The Performance of Different Parametric Ultrasounds in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis: Correlation with Radical Prostatectomy Specimens
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
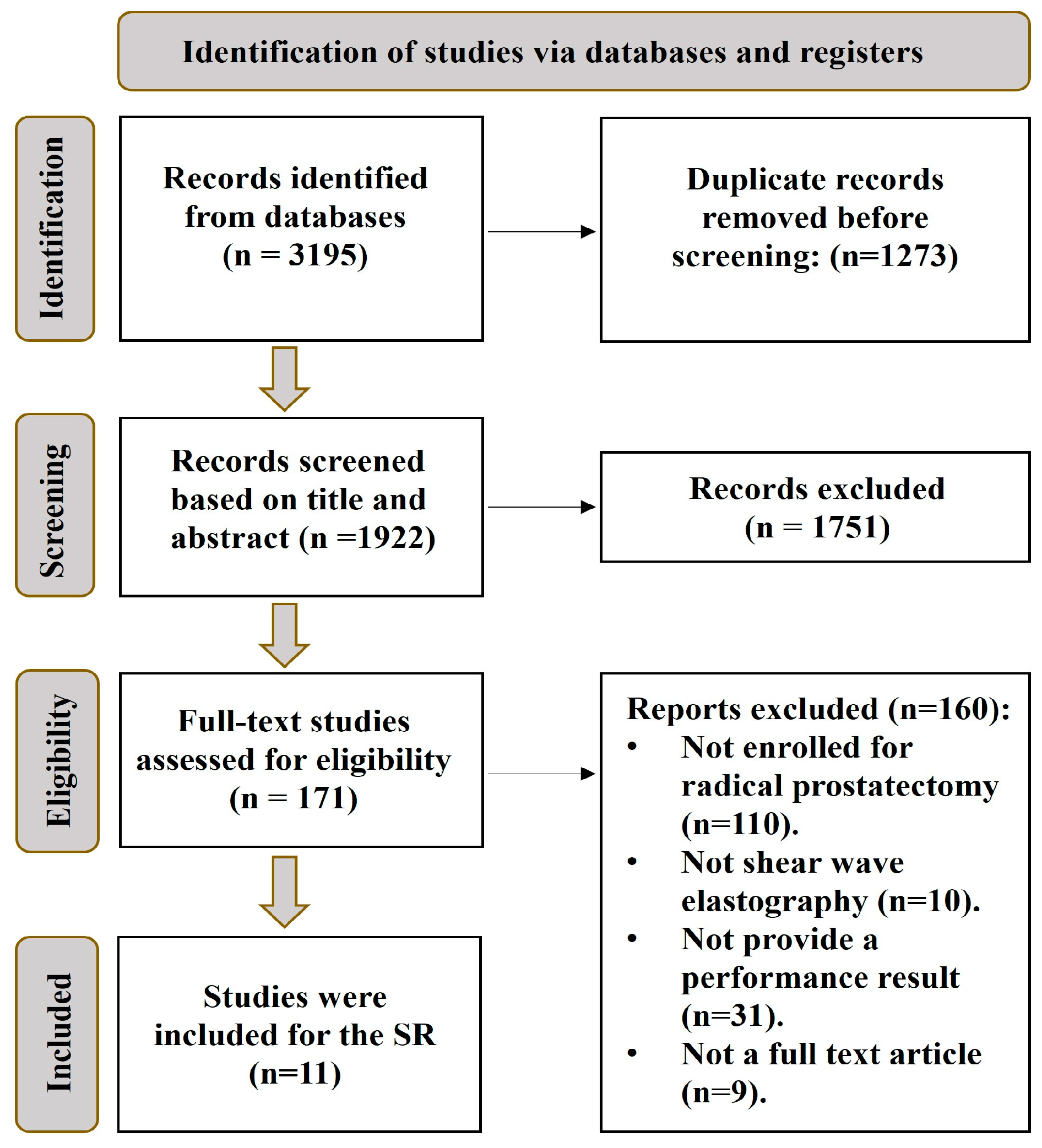
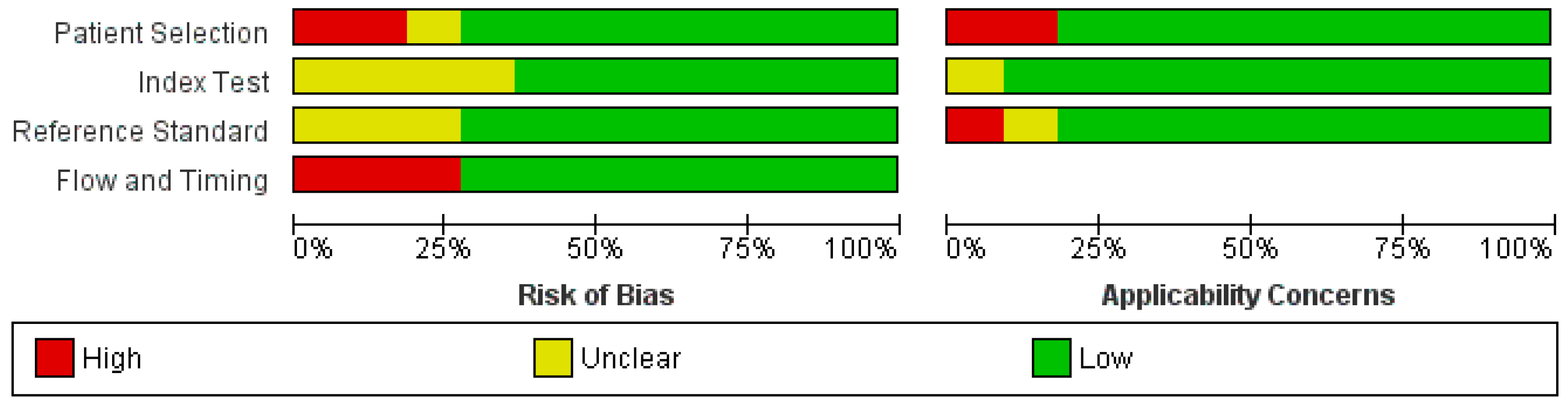
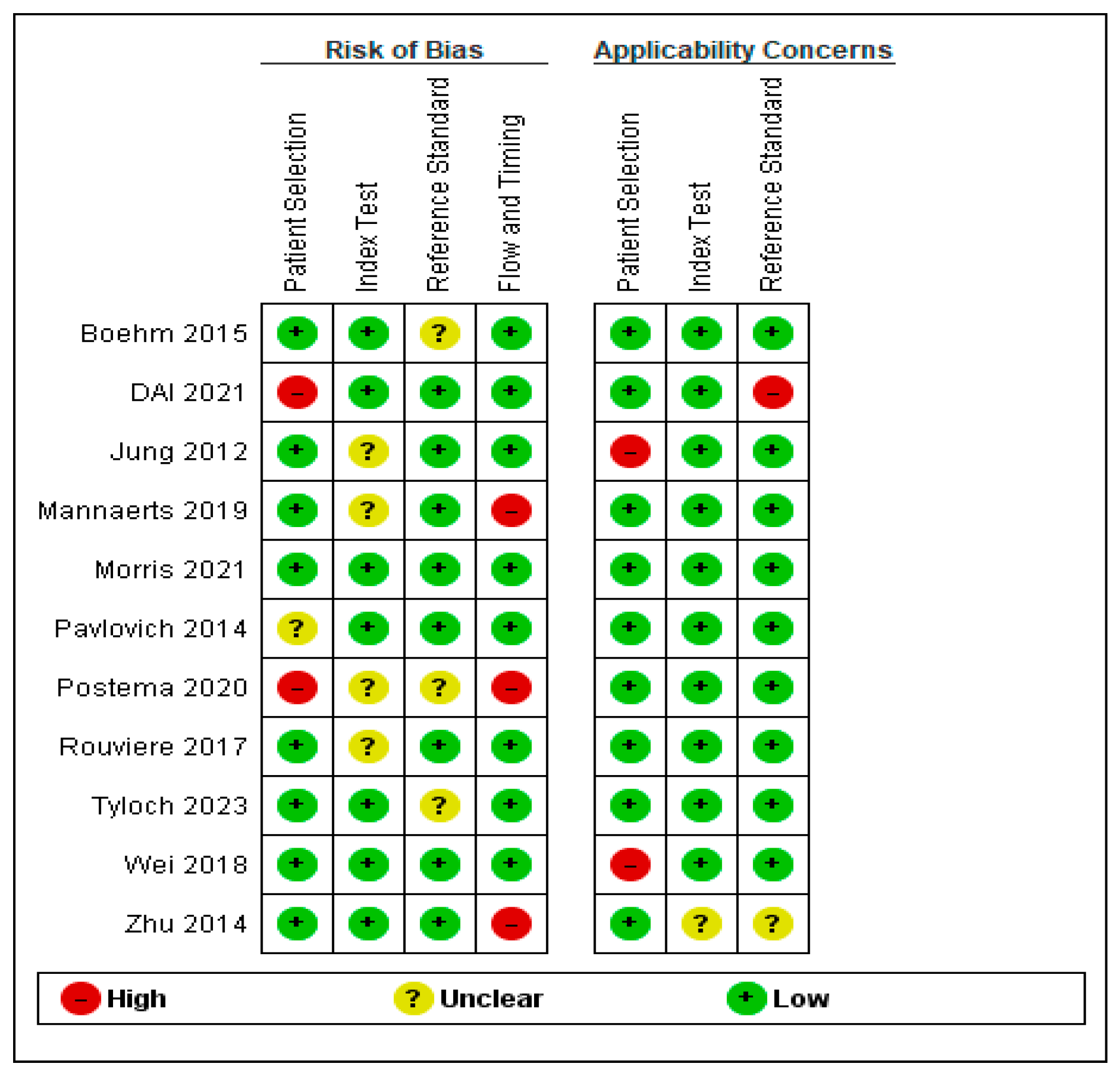
2. Materials and Methods
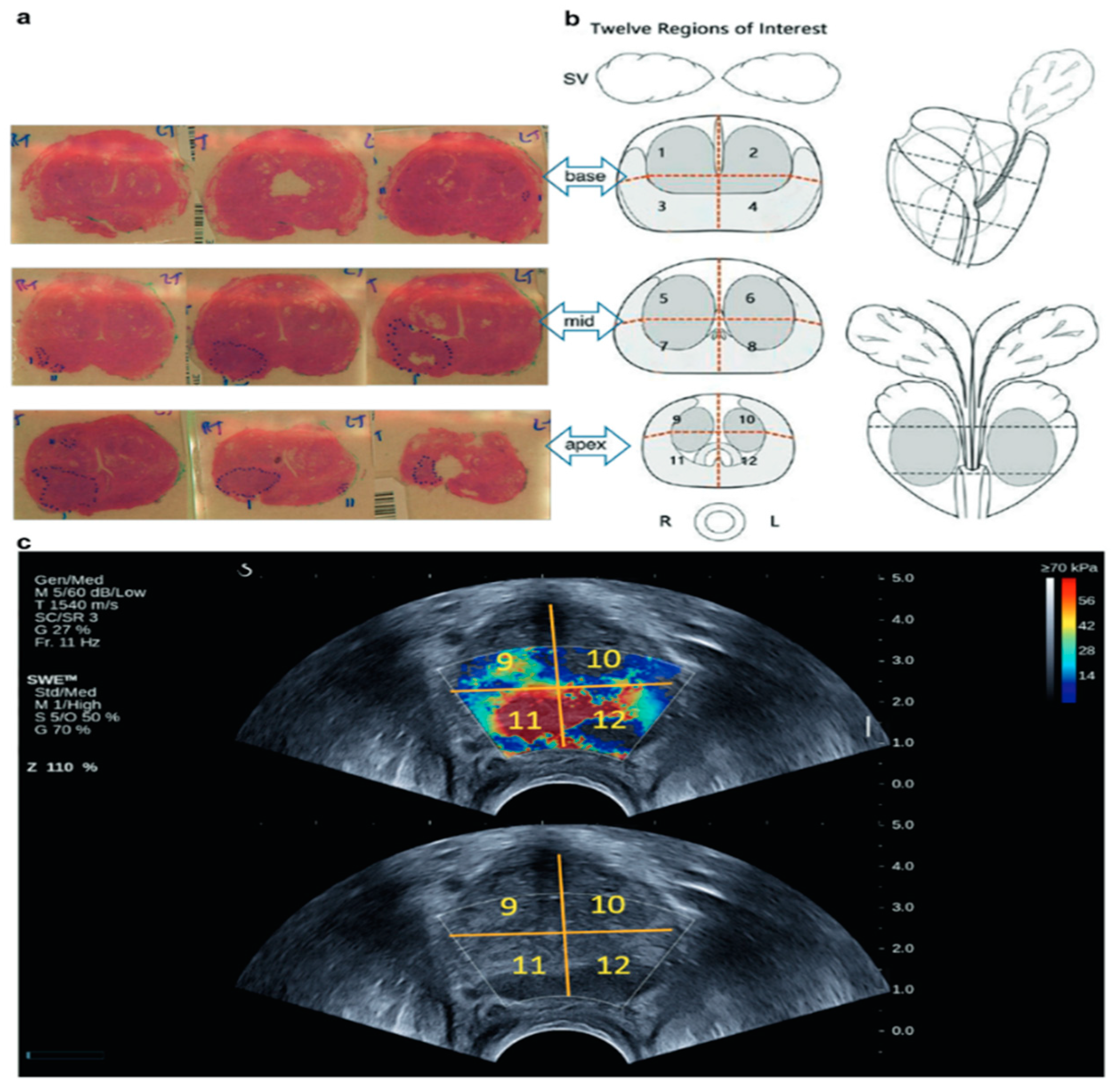
3. Results
3.1. Grayscale Ultrasound
3.2. Shear-Wave Elastography Ultrasound
3.3. Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound
3.4. Multiparametric Ultrasound
3.5. Other Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okwor, C.J.; Nnakenyi, I.D.; Agbo, E.O.; Nweke, M. Sensitivity and specificity of prostate-specific antigen and its surrogates towards the detection of prostate cancer in sub-Saharan Africa: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Afr. J. Urol. 2023, 29, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naji, L.; Randhawa, H.; Sohani, Z.; Dennis, B.; Lautenbach, D.; Kavanagh, O.; Bawor, M.; Banfield, L.; Profetto, J. Digital rectal examination for prostate cancer screening in primary care: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Fam. Med. 2018, 16, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacoub, J.H.; Verma, S.; Moulton, J.S.; Eggener, S.; Oto, A. Imaging-guided prostate biopsy: Conventional and emerging techniques. Radiographics 2012, 32, 819–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Ji, Z.; Yang, P.; Tian, Y. Predicting Gleason sum upgrading from biopsy to radical prostatectomy pathology: A new nomogram and its internal validation. BMC Urol. 2021, 21, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, N.; Simpkin, A.; Fowler, S.; Varma, M.; Kynaston, H.; Narahari, K. Pathological upgrading in prostate cancer treated with surgery in the United Kingdom: Trends and risk factors from the British Association of Urological Surgeons Radical Prostatectomy Registry. BMC Urol. 2019, 19, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, J.I.; Feng, Z.; Trock, B.J.; Pierorazio, P.M. Upgrading and downgrading of prostate cancer from biopsy to radical prostatectomy: Incidence and predictive factors using the modified gleason grading system and factoring in tertiary grades. Eur. Urol. 2012, 61, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calio, B.P.; Sidana, A.; Sugano, D.; Gaur, S.; Maruf, M.; Jain, A.L.; Merino, M.J.; Choyke, P.L.; Wood, B.J.; Pinto, P.A.; et al. Risk of Upgrading from Prostate Biopsy to Radical Prostatectomy Pathologyd-Does Saturation Biopsy of Index Lesion during Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Transrectal Ultrasound Fusion Biopsy Help? J. Urol. 2018, 199, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, M.; Lenon, M.S.L.; Storino Ramacciotti, L.; Medina, L.G.; Sayegh, A.S.; La Riva, A.; Perez, L.C.; Ghoreifi, A.; Lizana, M.; Jadvar, D.S.; et al. Multiparametric ultrasound of prostate: Role in prostate cancer diagnosis. Ther. Adv. Urol. 2022, 14, 17562872221145625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salo, J.O.; Rannikko, S.; Makinen, J.; Lehtonen, T. Echogenic Structure of Prostatic Cancer Imaged on Radical Prostatectomy Specimens. Prostate 1987, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifkin, M.D.; McGlynn, E.T.; Choi, H.H.F. Echogenicity of Prostate Cancer Correlated with Histologic Grade and Stromal Fibrosis: Endorectal US Studies. Radiology 1989, 170, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Moorselaar, R.J.A.; Voest, E.E. Angiogenesis in Prostate Cancer: Its Role in Disease Progression and Possible Therapeutic Approaches. 2002. Available online: www.elsevier.com/locate/mce (accessed on 21 March 2024).
- Bigler, S.A.; Deering, R.E.; Brawer, M.K. Comparison of Microscopic Vascularity in Benign and Malignant Prostate Tissue. Hum. Pathol. 1993, 24, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taverna, G.; Grizzi, F.; Colombo, P.; Graziotti, P. Is angiogenesis a hallmark of prostate cancer? Front. Oncol. 2013, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivas, N.; Goussia, A.; Stefanou, D.; Giannakis, D. Microvascular density and immunohistochemical expression of VEGF, VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 in benign prostatic hyperplasia, high-grade prostate intraepithelial neoplasia and prostate cancer. Cent. Eur. J. Urol. 2016, 69, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melegh, Z.; Oltean, S. Targeting angiogenesis in prostate cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.; Mischi, M.; Scheepens, W.; De La Rosette, J.J.; Wijkstra, H. Angiogenesis in prostate cancer: Onset, progression and imaging. BJU Int. 2012, 110, E794–E808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignee, A.; Jedrejczyk, M.; Schuessler, G.; Jakubowski, W.; Dietrich, C.F. Quantitative contrast enhanced ultrasound of the liver for time intensity curves-Reliability and potential sources of errors. Eur. J. Radiol. 2010, 73, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, F.; Uemura, H. The utility and limitations of contrast-enhanced ultrasound for the diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer. Sensors 2015, 15, 4947–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Feng, Y.; Huang, P.; Jin, J. Adverse reactions after the use of SonoVue contrast agent Characteristics and nursing care experience. Medicine 2019, 98, e17745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyloch, D.J.; Tyloch, J.F.; Adamowicz, J.; Neska-Długosz, I.; Grzanka, D.; Van Breda, S.; Drewa, T. Comparison of Strain and Shear Wave Elastography in Prostate Cancer Detection. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2023, 49, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postema, A.; Mischi, M.; de la Rosette, J.; Wijkstra, H. Multiparametric ultrasound in the detection of prostate cancer: A systematic review. World J. Urol. 2015, 33, 1651–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, D.; Kernohan, N.; Li, C.; Nabi, G. Comparative Assessment of Different Ultrasound Technologies in the Detection of Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancer 2023, 15, 4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, R.G.; Memo, R.; Schaub, C.R. Shear wave ultrasound elastography of the prostate: Initial results. Ultrasound Q. 2012, 28, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, P.F.; Rutjes, A.W.; Westwood, M.E.; Mallett, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Leeflang, M.M.G.; Sterne, J.A.C.; Bossuyt, P.M.M.; The QUADAS-2 Group. Quadas-2: A revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, K.; Mistry, H.; Tsertsvadze, A.; Royle, P.; McCarthy, N.; Taylor-Phillips, S.; Manuel, R.; Mason, J. Multiplex tests to identify gastrointestinal bacteria, viruses and parasites in people with suspected infectious gastroenteritis: A systematic review and economic analysis. Health Technol. Assess 2017, 21, 1–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, R.; Trépel, D.; Perry, A.; Ali, S.; Duffy, S.; Gabe, R.; Gilbody, S.; Glanville, J.; Hewitt, C.; Manea, L.; et al. Screening for psychological and mental health difficulties in young people who offend: A systematic review and decision model. Health Technol. Assess. 2015, 19, 1–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Qi, T.; Jiang, J.; Qi, J.; Yu, Y.; Yao, X. Prostate cancer detection with real-time elastography using a bi-plane transducer: Comparison with step section radical prostatectomy pathology. World J. Urol. 2014, 32, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovich, C.P.; Cornish, T.C.; Mullins, J.K.; Fradin, J.; Mettee, L.Z.; Connor, J.T.; Reese, A.C.; Askin, F.B.; Luck, R.; Epstein, J.I.; et al. High-resolution transrectal ultrasound: Pilot study of a novel technique for imaging clinically localized prostate cancer. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2014, 32, 34.e27–34.e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannaerts, C.K.; Wildeboer, R.R.; Remmers, S.; van Kollenburg, R.A.A.; Kajtazovic, A.; Hagemann, J.; Postema, A.W.; van Sloun, R.J.G.; Roobol, M.J.; Tilki, D.; et al. Multiparametric Ultrasound for Prostate Cancer Detection and Localization: Correlation of B-mode, Shear Wave Elastography and Contrast Enhanced Ultrasound with Radical Prostatectomy Specimens. J. Urol. 2019, 202, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, K.; Salomon, G.; Beyer, B.; Schiffmann, J.; Simonis, K.; Graefen, M.; Budaeus, L. Shear wave elastography for localization of prostate cancer lesions and assessment of elasticity thresholds: Implications for targeted biopsies and active surveillance protocols. J. Urol. 2015, 193, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouvière, O.; Melodelima, C.; Hoang Dinh, A.; Bratan, F.; Pagnoux, G.; Sanzalone, T.; Crouzet, S.; Colombel, M.; Mège-Lechevallier, F.; Souchon, R. Stiffness of benign and malignant prostate tissue measured by shear-wave elastography: A preliminary study. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 1858–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Li, C.; Szewczyk-Bieda, M.; Upreti, D.; Lang, S.; Huang, Z.; Nabi, G. Performance Characteristics of Transrectal Shear Wave Elastography Imaging in the Evaluation of Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer: A Prospective Study. J. Urol. 2018, 200, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.B.; Xu, J.; Yu, B.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhan, J. Correlation of Stiffness of Prostate Cancer Measured by Shear Wave Elastography with Grade Group: A Preliminary Study. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2021, 47, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, D.C.; Chan, D.Y.; Palmeri, M.L.; Polascik, T.J.; Foo, W.C.; Nightingale, K.R. Prostate Cancer Detection Using 3-D Shear Wave Elasticity Imaging. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2021, 47, 1670–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, E.M.; Wiggermann, P.; Greis, C.; Eder, F.; Ehrich, J.; Jung, W.; Schreyer, A.G.; Stroszczynski, C.; Ganzer, R. First results of endocavity evaluation of the microvascularization of malignant prostate tumors using contrast enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) including perfusion analysis: First results. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2012, 52, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postema, A.W.; Gayet, M.C.W.; van Sloun, R.J.G.; Wildeboer, R.R.; Mannaerts, C.K.; Schalk, S.G.; Kajtazovic, A.; van der Poel, H.; Mulders, P.F.A.; Beerlage, H.P.; et al. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound with dispersion analysis for the localization of prostate cancer: Correlation with radical prostatectomy specimens. World J. Urol. 2020, 38, 2811–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, M.L.; Cowan, J.E.; Carroll, P.R.; Shinohara, K. The adjunctive use of power Doppler imaging in the preoperative assessment of prostate cancer. BJU Int. 2010, 105, 1237–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannaerts, C.K.; Wildeboer, R.R.; Postema, A.W.; Hagemann, J.; Budäus, L.; Tilki, D.; Mischi, M.; Wijkstra, H. Multiparametric ultrasound: Evaluation of greyscale, shear wave elastography and contrast-enhanced ultrasound for prostate cancer detection and localization in correlation to radical prostatectomy specimens. BMC Urol. 2018, 18, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, V.S.; Burk, R.S.; Creehan, S.; Grap, M.J. Utility of high-frequency ultrasound: Moving beyond the surface to detect changes in skin integrity. Plast. Surg. Nurs. 2014, 34, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso Dias, A.; Ghai, S. Micro-Ultrasound: Current Role in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis and Future Possibilities. Cancers 2023, 15, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, F.; McLeary, R.D.; Kumasaka, G.H.; Borlaza, G.S.; Straub, W.H.; Gray, J.M.; Meadows, T.R.; Lee, F., Jr.; Solomon, M.H.; McHugh, T.A.; et al. Transrectal Ultrasound in the Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer: Location, Echogenicity, Histopathology, and Staging. Prostate 1985, 7, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egawa, S.; Wheeler, T.M.; Greene, D.R.; Scardino, P.T. Unusual Hyperechoic Appearance of Prostate Cancer on Transrectal Ultrasonography. Br. J. Urol. 1992, 69, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Sakamoto, N. Relationship of Ultrasonographic Findings to Histology in Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 1994, 26, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boczko, J.; Messing, E.; Dogra, V. Transrectal Sonography in Prostate Evaluation. Radiol. Clin. North. Am. 2006, 44, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.W.; Lee, S. Usefulness of grayscale values measuring hypoechoic lesions for predicting prostate cancer: An experimental pilot study. Prostate Int. 2022, 10, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wu, S.; Huang, L. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound evaluation of the prostate before transrectal ultrasound-guided biopsy can improve diagnostic sensitivity: A STARD-compliant article. Medicine 2020, 99, E19946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvain, J.L.; Palascak, P.; Bourscheid, D.; Chabi, C.; Atassi, A.; Bremon, J.M.; Palascak, R. Value of Power Doppler and 3D Vascular Sonography as a Method for Diagnosis and Staging of Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2003, 44, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Cho, J.Y.; Kim, S.H. Shear Wave Elastography for Detection of Prostate Cancer: A Preliminary Study. Korean J. Radiol. 2014, 15, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, R.; Ranganathan, P. Understanding diagnostic tests—Part 3: Receiver operating characteristic curves. Perspect. Clin. Res. 2018, 9, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Ruan, L.; Ren, W.; Dun, G.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, Q. Stiffness of prostate gland measured by transrectal real-time shear wave elastography for detection of prostate cancer: A feasibility study. Br. J. Radiol. 2009, 92, 20180970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Cao, R.; Varghese, T.; Bidaut, L.; Nabi, G. Transrectal quantitative shear wave elastography in the detection and characterisation of prostate cancer. Surg. Endosc. 2013, 27, 3280–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosgrove, D. Ultrasound contrast agents: An overview. Eur. J. Radiol. 2006, 60, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, C.F.; Averkiou, M.; Nielsen, M.B.; Barr, R.G.; Burns, P.N.; Calliada, F.; Cantisani, V.; Choi, B.; Chammas, M.C.; Clevert, D.A.; et al. How to perform Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS). Ultrasound Int. Open. 2018, 4, E2–E15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezquer, A.; Hrescak, M.C.O.; Sanagua, C.; Roggia-Rebullida, P.; López, R.; Cenice, F.; Veglia, F.H.; Veglia, F.; Fernández, A. Transrectal doppler ultrasound during prostate biopsy: Clinical utility and limitations PALABRAS CLAVE. Actas Urol. Esp. 2015, 39, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, S.; Wu, S.; Chen, C.; Zhu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, L.; Xu, R. Performance Characteristics of 3-D Power Doppler Ultrasound (3-D-Pd) with The Virtual Organ Computer-Aided Analysis (Vocal) Technique in the Detection of Prostate Cancer. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2022, 48, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Liang, L.; Xie, X.I.; Yuan, J.; He, W.; Chen, J.; Kuang, Y. Endorectal power Doppler/grayscale ultrasound-guided biopsies vs. multiparametric MRI/ultrasound fusion-guided biopsies in males with high risk of prostate cancer: A prospective cohort study. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 4765–4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.W.; Li, H.L.; Du, J.; Xia, J.G.; Guo, Y.F.; Xin, M.; Li, F.H. Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography with contrast-tuned imaging technology for the detection of prostate cancer: Comparison with conventional ultrasonography. BJU Int. 2012, 109, 1620–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drudi, F.M.; Cantisani, V.; Angelini, F.; Ciccariello, M.; Messineo, D.; Ettorre, E.; Liberatore, M.; Scialpi, M. Multiparametric MRI versus multiparametric US in the detection of prostate cancer. Anticancer. Res. 2019, 39, 3101–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brock, M.; Eggert, T.; Palisaar, R.J.; Roghmann, F.; Braun, K.; Löppenberg, B.; Sommerer, F.; Noldus, J.; von Bodman, C. Multiparametric Ultrasound of the Prostate: Adding Contrast Enhanced Ultrasound to Real-Time Elastography to Detect Histopathologically Confirmed Cancer. J. Urol. 2013, 189, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. MetaArXiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Criteria | Inclusion | Exclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Settings | All Countries | None |
| Participants | Male patients [all ages] with a suspicion of prostate cancer, based on biopsy | No radical prostatectomy enrolled |
| Modality | Ultrasound parametric such as: Grayscale, shear-wave elastography, Doppler, contrast-enhanced ultrasound, and combination multiparametric ultrasound | Studies that did not examine these devices. |
| Outcomes | Studies that report sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, accuracy, and AUC. | Studies that do not report at least sensitivity or specificity. |
| Study Type | In vivo studies Prospective and retrospective studies Randomized Clinical trial non-randomized | In vitro studiesReview articlesSystematic review |
| Publication Type | Journal articles | Conference abstract, study protocol, report, dissertation, books, and non-professional journal |
| Publication Year | Publication date 2012 and after | Publication date before 2012 |
| Language | English | All other languages |
| Modality | Author [Year] | Number of Patients | Lesion Size | Sensitivity % | Specificity % | PPV | NPV | Accuracy % | AUC % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grayscale
ultrasound | Zhu et al., 2014 [28] | 56 | ≤5 mm, ≥5 mm | 40.2 | 93.4 | 77.0 | |||
| Pavlovich et al., 2014 [29] | 25 | ≥5 mm | 37.7 | 65.4 | 48.1 | 55.2 | |||
| Mannaerts et al., 2019 [30] | 50 | ≥5 mm | 55 | 61 | 59 | 57 | |||
|
Shear-wave
elastography ultrasound | Boehm et al., 2015 [31] | 60 | ≥5 mm | 81.1 | 69.1 | 47.2 | |||
| Rouvière et al., 2017 [32] | 31 | ≤5 mm, ≥5 mm | 61 | 67.1 | 77.8 | 76 | |||
| Wei et al., 2018 [33] | 212 | ≥5 mm | 88.6 | 97.3 | 86.3 | 97.8 | 96 | 97 | |
| Mannaerts et al., 2019 [30] | 50 | ≥5 mm | 55 | 61 | 59 | 57 | |||
| Dai et al., 2021 [34] | 42 | ≥5 mm | 76 | 77.2 | 75.7 | ||||
| Morris et al., 2021 [35] | 36 | 81 | 82 | 69 | 89 | 84 | |||
| Tyloch et al., 2023 [21] | 30 | ≥5 mm | 65.3 | 70.2 | |||||
|
Contrast
enhanced ultrasound | Jung et al., 2012 [36] | 20 | 71 | 88 | 89 | 45 | |||
| Mannaerts et al., 2019 [30] | 50 | ≥5 mm | 59 | 63 | 62 | 60 | |||
| Postema et al., 2020 [37] | 133 | ≥5 mm | 81 | 64 | 78 | ||||
| Multiparametric ultrasound | Mannaerts et al., 2019 [30] | 50 | ≥5 mm | 74 | 59 | 65 | 70 |
| Modality | Sensitivity % | Specificity % |
|---|---|---|
| Grayscale ultrasound | 55 | 61 |
| Shear-wave elastography ultrasound | 73 | 78 |
| Contrast-enhanced ultrasound | 70 | 62 |
| Multiparametric ultrasound | 74 | 59 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jawli, A.; Nabi, G.; Huang, Z. The Performance of Different Parametric Ultrasounds in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis: Correlation with Radical Prostatectomy Specimens. Cancers 2024, 16, 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081502
Jawli A, Nabi G, Huang Z. The Performance of Different Parametric Ultrasounds in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis: Correlation with Radical Prostatectomy Specimens. Cancers. 2024; 16(8):1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081502
Chicago/Turabian StyleJawli, Adel, Ghulam Nabi, and Zhihong Huang. 2024. "The Performance of Different Parametric Ultrasounds in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis: Correlation with Radical Prostatectomy Specimens" Cancers 16, no. 8: 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081502
APA StyleJawli, A., Nabi, G., & Huang, Z. (2024). The Performance of Different Parametric Ultrasounds in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis: Correlation with Radical Prostatectomy Specimens. Cancers, 16(8), 1502. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081502








