The Efficacy and Safety of a Microwave Ablation System with a Dipole Antenna Design Featuring Floating Sleeves and Anti-Phase Technology in Stereotactic Percutaneous Liver Tumor Ablation: Results from a Prospective Study
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patient Enrollment
2.2. MWA Procedure and Follow-Up Imaging
2.3. Endpoints and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographics, Tumor and Treatment Characteristics, and Lesion Distribution
3.2. Primary Technique Efficacy
3.3. Complications and Side Effects
3.4. Ablation Defect Size, Volume, and SI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crocetti, L.; de Baére, T.; Pereira, P.L.; Tarantino, F.P. CIRSE Standards of Practice on Thermal Ablation of Liver Tumours. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2020, 43, 951–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forner, A.; Reig, M.; Bruix, J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2018, 391, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Cutsem, E.; Cervantes, A.; Adam, R.; Sobrero, A.; van Krieken, J.H.; Aderka, D.; Aranda Aguilar, E.; Bardelli, A.; Benson, A.; Bodoky, G.; et al. ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1386–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, A.; Cervantes, A.; Chau, I.; Daniele, B.; Llovet, J.M.; Meyer, T.; Nault, J.-C.; Neumann, U.; Ricke, J.; Sangro, B.; et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, iv238–iv255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinguely, P.; Ruiter, S.J.S.; Engstrand, J.; de Haas, R.J.; Nilsson, H.; Candinas, D.; de Jong, K.P.; Freedman, J. A prospective multicentre trial on survival after Microwave Ablation VErsus Resection for Resectable Colorectal liver metastases (MAVERRIC). Eur. J. Cancer 2023, 187, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinguely, P.; Paolucci, I.; Ruiter, S.J.S.; Weber, S.; de Jong, K.P.; Candinas, D.; Freedman, J.; Engstrand, J. Stereotactic and Robotic Minimally Invasive Thermal Ablation of Malignant Liver Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 713685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, L.P.; Lürken, L.; Verloh, N.; Haimerl, M.; Michalik, K.; Schaible, J.; Stroszczynski, C.; Wiggermann, P. Stereotactically navigated percutaneous microwave ablation (MWA) compared to conventional MWA: A matched pair analysis. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2018, 13, 1991–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engstrand, J.; Toporek, G.; Harbut, P.; Jonas, E.; Nilsson, H.; Freedman, J. Stereotactic CT-Guided Percutaneous Microwave Ablation of Liver Tumors With the Use of High-Frequency Jet Ventilation: An Accuracy and Procedural Safety Study. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 208, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, B.J.J.; Yeong, C.H.; Goh, K.L.; Yoong, B.K.; Ho, G.F.; Yim, C.C.W.; Kulkarni, A. Robotic-assisted thermal ablation of liver tumours. Eur. Radiol. 2015, 25, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charalampopoulos, G.; Bale, R.; Filippiadis, D.; Odisio, B.C.; Wood, B.; Solbiati, L. Navigation and Robotics in Interventional Oncology: Current Status and Future Roadmap. Diagnostics 2023, 14, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaible, J.; Lürken, L.; Wiggermann, P.; Verloh, N.; Einspieler, I.; Zeman, F.; Schreyer, A.G.; Bale, R.; Stroszczynski, C.; Beyer, L. Primary efficacy of percutaneous microwave ablation of malignant liver tumors: Comparison of stereotactic and conventional manual guidance. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, T.C.; Kwan, J.; Pua, U. Advanced Techniques in the Percutaneous Ablation of Liver Tumours. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molla, N.; AlMenieir, N.; Simoneau, E.; Aljiffry, M.; Valenti, D.; Metrakos, P.; Boucher, L.M.; Hassanain, M. The role of interventional radiology in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr. Oncol. 2014, 21, e480–e492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubner, M.G.; Brace, C.L.; Hinshaw, J.L.; Lee, F.T. Microwave tumor ablation: Mechanism of action, clinical results, and devices. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 21, S192–S203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, K.; Georgiades, C. Radiofrequency ablation: Mechanism of action and devices. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 21, S179–S186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erinjeri, J.P.; Clark, T.W.I. Cryoablation: Mechanism of action and devices. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 21, S187–S191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulou, L.S.; Botsa, E.; Thanou, I.; Ziakas, P.D.; Thanos, L. Percutaneous microwave ablation vs radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 1054–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, C.C.N.; Lee, K.F.; Cheung, S.Y.S.; Chu, C.C.M.; Fong, A.K.W.; Wong, J.; Hui, J.W.Y.; Fung, A.K.Y.; Lok, H.T.; Lo, E.Y.J.; et al. Prospective double-blinded randomized controlled trial of Microwave versus RadioFrequency Ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma (McRFA trial). HPB 2020, 22, 1121–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radosevic, A.; Quesada, R.; Serlavos, C.; Sánchez, J.; Zugazaga, A.; Sierra, A.; Coll, S.; Busto, M.; Aguilar, G.; Flores, D.; et al. Microwave versus radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of liver malignancies: A randomized controlled phase 2 trial. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, A.S.; Sampson, L.A.; Warner, T.F.; Mahvi, D.M.; Lee, F.T. Radiofrequency versus microwave ablation in a hepatic porcine model. Radiology 2005, 236, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, G.D.; Dodd, N.A.; Lanctot, A.C.; Glueck, D.A. Effect of variation of portal venous blood flow on radiofrequency and microwave ablations in a blood-perfused bovine liver model. Radiology 2013, 267, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, R.; Rempp, H.; Erhard, L.; Blumenstock, G.; Pereira, P.L.; Claussen, C.D.; Clasen, S. Comparison of four microwave ablation devices: An experimental study in ex vivo bovine liver. Radiology 2013, 268, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berber, E.; Sarioglu, A.G.; Akgun, E. A comparison of three different microwave systems for laparoscopic liver tumor ablation. J. Surg. Oncol. 2024, 129, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertram, J.M.; Yang, D.; Converse, M.C.; Webster, J.G.; Mahvi, D.M. A review of coaxial-based interstitial antennas for hepatic microwave ablation. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 34, 187–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallahi, H.; Prakash, P. Antenna Designs for Microwave Tissue Ablation. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 46, 495–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Rourke, A.P.; Haemmerich, D.; Prakash, P.; Converse, M.C.; Mahvi, D.M.; Webster, J.G. Current status of liver tumor ablation devices. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2007, 4, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Bertram, J.M.; Converse, M.C.; O’Rourke, A.P.; Webster, J.G.; Hagness, S.C.; Will, J.A.; Mahvi, D.M. A floating sleeve antenna yields localized hepatic microwave ablation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2006, 53, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blain, M.; Narayanan, G.; Ricoeur, A.; Kobe, A.; Mahendra, A.M.; Jacks, B.; Letty, Q.; Bonnet, B.; Tselikas, L.; Deschamps, F.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Percutaneous Liver Microwave Ablation Using a Fully Water-Cooled Choke Ring Antenna: First Multicenter Clinical Report. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2023, 46, 1086–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habert, P.; Di Bisceglie, M.; Hak, J.-F.; Brige, P.; Chopinet, S.; Mancini, J.; Bartoli, A.; Vidal, V.; Roux, C.; Tselikas, L.; et al. Percutaneous lung and liver CT-guided ablation on swine model using microwave ablation to determine ablation size for clinical practice. Int. J. Hyperth. 2021, 38, 1140–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namakshenas, P.; Tommaso, A.; Benedetta, C.; Alessandro, D.; Elena, D.; Ricci, M.; Santucci, D.; Saccomandi, P.; Faiella, E. Performance of an Anti-Phase Technology-Powered Microwave Ablation System on Ex Vivo Liver, Lung and Kidney: Analysis of Temperature Trend, Ablation Size and Sphericity. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2024, 47, 1392–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Solbiati, L.; Brace, C.L.; Breen, D.J.; Callstrom, M.R.; Charboneau, J.W.; Chen, M.-H.; Choi, B.I.; de Baère, T.; Dodd, G.D.; et al. Image-guided tumor ablation: Standardization of terminology and reporting criteria—A 10-year update. Radiology 2014, 273, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippiadis, D.K.; Binkert, C.; Pellerin, O.; Hoffmann, R.T.; Krajina, A.; Pereira, P.L. Cirse Quality Assurance Document and Standards for Classification of Complications: The Cirse Classification System. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2017, 40, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachenmayer, A.; Tinguely, P.; Maurer, M.H.; Frehner, L.; Knöpfli, M.; Peterhans, M.; Weber, S.; Dufour, J.-F.; Candinas, D.; Banz, V. Stereotactic image-guided microwave ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma using a computer-assisted navigation system. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 1975–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Shen, Q.; Liu, P.; Xu, Z.; Wu, P.; Lu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Huang, B.; Qian, G. Microwave ablation for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma that met up-to-seven criteria: Feasibility, local efficacy and long-term outcomes. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 3877–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.; Makkena, A.; Tantawi, M.; Velasquez-Botero, F.; Eisenbrey, J.R.; Shaw, C.M. Microwave ablation as a primary versus secondary treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2023, 29, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukund, A.; Ramalingam, R.; Anandpara, K.M.; Patidar, Y.; Vijayaraghavan, R.; Sarin, S.K. Efficacy and safety of percutaneous microwave ablation for hepatocellular carcinomas <4 cm in difficult location. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20191025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Liu, M.; Lu, R.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; He, X.; Blanco, R.; Li, C. Magnetic resonance-guided ablation of liver tumors: A systematic review and pooled analysis. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2020, 16, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schullian, P.; Johnston, E.; Laimer, G.; Putzer, D.; Eberle, G.; Amann, A.; Effenberger, M.; Maglione, M.; Freund, M.C.; Loizides, A.; et al. Frequency and risk factors for major complications after stereotactic radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors in 1235 ablation sessions: A 15-year experience. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 3042–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, P.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Dong, B. Malignant liver tumors: Treatment with percutaneous microwave ablation–complications among cohort of 1136 patients. Radiology 2009, 251, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baerlocher, M.O.; Nikolic, B.; Sze, D.Y. Adverse Event Classification: Clarification and Validation of the Society of Interventional Radiology Specialty-Specific System. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2023, 34, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiter, S.J.S.; Heerink, W.J.; de Jong, K.P. Liver microwave ablation: A systematic review of various FDA-approved systems. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 4026–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amabile, C.; Ahmed, M.; Solbiati, L.; Meloni, M.F.; Solbiati, M.; Cassarino, S.; Tosoratti, N.; Nissenbaum, Y.; Ierace, T.; Goldberg, S.N. Microwave ablation of primary and secondary liver tumours: Ex vivo, in vivo, and clinical characterisation. Int. J. Hyperth. 2017, 33, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
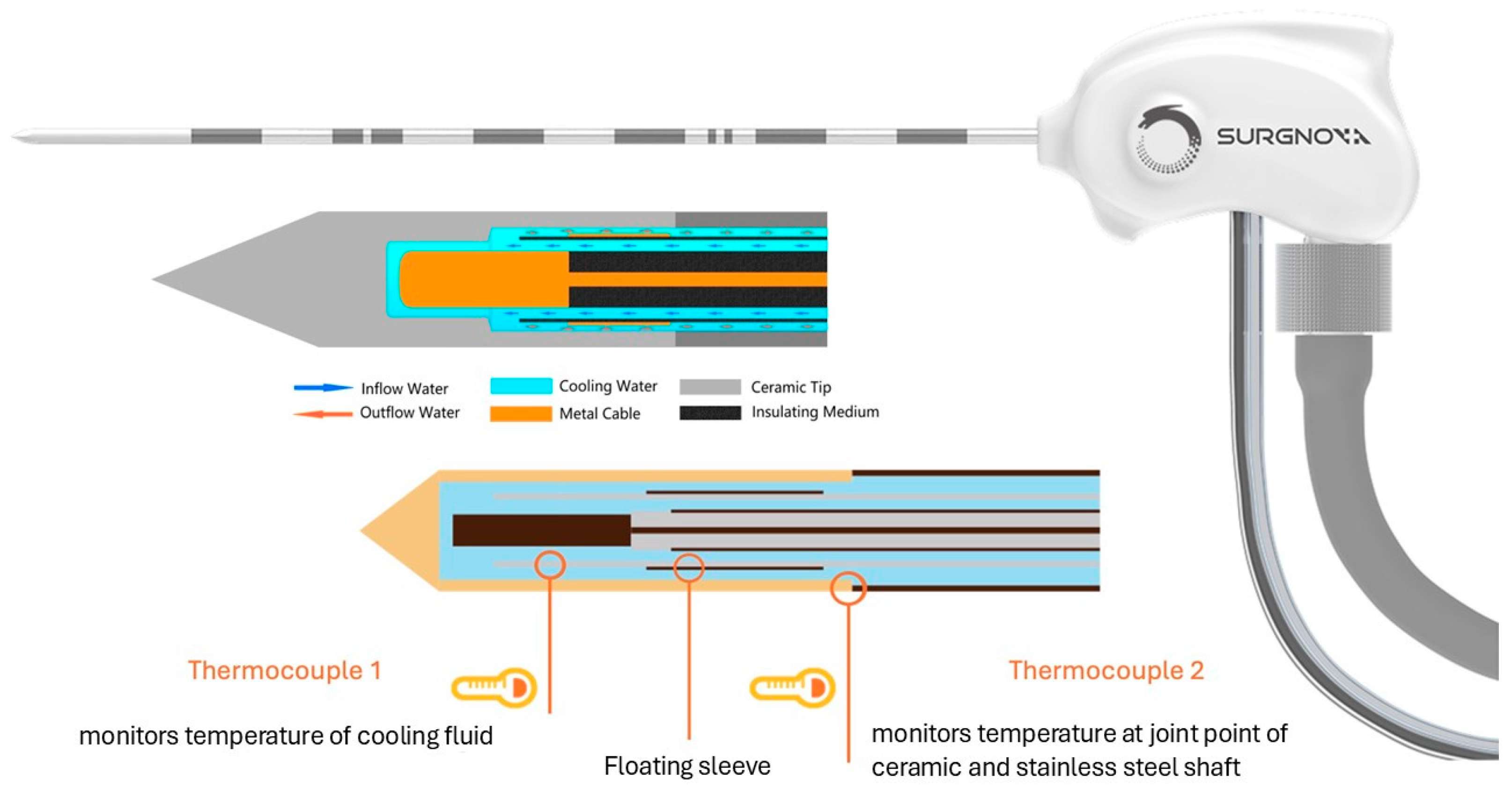

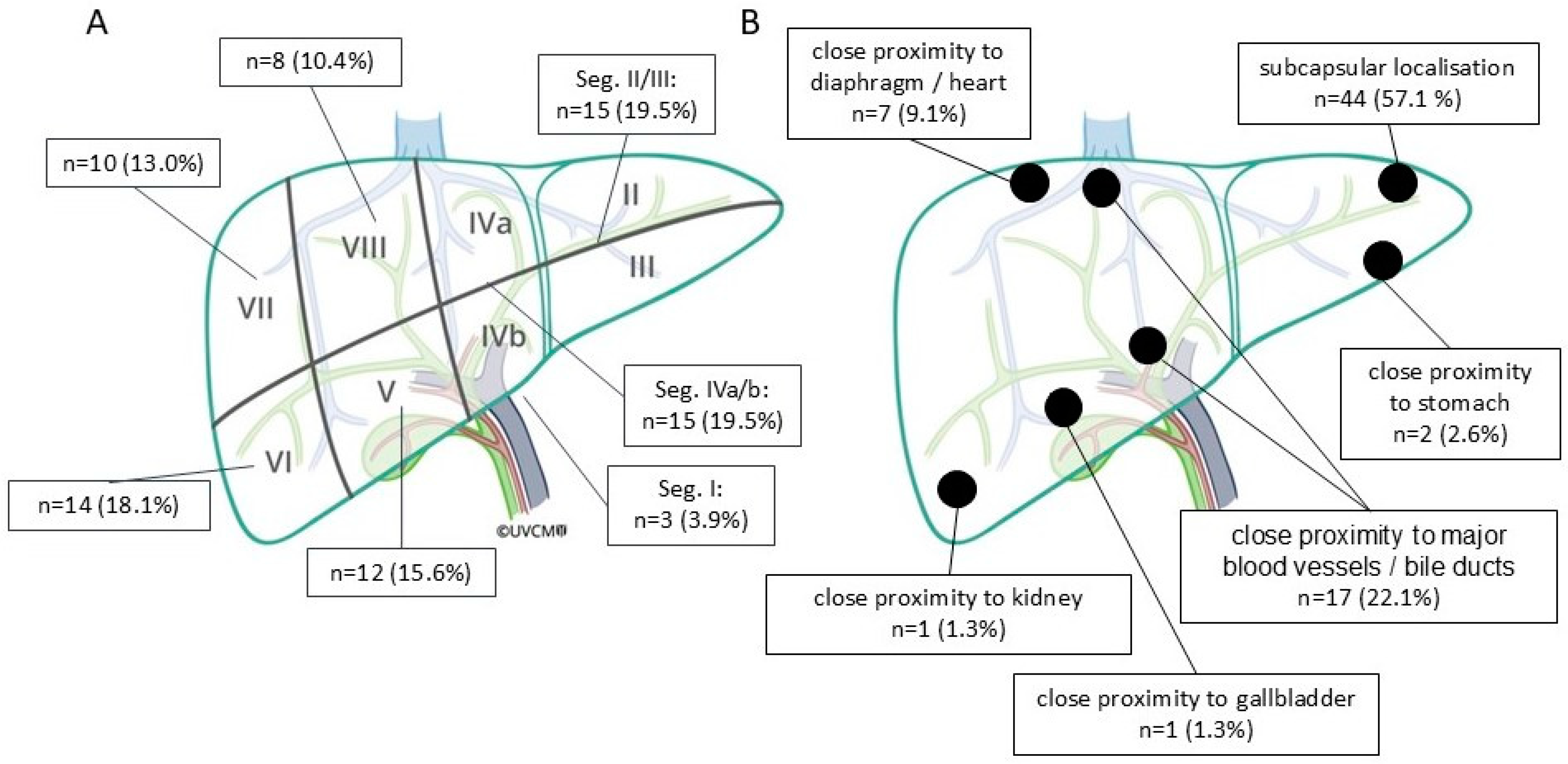
| Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Age, mean ± SD (range) | 64.9 ± 10.2 years (43–87 years) |
| Gender | |
| Female | 13 |
| Male | 37 |
| Number of tumors treated (n = number of patients) | 77 (n = 50) |
| Tumor entity | |
| Primary | 52 (n = 38) |
| HCC | 51 (n = 37) |
| CCC | 1 (n = 1) |
| Metastatic | 25 (n = 12) |
| Colorectal | 19 (n = 9) |
| Leiomyosarcoma | 3 (n = 1) |
| Angiosarcoma | 2 (n = 1) |
| Neuroendocrine tumor | 1 (n = 1) |
| Tumor long axis, mean ± SD (range) | 17.0 ± 7.4 mm (3–33 mm) |
| Tumor short axis, mean ± SD (range) | 12.9 ± 6.0 mm (2–31 mm) |
| Ablation power, mean ± SD (range) | 92.2 ± 14.2 Watts (50–100 Watts) |
| Ablation time, mean ± SD (range) | 7.7± 2.2 min (1.5–10 min) |
| No. of control scans per tumor, mean ± SD (range) | 2.6 ± 1.8 scans (1–11 scans) |
| DLP, mean ± SD (range) | 2006 ± 620 mGy·cm (952–3572 mGy·cm) |
| Intervention time, mean ± SD (range) | 89 ± 38 min (44–240 min) |
| Hospital stay after intervention, mean ± SD (range) | 2.0 ± 0.77 days (1–4 days) |
| CIRSE Complication Grade | Complication Onset | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Immediate | Minor abdominal wall bleeding several hours after the ablation, requiring no further treatment. |
| 1 | Immediate | Active arterial bleeding at the site of ablation, treated with transcatheter arterial embolization using a combination of Glubran® 2 (GEM Srl, Viareggio, Italy) and Lipiodol, resolved within same session as the ablation. |
| 1 | Immediate | Pneumothorax during the ablation, treated with a chest tube, resolved within the same session as the ablation. |
| 3 | Immediate | Active arterial bleeding several hours after the ablation, treated with transcatheter arterial embolization using coils. |
| 3 | Periprocedural | Liver abscess one week after the ablation, effectively treated with antibiotics and percutaneous CT-guided abscess drainage. |
| Ablation Parameters | Ablation Defect Long Axis (mm) | Ablation Defect Short Axis (mm) | Ablation Defect Volume (cm3) | Ablation Defect SI | Number of Tumors | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| 100 W 10 min | 45.9 | 5.3 | 35.4 | 4.8 | 34.2 | 9.4 | 0.77 | 0.09 | 29 |
| 100 W 8 min | 40.5 | 4.6 | 30.6 | 4.6 | 30.5 | 14.8 | 0.77 | 0.14 | 14 |
| 100 W 7 min | 33.0 | 1.4 | 24.0 | 9.9 | 12.1 | 1.5 | 0.72 | 0.27 | 2 |
| 100 W 5 min | 36.1 | 7.3 | 27.5 | 4.9 | 19.5 | 6.4 | 0.77 | 0.09 | 12 |
| 75 W 10 min | 44.0 | - | 33.0 | - | 35.0 | - | 0.75 | - | 1 |
| 75 W 8 min | 38.3 | 7.4 | 33.7 | 9.3 | 34.6 | 14.5 | 0.87 | 0.12 | 3 |
| 75 W 7 min | 42.5 | 3.5 | 27.5 | 2.1 | 19.8 | 1.2 | 0.65 | 0.10 | 2 |
| 75 W 5 min | 34.7 | 6.3 | 27.9 | 4.6 | 14.6 | 4.9 | 0.81 | 0.08 | 10 |
| 50 W 10 min | 32.0 | - | 18.0 | - | 13.1 | - | 0.56 | - | 1 |
| 50 W 5 min | 26.5 | 9.2 | 20.0 | 1.4 | 4.3 | 0.1 | 0.79 | 0.22 | 2 |
| 50 W 1.5 min | 22.0 | - | 19.0 | - | 3.6 | - | 0.86 | - | 1 |
| Parameters | Long Axis (mm) | Short Axis (mm) | Volume (cm3) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Surgnova | Dev | C | Surgnova | Dev | C | Surgnova | Dev | |
| 100 W 10 min | 45.9 | 45 | 0.9 | 35.4 | 45 | −9.6 | 34.2 | 47.7 | −13.5 |
| 100 W 8 min | 40.5 | 40 | 0.5 | 30.6 | 40 | −9.4 | 30.5 | 33.5 | −3 |
| 100 W 5 min | 36.1 | 35 | 1.1 | 27.5 | 35 | −7.5 | 19.5 | 22.4 | −2.9 |
| 75 W 10 min | 44.0 | 40 | 4.0 | 33.0 | 40 | −7.0 | 35.0 | 33.5 | 1.5 |
| 75 W 8 min | 38.3 | 35 | 3.3 | 33.7 | 35 | −1.3 | 34.6 | 22.4 | 12.2 |
| 75 W 5 min | 34.7 | 30 | 4.7 | 27.9 | 30 | −2.1 | 14.6 | 14.1 | 0.5 |
| 50 W 10 min | 32.0 | 35 | −3.0 | 18.0 | 35 | −17 | 13.1 | 22.4 | −9.3 |
| 50 W 5 min | 26.5 | 25 | 1.5 | 20.0 | 25 | −5 | 4.3 | 8.2 | −3.9 |
| Parameters | Long Axis (mm) | Short Axis (mm) | Volume (cm3) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Habert | Dev | C | Habert | Dev | C | Habert | Dev | |
| 100 W 10 min | 45.9 | 45 | 0.9 | 35.4 | 32 | 3.4 | 34.2 | 24.3 | 9.9 |
| 100 W 8 min | 40.5 | 38 | 2.5 | 30.6 | 29 | 1.6 | 30.5 | 16.3 | 14.2 |
| 75 W 10 min | 44 | 38 | 6 | 33 | 27 | 6 | 35 | 14.9 | 20.1 |
| 50 W 10 min | 32 | 31 | 1 | 18 | 25 | −7 | 13.1 | 10.1 | 3 |
| 50 W 5 min | 26.5 | 29 | −2.5 | 20.0 | 22 | −2 | 4.3 | 7.3 | −3 |
| Parameters | Long Axis (mm) | Short Axis (mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Blain | Dev | C | Blain | Dev | |
| 100 W 10 min | 45.9 | 44.7 | 1.2 | 35.4 | 33 | 2.4 |
| 100 W 8 min | 40.5 | 39.5 | 1.0 | 30.5 | 28.8 | 1.7 |
| 75 W 10 min | 44 | 37.1 | 6.9 | 33 | 27.5 | 5.5 |
| 50 W 5 min | 26.5 | 24.3 | 2.2 | 20.0 | 18.9 | 1.1 |
| Parameters | Long Axis (mm) | Short Axis (mm) | SI | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Namakshenas | Dev | C | Namakshenas | Dev | C | Namakshenas | Dev | |
| 100 W 10 min | 45.9 | 42 | 3.9 | 35.4 | 41 | −5.6 | 0.77 | 0.98 | −0.21 |
| 100 W 5 min | 36.1 | 36 | 0.1 | 27.5 | 33 | −5.5 | 0.77 | 0.92 | −0.15 |
| 50 W 10 min | 32.0 | 33 | −1 | 18.0 | 33 | −15 | 0.56 | 1 | −0.44 |
| 50 W 5 min | 26.5 | 29 | −2.5 | 20.0 | 25 | −5 | 0.79 | 0.86 | −0.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Luerken, L.; Mayr, V.; Goetz, A.; Schlitt, A.; Stroszczynski, C.; Einspieler, I. The Efficacy and Safety of a Microwave Ablation System with a Dipole Antenna Design Featuring Floating Sleeves and Anti-Phase Technology in Stereotactic Percutaneous Liver Tumor Ablation: Results from a Prospective Study. Cancers 2024, 16, 4211. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16244211
Zhang L, Luerken L, Mayr V, Goetz A, Schlitt A, Stroszczynski C, Einspieler I. The Efficacy and Safety of a Microwave Ablation System with a Dipole Antenna Design Featuring Floating Sleeves and Anti-Phase Technology in Stereotactic Percutaneous Liver Tumor Ablation: Results from a Prospective Study. Cancers. 2024; 16(24):4211. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16244211
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Liang, Lukas Luerken, Vinzenz Mayr, Andrea Goetz, Alexandra Schlitt, Christian Stroszczynski, and Ingo Einspieler. 2024. "The Efficacy and Safety of a Microwave Ablation System with a Dipole Antenna Design Featuring Floating Sleeves and Anti-Phase Technology in Stereotactic Percutaneous Liver Tumor Ablation: Results from a Prospective Study" Cancers 16, no. 24: 4211. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16244211
APA StyleZhang, L., Luerken, L., Mayr, V., Goetz, A., Schlitt, A., Stroszczynski, C., & Einspieler, I. (2024). The Efficacy and Safety of a Microwave Ablation System with a Dipole Antenna Design Featuring Floating Sleeves and Anti-Phase Technology in Stereotactic Percutaneous Liver Tumor Ablation: Results from a Prospective Study. Cancers, 16(24), 4211. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16244211






