The Combination of Anti-CD47 Antibody with CTLA4 Blockade Enhances Anti-Tumor Immunity in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer via Normalization of Tumor Vasculature and Reprogramming of the Immune Microenvironment
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
2.2. Tumor Inoculation, Treatment, and Measurement
2.3. Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS)
2.4. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Immunofluorescence (IF)
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Routine Blood Test in Mice
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
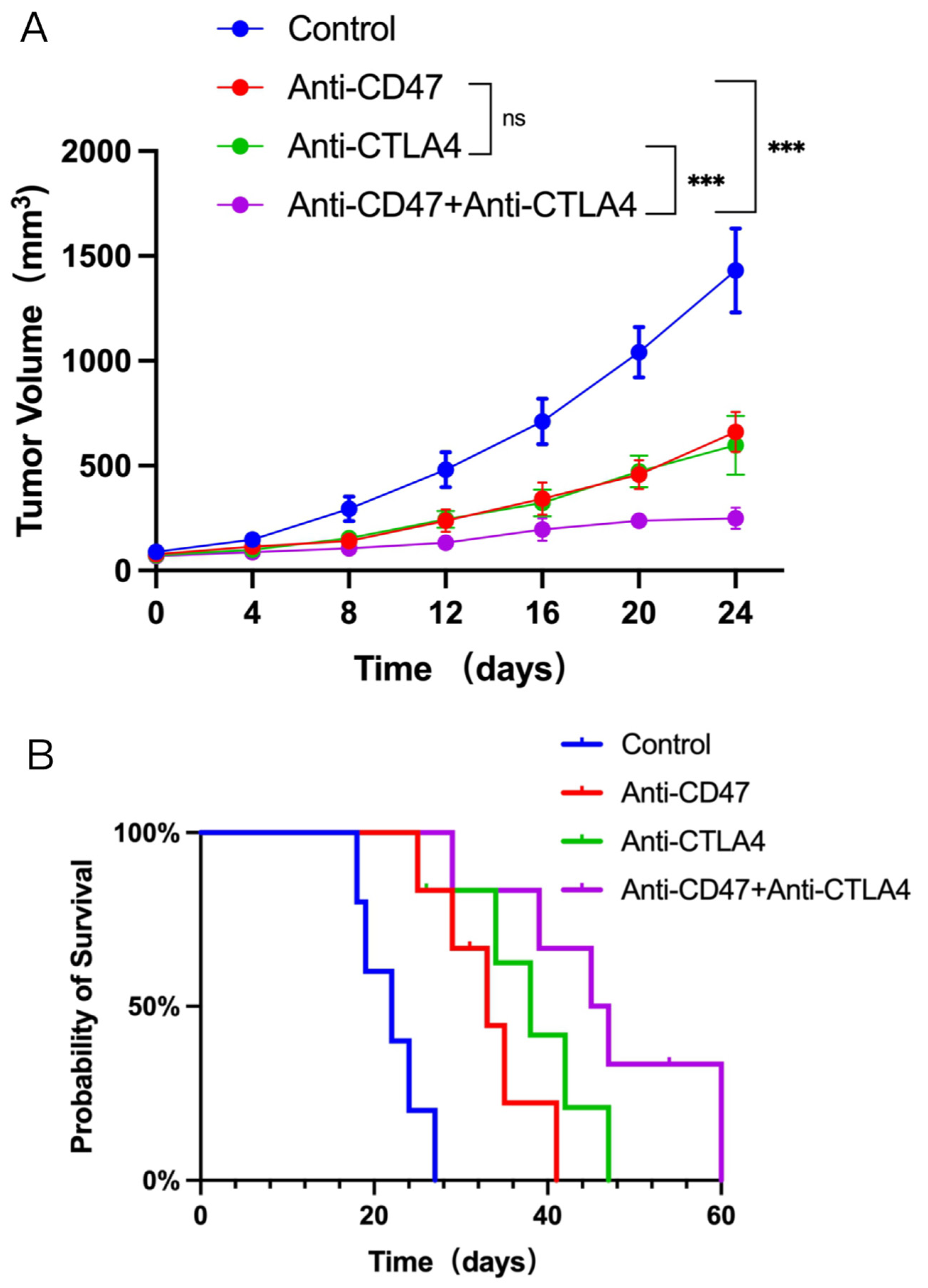
3.1. Dual CD47 and CTLA4 Blockade Impedes Tumor Growth and Improves Survival in NSCLC-Bearing Mice
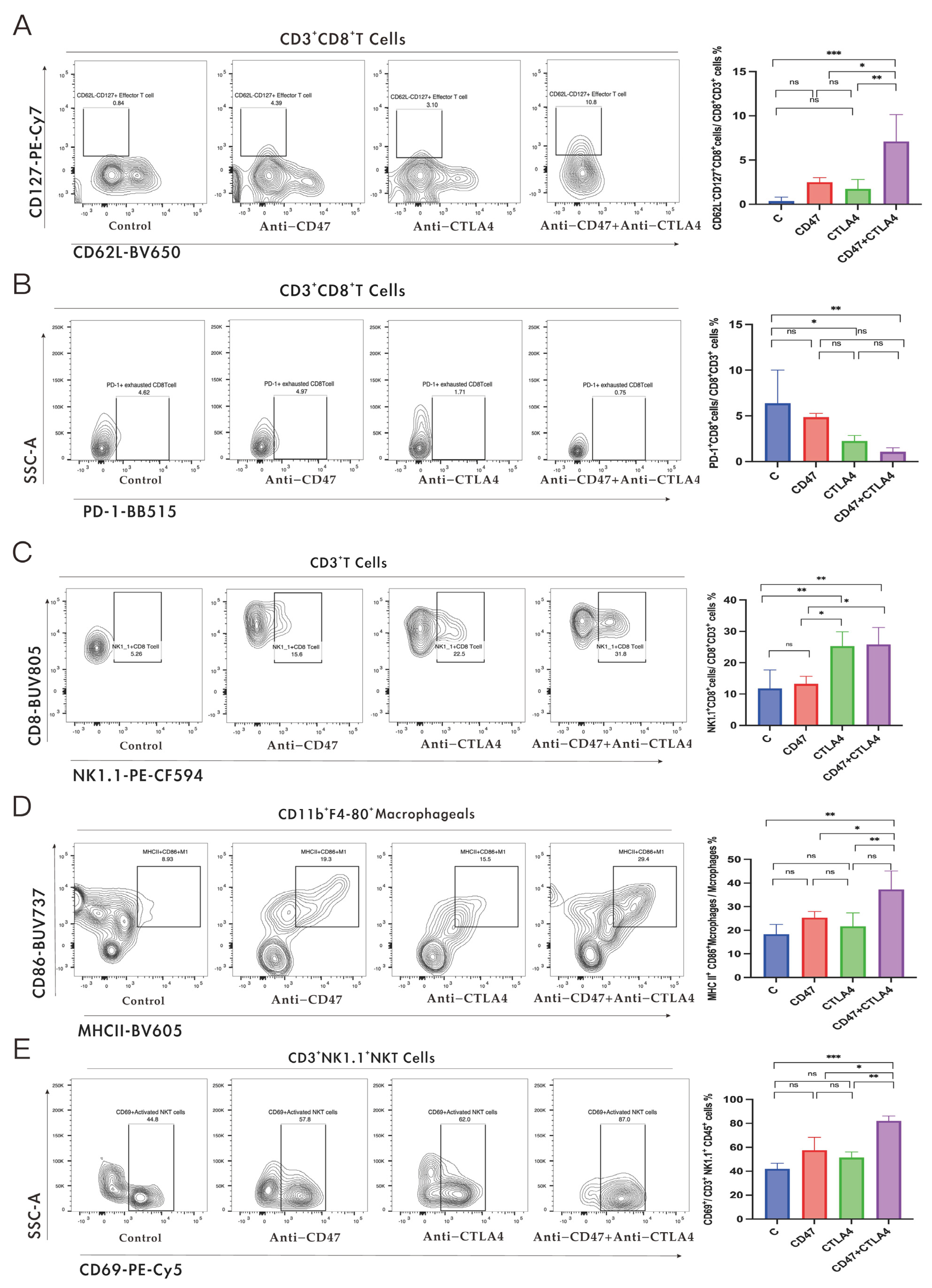
3.2. Alteration of Immune Cell Reprogramming in TME and Potentiation of Immunotherapy Response in NSCLC-Bearing Mice by a Combination of Anti-CD47 Ab and Anti-CTLA4 Ab
3.3. Upregulation of CTLA4 Level in NSCLC Cells by Anti-CD47 Ab via Regulation of Foxp1
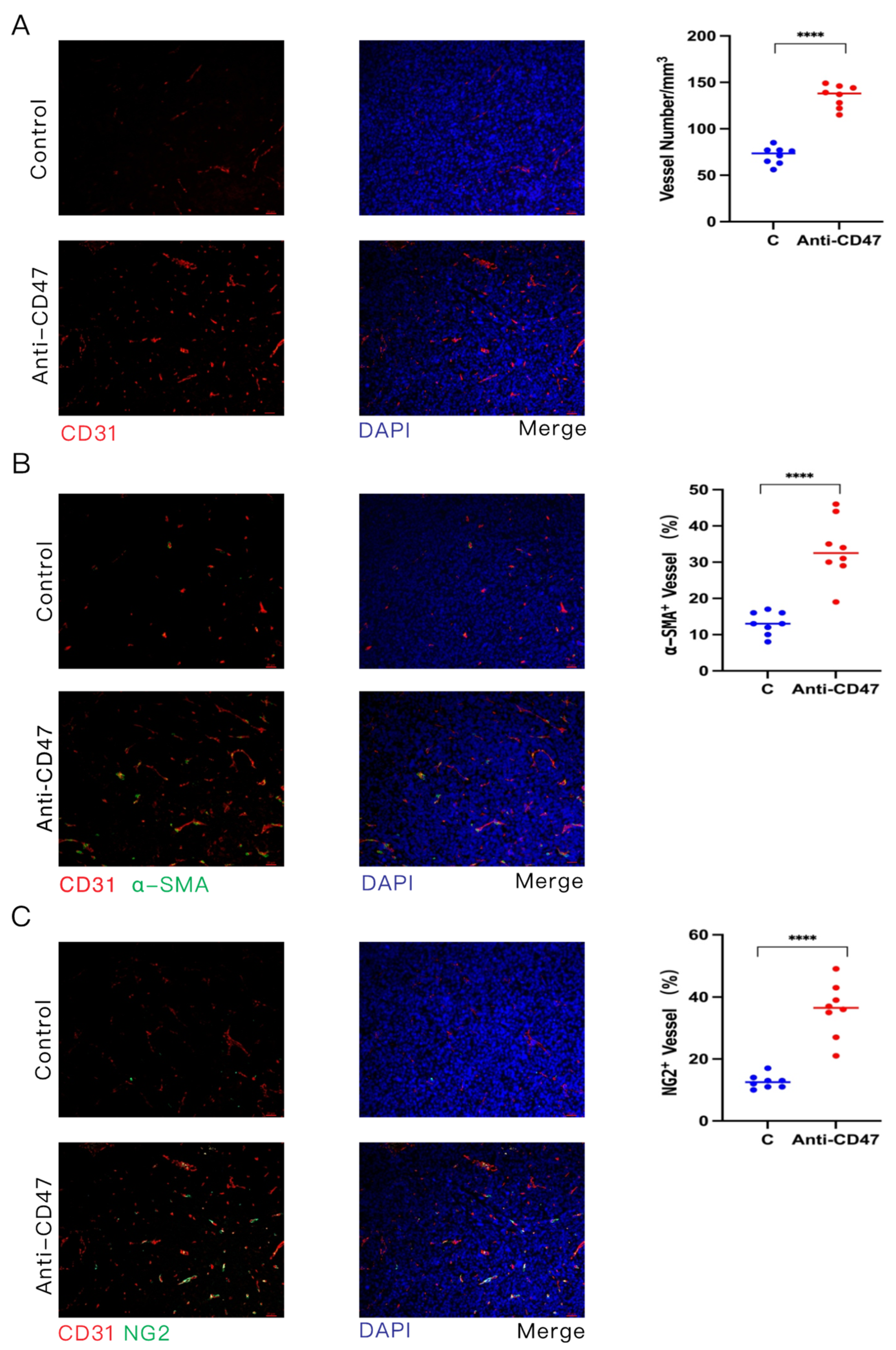
3.4. Anti-CD47 Ab Promotes Vascular Normalization of Tumors
3.5. Promotion of Tumor Vascular Normalization by Anti-CD47 Ab via Enhancement of CD4+ T Cell Tumor Infiltration
3.6. Alleviation of Anemia in NSCLC-Bearing Mice by Combined Targeting of CD47 and CTLA4
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barclay, N.; van den Berg, T.K. The Interaction Between Signal Regulatory Protein Alpha (SIRPα) and CD47: Structure, Function, and Therapeutic Target. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 25–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Sun, H.; Yu, J.; Tian, W.; Song, Y. Targeting CD47 for cancer immunotherapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, R.; Chen, X.; Hou, Y.; Jiang, J. Targeting CD47 as a Novel Immunotherapy for Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 924740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wei, H.; Gao, P.; Yu, H.; Wang, K.; Fu, Z.; Ju, B.; Zhao, M.; Dong, S.; Li, Z.; et al. CD47 promotes ovarian cancer progresion by inhibiting macrophage phagocytosis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 39021–39032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Tsujimoto, H.; Matsumura, K.; Kinoshita, M.; Takahata, R.; Matsumoto, Y.; Hiraki, S.; Ono, S.; Seki, S.; Yamamoto, J.; et al. CD47 is an adverse prognostic factor and a therapeutic target in gastric cancer. Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 1322–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiskopf, K.; Jahchan, N.S.; Schnorr, P.J.; Cristea, S.; Ring, A.M.; Maute, R.L.; Volkmer, A.K.; Volkmer, J.-P.; Liu, J.; Lim, J.S.; et al. CD47-blocking immunotherapies stimulate macrophage-mediated destruction of small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 2610–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winer, A.; Ghatalia, P.; Bubes, N.; Anari, F.; Varshavsky, A.; Kasireddy, V.; Liu, Y.; El-Deiry, W.S. Dual Checkpoint Inhibition with Ipilimumab plus Nivolumab After Progression on Sequential PD-1/PDL-1 Inhib-itors Pembrolizumab and Atezolizumab in a Patient with Lynch Syndrome, Metastatic Colon, and Localized Urothelial Cancer. Oncologist 2019, 24, 1416–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, J.; Mandalà, M.; Del Vecchio, M.; Gogas, H.J.; Arance, A.M.; Cowey, C.L.; Dalle, S.; Schenker, M.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Marquez-Rodas, I.; et al. Adjuvant Nivolumab versus Ipilimumab in Resected Stage III or IV Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1824–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Schenker, M.; Lee, K.H.; Provencio, M.; Nishio, M.; Lesniewski-Kmak, K.; Sangha, R.; Ahmed, S.; Raimbourg, J.; Feeney, K.; et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment in advanced non–small-cell lung cancer with high tumour mutational burden: Patient-reported outcomes results from the randomised, open-label, phase III CheckMate 227 trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 116, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, F.A.; Furness, A.J.S.; Litchfield, K.; Joshi, K.; Rosenthal, R.; Ghorani, E.; Solomon, I.; Lesko, M.H.; Ruef, N.; Roddie, C.; et al. Fc Effector Function Contributes to the Activity of Human Anti-CTLA-4 Antibodies. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 649–663.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulliard, Y.; Jolicoeur, R.; Windman, M.; Rue, S.M.; Ettenberg, S.; Knee, D.A.; Wilson, N.S.; Dranoff, G.; Brogdon, J.L. Activating Fc γ receptors contribute to the antitumor activities of immunoregulatory receptor-targeting antibodies. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, T.R.; Li, F.; Montalvo-Ortiz, W.; Sepulveda, M.A.; Bergerhoff, K.; Arce, F.; Roddie, C.; Henry, J.Y.; Yagita, H.; Wolchok, J.D.; et al. Fc-dependent depletion of tumor-infiltrating regulatory T cells co-defines the efficacy of anti–CTLA-4 therapy against melanoma. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 1695–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, T.N.; Schreiber, R.D. Neoantigens in cancer immunotherapy. Science 2015, 348, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klemm, F.; Joyce, J.A. Microenvironmental regulation of therapeutic response in cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkwill, F.R.; Capasso, M.; Hagemann, T. The tumor microenvironment at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 5591–5596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, A.L.; Soudja, S.M.; Deceneux, C.; Lauvau, G.; Marie, J.C. NK1.1+ CD8+ T cells escape TGF-β control and contribute to early microbial pathogen response. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Park, H.J.; Cheon, J.H.; Wu, L.; Van Kaer, L.; Hong, S. iNKT Cells Suppress Pathogenic NK1.1+CD8+ T Cells in DSSInduced Colitis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigeta, K.; Datta, M.; Hato, T.; Kitahara, S.; Chen, I.X.; Matsui, A.; Kikuchi, H.; Mamessier, E.; Aoki, S.; Ramjiawan, R.R.; et al. Dual Programmed Death Receptor-1 and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-2 Blockade Promotes Vascular Normalization and Enhances Antitumor Immune Responses in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2019, 71, 1247–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Dutta, P.; Liu, J.; Sabri, N.; Song, Y.; Li, W.X. Tumour cell-intrinsic CTLA4 regulates PD-L1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2018, 23, 535–542. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Ramjiawan, R.R.; Reiberger, T.; Ng, M.R.; Hato, T.; Huang, Y.; Ochiai, H.; Kitahara, S.; Unan, E.C.; Reddy, T.P.; et al. CXCR4 inhibition in tumor microenvironment facilitates anti-programmed death receptor-1 immunotherapy in sorafenibtreated hepatocellular carcinoma in mice. Hepatology 2014, 61, 1591–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopacki, C.; Pritykin, Y.; Rubtsov, Y.; Leslie, C.S.; Rudensky, A.Y. Transcription factor Foxp1 regulates Foxp3 chromatin binding and coordinates regulatory T cell function. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freimer, J.W.; Shaked, O.; Naqvi, S.; Sinnott-Armstrong, N.; Kathiria, A.; Garrido, C.M.; Chen, A.F.; Cortez, J.T.; Greenleaf, W.J.; Pritchard, J.K.; et al. Systematic discovery and perturbation of regulatory genes in human T cells reveals the architecture of immune networks. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, Y.; Volkmer, J.-P.; McKenna, K.; Civelek, M.; Lusis, A.J.; Miller, C.L.; Direnzo, D.; Nanda, V.; Ye, J.; Connolly, A.J.; et al. CD47-blocking antibodies restore phagocytosis and prevent atherosclerosis. Nature 2016, 536, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergers, G.; Song, S. The role of pericytes in blood-vessel formation and maintenance. Neuro-Oncology 2005, 7, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, S.P.; Stainier, D.Y.R. Molecular control of endothelial cell behaviour during blood vessel morphogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T. Mutual regulation of tumour vessel normalization and immunostimulatory reprogramming. Nature 2017, 544, 250–254. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, T.J.; Italiano, A.; Eskens, F.; Symeonides, S.N.; Bexon, A.S.; Graham, P.; Hinds, D.; Manning, P.; Chanda, S.; Karr, R.; et al. Phase 1-2 study of TI-061 alone and in combination with other anti-cancer agents in patients with advanced malignancies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, TPS3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallman, D.A.; Donnellan, W.B.; Asch, A.S.; Lee, D.J.; Al Malki, M.; Marcucci, G.; Pollyea, D.A.; Kambhampati, S.; Komrokji, R.S.; Van Elk, J.; et al. The first-in-class anti-CD47 antibody Hu5F9-G4 is active and well tolerated alone or with azaciti- dine in AML and MDS patients: Initial phase 1b results. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 7009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S. Targeted inhibition of CD47-SIRPa requires Fc-FcgR interactions to maximize activity in T-cell lymphomas. J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2019, 134, 1430–1440. [Google Scholar]
- Barkal, A.A.; Weiskopf, K.; Kao, K.S.; Gordon, S.R.; Rosental, B.; Yiu, Y.Y.; George, B.M.; Markovic, M.; Ring, N.G.; Tsai, J.M.; et al. Engagement of MHC class I by the inhibitory receptor LILRB1 suppresses macrophages and is a target of cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Hu, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Wen, D.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; et al. In situ sprayed bioresponsive immunotherapeutic gel for post-surgical cancer treatment. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 14, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, A.L.; Nath, P.R.; Allgauer, M.; Lessey-Morillon, E.C.; Sipes, J.M.; Ridnour, L.A.; Ii, Y.M.M.; Yu, Z.; Restifo, N.P.; Roberts, D.D. Antisense targeting of CD47 enhances human cytotoxic T-cell activity and increases survival of mice bearing B16 melanoma when combined with anti-CTLA4 and tumor irradiation. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2019, 68, 1805–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, M.; Schultze, J.L. Regulatory T cells in cancer. Blood 2006, 108, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappasodi, R.; Serganova, I.; Cohen, I.J.; Maeda, M.; Shindo, M.; Senbabaoglu, Y.; Watson, M.J.; Leftin, A.; Maniyar, R.; Verma, S.; et al. CTLA-4 blockade drives loss of Treg stability in glycolysis-low tumours. Nature 2021, 591, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selby, M.J.; Engelhardt, J.J.; Quigley, M.; Henning, K.A.; Chen, T.; Srinivasan, M.; Korman, A.J. Anti-CTLA-4 Antibodies of IgG2a Isotype Enhance Antitumor Activity through Reduction of Intratumoral Regulatory T Cells. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2013, 1, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamen, L.; Ordonia, B.; Myneni, S.; Chung, S. Method for Measurement of Antibody-Dependent Cellular Phagocytosis. Ther. Antibodies Methods Protoc. 2022, 19, 305–312. [Google Scholar]
- Gajewski, T.F.; Schreiber, H.; Fu, Y.-X. Innate and adaptive immune cells in the tumor microenvironment. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Lu, Z.; Xu, J. Targeting cluster of differentiation 47 improves the efficacy of anti-cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated protein 4 treatment via antigen presentation enhancement in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 3301–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Ren, Z.; Tseng, K.F.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Lu, C.; Cai, Y.; Minna, J.D.; Fu, Y.X. Dual targeting of CTLA-4 and CD47 on Treg cells promotes immunity against solid tumors. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabg8693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowshanravan, B.; Halliday, N.; Sansom, D.M. CTLA-4: A moving target in immunotherapy. Blood 2018, 131, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Chang, T.; Singh, S.P.; Lim, L.; Mannan, P.; Garfield, S.H.; Pendrak, M.L.; Soto-Pantoja, D.R.; Rosenberg, A.Z.; Jin, S.; et al. CD47 Signaling Regulates the Immunosuppressive Activity of VEGF in T Cells. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 3914–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isenberg, J.S.; Martin-Manso, G.; Maxhimer, J.B.; Roberts, D.D. Regulation of nitric oxide signalling by thrombospondin 1: Implications for anti-angiogenic therapies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhuang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Qiu, M.; Li, J.; Lin, Z.; Yi, H.; Liu, X.; Huang, C.; Tang, B.; Liu, B.; et al. The Combination of Anti-CD47 Antibody with CTLA4 Blockade Enhances Anti-Tumor Immunity in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer via Normalization of Tumor Vasculature and Reprogramming of the Immune Microenvironment. Cancers 2024, 16, 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040832
Zhuang Z, Zhou J, Qiu M, Li J, Lin Z, Yi H, Liu X, Huang C, Tang B, Liu B, et al. The Combination of Anti-CD47 Antibody with CTLA4 Blockade Enhances Anti-Tumor Immunity in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer via Normalization of Tumor Vasculature and Reprogramming of the Immune Microenvironment. Cancers. 2024; 16(4):832. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040832
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhuang, Zhan, Jinglin Zhou, Minglian Qiu, Jiamian Li, Zhuangheng Lin, Huihan Yi, Xuerong Liu, Changyu Huang, Binghua Tang, Bo Liu, and et al. 2024. "The Combination of Anti-CD47 Antibody with CTLA4 Blockade Enhances Anti-Tumor Immunity in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer via Normalization of Tumor Vasculature and Reprogramming of the Immune Microenvironment" Cancers 16, no. 4: 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040832
APA StyleZhuang, Z., Zhou, J., Qiu, M., Li, J., Lin, Z., Yi, H., Liu, X., Huang, C., Tang, B., Liu, B., & Li, X. (2024). The Combination of Anti-CD47 Antibody with CTLA4 Blockade Enhances Anti-Tumor Immunity in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer via Normalization of Tumor Vasculature and Reprogramming of the Immune Microenvironment. Cancers, 16(4), 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040832





