Effect of Fluorescence Lymph Node Mapping on Improving Diagnostic Values of CT D3 Lymph Node Staging for Right-Sided Colon Cancer
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Preoperative Abdominal CT Staging
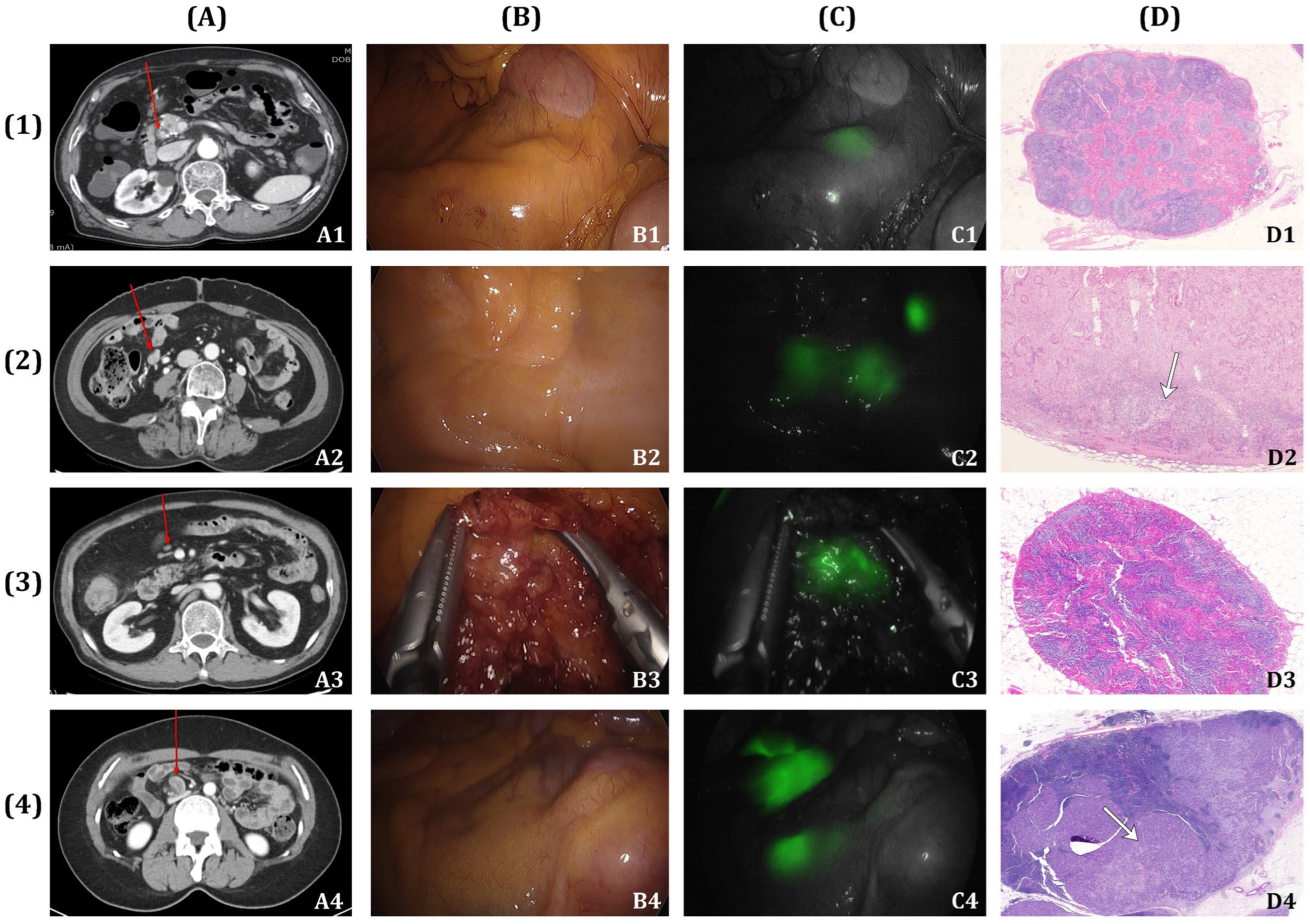
2.3. Fluorescence Lymph Nodes Mapping
2.4. Pathologic Evaluation
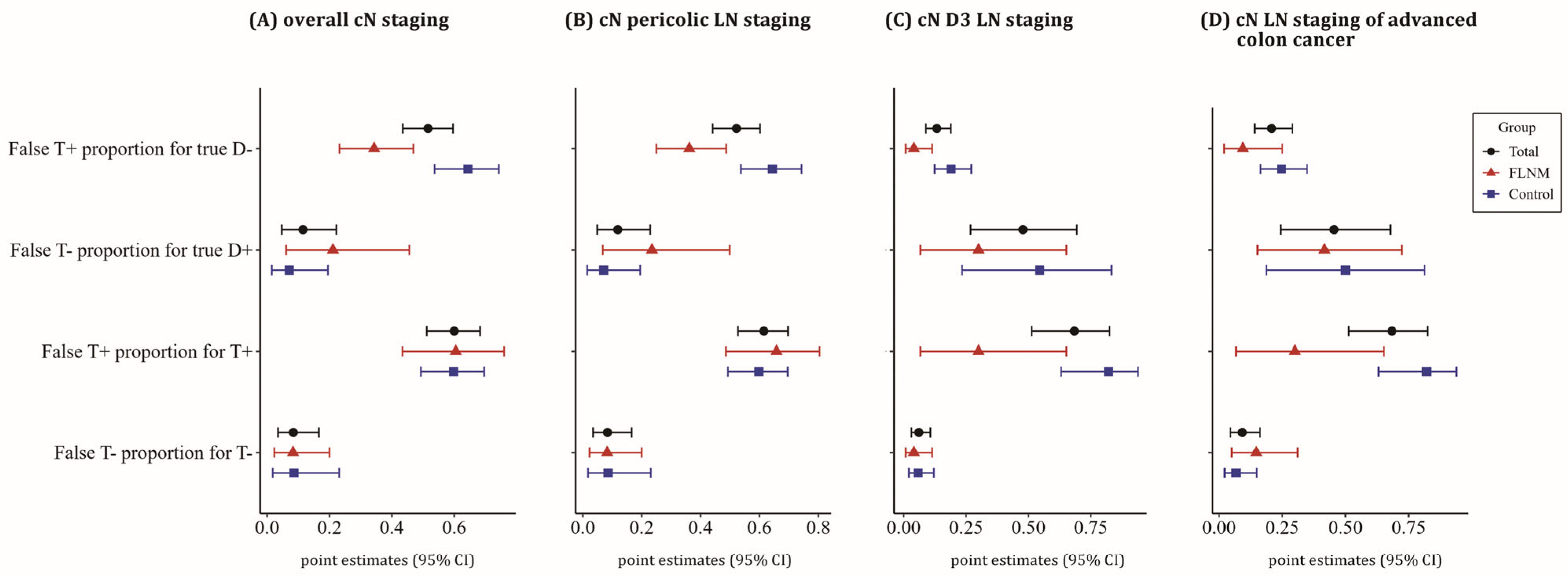
2.5. Diagnostic Values of Preoperative CT Staging
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient’s Characteristics
3.2. CT Staging and Pathologic Diagnosis
3.3. Diagnostic Value of CT Staging
3.4. Univariate and Multivariate Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ryu, H.S.; Kim, H.J.; Ji, W.B.; Kim, B.C.; Kim, J.H.; Moon, S.K.; Kang, S.I.; Kwak, H.D.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, C.H.; et al. Colon cancer: The 2023 Korean clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis and treatment. Ann. Coloproctol. 2024, 40, 89–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, G.M.; Lee, I.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Kye, B.H.; Cho, H.M.; Jang, J.H.; Kim, C.N.; Lee, K.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.G.; et al. Is Laparoscopic Complete Mesocolic Excision and Central Vascular Ligation Really Necessary for All Patients With Right-Sided Colon Cancer? Ann. Coloproctol. 2021, 37, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Su, X.; He, Z.; Zhang, C.; Lu, J.; Zhang, G.; Sun, Y.; Du, X.; Chi, P.; Wang, Z.; et al. Short-term outcomes of complete mesocolic excision versus D2 dissection in patients undergoing laparoscopic colectomy for right colon cancer (RELARC): A randomised, controlled, phase 3, superiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Kye, B.H.; Han, Y.D.; Cho, M.S.; Park, J.W.; Jeong, S.Y.; Song, S.H.; Park, J.S.; Park, S.Y.; et al. Surgical quality assessment for the prospective study of oncologic outcomes after laparoscopic modified complete mesocolic excision for nonmetastatic right colon cancer (PIONEER study). Int. J. Surg. 2024, 110, 1484–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkurti, J.; van den Berg, K.; van Erning, F.N.; Lahaye, M.J.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Nederend, J. Diagnostic accuracy of CT for local staging of colon cancer: A nationwide study in the Netherlands. Eur. J. Cancer 2023, 193, 113314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikkenk, D.J.; Sijmons, J.M.L.; Burghgraef, T.A.; Asaggau, I.; Vos, A.; da Costa, D.W.; Somers, I.; Verheijen, P.M.; Dekker, J.T.; Nagengast, W.B.; et al. Nationwide practice in CT-based preoperative staging of colon cancer and concordance with definitive pathology. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 49, 106941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, N.; Ishida, H.; Tanakaya, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Kumamoto, K.; Tanaka, T.; Hinoi, T.; Miyakura, Y.; Hasegawa, H.; Takayama, T.; et al. Japanese Society for Cancer of the Colon and Rectum (JSCCR) guidelines 2020 for the Clinical Practice of Hereditary Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 26, 1353–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonhardi, J.; Mehdorn, M.; Stelzner, S.; Scheuermann, U.; Höhn, A.K.; Seehofer, D.; Schnarkowski, B.; Denecke, T.; Meyer, H.J. Diagnostic accuracy and reliability of CT-based Node-RADS for colon cancer. Abdom. Radiol. 2024. epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karahacioglu, D.; Taskin, O.C.; Esmer, R.; Armutlu, A.; Saka, B.; Ozata, I.H.; Rencuzogullari, A.; Bugra, D.; Balik, E.; Adsay, V.; et al. Performance of CT in the locoregional staging of colon cancer: Detailed radiology-pathology correlation with special emphasis on tumor deposits, extramural venous invasion and T staging. Abdom. Radiol. 2024, 49, 1792–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, A.S.F.; Gundestrup, A.K.; Kleif, J.; Thanon, T.; Bertelsen, C.A. Accuracy of preoperative staging with multidetector computed tomography in colon cancer. Colorectal. Dis. 2021, 23, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaspour, E.; Karimzadhagh, S.; Monsef, A.; Joukar, F.; Mansour-Ghanaei, F.; Hassanipour, S. Application of radiomics for preoperative prediction of lymph node metastasis in colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2024, 110, 3795–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ippolito, D.; Maino, C.; Bianco, I.; Drago, S.G.; Piazza, R.; Tamini, N.; Nespoli, L.; Giandola, T.; Sironi, S. The usefulness of preoperative CT in colon cancer staging: Impact of radiologists’ experience. Abdom. Radiol. 2023, 48, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, G.M.; Yun, M.S.; Lee, I.Y.; Im, S.B.; Kim, K.H.; Park, S.B.; Kim, T.U.; Shin, D.H.; Nazir, A.M.; Ha, G.W. Clinical Effectiveness of Fluorescence Lymph Node Mapping Using ICG for Laparoscopic Right Hemicolectomy: A Prospective Case-Control Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 4927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, K.; Melling, N.; Giannou, A.D.; Reeh, M.; Mann, O.; Hackert, T.; Izbicki, J.R.; Perez, D.; Grass, J.K. Lymphatic Mapping in Colon Cancer Depending on Injection Time and Tracing Agent: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Designed Studies. Cancers 2023, 15, 3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Park, J.S.; Kim, H.J.; Woo, I.T.; Park, I.K.; Choi, G.S. Indocyanine Green Fluorescence Imaging-Guided Laparoscopic Surgery Could Achieve Radical D3 Dissection in Patients With Advanced Right-Sided Colon Cancer. Dis. Colon. Rectum. 2020, 63, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.M.; Son, G.M.; Lee, I.Y.; Shin, D.H.; Kim, T.K.; Park, S.B.; Kim, H.W. Optimal ICG dosage of preoperative colonoscopic tattooing for fluorescence-guided laparoscopic colorectal surgery. Surg. Endosc. 2022, 36, 1152–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, E.K.; Landolfi, F.; Castagnoli, F.; Park, S.J.; Boot, J.; Van den Berg, J.; Lee, J.M.; Beets-Tan, R. CT for lymph node staging of Colon cancer: Not only size but also location and number of lymph node count. Abdom. Radiol. 2021, 46, 4096–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, H.; Kawada, K.; Itatani, Y.; Okamura, R.; Oshima, N.; Okada, T.; Hida, K.; Obama, K. Timing of real-time indocyanine green fluorescence visualization for lymph node dissection during laparoscopic colon cancer surgery. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2023, 408, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Li, H.; Lu, X.; Yi, X.; Wan, J.; Liao, W.; Wang, J.; Ke, Y.; Tan, P.; Chen, J.; et al. Regional lymph nodes distribution pattern in central area of right-sided colon cancer: In-vivo detection and the update on the clinical exploration. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 2095–2105. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Liu, W.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, J.; Yi, C.; Zeng, G.; Chen, Y.; Song, W. Differential diagnostic value of radiomics models in benign versus malignant vertebral compression fractures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2024, 178, 111621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribero, D.; Mento, F.; Sega, V.; Lo Conte, D.; Mellano, A.; Spinoglio, G. ICG-Guided Lymphadenectomy during Surgery for Colon and Rectal Cancer-Interim Analysis of the GREENLIGHT Trial. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, G.M.; Ahn, H.M.; Lee, I.Y.; Ha, G.W. Multifunctional Indocyanine Green Applications for Fluorescence-Guided Laparoscopic Colorectal Surgery. Ann. Coloproctol. 2021, 37, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.F.; Naeem, A.; Ul Haq, I.; Riaz, S.; Shakeel, O.; Panteleimonitis, S.; Khattak, S.; Syed, A.A.; Parvaiz, A. Laparoscopy offers better clinical outcomes and long-term survival in patients with right colon cancer: Experience from national cancer center. Ann. Coloproctol. 2022, 38, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, C.; Pedrazzani, C.; Turri, G.; Fernandes, E.; Lazzarini, E.; De Luca, R.; Valdegamberi, A.; Ruzzenente, A.; Guglielmi, A. Comparison of Short-term Results after Laparoscopic Complete Mesocolic Excision and Standard Colectomy for Right-Sided Colon Cancer: Analysis of a Western Center Cohort. Ann. Coloproctol. 2021, 37, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Hokuto, D.; Koyama, F.; Matsuo, Y.; Nomi, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kamitani, N.; Sadamitsu, T.; Takei, T.; Matsumoto, Y.; et al. The Prognosis and Recurrence Pattern of Right- and Left-Sided Colon Cancer in Stage II, Stage III, and Liver Metastasis After Curative Resection. Ann. Coloproctol. 2021, 37, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikkenk, D.J.; Sterkenburg, A.J.; Burghgraef, T.A.; Akol, H.; Schwartz, M.P.; Arensman, R.; Verheijen, P.M.; Nagengast, W.B.; Consten, E.C.J. Robot-assisted fluorescent sentinel lymph node identification in early-stage colon cancer. Surg. Endosc. 2023, 37, 8394–8403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacım, N.A.; Akbaş, A.; Ulgen, Y.; Aktokmakyan, T.V.; Meric, S.; Tokocin, M.; Karabay, O.; Altinel, Y. Influence of colonic mesenteric area on the number of lymph node retrieval for colon cancer: A prospective cohort study. Ann. Coloproctol. 2023, 39, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.J.; Cao, Z.C.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Li, R.D.; Tong, J.L.; Zheng, Q. Application value of indocyanine green fluorescence imaging in guiding sentinel lymph node biopsy diagnosis of gastric cancer: Meta-analysis. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2024, 16, 1883–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Park, S.; Yi, N.; Kang, B.; Park, I.J. Colorectal cancer mortality trends in the era of cancer survivorship in Korea: 2000–2020. Ann. Coloproctol. 2022, 38, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Choo, J.M.; Kim, J.S.; Shin, S.H.; Kim, J.S.; Baek, S.J.; Kwak, J.M.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.H. Characteristics and outcomes of colorectal cancer surgery by age in a tertiary center in Korea: A retrospective review. Ann. Coloproctol. 2022, 38, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizawa, T. “Bon mariage” of artificial intelligence and intraoperative fluorescence imaging for safer surgery. Art. Int. Surg. 2023, 3, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinkawa, H.; Ishizawa, T. Artificial intelligence-based technology for enhancing the quality of simulation, navigation, and outcome prediction for hepatectomy. Art. Int. Surg. 2023, 3, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Reference (True) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Predicted | Event | No Event |
| Event | A | B |
| No Event | C | D |
| (1) | Apparent prevalence (or detection prevalence) = (A + B)/(A + B + C + D) | |
| (2) | True prevalence = (A + C)/(A + B + C + D) | |
| (3) | Sensitivity = A/(A + C) | |
| (4) | Specificity = D/(B + D) | |
| (5) | Positive predictive value = A/(A + B) | |
| (6) | Negative predictive value = D/(C + D) | |
| (7) | Positive likelihood ratio = Sensitivity/1 − Specificity | |
| (8) | Negative likelihood ratio = 1 − Sensitivity/Specificity | |
| (9) | False T+ proportion for true D− = B/(B + D) | |
| (10) | False T− proportion for true D+ = C/(A + C) | |
| (11) | False T+ proportion T+ = B/(A + B) | |
| (12) | False T− proportion T− = C/(C + D) | |
| (13) | Correctly classified proportion (Accuracy) = (A + D)/(A + B + C + D) | |
| Clinical Variables | FLNM (n = 86) | Control (n = 132) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | n (%) | |||
| Age, yr | mean ± SD | 67.7 ± 11.7 | 67.6 ± 10.5 | 0.974 |
| Sex | male | 45 (52.3) | 62 (47.0) | 0.439 |
| female | 41 (47.7) | 70 (53.0) | ||
| BMI (kg/m2) | mean ± SD | 23.7 ± 3.1 | 23.9 ± 2.8 | 0.602 |
| Cancer location | cecum | 10 (11.6) | 20 (15.2) | 0.538 |
| ascending colon | 51 (59.3) | 80 (60.6) | ||
| hepatic flexure | 19 (22.1) | 20 (15.2) | ||
| proximal transverse colon | 6 (7.0) | 12 (9.1) | ||
| cT status | cT1-2 | 51 (59.3) | 58 (43.9) | 0.027 |
| cT3-4 | 35 (40.7) | 74 (56.1) | ||
| cN status | cN0 | 48 (55.8) | 35 (26.5) | 0.000 |
| cN1-2 | 38 (44.2) | 97 (73.5) | ||
| pT status | pT1-2 | 38 (44.2) | 39 (29.5) | 0.027 |
| pT3-4 | 48 (55.8) | 93 (70.5) | ||
| pN status | pN0 | 67 (77.9) | 90 (68.2) | 0.118 |
| pN1-2 | 19 (22.1) | 42 (31.8) | ||
| Pathologic stage | I | 37 (43.0) | 34 (25.8) | 0.028 |
| II | 29 (33.7) | 55 (41.7) | ||
| III | 20 (23.3) | 43 (32.6) | ||
| Tumor size (cm) | mean ± SD | 3.8 ± 2.2 | 4.4 ± 2.4 | 0.078 |
| Differentiation | well | 42 (48.8) | 27 (20.5) | <0.001 |
| moderate | 42 (48.8) | 97 (73.5) | ||
| poorly | 2 (2.3) | 8 (6.1) | ||
| Cancer obstruction | positive | 16 (18.6) | 28 (21.2) | 0.639 |
| Lymphatic invasion | positive | 14 (16.3) | 26 (19.7) | 0.524 |
| Vascular invasion | positive | 4 (4.7) | 14 (10.6) | 0.118 |
| Perineural invasion | positive | 17 (19.8) | 26 (19.7) | 0.990 |
| cT1 | cT2 | cT3 | cT4 | Total | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | |||||||
| FLNM (n = 86) | |||||||
| LN (−) | 24 (100.0) | 23 (85.2) | 10 (62.5) | 10 (52.6) | 67 (77.9) | 0.001 | |
| LN (+) | |||||||
| Pelicolic LN | 0 (0.0) | 3 (11.1) | 1 (6.3) | 3 (15.8) | 7 (8.1) | ||
| D3 LN | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (6.3) | 1 (5.3) | 2 (2.3) | ||
| Pelicolic + D3 LN | 0 (0.0) | 1 (3.7) | 4 (25.0) | 5 (26.3) | 10 (11.6) | ||
| Control (n = 132) | |||||||
| LN (−) | 16 (94.1) | 30 (73.2) | 22 (68.8) | 22 (52.4) | 90 (68.2) | 0.081 | |
| LN (+) | |||||||
| Pelicolic LN | 1 (5.9) | 7 (17.1) | 8 (25.0) | 15 (35.7) | 31 (23.5) | ||
| D3 LN | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Pelicolic + D3 LN | 0 (0.0) | 4 (9.8) | 2 (6.3) | 5 (11.9) | 11 (8.3) | ||
| Total (n = 218) | |||||||
| LN (−) | 40 (97.6) | 53 (77.9) | 32 (66.7) | 32 (52.5) | 157 (92.0) | <0.001 | |
| LN (+) | |||||||
| Pelicolic LN | 1 (2.4) | 10 (14.7) | 9 (18.8) | 18 (29.5) | 38 (17.4) | ||
| D3 LN | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (2.1) | 1 (1.6) | 2 (0.9) | ||
| Pelicolic + D3 LN | 0 (0.0) | 5 (7.4) | 6 (12.5) | 10 (16.4) | 21 (9.6) | ||
| cN: pericolic LN | |||||
| cT1-2N0 | FLNM, n (%) | Control, n (%) | Total, n (%) | p value | |
| Accuracy | 39 (92.9) | 27 (93.1) | 66 (93.6) | 1.000 | |
| Under-staging | 3 (7.1) | 2 (6.9) | 5 (7.0) | ||
| Total | 42 (100) | 29 (100) | 71 (100) | ||
| cT3-4N0/cTAnyN1-2 | FLNM, n (%) | Control, n (%) | Total, n (%) | p value | |
| Accuracy | 18 (40.9) | 44 (42.7) | 62 (42.2) | 0.797 | |
| Over-staging | 25 (56.8) | 58 (56.3) | 83 (56.5) | ||
| Under-staging | 1 (2.3) | 1 (1.0) | 2 (1.4) | ||
| Total | 44 (100) | 103 (100) | 147 (100) | ||
| cN: D3 LN | |||||
| cT1-2N0 | FLNM, n (%) | Control, n (%) | Total, n (%) | p value | |
| Accuracy | 42 (100) | 28 (96.6) | 70 (98.6) | 0.408 | |
| Under-staging | 0 (0) | 1 (3.4) | 1 (1.4) | ||
| Total | 42 (100) | 29 (100) | 71 (100) | ||
| cT3-4N0/cTAnyN1-2 | FLNM, n (%) | Control, n (%) | Total, n (%) | p value | |
| Accuracy | 36 (81.8) | 75 (72.8) | 111 (75.5) | 0.031 | |
| Over-staging | 3 (6.8) | 23 (22.3) | 26 (17.7) | ||
| Under-staging | 5 (11.4) | 5 (4.9) | 10 (6.8) | ||
| Total | 44 (100) | 103 (100) | 147 (100) | ||
| Characteristics | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pathologic D3 LN Metastasis | p-Value | B | Exp (B) | 95% CI | p-Value | ||
| Negative | Positive | ||||||
| Cancer obstruction | 34 (17.4) | 10 (43.5) | 0.003 | ||||
| cT3-4 | 91 (46.7) | 18 (78.3) | 0.004 | ||||
| cN1-2 | 113 (57.9) | 22 (95.7) | <0.001 | ||||
| cN pericolic LN (+) | 113 (57.9) | 22 (95.7) | <0.001 | ||||
| cN D3 LN (+) | 26 (13.3) | 12 (52.2) | <0.001 | 2.478 | 11.917 | 3.507–40.492 | <0.001 |
| Lymphatic invasion | 28 (14.4) | 12 (52.2) | <0.001 | ||||
| Vascular invasion | 11 (5.6) | 7 (30.4) | <0.001 | 2.399 | 11.017 | 2.712–44.765 | <0.001 |
| Perineural invasion | 30 (15.4) | 13 (56.5) | <0.001 | 1.711 | 5.537 | 1.884–16.269 | 0.002 |
| Differentiation (moderate to poor) | 128 (65.6) | 21 (91.3) | 0.012 | 2.108 | 8.228 | 1.635–49.688 | 0.021 |
| FLNM | 74 (37.9) | 12 (52.2) | 0.187 | 1.950 | 7.028 | 2.081–23.737 | 0.002 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Son, G.M.; Kim, T.U.; Yun, M.S.; Kim, C.; Lee, I.Y.; Park, S.B.; Shin, D.-H.; Ha, G.W. Effect of Fluorescence Lymph Node Mapping on Improving Diagnostic Values of CT D3 Lymph Node Staging for Right-Sided Colon Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 3496. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203496
Son GM, Kim TU, Yun MS, Kim C, Lee IY, Park SB, Shin D-H, Ha GW. Effect of Fluorescence Lymph Node Mapping on Improving Diagnostic Values of CT D3 Lymph Node Staging for Right-Sided Colon Cancer. Cancers. 2024; 16(20):3496. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203496
Chicago/Turabian StyleSon, Gyung Mo, Tae Un Kim, Mi Sook Yun, ChangYeop Kim, In Young Lee, Su Bum Park, Dong-Hoon Shin, and Gi Won Ha. 2024. "Effect of Fluorescence Lymph Node Mapping on Improving Diagnostic Values of CT D3 Lymph Node Staging for Right-Sided Colon Cancer" Cancers 16, no. 20: 3496. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203496
APA StyleSon, G. M., Kim, T. U., Yun, M. S., Kim, C., Lee, I. Y., Park, S. B., Shin, D.-H., & Ha, G. W. (2024). Effect of Fluorescence Lymph Node Mapping on Improving Diagnostic Values of CT D3 Lymph Node Staging for Right-Sided Colon Cancer. Cancers, 16(20), 3496. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203496






