Simple Summary
Diffusion-weighted images (DWI) obtained by echo-planar imaging (EPI) are frequently degraded by susceptibility artifacts from air-soft tissue interfaces at complicated structures in the paranasal sinus, oral cavity, pharynx, and larynx. It has been suggested that DWI obtained by fast advanced spin-echo (FASE) or reconstructed with deep learning reconstruction (DLR) could be useful for image quality improvements. The purpose of this investigation using in vitro and in vivo studies was to determine the influence of sequence difference and application of DLR for DWI on image quality, apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) evaluation, and differentiation of malignant from benign head and neck tumors. In comparison with the EPI sequence, the FASE sequence and DLR can improve image quality and image distortion of DWIs without significantly influencing ADC measurements or the capability to differentiate malignant from benign head and neck tumors.
Abstract
Background: Diffusion-weighted images (DWI) obtained by echo-planar imaging (EPI) are frequently degraded by susceptibility artifacts. It has been suggested that DWI obtained by fast advanced spin-echo (FASE) or reconstructed with deep learning reconstruction (DLR) could be useful for image quality improvements. The purpose of this investigation using in vitro and in vivo studies was to determine the influence of sequence difference and of DLR for DWI on image quality, apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) evaluation, and differentiation of malignant from benign head and neck tumors. Methods: For the in vitro study, a DWI phantom was scanned by FASE and EPI sequences and reconstructed with and without DLR. Each ADC within the phantom for each DWI was then assessed and correlated for each measured ADC and standard value by Spearman’s rank correlation analysis. For the in vivo study, DWIs obtained by EPI and FASE sequences were also obtained for head and neck tumor patients. Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and ADC were then determined based on ROI measurements, while SNR of tumors and ADC were compared between all DWI data sets by means of Tukey’s Honest Significant Difference test. Results: For the in vitro study, all correlations between measured ADC and standard reference were significant and excellent (0.92 ≤ ρ ≤ 0.99, p < 0.0001). For the in vivo study, the SNR of FASE with DLR was significantly higher than that of FASE without DLR (p = 0.02), while ADC values for benign and malignant tumors showed significant differences between each sequence with and without DLR (p < 0.05). Conclusion: In comparison with EPI sequence, FASE sequence and DLR can improve image quality and distortion of DWIs without significantly influencing ADC measurements or differentiation capability of malignant from benign head and neck tumors.
1. Introduction
More than 90% of head and neck malignancies are accounted for by squamous cell carcinomas (SCC), followed by lymphomas [1]. While radiation therapy and surgical resection can lead to favorable results for early-stage head and neck SCC, the odds are less favorable for advanced stages. Therefore, early detection and diagnosis, as well as accurate staging for head and neck malignancies, are considered vital in routine clinical practice.
During the last few decades, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has been continuously and widely used as a useful imaging technique for diagnosis, staging, therapeutic evaluation, and prediction of therapeutic effects for conservative therapies. Moreover, diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is being clinically used and has been considered one of the key sequences for the management of head and neck tumors since the early 2000s [2,3,4]. DWI is frequently obtained by means of echo-planar imaging (EPI) sequence and is considered a functional MRI technique for various clinical purposes, allowing for the quantification of the diffusion of water molecules in a tumor by measuring the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC). However, one of the problems with using DWI for head and neck malignancies is the degradation of image quality, lesion conspicuity, and its effect on ADC measurements because of susceptibility artifacts from air-soft tissue interfaces at complicated structures in the paranasal sinus, oral cavity, pharynx, and larynx. Therefore, a few investigators have suggested during the past decade that, in comparison with EPI, spin-echo-based sequences, including fast advanced spin-echo (FASE), could be useful for DWI to overcome susceptibility artifacts and image distortion [5,6,7,8]. In addition, deep learning reconstruction (DLR) for image noise reduction on not only MRI but also CT was introduced in 2019 and has been in use since then [9,10,11,12,13]. However, no major studies have been published on the impact of DLR on quantitatively assessed DWI obtained by means of EPI and FASE sequences for head and neck malignancies. We hypothesized that DLR may be capable of improving image quality on DWI obtained by means of EPI as well as FASE sequences with little effect on the accuracy of differentiation of malignant from benign head and neck tumors. We also hypothesized that the FASE sequence can improve the image quality and accuracy of ADC measurements, regardless of whether or not DLR is used. The purpose of this study was thus to determine, by means of in vitro and in vivo studies, the influence of sequence difference and application of DLR for DWI on image quality, ADC evaluation, and differentiation of malignant from benign head and neck tumors.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol, Support, and Funding
This retrospective study was performed after obtaining institutional review board and written informed consents were waved from all subjects. Three of the authors are employees of Canon Medical Systems Corporation but did not have any control of the data in this study.
2.2. Quantitative Diffusion Phantom for In Vitro Study
As for the in vitro study, a diffusion phantom for quantitative study (High Precision Devices, Inc., Boulder, CO, USA), which was manufactured by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)/Radiological Society of North America (RSNA)-QIBA and recommended by the Quantitative Imaging Biomarker Alliance (QIBA), was used (Figure 1). This phantom contains 13 vials that have different concentrations of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) in an aqueous solution from each other [14] to evaluate the ADC of the content of each vial. The phantom was designed for quantitative mapping of the isotropic Gaussian diffusion of water molecules and generating physiologically relevant ADC values [15]. The concentrations of PVP in the aqueous solutions were as follows: vials 1–3; 0%, vials 4–5; 10%, vials 6–7; 20%, vials 8–9; 30%, vials 10–11; 40%, and vials: 12–13; 50% [15]. The room between the vials inside the phantom was filled with an ice-water bath at 0 °C to reduce the thermal difference between scanner locations and time points in ADC measurements [14].
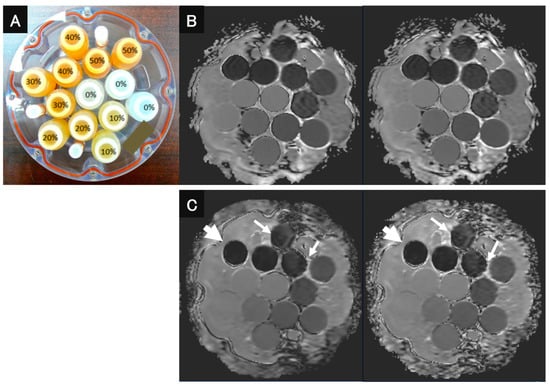
Figure 1.
QIBA recommended that DWI phantom and DWI images be obtained with both sequences and reconstructed with and without DLR. (A) QIBA recommended DWI phantom using 13 vials with different concentrations of PVP (polyvinylpyrrolidone). (B) (L to R: DWIEPI reconstructed with and without DWI) DWIEPI with DLR was not significantly different from DWIEPI without DLR. (C) (L to R: DWIFASE reconstructed with and without DWI) Image noise for DWIFASE with DLR was less than for DWIFASE without DLR (arrows). In addition, the image distortion of DWIFASEs with and without DLR showed less image distortion than DWIEPIs with and without DLR (large arrows).
2.3. Subjects for In Vivo Study
From the beginning of October 2020 until the end of July 2021, 74 consecutive patients with various head and neck tumors (39 men and 35 women, mean age 60.4 years, age range 12–93 years) underwent head and neck MRI. These 74 patients were histopathologically or clinicoradiologically diagnosed with head and neck tumors who had not been treated yet and were originally included in this study. Exclusion criteria were: (1) pediatric patients who needed anesthesia or sedation during MR examinations, (2) MR examinations without DWIs obtained by EPI and FASE sequences, (3) tumors with a long-axis diameter of less than 10 mm, and (4) severe susceptibility artifacts resulting from dental metal. Of the initial 74 cases, 16 were excluded due to criterion (2) (n = 2), criterion (3) (n = 11), and criterion (4) (n = 3). The final study sample thus consisted of 58 patients (30 men, 28 women; median age, 66 years, age range, 12–93 years old). The flow chart for patient selection is shown in Figure 2. In addition, details of patient characteristics are shown in Table 1.
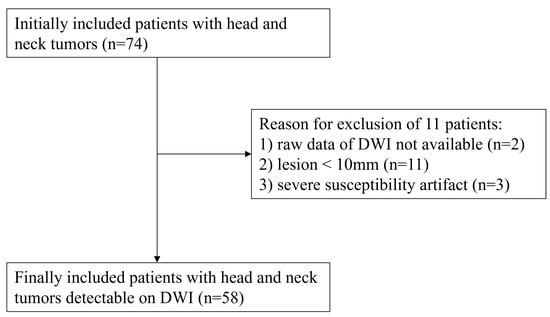
Figure 2.
Patient selection flow chart. The flow chart shows the patient selection from the original 74 patients to the final 58 patients.

Table 1.
Patient characteristics.
2.4. MR Imaging
All MR examinations for both the in vitro and in vivo study were performed with a 3T MR system (Vantage Centurian, Canon Medical Systems Corporation, Otawara, Japan) using a multiple phased-array surface coil (Atlas SPEEDER Head/Neck, Canon Medical Systems).
2.4.1. MR Imaging for In Vitro Study
For the in vitro study, the phantom was obtained five times using DWI with EPI and FASE by means of a head and neck coil with parallel imaging capability (Atlas SPEEDER Head/Neck, Canon Medical Systems). The parameters of DWI with EPI were: Repetition Time (TR)/Echo Time (TE), 6800/78 ms; TI, 240 ms; number of slices, 40; slice thickness, 3 mm; Field of View (FOV), 250 × 240 mm2; acquisition matrix, 136 × 80; number of excitations, 2; flip angle (FA), 90/180; reduction factor (SPEEDER factor), 2.5; b-value 0, 800 s/mm2. The parameters of DWI with FASE were: TR/TE, 20,800/78 ms; number of slices, 40; slice thickness; 3 mm; FOV, 250 × 240 mm2; acquisition matrix, 136 × 80; NEX, 3; FA, 90/140; reduction factor (SPEEDER factor), 2.5; b value 0, 800 s/mm2. Each data set of DWI with EPI and FASE was then reconstructed with and without DLR (Advanced intelligent Clear IQ Engine: AiCE, Canon Medical Systems). Details of DLR have been specified in previously published studies [12,13].
2.4.2. MR Imaging for In Vivo Study
As for the in vivo study, each subject underwent head and neck MR imaging with axial T2-weighted fast spin-echo (FSE) imaging and axial DWIs with single-shot EPI and FASE sequences using the same head and neck coil. Details of the scan protocols in this study are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Details of scan protocols for in vivo study.
For all patients, T2-weighted image (T2WI) with FSE was firstly obtained by compressed sensing with parallel imaging technique (Compressed SPEEDER, Canon Medical Systems) with the following parameters: repetition time (TR), 4800 ms; echo time (TE), 93.5 ms; flip angle (FA), 90/160 deg; acquisition matrix, 352 × 352; reconstruction matrix, 704 × 704; slice thickness, 3 mm; slice gap, 0 mm; number of slices, 40; field of view (FOV), 200 × 200 mm2; number of excitations (NEX), 1; reduction factor (Compressed Speeder factor), 3. Details of compressed sensing with parallel imaging techniques have been written in previously published articles [12,16]. Secondly, DWIs with EPI sequences (DWIEPI) were obtained by short inversion-time recovery (STIR) technique with the following parameters: TR, 6800 ms; TE, 78 ms; inversion time (TI), 240 ms; FA, 90/180 degrees; acquisition matrix, 136 × 80; reconstruction matrix, 272 × 260; slice thickness, 3 mm; slice gap, 0mm; number of slices, 40; FOV, 250 × 240 mm2; NEX, 2; reduction factor (SPEEDER factor), 2.5; b value, 0 and 800 s/mm2. Thirdly, DWIs with the FASE sequence (DWIFASE) were obtained with STIR with short TI technique using the following parameters: TR, 20,800 ms; TE, 78 ms; TI, 240 ms; FA, 90/140 degrees; acquisition matrix, 136 × 80; reconstruction matrix, 272 × 260; slice thickness, 3 mm; slice gap, 0 mm; number of slices, 40; FOV, 250 × 240 mm2; NEX, 3; reduction factor (SPEEDER factor), 2.5; b value, 0 and 800 s/mm2. Finally, each data set of DWI with EPI and FASE was reconstructed with and without DLR.
2.5. Image Analysis
2.5.1. Image Analysis for In Vitro Study
Signal intensity data obtained from each voxel on DWIs were fitted to a mono-exponential model to calculate the ADC by using the following built-in Tensor application (System software version 6.0: Canon Medical Systems):
where S(b) and S0 are the signal intensities with and without MPG pulse, respectively, and the quantity b equals the b-value (s/mm2). ADC for each phantom was measured by a board-certified head and neck radiologist (H.I.) with 15 years of experience. Circular regions of interest (ROIs) 10 mm in diameter were placed on the center slice and on another two slices 1.2 cm on either side of the center slice on each phantom, after which the mean ADC value within each phantom was calculated.
S(b) = S0 exp(−bADC)
2.5.2. Image Analysis for In Vivo Study
Image quality assessment was performed by using System software (version 6.0, Canon Medical Systems). A board-certified head and neck radiologist (H.I.) with 15 years of experience performed region of interest (ROI) measurements. Free-hand ROIs were set over each head and neck tumor on DWIFASE and DWIEPI with and without DLR, then the tumor’s signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) were measured. SNRs were calculated with the following formula based on previously published studies [16,17,18]:
where SItumor and SDtumor are the signal intensity and standard deviation of the tumor in the ROI placed on the tumor.
SNR = SItumor/SDtumor
To determine the difference in deformation among all DWIs, the margin of each tumor was traced by free-hand ROI on the same level for all sequences, and then the tumor’s area on each sequence was calculated. The deformation ratio (DR) was defined as the difference in the free-hand ROI area between each DWI and T2WI divided by the ROI area on T2WI. The formula of the calculation is as follows:
where AreaT2WI and AreaDWI are the tumor’s area on T2WI and each DWI sequence.
DR = |AreaT2WI − AreaDWI|/AreaT2WI
Another freehand ROI was placed as a reference over the spinal cord on the same level as the tumor on DWIFASE and DWIEPI with and without DLR, as in previous studies [5,19]. SNR and DR of the spinal cord on each DWI were also calculated using the same formula as the tumor shown above (Formulas (2) and (3)). Furthermore, to compare the difference in SNR and DR of tumors according to tumor location, all tumors were categorized into 4 groups according to their location in head and neck: (1) pharynx and larynx, (2) oral cavity and mandibular, where tumors often interfere with air, (3) salivary glands and (4) others, where tumors do not usually interfere with air.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.6.1. In Vitro Study
Statistical Analysis Was Performed Using JMP Software (version 14, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA).
To compare the measurement accuracy for ADC among DWIs obtained by EPI and FASE sequences and reconstructed with and without DLR, correlations between ADC values measured with each method and the standard reference among all phantoms were evaluated by Spearman’s rank correlation analysis. Measurement errors for ADC evaluation were then compared by means of the Wilcoxon signed-rank test among DWIs obtained by EPI and FASE sequences and reconstructed with and without DLR.
2.6.2. In Vivo Study
JMP software (version 14, SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA) was used for statistical analysis.
Tukey’s HSD test was performed to compare image acquisition and reconstruction times among all DWIs.
For a quantitative comparison of image quality among DWIs obtained by EPI and FASE sequences and reconstructed with and without DLR, SNR, and DR of overall tumors and of the spinal cord were compared among all methods by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s Honest Significant Difference (HSD) test. Moreover, the SNR and DR of a tumor in a given group were compared among all methods by using the same statistical analysis to determine the relationship between image quality and tumor location.
A Student t-test was used to compare the ADC values of benign and malignant tumors for each DWI. To assess the influence of sequence difference and DLR on ADC measurements, ADC values of benign and malignant tumors were also statistically compared among all DWI methods by means of Tukey’s HSD test.
To determine the capability of each method to differentiate malignant from benign tumors, a receiver operating characteristic (ROC)-based positive test was performed. Because Warthin tumor, adenoid hypertrophy and benign lymphadenopathy are known to show low ADC values though they are benign [20,21,22,23], additional ROC-based positive tests were also performed after patients with these etiologies had been excluded.
Finally, by applying each feasible threshold value, sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were compared by means of McNemar’s test among all DWI methods for all head and neck tumors except for Warthin tumor, adenoid hypertrophy, and benign lymphadenopathy.
A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered significant for all statistical analyses.
3. Results
3.1. In Vitro Study
Correlations between measured ADC and standard reference for all DWI methods are shown in Table 3. Correlations between measured ADC and standard reference for all methods were significant and excellent (0.92 ≤ ρ ≤ 0.99, p < 0.0001).

Table 3.
Correlations for ADC between standard reference and measured ADC for all DWI methods.
A comparison of measurement errors for ADC evaluation between EPI with and without DLR and between FASE with and without DLR is shown in Table 4. Measurement errors for FASE with DLR were significantly larger than those of FASE without DLR at all fantom concentrations (p < 0.001).

Table 4.
Comparison of measurement errors in ADCs for EPI and FASE with and without DLR.
3.2. In Vivo Study
The final group included 58 patients (30 men, 28 women; mean age, 60.6 ± 19.0 years; age range, 12–93 years). There were 15 patients in (1) the pharynx and larynx group, 12 patients in (2) the oral cavity group, 15 patients in (3) the salivary glands group, and 16 patients in (4) the group of ‘others’.
A representative case is shown in Figure 3.
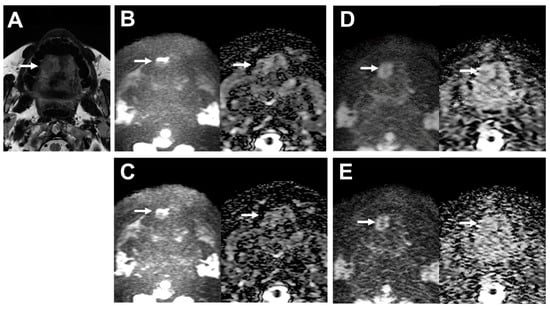
Figure 3.
39-year-old male patient with oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. (A) T2WI clearly depicts the lobulated shape of oral cavity cancer at the right side of the tongue (arrow). (B) (L to R, original DWI image and ADC map) Image of the tumor on DWI obtained by EPI with DLR shows deformation (arrows). SNR of the tumor was 4.43, and the deformation ratio (DR) compared with T2WI was 0.60. (C) (L to R, original DWI image and ADC map) The image of the tumor on DWI obtained by EPI without DLR is also deformed (arrows). SNR of the tumor was 4.58, and the deformation ratio (DR) compared with T2WI was 0.60. (D) (L to R, original DWI image and ADC map) The image of the tumor on DWI obtained by FASE with DLR is less deformed (arrows). SNR of the tumor was 7.08, and the deformation ratio (DR) compared with T2WI was 0.01. (E) (L to R, original DWI image and ADC map) The image of the tumor on DWI obtained by FASE without DLR is deformed (arrows). SNR of the tumor was 4.47, and the deformation ratio (DR) compared with T2WI was 0.21.
A comparison of results for image acquisition and reconstruction times among DWIsEPI with and without DLR and DWIsFASE with and without DLR is shown in Figure 4. Mean image acquisition and reconstruction times for DWIs with DLR (DWIEPI: 223.1 ± 9.6 s, DWIFASE: 437.0 ± 17.3 s) were significantly longer than for those without DLR (DWIEPI: 206.8 ± 8.9 s, p < 0.0001; DWIFASE: 420.8 ± 16.8 s, p < 0.0001). In addition, mean image acquisition and reconstruction times for DWIFASE with and without DLR were significantly longer than for those DWIEPI with and without DLR (p < 0.0001).
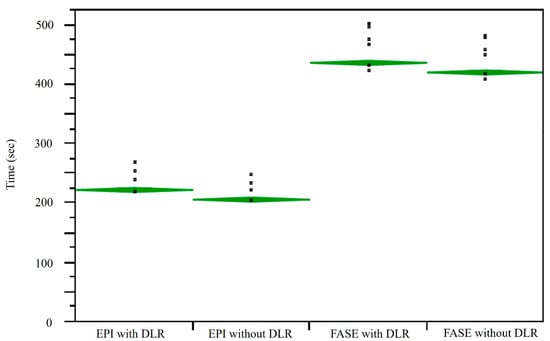
Figure 4.
Comparison of image acquisition and reconstruction times for DWIEPI with and without DLR and for DWIFASE with and without DLR. L to R: EPI with and without DLR, FASE with and without DLR. Mean image acquisition and reconstruction times for DWIFASE with and without DLR were significantly longer than those for DWIEPI with and without DLR (p < 0.0001). Mean image acquisition and reconstruction times for DWIEPI and DWIFASE with DLR were significantly longer than those for DWIEPI and DWIFASE without DLR (p < 0.0001).
Comparisons of SNR of overall tumors, the spinal cord and each tumor group for all DWI methods are shown in Table 5. SNRs of FASE with DLR (5.6 ± 2.4) were significantly higher than those of FASE without DLR in overall tumors (4.3 ± 1.6, p = 0.02).

Table 5.
Comparison of signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) for tumors and spinal cord.
Comparisons of DR of overall tumors, the spinal cord, and each tumor group for each sequence with and without DLR and all DWIs are shown in Table 6. For overall tumors, DRs of FASE with and without DLR (with DLR: 0.13 ± 0.17, without DLR: 0.19 ± 0.13) were significantly lower than those of EPI with and without DLR (with DLR: 0.37 ± 0.33, vs. FASE with DLR, p < 0.0001, vs. FASE without DLR, p = 0.001; without DLR: 0.36 ± 0.34, vs. FASE with DLR, p < 0.0001, vs. FASE without DLR, p = 0.003). For the spinal cord, DR of FASE with DLR (0.13 ± 0.13) was significantly lower than that of EPI with and without DLR (with DLR: 0.34 ± 0.30, p < 0.0001; without DLR: 0.31 ± 0.30, p = 0.0003). Moreover, the DR of FASE with DLR (0.10 ± 0.10) was significantly lower than that of EPI with and without DLR (with DLR: 0.33 ± 0.92, p = 0.03; without DLR: 0.32 ± 0.30, p = 0.04) for the pharynx and larynx group. In addition, the DR of FASE with DLR (0.06 ± 0.05) was significantly lower than that of EPI with and without DLR (with DLR: 0.47 ± 0.31, p = 0.001; without DLR: 0.40 ± 0.37, p = 0.009) for the oral cavity and mandibular group.

Table 6.
Comparison of deformation ratio (DR) for tumors and spinal cord.
Comparisons of ADCs for malignant and benign tumors between each DWI with and without DLR are shown in Table 7. ADC values for benign and malignant tumors showed significant differences between each sequence with and without DLR (p < 0.05).

Table 7.
A comparison of ADCs for malignant and benign tumors was obtained with each DWI method, with and without DLR, and with all methods.
Feasible threshold values and diagnostic performance of all DWI methods for all patients are shown in Table 8. The application of each threshold value for differentiating malignant tumors from benign tumors showed no significant differences in sensitivity, specificity, or accuracy for all DWI methods (p > 0.05). Feasible threshold values and diagnostic performance for all DWI methods for all head and neck tumors except for Warthin tumor, adenoid hypertrophy, and benign lymphadenopathy are shown in Table 9. The application of each threshold value for differentiating malignant tumors from benign tumors showed no significant differences in sensitivity, specificity, or accuracy for all DWI methods (p > 0.05).

Table 8.
Results of comparison of diagnostic performance of DWI methods with and without DLR for all tumors.

Table 9.
Comparison of Diagnostic Performance among all DWIs for all head and neck tumors except for Warthin tumor, adenoid hypertrophy, and benign lymphadenopathy.
4. Discussion
Our in vitro and in vivo study results demonstrate that DWIFASE with DLR delivered better quantitative image quality without little influence on ADC measurements than did DWIFASE without DLR on a 3T MR system. Moreover, the in vivo study findings showed that, in comparison with DWIEPI, using DWIFASE could reduce image distortions in head and neck tumors, especially those in the pharynx, larynx, oral cavity, and mandibular groups, regardless of whether DLR was used or not. However, there were no statistically significant differences between DWIEPI and DWIFASE for distinguishing malignant from benign head and neck tumors. To the best of our knowledge, this study was the first to use DLR for DWIs obtained by FASE and EPI sequences in in vivo and in vitro studies and determine its effect on image quality, ADC measurements, and differentiation between malignant and benign head and neck tumors.
As for the in vitro study, DWIs obtained with any of the methods showed significant and excellent correlations between measured ADC and the standard reference. However, DWIFASE was also considered less tolerant for ADC measurements than DWIEPI, and DLR had a greater effect on ADC measurements when DWIFASE was used.
In addition to the in vitro study, our in vivo study demonstrated that image acquisition and reconstruction times for DWIFASE with or without DLR were significantly longer than those for DWIEPI with or without DLR and that DLR could significantly improve SNR on DWI obtained by FASE sequence. These findings were comparatively compatible with those of previous studies [10,12,13,24,25,26,27,28,29]. Moreover, our study demonstrated that the overall distortion rates of DWIFASE with or without DLR were significantly smaller than those of DWIEPI with or without DLR. In addition, distortion ratios of DWIFASE with DLR showed significant improvements over those of DWIEPI with and without DLR for lesions in the “spinal cord”, “pharynx and larynx” and “oral cavity and mandibular” groups. The findings of the in vivo study indicate that the FASE sequence is potentially superior for head and neck DWIs to the EPI sequence in terms of improvements in image quality and ADC measurement. Findings of previous studies, which evaluated head and neck DWIs obtained with spin-echo (SE)-based sequences such as turbo SE or FASE sequence, suggest that DWIs thus obtained are more tolerant than DWIs obtained with EPI for various anatomical areas [5,6,7,8,9,10,30,31,32]. Considering these previous findings and our results, it can be easily assumed that DWI would be better than EPI for obtaining FASE sequences for head and neck tumors reconstructed with DLR in routine clinical practice.
The comparison of ADC values for benign and malignant tumors showed significant differences between each DWI reconstructed with and without DLR, although no significant differences in diagnostic performance were observed among all DWI data sets. This finding is compatible with those previously published for DWIs for prostatic cancer in a study [13]. It, therefore, seems preferable to obtain DWIs by using the FASE rather than the EPI sequence to improve image distortion, and it might be better to use DLR for image quality improvement for either sequence in head and neck tumor patients.
There are a few limitations to this study. First, the study population was small, and underlying pathological and clinical situations were varied so that no significant improvements in diagnostic performance could be observed. Large prospective cohort studies are thus warranted to demonstrate the actual clinical significance of DWIFASE or DLR in this setting. Second, the conventional parallel imaging technique was used for DWIFASE and DWIEPI acquisitions. However, recently clinically applied compressed sensing (CS) with and without parallel imaging or FASE acquisition with multiple k-space data acquisition using various time reduction techniques have been introduced as useful for acquisition time reduction [12,16,33] but have not been used or tested in this study. Moreover, DLR in this study was provided by a single vendor, so DLRs from other vendors could not be used. It would, therefore, be better to use DWIFASE with other acquisition techniques and other DLR methods in future studies to demonstrate the actual clinical significance of DWIFASE in this setting. Third, although free-hand ROI placement was carefully performed by an experienced head and neck radiologist, there were potential errors and variability outlining the head and neck tumors. ROI placement by blinded multiple radiologists could decrease the potential error and variability of ROI measurement.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, in comparison with the EPI sequence for the 3T MR system, the FASE sequence and DLR can improve image quality and image distortion of DWIs without significantly influencing ADC measurements in the in vivo or in vitro study or the capability to differentiate malignant from benign head and neck tumors.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.I.; methodology, H.I. and Y.O. (Yoshiharu Ohno); software, H.I., S.H. and H.N.; validation, H.I., K.M. and Y.O. (Yoshiyuki Ozawa); formal analysis, H.I., Y.O. (Yuki Obama) and T.U.; investigation, H.I., Y.O. (Yoshiharu Ohno), K.M., Y.K., Y.S., Y.T., Y.N., S.H., Y.O. (Yuki Obama), T.U. and H.N.; resources, H.I.; data curation, H.I. and K.M.; writing—original draft preparation, H.I.; writing—review and editing, H.I., Y.O. (Yoshiharu Ohno) and K.M.; visualization, H.I., K.Y., M.I., M.Y. and A.I.; supervision, H.I., Y.O. (Yoshiharu Ohno), Y.O. (Yuki Obama) and H.T.; project administration, H.I. and Y.O. (Yoshiharu Ohno); funding acquisition, H.I., Y.O. (Yoshiharu Ohno) and H.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (JSPS KAKENHI Grant No. 23K07074).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Fujita Health University Hospital Ethics Committee (protocol code HM22-328, approved in July 2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived due to the retrospective nature of the investigation. All patient data were anonymized, and confidentiality was maintained in this study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
Y.O. (Yoshiharu Ohno), H.N., and H.T. received a research grant from Canon Medical Systems Corporation, which also supported this work technically. K.Y., M.I., and M.Y. are employees of Canon Medical Systems Corporation, who had no control over any data or information submitted for publication nor any control over any parts of data or information included in this study.
Abbreviations
| SCC | squamous cell carcinoma |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| DWI | Diffusion-weighted imaging |
| EPI | Echo planar imaging |
| ADC | apparent diffusion coefficient |
| FASE | fast advanced spin-echo |
| DLR | Deep learning reconstruction |
| QIBA | Quantitative imaging biomarker alliance |
| PVP | Polyvinylpyrrolidone |
| FSE | Fast spin-echo |
| TR | Repetition time |
| TE | Echo time |
| FOV | Field of view |
| FA | Flip angle |
| NEX | number of excitations |
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio |
| DR | Deformation ratio |
| ROC | receiver operating characteristic |
References
- Noij, D.P.; Martens, R.M.; Marcus, J.T.; de Bree, R.; Leemans, C.R.; Castelijns, J.A.; de Jong, M.C.; de Graaf, P. Intravoxel incoherent motion magnetic resonance imaging in head and neck cancer: A systematic review of the diagnostic and prognostic value. Oral. Oncol. 2017, 68, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razek, A.A. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of head and neck. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2010, 34, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoeny, H.C.; De Keyzer, F. Extracranial applications of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Eur. Radiol. 2007, 17, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoeny, H.C.; De Keyzer, F.; King, A.D. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in the head and neck. Radiology 2012, 263, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikayama, R.; Yabuuchi, H.; Sonoda, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Nagatomo, K.; Kimura, M.; Kawanami, S.; Kamitani, T.; Kumazawa, S.; Honda, H. Comparison of intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging between turbo spin-echo and echo-planar imaging of the head and neck. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, Y.; Koyama, H.; Yoshikawa, T.; Takenaka, D.; Kassai, Y.; Yui, M.; Matsumoto, S.; Sugimura, K. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging using FASE sequence for 3T MR system: Preliminary comparison of capability for N-stage assessment by means of diffusion-weighted MR imaging using EPI sequence, STIR FASE imaging and FDG PET/CT for non-small cell lung cancer patients. Eur. J. Radiol. 2015, 84, 2321–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, Y.; Yui, M.; Takenaka, D.; Yoshikawa, T.; Koyama, H.; Kassai, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Oshima, Y.; Hamabuchi, N.; Hanamatsu, S.; et al. Computed DWI MRI Results in Superior Capability for N-Stage Assessment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Than That of Actual DWI, STIR Imaging, and FDG-PET/CT. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2023, 57, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panyarak, W.; Chikui, T.; Yamashita, Y.; Kamitani, T.; Yoshiura, K. Image Quality and ADC Assessment in Turbo Spin-Echo and Echo-Planar Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging of Tumors of the Head and Neck. Acad. Radiol. 2019, 26, e305–e316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higaki, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Tatsugami, F.; Nakaura, T.; Awai, K. Improvement of image quality at CT and MRI using deep learning. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2019, 37, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidoh, M.; Shinoda, K.; Kitajima, M.; Isogawa, K.; Nambu, M.; Uetani, H.; Morita, K.; Nakaura, T.; Tateishi, M.; Yamashita, Y.; et al. Deep Learning Based Noise Reduction for Brain MR Imaging: Tests on Phantoms and Healthy Volunteers. Magn. Reson. Med. Sci. 2020, 19, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsukiyo, R.; Ohno, Y.; Matsuyama, T.; Nagata, H.; Kimata, H.; Ito, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Murayama, K.; Kato, R.; Toyama, H. Deep learning-based and hybrid-type iterative reconstructions for CT: Comparison of capability for quantitative and qualitative image quality improvements and small vessel evaluation at dynamic CE-abdominal CT with ultra-high and standard resolutions. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2021, 39, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, T.; Ohno, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Iwase, A.; Fukuba, T.; Hanamatsu, S.; Obama, Y.; Ikeda, H.; Ikedo, M.; Yui, M.; et al. Compressed sensing and deep learning reconstruction for women’s pelvic MRI denoising: Utility for improving image quality and examination time in routine clinical practice. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 134, 109430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, T.; Ohno, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Murayama, K.; Ikedo, M.; Yui, M.; Hanamatsu, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Obama, Y.; Ikeda, H.; et al. Deep Learning Reconstruction of Diffusion-weighted MRI Improves Image Quality for Prostatic Imaging. Radiology 2022, 303, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, J.P.; Ding, Y.; Hwang, K.-P.; Cardenas, C.E.; Ai, H.; Fuller, C.D.; Stafford, R.J. Quantitative Evaluation of apparent diffusion coefficient in a large multi-unit institution using the QIBA diffusion phantom. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla-Dave, A.; Obuchowski, N.A.; Chenevert, T.L.; Jambawalikar, S.; Schwartz, L.H.; Malyarenko, D.; Huang, W.; Noworolski, S.M.; Young, R.J.; Shiroishi, M.S.; et al. Quantitative imaging biomarkers alliance (QIBA) recommendations for improved precision of DWI and DCE-MRI derived biomarkers in multicenter oncology trials. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 49, e101–e121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, H.; Ohno, Y.; Murayama, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Iwase, A.; Fukuba, T.; Toyama, H. Compressed sensing and parallel imaging accelerated T2 FSE sequence for head and neck MR imaging: Comparison of its utility in routine clinical practice. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 135, 109501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledano-Massiah, S.; Sayadi, A.; de Boer, R.; Gelderblom, J.; Mahdjoub, R.; Gerber, S.; Zuber, M.; Zins, M.; Hodel, J. Accuracy of the Compressed Sensing Accelerated 3D-FLAIR Sequence for the Detection of MS Plaques at 3T. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2018, 39, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vranic, J.E.; Cross, N.M.; Wang, Y.; Hippe, D.S.; de Weerdt, E.; Mossa-Basha, M. Compressed Sensing-Sensitivity Encoding (CS-SENSE) Accelerated Brain Imaging: Reduced Scan Time without Reduced Image Quality. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2019, 40, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolff-Gart, A.S.; Pouwels, P.J.; Noij, D.P.; Ljumanovic, R.; Vandecaveye, V.; de Keyzer, F.; de Bree, R.; de Graaf, P.; Knol, D.L.; Castelijns, J.A. Diffusion-weighted imaging of the head and neck in healthy subjects: Reproducibility of ADC values in different MRI systems and repeat sessions. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habermann, C.R.; Arndt, C.; Graessner, J.; Diestel, L.; Petersen, K.U.; Reitmeier, F.; Ussmueller, J.O.; Adam, G.; Jaehne, M. Diffusion-weighted echo-planar MR imaging of primary parotid gland tumors: Is a prediction of different histologic subtypes possible? AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2009, 30, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, M.; Motoori, K.; Hanazawa, T.; Nagai, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Ueda, T.; Funatsu, H.; Ito, H. Warthin tumor of the parotid gland: Diagnostic value of MR imaging with histopathologic correlation. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2004, 25, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kato, H.; Fujimoto, K.; Matsuo, M.; Mizuta, K.; Aoki, M. Usefulness of diffusion-weighted MR imaging for differentiating between Warthin’s tumor and oncocytoma of the parotid gland. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2017, 35, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surov, A.; Ryl, I.; Bartel-Friedrich, S.; Wienke, A.; Kösling, S. Diffusion weighted imaging of nasopharyngeal adenoid hypertrophy. Acta Radiol. 2015, 56, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.H.; Hwang, J.; Hong, S.S.; Lee, E.J.; Jeong, J.; Benkert, T.; Sung, J.; Arberet, S. Clinical feasibility of accelerated diffusion weighted imaging of the abdomen with deep learning reconstruction: Comparison with conventional diffusion weighted imaging. Eur. J. Radiol. 2022, 154, 110428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, J.; Keller, G.; Gassenmaier, S.; Nickel, D.; Koerzdoerfer, G.; Mostapha, M.; Almansour, H.; Afat, S.; Othman, A.E. Feasibility of an accelerated 2D-multi-contrast knee MRI protocol using deep-learning image reconstruction: A prospective intraindividual comparison with a standard MRI protocol. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 6215–6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, M.; Zhou, L.; Sun, J. Deep-learning-based 3D super-resolution MRI radiomics model: Superior predictive performance in preoperative T-staging of rectal cancer. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, D.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, L. Super-resolution reconstruction of knee magnetic resonance imaging based on deep learning. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 187, 105059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, R.F.; Zheng, L.Y.; Jin, K.P.; Sun, W.; Liao, S.; Zeng, M.S.; Dai, Y.M. Single-breath-hold T2WI liver MRI with deep learning-based reconstruction: A clinical feasibility study in comparison to conventional multi-breath-hold T2WI liver MRI. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 81, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.M.; Xu, J.R.; Hua, J.; Gu, H.Y.; Zhu, J.; Hu, J. Value of diffusion-weighted MR imaging performed with quantitative apparent diffusion coefficient values for cervical lymphadenopathy. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 38, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumeler, E.; Parlak, S.; Yazici, G.; Karabulut, E.; Kiratli, H.; Oguz, K.K. Single shot echo planar imaging (ssEPI) vs. single shot turbo spin echo (ssTSE) DWI of the orbit in patients with ocular melanoma. Br. J. Radiol. 2021, 94, 20200825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhappen, M.H.; Pouwels, P.J.; Ljumanovic, R.; van der Putten, L.; Knol, D.L.; De Bree, R.; Castelijns, J.A. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in head and neck cancer: Comparison between half-fourier acquired single-shot turbo spin-echo and EPI techniques. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, Y.; Takeda, C.; Kidoh, M.; Oda, S.; Aoki, R.; Ito, K.; Morita, K.; Haraoka, K.; Yamashita, Y.; Iizuka, H.; et al. Effects of Deep Learning Reconstruction Technique in High-Resolution Non-contrast Magnetic Resonance Coronary Angiography at a 3-Tesla Machine. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2021, 72, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshizako, T.; Yoshida, R.; Asou, H.; Nakamura, M.; Kitagaki, H. Comparison between turbo spin-echo and echo planar diffusion-weighted imaging of the female pelvis with 3T MRI. Acta Radiol. Open 2021, 10, 2058460121994737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).