Evaluation of Hi-C Sequencing for Detection of Gene Fusions in Hematologic and Solid Tumor Pediatric Cancer Samples
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
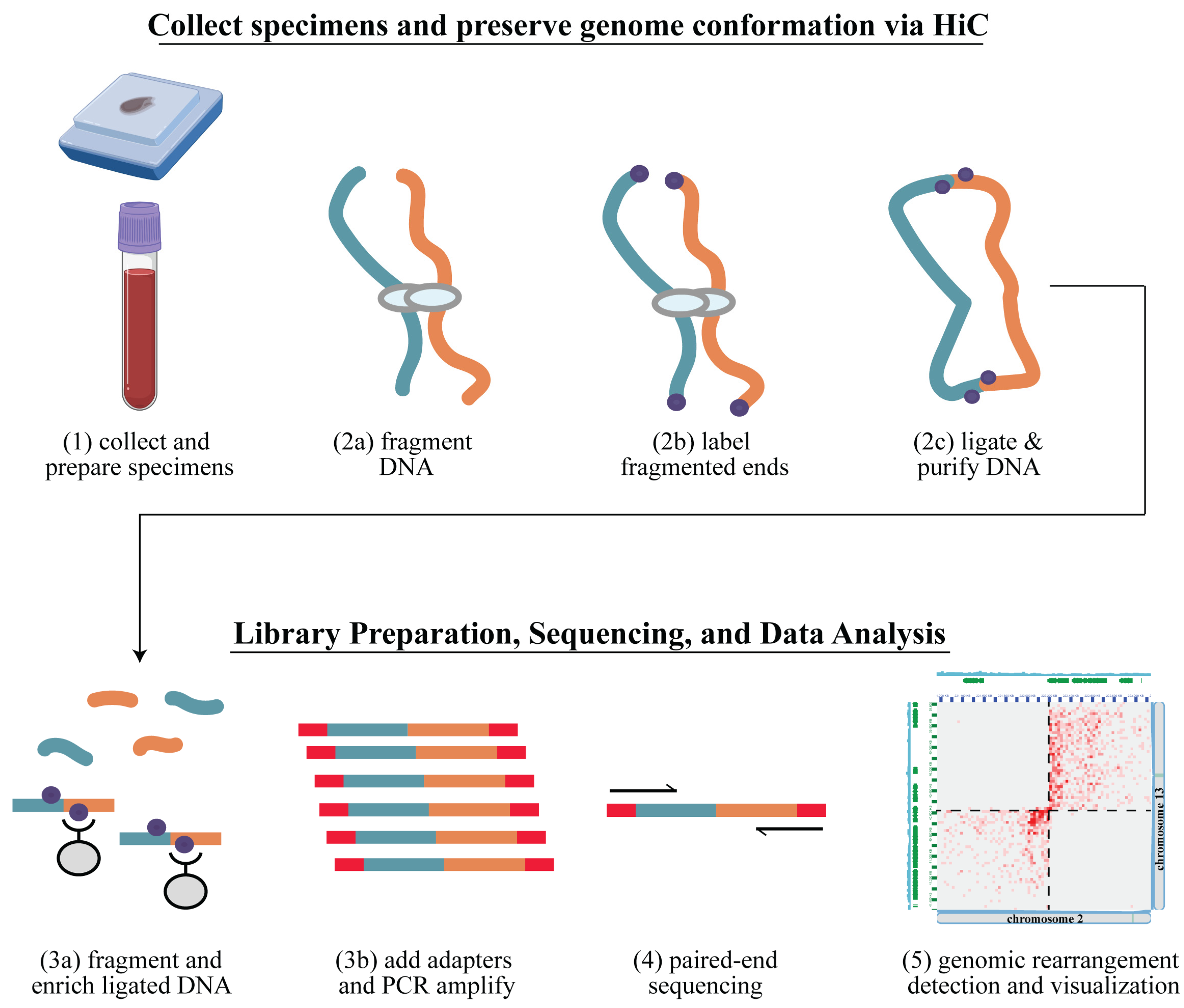
2.1. Overview
2.2. Samples–Solid Tumors
2.3. Samples–Leukemias
2.4. Arima-HiC Sequencing
2.5. Data Analysis Workflow
3. Results
3.1. Hi-C Library Preparation and Quality Assessment
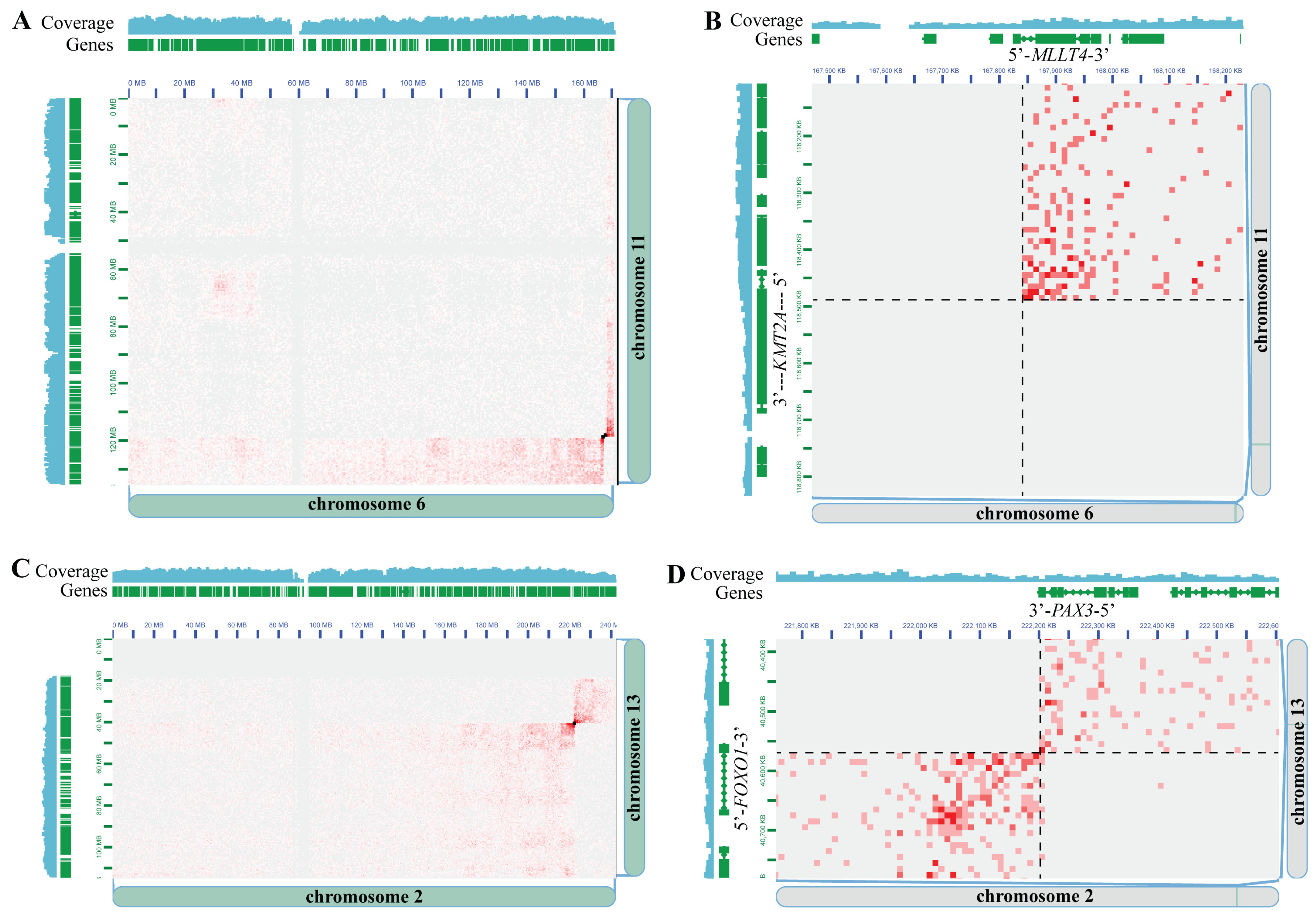
3.2. Hi-C Is Concordant with Gold-Standard Methods for Pediatric Cancer Clinical Cytogenetic Testing
3.3. Driver-Negative Leukemias–Discovery Cohort
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.A.; Vundamati, D.S.; Farooqi, M.S.; Guest, E. Precision Medicine in Pediatric Cancer: Current Applications and Future Prospects. High. Throughput 2018, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PDQ® Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board. Childhood Cancer Genomics (PDQ(R)): Health Professional Version. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/types/childhood-cancers/pediatric-genomics-hp-pdq (accessed on 7 February 2024).
- Grobner, S.N.; Worst, B.C.; Weischenfeldt, J.; Buchhalter, I.; Kleinheinz, K.; Rudneva, V.A.; Johann, P.D.; Balasubramanian, G.P.; Segura-Wang, M.; Brabetz, S.; et al. The landscape of genomic alterations across childhood cancers. Nature 2018, 555, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Edmonson, M.N.; Gawad, C.; Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Rusch, M.C.; Easton, J.; et al. Pan-cancer genome and transcriptome analyses of 1,699 paediatric leukaemias and solid tumours. Nature 2018, 555, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahal, Z.; Abdulhai, F.; Kadara, H.; Saab, R. Genomics of adult and pediatric solid tumors. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 1356–1386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.C.; Warren, L.M.; Cooley, L.D. Maintaining a methods database to optimize solid tumor tissue culture: Review of a 15-year database from a single institution. Cancer Genet. 2019, 233–234, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, A.; Sikkema-Raddatz, B.; de Leeuw, N.; Konrad, N.C.; Hastings, R.J.; Schoumans, J. Genome-wide arrays in routine diagnostics of hematological malignancies. Hum. Mutat. 2012, 33, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieder, H.; Sommerlad, C.; Mehraein, Y.; Giersberg, M.; Marben, K.; Rehder, H. Formalin-Fixed and Paraffin-Embedded Tissue Sections. In FISH Technology; Rautenstrauss, B.W., Liehr, T., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 148–161. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, J.F.; Aggarwal, N.; Smith, C.A.; Gollin, S.M.; Surti, U.; Rajkovic, A.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Yatsenko, S.A. Integration of microarray analysis into the clinical diagnosis of hematological malignancies: How much can we improve cytogenetic testing? Oncotarget 2015, 6, 18845–18862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkari, Y.; Dobin, S.; Best, R.G.; Leung, M.L. Exploring current challenges in the technologist workforce of clinical genomics laboratories. Genet. Med. Open 2023, 1, 100806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engvall, M.; Cahill, N.; Jonsson, B.I.; Hoglund, M.; Hallbook, H.; Cavelier, L. Detection of leukemia gene fusions by targeted RNA-sequencing in routine diagnostics. BMC Med. Genom. 2020, 13, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avenarius, M.R.; Miller, C.R.; Arnold, M.A.; Koo, S.; Roberts, R.; Hobby, M.; Grossman, T.; Moyer, Y.; Wilson, R.K.; Mardis, E.R.; et al. Genetic Characterization of Pediatric Sarcomas by Targeted RNA Sequencing. J. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 22, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebib, I.; Taylor, M.S.; Nardi, V.; Rivera, M.N.; Lennerz, J.K.; Cote, G.M.; Choy, E.; Lozano Calderon, S.A.; Raskin, K.A.; Schwab, J.H.; et al. Clinical Utility of Anchored Multiplex Solid Fusion Assay for Diagnosis of Bone and Soft Tissue Tumors. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2021, 45, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Liebers, M.; Zhelyazkova, B.; Cao, Y.; Panditi, D.; Lynch, K.D.; Chen, J.; Robinson, H.E.; Shim, H.S.; Chmielecki, J.; et al. Anchored multiplex PCR for targeted next-generation sequencing. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1479–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, M.; Pho, M.; Dutta, D.; Stephans, J.C.; Shak, S.; Kiefer, M.C.; Esteban, J.M.; Baker, J.B. Measurement of gene expression in archival paraffin-embedded tissues: Development and performance of a 92-gene reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction assay. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 164, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penland, S.K.; Keku, T.O.; Torrice, C.; He, X.; Krishnamurthy, J.; Hoadley, K.A.; Woosley, J.T.; Thomas, N.E.; Perou, C.M.; Sandler, R.S.; et al. RNA expression analysis of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tumors. Lab. Investig. 2007, 87, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.; Inaba, H.; Annesley, C.; Beck, J.; Colace, S.; Dallas, M.; DeSantes, K.; Kelly, K.; Kitko, C.; Lacayo, N.; et al. Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia, Version 2.2020, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2020, 18, 81–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.C.; Neveling, K.; Kanagal-Shamanna, R. Optical genome mapping for structural variation analysis in hematologic malignancies. Am. J. Hematol. 2022, 97, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.R.; Xu, J.; Dileep, V.; Zhan, Y.; Song, F.; Le, V.T.; Yardimci, G.G.; Chakraborty, A.; Bann, D.V.; Wang, Y.; et al. Integrative detection and analysis of structural variation in cancer genomes. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1388–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harewood, L.; Kishore, K.; Eldridge, M.D.; Wingett, S.; Pearson, D.; Schoenfelder, S.; Collins, V.P.; Fraser, P. Hi-C as a tool for precise detection and characterisation of chromosomal rearrangements and copy number variation in human tumours. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyyanki, T.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Q.; Hou, Y.; Jin, Q.; Xu, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, T.; Wang, X.; Song, F.; et al. Subtype-associated epigenomic landscape and 3D genome structure in bladder cancer. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, E.C.; Grand, R.S.; Perry, J.K.; Vickers, M.H.; Olins, A.L.; Olins, D.E.; O’Sullivan, J.M. Hi-C detects novel structural variants in HL-60 and HL-60/S4 cell lines. Genomics 2020, 112, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallard, C.; Johnston, M.J.; Bobyn, A.; Nikolic, A.; Argiropoulos, B.; Chan, J.A.; Guilcher, G.M.T.; Gallo, M. Hi-C detects genomic structural variants in peripheral blood of pediatric leukemia patients. Cold Spring Harb. Mol. Case Stud. 2022, 8, a006157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, R.; Wang, Q.; Schupp, P.G.; Nikolic, A.; Hilz, S.; Hong, C.; Grishanina, N.R.; Kwok, D.; Stevers, N.O.; Jin, Q.; et al. Glioblastoma evolution and heterogeneity from a 3D whole-tumor perspective. Cell 2024, 187, 446–463.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Huang, T.Y.; Hou, Y.; Bartom, E.; Lu, X.; Shilatifard, A.; Yue, F.; Saratsis, A. Epigenomic landscape and 3D genome structure in pediatric high-grade glioma. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Luan, Y.; Yue, F. EagleC: A deep-learning framework for detecting a full range of structural variations from bulk and single-cell contact maps. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabn9215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Song, F.; Lyu, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, Z.; Hou, Y.; Wang, X.; Luan, Y.; Jia, B.; et al. Subtype-specific 3D genome alteration in acute myeloid leukaemia. Nature 2022, 611, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Lee, D.S.; Chandran, S.; Le, V.T.; Bump, R.; Yasis, J.; Dallarda, S.; Marcotte, S.; Clock, B.; Haghani, N.; et al. Structural variants drive context-dependent oncogene activation in cancer. Nature 2022, 612, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, D.; Schmitt, A.D.; Louissaint, A.; Mata, D.A.; Massaro, S.; Nardi, V.; Xu, M.L. Large B-cell lymphoma with mystery rearrangement: Applying Hi-C to the detection of clinically relevant structural abnormalities. Br. J. Haematol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arima SV Pipeline for Mapping, SV Detection and QC. GitHub Repository 2023. Available online: https://github.com/ArimaGenomics/Arima-SV-Pipeline (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Wingett, S.; Ewels, P.; Furlan-Magaril, M.; Nagano, T.; Schoenfelder, S.; Fraser, P.; Andrews, S. HiCUP: Pipeline for mapping and processing Hi-C data. F1000Research 2015, 4, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, N.C.; Shamim, M.S.; Machol, I.; Rao, S.S.; Huntley, M.H.; Lander, E.S.; Aiden, E.L. Juicer Provides a One-Click System for Analyzing Loop-Resolution Hi-C Experiments. Cell Syst. 2016, 3, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, N.C.; Robinson, J.T.; Shamim, M.S.; Machol, I.; Mesirov, J.P.; Lander, E.S.; Aiden, E.L. Juicebox Provides a Visualization System for Hi-C Contact Maps with Unlimited Zoom. Cell Syst. 2016, 3, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, M.; Nguyen, A.; Islam, R.; Butler, C.; Tran, E.; Mullins, D.; Hicks, C. HolistIC: Leveraging Hi-C and whole genome shotgun sequencing for double minute chromosome discovery. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, O.S.; Luebeck, J.; Sridhar, S.; Wong, I.T.; Dixit, D.; Wang, S.; Prasad, G.; Rajkumar, U.; Pagadala, M.S.; Larson, J.D.; et al. Circular extrachromosomal DNA promotes tumor heterogeneity in high-risk medulloblastoma. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 2189–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Gujar, A.D.; Wong, C.H.; Tjong, H.; Ngan, C.Y.; Gong, L.; Chen, Y.A.; Kim, H.; Liu, J.; Li, M.; et al. Oncogenic extrachromosomal DNA functions as mobile enhancers to globally amplify chromosomal transcription. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 694–707.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmsauer, K.; Valieva, M.E.; Ali, S.; Chamorro Gonzalez, R.; Schopflin, R.; Roefzaad, C.; Bei, Y.; Dorado Garcia, H.; Rodriguez-Fos, E.; Puiggros, M.; et al. Enhancer hijacking determines extrachromosomal circular MYCN amplicon architecture in neuroblastoma. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Turner, K.M.; Nguyen, N.; Raviram, R.; Erb, M.; Santini, J.; Luebeck, J.; Rajkumar, U.; Diao, Y.; Li, B.; et al. Circular ecDNA promotes accessible chromatin and high oncogene expression. Nature 2019, 575, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, J.F.; Sukov, W.R.; Pitel, B.A.; Smoley, S.A.; Pearce, K.E.; Meyer, R.G.; Williamson, C.M.; Smadbeck, J.B.; Vasmatzis, G.; Hoppman, N.L.; et al. Acute leukemias harboring KMT2A/MLLT10 fusion: A 10-year experience from a single genomics laboratory. Genes. Chromosomes Cancer 2019, 58, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Paediatric Tumours. In WHO Classification of Tumours, 5th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Pollard, J.A.; Guest, E.; Alonzo, T.A.; Gerbing, R.B.; Loken, M.R.; Brodersen, L.E.; Kolb, E.A.; Aplenc, R.; Meshinchi, S.; Raimondi, S.C.; et al. Gemtuzumab Ozogamicin Improves Event-Free Survival and Reduces Relapse in Pediatric KMT2A-Rearranged AML: Results from the Phase III Children’s Oncology Group Trial AAML0531. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3149–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Weelderen, R.E.; Klein, K.; Harrison, C.J.; Jiang, Y.; Abrahamsson, J.; Arad-Cohen, N.; Bart-Delabesse, E.; Buldini, B.; De Moerloose, B.; Dworzak, M.N.; et al. Measurable Residual Disease and Fusion Partner Independently Predict Survival and Relapse Risk in Childhood KMT2A-Rearranged Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Study by the International Berlin-Frankfurt-Munster Study Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 2963–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirabayashi, S.; Butler, E.R.; Ohki, K.; Kiyokawa, N.; Bergmann, A.K.; Moricke, A.; Boer, J.M.; Cave, H.; Cazzaniga, G.; Yeoh, A.E.J.; et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of B-ALL with ZNF384 rearrangements: A retrospective analysis by the Ponte di Legno Childhood ALL Working Group. Leukemia 2021, 35, 3272–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raetz, E.A.; Teachey, D.T.; Minard, C.; Liu, X.; Norris, R.E.; Denic, K.Z.; Reid, J.; Evensen, N.A.; Gore, L.; Fox, E.; et al. Palbociclib in combination with chemotherapy in pediatric and young adult patients with relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia and lymphoma: A Children’s Oncology Group study (AINV18P1). Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2023, 70, e30609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, B.; Mattison, R.J.; Abboud, R.; Abdelmessieh, P.; Patricia Aoun, P.; Burke, P.W.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Lurie, R.H.; Fathi, A.T.; Gauthier, J.; et al. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia, Version 4.2023, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2024. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/guidelines-detail (accessed on 11 July 2024).
- Quessada, J.; Cuccuini, W.; Saultier, P.; Loosveld, M.; Harrison, C.J.; Lafage-Pochitaloff, M. Cytogenetics of Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Review of the Current Knowledge. Genes 2021, 12, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Sample ID | Cancer Type | Sample Source | Preservation (If Any) | Prior Cytogenetic Test Result | Hi-C Test Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AML C1 | AML | PBMCs | 90% FBS/10% DMSO | CBFA2T3::GLIS2 | CBFA2T3::GLIS2 |
| AML C2 | AML | Bone Marrow | None | Negative * | Negative |
| AML C3 | AML | Bone Marrow | None | RUNX1::RUNX1T1 | RUNX1::RUNX1T1 |
| AML C4 | AML | Bone Marrow | 90% FBS/10% DMSO | MYH11::CBFB | MYH11::CBFB |
| AML C5 | AML | Bone Marrow | 90% FBS/10% DMSO | Negative ** | Negative |
| AML C6 | AML | Bone Marrow | 90% FBS/10% DMSO | KMT2A::MLLT4 *** | KMT2A::MLLT4 |
| AML C7 | AML | Bone Marrow | 90% FBS/10% DMSO | RUNX1::RUNX1T1 | RUNX1::RUNX1T1 |
| ARMS C1 | A-RMS | Tissue | FFPE | FOXO1-r | PAX3::FOXO1 |
| ARMS C2 | A-RMS | Tissue | FFPE | PAX3::FOXO1 | PAX3::FOXO1 |
| ARMS C3 | A-RMS | Tissue | FFPE | PAX3::FOXO1 | PAX3::FOXO1 |
| ARMS C4 | A-RMS | Tissue | FFPE | FOXO1-r | PAX7::FOXO1 |
| ARMS C5 | A-RMS | Tissue | FFPE | FOX7::FOXO1 | PAX7::FOXO1 |
| Sample ID | Cancer Type | Sample Source | Preservation (If Any) | Prior Dx Test Result | Hi-C Test Result | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AML D1 | AML | PBMCs | 90% FBS/10% DMSO | Negative | KMT2A::MLLT10 | Dx, Px, Tx |
| T-ALL D1 | T-ALL | Bone Marrow | 90% FBS/10% DMSO | Negative | SKAP2::CDK6 | Tx * |
| T-ALL D2 | T-ALL | Bone Marrow | None | Negative | Negative | N/A |
| B-ALL D1 | B-ALL | Bone Marrow | None | Negative | Negative | N/A |
| B-ALL D2 | B-ALL | Bone Marrow | None | Negative | Negative | N/A |
| B-ALL D3 | B-ALL | Bone Marrow | 90% FBS/10% DMSO | Negative | Negative | N/A |
| B-ALL D4 | B-ALL | Bone Marrow | 90% FBS/10% DMSO | Negative | Negative | N/A |
| B-ALL D5 | B-ALL | PBMCs | 90% FBS/10% DMSO | Negative | Negative | N/A |
| B-ALL D6 | B-ALL | Bone Marrow | 90% FBS/10% DMSO | Negative | ZNF384::EP300 | Dx, Px |
| B-ALL D7 | B-ALL | Bone Marrow | 90% FBS/10% DMSO | Negative | ABHD17B::PTK2B | Dx, Px ** |
| B-ALL D8 | B-ALL | Bone Marrow | 90% FBS/10% DMSO | Negative | ZNF384-EP300 | Dx, Px |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schmitt, A.D.; Sikkink, K.; Ahmed, A.A.; Melnyk, S.; Reid, D.; Van Meter, L.; Guest, E.M.; Lansdon, L.A.; Pastinen, T.; Pushel, I.; et al. Evaluation of Hi-C Sequencing for Detection of Gene Fusions in Hematologic and Solid Tumor Pediatric Cancer Samples. Cancers 2024, 16, 2936. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16172936
Schmitt AD, Sikkink K, Ahmed AA, Melnyk S, Reid D, Van Meter L, Guest EM, Lansdon LA, Pastinen T, Pushel I, et al. Evaluation of Hi-C Sequencing for Detection of Gene Fusions in Hematologic and Solid Tumor Pediatric Cancer Samples. Cancers. 2024; 16(17):2936. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16172936
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchmitt, Anthony D., Kristin Sikkink, Atif A. Ahmed, Shadi Melnyk, Derek Reid, Logan Van Meter, Erin M. Guest, Lisa A. Lansdon, Tomi Pastinen, Irina Pushel, and et al. 2024. "Evaluation of Hi-C Sequencing for Detection of Gene Fusions in Hematologic and Solid Tumor Pediatric Cancer Samples" Cancers 16, no. 17: 2936. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16172936
APA StyleSchmitt, A. D., Sikkink, K., Ahmed, A. A., Melnyk, S., Reid, D., Van Meter, L., Guest, E. M., Lansdon, L. A., Pastinen, T., Pushel, I., Yoo, B., & Farooqi, M. S. (2024). Evaluation of Hi-C Sequencing for Detection of Gene Fusions in Hematologic and Solid Tumor Pediatric Cancer Samples. Cancers, 16(17), 2936. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16172936







