Histopathological Growth Patterns Determine the Outcomes of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis Following Liver Resection
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Histopathologic Growth Patterns and Primary Tumor Characteristics
1.2. Histopathologic Growth Patterns, Immune Scores, and Immunotherapy
1.3. Vessel Co-Option and Genetics
2. Methods
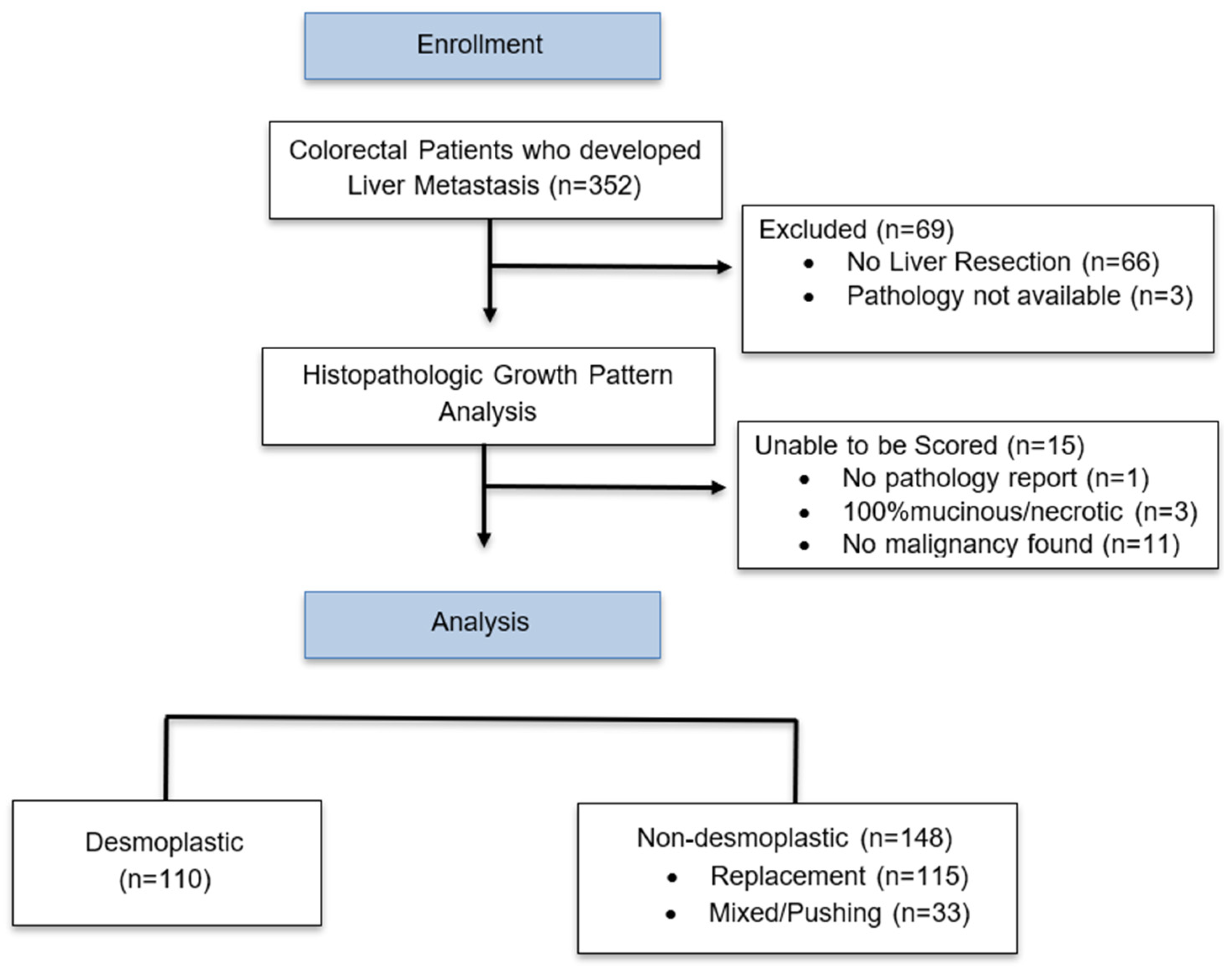
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Determination of Tumor Histopathologic Growth Pattern
2.3. Next Generation Sequencing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
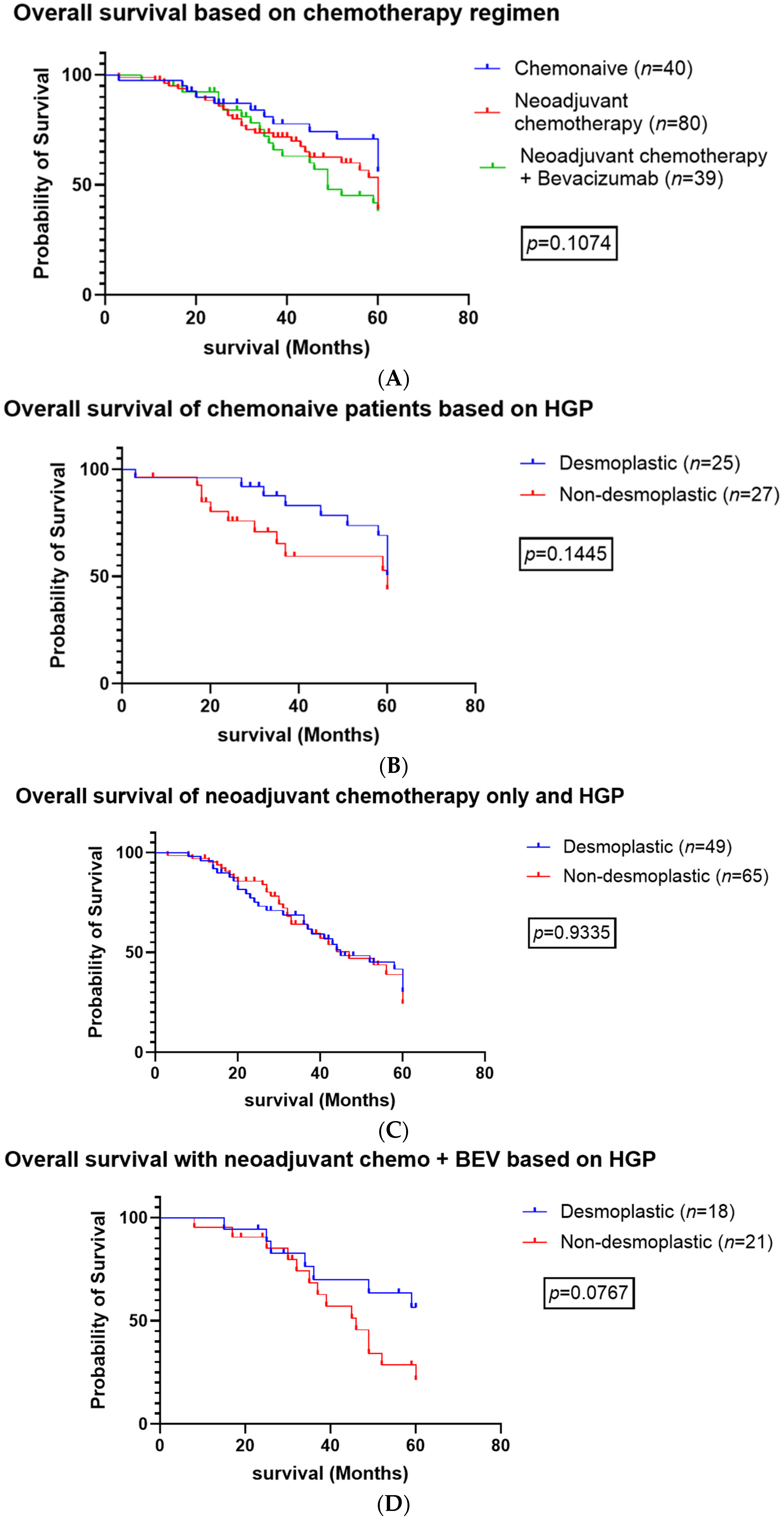
3.1. Systemic Therapy
3.2. Mutation Analysis
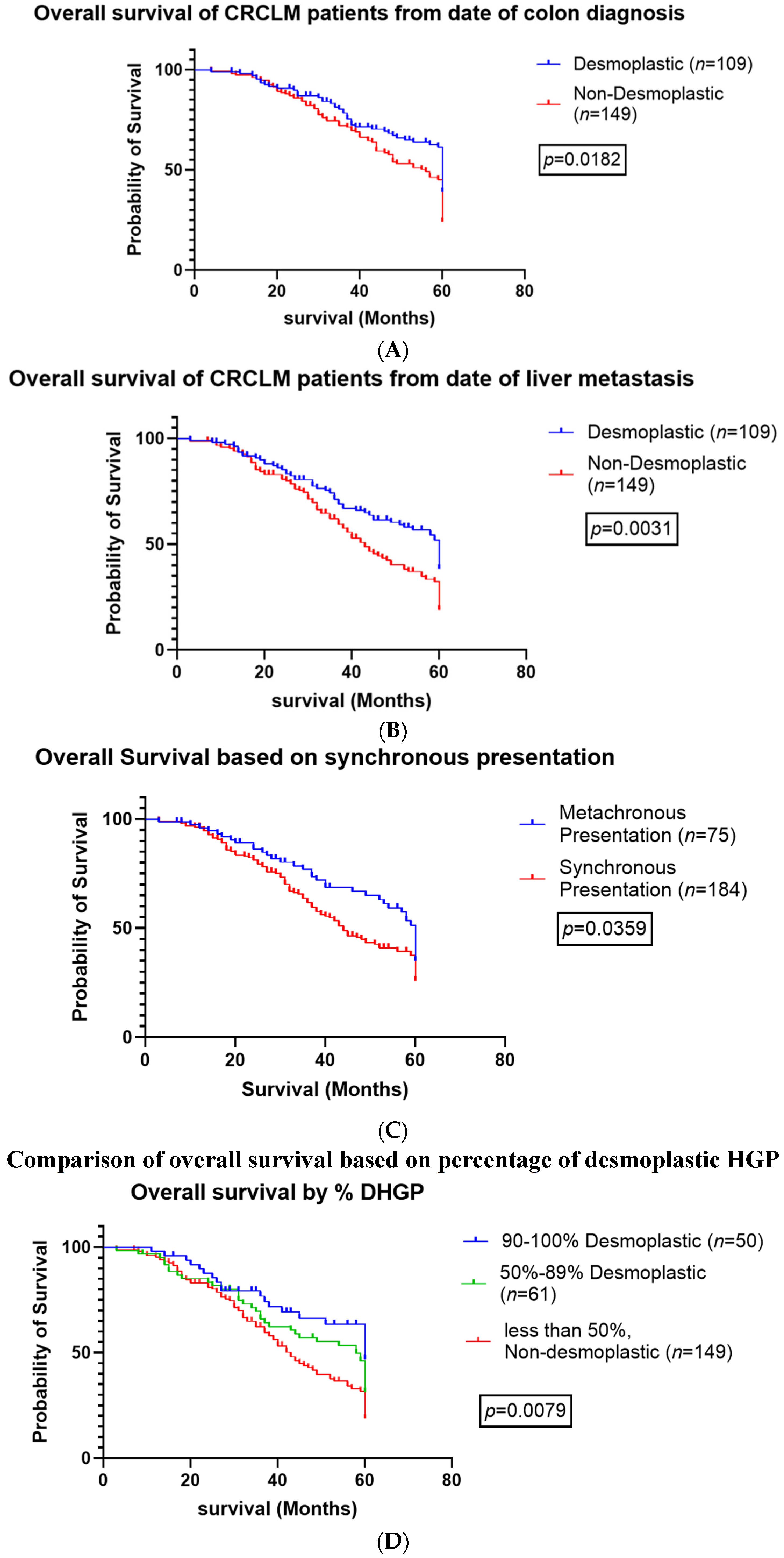
3.3. Survival Analysis
3.4. Extrahepatic and Recurrent Disease
3.5. Univariate and Multivariate Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BEV | bevacizumab |
| CDR | Crohn’s disease-like response |
| CRCLM | colorectal cancer liver metastasis |
| CRS | cancer risk score |
| DFS | disease free survival |
| HA | hyaluronic acid |
| HGP | histopathologic growth patterns |
| dHGP | desmoplastic histopathologic growth patterns |
| rHGP | replacement histopathologic growth patterns |
| IHC | immunohistochemistry |
| LM | liver metastasis |
| LR | liver resection |
| MSI | microsatellite instability |
| MVD | microvascular density |
| OS | overall survival |
| PFS | progression free survival |
| RFS | recurrence free survival |
| TBS | tumor budding score |
References
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmoll, H.J.; Van Cutsem, E.; Stein, A.; Valentini, V.G.; Limelius, B.; Haustermans, K.; Nordlinger, B.; van de Velde, C.J.; Balmana, J.; Regula, J.; et al. ESMO Consensus Guidelines for management of patients with colon and rectal cancer. A personalized approach to clinical decision making. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 2479–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemke, J.; Cammerer, G.; Ganser, J.; Scheele, J.; Xu, P.; Sander, S.; Henne-Bruns, D.; Kornmann, M. Survival and Prognostic Factors of Colorectal Liver Metastases after Surgical and Nonsurgical Treatment. Clin. Color. Cancer 2016, 15, e183–e192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbard, J.M.; Grothey, A. Colorectal cancer in 2014: Progress in defining first-line and maintenance therapies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 12, 73–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, P.B.; Colpaert, C.; Salgado, R.; Royers, R.; Hellemans, H.; Van den Heuvel, E.; Goovaerts, G.; Dirix, L.Y.; Van Marck, E. Liver metastases from colorectal adenocarcinomas grow in three patterns with different angiogenesis and desmoplasia. J. Pathol. 2001, 195, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frentzas, S.; Simoneau, E.; Bridgeman, V.L.; Vermeulen, P.B.; Foo, S.; Kostaras, E.; Nathan, M.; Wotherspoon, A.; Gao, Z.H.; Shi, Y.; et al. Vessel co-option mediates resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy in liver metastases. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nierop, P.M.H.; Galjart, B.; Höppener, D.J.; van der Stok, E.P.; Coebergh van den Braak, R.R.J.; Vermeulen, P.B.; Grünhagen, D.J.; Verhoef, C. Salvage treatment for recurrences after first resection of colorectal liver metastases: The impact of histopathological growth patterns. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2019, 36, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galjart, B.; Nierop, P.M.H.; van der Stok, E.P.; van den Braak, R.R.J.C.; Höppener, D.J.; Daelemans, S.; Dirix, L.Y.; Verhoef, C.; Vermeulen, P.B.; Grünhagen, D.J. Angiogenic desmoplastic histopathological growth pattern as a prognostic marker of good outcome in patients with colorectal liver metastases. Angiogenesis 2019, 22, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.C.; Alexandrino, H.; Cipriano, M.A.; Alves, F.C.; Tralhão, J.G. Predicting liver metastases growth patterns: Current status and future possibilities. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 71, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nierop, P.M.H.; Höppener, D.J.; van der Stok, E.P.; Galjart, B.; Buisman, F.E.; Balachandran, V.P.; Jarnagin, W.R.; Kingham, T.P.; Allen, P.J.; Shia, J.; et al. Histopathological growth patterns and positive margins after resection of colorectal liver metastases. HPB 2020, 22, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, C.F.; Bozoky, B.; Gerling, M. Growth patterns of colorectal cancer liver metastases and their impact on prognosis: A systematic review. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2018, 5, e000217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dam, P.J.; van der Stok, E.P.; Teuwen, L.A.; Van den Eynden, G.G.; Illemann, M.; Frentzas, S.; Majeed, A.W.; Eefsen, R.L.; Coebergh van den Braak, R.R.J.; Lazaris, A.; et al. International consensus guidelines for scoring the histopathological growth patterns of liver metastasis. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 1427–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcão, D.; Alexandrino, H.; Caetano Oliveira, R.; Martins, J.; Ferreira, L.; Martins, R.; Serôdio, M.; Martins, M.; Tralhão, J.G.; Cipriano, M.A.; et al. Histopathologic patterns as markers of prognosis in patients undergoing hepatectomy for colorectal cancer liver metastases—Pushing growth as an independent risk factor for decreased survival. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 44, 1212–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, S.; von Moos, R.; Mey, U.; Camenisch Gross, U.; Freyholdt, T.; Cathomas, R. Efficacy of triplet combination chemotherapy with oxaliplatin, irinotecan and capecitabine (OCX) in metastatic colorectal cancer in relation to RAS/RAF mutation status: Results of a retrospective analysis. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2014, 37, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siriwardana, P.N.; Luong, T.V.; Watkins, J.; Turley, H.; Ghazaley, M.; Gatter, K.; Harris, A.L.; Hochhauser, D.; Davidson, B.R. Biological and Prognostic Significance of the Morphological Types and Vascular Patterns in Colorectal Liver Metastases (CRLM): Looking Beyond the Tumor Margin. Medicine 2016, 95, e2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, R.S.; Herman, P.; Lupinacci, R.M.; Lai, Q.; Mello, E.S.; Coelho, F.F.; Perini, M.V.; Pugliese, V.; Andraus, W.; Cecconello, I.; et al. Tumor growth pattern as predictor of colorectal liver metastasis recurrence. Am. J. Surg. 2014, 207, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyström, H.; Naredi, P.; Berglund, A.; Palmqvist, R.; Tavelin, B.; Sund, M. Liver-metastatic potential of colorectal cancer is related to the stromal composition of the tumour. Anticancer. Res. 2012, 32, 5183–5191. [Google Scholar]
- Eefsen, R.L.; Vermeulen, P.B.; Christensen, I.J.; Laerum, O.D.; Mogensen, M.B.; Rolff, H.C.; Van Den Eynden, G.G.; Høyer-Hansen, G.; Osterlind, K.; Vainer, B.; et al. Growth pattern of colorectal liver metastasis as a marker of recurrence risk. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2015, 32, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, K.; Rolff, H.C.; Eefsen, R.L.; Vainer, B. The morphological growth patterns of colorectal liver metastases are prognostic for overall survival. Mod. Pathol. 2014, 27, 1641–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Eynden, G.G.; Bird, N.C.; Majeed, A.W.; Van Laere, S.; Dirix, L.Y.; Vermeulen, P.B. The histological growth pattern of colorectal cancer liver metastases has prognostic value. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2012, 29, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eefsen, R.L.; Van den Eynden, G.G.; Høyer-Hansen, G.; Brodt, P.; Laerum, O.D.; Vermeulen, P.B.; Christensen, I.J.; Wettergren, A.; Federspiel, B.; Willemoe, G.L.; et al. Histopathological growth pattern, proteolysis and angiogenesis in chemonaive patients resected for multiple colorectal liver metastases. J. Oncol. 2012, 2012, 907971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbari, N.N.; Bork, U.; Schölch, S.; Reissfelder, C.; Thorlund, K.; Betzler, A.; Kahlert, C.; Schneider, M.; Ulrich, A.B.; Büchler, M.W.; et al. Metastatic Spread Emerging from Liver Metastases of Colorectal Cancer: Does the Seed Leave the Soil Again? Ann. Surg. 2016, 263, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stremitzer, S.; Vermeulen, P.; Graver, S.; Kockx, M.; Dirix, L.; Yang, D.; Zhang, W.; Stift, J.; Wrba, F.; Gruenberger, T.; et al. Immune phenotype and histopathological growth pattern in patients with colorectal liver metastases. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaris, A.; Amri, A.; Petrillo, S.K.; Zoroquiain, P.; Ibrahim, N.; Salman, A.; Gao, Z.H.; Vermeulen, P.B.; Metrakos, P. Vascularization of colorectal carcinoma liver metastasis: Insight into stratification of patients for anti-angiogenic therapies. J. Pathol. Clin. Res. 2018, 4, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremolini, C.; Milione, M.; Marmorino, F.; Morano, F.; Zucchelli, G.; Mennitto, A.; Prisciandaro, M.; Lonardi, S.; Pellegrinelli, A.; Rossini, D.; et al. Differential histopathologic parameters in colorectal cancer liver metastases resected after triplets plus bevacizumab or cetuximab: A pooled analysis of five prospective trials. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, N.S.; Lazaris, A.; Rada, M.; Petrillo, S.K.; Huck, L.; Hussain, S.; Ouladan, S.; Gao, Z.H.; Gregorieff, A.; Essalmani, R.; et al. Angiopoietin1 Deficiency in Hepatocytes Affects the Growth of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastases (CRCLM). Cancers 2019, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Nordlinger, B.; Adam, R.; Köhne, C.H.; Pozzo, C.; Poston, G.; Ychou, M.; Rougier, P. European Colorectal Metastases Treatment Group. Towards a pan-European consensus on the treatment of patients with colorectal liver metastases. Eur. J. Cancer 2006, 42, 2212–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stessels, F.; Van den Eynden, G.; Van der Auwera, I.; Salgado, R.; Van den Heuvel, E.; Harris, A.L.; Jackson, D.G.; Colpaert, C.G.; van Marck, E.A.; Dirix, L.Y.; et al. Breast adenocarcinoma liver metastases, in contrast to colorectal cancer liver metastases, display a non-angiogenic growth pattern that preserves the stroma and lacks hypoxia. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 90, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnhill, R.; Vermeulen, P.; Daelemans, S.; van Dam, P.J.; Roman-Roman, S.; Servois, V.; Hurbain, I.; Gardrat, S.; Raposa, G.; Nicolas, A.; et al. Replacement and desmoplastic histopathological growth patterns: A pilot study of prediction of outcome in patients with uveal melanoma liver metastases. J. Pathol. Clin. Res. 2018, 4, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, T.; Verbeke, C.S.; Strobel, O.; Rutkowski, W.; Villard, C.; Moro, C.F.; Del Chiaro, M.; Büchler, M.; Heuchel, R.; Löhr, M. Immunohistochemical profiling of liver metastases and matched-pair analysis in patients with metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreatology 2019, 19, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczynski, E.A.; Vermeulen, P.B.; Pezzella, F.; Kerbel, R.S.; Reynolds, A.R. Vessel co-option in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 469–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temido, M.J.; Caetano Oliveira, R.; Martins, R.; Serôdio, M.; Costa, B.; Carvalho, C.; Santos, E.; Ferreira, L.; Teixeira, P.; Cipriano, M.A.; et al. Prognostic Factors After Hepatectomy for Gastric Adenocarcinoma Liver Metastases: Desmoplastic Growth Pattern as the Key to Improved Overall Survival. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 11689–11699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozaka, K.; Sasaki, M.; Fujii, T.; Harada, K.; Zen, Y.; Sato, Y.; Sawada, S.; Minato, H.; Matsui, O.; Nakanuma, Y. A subgroup of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma with an infiltrating replacement growth pattern and a resemblance to reactive proliferating bile ductules: ‘bile ductular carcinoma’. Histopathology 2007, 51, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlok, A.; Vermeulen, P.; Leduc, S.; Latacz, E.; Botzenhart, L.; Richard, F.; De Schepper, M.; Geukens, T.; Lucidi, V.; Ignatiadis, M.; et al. Association between the histopathological growth patterns of liver metastases and survival after hepatic surgery in breast cancer patients. NPJ Breast Cancer 2020, 6, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajaganeshan, R.; Prasad, R.; Guillou, P.J.; Chalmers, C.R.; Scott, N.; Sarkar, R.; Poston, G.; Jayne, D.G. The influence of invasive growth pattern and microvessel density on prognosis in colorectal cancer and colorectal liver metastases. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 1112–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Lin, H.; Li, S. Prognoses of different pathological subtypes of colorectal cancer at different stages: A population-based retrospective cohort study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, C.; Huang, J.; Xie, Z.; Chen, X.; Zheng, Z.; Li, E.; Zou, H. The possibilities of LOXL4 as a prognostic marker for carcinomas. Amino Acids. 2023, 55, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gültekin, M.A.; Türk, H.M.; Beşiroğlu, M.; Toprak, H.; Yurtsever, I.; Yilmaz, T.F.; Sharifov, R.; Uysal, Ö. Relationship between KRAS mutation and diffusion weighted imaging in colorectal liver metastases; Preliminary study. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 125, 108895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, V.; Lazaris, A.; Mayer, T.Z.; Petrillo, S.K.; Alamri, H.; Rada, M.; Jarrouj, G.; Park, W.Y.; Gao, Z.H.; McDonald, P.P.; et al. Neutrophils expressing lysyl oxidase-like 4 protein are present in colorectal cancer liver metastases resistant to anti-angiogenic therapy. J. Pathol. 2020, 251, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Wei, J.; Tong, T.; Sheng, W.; Zhang, Y.; Han, Y.; Gu, D.; Hong, N.; Ye, Y.; Tian, J.; et al. Prediction of Histopathologic Growth Patterns of Colorectal Liver Metastases with a Noninvasive Imaging Method. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 4587–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dueland, S.; Grut, H.; Syversveen, T.; Hagness, M.; Line, P.D. Selection criteria related to long-term survival following liver transplantation for colorectal liver metastasis. Am. J. Transplant. 2020, 20, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Line, P.D.; Hagness, M.; Dueland, S. The Potential Role of Liver Transplantation as a Treatment Option in Colorectal Liver Metastases. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 2018, 8547940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simoneau, E.; D’Angelica, M.; Halazun, K.J. Liver transplantation for colorectal liver metastasis. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2019, 24, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grut, H.; Solberg, S.; Seierstad, T.; Revheim, M.E.; Egge, T.S.; Larsen, S.G.; Line, P.D.; Dueland, S. Growth rates of pulmonary metastases after liver transplantation for unresectable colorectal liver metastases. Br. J. Surg. 2018, 105, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupertus, K.; Dahlem, C.; Menger, M.D.; Schilling, M.K.; Kollmar, O. Rapamycin inhibits hepatectomy-induced stimulation of metastatic tumor growth by reduction of angiogenesis, microvascular blood perfusion, and tumor cell proliferation. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2009, 16, 2629–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toso, C.; Kneteman, N.M.; James Shapiro, A.M.; Bigam, D.L. The estimated number of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma selected for liver transplantation using expanded selection criteria. Transpl. Int. 2009, 22, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Desmoplastic | Non-Desmoplastic | |
|---|---|---|
| Survival analysis | Increased OS, MS, DFS, PFS | Decreased OS, MS, DFS, PFS |
| Surgical outcomes | Increased rate of successful re-resection for recurrent disease | Increased risk of R1 resection; increased risk of incomplete resection |
| Response to systemic chemotherapy | Good response to chemotherapy | Decreased response |
| Response to targeted therapy | Good response | Poor response to anti-VEGF and anti-EGFR therapy |
| Disease recurrence | Lower rate of overall disease recurrence; increased rate of hepatic recurrence compared with extrahepatic recurrence | Increased rate of overall recurrence; increased rate of extrahepatic recurrence compared with hepatic recurrence |
| Immune landscape | Increased lymphocyte infiltration; increased numbers of CD3+ and CD8+ immune cells | Decreased lymphocyte infiltration; adaptive immune phenotype with neutrophils present |
| Primary colon tumor | Lower tumor budding score; pushing colon tumor margin | High tumor budding score; infiltrative colon tumor margin |
| Characteristics | Univariate | Multivariate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio | 95% CI | p-Value | Hazard Ratio | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Liver tumor histology | ||||||
| Desmoplastic | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Non-desmoplastic | 1.70 | 1.23–2.34 | 0.0010 | 1.54 | 1.09–2.15 | 0.0133 |
| Synchronous presentation | ||||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Yes | 4.30 | 2.79–6.65 | <0.0001 | 4.13 | 2.63–6.48 | <0.0001 |
| Neoadjuvant chemotherapy before primary resection | ||||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Yes | 1.87 | 1.36–2.55 | <0.0001 | 1.80 | 1.30–2.50 | 0.0004 |
| Adjuvant chemotherapy after liver resection | ||||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Yes | 1.51 | 0.82–2.83 | 0.1819 | 1.54 | 0.80–2.98 | 0.1960 |
| TNM stage of primary tumor | ||||||
| 1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| 2 | 1.67 | 0.39–7.13 | 0.4875 | 1.82 | 0.42–7.79 | 0.4208 |
| 3 | 2.96 | 0.43–12.09 | 0.1299 | 2.76 | 0.67–11.29 | 0.1588 |
| 4 | 4.98 | 1.20–20.69 | 0.0273 | 5.92 | 1.41–24.77 | 0.0149 |
| KRAS | ||||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Yes | 1.43 | 0.99–2.09 | 0.0600 | 1.56 | 1.03–2.36 | 0.0373 |
| Location of primary tumor | ||||||
| Bilateral | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Right | 3.75 | 0.91–15.39 | 0.0670 | 3.32 | 0.79–14.00 | 0.1022 |
| Left | 2.26 | 0.55–9.32 | 0.2592 | 2.00 | 0.48–8.34 | 0.3442 |
| Rectum | 2.53 | 0.62–10.34 | 0.1950 | 2.13 | 0.52–8.78 | 0.2975 |
| Volume of primary tumor | ||||||
| 1.003 | 0.995–1.010 | 0.4924 | 1.002 | 0.995–1.010 | 0.5749 | |
| Greatest dimension of liver tumor | ||||||
| 0.968 | 0.912–1.028 | 0.4822 | 0.3673 | 0.907–1.029 | 0.2803 | |
| Development of extra-hepatic metastatic disease | ||||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Yes | 1.82 | 1.29–2.57 | 0.0006 | 1.88 | 1.3–2.72 | 0.0007 |
| Multiple of extra-hepatic metastatic site | ||||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Yes | 1.96 | 1.44–2.67 | <0.0001 | 2.02 | 1.46–2.80 | <0.0001 |
| Liver metastatic recurrence | ||||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Yes | 1.46 | 1.02–2.10 | 0.0403 | 1.81 | 1.13–2.88 | 0.0127 |
| Never fully resected | 3.42 | 2.25–5.22 | <0.0001 | 1.32 | 0.79–2.22 | 0.2871 |
| Liver resection with and without BEV | ||||||
| Chemonaive | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Neoadjuvent | 2.26 | 1.42–3.59 | 0.0005 | 1.93 | 0.97–3.82 | 0.0602 |
| BEV | 1.68 | 1.02–2.76 | 0.0415 | 2.98 | 1.47–6.02 | 0.0024 |
| Number of clinically relevant mutations in liver tumors | ||||||
| 0 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| 1 | 1.76 | 1.10–2.81 | 0.0177 | 2.06 | 1.24–3.43 | 0.0053 |
| 2 | 1.20 | 0.64–2.27 | 0.5666 | 1.45 | 0.73–2.87 | 0.2912 |
| 3 | 13.42 | 1.71–105.69 | 0.0136 | 16.81 | 2.00–141.45 | 0.0094 |
| Number of clinically relevant mutations in primary tumor | ||||||
| 0 | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| 1 | 1.42 | 0.80–2.52 | 0.2326 | 1.74 | 0.93–3.28 | 0.0838 |
| 2 | 1.21 | 0.55–2.64 | 0.6412 | 1.62 | 0.72–3.67 | 0.2459 |
| 3 | 39.98 | 3.56–448.71 | 0.0028 | 63.79 | 4.62–881.05 | 0.0019 |
| Characteristics | Univariate | Multivariate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio | 95% CI | p-Value | Hazard Ratio | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Number of liver tumors at 1st diagnosis | ||||||
| 1.103 | 1.045–1.163 | 0.0003 | 1.095 | 1.035–1.158 | 0.0016 | |
| Greatest dimension of liver tumor | ||||||
| 1.034 | 0.954–1.056 | 0.8781 | 0.999 | 0.947–1.054 | 0.9685 | |
| Development of extra-hepatic metastatic disease | ||||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Yes | 2.03 | 1.49–2.78 | <0.0001 | 2.10 | 1.50–2.93 | <0.0001 |
| Development of pulmonary metastasis | ||||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Yes | 2.02 | 1.50–2.72 | <0.0001 | 2.01 | 1.46–2.93 | <0.0001 |
| Liver metastasis recurrence | ||||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Yes | 1.37 | 0.99–1.89 | 0.0543 | 1.35 | 0.96–1.90 | 0.0866 |
| Multiple of extra-hepatic metastatic site | ||||||
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Yes | 2.09 | 1.57–2.77 | <0.0001 | 2.16 | 1.60–2.91 | <0.0001 |
| Resection with and without BEV | ||||||
| Chemo-naive | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||||
| Neoadjuvent | 1.89 | 1.27–2.80 | 0.0018 | 1.61 | 1.07–2.42 | 0.0230 |
| BEV | 1.27 | 0.83–1.95 | 0.2748 | 1.07 | 0.68–1.69 | 0.7589 |
| Desmoplastic | Non-Desmoplastic | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n = 110 | n = 148 | ||
| Age at diagnosis, mean (SD) | 62.4 ± 10.22 | 60.57 ± 10.13 | 0.1250 |
| BMI, mean (SD) | 26.80 ± 5.66 | 26.96 ± 4.63 | 0.6221 |
| Mean size of primary tumor, cm (SD) | 13.79 ± 29.14 | 8.03 ± 11.76 | 0.1375 |
| Number of liver tumors at 1st diagnosis, mean (SD) | 3.07 ± 2.35 | 3.41 ± 2.03 | 0.0592 |
| Volume of primary tumor, mean (SD) | 13.79 ± 29.14 | 7.98 ± 11.69 | 0.1372 |
| Greatest dimension of liver tumor cm (SD) | 3.34 ± 2.35 | 3.86 ± 2.78 | 0.0470 |
| Number of liver tumors at initial diagnosis | 3.07 ± 2.35 | 3.40 ± 2.03 | 0.0581 |
| Synchronous presentation | 82 (74.5%) | 101 (68.2%) | 0.2702 |
| Systemic therapy | |||
| Chemo-naive | 25(24.3%) | 27 (19.9%) | 0.4123 |
| Neoadjuvant chemotherapy | 78 (75.7%) | 109 (80.1%) | 0.4123 |
| Neoadjuvant chemotherapy + bevacizumab | 28 (35.9%) | 45 (41.3%) | 0.4565 |
| Metastatic disease | |||
| Development of extrahepatic metastasis | 59 (53.6%) | 106 (73.6%) | 0.0009 |
| Multiple extrahepatic metastatic sites | 36 (33.3%) | 61 (42.1%) | 0.1575 |
| Development of pulmonary metastasis | 51 (46.4%) | 97 (67.8%) | 0.0006 |
| Liver metastatic recurrence | |||
| Yes | 46 (29.5%) | 69 (39.2%) | 0.0375 |
| No | 48 (44.4%) | 45 (30.6%) | |
| Never fully resected | 14 (13.0%) | 33 (22.4%) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krzywoń, L.; Lazaris, A.; Petrillo, S.K.; Zlotnik, O.; Gao, Z.-H.; Metrakos, P. Histopathological Growth Patterns Determine the Outcomes of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis Following Liver Resection. Cancers 2024, 16, 3148. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16183148
Krzywoń L, Lazaris A, Petrillo SK, Zlotnik O, Gao Z-H, Metrakos P. Histopathological Growth Patterns Determine the Outcomes of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis Following Liver Resection. Cancers. 2024; 16(18):3148. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16183148
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrzywoń, Lucyna, Anthoula Lazaris, Stephanie K. Petrillo, Oran Zlotnik, Zu-Hua Gao, and Peter Metrakos. 2024. "Histopathological Growth Patterns Determine the Outcomes of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis Following Liver Resection" Cancers 16, no. 18: 3148. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16183148
APA StyleKrzywoń, L., Lazaris, A., Petrillo, S. K., Zlotnik, O., Gao, Z.-H., & Metrakos, P. (2024). Histopathological Growth Patterns Determine the Outcomes of Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis Following Liver Resection. Cancers, 16(18), 3148. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16183148








