Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 (FGF2) Activates Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Signaling in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST): An Autocrine Mechanism Contributing to Imatinib Mesylate (IM) Resistance
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. FGF and VEGF Signaling Profile in IM-Resistant GISTs
2.2. Cross-Talk between FGFR and VEGFR Signaling in IM-Resistant GISTs
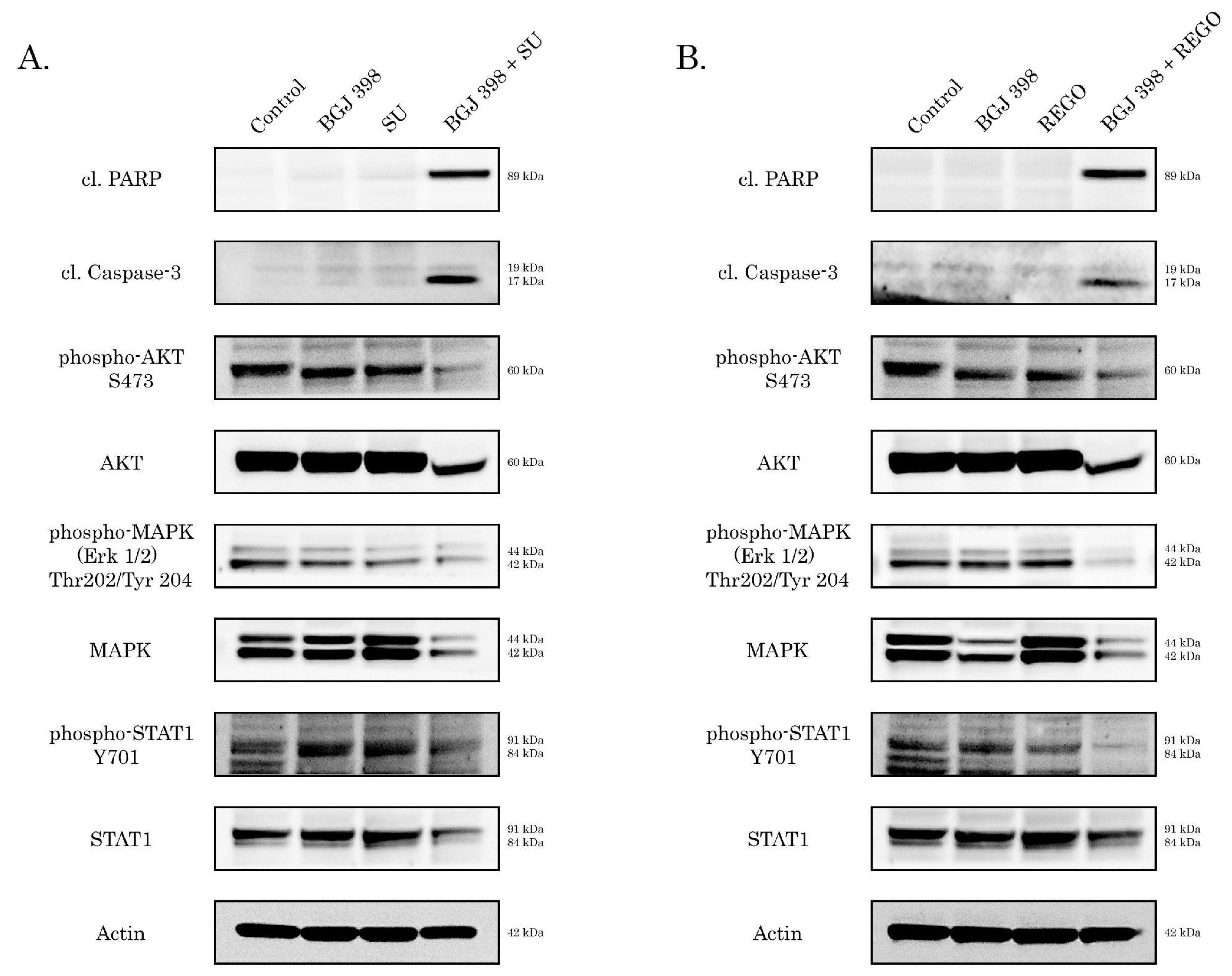
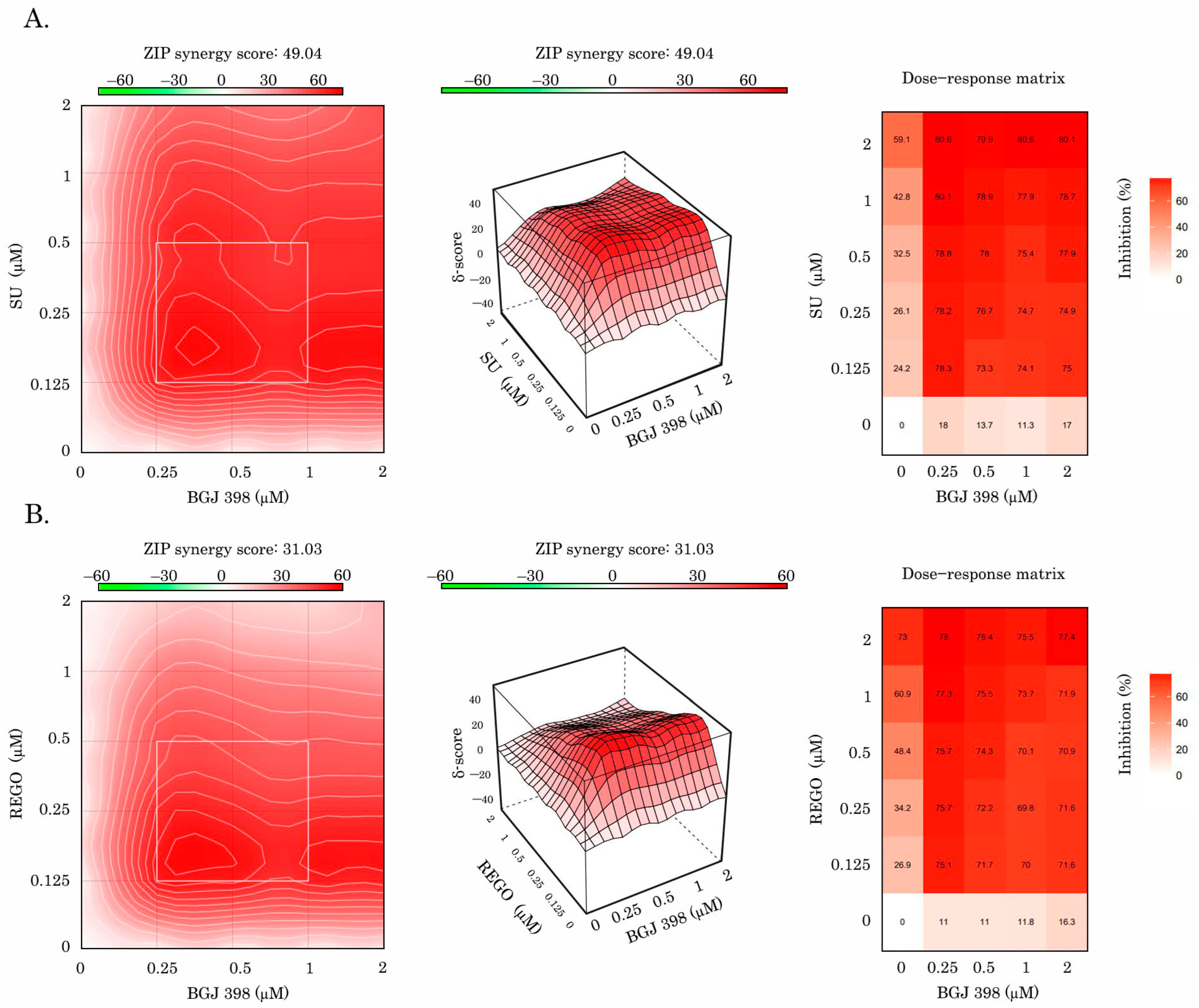
2.3. Inhibition of FGF Pathway Increases Sensitivity of IM-Resistant GIST to Anti-VEGF Therapy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical Compounds
4.2. Antibodies
4.3. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
4.4. Cellular Survival MTS-Based Assay
4.5. Real-Time Monitoring of Cell Proliferation
4.6. Crystal Violet Staining
4.7. Western Blotting and Co-Immunoprecipitation (Co-IP)
4.8. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.9. KIT Gene Silencing Using siRNA
4.10. RNA Extraction and Real-Time Quantitative PCR
4.11. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
4.12. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hirota, S.; Isozaki, K.; Moriyama, Y.; Hashimoto, K.; Nishida, T.; Ishiguro, S.; Kitamura, Y. Gain-of function mutations of c-kit in human gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science 1998, 279, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, B.P.; Singer, S.; Tsao, C.; Duensing, A.; Lux, M.L.; Ruiz, R.; Hibbard, M.K.; Chen, C.J.; Xiao, S.; Tuveson, D.A.; et al. KIT activation is a ubiquitous feature of gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 8118–8121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, M.C.; Corless, C.L.; Duensing, A.; McGreevey, L.; Chen, C.J.; Joseph, N.; Singer, S.; Griffith, D.J.; Haley, A.; Town, A.; et al. PDGFRA activating mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science 2003, 299, 708–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verweij, J.; van Oosterom, A.; Blay, J.Y.; Judson, I.; Rodenhuis, S.; van der Graaf, W.; Radford, J.; Le Cesne, A.; Hogendoorn, P.C.; di Paola, E.D.; et al. Imatinib mesylate (STI-571 Glivec, Gleevec) is an active agent for gastrointestinal stromal tumours, but does not yield responses in other soft-tissue sarcomas that are unselected for a molecular target. Results from an EORTC Soft Tissue and Bone Sarcoma Group phase II study. Eur. J. Cancer. 2003, 39, 2006–2011. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gronchi, A.; Blay, J.Y.; Trent, J.C. The role of high-dose imatinib in the management of patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Cancer 2010, 116, 1847–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, C.M.; Gutierrez Sainz, L.; Chi, P. The management of metastatic GIST: Current standard and investigational therapeutics. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardelmann, E.; Thomas, N.; Merkelbach-Bruse, S.; Pauls, K.; Speidel, N.; Büttner, R.; Bihl, H.; Leutner, C.C.; Heinicke, T.; Hohenberger, P. Acquired resistance to imatinib in gastrointestinal stromal tumours caused by multiple KIT mutations. Lancet Oncol. 2005, 6, 249–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramza, A.W.; Corless, C.L.; Heinrich, M.C. Resistance to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 7510–7518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonescu, C.R.; Besmer, P.; Guo, T.; Arkun, K.; Hom, G.; Koryotowski, B.; Leversha, M.A.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Desantis, D.; Singer, S.; et al. Acquired resistance to imatinib in gastrointestinal stromal tumor occurs through secondary gene mutation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 4182–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetri, G.D.; van Oosterom, A.T.; Garrett, C.R.; Blackstein, M.E.; Shah, M.H.; Verweij, J.; McArthur, G.; Judson, I.R.; Heinrich, M.C.; Morgan, J.A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of sunitinib in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumour after failure of imatinib: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2006, 368, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetri, G.D.; Reichardt, P.; Kang, Y.K.; Blay, J.Y.; Rutkowski, P.; Gelderblom, H.; Hohenberger, P.; Leahy, M.; von Mehren, M.; Joensuu, H.; et al. Efficacy and safety of regorafenib for advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumours after failure of imatinib and sunitinib (GRID): An international, multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B.D.; Kaufman, M.D.; Lu, W.P.; Gupta, A.; Leary, C.B.; Wise, S.C.; Rutkoski, T.J.; Ahn, Y.M.; Al-Ani, G.; Bulfer, S.L.; et al. Ripretinib (DCC-2618) Is a Switch Control Kinase Inhibitor of a Broad Spectrum of Oncogenic and Drug-Resistant KIT and PDGFRA Variants. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 738–751.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Mehren, M.; Heinrich, M.C.; George, S.; Zalcberg, J.R.; Bauer, S.; Gelderblom, H.; Schöffski, P.; Serrano, C.; Jones, R.L.; Attia, S.; et al. Ripretinib as ≥4th-line treatment in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor: Long-term update from the phase III INVICTUS study. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, S1120–S1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, M.C.; Jones, R.L.; von Mehren, M.; Bauer, S.; Kang, Y.K.; Schoffski, P.; Eskens, F.; Mir, O.; Cassier, P.; Serrano, C.; et al. Clinical activity of avapritinib in ≥ fourth-line (4L+) and PDGFRA Exon 18 gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, M.C.; Jones, R.L.; von Mehren, M.; Schöffski, P.; Serrano, C.; Kang, Y.K.; Cassier, P.A.; Mir, O.; Eskens, F.; Tap, W.D.; et al. Avapritinib in advanced PDGFRA D842V-mutant gastrointestinal stromal tumour (NAVIGATOR): A multicentre, open-label, phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, M.C.; Zhang, X.; Jones, R.L.; George, S.; Serrano, C.; Deng, Y.; Bauer, S.; Cai, S.; Wu, X.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Clinical benefit of avapritinib in KIT-mutant gastrointestinal stromal tumors: A post hoc analysis of the phase I NAVIGATOR and phase I/II CS3007-001 studies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurama, K.; Noma, K.; Takaoka, M.; Tomono, Y.; Watanabe, N.; Hatakeyama, S.; Ohmori, O.; Hirota, S.; Motoki, T.; Shirakawa, Y.; et al. Inhibition of focal adhesion kinase as a potential therapeutic strategy for imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarn, C.; Rink, L.; Merkel, E.; Flieder, U.; Pathak, H.; Koumbi, D.; Testa, J.R.; Eisenberg, B.; Von Mehren, M.; Godwin, A.K. Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor is a potential therapeutic target for gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 8387–8392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, D.; Cooke, L.; Riley, C.; Swart, R.; Simons, B.; Della Croce, K.; Wisner, L.; Iorio, M.; Shakalya, K.; Garewal, H.; et al. A novel tyrosine kinase switch is a mechanism of imatinib resistance in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3909–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javidi-Sharifi, N.; Traer, E.; Martinez, J.; Gupta, A.; Taguchi, T.; Dunlap, J.; Heinrich, M.C.; Corless, C.L.; Rubin, B.P.; Druker, B.J.; et al. Crosstalk between KIT and FGFR3 Promotes Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Cell Growth and Drug Resistance. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 880–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Huynh, H.; Li, X.; Ruddy, D.; Wang, Y.; Ong, R.; Chow, P.; Qiu, S.; Tam, A.; Rakiec, D.P.; et al. FGFR-Mediated Reactivation of MAPK Signaling Attenuates Antitumor Effects of Imatinib in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boichuk, S.; Galembikova, A.; Dunaev, P.; Valeeva, E.; Shagimardanova, E.; Gusev, O.; Khaiboullina, S. A Novel Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Switch Promotes Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Drug Resistance. Molecules 2017, 22, 2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boichuk, S.; Galembikova, A.; Dunaev, P.; Micheeva, E.; Valeeva, E.; Novikova, M.; Khromova, N.; Kopnin, P. Targeting of FGF-Signaling Re-Sensitizes Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST) to Imatinib In Vitro and In Vivo. Molecules 2018, 23, 2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boichuk, S.; Galembikova, A.; Mikheeva, E.; Bikinieva, F.; Aukhadieva, A.; Dunaev, P.; Khalikov, D.; Petrov, S.; Kurtasanov, R.; Valeeva, E.; et al. Inhibition of FGF2-Mediated Signaling in GIST—Promising Approach for Overcoming Resistance to Imatinib. Cancers 2020, 12, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boichuk, S.; Dunaev, P.; Skripova, V.; Galembikova, A.; Bikinieva, F.; Shagimardanova, E.; Gazizova, G.; Deviatiiarov, R.; Valeeva, E.; Mikheeva, E.; et al. Unraveling the Mechanisms of Sensitivity to Anti-FGF Therapies in Imatinib-Resistant Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST) Lacking Secondary KIT Mutations. Cancers 2023, 15, 5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.; Nguyen, L.T.; Hatanaka, K.; Schachterle, W.; Chen, P.Y.; Zhuang, Z.W.; Black, B.L.; Simons, M. FGF-dependent regulation of VEGF receptor 2 expression in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2668–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seghezzi, G.; Patel, S.; Ren, C.J.; Gualandris, A.; Pintucci, G.; Robbins, E.S.; Shapiro, R.L.; Galloway, A.C.; Rifkin, D.B.; Mignatti, P. Fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2) induces vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in the endothelial cells of forming capillaries: An autocrine mechanism contributing to angiogenesis. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 141, 1659–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendel, D.B.; Laird, A.D.; Xin, X.; Louie, S.G.; Christensen, J.G.; Li, G.; Schreck, R.E.; Abrams, T.J.; Ngai, T.J.; Lee, L.B.; et al. In vivo antitumor activity of SU11248, a novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting vascular endothelial growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor receptors: Determination of a pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic relationship. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 327–337. [Google Scholar]
- Motzer, R.J.; Hutson, T.E.; Glen, H.; Michaelson, M.D.; Molina, A.; Eisen, T.; Jassem, J.; Zolnierek, J.; Maroto, J.P.; Mellado, B.; et al. Lenvatinib, everolimus, and the combination in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A randomised, phase 2, open-label, multicentre trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Farrell, A.M.; Abrams, T.J.; Yuen, H.A.; Ngai, T.J.; Louie, S.G.; Yee, K.W.; Wong, L.M.; Hong, W.; Lee, L.B.; Town, A.; et al. SU11248 is a novel FLT3 tyrosine kinase inhibitor with potent activity in vitro and in vivo. Blood 2003, 101, 3597–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, L.J.; Abrams, T.J.; Long, K.R.; Ngai, T.J.; Olson, L.M.; Hong, W.; Keast, P.K.; Brassard, J.A.; O’Farrell, A.M.; Cherrington, J.M.; et al. SU11248 inhibits tumor growth and CSF-1R-dependent osteolysis in an experimental breast cancer bone metastasis model. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2003, 20, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, M.C.; Corless, C.L.; Demetri, G.D.; Blanke, C.D.; von Mehren, M.; Joensuu, H.; McGreevey, L.S.; Chen, C.J.; Van den Abbeele, A.D.; Druker, B.J.; et al. Kinase mutations and imatinib response in patients with metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 4342–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corless, C.L.; McGreevey, L.; Haley, A.; Town, A.; Heinrich, M.C. KIT mutations are common in incidental gastrointestinal stromal tumors one centimeter or less in size. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 160, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikezoe, T.; Yang, Y.; Nishioka, C.; Bandobashi, K.; Nakatani, H.; Taguchi, T.; Koeffler, H.P.; Taguchi, H. Effect of SU11248 on gastrointestinal stromal tumor-T1 cells: Enhancement of growth inhibition via inhibition of 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling. Cancer Sci. 2006, 97, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, T.A.; Wodicka, L.M.; Shah, N.P.; Velasco, A.M.; Fabian, M.A.; Treiber, D.K.; Milanov, Z.V.; Atteridge, C.E.; Biggs, W.H., 3rd; Edeen, P.T.; et al. Inhibition of drug-resistant mutants of ABL, KIT, and EGF receptor kinases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11011–11016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prenen, H.; Cools, J.; Mentens, N.; Folens, C.; Sciot, R.; Schöffski, P.; Van Oosterom, A.; Marynen, P.; Debiec-Rychter, M. Efficacy of the kinase inhibitor SU11248 against gastrointestinal stromal tumor mutants refractory to imatinib mesylate. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 2622–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, M.C.; Maki, R.G.; Corless, C.L.; Antonescu, C.R.; Fletcher, J.A.; Fletcher, C.D.; Huang, X.; Baum, C.M.; Demetri, G.D. Sunitinib (SU) response in imatinib-resistant (IM-R) GIST correlates with KIT and PDGFRA mutation status. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 9502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, M.C.; Maki, R.G.; Corless, C.L.; Antonescu, C.R.; Harlow, A.; Griffith, D.; Town, A.; McKinley, A.; Ou, W.B.; Fletcher, J.A.; et al. Primary and secondary kinase genotypes correlate with the biological and clinical activity of sunitinib in imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumor. J Clin Oncol. 2008, 26, 5352–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetri, G.D.; Heinrich, M.C.; Fletcher, J.A.; Fletcher, C.D.; Van den Abbeele, A.D.; Corless, C.L.; Antonescu, C.R.; George, S.; Morgan, J.A.; Chen, M.H.; et al. Molecular target modulation, imaging, and clinical evaluation of gastrointestinal stromal tumor patients treated with sunitinib malate after imatinib failure. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5902–5909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, J.; Shankar, S.; Heinrich, M.C.; Fletcher, J.A.; Fletcher, C.D.; Manola, J.; Morgan, J.A.; Corless, C.L.; George, S.; Tuncali, K.; et al. Clonal evolution of resistance to imatinib in patients with metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 5398–5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardelmann, E.; Merkelbach-Bruse, S.; Pauls, K.; Thomas, N.; Schildhaus, H.U.; Heinicke, T.; Speidel, N.; Pietsch, T.; Buettner, R.; Pink, D.; et al. Polyclonal evolution of multiple secondary KIT mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumors under treatment with imatinib mesylate. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 1743–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liegl, B.; Kepten, I.; Le, C.; Zhu, M.; Demetri, G.D.; Heinrich, M.C.; Fletcher, C.D.; Corless, C.L.; Fletcher, J.A. Heterogeneity of kinase inhibitor resistance mechanisms in GIST. J. Pathol. 2008, 216, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Chen, T.; Ding, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. Inhibition of FGF-FGFR and VEGF-VEGFR signalling in cancer treatment. Cell Prolif. 2021, 54, e13009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAuliffe, J.C.; Lazar, A.J.; Yang, D.; Steinert, D.M.; Qiao, W.; Thall, P.F.; Raymond, A.K.; Benjamin, R.S.; Trent, J.C. Association of intratumoral vascular endothelial growth factor expression and clinical outcome for patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors treated with imatinib mesylate. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 6727–6734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Nakatani, H.; Taguchi, T.; Nakano, T.; Okabayashi, T.; Sugimoto, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Araki, K. STI571 (Glivec) suppresses the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in the gastrointestinal stromal tumor cell line, GIST-T1. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, M.; Yamamoto, H.; Nakamura, N.; Oda, Y.; Yao, T.; Kakeji, Y.; Baba, H.; Maehara, Y.; Tsuneyoshi, M. Prognostic significance of angiogenesis in gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Mod. Pathol. 2007, 20, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golfmann, K.; Meder, L.; Koker, M.; Volz, C.; Borchmann, S.; Tharun, L.; Dietlein, F.; Malchers, F.; Florin, A.; Büttner, R.; et al. Synergistic anti-angiogenic treatment effects by dual FGFR1 and VEGFR1 inhibition in FGFR1-amplified breast cancer. Oncogene 2018, 37, 5682–5693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunoda, S.; Nakamura, T.; Sakurai, H.; Saiki, I. Fibroblast growth factor-2-induced host stroma reaction during initial tumor growth promotes progression of mouse melanoma via vascular endothelial growth factor A-dependent neovascularization. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Greisler, H.P. Angiogenic effect of fibroblast growth factor-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor and their synergism in a novel in vitro quantitative fibrin-based 3-dimensional angiogenesis system. Surgery 2002, 132, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, K.; Watanabe Miyano, S.; Minoshima, Y.; Matsui, J.; Funahashi, Y. Activated FGF2 signaling pathway in tumor vasculature is essential for acquired resistance to anti-VEGF therapy. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Chen, R.; Sun, G.; Liu, X.; Lin, X.; He, C.; Xing, L.; Liu, L.; Jensen, L.D.; Kumar, A.; et al. VEGF-B prevents excessive angiogenesis by inhibiting FGF2/FGFR1 pathway. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2023, 8, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, J.H.; Buzzelli, J.N.; Jones, K.; Franchini, F.; Gordon-Weeks, A.; Markelc, B.; Chen, J.; Kim, J.; Cao, Y.; Muschel, R.J. FGF2 alters macrophage polarization, tumour immunity and growth and can be targeted during radiotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, E.A.; Ullman, J.G.; Leatherman, J.M.; Asquith, J.M.; Hansen, T.R.; Armstrong, T.D.; Hicklin, D.J.; Jaffee, E.M.; Emens, L.A. A vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 inhibitor enhances antitumor immunity through an immune-based mechanism. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 3951–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yan, J.; Liu, B. Targeting VEGF/VEGFR to Modulate Antitumor Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, M. FGFR inhibitors: Effects on cancer cells, tumor microenvironment and whole-body homeostasis (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Kan, A.; Lyu, N.; Mu, L.; Han, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, Y.; Liao, S.; Li, S.; et al. Dual Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor and Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Inhibition Elicits Antitumor Immunity and Enhances Programmed Cell Death-1 Checkpoint Blockade in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2020, 9, 338–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, M.; Li, H.; Cao, H.; Huang, Y.; Yu, W.; Shen, C.; Gu, J. Dual FGFR and VEGFR inhibition synergistically restrain hexokinase 2-dependent lymphangiogenesis and immune escape in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 58, 908–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarabipour, S.; Hristova, K. Mechanism of FGF receptor dimerization and activation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabipour, S. Parallels and Distinctions in FGFR, VEGFR, and EGFR Mechanisms of Transmembrane Signaling. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 3159–3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonzo-Méndez, M.A.; Strub, M.P.; Taraska, J.W. Crosstalk of growth factor receptors at plasma membrane clathrin-coated sites. bioRxiv 2024, 18, 2024.05.16.594559. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Zhen, Y.; Shi, L.; Vu, P.; Greninger, P.; Adil, R.; Merritt, J.; Egan, R.; Wu, M.J.; Yin, X.; et al. EGFR Inhibition Potentiates FGFR Inhibitor Therapy and Overcomes Resistance in FGFR2 Fusion-Positive Cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 1378–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.Y.; Qin, L.; Zhuang, Z.W.; Tellides, G.; Lax, I.; Schlessinger, J.; Simons, M. The docking protein FRS2α is a critical regulator of VEGF receptors signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5514–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, F.; Cremante, M.; Dalmasso, B.; Pirrone, C.; Lagodin D’Amato, A.; Grassi, M.; Comandini, D. Molecular Tailored Therapeutic Options for Advanced Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GISTs): Current Practice and Future Perspectives. Cancers 2023, 15, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schöffski, P.; Mir, O.; Kasper, B.; Papai, Z.; Blay, J.Y.; Italiano, A.; Benson, C.; Kopeckova, K.; Ali, N.; Dileo, P.; et al. Activity and safety of the multi-target tyrosine kinase inhibitor cabozantinib in patients with metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumour after treatment with imatinib and sunitinib: European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer phase II trial 1317 ‘CaboGIST’. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 134, 62–74. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical Trials NCT04193553—Multicentre Placebo-controlled Double-Blinded Phase II Study of Lenvatinib Efficacy in Patients with Locally Advanced or Metastatic GIST (Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor) After Imatinib/Sunitinib Failure (LENVAGIST). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT04193553 (accessed on 3 July 2024).
- Clinical Trials NCT05751733—Apatinib Mesylate versus Standard Second-Line TKI in the Treatment of Advanced GIST. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05751733 (accessed on 3 July 2024).
- Clinical Trials NCT02638766—Single Agent Regorafenib in First-line for Metastatic/Unresectable KIT/PDGFR Wild Type GIST (REGISTRI). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02638766 (accessed on 3 July 2024).
- Shen, G.; Zheng, F.; Ren, D.; Du, F.; Dong, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, F.; Ahmad, R.; Zhao, J. Anlotinib: A novel multi-targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitor in clinical development. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Song, Y.; Shou, J.; Bai, Y.; Li, H.; Xie, X.; Luo, H.; Ren, X.; Liu, J.; Ye, D.; et al. Anlotinib for Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Previously Treated With One Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor: A Phase 2 Trial. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Fang, Z.; Hong, X.; Yao, Y.; Sun, P.; Wang, G.; Du, F.; Sun, Y.; Wu, Q.; Qu, G.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Anlotinib, a Multikinase Angiogenesis Inhibitor, in Patients with Refractory Metastatic Soft-Tissue Sarcoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 5233–5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Du, F.; Gao, M.; Ji, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; et al. Anlotinib for the Treatment of Patients with Locally Advanced or Metastatic Medullary Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 2018, 28, 1455–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, T.; Sonobe, H.; Toyonaga, S.; Yamasaki, I.; Shuin, T.; Takano, A.; Araki, K.; Akimaru, K.; Yuri, K. Conventional and molecular cytogenetic characterization of a new human cell line, GIST-T1, established from gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Lab. Investig. 2002, 82, 663–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, S.; Duensing, A.; Demetri, G.D.; Fletcher, J.A. KIT oncogenic signaling mechanisms in imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumor: PI3-kinase/AKT is a crucial survival pathway. Oncogene 2007, 26, 7560–7568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenbaum, M.C. What is synergy? Pharmacol. Rev. 1989, 41, 93–141. [Google Scholar]
- Loewe, S. The problem of synergism and antagonism of combined drugs. Arzneimittelforschung 1953, 3, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bliss, C.I. The toxicity of poisons applied jointly. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1939, 26, 585–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, B.; Wennerberg, K.; Aittokallio, T.; Tang, J. Searching for Drug Synergy in Complex Dose-Response Landscapes Using an Interaction Potency Model. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilà-González, M.; Kelaini, S.; Magee, C.; Caines, R.; Campbell, D.; Eleftheriadou, M.; Cochrane, A.; Drehmer, D.; Tsifaki, M.; O’Neill, K.; et al. Enhanced Function of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Endothelial Cells Through ESM1 Signaling. Stem Cells 2019, 37, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, M.; Vichi, D.; Toscano, A.; Zappoli Thyrion, G.D.; Parretti, E.; Mello, G.; Gheri, G.; Pacini, A.; Sgambati, E. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor types 1, 2 and 3 in placenta from pregnancies complicated by hypertensive disorders. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2007, 19, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Cell Line | GIST T-1 | GIST T-1R | GIST 430 |
|---|---|---|---|
| IM | 0.04 ± 0.0003 | 47.1 ± 1.3 | 54.3 ± 7.9 |
| Fold increase relative to GIST T-1 | 1177.5 | 1357.5 | |
| Fold increase relative to GIST T-1R | 1.15 | ||
| SU | 0.016 ± 0.0001 | 5.2 ± 0.5 | 15.3 ± 2.4 |
| Fold increase relative to GIST T-1 | 325.0 | 956.2 | |
| Fold increase relative to GIST T-1R | 2.94 | ||
| REGO | 0.029 ± 0.003 | 2.2 ± 0.3 | 14.8 ± 1.9 |
| Fold increase relative to GIST T-1 | 76.0 | 510.4 | |
| Fold increase relative to GIST T-1R | 6.7 |
| Cell Line | BGJ 398 + RTKi | ZIP | Bliss | Loewe | HSA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GIST T-1R | SU | 49.04 | 49.05 | 34.45 | 49.69 |
| REGO | 31.03 | 31.00 | 10.98 | 31.07 | |
| GIST 430 | SU | −38.21 | −39.24 | −6.11 | −34.82 |
| REGO | −29.77 | −30.59 | −8.64 | −21.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boichuk, S.; Dunaev, P.; Galembikova, A.; Valeeva, E. Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 (FGF2) Activates Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Signaling in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST): An Autocrine Mechanism Contributing to Imatinib Mesylate (IM) Resistance. Cancers 2024, 16, 3103. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16173103
Boichuk S, Dunaev P, Galembikova A, Valeeva E. Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 (FGF2) Activates Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Signaling in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST): An Autocrine Mechanism Contributing to Imatinib Mesylate (IM) Resistance. Cancers. 2024; 16(17):3103. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16173103
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoichuk, Sergei, Pavel Dunaev, Aigul Galembikova, and Elena Valeeva. 2024. "Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 (FGF2) Activates Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Signaling in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST): An Autocrine Mechanism Contributing to Imatinib Mesylate (IM) Resistance" Cancers 16, no. 17: 3103. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16173103
APA StyleBoichuk, S., Dunaev, P., Galembikova, A., & Valeeva, E. (2024). Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 (FGF2) Activates Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Signaling in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST): An Autocrine Mechanism Contributing to Imatinib Mesylate (IM) Resistance. Cancers, 16(17), 3103. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16173103







