The Role of Systematic Lymphadenectomy in Low-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Study Selection
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Quality Assessment of Studies
3. Results
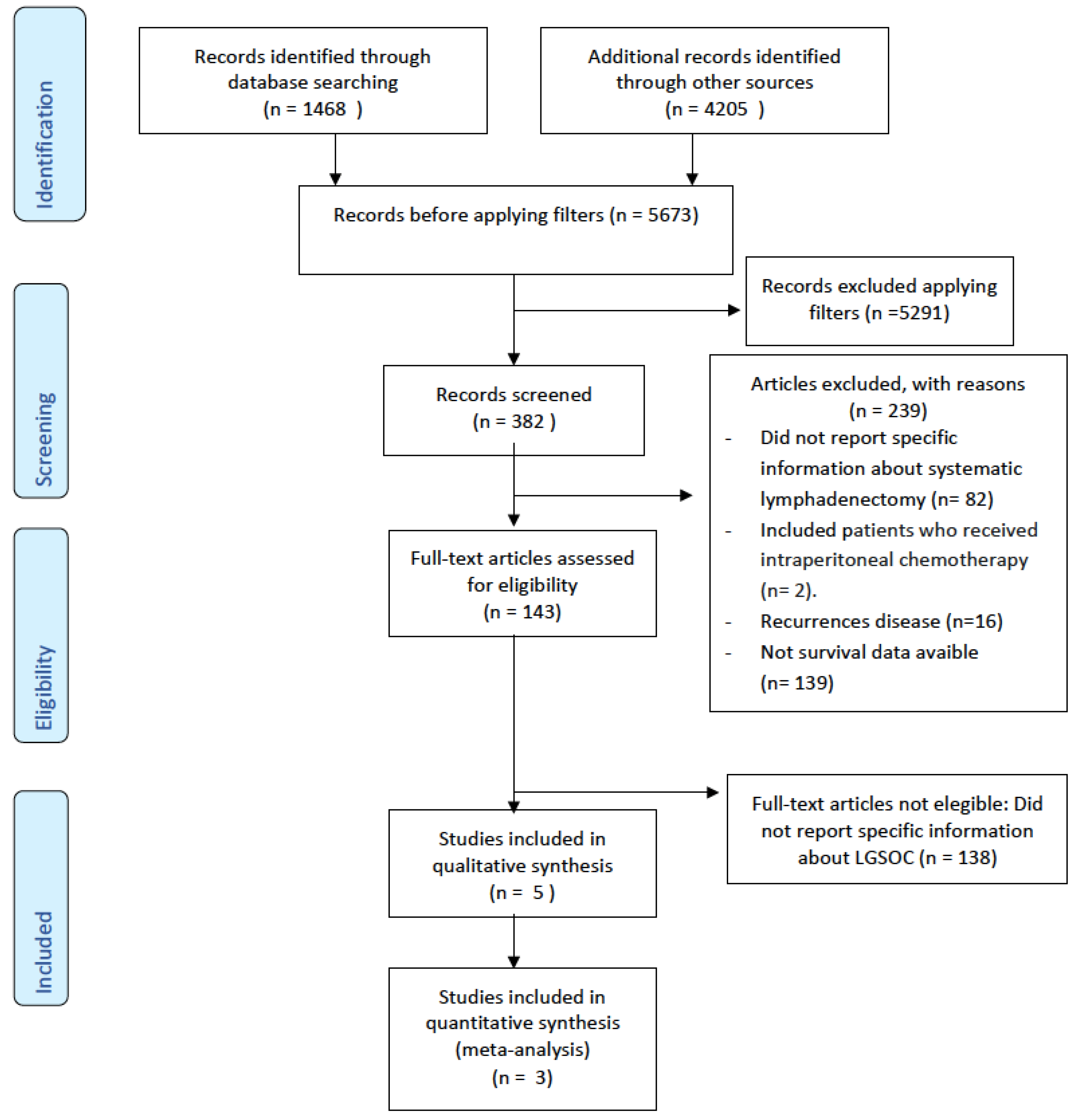
3.1. Evidence Acquisition
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Qualitative Synthesis
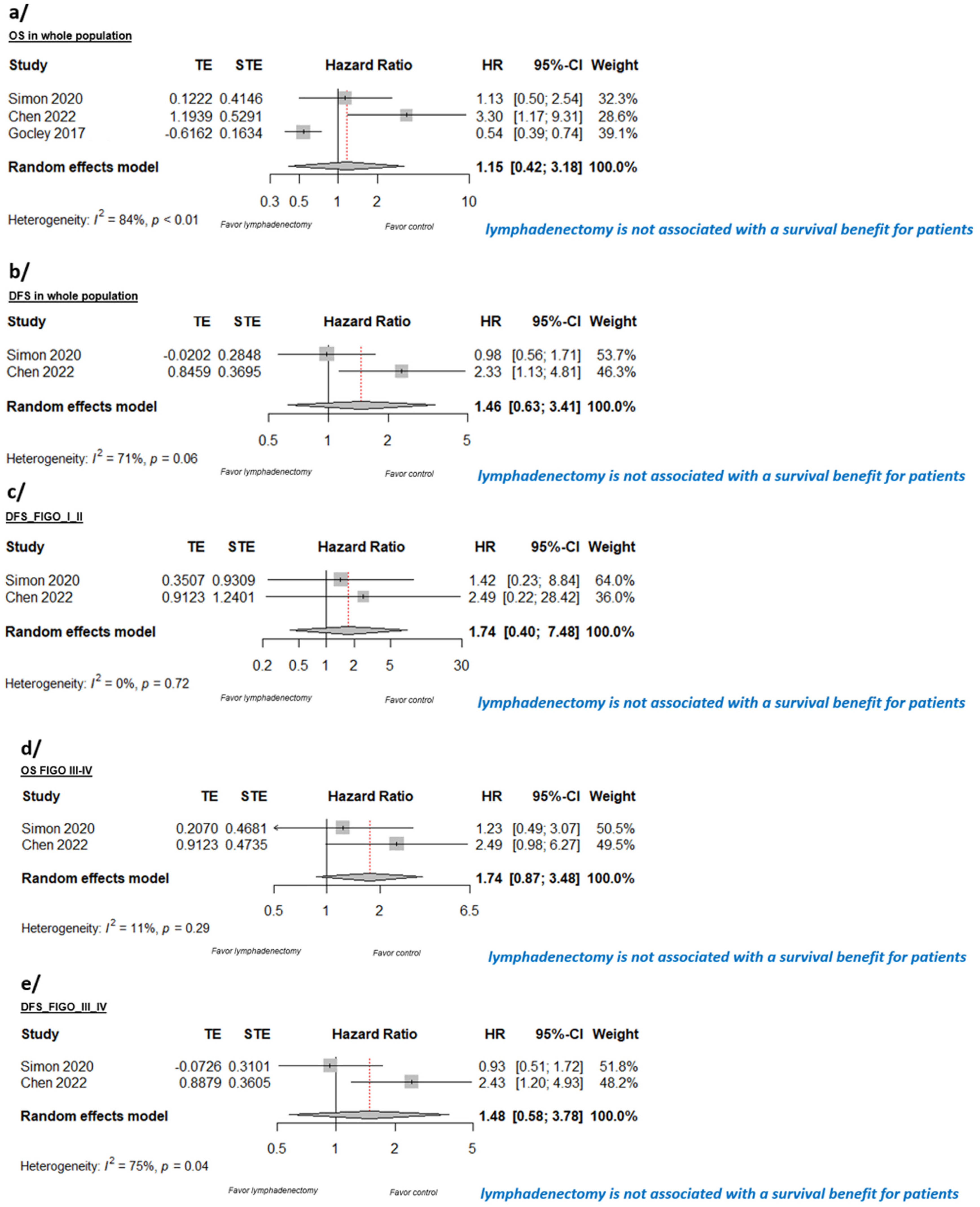
3.4. Quantitative Synthesis
3.5. Quality Assessments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cabasag, C.J.; Fagan, P.J.; Ferlay, J.; Vignat, J.; Laversanne, M.; Liu, L.; van der Aa, M.A.; Bray, F.; Soerjomataram, I. Ovarian Cancer Today and Tomorrow: A Global Assessment by World Region and Human Development Index Using GLOBOCAN 2020. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 151, 1535–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malpica, A.; Deavers, M.T.; Lu, K.; Bodurka, D.C.; Atkinson, E.N.; Gershenson, D.M.; Silva, E.G. Grading Ovarian Serous Carcinoma Using a Two-Tier System. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2004, 28, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zantow, E.; Chen, A.; Zhao, D.; Mashburn, S.; Underwood, H.; Baste Subia, M.N.; Zuna, R.; Moore, K.N.; Holman, L.L. Clinical Factors Associated with Short- and Long-Term Survival in Low Grade Ovarian Carcinoma. Gynecol. Oncol. 2017, 147, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadducci, A.; Cosio, S. Therapeutic Approach to Low-Grade Serous Ovarian Carcinoma: State of Art and Perspectives of Clinical Research. Cancers 2020, 12, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Cliby, W.A. Advanced Ovarian Cancer: Weighing the Risks and Benefits of Surgery. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 63, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggink, F.A.; Koopmans, C.M.; Nijman, H.W. Surgery for Patients with Newly Diagnosed Advanced Ovarian Cancer: Which Patient, When and Extent? Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2017, 29, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, R.; McIndoe, G.; Sundar, S. Optimum Surgery in Advanced-Stage Ovarian Cancer. R. Coll. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2011, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Raspagliesi, F.; Bogani, G.; Ditto, A.; Martinelli, F.; Chiappa, V.; Borghi, C.; Scaffa, C.; Morano, F.; Maltese, G.; Lorusso, D. Implementation of Extensive Cytoreduction Resulted in Improved Survival Outcomes for Patients with Newly Diagnosed Advanced-Stage Ovarian, Tubal, and Peritoneal Cancers. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 24, 3396–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.K.; Chi, D.S. Maximal Cytoreductive Effort in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Surgery. J. Gynecol. Oncol. 2010, 21, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura-Sampedro, J.J.; Morales-Soriano, R.; Arjona-Sánchez, Á.; Cascales-Campos, P. Secondary Surgical Cytoreduction Needs to Be Assessed Taking into Account Surgical Technique, Completeness of Cytoreduction, and Extent of Disease. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 18, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slomovitz, B.; Gourley, C.; Carey, M.S.; Malpica, A.; Shih, I.M.; Huntsman, D.; Fader, A.N.; Grisham, R.N.; Schlumbrecht, M.; Sun, C.C.; et al. Low-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer: State of the Science. Gynecol. Oncol. 2020, 156, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero-Macías, R.; Rigolet, P.; Mikhael, E.; Krell, J.; Villefranque, V.; Lecuru, F.; Fotopoulou, C. Traditional Systemic Treatment Options in Advanced Low-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer after Successful Cytoreduction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2022, 14, 3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monk, B.J.; Grisham, R.N.; Banerjee, S.; Kalbacher, E.; Mirza, M.R.; Romero, I.; Vuylsteke, P.; Coleman, R.L.; Hilpert, F.; Oza, A.M.; et al. MILO/ENGOT-Ov11: Binimetinib Versus Physician’s Choice Chemotherapy in Recurrent or Persistent Low-Grade Serous Carcinomas of the Ovary, Fallopian Tube, or Primary Peritoneum. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gershenson, D.M.; Gourley, C.; Paul, J. MEK Inhibitors for the Treatment of Low-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer: Expanding Therapeutic Options for a Rare Ovarian Cancer Subtype. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3731–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harter, P.; Sehouli, J.; Lorusso, D.; Reuss, A.; Vergote, I.; Marth, C.; Kim, J.-W.; Raspagliesi, F.; Lampe, B.; Aletti, G.; et al. A Randomized Trial of Lymphadenectomy in Patients with Advanced Ovarian Neoplasms. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, D.K.; Alvarez, R.D.; Backes, F.J.; Bakkum-Gamez, J.N.; Barroilhet, L.; Behbakht, K.; Berchuck, A.; Chen, L.M.; Chitiyo, V.C.; Cristea, M.; et al. NCCN Guidelines® Insights: Ovarian Cancer, Version 3.2022. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2022, 20, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wafa, M.; Braicu, E.I.; Muallem, M.Z.; Richter, R.; Taube, E.; Sehouli, J.; Grabowski, J.P. Incidence and Pattern of Spread of Lymph Node Metastasis in Patients With Low-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer. Anticancer. Res. 2019, 39, 5617–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stovold, E.; Beecher, D.; Foxlee, R.; Noel-Storr, A. Study Flow Diagrams in Cochrane Systematic Review Updates: An Adapted PRISMA Flow Diagram. Syst. Rev. 2014, 3, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chu, R.; Shen, Y.; Yao, Q.; Chen, J.; Qin, T.; Li, L.; Chen, G.; Gao, Q.; Sun, C.; et al. Evaluation of the Prognostic Value of Lymphadenectomy for Low-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer: A Case-Control Multicenter Retrospective Study. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 23, 101476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, V.; Ngo, C.; Pujade-Lauraine, E.; Ferron, G.; Pomel, C.; Leblanc, E.; Nadeau, C.; Ray-Cocquard, I.; Lecuru, F.; Bonsang-Kitzis, H. Should We Abandon Systematic Pelvic and Paraaortic Lymphadenectomy in Low-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer? Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 27, 3882–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gockley, A.; Melamed, A.; Bregar, A.J.; Clemmer, J.T.; Birrer, M.; Schorge, J.O.; Del Carmen, M.G.; Alejandro Rauh-Hain, J. Outcomes of Women with High-Grade and Low-Grade Advanced-Stage Serous Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 129, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Study Quality Assessment Tools. NHLBI, NIH. Available online: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/study-quality-assessment-tools (accessed on 24 September 2023).
- Nasioudis, D.; Latif, N.A.; Haggerty, A.F.; Giuntoli, R.L.; Kim, S.H.; Ko, E.M. Outcomes of Comprehensive Lymphadenectomy for Patients with Advanced Stage Ovarian Carcinoma and Rare Histologic Sub-Types. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2021, 31, 1132–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yin, J.; Li, Y.; Gu, Y.; Wang, W.; Shan, Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Qin, M.; Cai, Y.; Jin, Y.; et al. Systematic Lymph Node Dissection May Be Abolished in Patients With Apparent Early-Stage Low-Grade Mucinous and Endometrioid Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 705720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ding, J.; Zheng, H.; Xu, L.; Li, W.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, X.; Ma, C.; Zhang, F.; Zhong, P.; et al. Speculation on Optimal Numbers of Examined Lymph Node for Early-Stage Epithelial Ovarian Cancer from the Perspective of Stage Migration. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1265631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ye, X.; Zhou, B.; Liu, Y.; Feng, M.; Lv, W.; Lu, D.; Cui, X.; Liu, J. Nomogram for Predicting Lymph Node Metastasis in Patients with Ovarian Cancer Using Ultrasonography: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, F.; Gu, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Li, L.; Xiao, Y. Lymphadenectomy and Optimal Excise Lymph Nodes Count for Early-Stage Primary Fallopian Tube Cancer: A SEER-Based Study. BMC Womens Health 2023, 23, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Liu, K.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; Li, H.W.; Guo, H.; Zhang, H.; Xiang, L.; Feng, X.; Wang, X.; et al. A Prospective Randomized Multicenter Trial for Lymphadenectomy in Early-Stage Ovarian Cancer: LOVE Study. J. Gynecol. Oncol. 2023, 34, e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogani, G.; Borghi, C.; Ditto, A.; Signorelli, M.; Martinelli, F.; Chiappa, V.; Scaffa, C.; Perotto, S.; Leone Roberti Maggiore, U.; Montanelli, L.; et al. Impact of Surgical Route in Influencing the Risk of Lymphatic Complications After Ovarian Cancer Staging. J. Minim. Invasive Gynecol. 2017, 24, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musacchio, L.; Turinetto, M.; Arenare, L.; Bartoletti, M.; Califano, D.; Tuninetti, V.; Marchetti, C.; Cormio, G.; Loizzi, V.; Pisano, C.; et al. Effect of Bevacizumab in Advanced Low Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer: Data from the MITO 22 Trial. Gynecol. Oncol. 2023, 172, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study (Year) | Design | Setting | Arms | Follow-Up (Months) | Patients (n) | Population | Age (Years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simon V. (2020) [20] | Retrospective cohort | TMRG Database | Lymphadenectomy vs. no lymphadenectomy. | Median: 27.5 | 126 | LGSOC | 53 (19–82) |
| Chen Z. (2022) [19] | Retrospective | Multiple medical centers | Lymphadenectomy, no lymphadenectomy. | Varied | 155 78 (PSM) | LGSOC | 47 (21–79) |
| Nasioudis D. (2021) [23] | Retrospective | National Cancer Database | Comprehensive lymphadenectomy, no comprehensive lymphadenectomy. | Median of 46.3 for no lymphadenectomy; median of 53.75 for those with lymphadenectomy. | 90 LGSOC | Stage III–IV clear-cell, endometrioid, mucinous, and low-grade serous carcinoma patients | 57 (17–89) |
| Gockley (2017) [21] | Retrospective PSM | National Cancer Database | Low-grade serous ovarian cancer, high-grade serous ovarian cancer; lymph vs no lymph from PSM. | Median: 72.7 | 755 LGSOC 404 (PSM) | Women 18 years and older diagnosed with advanced-stage (IIIC and IV) serous ovarian carcinoma | 53.6 ± 15.34 |
| Chen J. (2021) [24] | Retrospective | Single center | Three types of Lymph | Median: 85.2 | 59 LGSOC | LGEOC—LG-SOC, LG-MOC, or LG-EOC | - |
| Study, Date | Control Arm | Intervention Arm | Primary Endpoint | Median DFS (Mo) | HR | 95%CI | Median OS (Mo) | HR | 95%CI | Other OS Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simon V. (2020) [20] | No lymphadenectomy (31) | Lymphadenectomy (91) | Overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) | 41 | 0.98 | [0.56; 1.71] | 130 | 1.13 | [0.50; 2.54] | |
| Chen Z. (2022) [19] | No lymphadenectomy (39) | Lymphadenectomy (39) | Prognostic value of lymphadenectomy in patients with LGSOC | 65 | 2.33 | [1.13; 4.81] | 90 | 3.30 | [1.17; 9.31] | |
| Nasioudis D. (2021) [23] | No lymphadenectomy (60) | Comprehensive lymphadenectomy (30) | The impact of comprehensive lymphadenectomy on the survival of patients with advanced-stage epithelial ovarian carcinoma | - | 90.32 mo * | |||||
| Gockley (2017) [21] | No lymphadenectomy (202) | Lymphadenectomy (202) | The identification of factors associated with survival among patients with advanced-stage low-grade serous ovarian cancer | - | - | - | 106.5 | 0.54 | [0.39; 0.74] | |
| Chen J. (2021) [24] | No lymphadenectomy (22) | Lymphadenectomy (37) | Disease-specific overall survival (OS) | 5y-OS * 82% |
| Study, Year | Criteria | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | |
| Simon, 2020 [20] | NA | NA | NA | |||||||||||
| Chen, 2022 [19] | NA | NA | NA | |||||||||||
| Gokley, 2017 [21] | NA | NA | NA | |||||||||||
| Nasioudis, 2021 [23] | NA | NA | NA | |||||||||||
| Chen, 2021 [24] | NA | NA | NA | |||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montero-Macías, R.; Segura-Sampedro, J.J.; Rigolet, P.; Lecuru, F.; Craus-Miguel, A.; Castillo-Tuñón, J.M. The Role of Systematic Lymphadenectomy in Low-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2024, 16, 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050955
Montero-Macías R, Segura-Sampedro JJ, Rigolet P, Lecuru F, Craus-Miguel A, Castillo-Tuñón JM. The Role of Systematic Lymphadenectomy in Low-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2024; 16(5):955. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050955
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontero-Macías, Rosa, Juan José Segura-Sampedro, Pascal Rigolet, Fabrice Lecuru, Andrea Craus-Miguel, and Juan Manuel Castillo-Tuñón. 2024. "The Role of Systematic Lymphadenectomy in Low-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Cancers 16, no. 5: 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050955
APA StyleMontero-Macías, R., Segura-Sampedro, J. J., Rigolet, P., Lecuru, F., Craus-Miguel, A., & Castillo-Tuñón, J. M. (2024). The Role of Systematic Lymphadenectomy in Low-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 16(5), 955. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050955








