary central nervous system lymphoma: Initial features, outcome, and late effects in 75 children and adolescents. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 4291–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abla, O.; Weitzman, S.; Blay, J.Y.; O’Neill, B.P.; Abrey, L.E.; Neuwelt, E.; Doolittle, N.D.; Baehring, J.; Pradhan, K.; Martin, S.E.; et al. Primary CNS lymphoma in children and adolescents: A descriptive analysis from the International Primary CNS Lymphoma Collaborative Group (IPCG). Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Georgakis, M.K.; Papathoma, P.; Ryzhov, A.; Zivkovic-Perisic, S.; Eser, S.; Taraszkiewicz, L.; Sekerija, M.; Zagar, T.; Antunes, L.; Zborovskaya, A.; et al. Malignant central nervous system tumors among adolescents and young adults (15–39 years old) in 14 Southern-Eastern European registries and the US Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results program: Mortality and survival patterns. Cancer 2017, 123, 4458–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hans, C.P.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Greiner, T.C.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Delabie, J.; Ott, G.; Müller-Hermelink, H.K.; Campo, E.; Braziel, R.M.; Jaffe, E.S.; et al. Confirmation of the molecular classification of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by immunohistochemistry using a tissue microarray. Blood 2004, 103, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, S.L.; Tong, J.H.; Chow, C.; Kwan, J.S.; Lung, R.W.; Chung, L.Y.; Tin, E.K.; Wong, S.S.; Cheung, A.H.; Lau, R.W.; et al. Distinct Molecular Landscape of Epstein-Barr Virus Associated Pulmonary Lymphoepithelioma-Like Carcinoma Revealed by Genomic Sequencing. Cancers 2020, 12, 2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.W.; Chau, S.L.; Tong, J.H.; Chow, C.; Kwan, J.S.H.; Chung, L.Y.; Lung, R.W.; Tong, C.Y.; Tin, E.K.; Law, P.P.; et al. The Landscape of Actionable Molecular Alterations in Immunomarker-Defined Large-Cell Carcinoma of the Lung. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, A.; Labreche, K.; Daniau, M.; Boisselier, B.; Gauchotte, G.; Royer-Perron, L.; Rahimian, A.; Lemoine, F.; de la Grange, P.; Guégan, J.; et al. Identification of novel recurrent ETV6-IgH fusions in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Neuro-Oncology 2018, 20, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.R.; Shi, Z.F.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Chan, A.K.; Aibaidula, A.; Wang, W.W.; Kwan, J.S.H.; Poon, W.S.; Chen, H.; Li, W.C.; et al. IDH mutant lower grade (WHO Grades II/III) astrocytomas can be stratified for risk by CDKN2A, CDK4 and PDGFRA copy number alterations. Brain Pathol. 2020, 30, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukumura, K.; Kawazu, M.; Kojima, S.; Ueno, T.; Sai, E.; Soda, M.; Ueda, H.; Yasuda, T.; Yamaguchi, H.; Lee, J.; et al. Genomic characterization of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Nam, S.J.; Kwon, D.; Kim, H.; Lee, E.; Kim, T.M.; Heo, D.S.; Park, S.H.; Kim, C.W.; Jeon, Y.K. MYC and BCL2 overexpression is associated with a higher class of Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center prognostic model and poor clinical outcome in primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the central nervous system. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandlund, J.T.; Downing, J.R.; Crist, W.M. Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma in childhood. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 1238–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunn, A.; Nagel, I.; Montesinos-Rongen, M.; Klapper, W.; Vater, I.; Paulus, W.; Hans, V.; Blumcke, I.; Weis, J.; Siebert, R.; et al. Frequent triple-hit expression of MYC, BCL2, and BCL6 in primary lymphoma of the central nervous system and absence of a favorable MYC(low)BCL2 (low) subgroup may underlie the inferior prognosis as compared to systemic diffuse large B cell lymphomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 126, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, D.; Tan, K.L.; Steidl, C.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Al Moosawi, M.; Shenkier, T.N.; Connors, J.M.; Sehn, L.H.; Savage, K.J.; Scott, D.W.; et al. Molecular features of a large cohort of primary central nervous system lymphoma using tissue microarray. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 3953–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cady, F.M.; O’Neill, B.P.; Law, M.E.; Decker, P.A.; Kurtz, D.M.; Giannini, C.; Porter, A.B.; Kurtin, P.J.; Johnston, P.B.; Dogan, A.; et al. Del(6)(q22) and BCL6 rearrangements in primary CNS lymphoma are indicators of an aggressive clinical course. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 4814–4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorofchian, S.; El-Achi, H.; Yan, Y.; Esquenazi, Y.; Ballester, L.Y. Characterization of genomic alterations in primary central nervous system lymphomas. J. Neurooncol. 2018, 140, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minderman, M.; Amir, A.; Kraan, W.; Schilder-Tol, E.J.M.; Oud, M.E.C.M.; Scheepstra, C.G.; Noorduyn, A.L.; Kluin, P.M.; Kersten, M.J.; Spaargaren, M.; et al. Immune evasion in primary testicular and central nervous system lymphomas: HLA loss rather than 9p24.1/PD-L1/PD-L2 alterations. Blood 2021, 138, 1194–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Liu, W.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, H.; Xiao, D.; Su, W.; Zeng, R.; Feng, Y.; Duan, Y.; Zhou, J.; et al. Analysis of Genomic Alteration in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma and the Expression of Some Related Genes. Neoplasia 2018, 20, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, K.; Sakata-Yanagimoto, M.; Okoshi, Y.; Goshima, Y.; Yanagimoto, S.; Nakamoto-Matsubara, R.; Sato, T.; Noguchi, M.; Takano, S.; Ishikawa, E.; et al. MYD88 (L265P) mutation is associated with an unfavourable outcome of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 177, 492–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, W.K.; Chai, X.; Ghosh, S.; Ray, D.; Wang, M.; Rasheed, S.A.K.; Casey, P.J. Gα-13 induces CXC motif chemokine ligand 5 expression in prostate cancer cells by transactivating NF-κB. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 18192–18206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, R.M.; Shaffer, A.L., 3rd; Phelan, J.D.; Staudt, L.M. B-cell receptor signaling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Semin. Hematol. 2015, 52, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.E.; Ngo, V.N.; Lenz, G.; Tolar, P.; Young, R.M.; Romesser, P.B.; Kohlhammer, H.; Lamy, L.; Zhao, H.; Yang, Y.; et al. Chronic active B-cell-receptor signalling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Nature 2010, 463, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nihira, K.; Ando, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Kagami, Y.; Miki, Y.; Yoshida, K. Pim-1 controls NF-kappaB signalling by stabilizing RelA/p65. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radke, J.; Ishaque, N.; Koll, R.; Gu, Z.; Schumann, E.; Sieverling, L.; Uhrig, S.; Hubschmann, D.; Toprak, U.H.; Lopez, C.; et al. The genomic and transcriptional landscape of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, B.W.; Anastasi, J.; Hyjek, E.M.; Bies, J.; Reddy, P.L.; Dong, J.; Joseph, L.; Thirman, M.J.; Wroblewski, K.; Wolff, L.; et al. PIM1 gene cooperates with human BCL6 gene to promote the development of lymphomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5735–5739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorer, H.; Zimmermann, M.; Makarova, O.; Oschlies, I.; Klapper, W.; Lang, P.; von Stackelberg, A.; Fleischhack, G.; Worch, J.; Juergens, H.; et al. Primary central nervous system lymphoma in children and adolescents: Low relapse rate after treatment according to Non-Hodgkin-Lymphoma Berlin-Frankfurt-Munster protocols for systemic lymphoma. Haematologica 2014, 99, e238–e241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giulino-Roth, L.; Abla, O.; Batchelor, T.T. Management of primary central nervous system lymphoma in children. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2016, 2016, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, C.; Maragkos, G.A.; Alterman, R.L.; Uhlmann, E.; Pihan, G.; Varma, H. GCB-type is a favorable prognostic factor in primary CNS diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2021, 83, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Zhou, D.; Wang, L.; Zhu, L.; Ye, X. MYD88(L265P) and CD79B double mutations type (MCD type) of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Mechanism, clinical characteristics, and targeted therapy. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2022, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, W.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, M.; Zheng, L.; Tang, J.; Zhang, S.; et al. Whole-Genome/Exome Sequencing Uncovers Mutations and Copy Number Variations in Primary Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma of the Central Nervous System. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 878618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, T.K.; Kovach, A.E.; Grover, N.S.; Huang, L.C.; Lee, L.A.; Rubinstein, S.M.; Wang, Y.; Morgan, D.S.; Greer, J.P.; Park, S.I.; et al. Clinicopathologic correlates of MYD88 L265P mutation and programmed cell death (PD-1) pathway in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2019, 60, 2880–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebid, O.A.E.H.; Ezz El Arab, L.R.; Saad, A.S.; Ezz El Din, M.; Mostafa, N.; Swellam, M. Prognostic impact of MYD88 and TP53 mutations in diffuse large B Cell lymphoma. Ann. Hematol. 2023, 102, 3477–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobbers, J.M.; Wolter, M.; Reifenberger, J.; Ring, G.U.; Jessen, F.; An, H.X.; Niederacher, D.; Schmidt, E.E.; Ichimura, K.; Floeth, F.; et al. Frequent inactivation of CDKN2A and rare mutation of TP53 in PCNSL. Brain Pathol. 1998, 8, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deckert-Schluter, M.; Rang, A.; Wiestler, O.D. Apoptosis and apoptosis-related gene products in primary non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 1998, 96, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montesinos-Rongen, M.; Zuhlke-Jenisch, R.; Gesk, S.; Martin-Subero, J.I.; Schaller, C.; Van Roost, D.; Wiestler, O.D.; Deckert, M.; Siebert, R. Interphase cytogenetic analysis of lymphoma-associated chromosomal breakpoints in primary diffuse large B-cell lymphomas of the central nervous system. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2002, 61, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jardin, F.; Jais, J.P.; Molina, T.J.; Parmentier, F.; Picquenot, J.M.; Ruminy, P.; Tilly, H.; Bastard, C.; Salles, G.A.; Feugier, P.; et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphomas with CDKN2A deletion have a distinct gene expression signature and a poor prognosis under R-CHOP treatment: A GELA study. Blood 2010, 116, 1092–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosrati, A.; Monabati, A.; Sadeghipour, A.; Radmanesh, F.; Safaei, A.; Movahedinia, S. MYC, BCL2, and BCL6 rearrangements in primary central nervous system lymphoma of large B cell type. Ann. Hematol. 2019, 98, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Primary CNS lymphomas (PCNSLs) of children and young adults have only very rarely been studied for molecular landscape. |
| 34 such cases now studied by targeted sequencing, IHC and FISH. |
| Majority of cases (61%) were immunohistochemically GCB subtype. |
| Only rare instances (5%) of gene rearrangement was detected by FISH. |
| Only 10 cases (32%) showed MYD88 mutations and only three mutations were of L265P. |
| In summary, common molecular findings in PCNSLs of older patients were only sparingly present in pediatric and young adult cases. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Z.-F.; Li, K.K.-W.; Liu, A.P.-Y.; Chung, N.Y.-F.; Wong, S.-C.; Chen, H.; Woo, P.Y.-M.; Chan, D.T.-M.; Mao, Y.; Ng, H.-K. The Molecular Landscape of Primary CNS Lymphomas (PCNSLs) in Children and Young Adults. Cancers 2024, 16, 1740. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091740
Shi Z-F, Li KK-W, Liu AP-Y, Chung NY-F, Wong S-C, Chen H, Woo PY-M, Chan DT-M, Mao Y, Ng H-K. The Molecular Landscape of Primary CNS Lymphomas (PCNSLs) in Children and Young Adults. Cancers. 2024; 16(9):1740. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091740
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Zhi-Feng, Kay Ka-Wai Li, Anthony Pak-Yin Liu, Nellie Yuk-Fei Chung, Sze-Ching Wong, Hong Chen, Peter Yat-Ming Woo, Danny Tat-Ming Chan, Ying Mao, and Ho-Keung Ng. 2024. "The Molecular Landscape of Primary CNS Lymphomas (PCNSLs) in Children and Young Adults" Cancers 16, no. 9: 1740. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091740
APA StyleShi, Z.-F., Li, K. K.-W., Liu, A. P.-Y., Chung, N. Y.-F., Wong, S.-C., Chen, H., Woo, P. Y.-M., Chan, D. T.-M., Mao, Y., & Ng, H.-K. (2024). The Molecular Landscape of Primary CNS Lymphomas (PCNSLs) in Children and Young Adults. Cancers, 16(9), 1740. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16091740





