Effect of Clinical Complete Remission Following Neoadjuvant Pembrolizumab or Chemotherapy in Bladder-Preservation Strategy in Patients with Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Declining Definitive Local Therapy
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Statistical Analysis
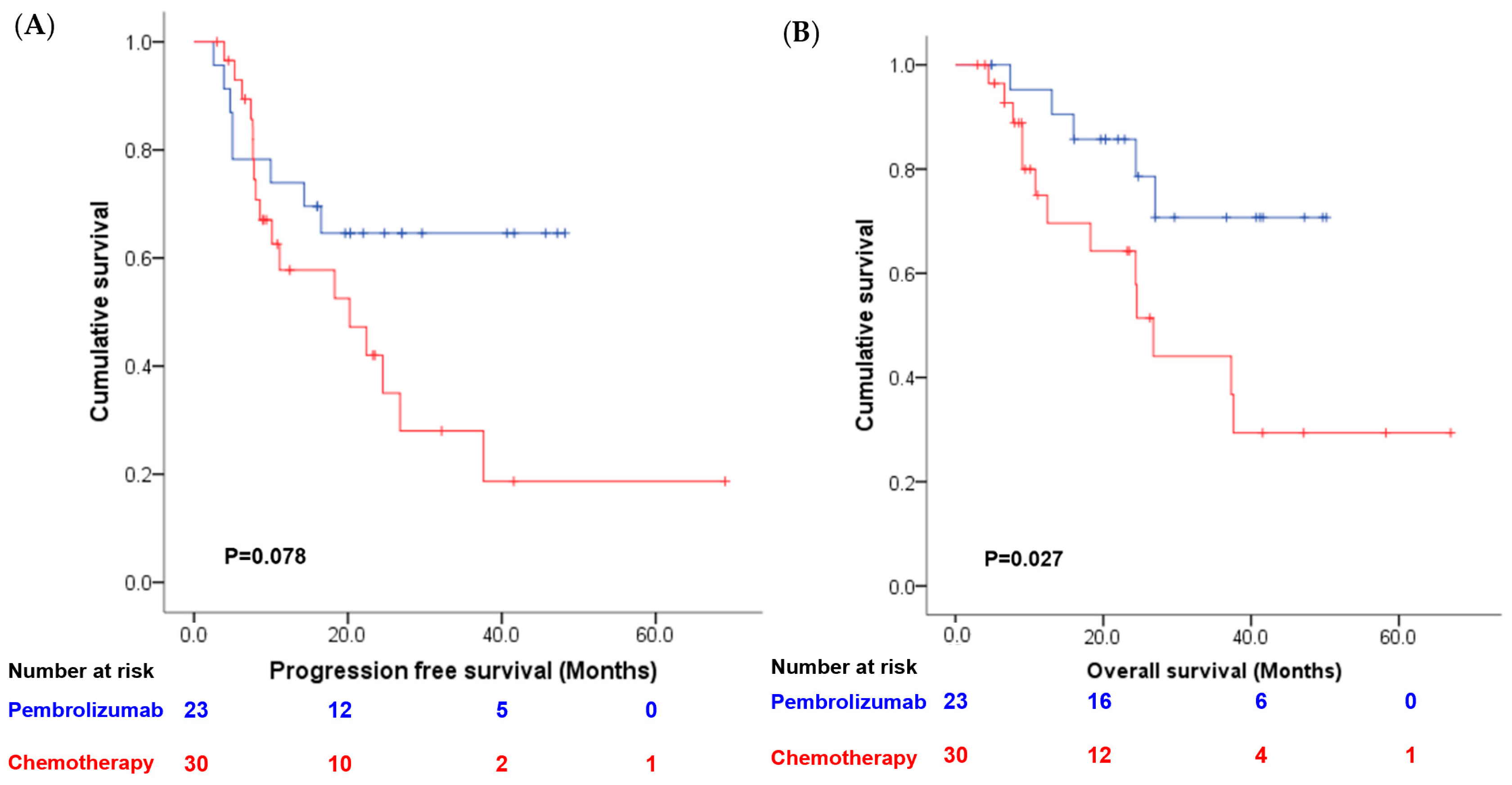
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alfred Witjes, J.; Lebret, T.; Comperat, E.M.; Cowan, N.C.; De Santis, M.; Bruins, H.M.; Hernandez, V.; Espinos, E.L.; Dunn, J.; Rouanne, M.; et al. Updated 2016 EAU Guidelines on Muscle-invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochner, B.H.; Dalbagni, G. Reply to Siebren Dijkstra and Carl J. Wijburg’s Letter to the Editor re: Bernard H. Bochner, Guido Dalbagni, Karim H. Marzouk; et al. Randomized Trial Comparing Open Radical Cystectomy and Robot-assisted Laparoscopic Radical Cystectomy: Oncologic Outcomes. Eur. Urol. 2018, 74, 465–471. Can the Pattern of Cancer Recurrence Truly be Assigned to the Surgical Modality? Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, e138–e139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johar, R.S.; Hayn, M.H.; Stegemann, A.P.; Ahmed, K.; Agarwal, P.; Balbay, M.D.; Hemal, A.; Kibel, A.S.; Muhletaler, F.; Nepple, K.; et al. Complications after robot-assisted radical cystectomy: Results from the International Robotic Cystectomy Consortium. Eur. Urol. 2013, 64, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossman, H.B.; Natale, R.B.; Tangen, C.M.; Speights, V.O.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Trump, D.L.; deVere White, R.W.; Sarosdy, M.F.; Wood, D.P., Jr.; Raghavan, D.; et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus cystectomy compared with cystectomy alone for locally advanced bladder cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschini, M.; Gandaglia, G.; Deho, F.; Salonia, A.; Briganti, A.; Montorsi, F. Bladder cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.K.; Kim, J.H.; Park, J.Y.; Gwon, Y.N.; Kim, K.M.; Yang, W.J.; Doo, S.W.; Song, Y.S. Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Prior to Radical Cystectomy for Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer with Variant Histology: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Survival Outcomes and Pathological Features. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2023, 22, e53–e65.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winoker, J.S.; Liaw, C.W.; Galsky, M.D.; Wiklund, P.; Mehrazin, R. Clinical Complete Response after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer: A Call for Standardized Assessments and Definitions. Eur. Urol. Focus. 2020, 6, 627–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblatt, R.; Sherif, A.; Rintala, E.; Wahlqvist, R.; Ullen, A.; Nilsson, S.; Malmstrom, P.U.; Nordic Urothelial Cancer, G. Pathologic downstaging is a surrogate marker for efficacy and increased survival following neoadjuvant chemotherapy and radical cystectomy for muscle-invasive urothelial bladder cancer. Eur. Urol. 2012, 61, 1229–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, B.; Calogero, A.; Scafuri, L.; Ferro, M.; Lucarelli, G.; Di Zazzo, E.; Sicignano, E.; Falcone, A.; Romano, L.; De Luca, L.; et al. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors as a Neoadjuvant/Adjuvant Treatment of Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2022, 14, 2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Necchi, A.; Anichini, A.; Raggi, D.; Briganti, A.; Massa, S.; Luciano, R.; Colecchia, M.; Giannatempo, P.; Mortarini, R.; Bianchi, M.; et al. Pembrolizumab as Neoadjuvant Therapy Before Radical Cystectomy in Patients with Muscle-Invasive Urothelial Bladder Carcinoma (PURE-01): An Open-Label, Single-Arm, Phase II Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 3353–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herr, H.W. Outcome of patients who refuse cystectomy after receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Eur. Urol. 2008, 54, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, C.N.; Pansadoro, V.; Calabro, F.; Schnetzer, S.; Giannarelli, D.; Emiliozzi, P.; De Paula, F.; Scarpone, P.; De Carli, P.; Pizzo, M.; et al. Can patient selection for bladder preservation be based on response to chemotherapy? Cancer 2003, 97, 1644–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robins, D.; Matulay, J.; Lipsky, M.; Meyer, A.; Ghandour, R.; DeCastro, G.; Anderson, C.; Drake, C.; Benson, M.; McKiernan, J.M. Outcomes Following Clinical Complete Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Muscle-invasive Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder in Patients Refusing Radical Cystectomy. Urology 2018, 111, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazza, P.; Moran, G.W.; Li, G.; Robins, D.J.; Matulay, J.T.; Herr, H.W.; Decastro, G.J.; McKiernan, J.M.; Anderson, C.B. Conservative Management Following Complete Clinical Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy of Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer: Contemporary Outcomes of a Multi-Institutional Cohort Study. J. Urol. 2018, 200, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrelli, F.; Coinu, A.; Cabiddu, M.; Ghilardi, M.; Vavassori, I.; Barni, S. Correlation of pathologic complete response with survival after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in bladder cancer treated with cystectomy: A meta-analysis. Eur. Urol. 2014, 65, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Xie, R.Y.; Cao, C.Z.; Shang, B.Q.; Shi, H.Z.; Shou, J.Z. Disease Management of Clinical Complete Responders to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy of Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: A Review of Literature. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 816444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murasawa, H.; Koie, T.; Ohyama, C.; Yamamoto, H.; Imai, A.; Hatakeyama, S.; Yoneyama, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; Iwabuchi, I.; Ogasawara, M.; et al. The utility of neoadjuvant gemcitabine plus carboplatin followed by immediate radical cystectomy in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer who are ineligible for cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 22, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphael, M.J.; Booth, C.M. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer: Underused across the 49(th) parallel. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2019, 13, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scafuri, L.; Sciarra, A.; Crocetto, F.; Ferro, M.; Buonerba, C.; Ugliano, F.; Guerra, G.; Sanseverino, R.; Lorenzo, G.D. Does perioperative systemic therapy represent the optimal therapeutic paradigm in organ-confined, muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma? Future Sci. OA 2021, 7, FSO770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.W.; Kwon, W.A.; Nguyen, N.T.; Phan, D.T.T.; Seo, H.K. Approaches to Clinical Complete Response after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: Possibilities and Limitations. Cancers 2023, 15, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galsky, M.D.; Daneshmand, S.; Izadmehr, S.; Gonzalez-Kozlova, E.; Chan, K.G.; Lewis, S.; Achkar, B.E.; Dorff, T.B.; Cetnar, J.P.; Neil, B.O.; et al. Gemcitabine and cisplatin plus nivolumab as organ-sparing treatment for muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A phase 2 trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 2825–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Chen, J.; Ou, Z.; Chen, H.; Liu, Z.; Chen, M.; Zhang, R.; Yu, A.; Cao, R.; Zhang, E.; et al. Neoadjuvant immunotherapy, chemotherapy, and combination therapy in muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A multi-center real-world retrospective study. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellmunt, J.; de Wit, R.; Fradet, Y.; Climent, M.A.; Petrylak, D.P.; Lee, J.L.; Fong, L.; Necchi, A.; Sternberg, C.N.; O’Donnell, P.H.; et al. Putative Biomarkers of Clinical Benefit with Pembrolizumab in Advanced Urothelial Cancer: Results from the KEYNOTE-045 and KEYNOTE-052 Landmark Trials. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 2050–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivas, P.; Plimack, E.R.; Balar, A.V.; Castellano, D.; O’Donnell, P.H.; Bellmunt, J.; Powles, T.; Hahn, N.M.; de Wit, R.; Bajorin, D.F.; et al. Pembrolizumab as First-line Therapy in Cisplatin-ineligible Advanced Urothelial Cancer (KEYNOTE-052): Outcomes in Older Patients by Age and Performance Status. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2020, 3, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuky, J.; Balar, A.V.; Castellano, D.; O’Donnell, P.H.; Grivas, P.; Bellmunt, J.; Powles, T.; Bajorin, D.; Hahn, N.M.; Savage, M.J.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes in KEYNOTE-052: Phase II Study Investigating First-Line Pembrolizumab in Cisplatin-Ineligible Patients with Locally Advanced or Metastatic Urothelial Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2658–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balar, A.V.; Castellano, D.E.; Grivas, P.; Vaughn, D.J.; Powles, T.; Vuky, J.; Fradet, Y.; Lee, J.L.; Fong, L.; Vogelzang, N.J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of pembrolizumab in metastatic urothelial carcinoma: Results from KEYNOTE-045 and KEYNOTE-052 after up to 5 years of follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fradet, Y.; Bellmunt, J.; Vaughn, D.J.; Lee, J.L.; Fong, L.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Climent, M.A.; Petrylak, D.P.; Choueiri, T.K.; Necchi, A.; et al. Randomized phase III KEYNOTE-045 trial of pembrolizumab versus paclitaxel, docetaxel, or vinflunine in recurrent advanced urothelial cancer: Results of >2 years of follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basile, G.; Bandini, M.; Gibb, E.A.; Ross, J.S.; Raggi, D.; Marandino, L.; Costa de Padua, T.; Crupi, E.; Colombo, R.; Colecchia, M.; et al. Neoadjuvant Pembrolizumab and Radical Cystectomy in Patients with Muscle-Invasive Urothelial Bladder Cancer: 3-Year Median Follow-Up Update of PURE-01 Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 5107–5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powles, T.; Park, S.H.; Caserta, C.; Valderrama, B.P.; Gurney, H.; Ullen, A.; Loriot, Y.; Sridhar, S.S.; Sternberg, C.N.; Bellmunt, J.; et al. Avelumab First-Line Maintenance for Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma: Results from the JAVELIN Bladder 100 Trial after >/=2 Years of Follow-Up. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 3486–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDaniel, A.S.; Alva, A.; Zhan, T.; Xiao, H.; Cao, X.; Gursky, A.; Siddiqui, J.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Jiang, H.; Lee, C.T.; et al. Expression of PDL1 (B7-H1) Before and After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Urothelial Carcinoma. Eur. Urol. Focus 2016, 1, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, A.C.; Lee, F.C.; Izard, J.P.; Harris, W.P.; Cheng, H.H.; Zhao, S.; Gore, J.L.; Lin, D.W.; Porter, M.P.; Yu, E.Y.; et al. Role of maximal endoscopic resection before cystectomy for invasive urothelial bladder cancer. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2014, 12, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Pembrolizumab Group | Chemotherapy Group | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. Patient | 23 | 30 | |
| Age (Mean ± SD), years | 72.1 ± 12.2 | 68.6 ± 11.7 | 0.291 |
| Gender | 0.891 | ||
| Male | 18 (78.3%) | 23 (76.7%) | |
| Female | 5 (21.7%) | 7 (23.3%) | |
| Stage | 0.477 | ||
| T2N0 | 13 (56.5%) | 14 (46.7%) | |
| T3N0 | 10 (43.5%) | 16 (53.3%) | |
| PD-L1 status | 0.028 | ||
| CPS ≥ 10% | 17 (73.9%) | 12 (40.0%) | |
| CPS < 10% | 5 (21.7%) | 10 (33.3%) | |
| unknown | 1 (4.3%) | 8 (26.7%) | |
| Performance status | 0.125 | ||
| 0, 1 | 14 (60.9%) | 24 (80%) | |
| ≥2 | 9 (39.1%) | 6 (20%) | |
| Cisplatin eligibility | 0.001 | ||
| Yes | 7 (30.4%) | 23 (76.7%) | |
| No | 16 (69.6%) | 7 (23.3%) |
| Pembrolizumab Group | Chemotherapy Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. Patient | 23 | 30 | ||
| Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | |
| Hypothyroidism | 2 (8.7%) | 1 (4.3%) | 1 (3.3%) | 0 |
| hyperthyroidism | 1 (4.3%) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| AST/ALT increase | 0 | 1 (4.3%) | 4 (13.3%) | 1 (3.3%) |
| Thrombocytopenia | 1 (4.3%) | 0 | 8 (26.7%) | 4 (13.3%) |
| Leukopenia | 1 (4.3%) | 0 | 5 (16.7%) | 4 (13.3%) |
| Anemia | 2 (8.7%) | 0 | 4 (13.3%) | 4 (13.3%) |
| Diarrhea | 1 (4.3%) | 0 | 4 (13.3%) | 1 (3.3%) |
| Nausea | 1(4.3%) | 0 | 2 (6.7%) | 3 (10.0%) |
| Pruritis | 1 (4.3%) | 0 | 1 (3.3%) | 0 |
| Pembrolizumab Group | Chemotherapy Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. Patient | 23 | 30 | ||
| Initial response | cCR (n = 12) | Non-cCR (n = 11) | cCR (n = 11) | Non-cCR (n = 19) |
| NMIBC recurrence | 1 (8.3%) | 4 (36.3%) | 3 (27.3%) | 5 (26.3%) |
| MIBC recurrence | 0 (0%) | 2 (18.2%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (10.5%) |
| Distant metastasis | 0 (0%) | 1 (4.3%) | 1 (9.1%) | 6 (31.6%) |
| Progression-Free Survival | Overall Survival | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Univariate | Multivariate | Univariate | Multivariate | ||||
| HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | |
| Age | 1.002 (0.969–1.036) | 0.912 | 0.984 (0.940–1.030) | 0.489 | 1.005 (0.968–1.042) | 0.807 | 0.980 (0.928–1.035) | 0.469 |
| Gender | 0.760 (0.327–1.768) | 0.524 | 1.037 (0.414–2.598) | 0.939 | 0.671 (0.250–1.798) | 0.427 | 1.121 (0.379–3.321) | 0.836 |
| Stage (III vs. II) | 2.054 (0.915–4.615) | 0.081 | 0.903 (0.345–2.3366) | 0.836 | 4.014 (1.424–11.312) | 0.009 | 3.129 (0.864–11.330) | 0.082 |
| Cisplatin-ineligible | 0.993 (0.450–2.191) | 0.985 | 0.468 (0.138–1.583) | 0.222 | 1.378 (0.533–3.587) | 0.508 | 0.883 (0.215–3.626) | 0.863 |
| Pem vs. CT | 0.474 (0.203–1.107) | 0.085 | 0.427 (0.151–1.206) | 0.108 | 0.328 (0.116–0.925) | 0.035 | 0.335 (0.092–1.219) | 0.097 |
| cCR vs. non cCR | 0.127 (0.045–0.357) | <0.001 | 0.121 (0.038–0.387) | <0.001 | 0.215 (0.077–0.601) | 0.003 | 0.204 (0.062–0.668) | 0.009 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, P.-H.; Chen, H.-Y.; Chang, Y.-S.; Su, P.-J.; Huang, W.-K.; Lin, C.-F.; Hsieh, J.C.-H.; Wu, C.-T. Effect of Clinical Complete Remission Following Neoadjuvant Pembrolizumab or Chemotherapy in Bladder-Preservation Strategy in Patients with Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Declining Definitive Local Therapy. Cancers 2024, 16, 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050894
Chang P-H, Chen H-Y, Chang Y-S, Su P-J, Huang W-K, Lin C-F, Hsieh JC-H, Wu C-T. Effect of Clinical Complete Remission Following Neoadjuvant Pembrolizumab or Chemotherapy in Bladder-Preservation Strategy in Patients with Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Declining Definitive Local Therapy. Cancers. 2024; 16(5):894. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050894
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Pei-Hung, Hung-Yi Chen, Yueh-Shih Chang, Po-Jung Su, Wen-Kuan Huang, Cheng-Feng Lin, Jason Chia-Hsun Hsieh, and Chun-Te Wu. 2024. "Effect of Clinical Complete Remission Following Neoadjuvant Pembrolizumab or Chemotherapy in Bladder-Preservation Strategy in Patients with Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Declining Definitive Local Therapy" Cancers 16, no. 5: 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050894
APA StyleChang, P.-H., Chen, H.-Y., Chang, Y.-S., Su, P.-J., Huang, W.-K., Lin, C.-F., Hsieh, J. C.-H., & Wu, C.-T. (2024). Effect of Clinical Complete Remission Following Neoadjuvant Pembrolizumab or Chemotherapy in Bladder-Preservation Strategy in Patients with Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Declining Definitive Local Therapy. Cancers, 16(5), 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16050894







