A Retrospective Review and Comprehensive Tumour Profiling of Advanced Non-Melanomatous Cutaneous Spindle Cell Neoplasms Treated with Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry
2.3. DNA and RNA Isolation
2.4. RNA Sequencing
2.5. Whole-Exome Sequencing (WES)
2.6. Tumour Mutational Burden (TMB) and Signature Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
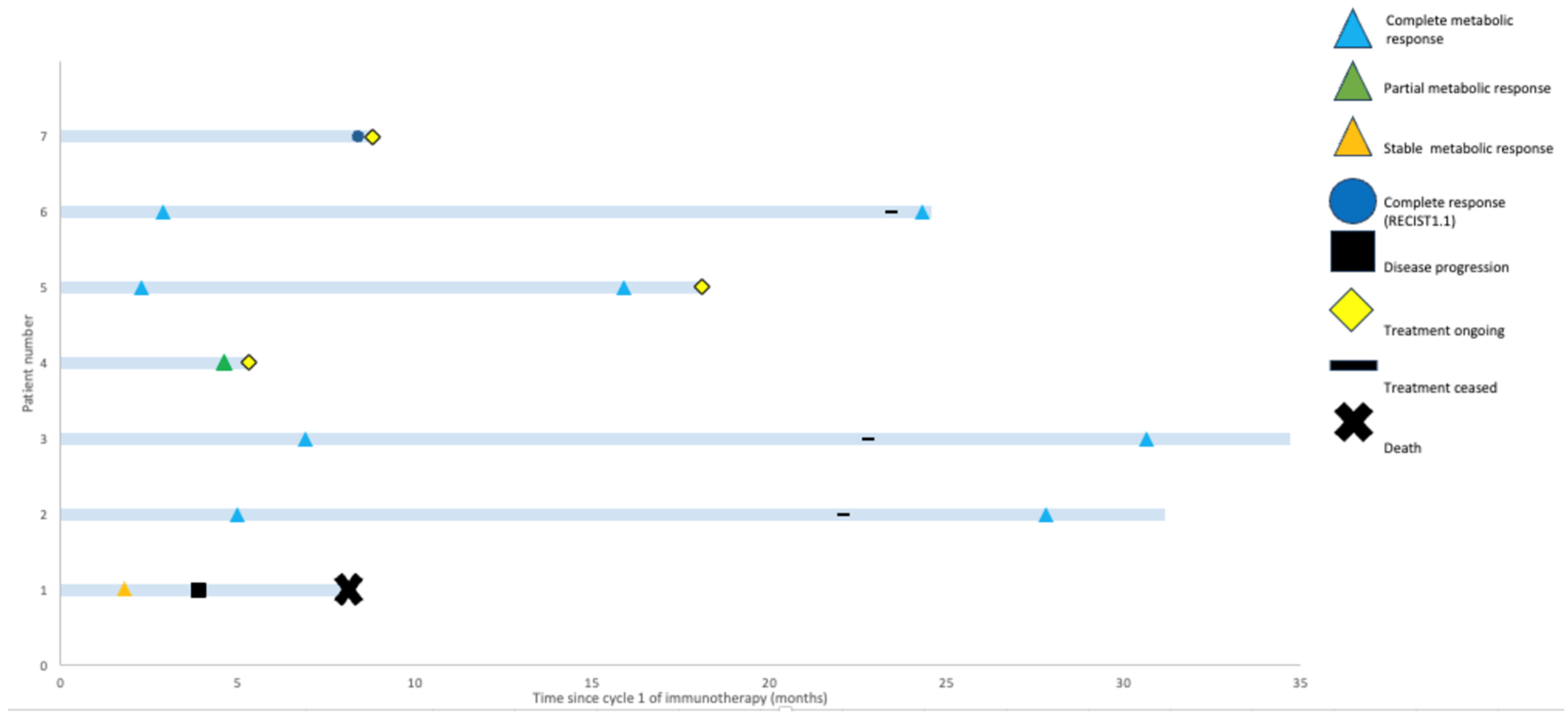
3.2. Response Assessments
3.3. Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry
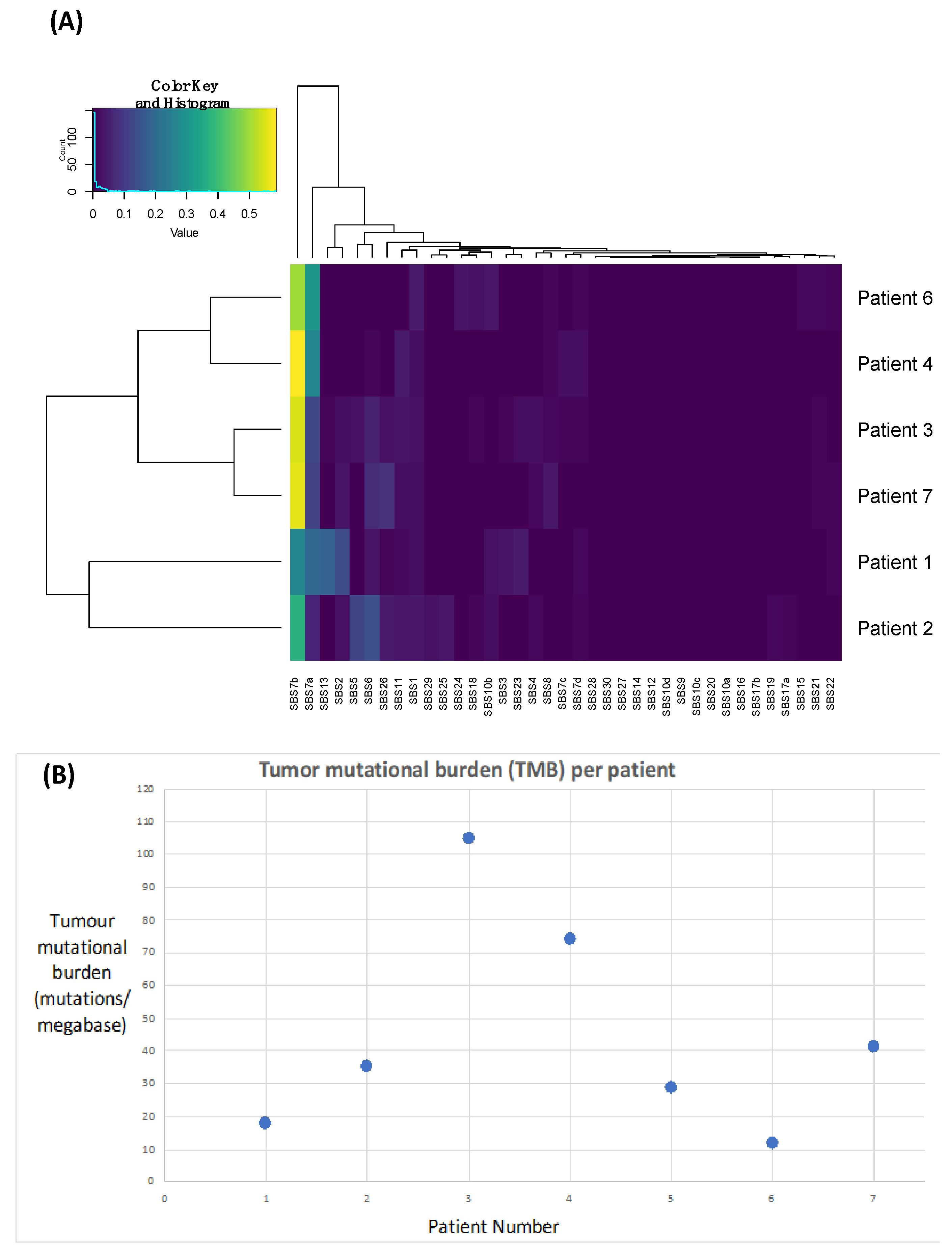
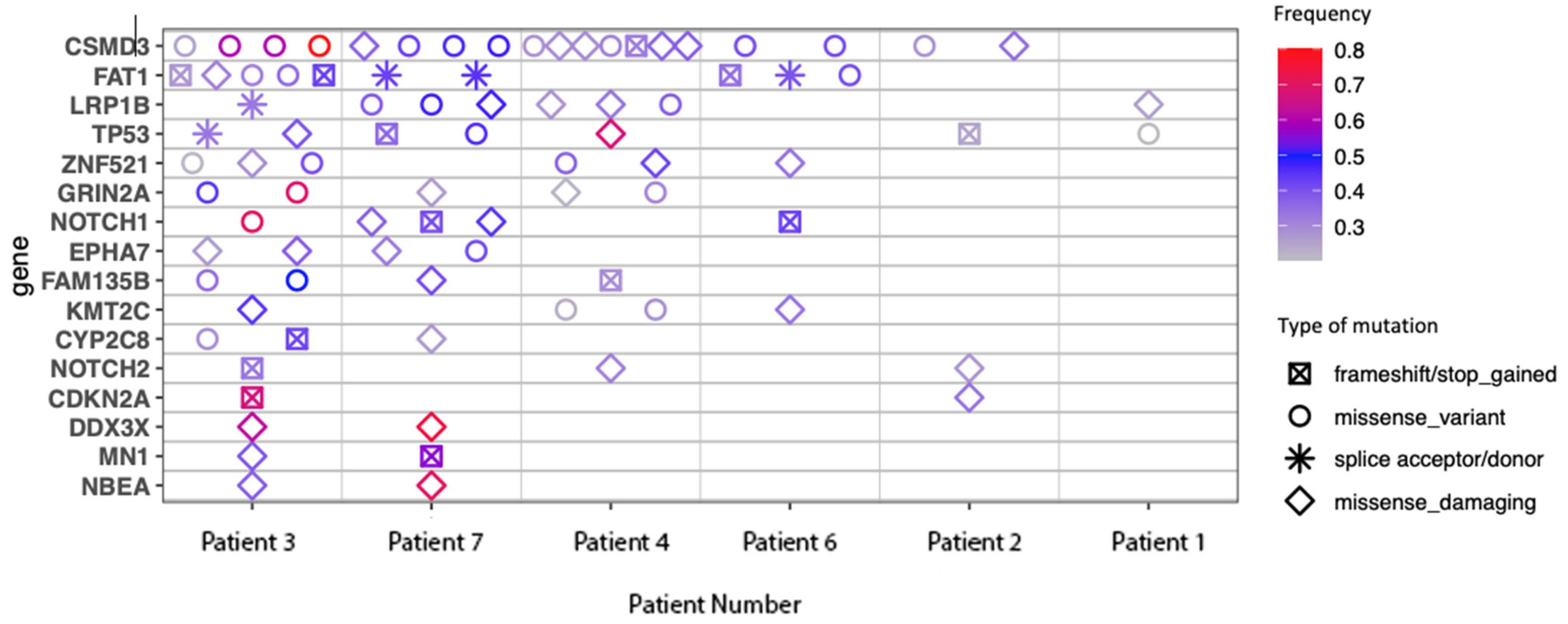
3.4. Genomic Characterisation, TMB and Analysis for UV-Associated Mutational Signatures
3.5. Exploratory Immune Cell and Immune Checkpoint Immunohistochemistry
3.6. SingScore for Interferon–Gamma Signatures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, J.H.; Ro, J.Y. Cutaneous Spindle Cell Neoplasms: Pattern-Based Diagnostic Approach. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018, 142, 958–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardío, J.C.; Pinedo, F.; Aramburu, J.A.; Suárez-Massa, D.; Pampín, A.; Requena, L.; Santonja, C. Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma: A more aggressive neoplasm than previously estimated. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2016, 43, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, K.; Goodlad, J.R.; Brenn, T. Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma: Adverse histologic features predict aggressive behavior and allow distinction from atypical fibroxanthoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2012, 36, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helbig, D. Hemato-Oncological Diseases as Risk Factor for Recurrence or Metastasis of Pleomorphic Dermal Sarcoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 873771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helbig, D.; Ziemer, M.; Dippel, E.; Erdmann, M.; Hillen, U.; Leiter, U.; Mentzel, T.; Osterhoff, G.; Ugurel, S.; Utikal, J.; et al. S1-guideline atypical fibroxanthoma (AFX) and pleomorphic dermal sarcoma (PDS). J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2022, 20, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helbig, D.; Klein, S. Immune checkpoint inhibitors for unresectable or metastatic pleomorphic dermal sarcomas. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 975342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ørholt, M.; Abebe, K.; Rasmussen, L.E.; Aaberg, F.L.; Lindskov, L.J.; Schmidt, G.; Wagenblast, A.L.; Petersen, M.M.; Loya, A.C.; Daugaard, S.; et al. Atypical fibroxanthoma and pleomorphic dermal sarcoma: Local recurrence and metastasis in a nationwide population-based cohort of 1118 patients. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2023, 89, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migden, M.R.; Khushalani, N.I.; Chang, A.L.S.; Lewis, K.D.; Schmults, C.D.; Hernandez-Aya, L.; Meier, F.; Schadendorf, D.; Guminski, A.; Hauschild, A.; et al. Cemiplimab in locally advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: Results from an open-label, phase 2, single-arm trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migden, M.R.; Rischin, D.; Schmults, C.D.; Guminski, A.; Hauschild, A.; Lewis, K.D.; Chung, C.H.; Hernandez-Aya, L.; Lim, A.M.; Chang, A.L.S.; et al. PD-1 Blockade with Cemiplimab in Advanced Cutaneous Squamous-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rischin, D.; Khushalani, N.I.; Schmults, C.D.; Guminski, A.; Chang, A.L.S.; Lewis, K.D.; Lim, A.M.; Hernandez-Aya, L.; Hughes, B.G.M.; Schadendorf, D.; et al. Integrated analysis of a phase 2 study of cemiplimab in advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: Extended follow-up of outcomes and quality of life analysis. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grob, J.J.; Gonzalez, R.; Basset-Seguin, N.; Vornicova, O.; Schachter, J.; Joshi, A.; Meyer, N.; Grange, F.; Piulats, J.M.; Bauman, J.R.; et al. Pembrolizumab Monotherapy for Recurrent or Metastatic Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Single-Arm Phase II Trial (KEYNOTE-629). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2916–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, J.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Gonzalez, R.; Grob, J.-J.; Rutkowski, P.; Lao, C.D.; Cowey, C.L.; Schadendorf, D.; Wagstaff, J.; Dummer, R.; et al. Five-Year Survival with Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacuna, K.; Bose, S.; Ingham, M.; Schwartz, G. Therapeutic advances in leiomyosarcoma. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1149106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Fitzgerald, B.; Perry, E.; Pathak, A.; Chao, H.H. Prolonged Response to Pembrolizumab in Spindle Cell Squamous Cell Carcinoma Metastatic to the Central Nervous System. J. Investig. Med. High Impact Case Rep. 2019, 7, 2324709619850216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, D.M.; Faulkner-Jones, B.E.; Stone, J.R.; Drews, R.E. Complete pathologic response of metastatic cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma and allograft rejection after treatment with combination immune checkpoint blockade. JAAD Case Rep. 2017, 3, 412–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Quaas, A.; Noh, K.W.; Cartolano, M.; Abedpour, N.; Mauch, C.; Quantius, J.; Reinhardt, H.C.; Buettner, R.; Peifer, M.; et al. Integrative Analysis of Pleomorphic Dermal Sarcomas Reveals Fibroblastic Differentiation and Susceptibility to Immunotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 5638–5645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, S.; Mauch, C.; Wagener-Ryczek, S.; Schoemmel, M.; Buettner, R.; Quaas, A.; Helbig, D. Immune-phenotyping of pleomorphic dermal sarcomas suggests this entity as a potential candidate for immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2019, 68, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Persa, O.D.; Mauch, C.; Noh, K.W.; Pappesch, R.; Wagener-Ryczek, S.; Buettner, R.; Quaas, A.; Helbig, D. First report on two cases of pleomorphic dermal sarcoma successfully treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, e1665977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, O.; McTigue, C.; Wong, Z.W.; Syme, D.B.; Hunter-Smith, D.J. Complete response of metastatic pleomorphic dermal sarcoma to anti-PD-1 therapy. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 183, e189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuck, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, R.L.; Jacene, H.; Kasamon, Y.; Lodge, M.A. From RECIST to PERCIST: Evolving Considerations for PET response criteria in solid tumors. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50 (Suppl. S1), 122s–150s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elder, D.E.; Massi, D.; Scolyer, R.A.; Willemze, R. WHO Classification of Skin Tumours, 5th ed.; World Health Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- Solomon, B.; Young, R.J.; Bressel, M.; Urban, D.; Hendry, S.; Thai, A.; Angel, C.; Haddad, A.; Kowanetz, M.; Fua, T.; et al. Prognostic Significance of PD-L1(+) and CD8(+) Immune Cells in HPV(+) Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, B.; Young, R.J.; Bressel, M.; Cernelc, J.; Savas, P.; Liu, H.; Urban, D.; Thai, A.; Cooper, C.; Fua, T.; et al. Identification of an excellent prognosis subset of human papillomavirus-associated oropharyngeal cancer patients by quantification of intratumoral CD103+ immune cell abundance. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1638–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agilent_Technologies. PD-L1 IHC 22C3 pharmDx Interpretation Manual—Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC); Agilent_Technologies: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Patro, R.; Duggal, G.; Love, M.I.; Irizarry, R.A.; Kingsford, C. Salmon provides fast and bias-aware quantification of transcript expression. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewels, P.A.; Peltzer, A.; Fillinger, S.; Patel, H.; Alneberg, J.; Wilm, A.; Garcia, M.U.; Di Tommaso, P.; Nahnsen, S. The nf-core framework for community-curated bioinformatics pipelines. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayers, M.; Lunceford, J.; Nebozhyn, M.; Murphy, E.; Loboda, A.; Kaufman, D.R.; Albright, A.; Cheng, J.D.; Kang, S.P.; Shankaran, V.; et al. IFN-γ–related mRNA profile predicts clinical response to PD-1 blockade. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 2930–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroutan, M.; Bhuva, D.D.; Lyu, R.; Horan, K.; Cursons, J.; Davis, M.J. Single sample scoring of molecular phenotypes. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, F.; Garcia, M.U.; Folkersen, L.; Pedersen, A.S.; Lescai, F.; Jodoin, S.; Miller, E.; Seybold, M.; Wacker, O.; Smith, N.; et al. Scalable and efficient DNA sequencing analysis on different compute infrastructures aiding variant discovery. bioRxiv 2023. bioRxiv:2023.2007.2019.549462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1303.3997. [Google Scholar]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cingolani, P.; Platts, A.; Wang, L.L.; Coon, M.; Nguyen, T.; Wang, L.; Land, S.J.; Lu, X.; Ruden, D.M. A program for annotating and predicting the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms, SnpEff: SNPs in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster strain w1118; iso-2; iso-3. Fly 2012, 6, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantini, D.; Vidimar, V.; Yu, Y.; Condello, S.; Meeks, J.J. MutSignatures: An R package for extraction and analysis of cancer mutational signatures. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, J.G.; Bamford, S.; Jubb, H.C.; Sondka, Z.; Beare, D.M.; Bindal, N.; Boutselakis, H.; Cole, C.G.; Creatore, C.; Dawson, E.; et al. COSMIC: The Catalogue Of Somatic Mutations In Cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 47, D941–D947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jia, M.; He, Z.; Liu, X.-S. APOBEC3B and APOBEC mutational signature as potential predictive markers for immunotherapy response in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3924–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, A.; Tan, C.Z.; Kuonen, F.; Hodgkinson, L.M.; Chiang, F.; Cho, R.J.; South, A.P.; Tang, J.Y.; Chang, A.L.S.; Rieger, K.E.; et al. Genetic Mutations Underlying Phenotypic Plasticity in Basosquamous Carcinoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 2263–2271.e2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, N.; Liu, J.; Xu, M.; Liang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Xing, Y.; Diao, F. CSMD3 is Associated with Tumor Mutation Burden and Immune Infiltration in Ovarian Cancer Patients. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 7647–7657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Kong, Y.; Shi, F.; Sheng, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, Q. Favorable immune checkpoint inhibitor outcome of patients with melanoma and NSCLC harboring FAT1 mutations. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdag, G.; Schaefer, J.T.; Smolkin, M.E.; Deacon, D.H.; Shea, S.M.; Dengel, L.T.; Patterson, J.W.; Slingluff, C.L., Jr. Immunotype and Immunohistologic Characteristics of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells Are Associated with Clinical Outcome in Metastatic Melanoma. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 1070–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carstens, J.L.; Correa de Sampaio, P.; Yang, D.; Barua, S.; Wang, H.; Rao, A.; Allison, J.P.; LeBleu, V.S.; Kalluri, R. Spatial computation of intratumoral T cells correlates with survival of patients with pancreatic cancer. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cass, S.H.; Tobin, J.W.D.; Seo, Y.D.; Gener-Ricos, G.; Keung, E.Z.; Burton, E.M.; Davies, M.A.; McQuade, J.L.; Lazar, A.J.; Mason, R.; et al. Efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors for the treatment of advanced melanoma in patients with concomitant chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, L.S.; Chen, L.; Oke, T.F.; Schaffer, T.B.; Boudadi, K.; Ngo, J.T.; Gross, J.M.; Kemberling, H.; Diaz, L.A.; Lipson, E.; et al. Anti-PD-1 elicits regression of undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcomas with UV-mutation signatures. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolchok, J.D.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Gonzalez, R.; Grob, J.J.; Rutkowski, P.; Lao, C.D.; Cowey, C.L.; Schadendorf, D.; Wagstaff, J.; Dummer, R.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes with Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab or Nivolumab Alone Versus Ipilimumab in Patients with Advanced Melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, L.S.; Cavanagh, K.; Hicks, R.J.; Callahan, J.; Xie, J.; Cardin, A.; Lim, A.M.; Rischin, D. FDG-PET/CT imaging for evaluating durable responses to immune check point inhibitors in patients with advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Imaging 2021, 21, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariño-Enríquez, A.; Hornick, J.L. Spindle cell tumors of adults. In Practical Soft Tissue Pathology: A Diagnostic Approach E-Book: A Volume in the Pattern Recognition Series; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Ishida, Y.; Agata, Y.; Shibahara, K.; Honjo, T. Induced expression of PD-1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. Embo J. 1992, 11, 3887–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, F.; Aguilera, J.V.; Palermo, B.; Markovic, S.N.; Nisticò, P.; Signore, A. Relevance of immune cell and tumor microenvironment imaging in the new era of immunotherapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnewies, M.; Roberts, E.W.; Kersten, K.; Chan, V.; Fearon, D.F.; Merad, M.; Coussens, L.M.; Gabrilovich, D.I.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S.; Hedrick, C.C.; et al. Understanding the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) for effective therapy. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marabelle, A.; Fakih, M.G.; Lopez, J.; Shah, M.; Shapira-Frommer, R.; Nakagawa, K.; Chung, H.C.; Kindler, H.L.; Lopez-Martin, J.A.; Miller, W.; et al. 1192O—Association of tumour mutational burden with outcomes in patients with select advanced solid tumours treated with pembrolizumab in KEYNOTE-158. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, v477–v478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
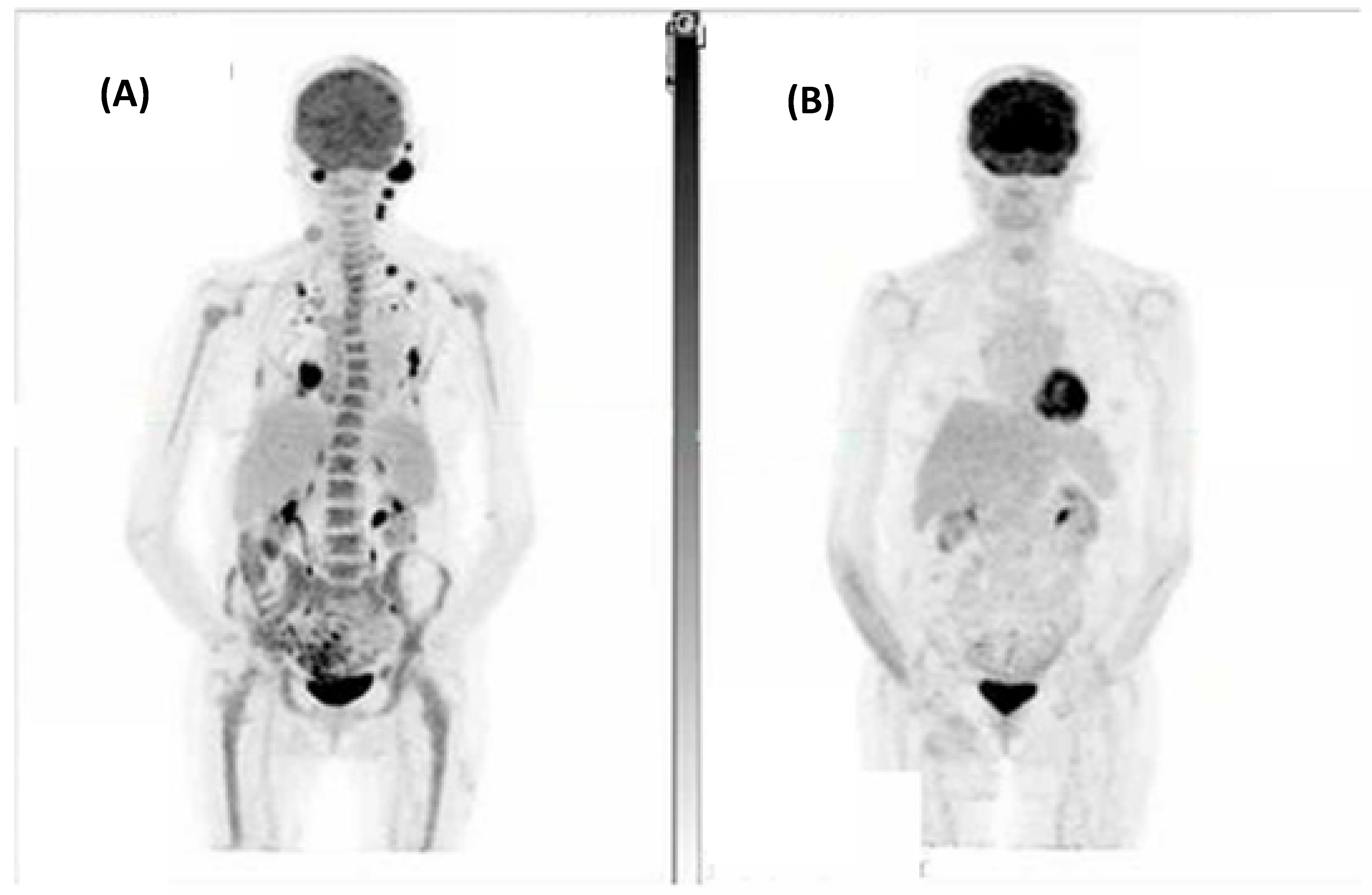
| Case | Age (Years), Sex | Site of Disease | Stage | Treatment Received | Best Response on Imaging * | Immunocompromised | Prior Systemic Therapy | Progressed? | Pathology Review Final Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 73, male | Scalp | Locally advanced without nodal involvement | Cemiplimab | Stable metabolic disease | Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia | No | Yes, after 8 cycles | Spindle cell cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma |
| 2 | 79, female | Scalp | Metastatic | Cemiplimab | Complete metabolic response | No | No | No | Spindle cell cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma |
| 3 | 66, male | Scalp | Metastatic | Cemiplimab | Complete metabolic response | Multiple myeloma | No | No | Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma |
| 4 | 66, female | Cheek | Locally advanced with nodal involvement | Cemiplimab | Partial metabolic response | Follicular lymphoma | No | No | Cutaneous spindle cell malignancy—subclassification unclear |
| 5 | 75, male | Cheek | Locally advanced with nodal involvement | Cemiplimab | Complete metabolic response | No | No | No | Cutaneous spindle cell malignancy—subclassification unclear |
| 6 | 70, male | Temple | Locally advanced with nodal involvement | Cemiplimab | Complete metabolic response | No | No | No | Spindle cell cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma |
| 7 | 74, male | Preauricular | Metastatic | Pembrolizumab | Complete response | Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia | No | No | Pleomorphic dermal sarcoma |
| Epithelial and Squamous Differentiation | Melanomatous Differentiation | Muscle Differentiation | Endothelial Differentiation | Other | Mesenchymal Differentiation | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient No. + Histology | AE1/3 | HMWCK | CK5/6 | p40 | p63 | SOX10 | Melan-A | SMA | Desmin | CD31 | ERG | CD34 | CD10 | PDGFRA | PDGFRB |
| 1 SpSCC | 80%+ | 80%+ | 80%+ | 80%+ | 80%+ | - | - | 80%+ | - | - | - | - | 80%+ | - | - |
| 2 SpSCC | 80%+ | 80%+ | 80%+ | 60% | 80%+ | - | - | - | - | 60% | - | - | 80%+ | - | - |
| 3 PDS | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 80%+ | - | - |
| 4 Unclear SpN | - | - | - | - | 80%+ | - | - | 10% | - | - | - | - | 80%+ | - | - |
| 5 Unclear SpN | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 80%+ | - | - | - | - | - | 80%+ |
| 6 SpSCC | - | 30% | 30% | 50% | 70% | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 7 PDS | - | - | - | - | 10% | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 80%+ | - | - |
| T-Cell Markers | B-Cell Markers | Immune-Checkpoints | Tumor Mutational Burden (mt/mb) | Ultraviolet-Mutational Signature (7a/7b) | Best Response | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient | Assessment # | ||||||||||
| CD103 | CD4 | CD3 | CD8 | CD20 | PD-L1 | TIGIT | LAG3 | ||||
| 1 | 1 | 20 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 17.94 | Yes | Stable metabolic disease |
| 2 | 1 | 20 | 30 | 10 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 10 | 35.34 | Yes | Complete metabolic response |
| 3 | 1 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 104.87 | Yes | Complete metabolic response |
| 4 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 74.04 | Yes | Partial metabolic response |
| 5 * | 29 | Yes | Complete metabolic response | ||||||||
| 6 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 12.02 | Yes | Complete metabolic response |
| 7 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 41.17 | Yes | Complete response |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McLean, L.S.; Lim, A.M.; Angel, C.; Young, R.J.; Pizzolla, A.; Archer, S.; Solomon, B.J.; Thai, A.A.; Lewin, J.; Rischin, D. A Retrospective Review and Comprehensive Tumour Profiling of Advanced Non-Melanomatous Cutaneous Spindle Cell Neoplasms Treated with Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors. Cancers 2024, 16, 1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081452
McLean LS, Lim AM, Angel C, Young RJ, Pizzolla A, Archer S, Solomon BJ, Thai AA, Lewin J, Rischin D. A Retrospective Review and Comprehensive Tumour Profiling of Advanced Non-Melanomatous Cutaneous Spindle Cell Neoplasms Treated with Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors. Cancers. 2024; 16(8):1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081452
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcLean, Luke S., Annette M. Lim, Christopher Angel, Richard J. Young, Angela Pizzolla, Stuart Archer, Benjamin J. Solomon, Alesha A. Thai, Jeremy Lewin, and Danny Rischin. 2024. "A Retrospective Review and Comprehensive Tumour Profiling of Advanced Non-Melanomatous Cutaneous Spindle Cell Neoplasms Treated with Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors" Cancers 16, no. 8: 1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081452
APA StyleMcLean, L. S., Lim, A. M., Angel, C., Young, R. J., Pizzolla, A., Archer, S., Solomon, B. J., Thai, A. A., Lewin, J., & Rischin, D. (2024). A Retrospective Review and Comprehensive Tumour Profiling of Advanced Non-Melanomatous Cutaneous Spindle Cell Neoplasms Treated with Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors. Cancers, 16(8), 1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16081452






