Effects of Intraoperative Opioid Use and a Combined Anesthesia Protocol in Patients Undergoing Radical Cystectomy for Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder—A Single-Center Experience
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Anesthesia Protocol
2.3. Outcomes and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
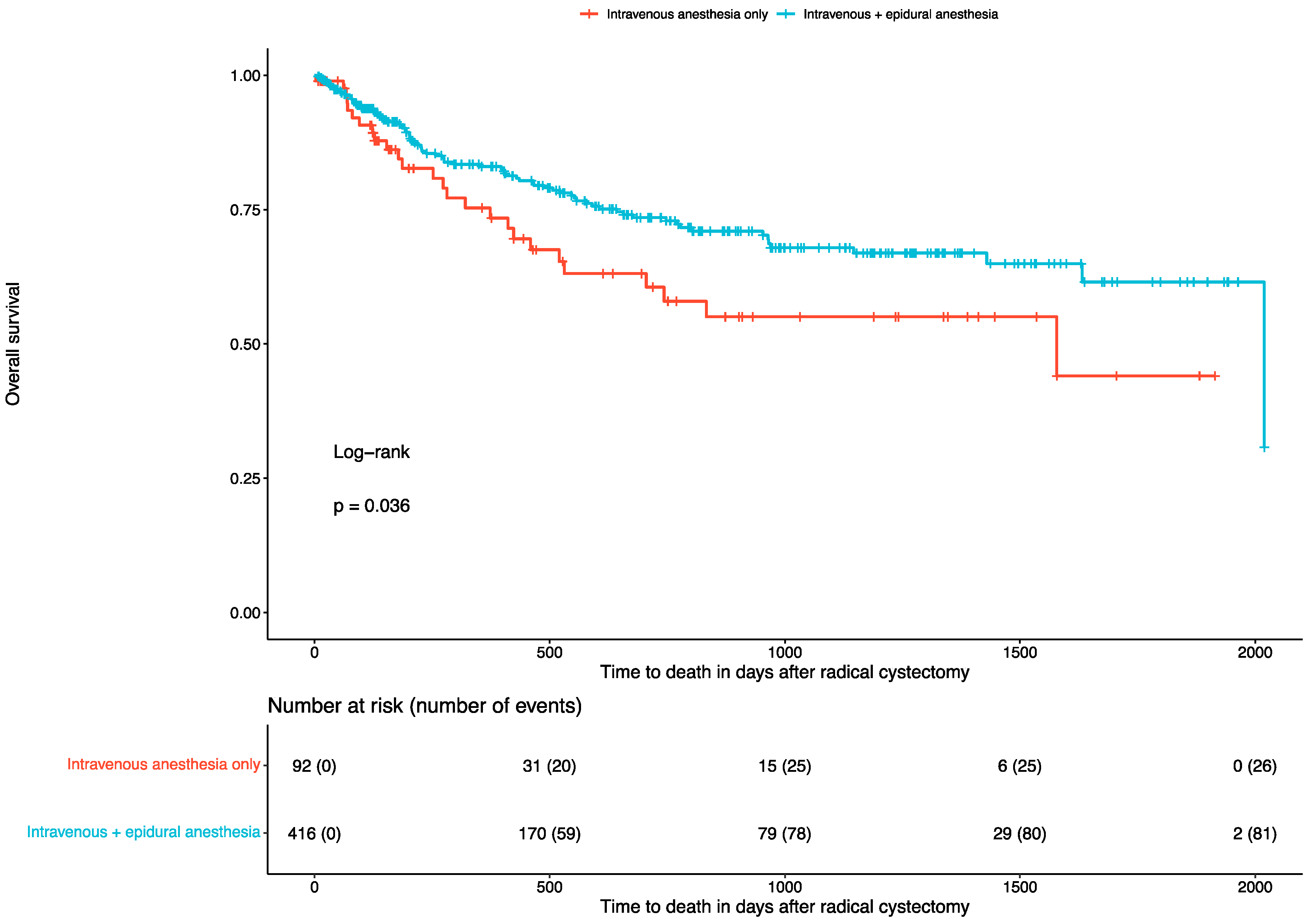
3.2. Overall Survival and Recurrence Rates
3.3. Blood Transfusions, Severe Clavien–Dindo Complications, and Intensive Care Unit (ICU) Admissions
3.4. Length of Hospital Stay and Blood Loss
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lenis, A.T.; Lec, P.M.; Chamie, K. Urinary Diversion. JAMA 2020, 324, 2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsimperis, S.; Tzelves, L.; Tandogdu, Z.; Ta, A.; Geraghty, R.; Bellos, T.; Manolitsis, I.; Pyrgidis, N.; Schulz, G.B.; Sridhar, A.; et al. Complications After Radical Cystectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials with a Meta-regression Analysis. Eur. Urol. Focus 2023, 9, 920–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klemm, J.; Rink, M.; von Deimling, M.; Koelker, M.; Gild, P.; Shariat, S.F.; Dahlem, R.; Fisch, M.; Vetterlein, M.W. Time-to-complication Patterns After Radical Cystectomy: A Secondary Analysis of a 30-day Morbidity Assessment Using the European Association of Urology Quality Criteria for Standardized Reporting. Eur. Urol. Focus 2023, 9, 1072–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Gan, C.; Ahmed, K.; Ismail, A.F.; Watkins, J.; Summers, J.A.; Peacock, J.L.; Rimington, P.; Dasgupta, P. A Single-centre Early Phase Randomised Controlled Three-arm Trial of Open, Robotic, and Laparoscopic Radical Cystectomy (CORAL). Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraj, K.S.; Abdul-Muhsin, H.M.; Rose, K.M.; Navaratnam, A.K.; Patton, M.W.; Eversman, S.; Singh, R.; Eversman, W.G.; Cheney, S.M.; Tyson, M.D.; et al. Robot Assisted Radical Cystectomy vs. Open Radical Cystectomy: Over 10 years of the Mayo Clinic Experience. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2019, 37, 862–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyrgidis, N.; Schulz, G.B.; Volz, Y.; Ebner, B.; Rodler, S.; Westhofen, T.; Eismann, L.; Marcon, J.; Stief, C.G.; Jokisch, F. The impact of perioperative risk factors on long-term survival after radical cystectomy: A prospective, high-volume cohort study. World J. Urol. 2024, 42, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekala, K.R.; Jacobs, B.L.; Davies, B.J. The Shrinking Grey Zone of Postoperative Narcotics in the Midst of the Opioid Crisis: The No-opioid Urologist. Eur. Urol. Focus 2020, 6, 1168–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silagy, A.W.; Hannum, M.L.; Mano, R.; Attalla, K.; Scarpa, J.R.; DiNatale, R.G.; Marcon, J.; Coleman, J.A.; Russo, P.; Tan, K.S.; et al. Impact of intraoperative opioid and adjunct analgesic use on renal cell carcinoma recurrence: Role for onco-anaesthesia. Br. J. Anaesth. 2020, 125, e402–e404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forget, P.; Tombal, B.; Scholtès, J.L.; Nzimbala, J.; Meulders, C.; Legrand, C.; Van Cangh, P.; Cosyns, J.-P.; De Kock, M. Do intraoperative analgesics influence oncological outcomes after radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer? Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2011, 28, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cata, J.P.; Zafereo, M.; Villarreal, J.; Unruh, B.D.; Truong, A.; Truong, D.-T.; Feng, L.; Gottumukkala, V. Intraoperative opioids use for laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma surgery and recurrence: A retrospective study. J. Clin. Anesthesia 2015, 27, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Teng, L.; Zhang, W.; Lin, S.; Liu, X.; Dai, J.; Shao, H.; Li, X.; Liu, Q.; Zou, H. Dose of intra-operative opioids has no impact on recurrence or survival in primary liver cancer. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 4927–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forget, P.; Vandenhende, J.; Berliere, M.; Machiels, J.-P.; Nussbaum, B.; Legrand, C.; De Kock, M. Do intraoperative analgesics influence breast cancer recurrence after mastectomy? A retrospective analysis. Anesthesia Analg. 2010, 110, 1630–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wigmore, T.; Farquhar-Smith, P. Opioids and cancer: Friend or foe? Curr. Opin. Support. Palliat. Care 2016, 10, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chipollini, J.; Alford, B.; Boulware, D.C.; Forget, P.; Gilbert, S.M.; Lockhart, J.L.; Pow-Sang, J.M.; Sexton, W.J.; Spiess, P.E.; Poch, M.A.; et al. Epidural anesthesia and cancer outcomes in bladder cancer patients: Is it the technique or the medication? A matched-cohort analysis from a tertiary referral center. BMC Anesthesiol. 2018, 18, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persu, C.; Ciofu, I.; Petrescu, A.; Chirca, N.; Cauni, V. Bladder Wall Structure Alterations in Patients Treated With Botulinum Toxin for Detrusor Overactivity-A Morphological Study. In Vivo 2023, 37, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; STROBE Initiative. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet 2007, 370, 1453–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.; Saiers, J.H.; Abram, S.; Schlicht, C. Accuracy in Equianalgesic Dosing. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2001, 21, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldman, S.D. Pain Management E-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; 1248p. [Google Scholar]
- Mitropoulos, D.; Artibani, W.; Biyani, C.S.; Jensen, J.B.; Rouprêt, M.; Truss, M. Validation of the Clavien–Dindo Grading System in Urology by the European Association of Urology Guidelines Ad Hoc Panel. Eur. Urol. Focus 2018, 4, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-F.; Xu, Q.-X.; Liao, L.-D.; Xu, X.-E.; Wu, J.-Y.; Wu, Z.-Y.; Shen, J.-H.; Li, E.-M.; Xu, L.-Y. Association of mu-opioid receptor expression with lymph node metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis. Esophagus 2015, 28, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Pan, J.; Chen, Y.; Xing, W.; Yan, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zeng, W. The mu-opioid receptor is a molecular marker for poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma and represents a potential therapeutic target. Br. J. Anaesth. 2019, 122, e157–e167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.M.; Wong, Y.H. Mu-Opioid Receptor-Mediated Phosphorylation of IκB Kinase in Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells. Neurosignals 2005, 14, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.W.; Shavit, Y.; Terman, G.W.; Gale, R.P.; Liebeskind, J.C. Stress and morphine affect survival of rats challenged with a mammary ascites tumor (MAT 13762B). Nat. Immun. Cell Growth Regul. 1983, 3, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sawaya, B.E.; Deshmane, S.L.; Mukerjee, R.; Fan, S.; Khalili, K. TNF alpha production in morphine-treated human neural cells is NF-kappaB-dependent. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2009, 4, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridharan, K.; Sivaramakrishnan, G. Comparison of Fentanyl, Remifentanil, Sufentanil and Alfentanil in Combination with Propofol for General Anesthesia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Curr. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 14, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Gao, T.; Li, Y.; Cui, K.; Fang, B. Effect of combined epidural–general anesthesia on long-term survival of patients with colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2022, 37, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Pang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Liu, H. Effects of epidural anesthesia on the prognosis of ovarian cancer—A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023, 23, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrgidis, N.; Volz, Y.; Ebner, B.; Kazmierczak, P.M.; Enzinger, B.; Hermans, J.; Buchner, A.; Stief, C.; Schulz, G.B. The effect of hospital caseload on perioperative mortality, morbidity and costs in bladder cancer patients undergoing radical cystectomy: Results of the German nationwide inpatient data. World J. Urol. 2024, 42, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens-Laan, C.A.; Gooiker, G.A.; van Gijn, W.; Post, P.N.; Bosch, J.R.; Kil, P.J.; Wouters, M.W. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the relationship between hospital/surgeon volume and outcome for radical cystectomy: An update for the ongoing debate. Eur. Urol. 2011, 59, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruins, H.M.; Veskimäe, E.; Hernández, V.; Neuzillet, Y.; Cathomas, R.; Compérat, E.M.; Cowan, N.C.; Gakis, G.; Espinós, E.L.; Lorch, A.; et al. The Importance of Hospital and Surgeon Volume as Major Determinants of Morbidity and Mortality After Radical Cystectomy for Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Recommendations by the European Association of Urology Muscle-invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer Guideline Panel. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2020, 3, 131–144. [Google Scholar]
- Warner, M.A.; Arnal, D.; Cole, D.J.; Hammoud, R.; Haylock-Loor, C.; Ibarra, P.; Joshi, M.; Khan, F.A.; Lebedinskii, K.M.; Mellin-Olsen, J.; et al. Anesthesia Patient Safety: Next Steps to Improve Worldwide Perioperative Safety by 2030. Anesthesia Analg. 2022, 135, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrgidis, N.; Sokolakis, I.; Haltmair, G.; Hatzichristodoulou, G. The effect of urinary diversion on renal function after cystectomy for bladder cancer: Comparison between ileal conduit, orthotopic ileal neobladder, and heterotopic ileocecal pouch. World J. Urol. 2022, 40, 3091–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udovicich, C.; Perera, M.; Huq, M.; Wong, L.; Lenaghan, D. Hospital volume and perioperative outcomes for radical cystectomy: A population study. BJU Int. 2017, 119, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | Overall, n = 508 | Intravenous Anesthesia Only, n = 92 | Intravenous + Epidural Anesthesia, n = 416 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 73 (64–78) | 73 (65–78) | 73 (64–78) | >0.9 |
| Males | 383 (75%) | 70 (76%) | 313 (75%) | >0.9 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26 (24–28) | 27 (23–28) | 26 (24–28) | >0.9 |
| Smokers | 250 (61%) | 37 (48%) | 213 (65%) | 0.01 |
| Alcohol consumption | 110 (32%) | 18 (27%) | 92 (33%) | 0.5 |
| Heart disease | 159 (32%) | 38 (41%) | 121 (30%) | 0.04 |
| Hypertension | 280 (56%) | 54 (59%) | 226 (55%) | 0.6 |
| Diabetes | 172 (34%) | 29 (32%) | 143 (35%) | 0.6 |
| ASA | 0.04 | |||
| 1 | 4 (0.8%) | 0 (0%) | 4 (1.0%) | |
| 2 | 90 (18%) | 17 (19%) | 73 (18%) | |
| 3 | 402 (79%) | 68 (76%) | 334 (80%) | |
| 4 | 10 (2.0%) | 5 (5.6%) | 5 (1.2%) | |
| Urinary diversion | 0.3 | |||
| Ileal conduit | 292 (57%) | 61 (66%) | 231 (56%) | |
| Neobladder | 203 (40%) | 29 (32%) | 174 (42%) | |
| Pouch | 5 (1.0%) | 1 (1.1%) | 4 (1.0%) | |
| Ureterocutaneostomy | 8 (1.6%) | 1 (1.1%) | 7 (1.7%) | |
| Operative time (min) | 223 (186–265) | 224 (192–269) | 223 (186–265) | 0.9 |
| Blood loss (mL) | 400 (200–700) | 400 (200–700) | 400 (200–700) | 0.5 |
| T after cystectomy | >0.9 | |||
| ≤T2 | 156 (31%) | 28 (30%) | 128 (32%) | |
| ≥T3 | 342 (69%) | 64 (70%) | 278 (68%) | |
| Positive lymph nodes | 120 (27%) | 25 (31%) | 95 (26%) | 0.4 |
| Positive surgical margins | 68 (14%) | 12 (13%) | 56 (14%) | >0.9 |
| Hospital stay (days) | 19 (16–22) | 18 (16–21) | 19 (16–22) | 0.5 |
| Perioperative chemotherapy | 184 (36%) | 27 (29%) | 157 (38%) | 0.2 |
| Clavien–Dindo complications | 0.2 | |||
| No | 273 (61%) | 43 (54%) | 230 (62%) | |
| 1 | 5 (1.1%) | 3 (3.8%) | 2 (0.5%) | |
| 2 | 107 (24%) | 21 (26%) | 86 (23%) | |
| 3 | 28 (6.2%) | 5 (6.3%) | 23 (6.2%) | |
| 4 | 30 (6.7%) | 7 (8.8%) | 23 (6.2%) | |
| 5 | 6 (1.3%) | 1 (1.3%) | 5 (1.4%) | |
| Allogeneic blood transfusion | 106 (21%) | 25 (27%) | 81 (20%) | 0.14 |
| Admission to ICU | 188 (37%) | 47 (51%) | 141 (34%) | 0.003 |
| Sufentanil (µg) | 10 (10–30) | 10 (8–20) | 10 (10–30) | 0.08 |
| Remifentanil (µg) | 2317 (1380–3565) | 3112 (1272–4277) | 2243 (1408–3367) | 0.08 |
| 10 MME | 7 (2–89) | 8 (2–74) | 7 (2–89) | 0.5 |
| Outcome | Univariate Cox Regression | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p-Value | ||
| Mortality | Type of anesthesia | |||
| Intravenous anesthesia only | — | — | ||
| Intravenous + epidural anesthesia | 0.63 | 0.40, 0.97 | 0.037 | |
| High dose of remifentanil | 0.76 | 0.39, 1.46 | 0.4 | |
| High dose of sufentanil | 1.08 | 0.71, 1.64 | 0.7 | |
| High dose of MME | 0.96 | 0.63, 1.47 | 0.8 | |
| Epidural anesthesia | 0.67 | 0.45, 1.02 | 0.059 | |
| Recurrence | Type of anesthesia | |||
| Intravenous anesthesia only | — | — | ||
| Intravenous + epidural anesthesia | 1.10 | 0.64, 1.87 | 0.7 | |
| High dose of remifentanil | 1.36 | 0.78, 2.36 | 0.3 | |
| High dose of sufentanil | 1.04 | 0.68, 1.60 | 0.9 | |
| High dose of MME | 1.44 | 0.94, 2.1 | 0.07 | |
| Epidural anesthesia | 1.18 | 0.74, 1.89 | 0.5 | |
| Outcome | Univariate Logistic Regression | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p-Value | ||
| Transfusion | Type of anesthesia | |||
| Intravenous anesthesia only | — | — | ||
| Intravenous + epidural anesthesia | 0.65 | 0.39, 1.11 | 0.10 | |
| High dose of remifentanil | 1.08 | 0.51, 2.19 | 0.8 | |
| High dose of sufentanil | 1.15 | 0.70, 1.84 | 0.6 | |
| High dose of MME | 1.09 | 0.66, 1.76 | 0.7 | |
| Epidural anesthesia | 0.62 | 0.39, 1.01 | 0.052 | |
| Severe Clavien–Dindo complications | Type of anesthesia | |||
| Intravenous anesthesia only | — | — | ||
| Intravenous + epidural anesthesia | 0.83 | 0.44, 1.66 | 0.6 | |
| High dose of remifentanil | 0.98 | 0.34, 2.50 | >0.9 | |
| High dose of sufentanil | 1.04 | 0.55, 1.87 | >0.9 | |
| High dose of MME | 1.14 | 0.61, 2.05 | 0.7 | |
| Epidural anesthesia | 0.68 | 0.38, 1.25 | 0.2 | |
| Admission to intensive care unit | Type of anesthesia | |||
| Intravenous anesthesia only | — | — | ||
| Intravenous + epidural anesthesia | 0.49 | 0.31, 0.77 | 0.002 | |
| High dose of remifentanil | 0.73 | 0.38, 1.37 | 0.3 | |
| High dose of sufentanil | 1.05 | 0.70, 1.58 | 0.8 | |
| High dose of MME | 1.24 | 0.82, 1.87 | 0.3 | |
| Epidural anesthesia | 0.61 | 0.4, 0.93 | 0.02 | |
| Outcome | Univariate Linear Regression | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beta | 95% CI | p-Value | ||
| Length of hospital stay (days) | Type of anesthesia | |||
| Intravenous anesthesia only | — | — | ||
| Intravenous + epidural anesthesia | −0.40 | −2.3, 1.5 | 0.7 | |
| High dose of remifentanil | 2.3 | −0.04, 4.6 | 0.054 | |
| High dose of sufentanil | 0.45 | −1.1, 2.0 | 0.6 | |
| High dose of MME | −0.05 | −1.7, 1.6 | >0.9 | |
| Epidural anesthesia | −0.41 | −2.1, 1.3 | 0.6 | |
| Blood loss (mL) | Type of anesthesia | |||
| Intravenous anesthesia only | — | — | ||
| Intravenous + epidural anesthesia | −7.8 | −119, 103 | 0.9 | |
| High dose of remifentanil | 82 | −41, 205 | 0.2 | |
| High dose of sufentanil | 51 | −48, 149 | 0.3 | |
| High dose of MME | 65 | −33, 164 | 0.2 | |
| Epidural anesthesia | 21 | −81, 122 | 0.7 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marcon, J.; Yefsah, F.; Schulz, G.B.; Weinhold, P.; Rodler, S.; Eismann, L.; Volz, Y.; Pfitzinger, P.L.; Stief, C.G.; Kowalski, C.; et al. Effects of Intraoperative Opioid Use and a Combined Anesthesia Protocol in Patients Undergoing Radical Cystectomy for Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder—A Single-Center Experience. Cancers 2024, 16, 3411. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193411
Marcon J, Yefsah F, Schulz GB, Weinhold P, Rodler S, Eismann L, Volz Y, Pfitzinger PL, Stief CG, Kowalski C, et al. Effects of Intraoperative Opioid Use and a Combined Anesthesia Protocol in Patients Undergoing Radical Cystectomy for Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder—A Single-Center Experience. Cancers. 2024; 16(19):3411. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193411
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarcon, Julian, Fatima Yefsah, Gerald B. Schulz, Philipp Weinhold, Severin Rodler, Lennert Eismann, Yannic Volz, Paulo L. Pfitzinger, Christian G. Stief, Christian Kowalski, and et al. 2024. "Effects of Intraoperative Opioid Use and a Combined Anesthesia Protocol in Patients Undergoing Radical Cystectomy for Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder—A Single-Center Experience" Cancers 16, no. 19: 3411. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193411
APA StyleMarcon, J., Yefsah, F., Schulz, G. B., Weinhold, P., Rodler, S., Eismann, L., Volz, Y., Pfitzinger, P. L., Stief, C. G., Kowalski, C., Siegl, D., Buchner, A., Pyrgidis, N., & Jokisch, J.-F. (2024). Effects of Intraoperative Opioid Use and a Combined Anesthesia Protocol in Patients Undergoing Radical Cystectomy for Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder—A Single-Center Experience. Cancers, 16(19), 3411. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193411






