An Exogenous Ketone Ester Slows Tumor Progression in Murine Breast and Renal Cancer Models
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Diets
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Seahorse Assay
2.4. In Vivo Tumor Modeling
2.5. Blood Glucose and B-Hydroxybutyrate Measurements
2.6. Quantitative Magnetic Resonance
2.7. NanoString Immunogenetic Profiling
2.8. Western Blot
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
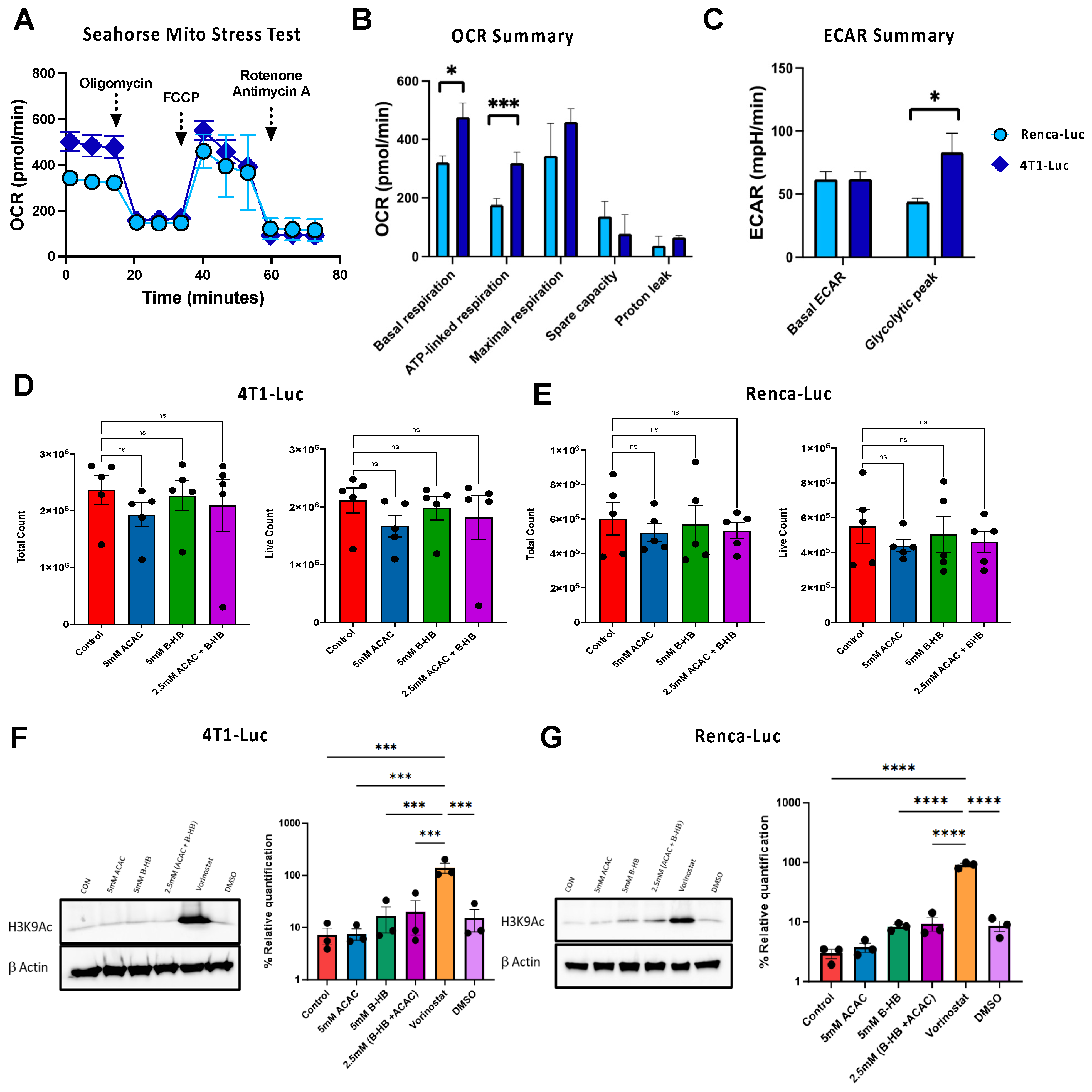
3.1. Metabolic Phenotyping Reveals Divergent Bioenergetic Profiles between 4T1 Mammary and Renca Renal Carcinoma Cell Lines
3.2. Ketones Do Not Impair 4T1-Luc or Renca-Luc Growth or Histone Deacetylase Activity In Vitro
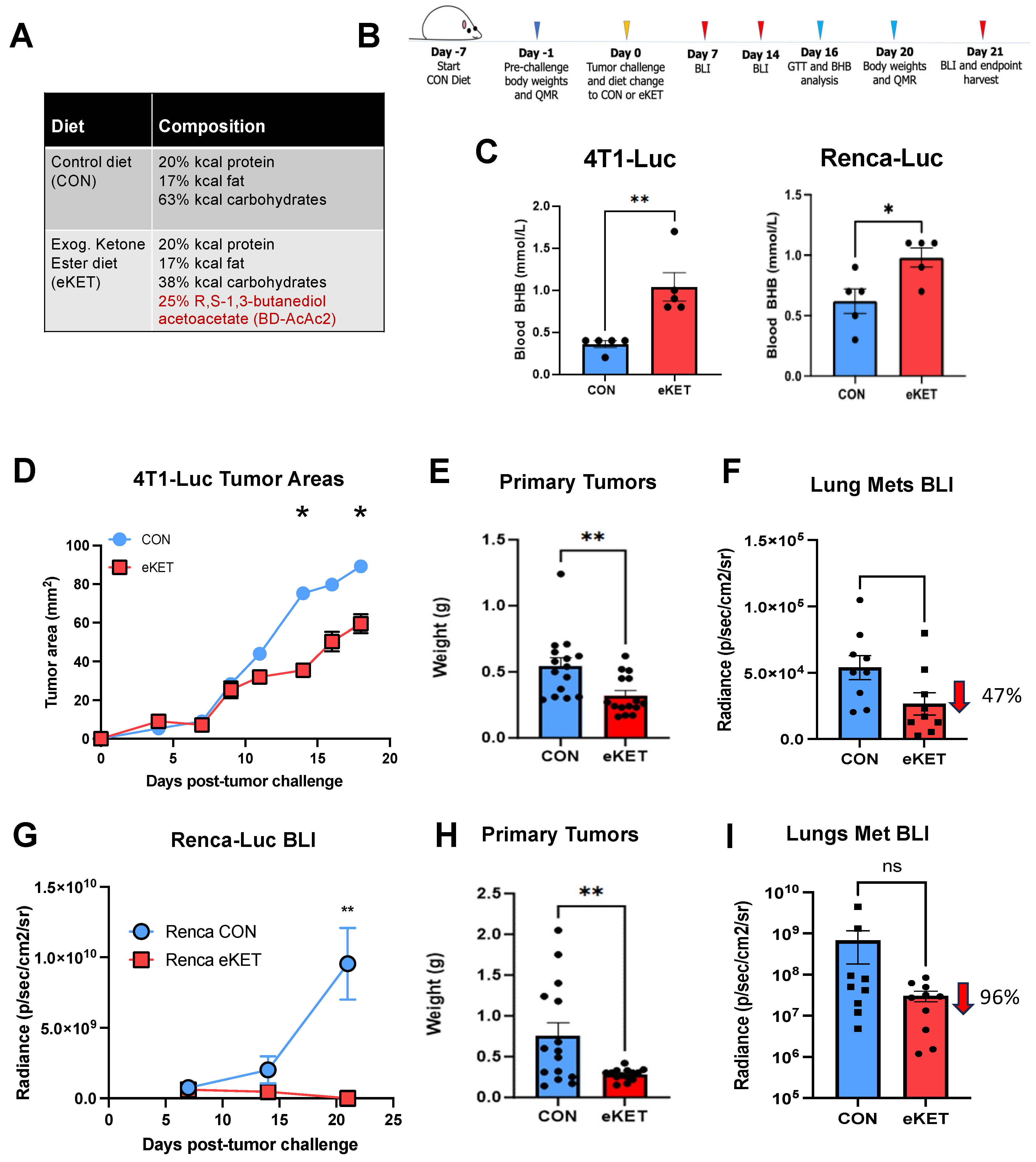
3.3. The eKET Diet Displays Efficacy in Slowing Tumor Progression in Mammary and Renal Carcinoma Models
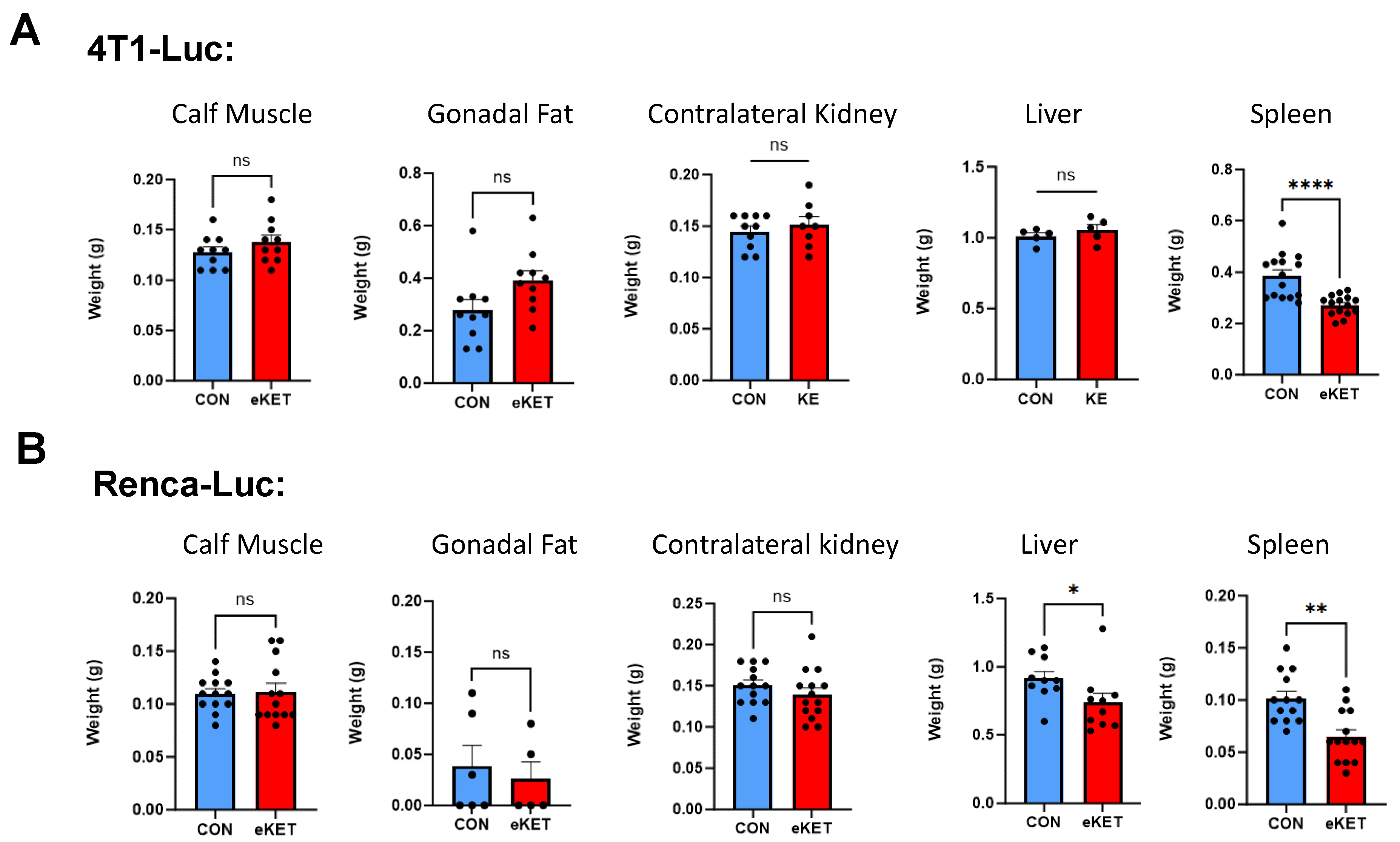
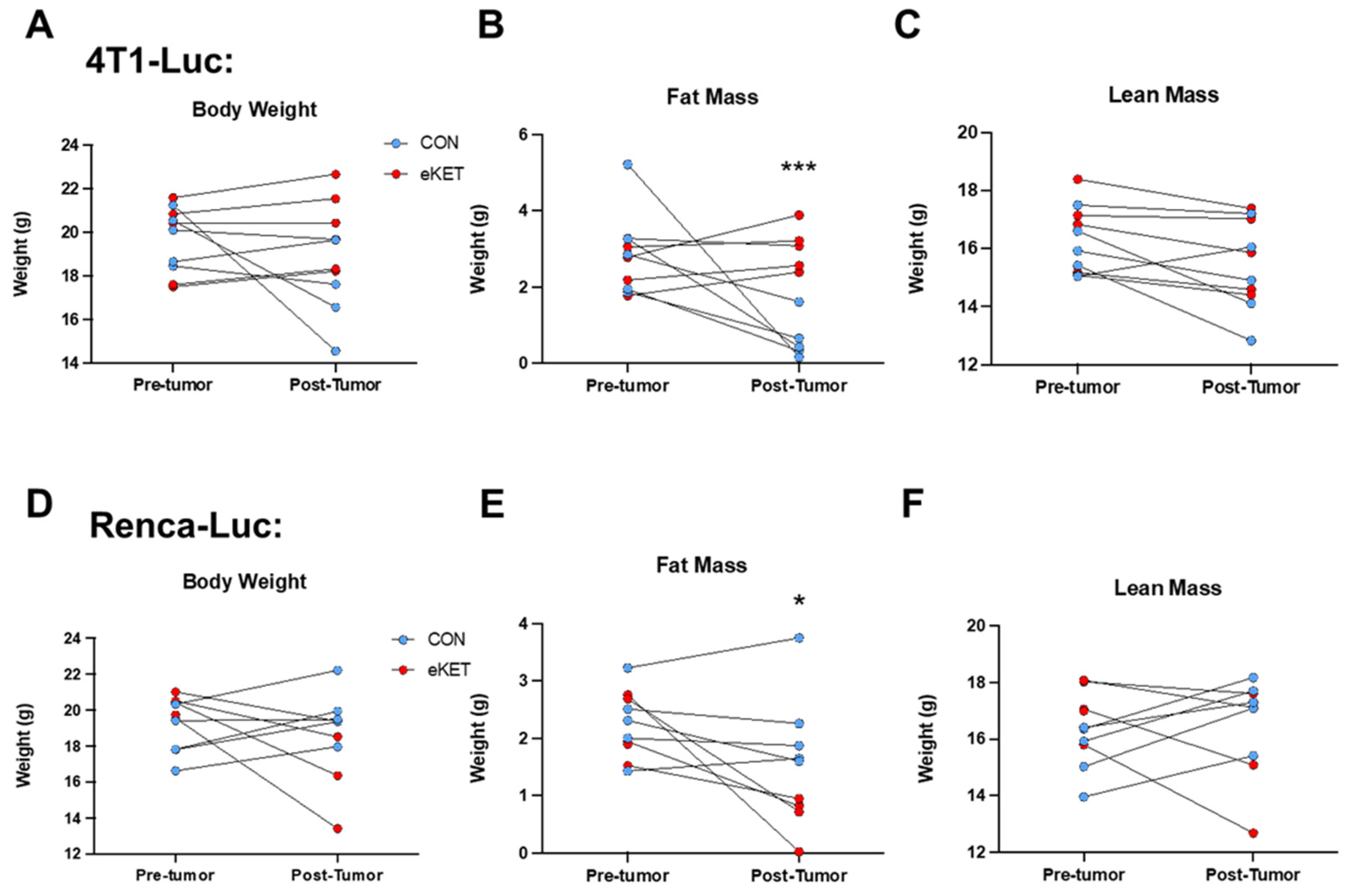
3.4. The Safety Profile of eKET Diet Administration Differs between Mammary and Renal Tumor Models
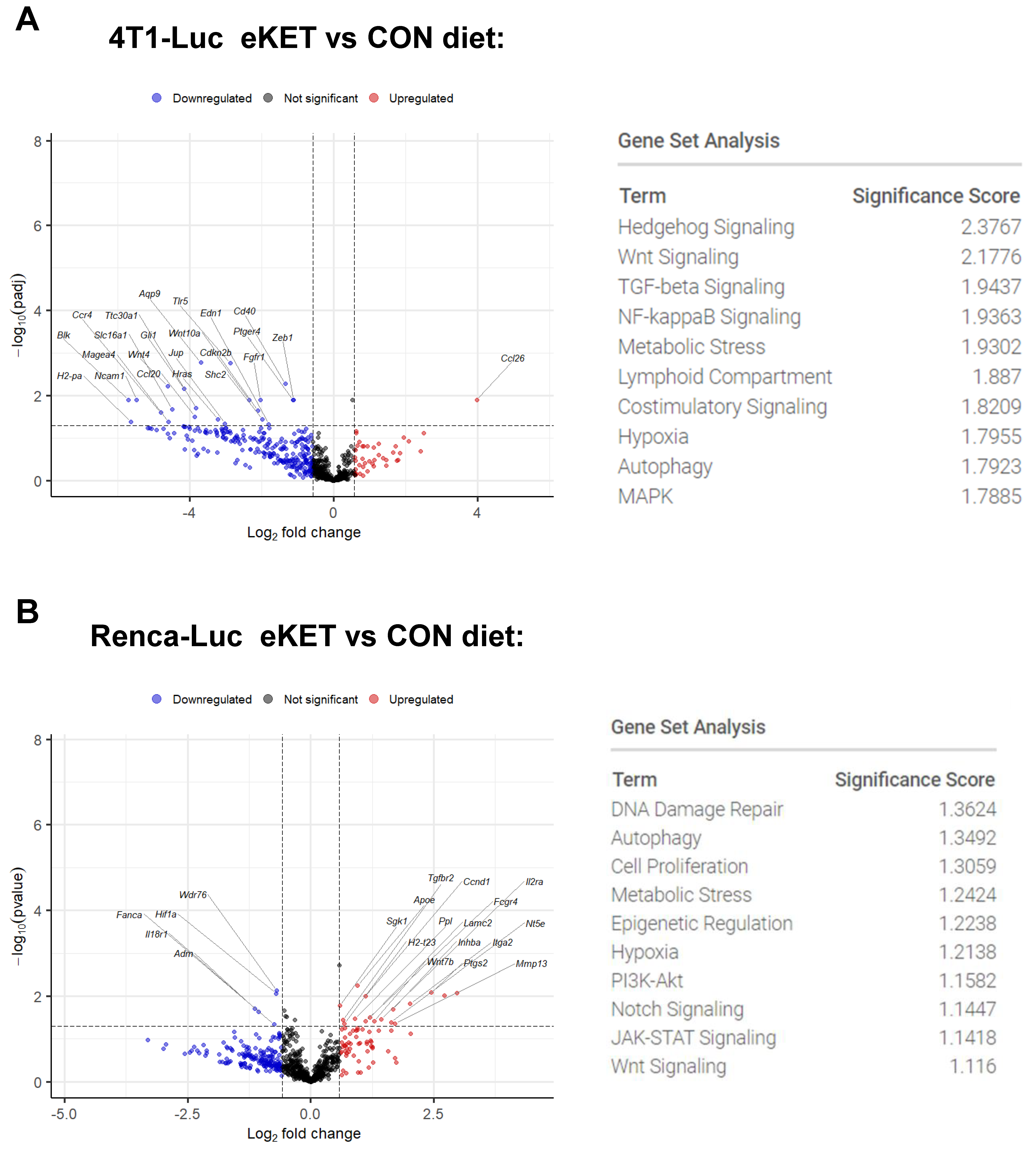
3.5. Immunogenetic Profiling Reveals Distinct Tumor-Specific Mechanisms Underlying the Antitumor and Antimetastatic Effects of the eKET Diet
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Montégut, L.; de Cabo, R.; Zitvogel, L.; Kroemer, G. Science-Driven Nutritional Interventions for the Prevention and Treatment of Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 2258–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turbitt, W.J.; Demark-Wahnefried, W.; Peterson, C.M.; Norian, L.A. Targeting Glucose Metabolism to Enhance Immunotherapy: Emerging Evidence on Intermittent Fasting and Calorie Restriction Mimetics. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodabakhshi, A.; Seyfried, T.N.; Kalamian, M.; Beheshti, M.; Davoodi, S.H. Does a ketogenic diet have beneficial effects on quality of life, physical activity or biomarkers in patients with breast cancer: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Nutr. J. 2020, 19, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.C.; Anderson, C.M.; Rodman, S.N.; Buranasudja, V.; McCormick, M.L.; Davis, A.; Loth, E.; Bodeker, K.L.; Ahmann, L.; Parkhurst, J.R.; et al. Ketogenic Diet with Concurrent Chemoradiation in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Preclinical and Phase 1 Trial Results. Radiat. Res. 2021, 196, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, J.; Brown, N.I.; Williams, S.; Plaisance, E.P.; Fontaine, K.R. Ketogenic Diet for Cancer: Critical Assessment and Research Recommendations. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, S.; Rahmy, S.; Gan, D.; Liu, G.; Zhu, Y.; Manyak, M.; Duong, L.; He, J.; Schofield, J.H.; Schafer, Z.T.; et al. Ketogenic Diet Alters the Epigenetic and Immune Landscape of Prostate Cancer to Overcome Resistance to Immune Checkpoint Blockade Therapy. Cancer Res. 2024, 84, 1597–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.R.; Kim, S.R.; Cho, W.; Lee, S.-G.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, E.; Kim, J.-H.; Yu, J.-W.; Lee, B.-W.; et al. Short Term Isocaloric Ketogenic Diet Modulates NLRP3 Inflammasome Via B-hydroxybutyrate and Fibroblast Growth Factor 21. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 843520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youm, Y.-H.; Nguyen, K.Y.; Grant, R.W.; Goldberg, E.L.; Bodogai, M.; Kim, D.; D’Agostino, D.; Planavsky, N.; Lupfer, C.; Kanneganti, T.-D.; et al. The ketone metabolite β-hydroxybutyrate blocks NLRP3 inflammasome–mediated inflammatory disease. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.P.; Cunningham, R.P.; Davis, R.A.H.; Deemer, S.E.; Roberts, B.M.; Plaisance, E.P.; Rector, R.S. A dietary ketone ester mitigates histological outcomes of NAFLD and markers of fibrosis in high-fat diet fed mice. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2021, 320, G564–G572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiannis, F.; Peukert, K.; Surace, L.; Michla, M.; Nikolka, F.; Fox, M.; Weiss, P.; Feuerborn, C.; Maier, P.; Schulz, S.; et al. Impaired ketogenesis ties metabolism to T cell dysfunction in COVID-19. Nature 2022, 609, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkenhain, K.; Daraei, A.; Forbes, S.C.; Little, J.P. Effects of Exogenous Ketone Supplementation on Blood Glucose: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Adv. Nutr. Int. Rev. J. 2022, 13, 1697–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puchalska, P.; Crawford, P.A. Metabolic and Signaling Roles of Ketone Bodies in Health and Disease. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2021, 41, 49–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, J.J.; Neudorf, H.; Little, J.P. 14-Day Ketone Supplementation Lowers Glucose and Improves Vascular Function in Obesity: A Randomized Crossover Trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 1738–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veech, R.L. Ketone ester effects on metabolism and transcription. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 2004–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poffé, C.; Ramaekers, M.; Van Thienen, R.; Hespel, P. Ketone ester supplementation blunts overreaching symptoms during endurance training overload. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 3009–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkenhain, K.; Islam, H.; Little, J.P. Exogenous ketone supplementation: An emerging tool for physiologists with potential as a metabolic therapy. Exp. Physiol. 2022, 108, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, A.; Ari, C.; Arnold, P.; Seyfried, T.; D’Agostino, D. Ketone supplementation decreases tumor cell viability and prolongs survival of mice with metastatic cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 1711–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrere, G.; Alou, M.T.; Liu, P.; Goubet, A.-G.; Fidelle, M.; Kepp, O.; Durand, S.; Iebba, V.; Fluckiger, A.; Daillère, R.; et al. Ketogenic diet and ketone bodies enhance the anticancer effects of PD-1 blockade. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, L.; Li, Y.; Cao, Y.; Meng, G.; Peng, J.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, T.; Zhang, L.; Sun, B.; et al. Pan-Cancer Analysis of Glycolytic and Ketone Bodies Metabolic Genes: Implications for Response to Ketogenic Dietary Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 689068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, B.P.; Wongrakpanich, A.; Francis, M.B.; Salem, A.K.; Norian, L.A. A Therapeutic Microparticle-Based Tumor Lysate Vaccine Reduces Spontaneous Metastases in Murine Breast Cancer. AAPS J. 2014, 16, 1194–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norian, L.A.; Kresowik, T.P.; Rosevear, H.M.; James, B.R.; Rosean, T.R.; Lightfoot, A.J.; Kucaba, T.A.; Schwarz, C.; Weydert, C.J.; Henry, M.D.; et al. Eradication of Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma after Adenovirus-Encoded TNF-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand (TRAIL)/CpG Immunotherapy. PLOS ONE 2012, 7, e31085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boi, S.K.; Orlandella, R.M.; Gibson, J.T.; Turbitt, W.J.; Wald, G.; Thomas, L.; Rosean, C.B.; E Norris, K.; Bing, M.; Bertrand, L.; et al. Obesity diminishes response to PD-1-based immunotherapies in renal cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandella, R.M.; Turbitt, W.J.; Gibson, J.T.; Boi, S.K.; Li, P.; Smith, D.L.; Norian, L.A. The Antidiabetic Agent Acarbose Improves Anti-PD-1 and Rapamycin Efficacy in Preclinical Renal Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turbitt, W.J.; Boi, S.K.; Gibson, J.T.; Orlandella, R.M.; Norian, L.A. Diet-Induced Obesity Impairs Outcomes and Induces Multi-Factorial Deficiencies in Effector T Cell Responses Following Anti-CTLA-4 Combinatorial Immunotherapy in Renal Tumor-Bearing Mice. Cancers 2021, 13, 2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, B.P.; Chitphet, K.; Wongrakpanich, A.; Wafa, E.I.; Norian, L.A.; Salem, A.K. Biotinylated Streptavidin Surface Coating Improves the Efficacy of a PLGA Microparticle-Based Cancer Vaccine. Bioconjugate Chem. 2020, 31, 2147–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborti, A.; Graham, C.; Chehade, S.; Vashi, B.; Umfress, A.; Kurup, P.; Vickers, B.; Chen, H.A.; Telange, R.; Berryhill, T.; et al. High Fructose Corn Syrup-Moderate Fat Diet Potentiates Anxio-Depressive Behavior and Alters Ventral Striatal Neuronal Signaling. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, S.; Han, X.; Xiang, Y.; Qian, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, T.; Tian, K.; Shen, K.; Yang, J.; Ma, X. Metabolic reprogramming in cancer: Mechanisms and therapeutics. Medcomm 2023, 4, e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehuédé, C.; Dupuy, F.; Rabinovitch, R.; Jones, R.G.; Siegel, P.M. Metabolic Plasticity as a Determinant of Tumor Growth and Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 5201–5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deemer, S.E.; Davis, R.A.H.; Gower, B.A.; Koutnik, A.P.; Poff, A.M.; Dickinson, S.L.; Allison, D.B.; D’Agostino, D.P.; Plaisance, E.P. Concentration-Dependent Effects of a Dietary Ketone Ester on Components of Energy Balance in Mice. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushing, K.A.; Bolyard, M.L.; Kelty, T.; Wieschhaus, N.; Pavela, G.; Rector, R.S.; Plaisance, E.P. Dietary ketone ester attenuates the accretion of adiposity and liver steatosis in mice fed a high-fat, high-sugar diet. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1165224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, G.F., Jr. Fuel Metabolism in Starvation. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2006, 26, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puchalska, P.; Crawford, P.A. Multi-dimensional Roles of Ketone Bodies in Fuel Metabolism, Signaling, and Therapeutics. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 262–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modica, L.C.M.; Flores-Felix, K.; Casachahua, L.J.D.; Asquith, P.; Tschiffely, A.; Ciarlone, S.; Ahlers, S.T. Impact of ketogenic diet and ketone diester supplementation on body weight, blood glucose, and ketones in Sprague Dawley rats fed over two weeks. Food Chem. Mol. Sci. 2021, 3, 100029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baracos, V.E.; Martin, L.; Korc, M.; Guttridge, D.C.; Fearon, K.C.H. Cancer-associated cachexia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 17105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupre’, S.A.; Hunter, K.W. Murine mammary carcinoma 4T1 induces a leukemoid reaction with splenomegaly: Association with tumor-derived growth factors. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2007, 82, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; TeSlaa, T.; Ng, S.; Nofal, M.; Wang, L.; Lan, T.; Zeng, X.; Cowan, A.; McBride, M.; Lu, W.; et al. Ketogenic diet and chemotherapy combine to disrupt pancreatic cancer metabolism and growth. Med 2022, 3, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburg, O.; Wind, F.; Negelein, E. The metabolism of tumors in the body. J. Gen. Physiol. 1927, 8, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Espin, C.; Agudo, A. The Role of Diet in Prognosis among Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Dietary Patterns and Diet Interventions. Nutrients 2022, 14, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lussier, D.M.; Woolf, E.C.; Johnson, J.L.; Brooks, K.S.; Blattman, J.N.; Scheck, A.C. Enhanced immunity in a mouse model of malignant glioma is mediated by a therapeutic ketogenic diet. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, D.; Vora, A.; Bhatt, L.K. The Wnt/β-catenin pathway in breast cancer therapy: A pre-clinical perspective of its targeting for clinical translation. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2021, 22, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Sun, Y.; Ma, L. ZEB1: At the crossroads of epithelial-mesenchymal transition, metastasis and therapy resistance. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolf, E.C.; Curley, K.L.; Liu, Q.; Turner, G.H.; Charlton, J.A.; Preul, M.C.; Scheck, A.C. The Ketogenic Diet Alters the Hypoxic Response and Affects Expression of Proteins Associated with Angiogenesis, Invasive Potential and Vascular Permeability in a Mouse Glioma Model. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Xiang, W.; Chen, Z.; Wang, G.; Cao, R.; Zhou, F.; Meng, Z.; Luo, Y.; Chen, L. Hypoxia-induced PLOD2 promotes clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression via modulating EGFR-dependent AKT pathway activation. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schödel, J.; Grampp, S.; Maher, E.R.; Moch, H.; Ratcliffe, P.J.; Russo, P.; Mole, D.R. Hypoxia, Hypoxia-inducible Transcription Factors, and Renal Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2015, 69, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Wang, F.; Ma, B.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, Q. Identifying Hypoxia Characteristics to Stratify Prognosis and Assess the Tumor Immune Microenvironment in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 606816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, X. HIF1A predicts the efficacy of anti-PD-1 therapy in advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 26, 101554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schokrpur, S.; Hu, J.; Moughon, D.L.; Liu, P.; Lin, L.C.; Hermann, K.; Mangul, S.; Guan, W.; Pellegrini, M.; Xu, H.; et al. CRISPR-Mediated VHL Knockout Generates an Improved Model for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ogbonna, H.N.; Roberts, Z.; Godwin, N.; Muri, P.; Turbitt, W.J.; Swalley, Z.N.; Dempsey, F.R.; Stephens, H.R.; Zhang, J.; Plaisance, E.P.; et al. An Exogenous Ketone Ester Slows Tumor Progression in Murine Breast and Renal Cancer Models. Cancers 2024, 16, 3390. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193390
Ogbonna HN, Roberts Z, Godwin N, Muri P, Turbitt WJ, Swalley ZN, Dempsey FR, Stephens HR, Zhang J, Plaisance EP, et al. An Exogenous Ketone Ester Slows Tumor Progression in Murine Breast and Renal Cancer Models. Cancers. 2024; 16(19):3390. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193390
Chicago/Turabian StyleOgbonna, Henry Nnaemeka, Zachary Roberts, Nicholas Godwin, Pia Muri, William J. Turbitt, Zoey N. Swalley, Francesca R. Dempsey, Holly R. Stephens, Jianqing Zhang, Eric P. Plaisance, and et al. 2024. "An Exogenous Ketone Ester Slows Tumor Progression in Murine Breast and Renal Cancer Models" Cancers 16, no. 19: 3390. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193390
APA StyleOgbonna, H. N., Roberts, Z., Godwin, N., Muri, P., Turbitt, W. J., Swalley, Z. N., Dempsey, F. R., Stephens, H. R., Zhang, J., Plaisance, E. P., & Norian, L. A. (2024). An Exogenous Ketone Ester Slows Tumor Progression in Murine Breast and Renal Cancer Models. Cancers, 16(19), 3390. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193390








