Skin Cancer Recognition Using Unified Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
- ▪ Analyzing the state-of-the-art deep learning techniques employed for skin cancer lesion recognition;
- ▪ Conducting a comprehensive evaluation of the latest YOLO models, namely, YOLOv3, YOLOv4, YOLOv5, and YOLOv7, in terms of their performance and computational efficiency;
- ▪ Designing and implementing a YOLO-based approach for accurate skin cancer lesion recognition, focusing on the identification of “Malignant Melanoma”, “Benign Nevus”, and “Seborrheic Keratosis” lesions;
- ▪ Assessing the performance of the proposed system in comparison to the existing methods, using established metrics such as accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and computational time.
2. Literature Review
3. Methodology
3.1. YOLOv3-Based Model
3.2. YOLOv4-Based Model
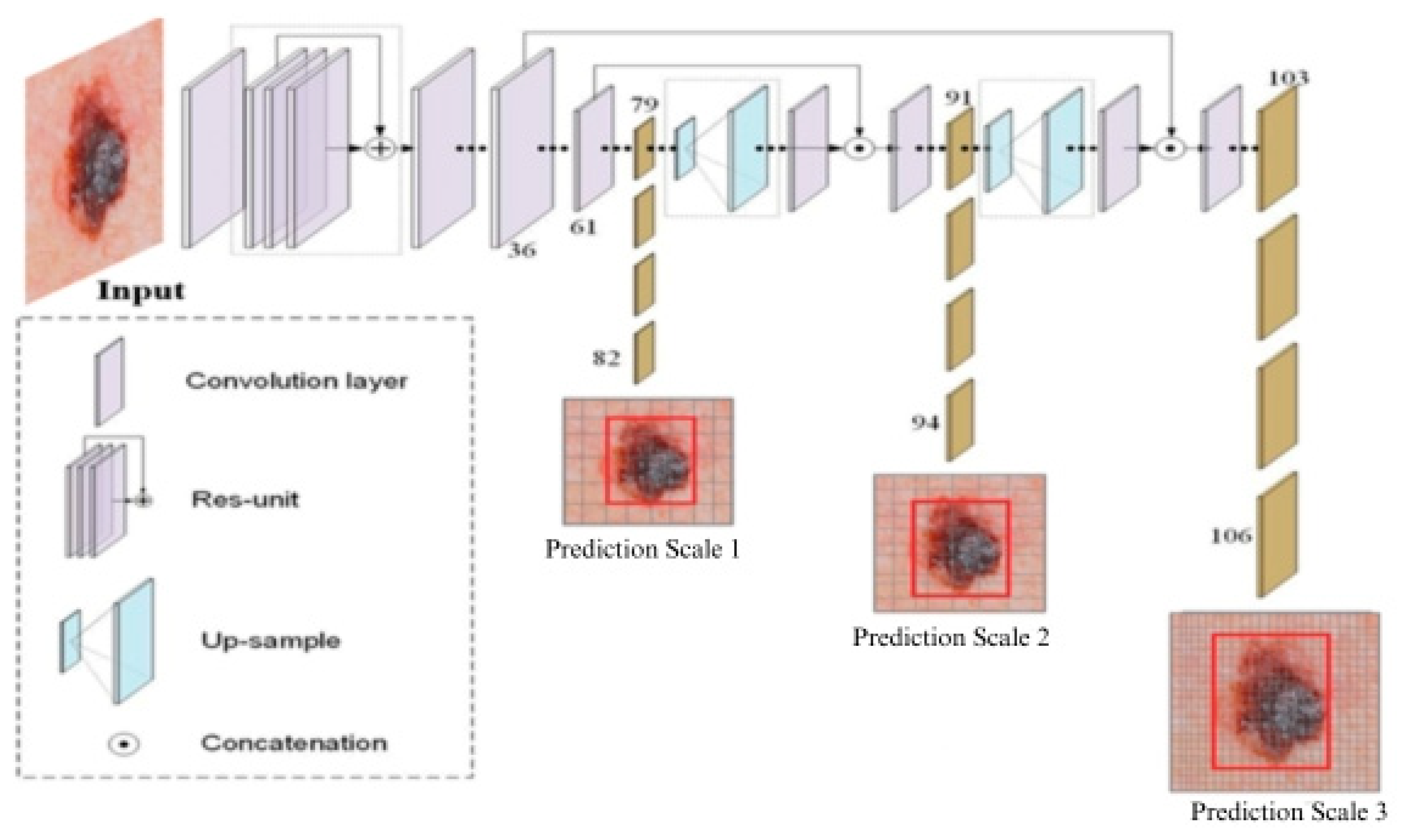
3.3. YOLOv5-Based Model
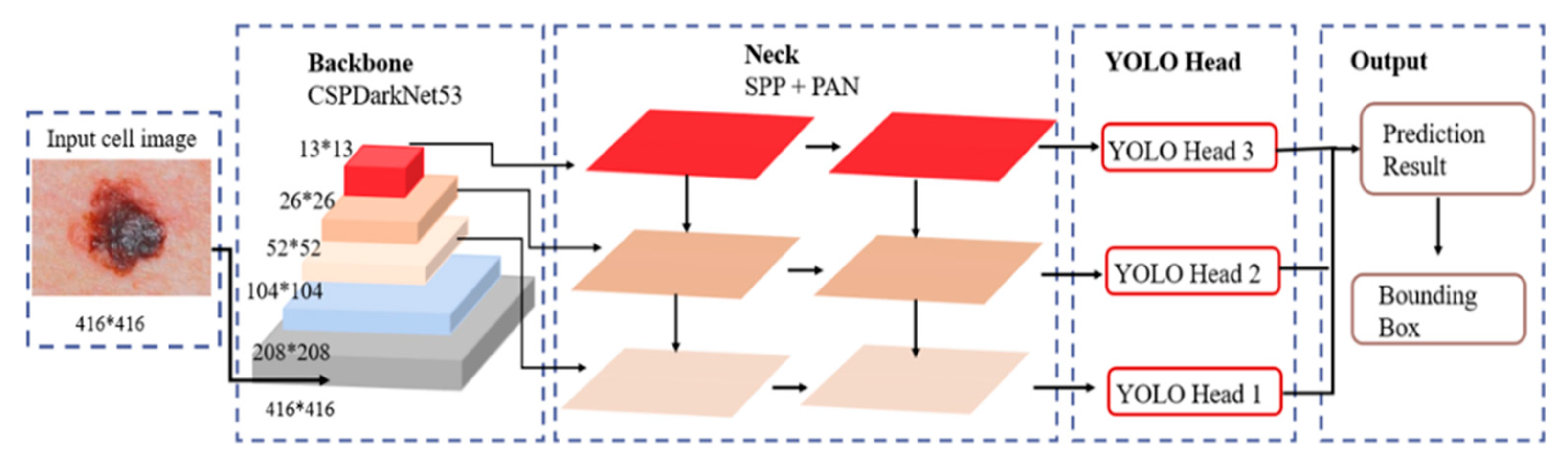
3.4. YOLOv7-Based Model
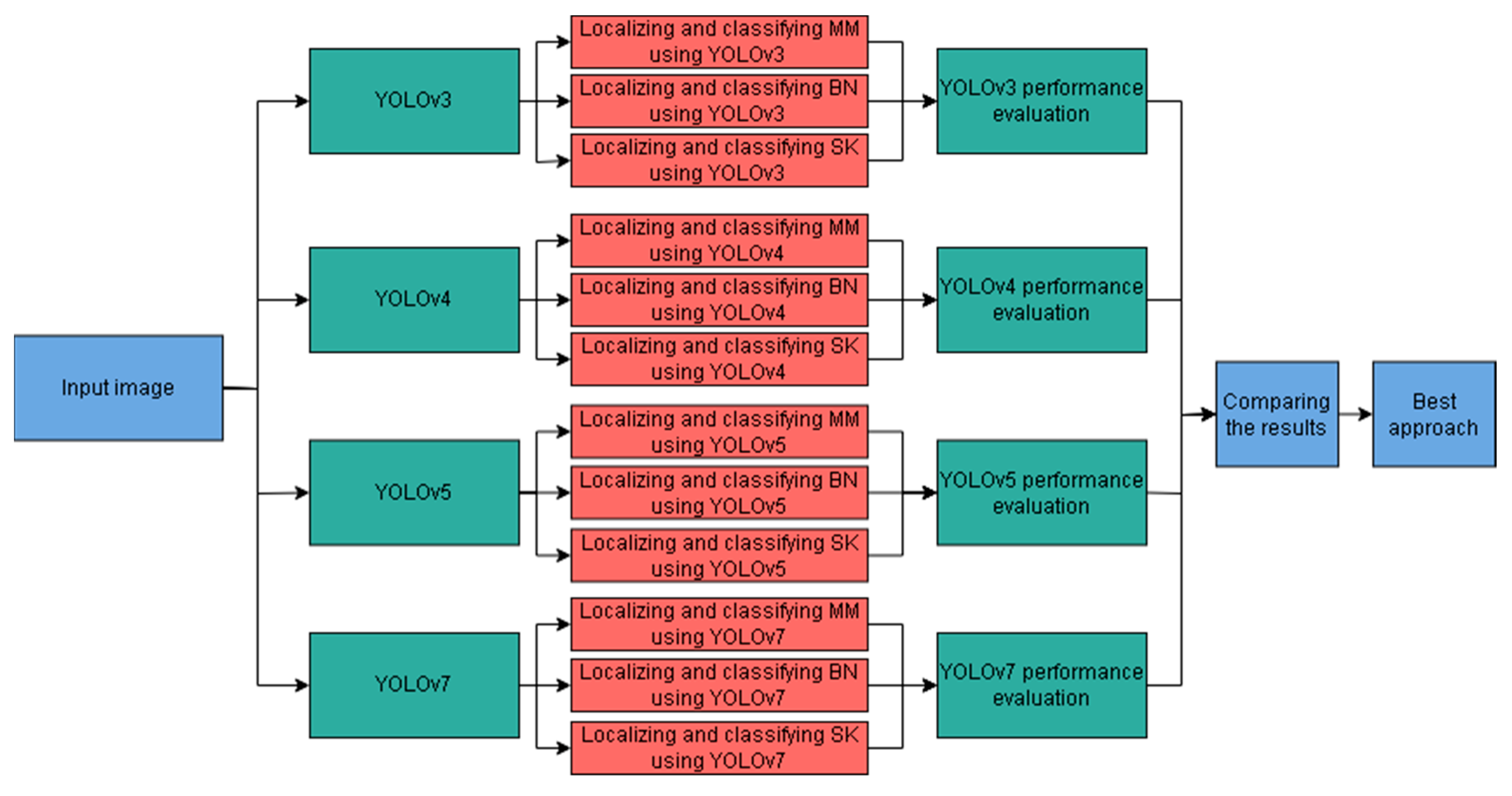
3.5. Proposed Skin Lesion Recognition Approach
4. Experiments
4.1. Performance Measures
- Intersection over Union (IoU): Quantifies the spatial overlap between predicted and ground truth bounding boxes (0–1 scale; 1 = perfect overlap), which is shown in Equation (1).
- Average Precision (AP): Integrates IoU, precision, and recall across various confidence thresholds, summarizing the localization and classification accuracy for each class, which is shown in Equation (2).
- Mean Average Precision (mAP): Averages AP across all classes, providing a single overall performance indicator, which is shown in Equation (3).
- F1-measure: Harmonic mean of precision and recall, offering a balanced view of model performance for each class, which is shown in Equation (4).
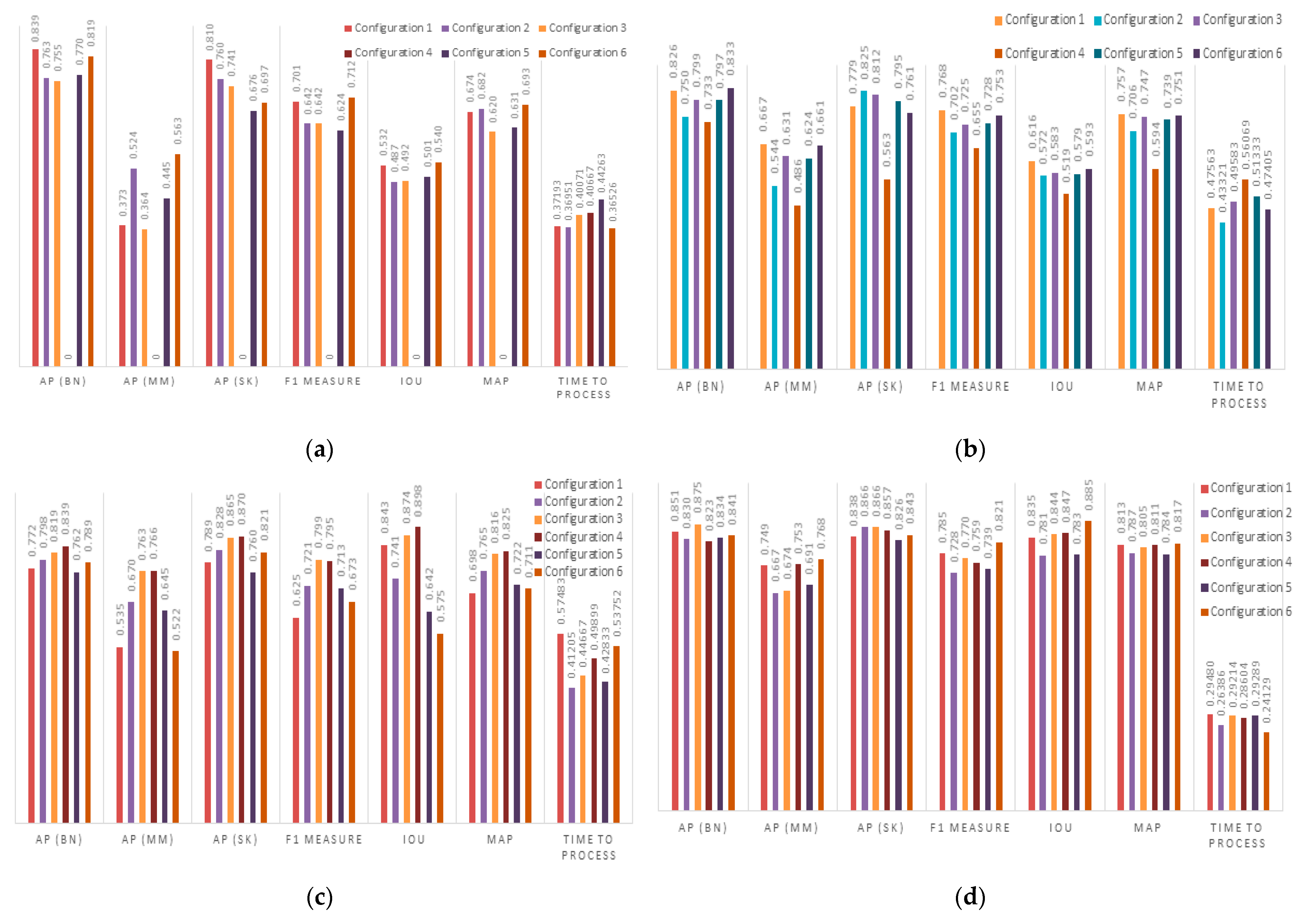
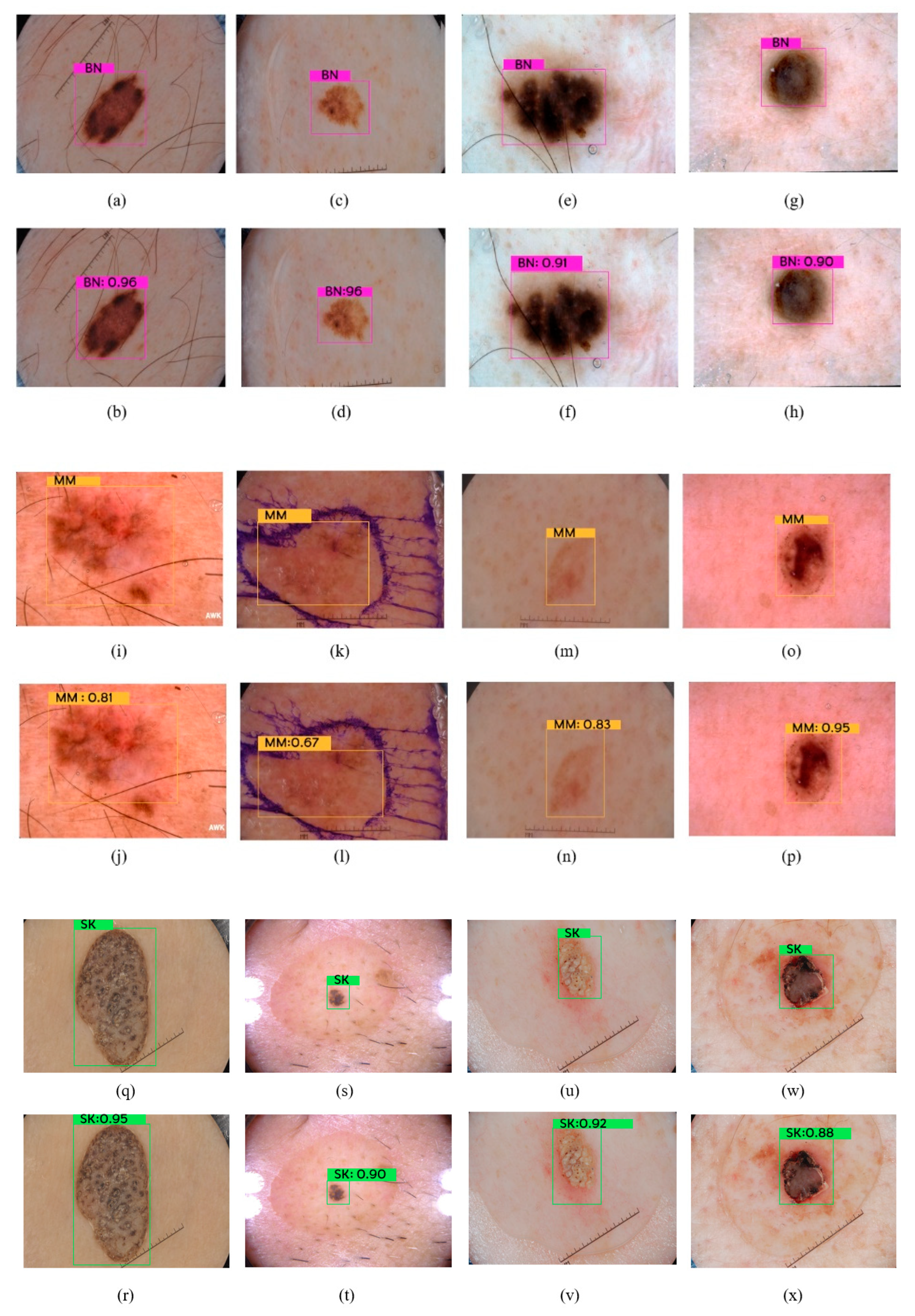
4.2. Results
4.3. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skin Cancer|World Cancer Research Fund International. WCRF International. 2021. Available online: https://www.wcrf.org/dietandcancer/skin-cancer/ (accessed on 9 February 2023).
- Melanoma Skin Cancer Statistics. American Cancer Society. 2022. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/melanoma-skin-cancer/about/key-statistics.html (accessed on 9 February 2023).
- Rundle, C.W.; Militello, M.; Barber, C.; Presley, C.L.; Rietcheck, H.R.; Dellavalle, R.P. Epidemiologic Burden of Skin Cancer in the US and Worldwide. Curr. Dermatol. Rep. 2020, 9, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante di Ruffano, L.; Takwoingi, Y.; Dinnes, J.; Chuchu, N.; Bayliss, S.E.; Davenport, C.; Matin, R.N.; Godfrey, K.; O’Sullivan, C.; Gulati, A.; et al. Computer-assisted diagnosis techniques (dermoscopy and spectroscopy-based) for diagnosing skin cancer in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 2018, CD013186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fargnoli, M.C.; Kostaki, D.; Piccioni, A.; Micantonio, T.; Peris, K. Dermoscopy in the diagnosis and management of non-melanoma skin cancers. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2012, 22, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigurdsson, S.; Philipsen, P.; Hansen, L.; Larsen, J.; Gniadecka, M.; Wulf, H. Detection of Skin Cancer by Classification of Raman Spectra. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2004, 51, 1784–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lützow-Holm, C.; Gjersvik, P.; Helsing, P. Melanom, føflekk eller talgvorte? Tidsskr. Nor. Legeforening 2013, 133, 1167–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berseth, M. ISIC 2017—Skin Lesion Analysis towards Melanoma Detection. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.00523. [Google Scholar]
- Agrahari, P.; Agrawal, A.; Subhashini, N. Skin Cancer Detection Using Deep Learning. In Futuristic Communication and Network Technologies; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 179–190. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, G.; Kumar, A.; Abdurohman, M. Classifiers for the Detection of Skin Cancer. In Smart Computing and Informatics; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 351–360. [Google Scholar]
- Hasya, H.; Nuha, H.; Abdurohman, M. Real Time-Based Skin Cancer Detection System Using Convolutional Neural Network and YOLO. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference of Computer and Informatics Engineering (IC2IE), Depok, Indonesia, 14–15 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Zafar, M.; Sharif, M.I.; Sharif, M.I.; Kadry, S.; Bukhari, S.A.C.; Rauf, H.T. Skin Lesion Analysis and Cancer Detection Based on Machine/Deep Learning Techniques: A Comprehensive Survey. Life 2023, 13, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Singh, S.; Das, A.; Bag, R. Diagnoses of Melanoma Lesion Using YOLOv3. In Computational Advancement in Communication, Circuits and Systems; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 291–302. [Google Scholar]
- Ünver, H.; Ayan, E. Skin Lesion Segmentation in Dermoscopic Images with Combination of YOLO and GrabCut Algorithm. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheria, F.; Tarokh, M.; Ziaratbanb, M. Semantic Segmentation of Lesions from Dermoscopic Images using Yolo-DeepLab Networks. Int. J. Eng. 2021, 34, 458–469. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, S.; Gupta, D.; Tiwari, A. Detector-Segmentor Network for Skin Lesion Localization and Segmentation. In Computer Vision, Pattern Recognition, Image Processing, and Graphics; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 589–599. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Barman, S.D.; Islam, S.; Reza, A.W. Skin cancer detection using convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computing and Artificial Intelligence, Bali, Indonesia, 19–22 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kalouche, S.; Ng, A.; Duchi, J. Vision-Based Classification of Skin Cancer Using Deep Learning. 2016. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Vision-Based-Classification-of-Skin-Cancer-using-Kalouche/b57ba909756462d812dc20fca157b3972bc1f533 (accessed on 9 February 2023).
- Demir, A.; Yilmaz, F.; Köse, O. Early detection of skin cancer using deep learning architectures: Resnet-101 and inception-v3. In Proceedings of the Medical Technologies Congress (TIPTEKNO), Izmir, Turkey, 3–5 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hosny, K.; Kassem, M.; Foaud, M. Skin cancer classification using deep learning and transfer learning. In Proceedings of the 9th Cairo International Biomedical Engineering Conference (CIBEC), Cairo, Egypt, 20–22 December 2018; pp. 90–93. [Google Scholar]
- Thurnhofer-Hemsi, K.; Domínguez, E. A Convolutional Neural Network Framework for Accurate Skin Cancer Detection. Neural Process. Lett. 2020, 53, 3073–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nersisson, R.; Iyer, T.; Raj, A.J.; Rajangam, V. A Dermoscopic Skin Lesion Classification Technique Using YOLO-CNN and Traditional Feature Model. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2021, 46, 9797–9808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Singh, S.K.; Chakraborty, A.; Das, A.; Bag, R. Melanoma Diagnosis Using Deep Learning and Fuzzy Logic. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Hamian, M. Skin Cancer Detection Based on Extreme Learning Machine and a Developed Version of Thermal Exchange Optimization. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2021, 2021, 9528664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florkowski, M. Classification of Partial Discharge Images Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Energies 2020, 13, 5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, G. Deep Belief Networks. Scholarpedia. 2022. Available online: http://scholarpedia.org/article/Deep_belief_networks (accessed on 26 February 2023).
- Simonyan, R.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS’12), Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 3–6 December 2012; Volume 1, pp. 1097–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Maaten, L. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6517–6525. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, Y.; Sommella, P.; O’Nils, M.; Liguori, C.; Lundgren, J. Automatic detection of melanoma with yolo deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the E-Health and Bioengineering Conference (EHB), Iasi, Romania, 21–23 November 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, S.; Haque, A.; Neubert, J. Automatic Diagnosis of Melanoma from Dermoscopic Image Using Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems (CISS), Princeton, NJ, USA, 21–23 March 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz, M.; Masood, M.; Javed, A.; Iqbal, J.; Nazir, T.; Mehmood, A.; Ashraf, R. Melanoma localization and classification through faster region-based convolutional neural network and SVM. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 28953–28974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartanto, C.A.; Wibowo, A. Development of Mobile Skin Cancer Detection using Faster R-CNN and MobileNet v2 Model. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Information Technology, Computer, and Electrical Engineering (ICITACEE), Semarang, Indonesia, 24–25 September 2020; pp. 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- Veneman, R. Real-Time Skin Cancer Detection Using Neural Networks on an Embedded Device; University of Twente: Enschede, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xue, Y.; Bi, X.; Chen, Z. Improved YOLO V3 Network for Basal Cell Carcinomas and Bowen’s Disease Detection. Preprint. 2021. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/352206363_Improved_YOLO_V3_Network_for_Basal_Cell_Carcinomas_and_Bowen%27s_Disease_Detection (accessed on 9 February 2024).
- Lin, T.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–25 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Liao, H.-Y.M.; Wu, Y.-H.; Chen, P.-Y.; Hsieh, J.-W.; Yeh, I.-H. CSPNet: A New Backbone that can Enhance Learning Capability of CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 1571–1580. [Google Scholar]
- Iandola, F.; Moskewicz, M.; Karayev, S.; Girshick, R.; Darrell, T.; Keutzer, K. DenseNet: Implementing efficient convnet descriptor pyramids. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1404.1869. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial Pyramid Pooling in Deep Convolutional Networks for Visual Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path Aggregation Network for Instance Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8759–8768. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; He, T.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, J.; Li, K. Bag of freebies for training object detection neural networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.04103. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Ye, R.; Ren, D. Distance-IoU loss: Faster and better learning for bounding box regression. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.08287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.02696. [Google Scholar]
- Rochet, F.; Elahi, T. Towards Flexible Anonymous Networks. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.03764. [Google Scholar]
- Codella, N.C.F.; Gutman, D.; Celebi, M.E.; Helba, B.; Marchetti, M.A.; Dusza, S.W.; Kalloo, A.; Liopyris, K.; Mishra, N.; Kittler, H.; et al. Skin lesion analysis toward melanoma detection: A challenge at the 2017 International symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI), hosted by the international skin imaging collaboration (ISIC). In Proceedings of the IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Washington, DC, USA, 4–7 April 2018; pp. 168–172. [Google Scholar]
- Rastegar, H.; Giveki, D. Designing a new deep convolutional neural network for skin lesion recognition. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 18907–18923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, D.; El-khatib, M.; Ichim, L. Skin Lesion Classification Using Collective Intelligence of Multiple Neural Networks. Sensors 2022, 22, 4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschandl, P.; Rosendahl, C.; Kittler, H. The HAM10000 dataset, a large collection of multi-source dermatoscopic images of common pigmented skin lesions. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotemberg, V.; Kurtansky, N.; Betz-Stablein, B.; Caffery, L.; Chousakos, E.; Codella, N.; Combalia, M.; Dusza, S.; Guitera, P.; Gutman, D.; et al. A patient-centric dataset of images and metadata for identifying melanomas using clinical context. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Performance | Skin Cancer | Model | Ref. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specificity | Sensitivity | Melanoma | YOLOv3 [14] | [15] | |||
| 97.05 | 97.33 | ||||||
| 97.5 | 97.5 | ||||||
| 97.02 | 97.97 | ||||||
| Intersection Over Union (IOU) | Accuracy | Benign, Melanoma, Seborrheic Keratosis, Atypical Nevi, | YOLOv3 [14] | [16] | |||
| 90 | 94.4 | ||||||
| 86 | 96 | ||||||
| Mean Box IOU | Mean Average Precision (mAP) | Benign, Melanoma, Seborrheic Keratosis, Atypical Nevi, | YOLOv3 [14] | [17] | |||
| 79.03 | 91.85 | ||||||
| Jaccard | Dice | Specificity | Sensitivity | Accuracy | Melanoma | Faster R-CNN [19] | [18] |
| 80.9 | 91.5 | 97.3 | 96.8 | 95.9 | |||
| 89.1 | 95.2 | 98.8 | 97.5 | 97.9 | |||
| 80.9 | 94.7 | 98.1 | 97.2 | 97.1 | |||
| Performance | Skin Cancer | Model | Ref. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NPV | PPV | Specificity | Sensitivity | Accuracy | Normal Melanoma | Deep Believe Network [27] | [28] |
| 94.12 | 86.76 | 89.7 | 91.18 | 92.65 | |||
| F1-Score | Precision | Recall | Accuracy | Benign Malignant | CNN [29] | [20] | |
| 83.25 | 83.25 | 84 | 89.5 | ||||
| Accuracy | Benign Malignant | VGG-16 [30] | [21] | ||||
| 78 | |||||||
| Precision | Specificity | Sensitivity | Accuracy | Melanoma, Nevi, Atypical nevi | AlexNET [31] | [23] | |
| 97.73 | 98.93 | 98.33 | 98.61 | ||||
| Avg. F-measure | Avg. Precision | Avg. Recall | Accuracy | Architecture | Actinic Keratosis, Basal Cell Carcinoma, Benign Keratosis, Dermatofibroma, Nevi, Melanoma, Vascular | DenseNet2 [32] | [24] |
| 91.26 | 92.03 | 90.5 | 94.52 | Plain DenseNet2 | |||
| 85.05 | 85.3 | 84.8 | 91.73 | Two-level DenseNet2 | |||
| AUC | Precision | Recall | Accuracy | Benign Malignant | YOLOv2 [33] | [25] | |
| 0.95 | 85 | 88 | 94 | ||||
| AUC | Precision | Specificity | Sensitivity | Accuracy | Melanoma Non-Melanoma | YOLOv3 [14] | [26] |
| 0.99 | 97.5 | 99.37 | 97.5 | 99 | |||
| 0.99 | 97.44 | 99.38 | 97.44 | 99 | |||
| 0.99 | 94.64 | 98.13 | 94.22 | 97.11 | |||
| Performance | Skin Cancer | Model | Ref. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mAP | Model | Benign Malignant | YOLOv1 [34] YOLOv2 [33] YOLOv3 [14] | [36] | |||
| 37 | YOLOv1 | ||||||
| 83 | YOLOv2 | ||||||
| 77 | YOLOv3 | ||||||
| AUC | Specificity | Sensitivity | Accuracy | Melanoma Non-Melanoma | YOLOv2 [33] | [11] | |
| 91 | 85.9 | 86.35 | 86 | ||||
| mAP | F1-Score | Precision | Recall | Accuracy | Benign Malignant | YOLOv4 [35] | [40] |
| 89.34 | 85 | 81 | 89 | 94.04 | |||
| Precision | Recall | Accuracy | Skin Cancer | Basal Cell Carcinomas, Bowen’s Disease | YOLOv3 [14] | [41] | |
| 91.3 | 32.8 | 91.3 | BCC | ||||
| 90.9 | 30.3 | 90.9 | Bowen’s Disease | ||||
| Class Type | Training Set | Validation Set | Testing Set |
|---|---|---|---|
| Malignant Melanoma (MM) | 374 | 30 | 117 |
| Seborrheic Keratosis (SK) | 254 | 42 | 90 |
| Benign Nevus (BN) | 1372 | 78 | 393 |
| YOLOv3 | YOLOv4 | YOLOv5 | YOLOv7 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Configuration\Hyperparameter | Lr | M | B | Lr | M | B | Lr | M | B | Lr | M | B |
| Configuration 1 | 0.001 | 0.937 | 64 | 0.001 | 0.900 | 64 | 0.001 | 0.949 | 32 | 0.001 | 0.937 | 50 |
| Configuration 2 | 0.0001 | 0.949 | 64 | 0.0001 | 0.960 | 64 | 0.005 | 0.937 | 16 | 0.0001 | 0.949 | 50 |
| Configuration 3 | 0.001 | 0.950 | 16 | 0.001 | 0.949 | 32 | 0.01 | 0.937 | 32 | 0.001 | 0.950 | 32 |
| Configuration 4 | 0.1 | 0.990 | 32 | 0.01 | 0.990 | 32 | 0.01 | 0.900 | 16 | 0.01 | 0.949 | 16 |
| Configuration 5 | 0.01 | 0.949 | 32 | 0.01 | 0.937 | 64 | 0.001 | 0.949 | 64 | 0.01 | 0.990 | 32 |
| Configuration 6 | 0.005 | 0.900 | 64 | 0.005 | 0.900 | 64 | 0.01 | 0.950 | 64 | 0.005 | 0.900 | 60 |
| Validation Set | Test Set | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP(BN) | AP(MM) | AP(SK) | mAP | IoU | F1 | Time to Process (s) | AP(BN) | AP(MM) | AP(SK) | mAP | IoU | F1 | Time to Process (s) | |
| YOLOv3 | 81.9 | 56.3 | 69.7 | 69.3 | 53.9 | 69.2 | 0.36 | 79.5 | 42.7 | 60.5 | 60.9 | 50.8 | 65.0 | 0.45 |
| YOLOv4 | 82.6 | 66.7 | 77.9 | 75.7 | 61.6 | 76.8 | 0.47 | 81.5 | 52.6 | 65.4 | 66.5 | 60.8 | 72.0 | 0.50 |
| YOLOv5 | 83.9 | 76.3 | 86.7 | 82.5 | 89.8 | 79.9 | 0.49 | 81.6 | 61.9 | 74.9 | 72.8 | 87.4 | 74.2 | 0.51 |
| YOLOv7 | 84.1 | 76.8 | 84.3 | 81.7 | 88.5 | 82.1 | 0.24 | 80.1 | 64.9 | 81.3 | 75.4 | 86.3 | 77.9 | 0.31 |
| Class | No Data Augmentation | Data Augmentation |
|---|---|---|
| BN | 1372 | 2740 |
| MM | 254 | 2540 |
| SK | 374 | 2610 |
| Test Results | Class | AP | F1-Score | IoU | mAP | Processing Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No data augmentation | BN | 80.1 | 77.9 | 86.3 | 75.4 | 0.44 |
| MM | 64.9 | |||||
| SK | 81.3 | |||||
| Data augmentation—imbalanced | BN | 81.4 | 78.3 | 87.5 | 76.5 | 0.59 |
| MM | 66.8 | |||||
| SK | 81.4 | |||||
| Data augmentation—balanced | BN | 81.9 | 79.6 | 88.7 | 78.0 | 0.54 |
| MM | 68.4 | |||||
| SK | 83.8 |
| Approach | Class | AP | F1-Score | IoU | mAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN from [51] | BN | 74.3 | 73.5 | 92.7 | 72.2 |
| MM | 61.7 | ||||
| SK | 80.5 | ||||
| MobileNet-V2 from [52] | BN | 78.5 | 74.9 | 83.1 | 74.7 |
| MM | 67.4 | ||||
| SK | 78.1 | ||||
| Xception from [52] | BN | 77.0 | 76.6 | 85.9 | 75.1 |
| MM | 67.3 | ||||
| SK | 81.0 | ||||
| InceptionResNet-V2 from [52] | BN | 76.8 | 77.9 | 86.5 | 75.4 |
| MM | 67.4 | ||||
| SK | 82.0 | ||||
| Proposed YOLOv7 with balanced data augmentation | BN | 81.9 | 79.6 | 88.7 | 78.0 |
| MM | 68.4 | ||||
| SK | 83.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
AlSadhan, N.A.; Alamri, S.A.; Ben Ismail, M.M.; Bchir, O. Skin Cancer Recognition Using Unified Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Cancers 2024, 16, 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071246
AlSadhan NA, Alamri SA, Ben Ismail MM, Bchir O. Skin Cancer Recognition Using Unified Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Cancers. 2024; 16(7):1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071246
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlSadhan, Nasser A., Shatha Ali Alamri, Mohamed Maher Ben Ismail, and Ouiem Bchir. 2024. "Skin Cancer Recognition Using Unified Deep Convolutional Neural Networks" Cancers 16, no. 7: 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071246
APA StyleAlSadhan, N. A., Alamri, S. A., Ben Ismail, M. M., & Bchir, O. (2024). Skin Cancer Recognition Using Unified Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Cancers, 16(7), 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16071246






