Neoadjuvant Pembrolizumab Plus Chemotherapy in Early-Stage Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Nationwide Retrospective Turkish Oncology Group Study
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Neoadjuvant Treatment
2.3. Definitive Surgery and Adjuvant Treatment
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Efficacy of Neoadjuvant Regimens
2.6. Survival Outcomes
2.7. Safety Assessment
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Response to Neoadjuvant Treatment
3.3. Survival Outcomes
3.4. Safety
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zagami, P.; Carey, L.A. Triple negative breast cancer: Pitfalls and progress. NPJ Breast Cancer 2022, 8, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, K.A.; Spruck, C. Triple negative breast cancer therapy: Current and future perspectives (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 57, 1245–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popovic, L.S.; Matovina-Brko, G.; Popovic, M.; Punie, K.; Cvetanovic, A.; Lambertini, M. Targeting triple-negative breast cancer: A clinical perspective. Oncol. Res. 2023, 31, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostinetto, E.; Eiger, D.; Punie, K.; de Azambuja, E. Emerging therapeutics for patients with triple-negative breast cancer. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 23, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlanetto, J.; Loibl, S. Optimal systemic treatment for early triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Care 2020, 15, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, M.; Bekele, F.; Fekadu, G. Treatment strategies against triple-negative breast cancer: An updated review. Breast Cancer 2022, 14, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Wu, F.; Sun, D.; Zhang, H.; Jin, L.; Kang, X.; Wang, Z. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy combined with breast-conserving surgery in the treatment of triple-negative breast cancer. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 7847889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinterri, C.; Barbieri, E.; Sagona, A.; Bottini, A.; Canavese, G.; Gentile, D. De-escalation surgery in cT3-4 breast cancer patients after neoadjuvant therapy: Predictors of breast conservation and comparison of long-term oncological outcomes with mastectomy. Cancers 2024, 16, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.Y.; Gao, H.F.; Yang, X.; Zhu, T.; Zheng, X.X.; Ji, F.; Zhang, L.L.; Yang, C.Q.; Yang, M.; Li, J.Q.; et al. Neoadjuvant therapy in triple-negative breast cancer: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Breast 2022, 66, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spring, L.M.; Fell, G.; Arfe, A.; Sharma, C.; Greenup, R.; Reynolds, K.L.; Smith, B.L.; Alexander, B.; Moy, B.; Isakoff, S.J.; et al. Pathologic complete response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and impact on breast cancer recurrence and survival: A comprehensive meta-analysis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2838–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conforti, F.; Pala, L.; Sala, I.; Oriecuia, C.; De Pas, T.; Specchia, C.; Graffeo, R.; Pagan, E.; Queirolo, P.; Pennacchioli, E.; et al. Evaluation of pathological complete response as surrogate endpoint in neoadjuvant randomised clinical trials of early stage breast cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2021, 375, e066381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, P.; Cortes, J.; Pusztai, L.; McArthur, H.; Kümmel, S.; Bergh, J.; Denkert, C.; Park, Y.H.; Hui, R.; Harbeck, N.; et al. Pembrolizumab for early triple-negative breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, P.; Cortes, J.; Dent, R.; Pusztai, L.; McArthur, H.; Kümmel, S.; Bergh, J.; Denkert, C.; Park, Y.H.; Hui, R.; et al. Event-free survival with pembrolizumab in early triple-negative breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, M.I.; Master, V.A. Who really knows the performance status: The physician or the patient? Cancer 2021, 127, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ölmez, F.; Oğlak, S.C.; Ölmez, Ö.F.; Akbayır, Ö.; Yılmaz, E.; Akgöl, S.; Konal, M.; Seyhan, N.A.; Kinter, A.K. High expression of CD8 in the tumor microenvironment is associated with PD-1 expression and patient survival in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Turk. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 19, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuck, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, A.; Kieber-Emmons, T.; Makhoul, I.; Hutchins, L. Relevance of pathological complete response after neoadjuvant therapy for breast cancer. Breast Cancer 2016, 10, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freites-Martinez, A.; Santana, N.; Arias-Santiago, S.; Viera, A. Using the common terminology criteria for adverse events (CTCAE-Version 5.0) to evaluate the severity of adverse events of anticancer therapies. Actas Dermosifiliogr. (Engl. Ed.) 2021, 112, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santa-Maria, C.A.; O’Donnell, M.; Nunes, R.; Wright, J.L.; Stearns, V. Integrating immunotherapy in early-stage triple-negative breast cancer: Practical evidence-based considerations. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2022, 20, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, M.; Cortés, J.; Dent, R.; Pusztai, L.; McArthur, H.; Kümmel, S.; Denkert, C.; Park, Y.H.; Im, S.A.; Ahn, J.H.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy followed by pembrolizumab in patients with early triple-negative breast cancer: A secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2342107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Kaklamani, V. Updates on the preoperative immunotherapy for triple-negative breast cancer. Transl. Breast Cancer Res. 2023, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Stecklein, S.R.; Yoder, R.; Staley, J.M.; Schwensen, K.; O’Dea, A.; Nye, L.; Satelli, D.; Crane, G.; Madan, R.; et al. Clinical and biomarker findings of neoadjuvant pembrolizumab and carboplatin plus docetaxel in triple-negative breast cancer: NeoPACT phase 2 clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2024, 10, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Ende, N.S.; Nguyen, A.H.; Jager, A.; Kok, M.; Debets, R.; van Deurzen, C.H.M. Triple-negative breast cancer and predictive markers of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy: A systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asleh, K.; Riaz, N.; Nielsen, T.O. Heterogeneity of triple negative breast cancer: Current advances in subtyping and treatment implications. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assunção Ribeiro da Costa, R.E.; Rocha de Oliveira, F.T.; Nascimento Araújo, A.L.; Vieira, S.C. Impact of pathologic complete response on the prognosis of triple-negative breast cancer patients: A cohort study. Cureus 2023, 15, e37396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; O’Shaughnessy, J.; Zhao, J.; Haiderali, A.; Cortés, J.; Ramsey, S.D.; Briggs, A.; Hu, P.; Karantza, V.; Aktan, G.; et al. Association of pathologic complete response with long-term survival outcomes in triple-negative breast cancer: A meta-analysis. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 5427–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios, C.H.; Saji, S.; Harbeck, N.; Zhang, H.; Jung, K.H.; Patel, S.; Patel, S.; Duc, A.N.; Liste-Hermoso, M.; Chui, S.Y.; et al. Patient-reported outcomes from a randomized trial of neoadjuvant atezolizumab-chemotherapy in early triple-negative breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2022, 8, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutlu, Y.; Dae, S.A.; Yilmaz, F.; Erdem, D.; Sendur, M.A.N.; Akbas, S.; Senocak Tasci, E.; Bas, O.; Dane, F.; Sakin, A.; et al. Real-world efficacy and safety of first-line nivolumab plus chemotherapy in patients with advanced gastric, gastroesophageal junction, and esophageal adenocarcinoma: A nationwide observational turkish oncology group (TOG) study. Cancers 2024, 16, 2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Age, years; median (range) | 45 (27−85) |
| <65 | 99 (91.7) |
| ≥65 | 9 (8.3) |
| Menopausal status | |
| Premenopausal | 65 (60.2) |
| Postmenopausal | 43 (39.8) |
| ECOG performance status | |
| 0 | 88 (81.5) |
| 1 | 20 (18.5) |
| Primary lesion | |
| Single | 81 (75.0) |
| Multifocal | 17 (15.7) |
| Multicentric | 10 (9.3) |
| Histopathological type | |
| IDC | 89 (82.4) |
| Invasive carcinoma, NOS | 13 (12.1) |
| Metaplastic carcinoma | 5 (4.6) |
| Other | 1 (0.9) |
| Ki-67 index | |
| <20% | 7 (6.5) |
| >20% | 101 (93.5) |
| Primary tumor T stage | |
| T1–T2 | 89 (82.4) |
| T3–T4 | 19 (17.6) |
| Primary lymph nodal status | |
| Node-negative | 37 (34.3) |
| Node-positive | 71 (65.7) |
| Primary disease stage | |
| I | 3 (2.8) |
| II | 63 (58.3) |
| III | 42 (38.9) |
| PD-L1 status | |
| Negative | 65 (60.2) |
| Positive | 43 (39.8) |
| Schedule of carboplatin | |
| Weekly | 75 (69.4) |
| Every 3 weeks | 33 (30.6) |
| Surgery type | |
| BCS-SLNB | 55 (50.9) |
| BCS-AD | 13 (12.1) |
| SCM-SLNB | 31 (28.7) |
| MRM | 9 (8.3) |
| BRCA1/2 mutation status | |
| Negative | 51 (47.2) |
| Positive | 14 (13.0) |
| Unknown | 43 (39.8) |
| Adjuvant pembrolizumab | |
| No | 75 (69.4) |
| Yes | 33 (30.6) |
| Adjuvant capecitabine | |
| No | 70 (64.8) |
| Yes | 38 (35.2) |
| Variable | n (%) | 2-Years EFS (%) | Univariable p Value | Multivariable p Value | HR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | |||||
| <65 | 99 (91.7) | 89.7 | 0.09 | 0.96 | 1.76 (0.54–3.35) |
| ≥65 | 9 (8.3) | 59.3 | |||
| Menopausal status | |||||
| Premenopausal | 65 (60.2) | 85.7 | 0.53 | ||
| Postmenopausal | 43 (39.8) | 89.4 | |||
| ECOG performance status | |||||
| 0 | 88 (81.5) | 91.9 | 0.021 | 0.96 | 0.89 (0.51–3.54) |
| 1 | 20 (18.5) | 66.8 | |||
| Primary lesion | |||||
| Single | 81 (75.0) | 82.9 | 0.23 | ||
| Multifocal | 17 (15.7) | 84.8 | |||
| Multicentric | 10 (9.3) | NA | |||
| Histopathological type | |||||
| IDC | 89 (82.4) | 86.0 | 0.56 | 0.33 (0.13–0.85) | |
| Invasive carcinoma, NOS | 13 (12.1) | NA | |||
| Metaplastic carcinoma | 5 (4.6) | 75.0 | |||
| Other | 1 (0.9) | NA | |||
| Primary tumor T stage | |||||
| T1–T2 | 89 (82.4) | 84.2 | 0.15 | 2.0 (0.81–4.9) | |
| T3–T4 | 19 (17.6) | NA | |||
| Primary lymph node status | |||||
| Node-negative | 37 (34.3) | 94.4 | 0.26 | ||
| Node-positive | 71 (65.7) | 84.1 | |||
| Primary disease stage | |||||
| I | 3 (2.8) | NA | 0.99 | ||
| II | 63 (58.3) | 85.5 | |||
| III | 42 (38.9) | 89.6 | |||
| Schedule of carboplatin | |||||
| Weekly | 75 (69.4) | 91.1 | 0.032 | 0.28 | 1.11 (0.88–5.41) |
| Every 3 weeks | 33 (30.6) | 69.6 | |||
| PD-L1 status | |||||
| Negative | 65 (60.2) | 81.8 | 0.10 | ||
| Positive | 43 (39.8) | 95.8 | |||
| BRCA1/2 mutation status | |||||
| Negative | 51 (47.2) | 89.2 | 0.043 | 0.12 | 9.51 (0.54–27.1) |
| Positive | 14 (13.0) | 69.9 | |||
| Unknown | 43 (39.8) | 71.2 | |||
| Adjuvant pembrolizumab | |||||
| No | 75 (69.4) | 86.8 | 0.64 | ||
| Yes | 33 (30.6) | 86.6 | |||
| Adjuvant capecitabine | |||||
| No | 70 (64.8) | 75.1 | 0.014 | 0.90 | 1.28 (0.50–5.48) |
| Yes | 38 (35.2) | 97.3 | |||
| pCR | |||||
| Absent | 39 (36.1) | 71.9 | 0.009 | 0.031 | 5.90 (1.17–9.87) |
| Present | 69 (63.9) | 95.4 | |||
| Variable | n (%) | 2-Years OS (%) | Univariable p Value | Multivariable p Value | HR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | |||||
| <65 | 99 (91.7) | 93.4 | 0.44 | ||
| ≥65 | 9 (8.3) | 85.7 | |||
| Menopausal status | |||||
| Premenopausal | 65 (60.2) | 91.4 | 0.54 | ||
| Postmenopausal | 43 (39.8) | 95.8 | |||
| ECOG performance status | |||||
| 0 | 88 (81.5) | 97.1 | 0.021 | 0.76 | 0.12 (0.05–2.54) |
| 1 | 20 (18.5) | 77.0 | |||
| Primary lesion | |||||
| Single | 81 (75.0) | 89.9 | 0.36 | ||
| Multifocal | 17 (15.7) | NA | |||
| Multicentric | 10 (9.3) | NA | |||
| Histopathological type | |||||
| IDC | 89 (82.4) | 93.6 | 0.53 | ||
| Invasive carcinoma, NOS | 13 (12.1) | 89.4 | |||
| Metaplastic carcinoma | 5 (4.6) | NA | |||
| Other | 1 (0.9) | NA | |||
| Primary tumor T stage | |||||
| T1–T2 | 89 (82.4) | 90.9 | 0.24 | ||
| T3–T4 | 19 (17.6) | NA | |||
| Primary lymph node status | |||||
| Node-negative | 37 (34.3) | NA | 0.12 | ||
| Node-positive | 71 (65.7) | 89.4 | |||
| Primary disease stage | |||||
| I | 3 (2.8) | NA | 0.68 | ||
| II | 63 (58.3) | 94.7 | |||
| III | 42 (38.9) | 84.4 | |||
| Schedule of carboplatin | |||||
| Weekly | 75 (69.4) | 95.4 | 0.021 | 0.78 | 1.23 (0.77–2.89) |
| Every 3 weeks | 33 (30.6) | 77.2 | |||
| PD-L1 status | |||||
| Negative | 65 (60.2) | 88.3 | 0.07 | ||
| Positive | 43 (39.8) | NA | |||
| BRCA1/2 status | |||||
| Negative | 51 (47.2) | 96.0 | 0.009 | 0.99 | 1.54 (0.99–3.77) |
| Positive | 14 (13.0) | 72.4 | |||
| Unknown | 43 (39.8) | 73.3 | |||
| Adjuvant pembrolizumab | |||||
| No | 75 (69.4) | 88.1 | 0.10 | ||
| Yes | 33 (30.6) | 91.1 | |||
| Adjuvant capecitabine | |||||
| No | 70 (64.8) | 90.2 | 0.026 | 0.53 | 1.62 (0.78–2.12) |
| Yes | 38 (35.2) | 97.8 | |||
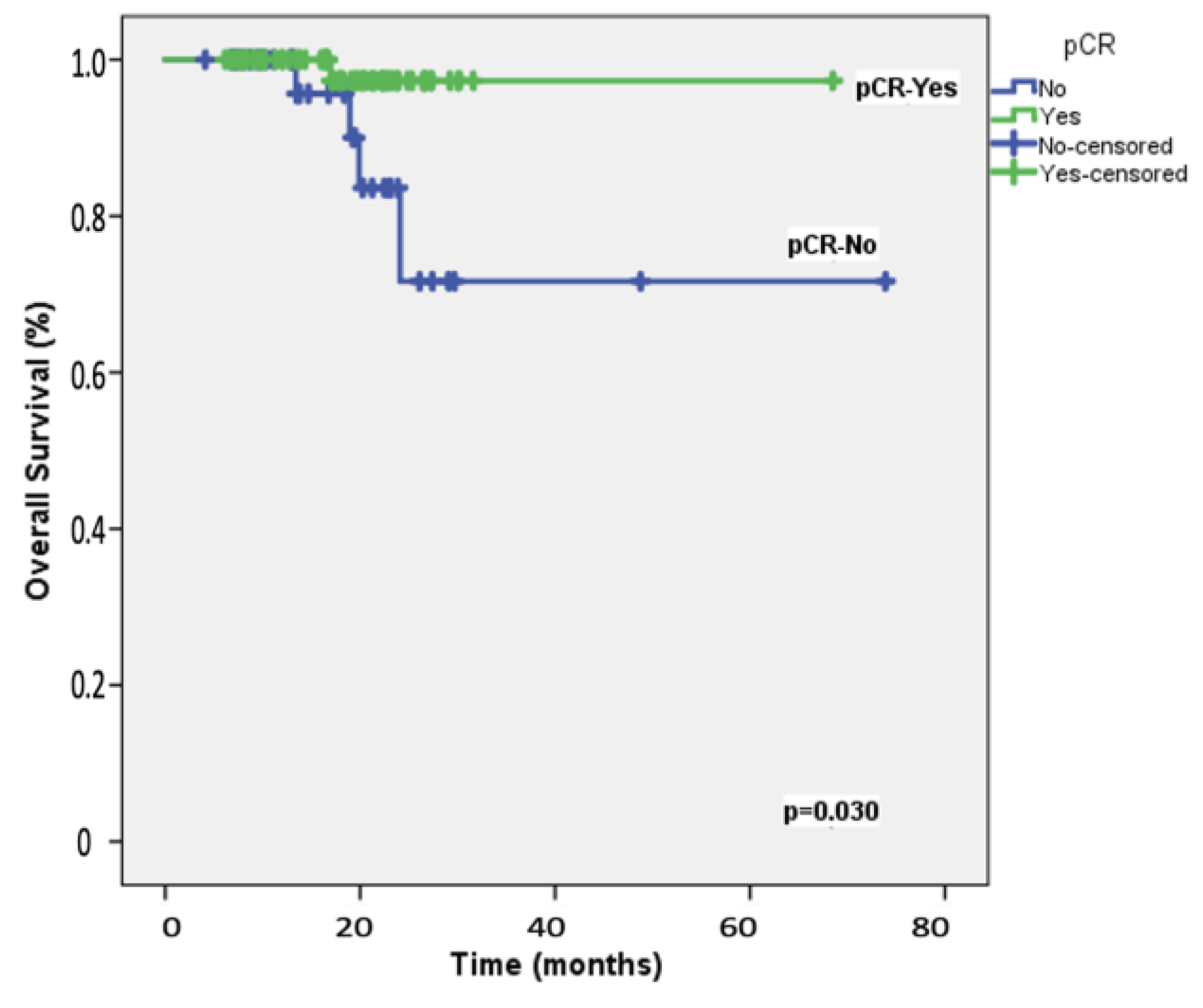
| pCR | |||||
| Absent | 39 (33.1) | 87.6 | 0.030 | 0.044 | 1.57 (1.02–2.64) |
| Present | 69 (63.9) | 97.6 | |||
| Adverse Event | Grade 1–2, n (%) | Grade 3–4, n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Alopecia | 75 (69.4) | 2 (1.8) |
| Nausea | 70 (64.8) | 4 (3.7) |
| Neutropenia | 52 (48.1) | 18 (16.6) |
| Fatigue | 45 (41.6) | 4 (3.7) |
| Vomiting | 36 (33.3) | 3 (2.8) |
| Anemia | 36 (33.3) | 7 (6.4) |
| Diarrhea | 32 (29.6) | 1 (0.9) |
| Peripheral neuropathy | 26 (24.1) | 2 (1.8) |
| Constipation | 25 (23.1) | - |
| Increased ALT | 22 (20.3) | 3 (2.8) |
| Increased AST | 21 (19.4) | 3 (2.8) |
| Rash | 21 (19.4) | - |
| Decreased appetite | 18 (16.6) | 4 (3.7) |
| Hypothyroidism | 12 (11.1) | 2 (1.8) |
| Stomatitis | 7 (6.4) | - |
| Thrombocytopenia | 7 (6.4) | - |
| Adrenal insufficiency | 1 (0.9) | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karci, E.; Bilici, A.; Bayram, B.; Celayir, M.; Ozyurt, N.; Uluc, B.O.; Eken, A.; Basaran, G.; Demirci, U.; Kemal, Y.; et al. Neoadjuvant Pembrolizumab Plus Chemotherapy in Early-Stage Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Nationwide Retrospective Turkish Oncology Group Study. Cancers 2024, 16, 3389. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193389
Karci E, Bilici A, Bayram B, Celayir M, Ozyurt N, Uluc BO, Eken A, Basaran G, Demirci U, Kemal Y, et al. Neoadjuvant Pembrolizumab Plus Chemotherapy in Early-Stage Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Nationwide Retrospective Turkish Oncology Group Study. Cancers. 2024; 16(19):3389. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193389
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarci, Ebru, Ahmet Bilici, Buket Bayram, Melisa Celayir, Neslihan Ozyurt, Başak Oyan Uluc, Aynur Eken, Gul Basaran, Umut Demirci, Yasemin Kemal, and et al. 2024. "Neoadjuvant Pembrolizumab Plus Chemotherapy in Early-Stage Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Nationwide Retrospective Turkish Oncology Group Study" Cancers 16, no. 19: 3389. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193389
APA StyleKarci, E., Bilici, A., Bayram, B., Celayir, M., Ozyurt, N., Uluc, B. O., Eken, A., Basaran, G., Demirci, U., Kemal, Y., Oruncu, M. B., Olmez, O. F., Selcukbiricik, F., Korkmaz, T., Erturk, I., Bilgetekin, I., Celik, S., Turkel, A., Alkan, A., ... Yildiz, O. (2024). Neoadjuvant Pembrolizumab Plus Chemotherapy in Early-Stage Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Nationwide Retrospective Turkish Oncology Group Study. Cancers, 16(19), 3389. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16193389





