Innovations in Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) in the Treatment of Lymphoma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
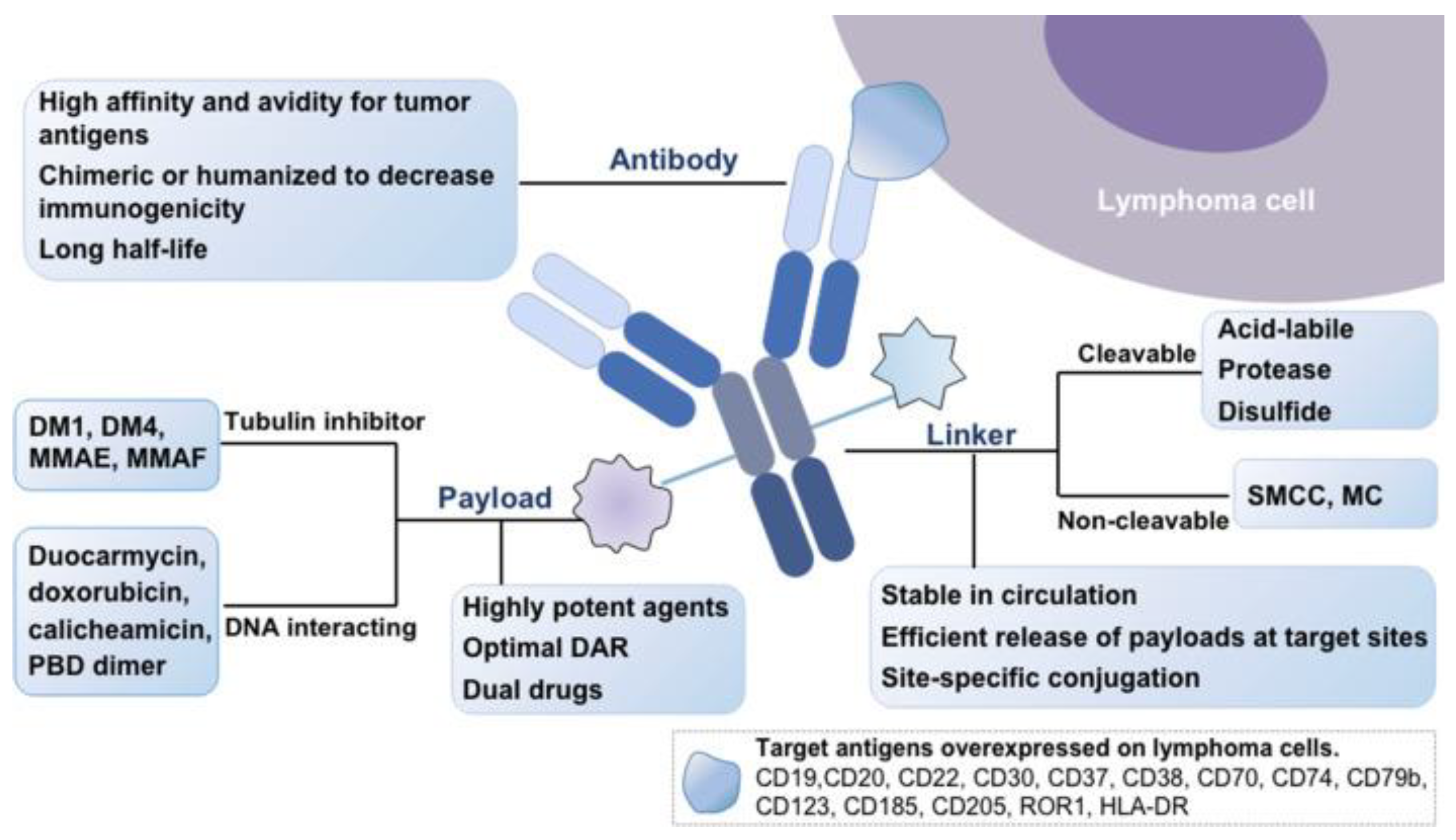
2. Basic Structuring of ADC
2.1. Monoclonal Antibodies
2.2. Payload
2.3. Chemical Linker
3. FDA-Approved ADCs for Lymphomas
4. Brentuximab Vedotin
BV in CD30-Positive T Cell Lymphomas
5. Polatuzumab Vedotin
5.1. PV in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
5.2. PV in Other B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas (B-NHL)
6. Loncastuximab Tesirine
6.1. LT in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
6.2. LT in Follicular Lymphomas
| Regimen | Phase | Disease | N. | ORR | CR | PFS | OS | Grade 3–4 AEs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BV-R-mini-CHP [108] | I | DLBCL ≥ 75 years old Frontline | 22 | 86% | 67% | 2-year PFS:60.6% | 2-year OS: 73.9% | Neutropenia (23%), fatigue (18%), pneumonia (18%), |
| BV+CHP [109] | II | PTCL with <10% CD30 expression Frontline | 55 | CD30- 83% CD30 low 74% | CD30- 56% CD30 low 59% | - | - | Total: 53% Febrile Neutropenia (18%) |
| BV+ICE (Ifosfamide, Carboplatin, Etoposide) [110] | I/II | R/R cHL | 45 | 91% | 74% | 2-year PFS: 80.4% | 2-year OS: 98% | Thrombocytopenia (80%), Neutropenia (73%) |
| BV+ Romidepsin [111] | I | CTCL regardless of CD30 | 7 | 80% | 0% | - | - | Fever (14%), Transaminitis (14%) |
| PV+Obintuzumab+Venetoclax [112] | Ib/II | R/R FL | 74 | - | 57% | 22.8 months, 1-year PFS: 73% | - | Neutropenia (39%), Thrombocytopenia (19%) |
| PV+Rituximab+Venetoclax [113] | Ib/II | R/R DLBCL | 48 | 65% | IRC- assessed: 29% INV-assessed: 31% | 4.4 months | 11 months | Neutropenia (53%), infections (16%) |
| PV+R-GemOx vs. R-GemoOx [114] | III | R/R DLBCL | 15 | 40% | 27% | - | - | Thrombocytopenia (20%), Neutropenia (13%) |
| PV+R-ICE [115] | II | R/R DLBCL | 38 | 92% (after 2 cycles) 89% (after 2–3 cycles) | 55% (after 2 cycles) 61% (after 2–3 cycles) | Anemia (43%), Thrombocytopenia (43%), Neutropenia (43%) | ||
| PV+Rituximab after CART [116] | II | R/R DLBCL | 8 | 50% (All PR) | - | 5 weeks | 15 weeks | 62.5% died |
| PV+Mosunetuzumab (Bispecific Ab targeting CD20 and CD3) [94] | Ib/II | R/R DLBCL | 120 | 59.2% | 46% | 11.4 months | 23.3 months | Neutropenia (25%), fatigue (6.7%) |
| LT+Ibrutinib [117] | II | R/R DLBCL | 35 GCB: 13 Non-GCB: 22 | All: 57.1% GCB: 77% Non-GCB: 45.5% | All: 34.3% GCB: 46.2% Non-GCB: 27.3% | - | - | All: Neutropenia (23%) Thrombocytopenia (17%) |
| LT+Ibrutinib [118] | I | MCL | 7 | 85.7% | 57% | Not stratified according to disease subtype | ||
| LT+Rituximab vs. R-GemoOx [119] | III | R/R DLBCL | 20 | 80% | 50% | 8.3 months | - | Elevated GGT (25%), Neutropenia (15%) |
| LT vs. Idelalisib [120] | II | R/R FL | 60 Target: 150 | - | 55% for LT 15% for Idelalisib | - | - | - |
| LT+Rituximab [121] | II | R/R FL | Estimated: 39 | Trial is still accruing | ||||
| LT+Venetoclax [122] | I | R/R NHL | Estimated: 36 | Trial is still accruing | ||||
| LT+R-CHOP [123] | I | First line frail DLBCL | Trial is withdrawn due to sponsor’s decision | |||||
| LT+Rituximab [124] | II | First line frail DLBCL | 41 | Trial is active | ||||
| LT after salvage immunotherapy in BTKi-treated/intolerant at R-BAC [125] | II | R/R MCL | Estimated: 56 | Trial is still accruing | ||||
| LT+PV, LT+Glofitamab, LT+Mosunetuzumab [126,127] | Ib | R/R NHL | Estimated: 200 | Trial is still accruing | ||||
| LT+Durvalumab [128] | I | R/R NHL | 13 | Trial is terminated due to limited number and no additional activity for the combination vs. LT monotherapy. | ||||
| LT [129] | II | WM after at least 2 prior lines, including an anti-CD20 antibody and BTKi | Estimated: 36 | Trial is still accruing | ||||
7. Other ADCs under Study, Development, and Evaluation for the Treatment of Lymphoma
7.1. CD19-Targeting Antibody Drug Conjugate
7.1.1. Coltuximab Ravtansine
7.1.2. Denintuzumab Mafodotin
7.2. CD22-Targeting Antibody Drug Conjugate
7.2.1. Inotuzumab Ozogamicin
7.2.2. Pinatuzumab Vedotin
7.3. CD25-Targeting Antibody Drug Conjugate
Camidanlumab Tesirine
7.4. CD37-Targeting Antibody Drug Conjugate
Naratuximab Emtansine
7.5. CD70-Targeting Antibody Drug Conjugate
Vorsetuzumab Mafodotin
7.6. ROR1-Targeting Antibody Drug Conjugates
7.6.1. Zilovertamab Vedotin
7.6.2. Cirmtuzumab-ADC-7
7.7. ADCs in Pre-Clinical Development
7.7.1. Novel CD30-Targeting ADC: SGN-35C
7.7.2. CD19 Targeting ADC: IKS03
7.7.3. CXCR5 Targeting ADC: VIP924
8. Future Directions of ADCs
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jamil, A.; Mukkamalla, S.K.R. Lymphoma; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Thandra, K.C.; Barsouk, A.; Saginala, K.; Padala, S.A.; Barsouk, A.; Rawla, P. Epidemiology of Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Med. Sci. 2021, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, M.; Lee-Ying, R.; Davies, G.; Stewart, C.; Oh, D.H.; Peters, A.; Stewart, D.A. Autologous transplantation improves survival rates for follicular lymphoma patients who relapse within two years of chemoimmunotherapy: A multi-center retrospective analysis of consecutively treated patients in the real world. Leuk. Lymphoma 2019, 60, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, P.; Vitolo, U.; Rambaldi, A.; Miceli, R.; Patriarca, F.; Gallamini, A.; Olivieri, A.; Benedetti, F.; Todeschini, G.; Rossi, G.; et al. Intensified chemo-immunotherapy with or without stem cell transplantation in newly diagnosed patients with peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2014, 28, 1885–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.Y.; Kridel, R. Treatment resistance in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2021, 35, 2151–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, D.C. Long-term toxicity of chemotherapy and radiotherapy in lymphoma survivors: Optimizing treatment for individual patients. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 13, 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, P.C.; Yi, A.; Horick, N.; Amonoo, H.L.; Newcomb, R.A.; Lavoie, M.W.; Rice, J.; Reynolds, M.J.; Ritchie, C.S.; Nipp, R.D.; et al. Clinical Outcomes, Treatment Toxicity, and Health Care Utilization in Older Adults with Aggressive Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Oncologist 2021, 26, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klener, P.; Klanova, M. Drug Resistance in Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, H.; Nakayama, T.; Miyata, Y.; Saito, S.; Nishiwaki, S.; Nakao, N.; Takeshita, K.; Naoe, T. Mast cells promote the growth of Hodgkin’s lymphoma cell tumor by modifying the tumor microenvironment that can be perturbed by bortezomib. Leukemia 2012, 26, 2269–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, F.C.; Lim, E.; Kridel, R.; Steidl, C. Novel insights into the disease dynamics of B-cell lymphomas in the Genomics Era. J. Pathol. 2018, 244, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coiffier, B.; Lepage, E.; Briere, J.; Herbrecht, R.; Tilly, H.; Bouabdallah, R.; Morel, P.; Van Den Neste, E.; Salles, G.; Gaulard, P.; et al. CHOP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierpont, T.M.; Limper, C.B.; Richards, K.L. Past, Present, and Future of Rituximab-The World’s First Oncology Monoclonal Antibody Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coiffier, B.; Thieblemont, C.; Van Den Neste, E.; Lepeu, G.; Plantier, I.; Castaigne, S.; Lefort, S.; Marit, G.; Macro, M.; Sebban, C.; et al. Long-term outcome of patients in the LNH-98.5 trial, the first randomized study comparing rituximab-CHOP to standard CHOP chemotherapy in DLBCL patients: A study by the Groupe d’Etudes des Lymphomes de l’Adulte. Blood 2010, 116, 2040–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, R.; Davies, A.; Ando, K.; Klapper, W.; Opat, S.; Owen, C.; Phillips, E.; Sangha, R.; Schlag, R.; Seymour, J.F.; et al. Obinutuzumab for the First-Line Treatment of Follicular Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1331–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polakis, P. Antibody Drug Conjugates for Cancer Therapy. Pharmacol. Rev. 2016, 68, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, R.; Subbiah, V.; Iyer, S.P. Evolving Landscape of Antibody Drug Conjugates in Lymphoma. Cancer J. 2022, 28, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolcher, A.W. Antibody drug conjugates: Lessons from 20 years of clinical experience. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 2168–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudacher, A.H.; Brown, M.P. Antibody drug conjugates and bystander killing: Is antigen-dependent internalisation required? Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 1736–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cecco, M.; Galbraith, D.N.; McDermott, L.L. What makes a good antibody-drug conjugate? Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2021, 21, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, A.T.; Price, L.S.L.; Schorzman, A.N.; Storrie, M.; Piscitelli, J.A.; Razo, J.; Zamboni, W.C. Factors Affecting the Pharmacology of Antibody-Drug Conjugates. Antibodies 2018, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, H.L.; Cardarelli, P.M.; Deshpande, S.; Gangwar, S.; Schroeder, G.M.; Vite, G.D.; Borzilleri, R.M. Antibody-drug conjugates: Current status and future directions. Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, I.R. Stability of IgG isotypes in serum. mAbs 2010, 2, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hock, M.B.; Thudium, K.E.; Carrasco-Triguero, M.; Schwabe, N.F. Immunogenicity of antibody drug conjugates: Bioanalytical methods and monitoring strategy for a novel therapeutic modality. AAPS J. 2015, 17, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Smith, S.W.; Ghone, S.; Tomczuk, B. Current ADC Linker Chemistry. Pharm. Res. 2015, 32, 3526–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdollahpour-Alitappeh, M.; Lotfinia, M.; Gharibi, T.; Mardaneh, J.; Farhadihosseinabadi, B.; Larki, P.; Faghfourian, B.; Sepehr, K.S.; Abbaszadeh-Goudarzi, K.; Abbaszadeh-Goudarzi, G.; et al. Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) for cancer therapy: Strategies, challenges, and successes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 5628–5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGavin, J.K.; Spencer, C.M. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin. Drugs 2001, 61, 1317–1322, discussion 1323–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Li, S.; Han, S.; Shi, C.; Zhang, Y. Antibody drug conjugate: The “biological missile” for targeted cancer therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.D.; Carter, P.J.; Pluckthun, A.; Vasquez, M.; Holgate, R.G.; Hotzel, I.; Popplewell, A.G.; Parren, P.W.; Enzelberger, M.; Rademaker, H.J.; et al. The INNs and outs of antibody nonproprietary names. MAbs 2016, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, W.Y.; Foote, J. Immunogenicity of engineered antibodies. Methods 2005, 36, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khongorzul, P.; Ling, C.J.; Khan, F.U.; Ihsan, A.U.; Zhang, J. Antibody-Drug Conjugates: A Comprehensive Review. Mol. Cancer Res. 2020, 18, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnst, K.E.; Banerjee, S.; Chen, H.; Deng, S.; Hwang, D.J.; Li, W.; Miller, D.D. Current advances of tubulin inhibitors as dual acting small molecules for cancer therapy. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 1398–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waight, A.B.; Bargsten, K.; Doronina, S.; Steinmetz, M.O.; Sussman, D.; Prota, A.E. Structural Basis of Microtubule Destabilization by Potent Auristatin Anti-Mitotics. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderl, J.; Faulstich, H.; Hechler, T.; Kulke, M. Antibody-drug conjugate payloads. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 1045, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberoi, H.K.; Garralda, E. Unmasking New Promises: Expanding the Antigen Landscape For Antibody-Drug Conjugates. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 4459–4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaghoubi, S.; Karimi, M.H.; Lotfinia, M.; Gharibi, T.; Mahi-Birjand, M.; Kavi, E.; Hosseini, F.; Sineh Sepehr, K.; Khatami, M.; Bagheri, N.; et al. Potential drugs used in the antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) architecture for cancer therapy. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 31–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennessy, E.J. Selective inhibitors of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL: Balancing antitumor activity with on-target toxicity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 2105–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa-Vazquez, V.; Ko, J.; Breunig, C.; Baumann, A.; Giesen, N.; Palfi, A.; Muller, C.; Lutz, C.; Hechler, T.; Kulke, M.; et al. HDP-101, an Anti-BCMA Antibody-Drug Conjugate, Safely Delivers Amanitin to Induce Cell Death in Proliferating and Resting Multiple Myeloma Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, H.; Simpson, N.; Ricks, T.K.; Leighton, J.K. An FDA oncology analysis of toxicities associated with PBD-containing antibody-drug conjugates. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 107, 104429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, P.J.; Hamilton, J.Z.; Jeffrey, S.C.; Hunter, J.H.; Doronina, S.O.; Okeley, N.M.; Miyamoto, J.B.; Anderson, M.E.; Stone, I.J.; Ulrich, M.L.; et al. Optimization of a PEGylated Glucuronide-Monomethylauristatin E Linker for Antibody-Drug Conjugates. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafeez, U.; Parakh, S.; Gan, H.K.; Scott, A.M. Antibody-Drug Conjugates for Cancer Therapy. Molecules 2020, 25, 4764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillow, T.H.; Schutten, M.; Yu, S.F.; Ohri, R.; Sadowsky, J.; Poon, K.A.; Solis, W.; Zhong, F.; Del Rosario, G.; Go, M.A.T.; et al. Modulating Therapeutic Activity and Toxicity of Pyrrolobenzodiazepine Antibody-Drug Conjugates with Self-Immolative Disulfide Linkers. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.L.; Fishkin, N.E.; Li, W.; Whiteman, K.R.; Kovtun, Y.; Reid, E.E.; Archer, K.E.; Maloney, E.K.; Audette, C.A.; Mayo, M.F.; et al. A New Class of Antibody-Drug Conjugates with Potent DNA Alkylating Activity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 1870–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.L.; Shizuka, M.; Wilhelm, A.; Salomon, P.; Reid, E.E.; Lanieri, L.; Sikka, S.; Maloney, E.K.; Harvey, L.; Qiu, Q.; et al. A DNA-Interacting Payload Designed to Eliminate Cross-Linking Improves the Therapeutic Index of Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs). Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 650–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Gou, L.; Li, W.; Wang, Y. Antibody-drug conjugates: Recent advances in payloads. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 4025–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amouzegar, A.; Chelvanambi, M.; Filderman, J.N.; Storkus, W.J.; Luke, J.J. STING Agonists as Cancer Therapeutics. Cancers 2021, 13, 2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanjulu, J.M.; Pesiridis, G.S.; Yang, J.; Concha, N.; Singhaus, R.; Zhang, S.Y.; Tran, J.L.; Moore, P.; Lehmann, S.; Eberl, H.C.; et al. Design of amidobenzimidazole STING receptor agonists with systemic activity. Nature 2018, 564, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.-R.; Bai, B.-F.; Liu, D.; Shi, R.; Zhou, Q.-M. Targeting the stimulator of interferon genes (STING) in breast cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1199152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, X.; Liu, S.; Cheng, K. The Role of Toll-Like Receptor in Inflammation and Tumor Immunity. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.; Garcia-Martinez, E.; Pitter, M.R.; Fucikova, J.; Spisek, R.; Zitvogel, L.; Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L. Trial Watch: Toll-like receptor agonists in cancer immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1526250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, S.E.; Pearson, C.I.; Gregorio, J.D.; Gonzalez, J.C.; Kenkel, J.A.; Hartmann, F.J.; Luo, A.; Ho, P.Y.; LeBlanc, H.; Blum, L.K.; et al. Immune-stimulating antibody conjugates elicit robust myeloid activation and durable antitumor immunity. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, H.; Pearson, C.; Kenkel, J.; Blum, L.; Ho, P.; Luo, A.; Laura, R.; Zhou, M.; Gregorio, J.; Luo, A.; et al. 605 Systemically administered HER2-targeted ISACs provoke a rapid, local response that engages the innate and adaptive arms of the immune system to eradicate tumors in preclinical models. J. Immuno Ther. Cancer 2020, 8, A361–A362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinworth, C.P.; Lithgow, H.; Churcher, I. Small molecule-mediated protein knockdown as a new approach to drug discovery. MedChemComm 2016, 7, 2206–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragovich, P.S. Degrader-antibody conjugates. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 3886–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.; Sathyamurthi, P.S.; Queisser, M.A.; Mullin, M.; Shrives, H.; Coe, D.M.; Burley, G.A. Antibody-Proteolysis Targeting Chimera Conjugate Enables Selective Degradation of Receptor-Interacting Serine/Threonine-Protein Kinase 2 in HER2+ Cell Lines. Bioconjug Chem. 2023, 34, 2049–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneiro, M.A.; Forte, N.; Shchepinova, M.M.; Kounde, C.S.; Chudasama, V.; Baker, J.R.; Tate, E.W. Antibody-PROTAC Conjugates Enable HER2-Dependent Targeted Protein Degradation of BRD4. ACS Chem. Biol. 2020, 15, 1306–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, R.P.; Bovee, T.D.; Doronina, S.O.; Burke, P.J.; Hunter, J.H.; Neff-LaFord, H.D.; Jonas, M.; Anderson, M.E.; Setter, J.R.; Senter, P.D. Reducing hydrophobicity of homogeneous antibody-drug conjugates improves pharmacokinetics and therapeutic index. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 733–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Jiang, F.; Lu, A.; Zhang, G. Linkers Having a Crucial Role in Antibody-Drug Conjugates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, B.M.; Wrasidlo, W.A.; Reisfeld, R.A. Antibody conjugates with morpholinodoxorubicin and acid-cleavable linkers. Bioconjugate Chem. 1990, 1, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillow, T.H.; Sadowsky, J.D.; Zhang, D.; Yu, S.F.; Del Rosario, G.; Xu, K.; He, J.; Bhakta, S.; Ohri, R.; Kozak, K.R.; et al. Decoupling stability and release in disulfide bonds with antibody-small molecule conjugates. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchikama, K.; An, Z. Antibody-drug conjugates: Recent advances in conjugation and linker chemistries. Protein Cell 2018, 9, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Xiao, D.; Xie, F.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Fan, S.; Zhou, X.; Li, S. Antibody-drug conjugates: Recent advances in linker chemistry. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 3889–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X. Antibody-drug conjugates for the treatment of lymphoma: Clinical advances and latest progress. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreca, M.; Lang, N.; Tarantelli, C.; Spriano, F.; Barraja, P.; Bertoni, F. Antibody-drug conjugates for lymphoma patients: Preclinical and clinical evidences. Explor. Target. Antitumor Ther. 2022, 3, 763–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Donk, N.W.; Dhimolea, E. Brentuximab vedotin. mAbs 2012, 4, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francisco, J.A.; Cerveny, C.G.; Meyer, D.L.; Mixan, B.J.; Klussman, K.; Chace, D.F.; Rejniak, S.X.; Gordon, K.A.; DeBlanc, R.; Toki, B.E.; et al. cAC10-vcMMAE, an anti-CD30-monomethyl auristatin E conjugate with potent and selective antitumor activity. Blood 2003, 102, 1458–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senter, P.D.; Sievers, E.L. The discovery and development of brentuximab vedotin for use in relapsed Hodgkin lymphoma and systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, Y.E.; Tadmor, T.; Podack, E.R.; Rosenblatt, J.D. CD30: An important new target in hematologic malignancies. Leuk. Lymphoma 2011, 52, 1641–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Currin, E.S.; Gopal, A.K. Treatment strategies for Hodgkin lymphoma recurring following autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Korean J. Hematol. 2012, 47, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Weyden, C.A.; Pileri, S.A.; Feldman, A.L.; Whisstock, J.; Prince, H.M. Understanding CD30 biology and therapeutic targeting: A historical perspective providing insight into future directions. Blood Cancer J. 2017, 7, e603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, J.M.; Jurczak, W.; Straus, D.J.; Ansell, S.M.; Kim, W.S.; Gallamini, A.; Younes, A.; Alekseev, S.; Illes, A.; Picardi, M.; et al. Brentuximab Vedotin with Chemotherapy for Stage III or IV Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straus, D.J.; Dlugosz-Danecka, M.; Connors, J.M.; Alekseev, S.; Illes, A.; Picardi, M.; Lech-Maranda, E.; Feldman, T.; Smolewski, P.; Savage, K.J.; et al. Brentuximab vedotin with chemotherapy for stage III or IV classical Hodgkin lymphoma (ECHELON-1): 5-year update of an international, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2021, 8, e410–e421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, A.F.; Li, H.; Castellino, S.M.; Rutherford, S.C.; Davison, K.; Evans, A.G.; Punnett, A.; Constine, L.S.; Hodgson, D.C.; Parsons, S.K.; et al. SWOG S1826: A Phase III, Randomized Study of Nivolumab Plus AVD or Brentuximab Vedotin Plus AVD in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Advanced Stage Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood 2020, 136 (Suppl. 1), 23–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evens, A.M.; Advani, R.H.; Helenowski, I.B.; Fanale, M.; Smith, S.M.; Jovanovic, B.D.; Bociek, G.R.; Klein, A.K.; Winter, J.N.; Gordon, L.I.; et al. Multicenter Phase II Study of Sequential Brentuximab Vedotin and Doxorubicin, Vinblastine, and Dacarbazine Chemotherapy for Older Patients With Untreated Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 3015–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younes, A.; Gopal, A.K.; Smith, S.E.; Ansell, S.M.; Rosenblatt, J.D.; Savage, K.J.; Ramchandren, R.; Bartlett, N.L.; Cheson, B.D.; de Vos, S.; et al. Results of a pivotal phase II study of brentuximab vedotin for patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2183–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Claro, R.A.; McGinn, K.; Kwitkowski, V.; Bullock, J.; Khandelwal, A.; Habtemariam, B.; Ouyang, Y.; Saber, H.; Lee, K.; Koti, K.; et al. U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval summary: Brentuximab vedotin for the treatment of relapsed Hodgkin lymphoma or relapsed systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 5845–5849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskowitz, C.H.; Nademanee, A.; Masszi, T.; Agura, E.; Holowiecki, J.; Abidi, M.H.; Chen, A.I.; Stiff, P.; Gianni, A.M.; Carella, A.; et al. Brentuximab vedotin as consolidation therapy after autologous stem-cell transplantation in patients with Hodgkin’s lymphoma at risk of relapse or progression (AETHERA): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 1853–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskowitz, C.H.; Walewski, J.; Nademanee, A.; Masszi, T.; Agura, E.; Holowiecki, J.; Abidi, M.H.; Chen, A.I.; Stiff, P.; Viviani, S.; et al. Five-year PFS from the AETHERA trial of brentuximab vedotin for Hodgkin lymphoma at high risk of progression or relapse. Blood 2018, 132, 2639–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harker-Murray, P.; Mauz-Korholz, C.; Leblanc, T.; Mascarin, M.; Michel, G.; Cooper, S.; Beishuizen, A.; Leger, K.J.; Amoroso, L.; Buffardi, S.; et al. Nivolumab and brentuximab vedotin with or without bendamustine for R/R Hodgkin lymphoma in children, adolescents, and young adults. Blood 2023, 141, 2075–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabattini, E.; Pizzi, M.; Tabanelli, V.; Baldin, P.; Sacchetti, C.S.; Agostinelli, C.; Zinzani, P.L.; Pileri, S.A. CD30 expression in peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Haematologica 2013, 98, e81–e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossard, C.; Dobay, M.P.; Parrens, M.; Lamant, L.; Missiaglia, E.; Haioun, C.; Martin, A.; Fabiani, B.; Delarue, R.; Tournilhac, O.; et al. Immunohistochemistry as a valuable tool to assess CD30 expression in peripheral T-cell lymphomas: High correlation with mRNA levels. Blood 2014, 124, 2983–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pro, B.; Advani, R.; Brice, P.; Bartlett, N.L.; Rosenblatt, J.D.; Illidge, T.; Matous, J.; Ramchandren, R.; Fanale, M.; Connors, J.M.; et al. Brentuximab vedotin (SGN-35) in patients with relapsed or refractory systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma: Results of a phase II study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2190–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, S.; O’Connor, O.A.; Pro, B.; Illidge, T.; Fanale, M.; Advani, R.; Bartlett, N.L.; Christensen, J.H.; Morschhauser, F.; Domingo-Domenech, E.; et al. Brentuximab vedotin with chemotherapy for CD30-positive peripheral T-cell lymphoma (ECHELON-2): A global, double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, S.; O’Connor, O.A.; Pro, B.; Trumper, L.; Iyer, S.; Advani, R.; Bartlett, N.L.; Christensen, J.H.; Morschhauser, F.; Domingo-Domenech, E.; et al. The ECHELON-2 Trial: 5-year results of a randomized, phase III study of brentuximab vedotin with chemotherapy for CD30-positive peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, S.M.; Scarisbrick, J.J.; Dummer, R.; Whittaker, S.; Duvic, M.; Kim, Y.H.; Quaglino, P.; Zinzani, P.L.; Bechter, O.; Eradat, H.; et al. Randomized phase 3 ALCANZA study of brentuximab vedotin vs physician’s choice in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: Final data. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 5098–5106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polson, A.G.; Calemine-Fenaux, J.; Chan, P.; Chang, W.; Christensen, E.; Clark, S.; de Sauvage, F.J.; Eaton, D.; Elkins, K.; Elliott, J.M.; et al. Antibody-drug conjugates for the treatment of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: Target and linker-drug selection. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2358–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, R.M.; Shaffer, A.L., 3rd; Phelan, J.D.; Staudt, L.M. B-cell receptor signaling in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Semin. Hematol. 2015, 52, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dornan, D.; Bennett, F.; Chen, Y.; Dennis, M.; Eaton, D.; Elkins, K.; French, D.; Go, M.A.; Jack, A.; Junutula, J.R.; et al. Therapeutic potential of an anti-CD79b antibody-drug conjugate, anti-CD79b-vc-MMAE, for the treatment of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2009, 114, 2721–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, J.M.; Morschhauser, F.; Andorsky, D.; Lee, C.; Sharman, J.P. Antibody-drug conjugates for previously treated aggressive lymphomas: Focus on polatuzumab vedotin. Expert. Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 13, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawalha, Y. Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Look at the Approved and Emerging Therapies. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilly, H.; Morschhauser, F.; Sehn, L.H.; Friedberg, J.W.; Trneny, M.; Sharman, J.P.; Herbaux, C.; Burke, J.M.; Matasar, M.; Rai, S.; et al. Polatuzumab Vedotin in Previously Untreated Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (No Date) FDA Approves Polatuzumab Vedotin-Piiq for Previously Untreated Diffuse, U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-polatuzumab-vedotin-piiq-previously-untreated-diffuse-large-b-cell-lymphoma-not (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Jerkeman, M.; Leppä, S.; Hamfjord, J.; Brown, P.; Ekberg, S.; José María Ferreri, A. S227: Initial safety data from the phase 3 polar bear trial in elderly or frail patients with diffuse large cell lymphoma, comparing r-pola-mini-chp andr-mini-chop. HemaSphere 2023, 7, e91359ec. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehn, L.H.; Herrera, A.F.; Flowers, C.R.; Kamdar, M.K.; McMillan, A.; Hertzberg, M.; Assouline, S.; Kim, T.M.; Kim, W.S.; Ozcan, M.; et al. Polatuzumab Vedotin in Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budde, L.E.; Olszewski, A.J.; Assouline, S.; Lossos, I.S.; Diefenbach, C.; Kamdar, M.; Ghosh, N.; Modi, D.; Sabry, W.; Naik, S.; et al. Mosunetuzumab with polatuzumab vedotin in relapsed or refractory aggressive large B cell lymphoma: A phase 1b/2 trial. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diefenbach, C.; Kahl, B.S.; McMillan, A.; Briones, J.; Banerjee, L.; Cordoba, R.; Miall, F.; Burke, J.M.; Hirata, J.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Polatuzumab vedotin plus obinutuzumab and lenalidomide in patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma: A cohort of a multicentre, single-arm, phase 1b/2 study. Lancet Haematol. 2021, 8, e891–e901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diefenbach, C.S.; Kahl, B.S.; Banerjee, L.; McMillan, A.K.; Miall, F.; Briones, J.; Cordoba, R.; Burke, J.M.; Hirata, J.; Sharma, S.; et al. A Phase Ib/II Study of Polatuzumab Vedotin Plus Obinutuzumab and Lenalidomide in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Follicular Lymphoma: Final Analysis and Progression-Free Survival Update. Blood 2022, 140 (Suppl. 1), 2286–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.L.; Assouline, S.; Kamdar, M.; Ghosh, N.; Naik, S.; Nakhoda, S.K.; Chavez, J.C.; Jia, T.; Pham, S.; Huw, L.-Y.; et al. Fixed Duration Mosunetuzumab Plus Polatuzumab Vedotin Has Promising Efficacy and a Manageable Safety Profile in Patients with BTKi Relapsed/Refractory Mantle Cell Lymphoma: Initial Results from a Phase Ib/II Study. Blood 2023, 142 (Suppl. 1), 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedder, T.F. CD19: A promising B cell target for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2009, 5, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wei, G.; Liu, D. CD19: A biomarker for B cell development, lymphoma diagnosis and therapy. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2012, 1, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horna, P.; Nowakowski, G.; Endell, J.; Boxhammer, R. Comparative Assessment of Surface CD19 and CD20 Expression on B-Cell Lymphomas from Clinical Biopsies: Implications for Targeted Therapies. Blood 2019, 134 (Suppl. 1), 5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zammarchi, F.; Corbett, S.; Adams, L.; Tyrer, P.C.; Kiakos, K.; Janghra, N.; Marafioti, T.; Britten, C.E.; Havenith, C.E.G.; Chivers, S.; et al. ADCT-402, a PBD dimer-containing antibody drug conjugate targeting CD19-expressing malignancies. Blood 2018, 131, 1094–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna Goparaju, A.W. The Anti-cd19 Antibody–Drug Conjugate Loncastuximab Tesirine, Touchoncology. 2022. Available online: https://touchoncology.com/lymphoma/journal-articles/the-anti-cd19-antibody-drug-conjugate-loncastuximab-tesirine (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Kahl, B.S.; Hamadani, M.; Radford, J.; Carlo-Stella, C.; Caimi, P.; Reid, E.; Feingold, J.M.; Ardeshna, K.M.; Solh, M.; Heffner, L.T.; et al. A Phase I Study of ADCT-402 (Loncastuximab Tesirine), a Novel Pyrrolobenzodiazepine-Based Antibody-Drug Conjugate, in Relapsed/Refractory B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 6986–6994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caimi, P.F.; Ai, W.; Alderuccio, J.P.; Ardeshna, K.M.; Hamadani, M.; Hess, B.; Kahl, B.S.; Radford, J.; Solh, M.; Stathis, A.; et al. Loncastuximab tesirine in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (LOTIS-2): A multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (no date b) FDA Grants Accelerated Approval, U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-grants-accelerated-approval-loncastuximab-tesirine-lpyl-large-b-cell-lymphoma (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Hamadani, M.; Radford, J.; Carlo-Stella, C.; Caimi, P.F.; Reid, E.; O’Connor, O.A.; Feingold, J.M.; Ardeshna, K.M.; Townsend, W.; Solh, M.; et al. Final results of a phase 1 study of loncastuximab tesirine in relapsed/refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2021, 137, 2634–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderuccio, J.P.; Alencar, A.J.; Schatz, J.H.; Kuker, R.; Pongas, G.; Reis, I.M.; Spiegel, J.Y.; Medina Andara, L.; Lekakis, L.J.; Gyedu, J.S.; et al. Limited Duration Loncastuximab Tesirine with Rituximab Induces High Complete Metabolic Response Rate in High-Risk Relapsed/Refractory Follicular Lymphoma—A Phase 2 Study. Blood 2023, 142 (Suppl. 1), 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reagan, P.M.; Portell, C.A.; Casulo, C.; Baran, A.M.; Magnuson, A.; Barr, P.M.; Lerman, Y.; French, K.N.; Friedberg, J.W. A Pilot Study of Brentuximab Vedotin, Rituximab and Dose Attenuated CHP in Patients 75 Years and Older with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2020, 136 (Suppl. 1), 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, S.; Jagadeesh, D.; Domingo Domènech, E.; Benedetti, F.; Rodriguez Izquierdo, A.; Bouabdallah, K.; Vitolo, U.; Illidge, T.; Liu, J.; Knowles, S.; et al. P1130: Frontline brentuximab vedotin and CHP (A+CHP) in patients with peripheral T-cell lymphoma with less than 10% CD30 expression: Initial safety and efficacy results from the phase 2 study SGN35-032. HemaSphere 2023, 7, e4008899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, R.C.; Cassaday, R.D.; Smith, S.D.; Fromm, J.R.; Cowan, A.J.; Warren, E.H.; Shadman, M.S.; Shustov, A.; Till, B.G.; Ujjani, C.S.; et al. Dose-dense brentuximab vedotin plus ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide for second-line treatment of relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma: A single centre, phase 1/2 study. Lancet Haematol. 2021, 8, e562–e571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barta, S.K.; Feldman, T.A.; DeSimone, J.A.; Kim, E.; Devajaran, K.; Wiest, D.; Fung, H.C.H.; Fisher, R.I.; Tan, C.; Khan, N. A Phase I Trial Assessing the Feasibility of Romidepsin Combined with Brentuximab Vedotin for Patients Requiring Systemic Therapy for Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2020, 136 (Suppl. 1), 24–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannerji, R.; Yuen, S.; Phillips, T.; Arthur, C.; Isufi, I.; Marlton, P.; Seymour, J.F.; Corradini, P.; Molinari, A.; Gritti, G.; et al. Polatuzumab vedotin + obinutuzumab + venetoclax in patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) follicular lymphoma (FL): Primary analysis of a phase 1B/2 trial. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 39 (Suppl. 2). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritti, G.; Marlton, P.; Phillips, T.J.; Arthur, C.; Bannerji, R.; Corradini, P.; Johnston, A.; Seymour, J.F.; Yuen, S.; Hirata, J.; et al. Polatuzumab Vedotin Plus Venetoclax with Rituximab in Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Primary Efficacy Analysis of a Phase Ib/II Study. Blood 2020, 136 (Suppl. 1), 45–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, A.; Haioun, C.; Sancho, J.-M.; Viardot, A.; Rodriguez Izquierdo, A.; Donato Martin, E.M.; García-Sancho, A.M.; Sandoval-Sus, J.; Tilly, H.; Vandenberghe, E.; et al. P1189: Initial safety run-in results of the phase iii polargo trial: Polatuzumab vedotin plus rituximab, gemcitabine, and oxaliplatin in patients with relapsed/refractory DIFFUSE LARGE B-CELL lymphoma. HemaSphere 2022, 6, 1075–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, A.F.; Chen, L.; Crombie, J.L.; Cohen, J.B.; Advani, R.H.; LaCasce, A.S.; Popplewell, L.L.; Puverel, S.; Peters, L.; Daniels, S.; et al. Polatuzumab Vedotin Combined with R-ICE (PolaR-ICE) As Second-Line Therapy in Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2022, 140 (Suppl. 1), 1065–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strati, P.; Watson, G.; Horowitz, S.B.; Nair, R.; Rodriguez, M.A.; Steiner, R.E.; Fayad, L.; Westin, J.R.; Neelapu, S.S. Clinical Efficacy of Polatuzumab Vedotin in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma after Standard of Care Axicabtagene Ciloleucel. Blood 2020, 136 (Suppl. 1), 16–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlo-Stella, C.; Zinzani, P.L.L.; Janakiram, M.; Dia, V.; He, X.; Ervin-Haynes, A.; Depaus, J. Planned Interim Analysis of a Phase 2 Study of Loncastuximab Tesirine Plus Ibrutinib in Patients with Advanced Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (LOTIS-3). Blood 2021, 138 (Suppl. 1), 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depaus, J.; Wagner-Johnston, N.; Zinzani, P.L.; Phillips, T.J.; Maly, J.; Ferrari, S.; Bachy, E.; Bryan, L.J.; Delwail, V.; Janakiram, M.; et al. Clinical activity of loncastuximab tesirine plus ibrutinib in non-hodgkin lymphoma: Updated lotis 3 phase 1 results. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 39 (Suppl. 2). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatek, M.; Grosicki, S.; Jiménez, J.L.; Mariño, S.F.P.; Snauwaert, S.; Kingsley, E.; Zacchetti, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Depaus, J. ABCL-515 Updated Results of the Safety Run-In of the Phase 3 LOTIS-5 Trial: Novel Combination of Loncastuximab Tesirine With Rituximab (Lonca-R) Versus Immunochemotherapy in Patients With R/R DLBCL. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2023, 23, S439–S440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlo-Stella, C.; Depaus, J.; Hess, B.T.; Kingsley, E.; Zinzani, P.L.; Ungar, D.; Dai, V.; Wang, L.; Ardeshna, K.M. A phase 2 randomized study of loncastuximab tesirine (lonca) versus (vs) idelalisib in patients (pts) with relapsed or refractory (r/r) follicular lymphoma (fl)–lotis-6. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 39 (Suppl. 2). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinicaltrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04998669 (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Clinicaltrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05053659 (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Clinicaltrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04974996 (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Clinicaltrials.gov. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05144009 (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Clinicaltrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05249959 (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Clinicaltrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04970901 (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Hess, B.T.; Collins, G.P.; Solh, M.; Gandhi, M.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Yu, E.; Zinzani, P.L. A Phase 1b Open-Label Study of Loncastuximab Tesirine in Combination with Other Anticancer Agents in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory (R/R) B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (LOTIS-7). Blood 2022, 140 (Suppl. 1), 12079–12080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskowitz, C.H.; Bastos-Oreiro, M.; Ungar, D.; Dautaj, I.; Kalac, M. Safety and Anti-Tumor Activity Study of Loncastuximab Tesirine and Durvalumab in Diffuse Large B-Cell, Mantle Cell, or Follicular Lymphoma. Blood 2019, 134, 2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinicaltrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05190705 (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Hong, E.E.; Erickson, H.; Lutz, R.J.; Whiteman, K.R.; Jones, G.; Kovtun, Y.; Blanc, V.; Lambert, J.M. Design of Coltuximab Ravtansine, a CD19-Targeting Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) for the Treatment of B-Cell Malignancies: Structure-Activity Relationships and Preclinical Evaluation. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 1703–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheuermann, R.H.; Racila, E. CD19 antigen in leukemia and lymphoma diagnosis and immunotherapy. Leuk. Lymphoma 1995, 18, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trneny, M.; Verhoef, G.; Dyer, M.J.; Yehuda, D.B.; Patti, C.; Canales, M.; López, A.; Awan, F.; Montgomery, P.; Janikova, A.; et al. Starlyte phase II study of coltuximab ravtansine (CoR, SAR3419) single agent: Clinical activity and safety in patients (pts) with relapsed/refractory (R/R) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL.; NCT01472887). J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32 (Suppl. 15), 8506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coiffier, B.; Thieblemont, C.; de Guibert, S.; Dupuis, J.; Ribrag, V.; Bouabdallah, R.; Morschhauser, F.; Navarro, R.; Le Gouill, S.; Haioun, C.; et al. A phase II, single-arm, multicentre study of coltuximab ravtansine (SAR3419) and rituximab in patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 173, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denintuzumab Mafodotin, National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Database. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Denintuzumab-mafodotin (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Fathi, A.T.; Borate, U.; DeAngelo, D.J.; O’Brien, M.M.; Trippett, T.; Shah, B.D.; Hale, G.A.; Foran, J.M.; Silverman, L.B.; Tibes, R.; et al. A Phase 1 Study of Denintuzumab Mafodotin (SGN-CD19A) in Adults with Relapsed or Refractory B-Lineage Acute Leukemia (B-ALL) and Highly Aggressive Lymphoma. Blood 2015, 126, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskowitz, C.H.; Fanale, M.A.; Shah, B.D.; Advani, R.H.; Chen, R.; Kim, S.; Kostic, A.; Liu, T.; Peng, J.; Forero-Torres, A. A Phase 1 Study of Denintuzumab Mafodotin (SGN-CD19A) in Relapsed/Refactory B-Lineage Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood 2015, 126, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinicaltrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02592876 (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Clinicaltrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02855359 (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Sullivan-Chang, L.; O’Donnell, R.T.; Tuscano, J.M. Targeting CD22 in B-cell malignancies: Current status and clinical outlook. BioDrugs 2013, 27, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricart, A.D. Antibody-drug conjugates of calicheamicin derivative: Gemtuzumab ozogamicin and inotuzumab ozogamicin. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 6417–6427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advani, A.; Coiffier, B.; Czuczman, M.S.; Dreyling, M.; Foran, J.; Gine, E.; Gisselbrecht, C.; Ketterer, N.; Nasta, S.; Rohatiner, A.; et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics, and preliminary clinical activity of inotuzumab ozogamicin, a novel immunoconjugate for the treatment of B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: Results of a phase I study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2085–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goy, A.; Forero, A.; Wagner-Johnston, N.; Christopher Ehmann, W.; Tsai, M.; Hatake, K.; Ananthakrishnan, R.; Volkert, A.; Vandendries, E.; Ogura, M. A phase 2 study of inotuzumab ozogamicin in patients with indolent B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma refractory to rituximab alone, rituximab and chemotherapy, or radioimmunotherapy. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 174, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Poon, K.A.; Yu, S.F.; Dere, R.; Go, M.; Lau, J.; Zheng, B.; Elkins, K.; Danilenko, D.; Kozak, K.R.; et al. DCDT2980S, an anti-CD22-monomethyl auristatin E antibody-drug conjugate, is a potential treatment for non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advani, R.H.; Lebovic, D.; Chen, A.; Brunvand, M.; Goy, A.; Chang, J.E.; Hochberg, E.; Yalamanchili, S.; Kahn, R.; Lu, D.; et al. Phase I Study of the Anti-CD22 Antibody-Drug Conjugate Pinatuzumab Vedotin with/without Rituximab in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory B-cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morschhauser, F.; Flinn, I.W.; Advani, R.; Sehn, L.H.; Diefenbach, C.; Kolibaba, K.; Press, O.W.; Salles, G.; Tilly, H.; Chen, A.I.; et al. Polatuzumab vedotin or pinatuzumab vedotin plus rituximab in patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma: Final results from a phase 2 randomised study (ROMULUS). Lancet Haematol. 2019, 6, e254–e265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorczyca, W. Flow Cytometry in Neoplastic Hematology: Morphologic—Immunophenotypic Correlation, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spriano, F.; Tarantelli, C.; Golino, G.; Gaudio, E.; Scalise, L.; Cascione, L.; Zucca, E.; Van Berkel, P.; Stathis, A.; Zammarchi, F.; et al. The ANTI-Cd25 antibody-drug conjugate camidanlumab tesirine (ADCT-301) presents a strong preclinical activity both as single agent and in combination in lymphoma cell lines. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 37 (Suppl. 2), 323–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamadani, M.; Collins, G.P.; Caimi, P.F.; Samaniego, F.; Spira, A.; Davies, A.; Radford, J.; Menne, T.; Karnad, A.; Zain, J.M.; et al. Camidanlumab tesirine in patients with relapsed or refractory lymphoma: A phase 1, open-label, multicentre, dose-escalation, dose-expansion study. Lancet Haematol. 2021, 8, e433–e445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoni, F.; Stathis, A. Staining the target: CD37 expression in lymphomas. Blood 2016, 128, 3022–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudio, E.; Tarantelli, C.; Arribas, A.; Cascione, L.; Kwee, I.; Rinaldi, A.; Ponzoni, M.; Pittau Bordone, R.; Stussi, G.; Rossi, D.; et al. Identification of Anti-Lymphoma Biomarkers of Response to the Anti-CD37 Antibody Drug Conjugate (ADC) IMGN529. Blood 2016, 128, 4187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stathis, A.; Flinn, I.W.; Madan, S.; Maddocks, K.; Freedman, A.; Weitman, S.; Zucca, E.; Munteanu, M.C.; Lia Palomba, M. Safety, tolerability, and preliminary activity of IMGN529, a CD37-targeted antibody-drug conjugate, in patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma: A dose-escalation, phase I study. Investig. New Drugs 2018, 36, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, M.Y.; Jagadeesh, D.; Grudeva-Popova, Z.; Trněný, M.; Jurczak, W.; Pylypenko, H.; André, M.; Dwivedy Nasta, S.; Rechavi-Robinson, D.; Toffanin, S.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of CD37-Targeting Naratuximab Emtansine PLUS Rituximab in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma and Other NON-Hodgkin’S B-Cell Lymphomas—A Phase 2 Study. Blood 2021, 138 (Suppl. 1), 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieswasser, T.; Van den Eynde, A.; Van Audenaerde, J.; De Waele, J.; Lardon, F.; Riether, C.; de Haard, H.; Smits, E.; Pauwels, P.; Jacobs, J. The CD70-CD27 axis in oncology: The new kids on the block. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oflazoglu, E.; Stone, I.J.; Gordon, K.; Wood, C.G.; Repasky, E.A.; Grewal, I.S.; Law, C.L.; Gerber, H.P. Potent anticarcinoma activity of the humanized anti-CD70 antibody h1F6 conjugated to the tubulin inhibitor auristatin via an uncleavable linker. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6171–6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannir, N.M.; Forero-Torres, A.; Ramchandren, R.; Pal, S.K.; Ansell, S.M.; Infante, J.R.; de Vos, S.; Hamlin, P.A.; Kim, S.K.; Whiting, N.C.; et al. Phase I dose-escalation study of SGN-75 in patients with CD70-positive relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma or metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Investig. New Drugs 2014, 32, 1246–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-Y.; Wang, L.; Pincus, L.; McCormick, F.; Gill, R.; Ai, W. Abstract 4589: Preclinical investigation of SGN-CD70A antibody-drug conjugate in T cell lymphomas. Cancer Res. 2017, 77 (Suppl. 13), 4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, T.; Barr, P.M.; Park, S.I.; Kolibaba, K.; Caimi, P.F.; Chhabra, S.; Kingsley, E.C.; Boyd, T.; Chen, R.; Carret, A.S.; et al. A phase 1 trial of SGN-CD70A in patients with CD70-positive diffuse large B cell lymphoma and mantle cell lymphoma. Investig. New Drugs 2019, 37, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, V.C.; Liu, Y.; Jordan, A.; McIntosh, J.; Li, Y.; Che, Y.; Jessen, K.A.; Lannutti, B.J.; Wang, M. The antibody drug conjugate VLS-101 targeting ROR1 is effective in CAR T-resistant mantle cell lymphoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.L.; Barrientos, J.C.; Furman, R.R.; Mei, M.; Barr, P.M.; Choi, M.Y.; de Vos, S.; Kallam, A.; Patel, K.; Kipps, T.J.; et al. Zilovertamab Vedotin Targeting of ROR1 as Therapy for Lymphoid Cancers. NEJM Evid. 2022, 1, EVIDoa2100001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, M.; Lee, S.T.; Mensah, F.; Modi, D.; Fossa, A.; Kim, W.S.; Paszkiewicz-Kozik, E.; Sawalha, Y.; Sevindik, Ö.G.; Norasetthada, L.; et al. Zilovertamab vedotin (MK 2140) in relapsed/refractory (R/R) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL): Early results from the phase 2 waveLINE-004 study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41 (Suppl. 16), 7531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinicaltrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05406401 (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Clinicaltrials.gov. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05139017 (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Choi, M.Y.; Widhopf, G.F., 2nd; Ghia, E.M.; Kidwell, R.L.; Hasan, M.K.; Yu, J.; Rassenti, L.Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Pittman, E.; et al. Phase I Trial: Cirmtuzumab Inhibits ROR1 Signaling and Stemness Signatures in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 22, 951–959 e953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinicaltrials.gov. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03088878 (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Hamblett, K.J.; Cochran, J.; Snead, K.; Jin, S.; Yumul, R.; Simmons, J.; Stone, I.; Lyski, R.; Schrum, J.P.; Lim, A.R.; et al. SGN-35C: A Novel CD30-Directed Antibody-Drug Conjugate for the Treatment of Lymphomas. Blood 2023, 142 (Suppl. 1), 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deckert, J.; Thirlway, J.; Mysliwy, J.; Lodge, A.; Park, Y.-H.; Ryu, H.-M.; Han, N.R.; Song, H.Y.; Chung, C.-W.; Lutz, R.J. IKS03, a Next Generation CD19-Targeted Antibody Drug Conjugate, Shows Potent Activity in Preclinical Models of Aggressive B-Cell Lymphomas. Blood 2022, 140 (Suppl. 1), 3134–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deckert, J.; Thirlway, J.; Mysliwy, J.; Lodge, A.; Lutz, R.J. IKS03, a Novel CD19-Targeted Antibody Drug Conjugate, Induces Target Dependent In Vivo Cell Killing of B-Cell Lymphoma Xenografts By DNA Crosslinking. Blood 2023, 142 (Suppl. 1), 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, M.; Ao, D.; Wei, X. CXCL13-CXCR5 axis: Regulation in inflammatory diseases and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2022, 1877, 188799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schomber, T.; Stelte-Ludwig, B.; Rebstock, A.-S.; v Ahsen, O.; Johnson, A.J.; Izumi, R.; Hamdy, A. Comparison of the CXCR5-Antibody Drug Conjugate (ADC.; VIP924) to a CD19-ADC and a CD79b-ADC in a Humanized Rec-1 Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL) Mouse Model. Blood 2023, 142 (Suppl. 1), 2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Challener, C.A. Optimization of Linker Chemistries for Antibody-Drug Conjugates. BioPharm International. 30 October 2023. Available online: https://www.biopharminternational.com/view/optimization-of-linker-chemistries-for-antibody-drug-conjugates (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Junutula, J.R.; Raab, H.; Clark, S.; Bhakta, S.; Leipold, D.D.; Weir, S.; Chen, Y.; Simpson, M.; Tsai, S.P.; Dennis, M.S.; et al. Site-specific conjugation of a cytotoxic drug to an antibody improves the therapeutic index. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.J.; Yu, C.; Wu, K.L.; Wang, X.; Liu, D.; Tian, Z.; Zhao, L.; Qi, X.; Loredo, A.; Chung, A.; et al. Synthesis of precision antibody conjugates using proximity-induced chemistry. Theranostics 2021, 11, 9107–9117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conjugate Development Services|Bioconjugates & ADCs. Abzena. 23 November 2023. Available online: https://abzena.com/capabilities/bioconjugates-and-chemistry/bioconjugates-adcs/ (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Fujii, T.; Matsuda, Y.; Seki, T.; Shikida, N.; Iwai, Y.; Ooba, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Isokawa, M.; Kawaguchi, S.; Hatada, N.; et al. AJICAP Second Generation: Improved Chemical Site-Specific Conjugation Technology for Antibody-Drug Conjugate Production. Bioconjug Chem. 2023, 34, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, S.; Inoue, K.; Mihara, Y.; Matsuda, Y. Tag-Free Antibody Modification Mediated by Lipoic Acid Ligase A: Application to Antibody-Drug Conjugates Production. ChemistrySelect 2023, 8, e202204706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DaSilva, J.O.; Yang, K.; Surriga, O.; Nittoli, T.; Kunz, A.; Franklin, M.C.; Delfino, F.J.; Mao, S.; Zhao, F.; Giurleo, J.T.; et al. A Biparatopic Antibody-Drug Conjugate to Treat MET-Expressing Cancers, Including Those that Are Unresponsive to MET Pathway Blockade. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 1966–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwach, J.; Abdellatif, M.; Stengl, A. More than Toxins-Current Prospects in Designing the Next Generation of Antibody Drug Conjugates. Front. Biosci. 2022, 27, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| ADC | Trade Name | Company | FDA Approval Lymphomas | Target Antigen | Year of Initial FDA Approval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brentuximab Vedotin | ADCETRIS® | Seagen Genetics, Millennium/Takeda | cHL, CD30+T cell lymphomas | CD30 | 2011 |
| Polatuzumab Vedotin | POLIVY® | Genentech, Roche | DLBCL | CD79B | 2019 |
| Loncastuximab Tesirine | ZYNLONTA® | ADC Therapeutics | DLBCL | CD19 | 2021 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Sbihi, A.; Alasfour, M.; Pongas, G. Innovations in Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) in the Treatment of Lymphoma. Cancers 2024, 16, 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040827
Al Sbihi A, Alasfour M, Pongas G. Innovations in Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) in the Treatment of Lymphoma. Cancers. 2024; 16(4):827. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040827
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Sbihi, Ali, Maryam Alasfour, and Georgios Pongas. 2024. "Innovations in Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) in the Treatment of Lymphoma" Cancers 16, no. 4: 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040827
APA StyleAl Sbihi, A., Alasfour, M., & Pongas, G. (2024). Innovations in Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) in the Treatment of Lymphoma. Cancers, 16(4), 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16040827






