Advancing Esophageal Cancer Treatment: Immunotherapy in Neoadjuvant and Adjuvant Settings
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
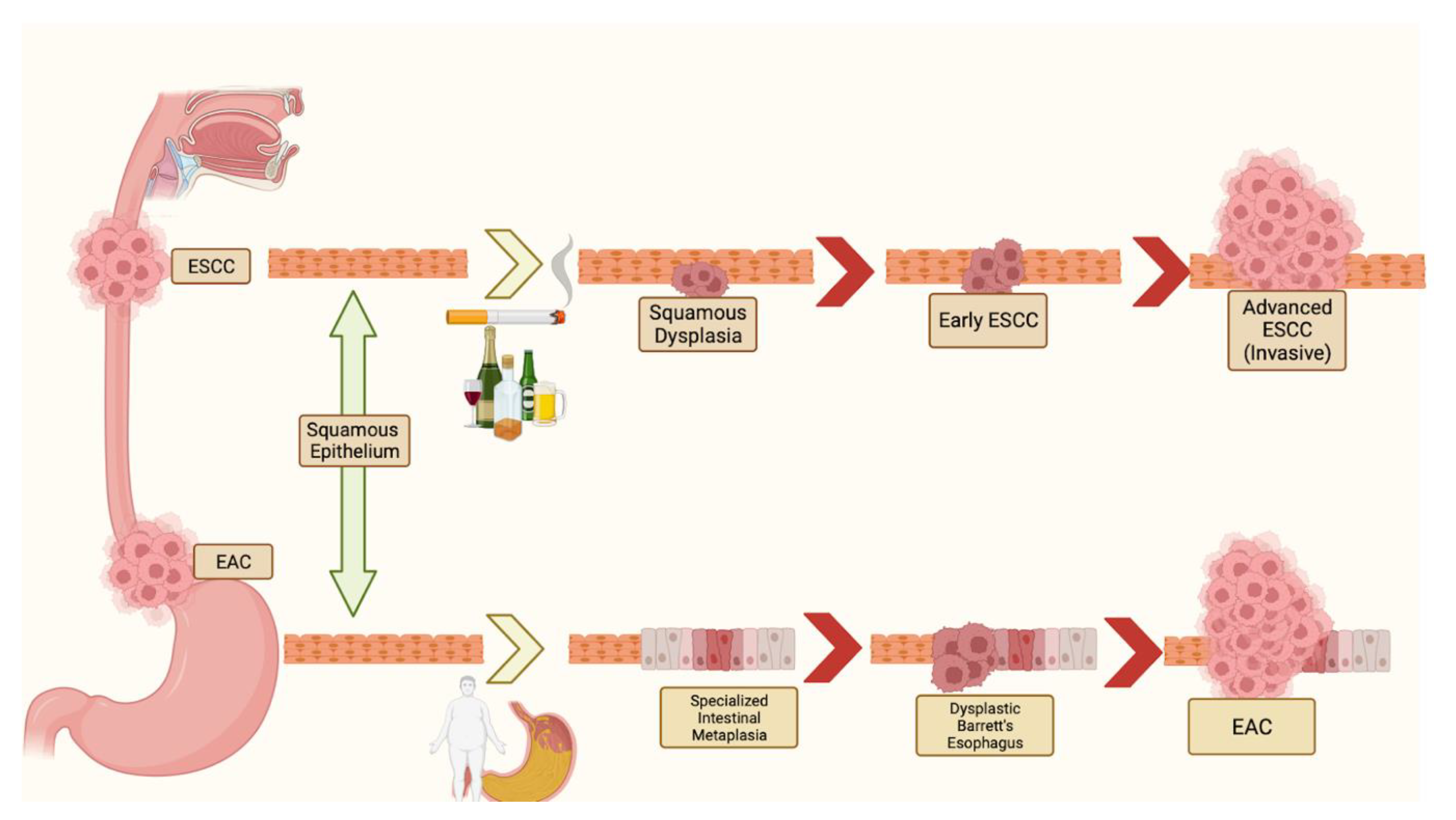
1. Introduction
2. Immunotherapy and the Tumor Microenvironment in EC
3. The Relationship between Immunotherapy and Chemoradiation
4. Immunotherapy in the Neoadjuvant Setting
5. Immunotherapy in the Adjuvant Setting
5.1. Adjuvant Immunotherapy and ESCC
5.2. Adjuvant Immunotherapy and EAC
6. Biomarkers of Prognostic Value
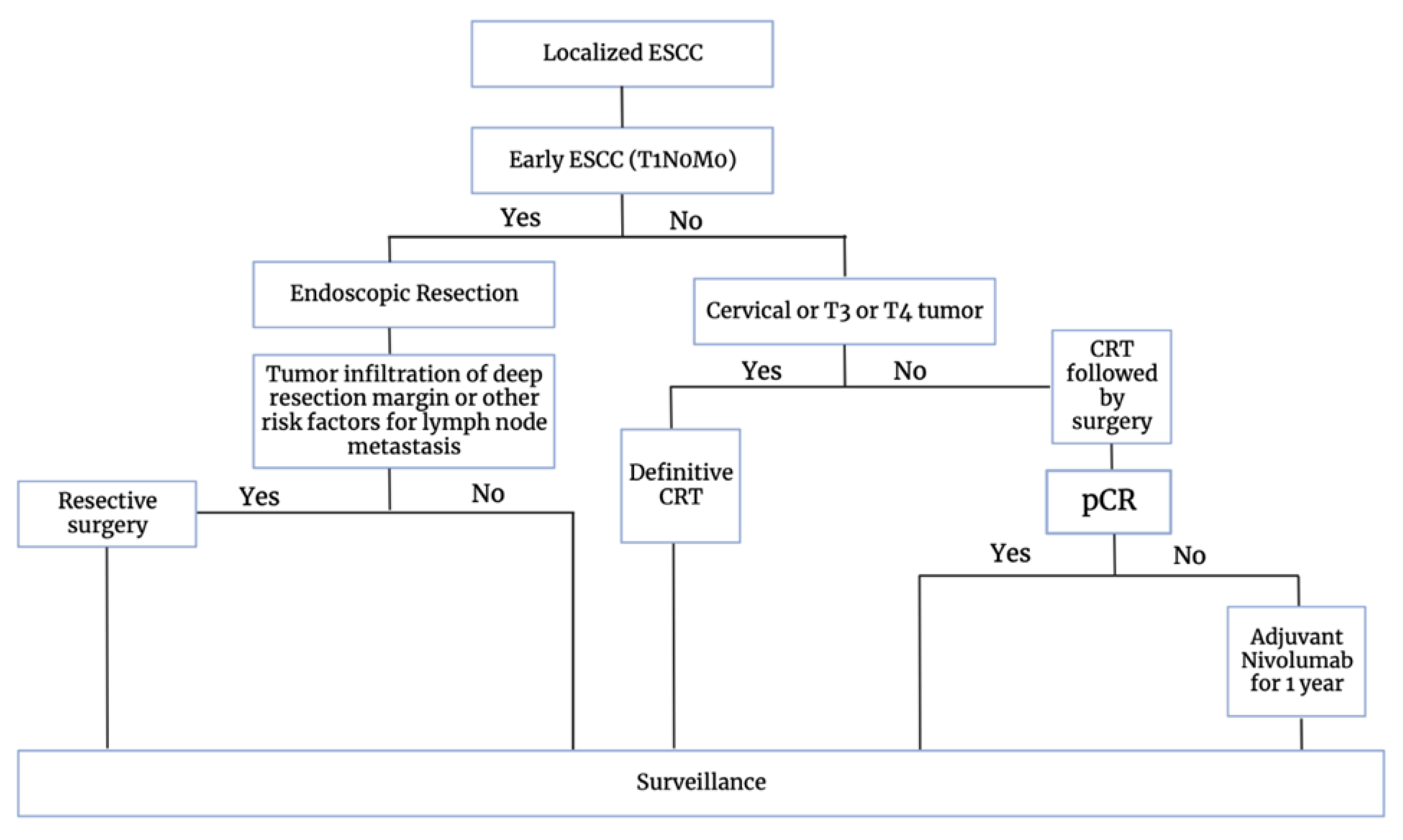
7. Current Treatment Strategies
ESMO 2023
8. Future Directions in the Management of EC
8.1. Next-Generation Checkpoint Inhibition
8.2. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte (TIL) Therapy
8.3. Personalized Treatment Strategies
8.4. CAR-T Cell Therapies
8.5. Cancer Vaccines
9. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EC | Esophageal Cancer |
| ESCC | Esophageal Squamous Cell Cancer |
| EAC | Esophageal Adenocarcinoma |
| CRT | Chemoradiation |
| LAEC | Locally Advanced Esophageal Cancer |
| ICI | Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors |
| GERD | Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| PD-1 | Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 |
| PD-L1 | Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1 |
| TME | Tumor Microenvironment |
| HER2 | Human Epidermal Growth Factor 2 |
References
- Wang, R.; Liu, S.; Chen, B.; Xi, M. Recent Advances in Combination of Immunotherapy and Chemoradiotherapy for Locally Advanced Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statistics for Esophageal Cancer | Esophageal Cancer Stats. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/esophagus-cancer/about/key-statistics.html (accessed on 23 November 2023).
- Uhlenhopp, D.J.; Then, E.O.; Sunkara, T.; Gaduputi, V. Epidemiology of esophageal cancer: Update in global trends, etiology and risk factors. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Cao, S.; Dong, X.; Rao, S.; Cai, K. Understanding Esophageal Cancer: The Challenges and Opportunities for the Next Decade. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, M.; Roshandel, G.; McCormack, V.; Malekzadeh, R. Current Status and Future Prospects for Esophageal Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tella, S.H.; Mara, K.; Chakrabarti, S.; Jin, Z.; Mahipal, A. A glimpse into the future of esophageal carcinoma in the United States: Predicting the future incidence until 2040 based on the current epidemiological data. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2023, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerner, T.; Carr, R.A.; Hsu, M.; Michel, A.; Tan, K.S.; Vos, E.; Sihag, S.; Bains, M.S.; Ku, G.Y.; Wu, A.J.; et al. Incidence and management of esophageal cancer recurrence to regional lymph nodes after curative esophagectomy. Int. J. Cancer. 2023, 152, 2109–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Han, H.; Wang, Z.; Shi, L.; Yang, M.; Qin, Y. Targeting the Microenvironment in Esophageal Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 684966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davern, M.; Donlon, N.E.; Power, R.; Hayes, C.; King, R.; Dunne, M.R.; Reynolds, J.V. The tumour immune microenvironment in oesophageal cancer. Br. J. Cancer. 2021, 125, 479–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Lu, M.; Xu, B.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, J.; Wu, C. B7-H1 expression associates with tumor invasion and predicts patient’s survival in human esophageal cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 6015–6023. [Google Scholar]
- Ohigashi, Y.; Sho, M.; Yamada, Y.; Tsurui, Y.; Hamada, K.; Ikeda, N.; Mizuno, T.; Yoriki, R.; Kashizuka, H.; Yane, K.; et al. Clinical significance of programmed death-1 ligand-1 and programmed death-1 ligand-2 expression in human esophageal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 2947–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchbinder, E.I.; Desai, A. CTLA-4 and PD-1 Pathways. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 39, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, Z.; Liu, Q.; Ai, D.; Chen, K.; Mariamidze, E.; Sumon, M.A.; Devnani, B.; Pihlak, R.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, K. Radiotherapy for Advanced Esophageal Cancer: From Palliation to Curation. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2023, 24, 1568–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, H.; Deng, W.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Kim, B.Y.S.; Story, M.D.; Jiang, W. The reciprocity between radiotherapy and cancer immunotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 1709–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, F.G.; Bourhis, J.; Coukos, G. Radiotherapy combination opportunities leveraging immunity for the next oncology practice. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yu, R.; Liu, Y. Combine radiotherapy and immunotherapy in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2023, 190, 104115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Hu, Y.; Lin, G.; Chen, C.; Li, H. Radiotherapy combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors in locally advanced/metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Clinical trials, efficacy and future directions. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Tu, C.; Yang, P.; Li, J.; Kepp, O.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, T.; et al. Carbon ion radiotherapy triggers immunogenic cell death and sensitizes melanoma to anti-PD-1 therapy in mice. OncoImmunology. 2022, 11, 2057892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, D.; Yu, J. Radiotherapy combined with immunotherapy: The dawn of cancer treatment. Sig Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Leng, X.; Mao, T.; Luo, X.; Zhou, L.; Yan, J.; Peng, L.; Fang, Q.; Liu, G.; Wei, X.; et al. Toripalimab Plus Paclitaxel and Carboplatin as Neoadjuvant Therapy in Locally Advanced Resectable Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Oncologist 2022, 27, e18–e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhao, S.; Zheng, Y.; Han, Y.; Chen, X.; Cheng, Z.; Wu, Y.; Feng, X.; Qi, W.; Chen, K.; et al. Preoperative pembrolizumab combined with chemoradiotherapy for oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma (PALACE-1). Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 144, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Ende, T.; de Clercq, N.C.; van Berge Henegouwen, M.I.; Gisbertz, S.S.; Geijsen, E.D.; Verhoeven, R.H.A.; Meijer, S.L.; Schokker, S.; Dings, M.P.G.; Bergman, J.J.G.H.M.; et al. Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy Combined with Atezolizumab for Resectable Esophageal Adenocarcinoma: A Single-arm Phase II Feasibility Trial (PERFECT). Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 3351–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, H.; Wang, T.; Luo, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Tong, L.; Dong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Valmasoni, M.; Kidane, B.; et al. A multicenter single-arm trial of sintilimab in combination with chemotherapy for neoadjuvant treatment of resectable esophageal cancer (SIN-ICE study). Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, D.; Chen, Q.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Tao, K.; Jiang, Y. The safety and efficacy of neoadjuvant PD-1 inhibitor with chemotherapy for locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2021, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Zhou, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, T.; Feng, S.; Ma, X. Neoadjuvant camrelizumab plus chemotherapy in treating locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients: A pilot study. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 19, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Hong, Z.-N.; Xie, S.; Lin, W.; Lin, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yang, X.; Lin, Z.; Lin, J.; Kang, M. Neoadjuvant sintilimab plus chemotherapy for locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A single-arm, single-center, phase 2 trial (ESONICT-1). Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Shao, C.; Pan, M.; Liu, H.; Dong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, L.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Neoadjuvant Pembrolizumab and Chemotherapy in Resectable Esophageal Cancer: An Open-Label, Single-Arm Study (PEN-ICE). Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 849984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Duan, H.; Ni, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Qi, H.; Gong, L.; Liu, H.; Tian, F.; Lu, Q.; et al. Tislelizumab combined with chemotherapy as neoadjuvant therapy for surgically resectable esophageal cancer: A prospective, single-arm, phase II study (TD-NICE). Int. J. Surg. 2022, 103, 106680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Lu, J.; Zhang, P.; Hong, Z.-N.; Kang, M. Toripalimab combined with docetaxel and cisplatin neoadjuvant therapy for locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A single-center, single-arm clinical trial (ESONICT-2). J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2022, 13, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, J.; Lin, W.; Shao, D.; Depypere, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Cui, F.; Du, Z.; Zeng, Y.; et al. Neoadjuvant camrelizumab plus chemotherapy for resectable, locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (NIC-ESCC2019): A multicenter, phase 2 study. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 151, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.; Zhao, L.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, B.; Liu, X.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, B.; Yang, Y.; Shang, Y.; et al. The Sequence of Chemotherapy and Toripalimab Might Influence the Efficacy of Neoadjuvant Chemoimmunotherapy in Locally Advanced Esophageal Squamous Cell Cancer-A Phase II Study. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 772450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Xing, X.; Yeung, S.-C.J.; Wang, S.; Chen, W.; Bao, Y.; Wang, F.; Feng, S.; Peng, F.; Wang, X.; et al. Neoadjuvant programmed cell death 1 blockade combined with chemotherapy for resectable esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e003497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Fu, X.; Cai, X.; Li, H.; Zhu, L.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.; et al. Multicenter, single-arm, phase II trial of camrelizumab and chemotherapy as neoadjuvant treatment for locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e004291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Qin, J.; Fang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Fang, Y.; Qu, D.; Zhang, R.; Zheng, Q.; et al. Phase Ib trial of camrelizumab combined with chemotherapy and apatinib for neoadjuvant treatment of locally advanced thoracic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Natl. Cancer Cent. 2022, 2, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hagen, P.; Hulshof, M.C.C.M.; van Lanschot, J.J.B.; Steyerberg, E.W.; van Henegouwen, M.I.B.; Wijnhoven, B.P.L.; Richel, D.J.; Nieuwenhuijzen, G.A.P.; Hospers, G.A.P.; Bonenkamp, J.J.; et al. Preoperative Chemoradiotherapy for Esophageal or Junctional Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2074–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.J.; Ajani, J.A.; Kuzdzal, J.; Zander, T.; Van Cutsem, E.; Piessen, G.; Mendez, G.; Feliciano, J.; Motoyama, S.; Lièvre, A.; et al. Adjuvant Nivolumab in Resected Esophageal or Gastroesophageal Junction Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1191–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, G.; Liang, F.; Zhang, C.; Yue, J.; Duan, X.; Ma, Z.; Chen, C.; Pang, Q.; et al. Pembrolizumab Combined with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Versus Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy Followed by Surgery for Locally Advanced Oesophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Protocol for a Multicentre, Prospective, Randomized-Controlled, Phase III Clinical Study (Keystone-002). Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 831345. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.-M.; Shen, L.; Shah, M.A.; Enzinger, P.; Adenis, A.; Doi, T.; Kojima, T.; Metges, J.-P.; Li, Z.; Kim, S.-B.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for first-line treatment of advanced oesophageal cancer (KEYNOTE-590): A randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet 2021, 398, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjigian, Y.Y.; Shitara, K.; Moehler, M.; Garrido, M.; Salman, P.; Shen, L.; Wyrwicz, L.; Yamaguchi, K.; Skoczylas, T.; Bragagnoli, A.C.; et al. First-line nivolumab plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for advanced gastric, gastro-oesophageal junction, and oesophageal adenocarcinoma (CheckMate 649): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.E.; Puccini, A.; Xiu, J.; Raghavan, D.; Lenz, H.; Korn, W.M.; Shields, A.F.; Philip, P.A.; Marshall, J.L.; Goldberg, R.M. Comparative Molecular Analyses of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Esophageal Adenocarcinoma, and Gastric Adenocarcinoma. Oncologist 2018, 23, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Zhou, J.; Liang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Luan, S.; Xiao, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Shang, Q.; Zeng, X.; et al. Immunotherapy resistance in esophageal cancer: Possible mechanisms and clinical implications. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obermannová, R.; Alsina, M.; Cervantes, A.; Leong, T.; Lordick, F.; Nilsson, M.; Grieken NCT van Vogel, A.; Smyth, E.C. Oesophageal cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 992–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauvin, J.-M.; Zarour, H.M. TIGIT in cancer immunotherapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Zhang, H.; Han, F.; Chen, X.; Lin, R.; Wang, W.; Qiu, H.; Zhuang, Z.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, W.; et al. CD155T/TIGIT Signaling Regulates CD8+ T-cell Metabolism and Promotes Tumor Progression in Human Gastric Cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 6375–6388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Zhao, E.; Zhu, C.; Zhao, W.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, G. TIGIT and PD-1 may serve as potential prognostic biomarkers for gastric cancer. Immunobiology 2020, 225, 151915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klempner, S.J.; Shitara, K.; Sison, A.; Scott, J.; Wishengrad, D.; Ronayne, J.; Rhee, J.; Mitra, S.; Nuyten, D.S.A.; Janjigian, Y.Y.; et al. STAR-221: A randomized, open-label, multicenter, phase 3 trial of domvanalimab, zimberelimab, and chemotherapy versus nivolumab and chemotherapy in previously untreated, locally advanced, unresectable or metastatic gastric, gastroesophageal junction, and esophageal adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, TPS4206. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Guo, W.; Geng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Qiu, B.; Tan, F.; Xue, Q.; Gao, S.; He, J. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in esophageal cancer: An updated meta-analysis of 30 studies with 5122 patients. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Lu, S.; Chard Dunmall, L.S.; Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y. Characterization of the Intra-tumoral B Cell Immunoglobulin Repertoire Is of Prognostic Value for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 896627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Kumagai, K.; Nasu, K.; Yoshizawa, T.; Kuwano, K.; Hamada, Y.; Kanazawa, H.; Suzuki, R. Clonal Expansion of Tumor-Infiltrating T Cells and Analysis of the Tumor Microenvironment within Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Relapsed after Definitive Chemoradiation Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesney, J.; Lewis, K.D.; Kluger, H.; Hamid, O.; Whitman, E.; Thomas, S.; Wermke, M.; Cusnir, M.; Domingo-Musibay, E.; Phan, G.Q.; et al. Efficacy and safety of lifileucel, a one-time autologous tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) cell therapy, in patients with advanced melanoma after progression on immune checkpoint inhibitors and targeted therapies: Pooled analysis of consecutive cohorts of the C-144-01 study. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e005755. [Google Scholar]
- Hoefnagel, S.J.M.; Boonstra, J.J.; Russchen, M.J.A.M.; Krishnadath, K.K. Towards Personalized Treatment Strategies for Esophageal Adenocarcinoma; A Review on the Molecular Characterization of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma and Current Research Efforts on Individualized Curative Treatment Regimens. Cancers 2021, 13, 4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Integrated genomic characterization of oesophageal carcinoma. Nature 2017, 541, 169–175. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.M.; Park, Y.-Y.; Park, E.S.; Cho, J.Y.; Izzo, J.G.; Zhang, D.; Kim, S.-B.; Lee, J.H.; Bhutani, M.S.; Swisher, S.G.; et al. Prognostic Biomarkers for Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Identified by Analysis of Tumor Transcriptome. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Yu, F.; Mao, Y.; Ju, Q.; Wu, Y.; Bai, W.; Wang, P.; Xu, R.; Jiang, M.; Shi, J. EphA2 chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells for the immunotherapy of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 2779–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, T.; Kato, H.; Fukuchi, M.; Nakajima, M.; Kuwano, H. EphA2 overexpression correlates with poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer. 2003, 103, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Wang, X.; Shi, H.; Jiang, M.; Xu, J.; Sun, M.; Xu, Q.; Addai, F.P.; Shi, H.; Gu, J.; et al. Development of chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells for the treatment of esophageal cancer. Tumori J. 2021, 107, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Ping, Y.; Wang, S.; Shi, X.; Lian, J.; Liu, K.; et al. Targeting CD276 by CAR-T cells induces regression of esophagus squamous cell carcinoma in xenograft mouse models. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 101138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, H.; He, X.; Xi, F.; Liu, J. JAK-STAT Domain Enhanced MUC1-CAR-T Cells Induced Esophageal Cancer Elimination. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 9813–9824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, S.; Wada, H.; Muro, K.; Niwa, Y.; Ueda, S.; Miyata, H.; Takiguchi, S.; Sugino, S.H.; Miyahara, Y.; Ikeda, H.; et al. Dose-dependent effects of NY-ESO-1 protein vaccine complexed with cholesteryl pullulan (CHP-NY-ESO-1) on immune responses and survival benefits of esophageal cancer patients. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iinuma, H.; Fukushima, R.; Inaba, T.; Tamura, J.; Inoue, T.; Ogawa, E.; Horikawa, M.; Ikeda, Y.; Matsutani, N.; Takeda, K.; et al. Phase I clinical study of multiple epitope peptide vaccine combined with chemoradiation therapy in esophageal cancer patients. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Trial | Phase | # Patients | Pathology | Clinical Stage | Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor | Immune Target | Chemotherapeutic Agents | Radiotherapy | Primary Endpoint | Pathologic Complete Response (pCR) | Safety-Grade ≥ 3 AE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PALACE-1 [21] | Ib | 20 | ESCC | II-IVA | Pembrolizumab | PD-1 | Carboplatin, Paclitaxel | 23 fractions of 1.8 Gy | Safety | 55.60% | 65% |
| PERFECT [22] | II | 40 | EAC | II-IVA | Atezolizumab | PD-L1 | Carboplatin, Paclitaxel | 23 fractions of 1.8 Gy | Feasibility | 40% | 30% |
| ESONICT-1 [26] | II | 30 | ESCC | III-IV | Sintilimab | PD-1 | Cisplatin, Albumin-bound paclitaxel | N/A | pCR, AEs | 21.70% | 3% |
| ESONICT-2 [29] | II | 20 | ESCC | III-IVA | Toripalimab | PD-1 | Cisplatin, Docetaxel | N/A | pCR, AEs | 16.70% | 20% |
| SIN-ICE [23] | Pilot Study | 23 | ESCC | II-IVA | Sintilimab | PD-1 | Docetaxel/Albumin-bound paclitaxel, Nedaplatin | N/A | pCR, safety | 35.30% | 30.40% |
| PEN-ICE [27] | II | 18 | ESCC | II-IVA | Pembrolizumab | PD-1 | Platinum-based two drug | N/A | Safety, Efficacy | 46.20% | 27.80% |
| TD-NICE [28] | II | 45 | ESCC | II-IVA | Tislelizumab | PD-1 | Nab-paclitaxel, Carboplatin | N/A | Major Pathologic Response (MPR) | 50% | 42.20% |
| NIC-ESCC2019 [30] | II | 56 | ESCC | II-IVA | Camrelizumab | PD-1 | Nab-paclitaxel, cisplatin | N/A | pCR | 13.70% | 10.70% |
| Shen et al. [24] | II | 28 | ESCC | II-IVA | Nivolumab, Pembrolizumab, Camrelizumab | PD-1 | Nab-paclitaxel, Carboplatin | N/A | Safety, Feasibility | 40.70% | 7.10% |
| Yang et al. [25] | Pilot | 16 | ESCC | II-IVA | Camrelizumab | PD-1 | Paclitaxel, Carboplatin | N/A | pCR | 31.30% | N/A (only mild and tolerable AE) |
| Xing et al. [31] | II | 30 | ESCC | II-IVA | Toripalimab | PD-1 | Paclitaxel, Cisplatin | N/A | pCR | 36% | 6.67% |
| Yang et al. [32] | Pilot | 23 | ESCC | II-III | Camrelizumab | PD-1 | Nab-paclitaxel, Carboplatin | N/A | Safety, Feasibility | 25% | 47.80% |
| He et al. [20] | II | 20 | ESCC | III-IVA | Toripalimab | PD-1 | Paclitaxel, Carboplatin | N/A | Safety, Feasibility, MPR | 18.80% | 20% |
| Liu et al. [33] | II | 60 | ESCC | III-IVA | Camrelizumab | PD-1 | Nab-paclitaxel, Carboplatin | N/A | pCR | 39.20% | 56.70% |
| Wang et al. [34] | Ib | 30 | ESCC | II-III | Camrelizumab | PD-1 | Nab-paclitaxel, nedaplatin, apatinib | N/A | Safety | 24.10% | 36.70% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, D.; Jeon, W.J.; Yang, C.; Castillo, D.R. Advancing Esophageal Cancer Treatment: Immunotherapy in Neoadjuvant and Adjuvant Settings. Cancers 2024, 16, 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020318
Park D, Jeon WJ, Yang C, Castillo DR. Advancing Esophageal Cancer Treatment: Immunotherapy in Neoadjuvant and Adjuvant Settings. Cancers. 2024; 16(2):318. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020318
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Daniel, Won Jin Jeon, Chieh Yang, and Dani Ran Castillo. 2024. "Advancing Esophageal Cancer Treatment: Immunotherapy in Neoadjuvant and Adjuvant Settings" Cancers 16, no. 2: 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020318
APA StylePark, D., Jeon, W. J., Yang, C., & Castillo, D. R. (2024). Advancing Esophageal Cancer Treatment: Immunotherapy in Neoadjuvant and Adjuvant Settings. Cancers, 16(2), 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020318






