Molecular Profiling of KIT/PDGFRA-Mutant and Wild-Type Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GISTs) with Clinicopathological Correlation: An 18-Year Experience at a Tertiary Center in Kuwait
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinicopathological Data
2.2. Molecular Analysis Data
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinicopathological Findings
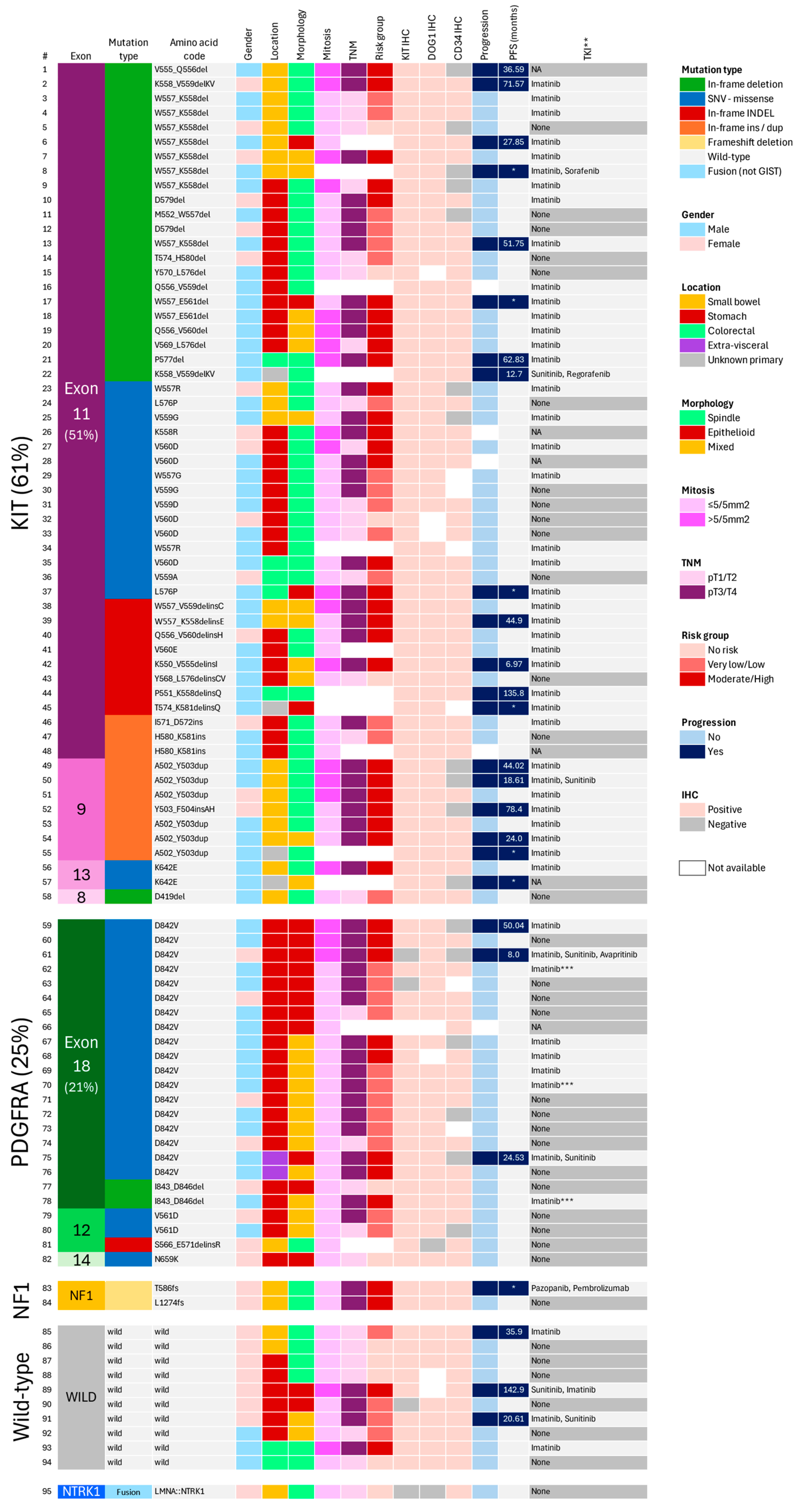
3.2. Genotype Analysis
3.2.1. Overall Frequencies
3.2.2. KIT/PDGFRA-Mutant GISTs
3.2.3. KIT/PDGFRA Wild-Type GISTs
3.2.4. Disease Progression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rubin, B.P.; Heinrich, M.C.; Corless, C.L. Gastrointestinal stromal tumour. Lancet 2007, 369, 1731–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kindblom, L.G.; Remotti, H.E.; Aldenborg, F.; Meis-Kindblom, J.M. Gastrointestinal pacemaker cell tumor (GIPACT): Gastrointestinal stromal tumors show phenotypic characteristics of the interstitial cells of Cajal. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 152, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Joensuu, H.; Hohenberger, P.; Corless, C.L. Gastrointestinal stromal tumour. Lancet 2013, 382, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, S.; Miceli, R.; Messerini, L.; Bearzi, I.; Mazzoleni, G.; Capella, C.; Arrigoni, G.; Sonzogni, A.; Sidoni, A.; Toffolatti, L.; et al. Natural history of imatinib-naive GISTs: A retrospective analysis of 929 cases with long-term follow-up and development of a survival nomogram based on mitotic index and size as continuous variables. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2011, 35, 1646–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukar, M.; Kapil, A.; Papenfuss, W.; Groman, A.; Grobmyer, S.R.; Hochwald, S.N. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) at uncommon locations: A large population based analysis. J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 111, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Alpert, L.; Cates, J.M.M.; Gonzalez, R.S.; Rare GIST Risk Stratification Group. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) arising in uncommon locations: Clinicopathologic features and risk assessment of esophageal, colonic, and appendiceal GISTs. Mod. Pathol. 2022, 35, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, M.; Monihan, J.M.; Sarlomo-Rikala, M.; Kovatich, A.J.; Carr, N.J.; Emory, T.S.; Sobin, L.H. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors/smooth muscle tumors (GISTs) primary in the omentum and mesentery: Clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 26 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1999, 23, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. WHO Classification of Tumours Series: Soft Tissue and Bone Tumours, 5th ed.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2020. Available online: https://tumourclassification.iarc.who.int/chapters/33 (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Lasota, J.; Miettinen, M. Clinical significance of oncogenic KIT and PDGFRA mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Histopathology 2008, 53, 245–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, S.; Gasparotto, D.; Miceli, R.; Toffolatti, L.; Gallina, G.; Scaramel, E.; Marzotto, A.; Boscato, E.; Messerini, L.; Bearzi, I.; et al. KIT, PDGFRA, and BRAF mutational spectrum impacts on the natural history of imatinib-naive localized GIST: A population-based study. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2015, 39, 922–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, T.; Kanda, T.; Kameyama, H.; Wakai, T. Neoadjuvant therapy for gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, S.; Isozaki, K.; Moriyama, Y.; Hashimoto, K.; Nishida, T.; Ishiguro, S.; Kawano, K.; Hanada, M.; Kurata, A.; Takeda, M.; et al. Gain-of-function mutations of c-kit in human gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science 1998, 279, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakahara, M.; Isozaki, K.; Hirota, S.; Miyagawa, J.; Hase-Sawada, N.; Taniguchi, M.; Nishida, T.; Kanayama, S.; Kitamura, Y.; Shinomura, Y.; et al. A novel gain-of-function mutation of c-kit gene in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Gastroenterology 1998, 115, 1090–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, M.C.; Corless, C.L.; Duensing, A.; McGreevey, L.; Chen, C.J.; Joseph, N.; Singer, S.; Griffith, D.J.; Haley, A.; Town, A.; et al. PDGFRA activating mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science 2003, 299, 708–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joensuu, H.; Wardelmann, E.; Sihto, H.; Eriksson, M.; Sundby Hall, K.; Reichardt, A.; Hartmann, J.T.; Pink, D.; Cameron, S.; Hohenberger, P.; et al. Effect of KIT and PDGFRA mutations on survival in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors treated with adjuvant imatinib: An exploratory analysis of a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, M.C.; Corless, C.L.; Demetri, G.D.; Blanke, C.D.; von Mehren, M.; Joensuu, H.; McGreevey, L.S.; Chen, C.J.; Van den Abbeele, A.D.; Druker, B.J.; et al. Kinase mutations and imatinib response in patients with metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 4342–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debiec-Rychter, M.; Sciot, R.; Le Cesne, A.; Schlemmer, M.; Hohenberger, P.; van Oosterom, A.T.; Blay, J.Y.; Leyvraz, S.; Stul, M.; Casali, P.G.; et al. KIT mutations and dose selection for imatinib in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Eur. J. Cancer. 2006, 42, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, M.C.; Jones, R.L.; von Mehren, M.; Schöffski, P.; Serrano, C.; Kang, Y.K.; Cassier, P.A.; Mir, O.; Eskens, F.; Tap, W.D.; et al. Avapritinib in advanced PDGFRA D842V-mutant gastrointestinal stromal tumour (NAVIGATOR): A multicentre, open-label, phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonescu, C.R.; Besmer, P.; Guo, T.; Arkun, K.; Hom, G.; Koryotowski, B.; Leversha, M.A.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Desantis, D.; Singer, S.; et al. Acquired resistance to imatinib in gastrointestinal stromal tumor occurs through secondary gene mutation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 4182–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, M.C.; Maki, R.G.; Corless, C.L.; Antonescu, C.R.; Harlow, A.; Griffith, D.; Town, A.; McKinley, A.; Ou, W.B.; Fletcher, J.A.; et al. Primary and secondary kinase genotypes correlate with the biological and clinical activity of sunitinib in imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumor. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 5352–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gounder, M.M.; Maki, R.G. Molecular basis for primary and secondary tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2011, 67 (Suppl. S1), S25–S43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakai, T.; Kanda, T.; Hirota, S.; Ohashi, A.; Shirai, Y.; Hatakeyama, K. Late resistance to imatinib therapy in a metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumour is associated with a second KIT mutation. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 90, 2059–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, C.; Nucifora, M.; Molinari, F.; Conca, E.; Anania, M.C.; Bordoni, A.; Saletti, P.; Mazzucchelli, L.; Pilotti, S.; Pierotti, M.A.; et al. KRAS and BRAF mutations predict primary resistance to imatinib in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 1769–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casali, P.G.; Abecassis, N.; Aro, H.T.; Bauer, S.; Biagini, R.; Bielack, S.; Bonvalot, S.; Boukovinas, I.; Bovee, J.V.M.G.; Brodowicz, T.; et al. Gastrointestinal stromal tumours: ESMO-EURACAN Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29 (Suppl. S4), iv68–iv78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janeway, K.A.; Kim, S.Y.; Lodish, M.; Nosé, V.; Rustin, P.; Gaal, J.; Dahia, P.L.; Liegl, B.; Ball, E.R.; Raygada, M.; et al. Defects in succinate dehydrogenase in gastrointestinal stromal tumors lacking KIT and PDGFRA mutations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agaram, N.P.; Wong, G.C.; Guo, T.; Maki, R.G.; Singer, S.; Dematteo, R.P.; Besmer, P.; Antonescu, C.R. Novel V600E BRAF mutations in imatinib-naive and imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2008, 47, 853–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belinsky, M.G.; Rink, L.; Cai, K.Q.; Capuzzi, S.J.; Hoang, Y.; Chien, J.; Godwin, A.K.; von Mehren, M. Somatic loss of function mutations in neurofibromin 1 and MYC associated factor X genes identified by exome-wide sequencing in a wild-type GIST case. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, T.; Tsujimoto, M.; Takahashi, T.; Hirota, S.; Blay, J.Y.; Wataya-Kaneda, M. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors in Japanese patients with neurofibromatosis type I. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huss, S.; Pasternack, H.; Ihle, M.A.; Merkelbach-Bruse, S.; Heitkötter, B.; Hartmann, W.; Trautmann, M.; Gevensleben, H.; Büttner, R.; Schildhaus, H.U.; et al. Clinicopathological and molecular features of a large cohort of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs) and review of the literature: BRAF mutations in KIT/PDGFRA wild-type GISTs are rare events. Hum. Pathol. 2017, 62, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boikos, S.A.; Pappo, A.S.; Killian, J.K.; LaQuaglia, M.P.; Weldon, C.B.; George, S.; Trent, J.C.; von Mehren, M.; Wright, J.A.; Schiffman, J.D.; et al. Molecular subtypes of KIT/PDGFRA wild-type gastrointestinal stromal tumors: A report from the National Institutes of Health Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Clinic. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergaard, L.K.; Oliveira, D.N.P.; Poulsen, T.S.; Høgdall, C.K.; Høgdall, E.V. Oncomine Comprehensive Assay v3 vs. Oncomine Comprehensive Assay Plus. Cancers 2021, 13, 5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, S.; Alkhaldi, S.S.; Alasousi, K.; Ali, R.H. Intestinal LMNA::NTRK1-fused spindle cell neoplasm with S100 and CD34 coexpression: A new case. BMJ Case Rep. 2022, 15, e251270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miettinen, M.; Sobin, L.H.; Lasota, J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors of the stomach: A clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic study of 1765 cases with long-term follow-up. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2005, 29, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, F.; Tian, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xu, G.; Liu, S.; Guo, M.; Lian, X.; Fan, D.; Zhang, H. Clinicopathological features and prognosis of colonic gastrointestinal stromal tumors: Evaluation of a pooled case series. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 40735–40745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wu, S.; Meng, Z.; Wu, H. Colonic gastrointestinal stromal tumor: A population-based analysis of incidence and survival. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2019, 2019, 3849850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasota, J.; Dansonka-Mieszkowska, A.; Sobin, L.H.; Miettinen, M. A great majority of GISTs with PDGFRA mutations represent gastric tumors of low or no malignant potential. Lab. Investig. 2004, 84, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, A.; Pantaleo, M.A.; Astolfi, A.; Indio, V.; Nannini, M. The identity of PDGFRA D842V-mutant gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST). Cancers 2021, 13, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardelmann, E.; Neidt, I.; Bierhoff, E.; Speidel, N.; Manegold, C.; Fischer, H.P.; Pfeifer, U.; Pietsch, T. c-kit mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumors occur preferentially in the spindle rather than in the epithelioid cell variant. Mod. Pathol. 2002, 15, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardelmann, E.; Hrychyk, A.; Merkelbach-Bruse, S.; Pauls, K.; Goldstein, J.; Hohenberger, P.; Losen, I.; Manegold, C.; Büttner, R.; Pietsch, T. Association of platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha mutations with gastric primary site and epithelioid or mixed cell morphology in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. J. Mol. Diagn. 2004, 6, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanamori, K.; Yamagata, Y.; Honma, Y.; Date, K.; Wada, T.; Hayashi, T.; Otsuki, S.; Sekine, S.; Yoshikawa, T.; Katai, H.; et al. Extra-gastrointestinal stromal tumor arising in the lesser omentum with a platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRA) mutation: A case report and literature review. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 18, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reith, J.D.; Goldblum, J.R.; Lyles, R.H.; Weiss, S.W. Extragastrointestinal (soft tissue) stromal tumors: An analysis of 48 cases with emphasis on histologic predictors of outcome. Mod. Pathol. 2000, 13, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, M.; Felisiak-Golabek, A.; Wang, Z.; Inaguma, S.; Lasota, J. GIST manifesting as a retroperitoneal tumor: Clinicopathologic immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic study of 112 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2017, 41, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agaimy, A.; Wünsch, P.H. Gastrointestinal stromal tumours: A regular origin in the muscularis propria, but an extremely diverse gross presentation. A review of 200 cases to critically re-evaluate the concept of so-called extra-gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2006, 391, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Künstlinger, H.; Huss, S.; Merkelbach-Bruse, S.; Binot, E.; Kleine, M.A.; Loeser, H.; Mittler, J.; Hartmann, W.; Hohenberger, P.; Reichardt, P.; et al. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors with KIT exon 9 mutations: Update on genotype-phenotype correlation and validation of a high-resolution melting assay for mutational testing. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2013, 37, 1648–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lux, M.L.; Rubin, B.P.; Biase, T.L.; Chen, C.J.; Maclure, T.; Demetri, G.; Xiao, S.; Singer, S.; Fletcher, C.D.; Fletcher, J.A. KIT extracellular and kinase domain mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 156, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasota, J.; Wozniak, A.; Sarlomo-Rikala, M.; Rys, J.; Kordek, R.; Nassar, A.; Sobin, L.H.; Miettinen, M. Mutations in exons 9 and 13 of KIT gene are rare events in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. A study of 200 cases. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 1091–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.; Debiec-Rychter, M.; Corless, C.L.; Reid, R.; Davidson, R.; White, J.D. Imatinib in the management of multiple gastrointestinal stromal tumors associated with a germline KIT K642E mutation. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2007, 131, 1393–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachet, J.B.; Landi, B.; Laurent-Puig, P.; Italiano, A.; Le Cesne, A.; Lévy, P.; Safar, V.; Duffaud, F.; Blay, J.Y.; Emile, J.F. Diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumour (GIST) and germline mutation of KIT exon 13. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 2531–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engin, G.; Eraslan, S.; Kayserili, H.; Kapran, Y.; Akman, H.; Akyuz, A.; Aykan, N.F. Imatinib response of gastrointestinal stromal tumor patients with germline mutation on KIT exon 13: A family report. World J. Radiol. 2017, 9, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Irún, A.; Villa-Puente, M.; García-Espinosa, R.; Cavadas-López, A. [Familial gastrointestinal stroma tumor due to mutation in exon 13 (K642E) of the KIT gene]. Med. Clin. 2012, 139, 512–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.L.; Trent, J.C.; Wu, E.F.; Fuller, G.N.; Ramdas, L.; Zhang, W.; Raymond, A.K.; Prieto, V.G.; Oyedeji, C.O.; Hunt, K.K.; et al. A missense mutation in KIT kinase domain 1 correlates with imatinib resistance in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 5913–5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, C.; Mariño-Enríquez, A.; Tao, D.L.; Ketzer, J.; Eilers, G.; Zhu, M.; Yu, C.; Mannan, A.M.; Rubin, B.P.; Demetri, G.D.; et al. Complementary activity of tyrosine kinase inhibitors against secondary kit mutations in imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waisbren, J.; Uthe, R.; Siziopikou, K.; Kaklamani, V. BRCA 1/2 gene mutation and gastrointestinal stromal tumours: A potential association. BMJ Case Rep. 2015, 2015, bcr2014208830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekido, Y.; Ohigashi, S.; Takahashi, T.; Hayashi, N.; Suzuki, K.; Hirota, S. Familial gastrointestinal stromal tumor with germline KIT mutations accompanying hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanella, N.C.; Scapulatempo-Neto, C.; Abrahão-Machado, L.F.; Torres De Oliveira, A.T.; Berardinelli, G.N.; Guimarães, D.P.; Reis, R.M. Lack of microsatellite instability in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 5221–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Sul, H.J.; Kim, J.G. Rare occurrence of microsatellite instability in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Medicina 2021, 57, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, R. Syndromic gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Hered. Cancer Clin. Pract. 2016, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, M.; Wang, Z.F.; Sarlomo-Rikala, M.; Osuch, C.; Rutkowski, P.; Lasota, J. Succinate dehydrogenase-deficient GISTs: A clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic study of 66 gastric GISTs with predilection to young age. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2011, 35, 1712–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killian, J.K.; Miettinen, M.; Walker, R.L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.J.; Waterfall, J.J.; Noyes, N.; Retnakumar, P.; Yang, Z.; Smith, W.I., Jr.; et al. Recurrent epimutation of SDHC in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 268ra177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agaimy, A.; Terracciano, L.M.; Dirnhofer, S.; Tornillo, L.; Foerster, A.; Hartmann, A.; Bihl, M.P. V600E BRAF mutations are alternative early molecular events in a subset of KIT/PDGFRA wild-type gastrointestinal stromal tumours. J. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 62, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparotto, D.; Rossi, S.; Polano, M.; Tamborini, E.; Lorenzetto, E.; Sbaraglia, M.; Mondello, A.; Massani, M.; Lamon, S.; Bracci, R.; et al. Quadruple-Negative GIST Is a Sentinel for Unrecognized Neurofibromatosis Type 1 Syndrome. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantaleo, M.A.; Nannini, M.; Corless, C.L.; Heinrich, M.C. Quadruple wild-type (WT) GIST: Defining the subset of GIST that lacks abnormalities of KIT, PDGFRA, SDH, or RAS signaling pathways. Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atiq, M.A.; Davis, J.L.; Hornick, J.L.; Dickson, B.C.; Fletcher, C.D.M.; Fletcher, J.A.; Folpe, A.L.; Mariño-Enríquez, A. Mesenchymal tumors of the gastrointestinal tract with NTRK rearrangements: A clinicopathological, immunophenotypic, and molecular study of eight cases, emphasizing their distinction from gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST). Mod. Pathol. 2021, 34, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wozniak, A.; Rutkowski, P.; Schöffski, P.; Ray-Coquard, I.; Hostein, I.; Schildhaus, H.U.; Le Cesne, A.; Bylina, E.; Limon, J.; Blay, J.Y.; et al. Tumor genotype is an independent prognostic factor in primary gastrointestinal stromal tumors of gastric origin: A european multicenter analysis based on ConticaGIST. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 6105–6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardelmann, E.; Losen, I.; Hans, V.; Neidt, I.; Speidel, N.; Bierhoff, E.; Heinicke, T.; Pietsch, T.; Büttner, R.; Merkelbach-Bruse, S. Deletion of Trp-557 and Lys-558 in the juxtamembrane domain of the c-kit protooncogene is associated with metastatic behavior of gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Int. J. Cancer. 2003, 106, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, J.; Poveda, A.; Llombart-Bosch, A.; Ramos, R.; López-Guerrero, J.A.; García del Muro, J.; Maurel, J.; Calabuig, S.; Gutierrez, A.; González de Sande, J.L.; et al. Deletions affecting codons 557-558 of the c-KIT gene indicate a poor prognosis in patients with completely resected gastrointestinal stromal tumors: A study by the Spanish Group for Sarcoma Research (GEIS). J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 6190–6198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Xu, J.; Zhao, W.; Tu, L.; Qiu, W.; Wang, C.; Shen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Cao, H. Prognostic value of mutational characteristics in gastrointestinal stromal tumors: A single-center experience in 275 cases. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontogianni-Katsarou, K.; Dimitriadis, E.; Lariou, C.; Kairi-Vassilatou, E.; Pandis, N.; Kondi-Paphiti, A. KIT exon 11 codon 557/558 deletion/insertion mutations define a subset of gastrointestinal stromal tumors with malignant potential. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 1891–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dematteo, R.P.; Gold, J.S.; Saran, L.; Gönen, M.; Liau, K.H.; Maki, R.G.; Singer, S.; Besmer, P.; Brennan, M.F.; Antonescu, C.R. Tumor mitotic rate, size, and location independently predict recurrence after resection of primary gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST). Cancer 2008, 112, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, M.; Makhlouf, H.; Sobin, L.H.; Lasota, J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors of the jejunum and ileum: A clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic study of 906 cases before imatinib with long-term follow-up. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2006, 30, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Variable | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Age at presentation | |
| Mean (SD) | 54.3 (13.1) |
| Range | 15.0–91.0 |
| Sex | |
| Male | 120 (60.0%) |
| Female | 80 (40.0%) |
| Location of primary tumor | |
| Stomach | 108 (54.0%) |
| Small bowel | 66 (33.0%) |
| Colorectal | 14 (7.0%) |
| Extra-visceral | 3 (1.5%) |
| Unknown primary | 9 (4.5%) |
| Size of primary tumor (cm) | |
| ≤2 (T1) | 32 (19.5%) |
| >2–≤5 (T2) | 42 (25.6%) |
| >5–≤10 (T3) | 55 (33.5%) |
| >10 (T4) | 35 (21.3%) |
| Not available | 36 |
| Histological phenotype | |
| Spindle | 127 (64.5%) |
| Epithelioid | 23 (11.7%) |
| Mixed | 47 (23.9%) |
| Not available | 3 |
| Mitosis | |
| ≤5/5 mm2 | 133 (75.1%) |
| >5/5 mm2 | 44 (24.9%) |
| Not available | 23 |
| Risk assessment | |
| No risk | 32 (19.2%) |
| Very low | 17 (10.2%) |
| Low | 43 (25.7%) |
| Moderate | 28 (16.8%) |
| High | 47 (28.1%) |
| Not available | 33 |
| Stage at presentation | |
| Stage I (I, IA, IB) | 92 (53.2%) |
| Stage II | 25 (14.5%) |
| Stage III (IIIA, IIIB) | 39 (22.5%) |
| Stage IVA | 17 (9.8%) |
| Not available | 27 |
| Small incidental GISTs | |
| Yes | 24 (12.0%) |
| No | 176 (88.0%) |
| Status at 1st pathology encounter | |
| Localized | 183 (91.5%) |
| Advanced | 17 (8.5%) |
| Gene | n (%) |
|---|---|
| KIT | 58 (61.05%) |
| Exon 11 | 48 (50.53%) |
| Exon 9 | 7 (7.37%) |
| Exon 13 | 2 (2.11%) |
| Exon 8 | 1 (1.05%) |
| PDGFRA | 24 (25.26%) |
| Exon 18 | 20 (21.05%) |
| Exon 12 | 3 (3.15%) |
| Exon 14 | 1 (1.05%) |
| NF1 | 2 (2.11%) |
| KIT/PDGFRA/RAS wild-type * | 10 (10.53%) |
| NTRK1 fusion ** | 1 (1.05%) |
| Variable | No Progression (n = 64) | Progression (n = 26) | Total (n = 90) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.304 a | |||
| Mean (SD) | 55.4 (13.6) | 52.2 (13.0) | 54.5 (13.4) | |
| Gene type | * 0.049 b | |||
| KIT | 35 (63.6%) | 19 (86.4%) | 54 (70.1%) | |
| PDGFRA | 20 (36.4%) | 3 (13.6%) | 23 (29.9%) | |
| Other | 9 | 4 | 13 | |
| Wild-type | 0.934 b | |||
| Yes | 7 (10.9%) | 3 (11.5%) | 10 (11.1%) | |
| No | 57 (89.1%) | 23 (88.5%) | 80 (88.9%) | |
| Location of primary tumor | * 0.001 b | |||
| Stomach | 43 (67.2%) | 7 (26.9%) | 50 (55.6%) | |
| Small bowel | 16 (25.0%) | 11 (42.3%) | 27 (30.0%) | |
| Colorectal | 4 (6.2%) | 3 (11.5%) | 7 (7.8%) | |
| Extra-visceral | 1 (1.6%) | 1 (3.8%) | 2 (2.2%) | |
| Unknown primary | 0 (0.0%) | 4 (15.4%) | 4 (4.4%) | |
| Size (cm) | * 0.002 a | |||
| Mean (SD) | 6.6 (5.0) | 11.3 (5.9) | 7.7 (5.5) | |
| Range | 0.4–25.0 | 5.0–24.0 | 0.4–25.0 | |
| Not available | 3 | 9 | 12 | |
| Histological phenotype | 0.119 b | |||
| Epithelioid | 8 (12.5%) | 8 (30.8%) | 16 (17.8%) | |
| Mixed | 20 (31.2%) | 6 (23.1%) | 26 (28.9%) | |
| Spindle | 36 (56.2%) | 12 (46.2%) | 48 (53.3%) | |
| TNM stage | * 0.002 b | |||
| pT1/T2 | 27 (44.3%) | 1 (5.3%) | 28 (35.0%) | |
| pT3/T4 | 34 (55.7%) | 18 (94.7%) | 52 (65.0%) | |
| Not available | 3 | 7 | 10 | |
| Mitosis | * 0.004 b | |||
| ≤5/5 mm2 | 52 (82.5%) | 10 (50.0%) | 62 (74.7%) | |
| >5/5 mm2 | 11 (17.5%) | 10 (50.0%) | 21 (25.3%) | |
| Not available | 1 | 6 | 7 | |
| Risk category | * <0.001 b | |||
| No risk | 11 (18.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 11 (13.8%) | |
| Very low/Low | 28 (45.9%) | 3 (15.8%) | 31 (38.8%) | |
| Moderate/High | 22 (36.1%) | 16 (84.2%) | 38 (47.5%) | |
| Not available | 3 | 7 | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, R.H.; Alsaber, A.R.; Mohanty, A.K.; Alnajjar, A.; Mohammed, E.M.A.; Alateeqi, M.; Jama, H.; Almarzooq, A.; Benobaid, N.; Alqallaf, Z.; et al. Molecular Profiling of KIT/PDGFRA-Mutant and Wild-Type Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GISTs) with Clinicopathological Correlation: An 18-Year Experience at a Tertiary Center in Kuwait. Cancers 2024, 16, 2907. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162907
Ali RH, Alsaber AR, Mohanty AK, Alnajjar A, Mohammed EMA, Alateeqi M, Jama H, Almarzooq A, Benobaid N, Alqallaf Z, et al. Molecular Profiling of KIT/PDGFRA-Mutant and Wild-Type Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GISTs) with Clinicopathological Correlation: An 18-Year Experience at a Tertiary Center in Kuwait. Cancers. 2024; 16(16):2907. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162907
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Rola H., Ahmad R. Alsaber, Asit K. Mohanty, Abdulsalam Alnajjar, Eiman M. A. Mohammed, Mona Alateeqi, Hiba Jama, Ammar Almarzooq, Noelle Benobaid, Zainab Alqallaf, and et al. 2024. "Molecular Profiling of KIT/PDGFRA-Mutant and Wild-Type Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GISTs) with Clinicopathological Correlation: An 18-Year Experience at a Tertiary Center in Kuwait" Cancers 16, no. 16: 2907. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162907
APA StyleAli, R. H., Alsaber, A. R., Mohanty, A. K., Alnajjar, A., Mohammed, E. M. A., Alateeqi, M., Jama, H., Almarzooq, A., Benobaid, N., Alqallaf, Z., Ahmed, A. A., Bahzad, S., & Alkandari, M. (2024). Molecular Profiling of KIT/PDGFRA-Mutant and Wild-Type Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GISTs) with Clinicopathological Correlation: An 18-Year Experience at a Tertiary Center in Kuwait. Cancers, 16(16), 2907. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162907






