H3K27me3 Loss in Central Nervous System Tumors: Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Post-Translational Modifications and Targeted Therapy
3. Histone H3 Family
4. H3K27me3: Pathophysiology
5. Immunohistochemistry Interpretation and Assessment by Pathologists
6. Diffuse Midline Glioma, H3 K27-Altered
7. Posterior Fossa Ependymoma
8. Oligodendroglioma, IDH-Mutant and 1p/19q-Codeleted
9. Meningioma
10. Therapeutic Implications
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dawson, M.A.; Kouzarides, T. Cancer epigenetics: From mechanism to therapy. Cell 2012, 150, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, O.; Thakur, J. Molecular Complexes at Euchromatin, Heterochromatin and Centromeric Chromatin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutter, A.R.; Hayes, J.J. A brief review of nucleosome structure. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 2914–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fyodorov, D.V.; Zhou, B.R.; Skoultchi, A.I.; Bai, Y. Emerging roles of linker histones in regulating chromatin structure and function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szerlong, H.J.; Hansen, J.C. Nucleosome distribution and linker DNA: Connecting nuclear function to dynamic chromatin structure. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 89, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wu, J.; Guo, H.; Yao, W.; Li, S.; Lu, Y.; Jia, Y.; Liang, X.; Tang, J.; Zhang, H. Post-translational modifications of histones: Mechanisms, biological functions, and therapeutic targets. MedComm 2023, 4, e292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothbart, S.B.; Strahl, B.D. Interpreting the language of histone and DNA modifications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1839, 627–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramazi, S.; Zahiri, J. Posttranslational modifications in proteins: Resources, tools and prediction methods. Database 2021, 2021, baab012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramazi, S.; Allahverdi, A.; Zahiri, J. Evaluation of post-translational modifications in histone proteins: A review on histone modification defects in developmental and neurological disorders. J. Biosci. 2020, 45, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robusti, G.; Vai, A.; Bonaldi, T.; Noberini, R. Investigating pathological epigenetic aberrations by epi-proteomics. Clin. Epigenet. 2022, 14, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audia, J.E.; Campbell, R.M. Histone Modifications and Cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a019521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.C.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Liao, C.C.; Chong, L.W.; Lee, C.Y.; Yu, Y.L.; Chou, R.H. Targeting post-translational modifications of histones for cancer therapy. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2015, 61, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, A.; Jha, S. Epimutations and Their Effect on Chromatin Organization: Exciting Avenues for Cancer Treatment. Cancers 2022, 15, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martire, S.; Banaszynski, L.A. The roles of histone variants in fine-tuning chromatin organization and function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 522–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddaway, R.; Milos, S.; Coyaud, É.; Yun, H.Y.; Morcos, S.M.; Pajovic, S.; Campos, E.I.; Raught, B.; Hawkins, C. The in vivo Interaction Landscape of Histones H3.1 and H3.3. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2022, 21, 100411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, K.; Henikoff, S. The histone variant H3.3 marks active chromatin by replication-independent nucleosome assembly. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovato, M.; Patil, V.; Gehre, M.; Noh, K.M. Histone Variant H3.3 Mutations in Defining the Chromatin Function in Mammals. Cells 2020, 9, 2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Chen, Q.Y. Dynamic Activity of Histone H3-Specific Chaperone Complexes in Oncogenesis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 11, 806974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, P.W.; Elsaesser, S.J.; Noh, K.M.; Stadler, S.C.; Allis, C.D. Daxx is an H3.3-specific histone chaperone and cooperates with ATRX in replication-independent chromatin assembly at telomeres. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14075–14080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, A.D.; Banaszynski, L.A.; Noh, K.M.; Lewis, P.W.; Elsaesser, S.J.; Stadler, S.; Dewell, S.; Law, M.; Guo, X.; Li, X.; et al. Distinct factors control histone variant H3.3 localization at specific genomic regions. Cell 2010, 140, 678–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.P.; Ilter, D.; Low, V.; Rosenzweig, A.; Shen, Z.J.; Schild, T.; Rivas, M.A.; Er, E.E.; McNally, D.R.; Mutvei, A.P.; et al. Dynamic Incorporation of Histone H3 Variants into Chromatin Is Essential for Acquisition of Aggressive Traits and Metastatic Colonization. Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 402–417.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Liegro, C.M.; Schiera, G.; Schirò, G.; Di Liegro, I. Involvement of the H3.3 Histone Variant in the Epigenetic Regulation of Gene Expression in the Nervous System, in Both Physiological and Pathological Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogliotti, Y.S.; Ross, P.J. Mechanisms of Histone H3 Lysine 27 Trimethylation Remodeling During Early Mammalian Development. Epigenetics 2012, 7, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezponda, T.; Licht, J.D. Molecular Pathways: Deregulation of Histone H3 Lysine 27 Methylation in Cancer-Different Paths, Same Destination. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 5001–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, P.; Taube, J.H. Regulating Methylation at H3K27: A Trick or Treat for Cancer Cell Plasticity. Cancers 2020, 12, 2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, K.H.; Hennighausen, L. EZH2 Methyltransferase and H3K27 Methylation in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, K.; Kim, K.; Yi, S.J. The Role of Histone Modifications: From Neurodevelopment to Neurodiseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal-Pra, S.; Hodgkinson, C.P.; Mirotsou, M.; Kirste, I.; Dzau, V.J. Demethylation of H3K27 Is Essential for the Induction of Direct Cardiac Reprogramming by miR Combo. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 1403–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, S.R.; Butty, V.L.; Levine, S.S.; Boyer, L.A. Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 Regulates Lineage Fidelity During Embryonic Stem Cell Differentiation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Völkel, P.; Dupret, B.; Le Bourhis, X.; Angrand, P.O. Diverse Involvement of EZH2 in Cancer Epigenetics. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2015, 7, 175–193. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, Q.; Feng, Y.; Liu, T.; Guo, W. Epigenetic Regulation of Cancer Progression by EZH2: From Biological Insights to Therapeutic Potential. Biomark. Res. 2018, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Hung, M.C. Regulation and Role of EZH2 in Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 46, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eich, M.L.; Athar, M.; Ferguson, J.E., III; Varambally, S. EZH2-Targeted Therapies in Cancer: Hype or a Reality. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 5449–5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrenoire, E.; McRonald, F.; Halsall, J.A.; Page, P.; Illingworth, R.S.; Taylor, A.M.; Davison, V.; O’Neill, L.P.; Turner, B.M. Immunostaining of Modified Histones Defines High-Level Features of the Human Metaphase Epigenome. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colón-Caraballo, M.; Monteiro, J.B.; Flores, I. H3K27me3 is an Epigenetic Mark of Relevance in Endometriosis. Reprod. Sci. 2015, 22, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyskjaer, I.; Lindsay, D.; Tirabosco, R.; Steele, C.D.; Lombard, P.; Strobl, A.C.; Rocha, A.M.; Davies, C.; Ye, H.; Bekers, E.; et al. H3K27me3 Expression and Methylation Status in Histological Variants of Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumours. J. Pathol. 2020, 252, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, N.; Yoshida, A.; Ichikawa, H.; Mori, T.; Nakamura, M.; Kawai, A.; Hiraoka, N. Immunohistochemistry for Trimethylated H3K27 in the Diagnosis of Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumours. Histopathology 2017, 70, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, I.M.; Fletcher, C.D.; Hornick, J.L. Loss of H3K27 Trimethylation Distinguishes Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors from Histologic Mimics. Mod. Pathol. 2016, 29, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleven, A.H.; Sannaa, G.A.; Briaire-de Bruijn, I.; Ingram, D.R.; van de Rijn, M.; Rubin, B.P.; de Vries, M.W.; Watson, K.L.; Torres, K.E.; Wang, W.L.; et al. Loss of H3K27 Trimethylation is a Diagnostic Marker for Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors and an Indicator for an Inferior Survival. Mod. Pathol. 2016, 29, 582–590, Erratum in Mod. Pathol. 2016, 29, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro, G.; Broggi, G.; Angelico, G.; Puzzo, L.; Vecchio, G.M.; Virzì, V.; Salvatorelli, L.; Ruggieri, M. Practical Approach to Histological Diagnosis of Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors: An Update. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, I.M.; Minkovsky, A.; Hornick, J.L. H3K27me3 Immunohistochemistry Highlights the Inactivated X Chromosome (Xi) and Predicts Sex in Non-neoplastic Tissues. Histopathology 2016, 69, 702–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.; Disteche, C.M.; Berletch, J.B. X Inactivation and Escape: Epigenetic and Structural Features. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugita, S.; Aoyama, T.; Emori, M.; Kido, T.; Takenami, T.; Sakuraba, K.; Terai, K.; Sugawara, T.; Tsujiwaki, M.; Hasegawa, T. Assessment of H3K27me3 Immunohistochemistry and Combination of NF1 and p16 Deletions by Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization in the Differential Diagnosis of Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor and Its Histological Mimics. Diagn. Pathol. 2021, 16, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto-Granada, C.N.; Wiesner, T.; Messina, J.L.; Jungbluth, A.A.; Chi, P.; Antonescu, C.R. Loss of H3K27me3 Expression Is a Highly Sensitive Marker for Sporadic and Radiation-Induced MPNST. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallero, S.G.; Bertero, L.; Morana, G.; Sciortino, P.; Bertin, D.; Mussano, A.; Ricci, F.S.; Peretta, P.; Fagioli, F. Pediatric Diffuse Midline Glioma H3K27-Altered: A Complex Clinical and Biological Landscape Behind a Neatly Defined Tumor Type. Front. Oncol. 2023, 12, 1082062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto, T.; Aoki, M.; Hamasaki, M.; Abe, H.; Nonaka, M.; Inoue, T.; Nabeshima, K. Midline Glioma in Adults: Clinicopathological, Genetic, and Epigenetic Analysis. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2020, 60, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, E.V.; Rajaram, V.; Cai, C.; Oberle, R.J.; Martin, G.R.; Raisanen, J.M.; White, C.L.; Foong, C.; Mickey, B.E.; Pan, E.; et al. Adult Brainstem Gliomas with H3K27M Mutation: Radiology, Pathology, and Prognosis. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 77, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Sharie, S.; Abu Laban, D.; Al-Hussaini, M. Decoding Diffuse Midline Gliomas: A Comprehensive Review of Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Treatment. Cancers 2023, 15, 4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castel, D.; Kergrohen, T.; Tauziède-Espariat, A.; Mackay, A.; Ghermaoui, S.; Lechapt, E.; Pfister, S.M.; Kramm, C.M.; Boddaert, N.; Blauwblomme, T.; et al. Histone H3 Wild-Type DIPG/DMG Overexpressing EZHIP Extend the Spectrum of Diffuse Midline Gliomas with PRC2 Inhibition Beyond H3-K27M Mutation. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 139, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Gong, J.; Yu, T.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, M.; Nie, L.; Chen, X.; Yue, Q.; Liu, Y.; Mao, Q.; et al. Diffuse Midline Gliomas With Histone H3 K27M Mutation in Adults and Children: A Retrospective Series of 164 Cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2022, 46, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, H.J.; Ji, S.; Picca, A.; Sanson, M.; Garcia, M.; Snuderl, M.; Schüller, U.; Picart, T.; Ducray, F.; Green, A.L.; et al. Clinical, Genomic, and Epigenomic Analyses of H3K27M-Mutant Diffuse Midline Glioma Long-Term Survivors Reveal a Distinct Group of Tumors with MAPK Pathway Alterations. Acta Neuropathol. 2023, 146, 849–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donev, K.; Sundararajan, V.; Johnson, D.; Balan, J.; Chambers, M.; Paulson, V.A.; Scherpelz, K.P.; Abdullaev, Z.; Quezado, M.; Cimino, P.J.; et al. Diffuse Hemispheric Glioma With H3 p.K28M [K27M] Mutation: Unusual Non-Midline Presentation of Diffuse Midline Glioma, H3 K27M-Altered? J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2024, 83, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianno, F.; Giovannoni, I.; Cafferata, B.; Diomedi-Camassei, F.; Minasi, S.; Barresi, S.; Buttarelli, F.R.; Alesi, V.; Cardoni, A.; Antonelli, M.; et al. Paediatric-Type Diffuse High-Grade Gliomas in the 5th CNS WHO Classification. Pathologica 2022, 114, 422–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajtler, K.W.; Witt, H.; Sill, M.; Jones, D.T.; Hovestadt, V.; Kratochwil, F.; Wani, K.; Tatevossian, R.; Punchihewa, C.; Johann, P.; et al. Molecular Classification of Ependymal Tumors across All CNS Compartments, Histopathological Grades, and Age Groups. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 728–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnam, D.; Gupta, K.; Kiran, T.; Saraswati, A.; Salunke, P.; Madan, R.; Kumar, N.; Radotra, B.D. Molecular Subgrouping of Ependymoma across Three Anatomic Sites and Their Prognostic Implications. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2022, 39, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godfraind, C.; Kaczmarska, J.M.; Kocak, M.; Dalton, J.; Wright, K.D.; Sanford, R.A.; Boop, F.A.; Gajjar, A.; Merchant, T.E.; Ellison, D.W. Distinct Disease-Risk Groups in Pediatric Supratentorial and Posterior Fossa Ependymomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 124, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massimino, M.; Miceli, R.; Giangaspero, F.; Boschetti, L.; Modena, P.; Antonelli, M.; Ferroli, P.; Bertin, D.; Pecori, E.; Valentini, L.; et al. Final Results of the Second Prospective AIEOP Protocol for Pediatric Intracranial Ependymoma. Neuro-Oncology 2016, 18, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nambirajan, A.; Sharma, A.; Rajeshwari, M.; Boorgula, M.T.; Doddamani, R.; Garg, A.; Suri, V.; Sarkar, C.; Sharma, M.C. EZH2 Inhibitory Protein [EZ-HIP/Cxorf67] Expression Correlates Strongly with H3K27me3 Loss in Posterior Fossa Ependymomas and Is Mutually Exclusive with H3K27M Mutations. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2021, 38, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routman, D.M.; Raghunathan, A.; Giannini, C.; Mahajan, A.; Beltran, C.; Nagib, M.G.; Nageswara Rao, A.A.; Skrypek, M.M.; Laack, N.N.I. Anaplastic Ependymoma and Posterior Fossa Grouping in a Patient with H3K27ME3 Loss of Expression but Chromosomal Imbalance. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 4, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Wu, T.; Wang, L.M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.W.; Zhang, S.; Li, P.; Wang, B.; Luo, L.; et al. Survival and Prognostic Factors of Adult Intracranial Ependymoma: A Single-Institutional Analysis of 236 Patients. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2021, 45, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.R.; Kuo, J.S. Reduced H3K27me3 Is a New Epigenetic Biomarker for Pediatric Posterior Fossa Ependymomas. Neurosurgery 2017, 81, N7–N8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Han, Z.; Kang, P.; Zhang, H.; Liao, Z.; Li, C.; Gong, J.; Liu, W.; Tian, Y. Prognostic Value of H3K27me3 in Children with Ependymoma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2020, 67, e28121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panwalkar, P.; Clark, J.; Ramaswamy, V.; Hawes, D.; Yang, F.; Dunham, C.; Yip, S.; Hukin, J.; Sun, Y.; Schipper, M.J.; et al. Immunohistochemical Analysis of H3K27me3 Demonstrates Global Reduction in Group-A Childhood Posterior Fossa Ependymoma and Is a Powerful Predictor of Outcome. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 134, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayliss, J.; Mukherjee, P.; Lu, C.; Jain, S.U.; Chung, C.; Martinez, D.; Sabari, B.; Margol, A.S.; Panwalkar, P.; Parolia, A.; et al. Lowered H3K27me3 and DNA Hypomethylation Define Poorly Prognostic Pediatric Posterior Fossa Ependymomas. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 366ra161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sousa, G.R.; Lira, R.C.P.; de Almeida Magalhães, T.; da Silva, K.R.; Nagano, L.F.P.; Saggioro, F.P.; Baroni, M.; Marie, S.K.N.; Oba-Shinjo, S.M.; Brandelise, S.; et al. A Coordinated Approach for the Assessment of Molecular Subgroups in Pediatric Ependymomas Using Low-Cost Methods. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 99, 1101–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, R.J.; Ghasemi, D.R.; Andreiuolo, F.; Zschernack, V.; Espariat, A.T.; Buttarelli, F.R.; Giangaspero, F.; Grill, J.; Haberler, C.; Paine, S.M.; et al. Optimizing Biomarkers for Accurate Ependymoma Diagnosis, Prognostication, and Stratification within International Clinical Trials: A BIOMECA Study. Neuro-Oncology 2023, 25, 1871–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritzmann, T.A.; Chapman, R.J.; Kilday, J.P.; Thorp, N.; Modena, P.; Dineen, R.A.; Macarthur, D.; Mallucci, C.; Jaspan, T.; Pajtler, K.W.; et al. SIOP Ependymoma I: Final Results, Long-Term Follow-Up, and Molecular Analysis of the Trial Cohort-A BIOMECA Consortium Study. Neuro-Oncology 2022, 24, 936–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübner, J.M.; Müller, T.; Papageorgiou, D.N.; Mauermann, M.; Krijgsveld, J.; Russell, R.B.; Ellison, D.W.; Pfister, S.M.; Pajtler, K.W.; Kool, M. EZHIP/CXorf67 Mimics K27M Mutated Oncohistones and Functions as an Intrinsic Inhibitor of PRC2 Function in Aggressive Posterior Fossa Ependymoma. Neuro-Oncology 2019, 21, 878–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.U.; Do, T.J.; Lund, P.J.; Rashoff, A.Q.; Diehl, K.L.; Cieslik, M.; Bajic, A.; Juretic, N.; Deshmukh, S.; Venneti, S.; et al. PFA Ependymoma-Associated Protein EZHIP Inhibits PRC2 Activity Through a H3 K27M-Like Mechanism. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michealraj, K.A.; Kumar, S.A.; Kim, L.J.; Cavalli, F.M.; Przelicki, D.; Wojcik, J.B.; Delaidelli, A.; Bajic, A.; Saulnier, O.; MacLeod, G.; et al. Metabolic Regulation of the Epigenome Drives Lethal Infantile Ependymoma. Cell 2020, 181, 1329–1345.e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanrıkulu, B.; Danyeli, A.E.; Özek, M.M. Is H3K27me3 Status Really a Strong Prognostic Indicator for Pediatric Posterior Fossa Ependymomas? A Single Surgeon, Single Center Experience. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2020, 36, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.D.S.D.; Torres Soares, C.; Dastoli, P.A.; Mendonça Nicácio, J.; de Seixas Alves, M.T.; Chen, M.J.; Cappellano, A.M.; Saba da Silva, N.; Cavalheiro, S. Survival Analysis and Prognostic Factors in Posterior Fossa Ependymomas in Children and Adolescents. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2023, 32, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jünger, S.T.; Andreiuolo, F.; Mynarek, M.; Dörner, E.; Zur Mühlen, A.; Rutkowski, S.; von Bueren, A.O.; Pietsch, T. Ependymomas in Infancy: Underlying Genetic Alterations, Histological Features, and Clinical Outcome. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2020, 36, 2693–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, T.R.; Wen, P.Y.; Lang-Orsini, M.; Chukwueke, U.N. World Health Organization 2021 Classification of Central Nervous System Tumors and Implications for Therapy for Adult-Type Gliomas: A Review. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 1493–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipski, K.; Braun, Y.; Zinke, J.; Roller, B.; Baumgarten, P.; Wagner, M.; Senft, C.; Zeiner, P.S.; Ronellenfitsch, M.W.; Steinbach, J.P.; et al. Lack of H3K27 Trimethylation Is Associated with 1p/19q Codeletion in Diffuse Gliomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 138, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, C.; Felix, M.; Weiss, T.; Herold-Mende, C.; Zhang, F.; Kockmann, T.; Sahm, F.; Aebersold, R.; Von Deimling, A.; Reuss, D.E. Histone Epiproteomic Profiling Distinguishes Oligodendroglioma, IDH-Mutant and 1p/19q Co-Deleted from IDH-Mutant Astrocytoma and Reveals Less Trimethylation of H3K27 in Oligodendrogliomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 139, 211–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habiba, U.; Sugino, H.; Yordanova, R.; Ise, K.; Tanei, Z.I.; Ishida, Y.; Tanikawa, S.; Terasaka, S.; Sato, K.I.; Kamoshima, Y.; et al. Loss of H3K27 Trimethylation Is Frequent in IDH1-R132H but Not in Non-Canonical IDH1/2 Mutated and 1p/19q Codeleted Oligodendroglioma: A Japanese Cohort Study. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2021, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekmezci, M.; Phillips, J.J.; Dirilenoglu, F.; Atasever-Rezanko, T.; Tihan, T.; Solomon, D.; Bollen, A.; Perry, A. Loss of H3K27 Trimethylation by Immunohistochemistry Is Frequent in Oligodendroglioma, IDH-Mutant and 1p/19q-Codeleted, but Is Neither a Sensitive Nor a Specific Marker. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 139, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitahama, K.; Iijima, S.; Sumiishi, A.; Hayashi, A.; Nagahama, K.; Saito, K.; Sasaki, N.; Kobayashi, K.; Shimizu, S.; Nagane, M.; et al. Reduced H3K27me3 Levels in Diffuse Gliomas: Association with 1p/19q Codeletion and Difference from H3K27me3 Loss in Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2021, 38, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammendola, S.; Caldonazzi, N.; Simbolo, M.; Piredda, M.L.; Brunelli, M.; Poliani, P.L.; Pinna, G.; Sala, F.; Ghimenton, C.; Scarpa, A.; et al. H3K27me3 Immunostaining Is Diagnostic and Prognostic in Diffuse Gliomas with Oligodendroglial or Mixed Oligoastrocytic Morphology. Virchows Arch. 2021, 479, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Cioffi, G.; Gittleman, H.; Patil, N.; Waite, K.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2012–2016. Neuro-Oncology 2019, 21, v1–v100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggio, I.; Franceschi, E.; Tosoni, A.; Nunno, V.D.; Gatto, L.; Lodi, R.; Brandes, A.A. Meningioma: Not Always a Benign Tumor. A Review of Advances in the Treatment of Meningiomas. CNS Oncol. 2021, 10, CNS72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauchotte, G.; Peyre, M.; Pouget, C.; Cazals-Hatem, D.; Polivka, M.; Rech, F.; Varlet, P.; Loiseau, H.; Lacomme, S.; Mokhtari, K.; et al. Prognostic Value of Histopathological Features and Loss of H3K27me3 Immunolabeling in Anaplastic Meningioma: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 79, 754–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, A.D.; Brøchner, C.B.; Mirian, C.; Haslund-Vinding, J.; Bartek, J., Jr.; Ekström, T.J.; Poulsen, F.R.; Scheie, D.; Mathiesen, T. Loss of H3K27me3 in WHO Grade 3 Meningioma. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2022, 39, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, L.M.; Hielscher, T.; Liechty, B.; Silverman, J.; Zagzag, D.; Sen, R.; Wu, P.; Golfinos, J.G.; Reuss, D.; Neidert, M.C.; et al. Loss of Histone H3K27me3 Identifies a Subset of Meningiomas with Increased Risk of Recurrence. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 135, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behling, F.; Fodi, C.; Gepfner-Tuma, I.; Kaltenbach, K.; Renovanz, M.; Paulsen, F.; Skardelly, M.; Honegger, J.; Tatagiba, M.; International Consortium on Meningiomas; et al. H3K27me3 Loss Indicates an Increased Risk of Recurrence in the Tübingen Meningioma Cohort. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cello, G.; Patel, R.V.; McMahon, J.T.; Santagata, S.; Bi, W.L. Impact of H3K27 Trimethylation Loss in Meningiomas: A Meta-Analysis. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2023, 11, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, V.M.; Luther, E.M.; Eichberg, D.G.; Morell, A.A.; Shah, A.H.; Komotar, R.J.; Ivan, M.E. The Emerging Relevance of H3K27 Trimethylation Loss in Meningioma: A Systematic Review of Recurrence and Overall Survival with Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2022, 163, 87–95.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzochi, L.L.; Cuzziol, C.I.; Nascimento Filho, C.H.V.D.; Dos Santos, J.A.; Castanhole-Nunes, M.M.U.; Pavarino, É.C.; Guerra, E.N.S.; Goloni-Bertollo, E.M. Use of histone methyltransferase inhibitors in cancer treatment: A systematic review. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 944, 175590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrillaga-Romany, I.; Gardner, S.L.; Odia, Y.; Aguilera, D.; Allen, J.E.; Batchelor, T.; Butowski, N.; Chen, C.; Cloughesy, T.; Cluster, A.; et al. ONC201 (Dordaviprone) in Recurrent H3 K27M-Mutant Diffuse Midline Glioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 1542–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odia, Y.; Koschmann, C.; Vitanza, N.A.; De Blank, P.; Aguilera, D.; Allen, J.; Daghistani, D.; Hall, M.; Khatib, Z.; Kline, C.; et al. Safety and pharmacokinetics of ONC201 (dordaviprone) administered two consecutive days per week in pediatric patients with H3 K27M-mutant glioma. Neuro-Oncology 2024, 26, S155–S164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, E.R.; Persson, M.L.; Fish, C.J.; Findlay, I.J.; Mueller, S.; Nazarian, J.; Hulleman, E.; van der Lugt, J.; Duchatel, R.J.; Dun, M.D. A review of current therapeutics targeting the mitochondrial protease ClpP in diffuse midline glioma, H3 K27-altered. Neuro-Oncology 2024, 26, S136–S154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, L.; Lindsay, H.; Kogiso, M.; Du, Y.; Braun, F.K.; Zhang, H.; Guo, L.; Zhao, S.; Injac, S.G.; Baxter, P.A.; et al. Evaluation of an EZH2 inhibitor in patient-derived orthotopic xenograft models of pediatric brain tumors alone and in combination with chemo- and radiation therapies. Lab. Investig. 2022, 102, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Wang, S.A.; Yang, W.B.; Lin, H.Y.; Lai, M.J.; Chen, H.C.; Kao, T.Y.; Hsu, F.L.; Nepali, K.; Hsu, T.I.; et al. First-in-Class Dual EZH2-HSP90 Inhibitor Eliciting Striking Antiglioblastoma Activity In Vitro and In Vivo. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 67, 2963–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahal, F.; Capdevielle, C.; Rousseau, B.; Izotte, J.; Dupuy, J.W.; Cappellen, D.; Chotard, G.; Ménard, M.; Charpentier, J.; Jecko, V.; et al. An EZH2 blocker sensitizes histone mutated diffuse midline glioma to cholesterol metabolism inhibitors through an off-target effect. Neurooncol. Adv. 2022, 4, vdac018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Marastoni, E.; Ammendola, S.; Rossi, S.; Giovannoni, I.; Broggi, G.; Masotto, B.; Feletti, A.; Barresi, V. H3 K27M Mutation in Rosette-Forming Glioneuronal Tumors: A Potential Diagnostic Pitfall. Virchows Arch. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, K.; Shim, Y.M.; Kim, E.E.; Kim, S.K.; Phi, J.H.; Park, C.K.; Choi, S.H.; Park, S.H. Epigenetic Alteration of H3K27me3 as a Possible Oncogenic Mechanism of Central Neurocytoma. Lab. Investig. 2023, 103, 100159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
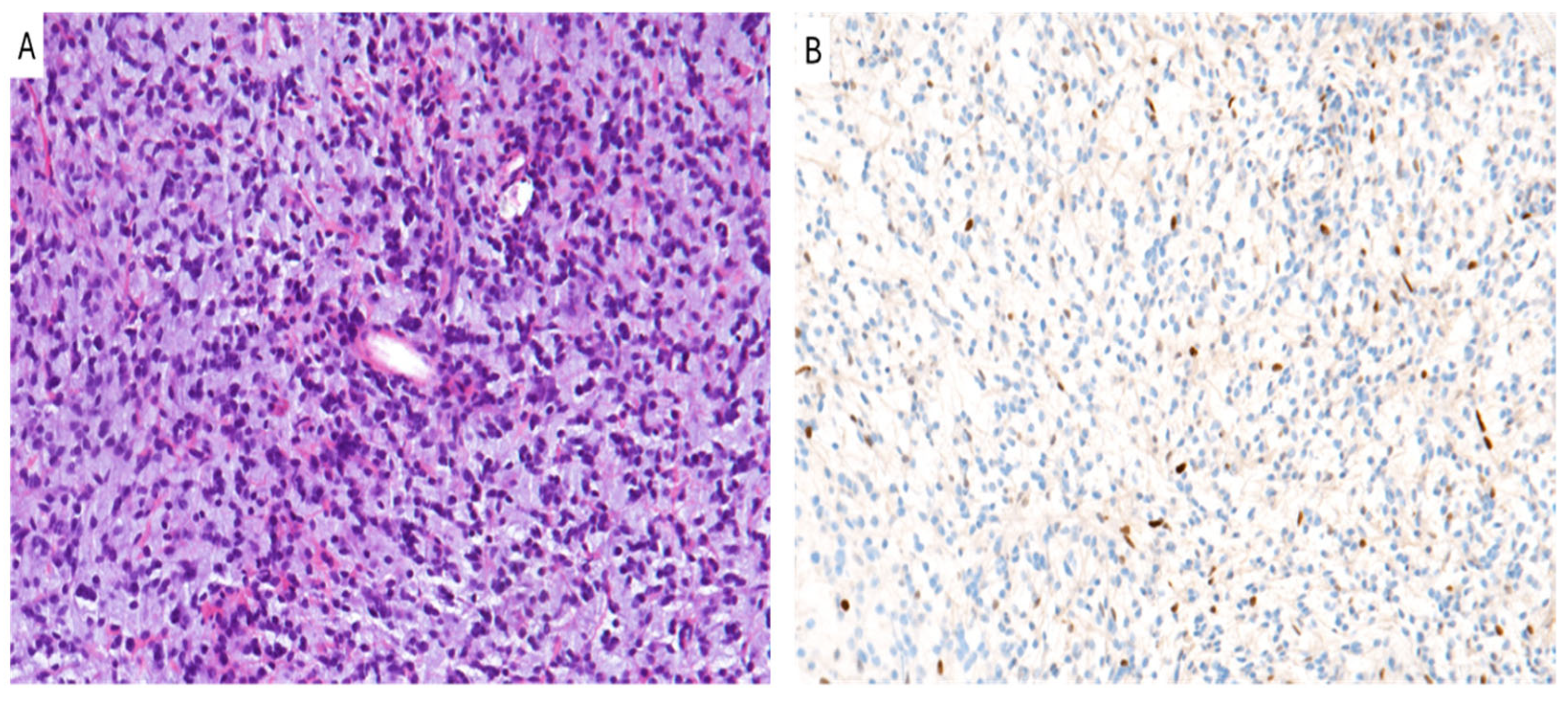
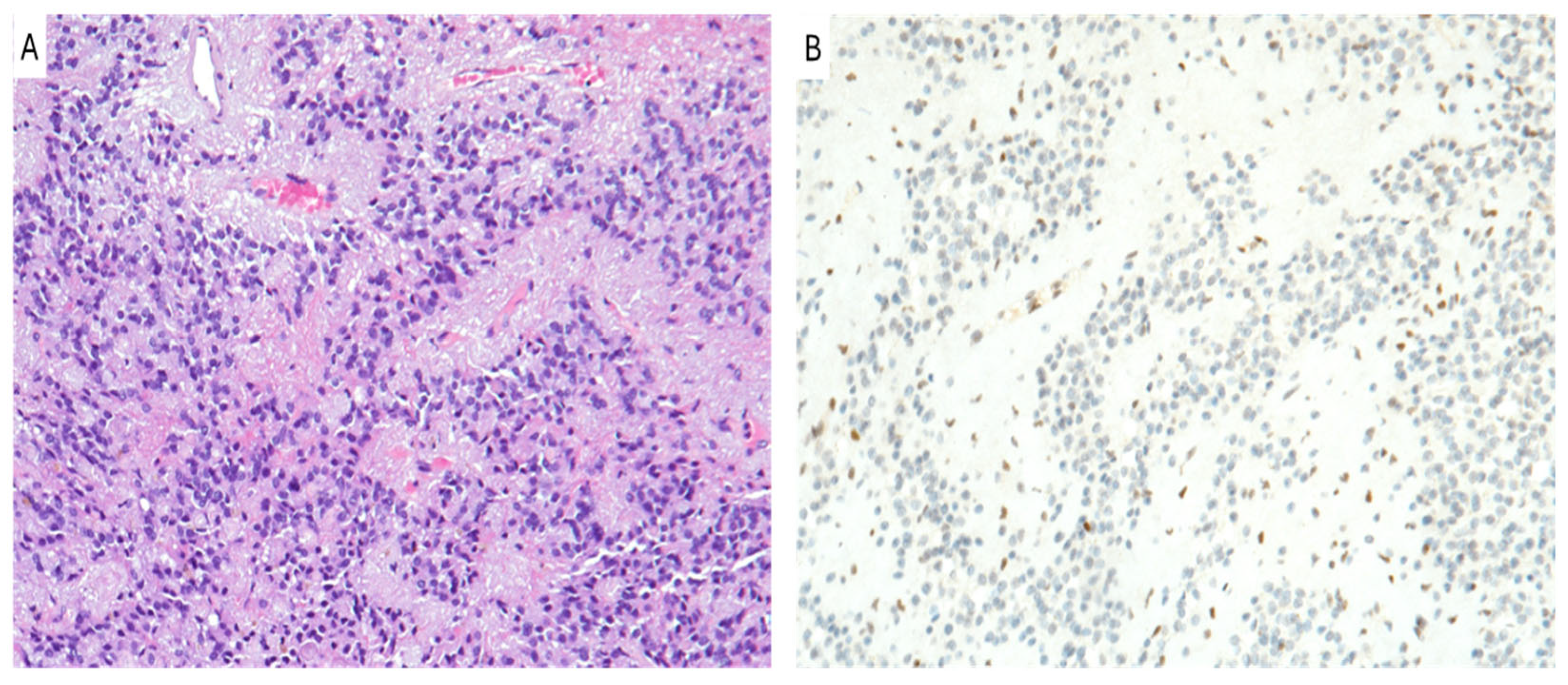
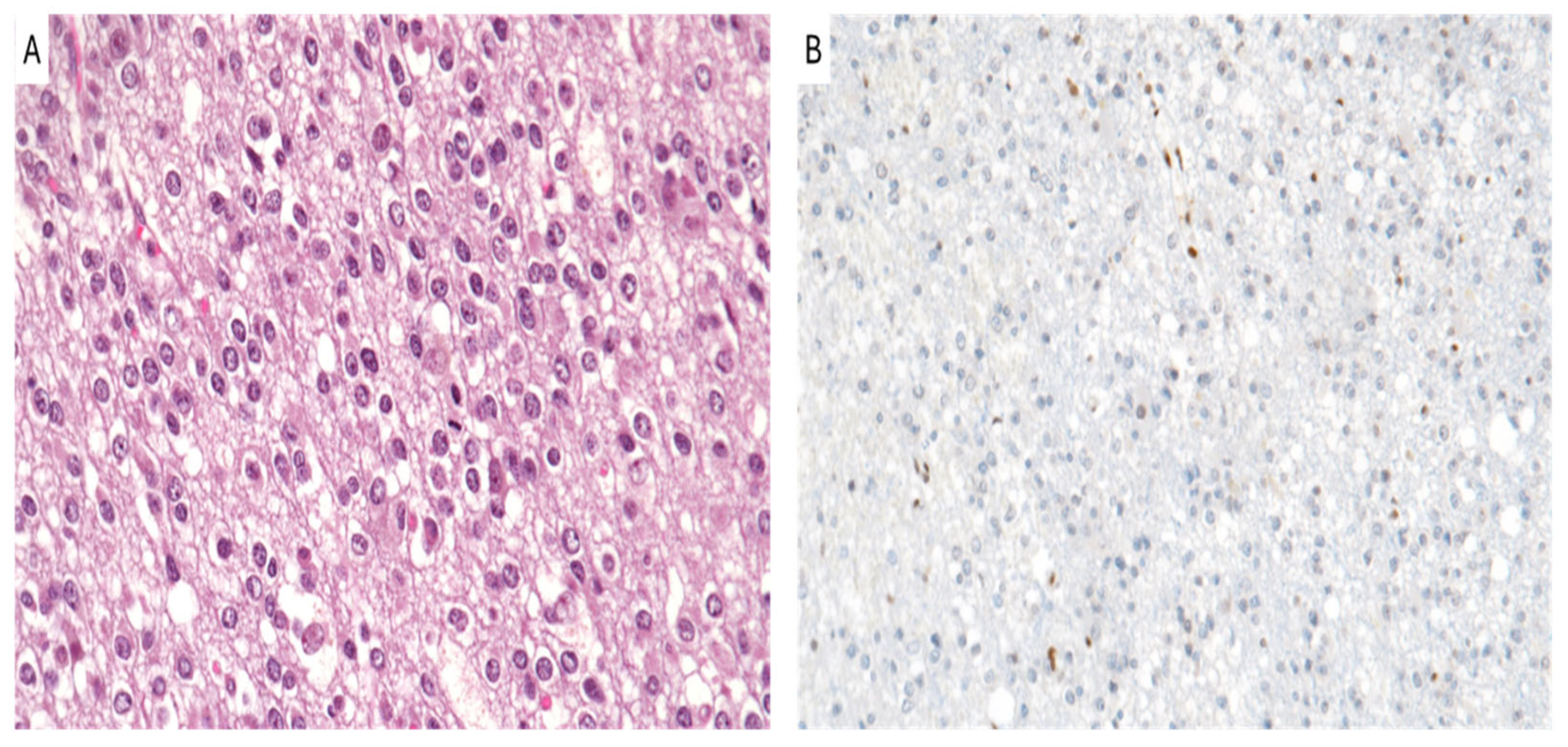
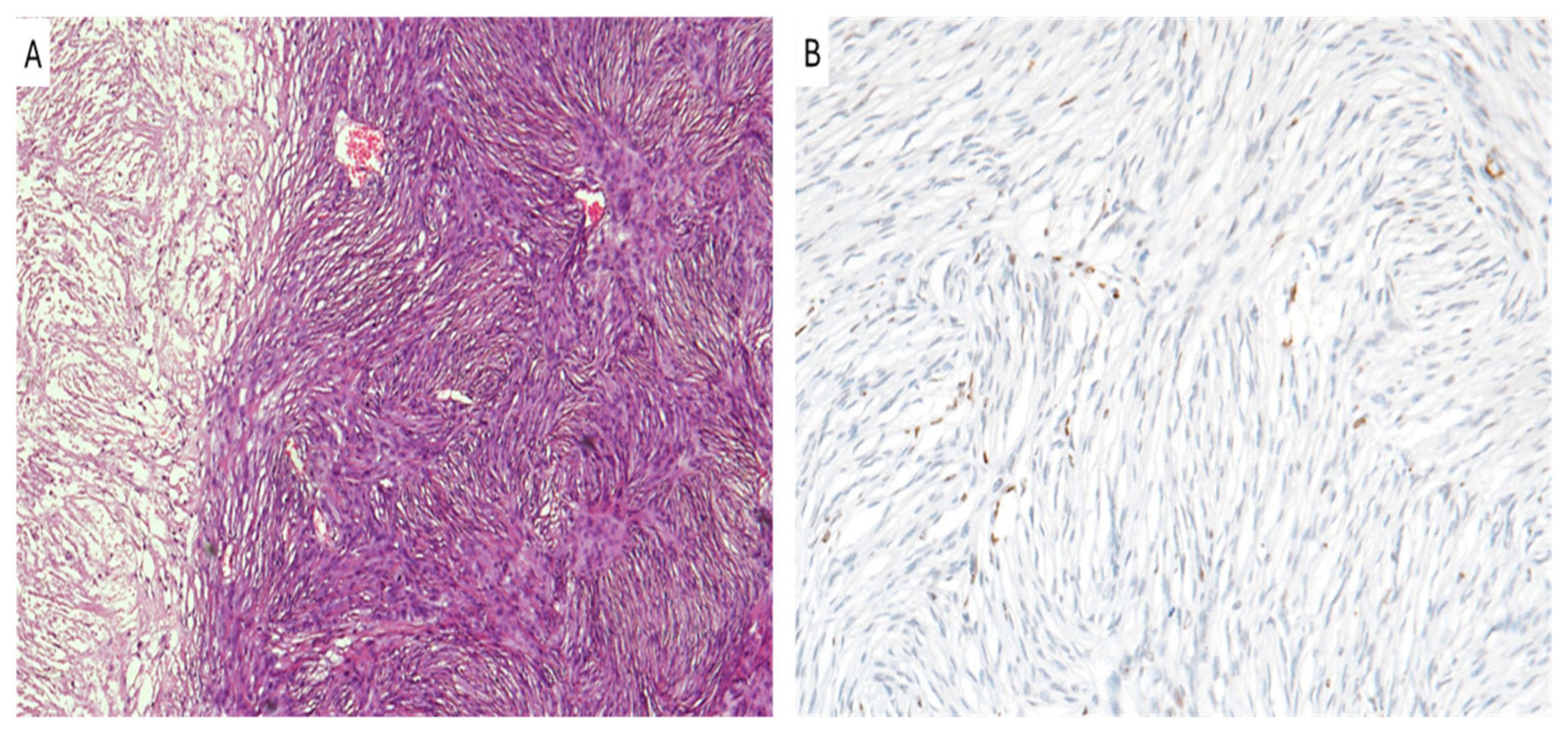
| Tumor Type | H3K27me3 Status | Prognosis | Therapy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diffuse midline glioma, H3 K27-altered | Loss of H3K27me3 (H3K27M) | Poor prognosis, short survival | EZH2/DOT1L inhibitors, Radiotherapy |
| Posterior Fossa Ependymoma | Loss of H3K27me3 in Group A (PFEA) | Poor prognosis in Group A (PFEA), better in Group B (PFEB) | Surgery, Radiotherapy, possible Chemotherapy |
| Oligodendroglioma, IDH-mutant and 1p19q-codeleted | Retained or loss of H3K27me3 | Depends on 1p/19q co-deletion; worse with H3K27me3 loss | Chemotherapy, Molecular targeted Therapy |
| Meningioma (grade 2 and 3) | Loss of H3K27me3 | Higher recurrence, worse prognosis | Epigenetic therapies, Radiotherapy |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Angelico, G.; Mazzucchelli, M.; Attanasio, G.; Tinnirello, G.; Farina, J.; Zanelli, M.; Palicelli, A.; Bisagni, A.; Barbagallo, G.M.V.; Certo, F.; et al. H3K27me3 Loss in Central Nervous System Tumors: Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Implications. Cancers 2024, 16, 3451. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203451
Angelico G, Mazzucchelli M, Attanasio G, Tinnirello G, Farina J, Zanelli M, Palicelli A, Bisagni A, Barbagallo GMV, Certo F, et al. H3K27me3 Loss in Central Nervous System Tumors: Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Implications. Cancers. 2024; 16(20):3451. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203451
Chicago/Turabian StyleAngelico, Giuseppe, Manuel Mazzucchelli, Giulio Attanasio, Giordana Tinnirello, Jessica Farina, Magda Zanelli, Andrea Palicelli, Alessandra Bisagni, Giuseppe Maria Vincenzo Barbagallo, Francesco Certo, and et al. 2024. "H3K27me3 Loss in Central Nervous System Tumors: Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Implications" Cancers 16, no. 20: 3451. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203451
APA StyleAngelico, G., Mazzucchelli, M., Attanasio, G., Tinnirello, G., Farina, J., Zanelli, M., Palicelli, A., Bisagni, A., Barbagallo, G. M. V., Certo, F., Zizzo, M., Koufopoulos, N., Magro, G., Caltabiano, R., & Broggi, G. (2024). H3K27me3 Loss in Central Nervous System Tumors: Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Implications. Cancers, 16(20), 3451. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16203451









