Potentiating Salvage Radiotherapy in Radiorecurrent Prostate Cancer Through Anti-CTLA4 Therapy: Implications from a Syngeneic Model
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
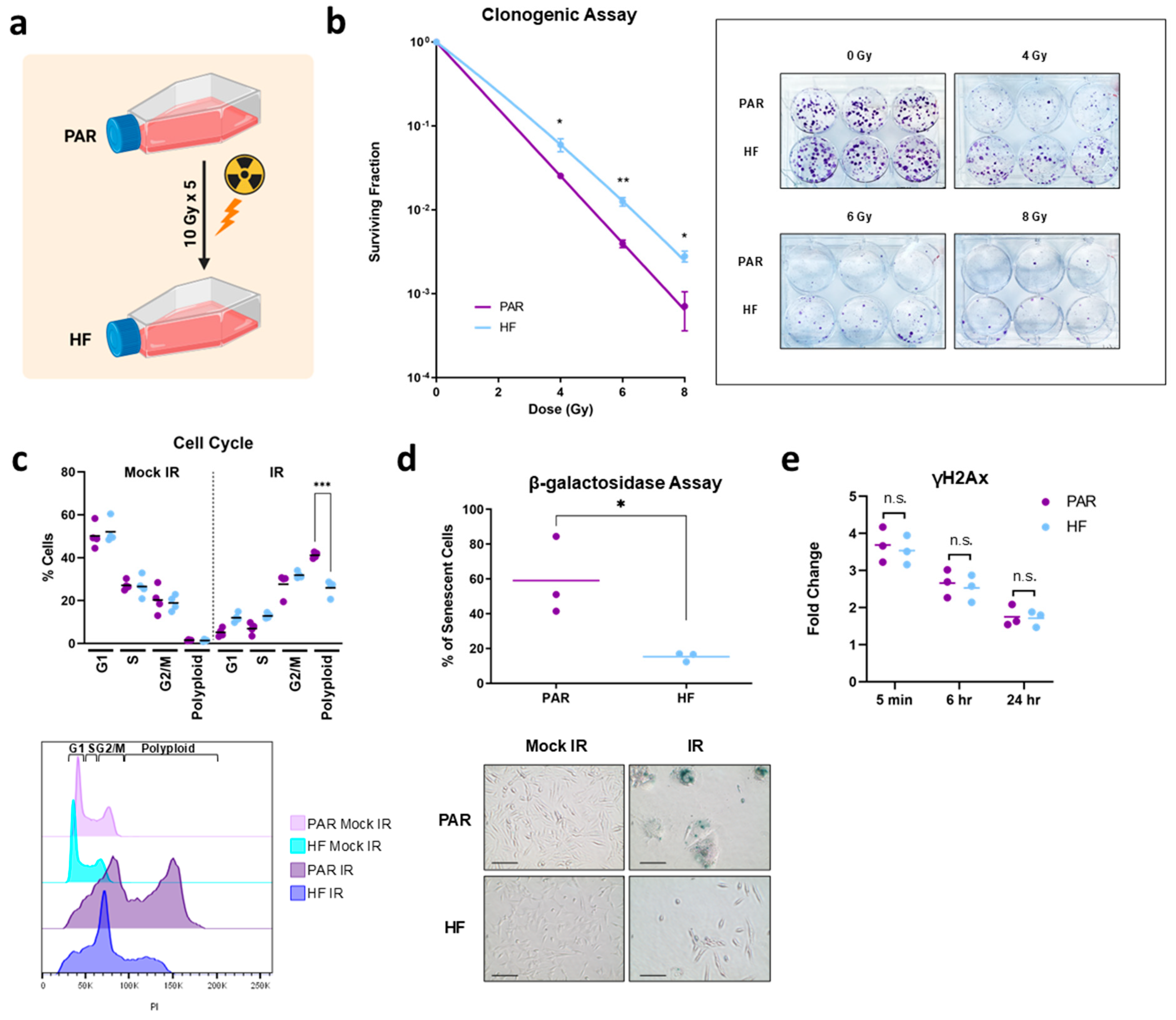
2.1. Generation of Radiation-Resistant Cell Line and Validation by Clonogenic Assay
2.2. Cell Cycle Assay
2.3. β-Galactosidase Senescence Assay
2.4. γH2AX Assay
2.5. Proliferation Assay
2.6. Wound Healing Assay
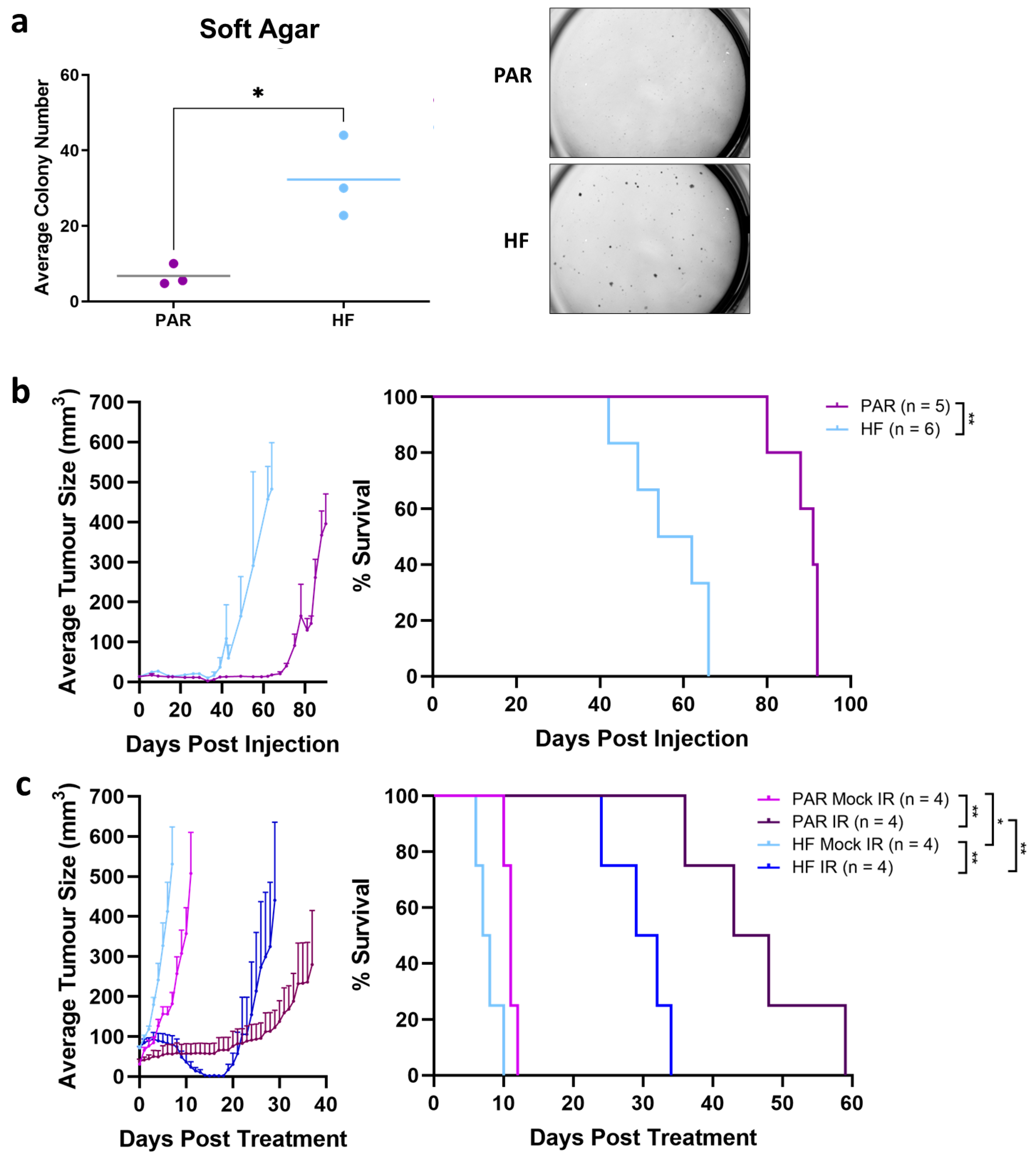
2.7. Soft Agar
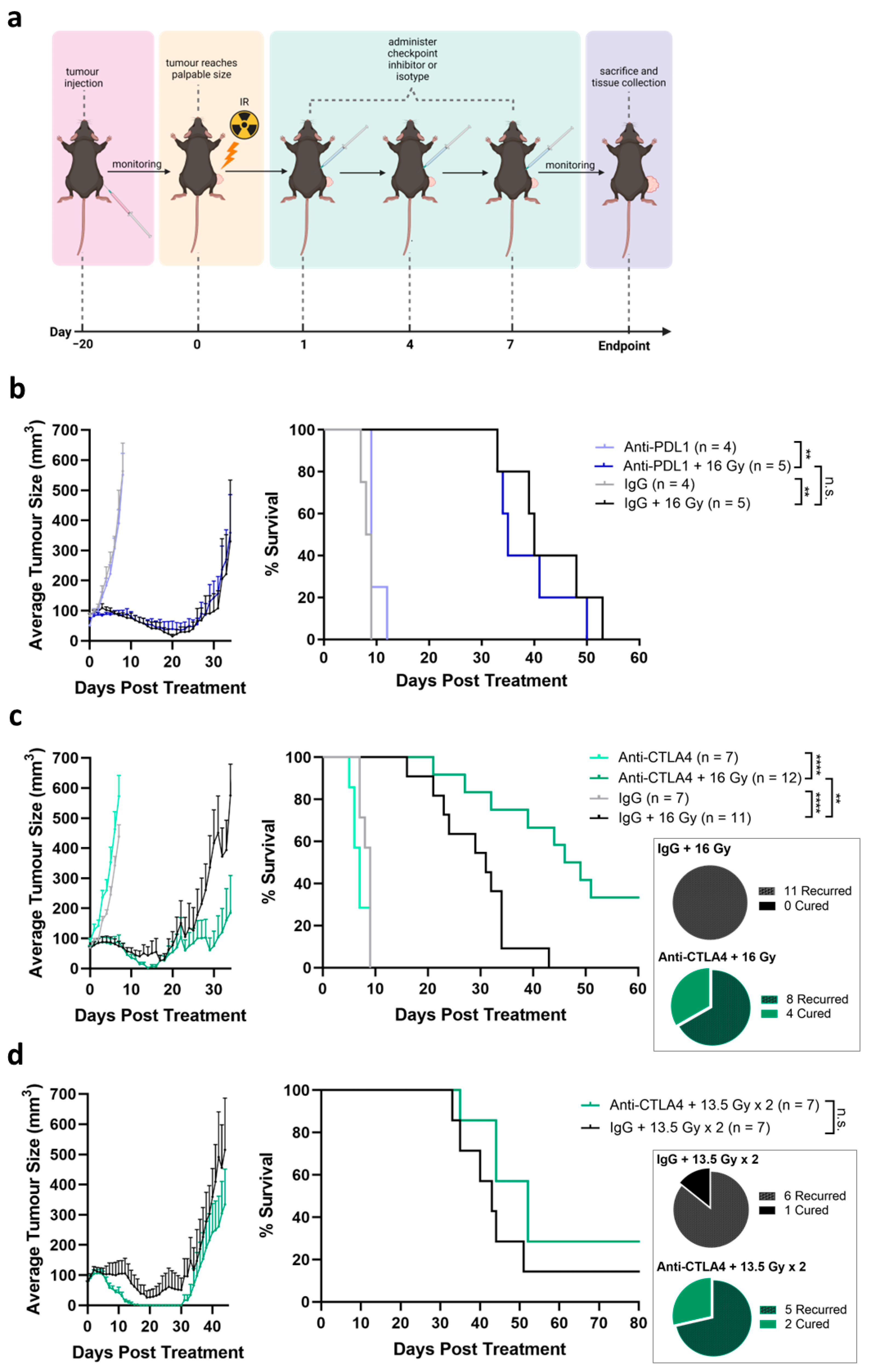
2.8. In Vivo Therapy Experiments
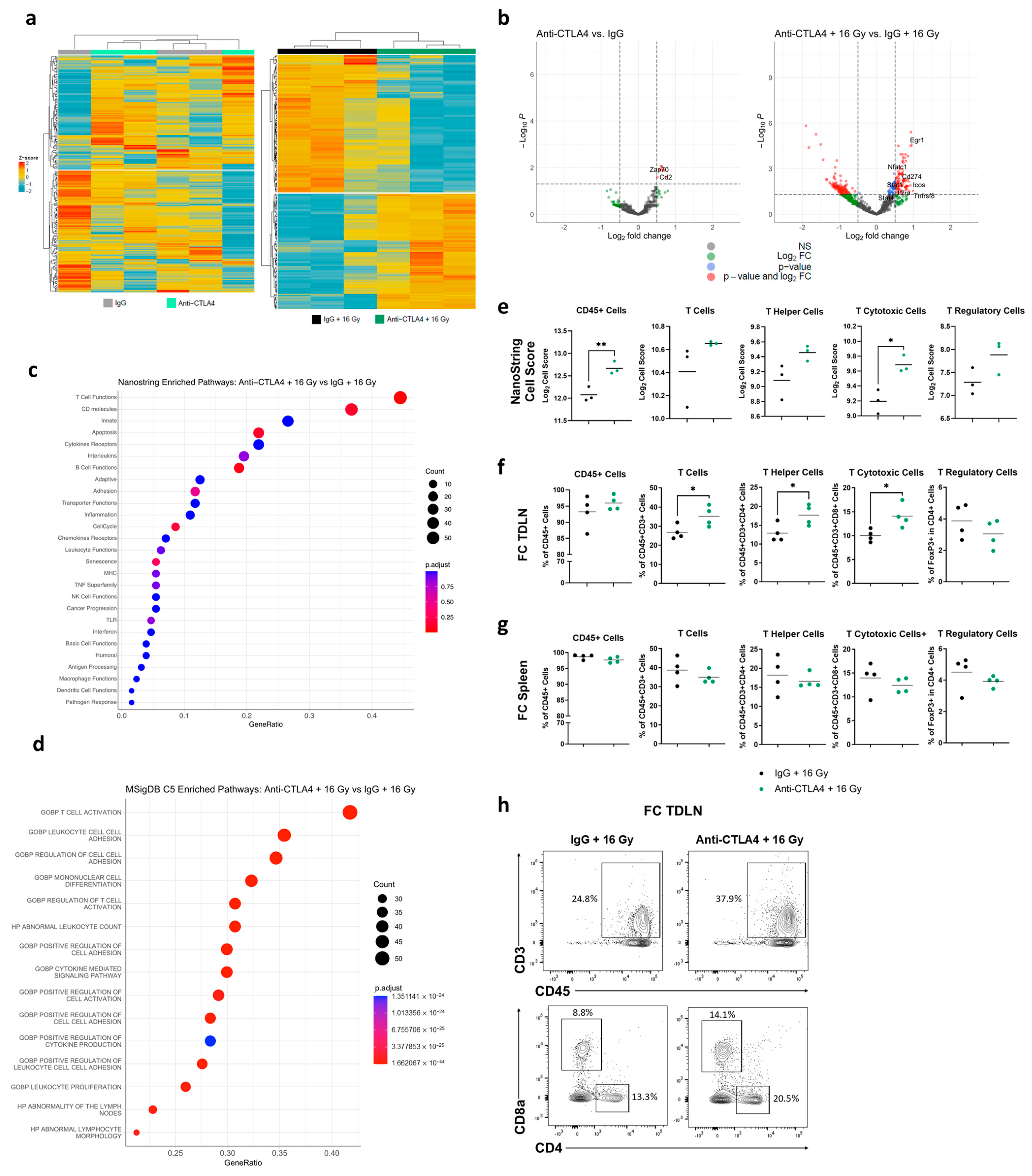
2.9. NanoString Analysis
2.10. Flow Cytometry
2.11. Ethics
2.12. Statistics
2.13. Role of Funding Source
3. Results
3.1. Generation and In Vitro Characterization of Radiorecurrent TRAMP-C2 HF
3.2. Enhanced Tumorgenicity and Radiorecurrent of TRAMP-C2 HF Compared to PAR In Vivo
3.3. Tumor Growth Delay Not Observed by Treatment by ICIs Alone
3.4. Tumor Response Induced by Combination of Radiation and Anti-CTLA4
3.5. Treatment with 16 Gy + Anti-CTLA4 Promoted T-Cell Activation in TDLNs
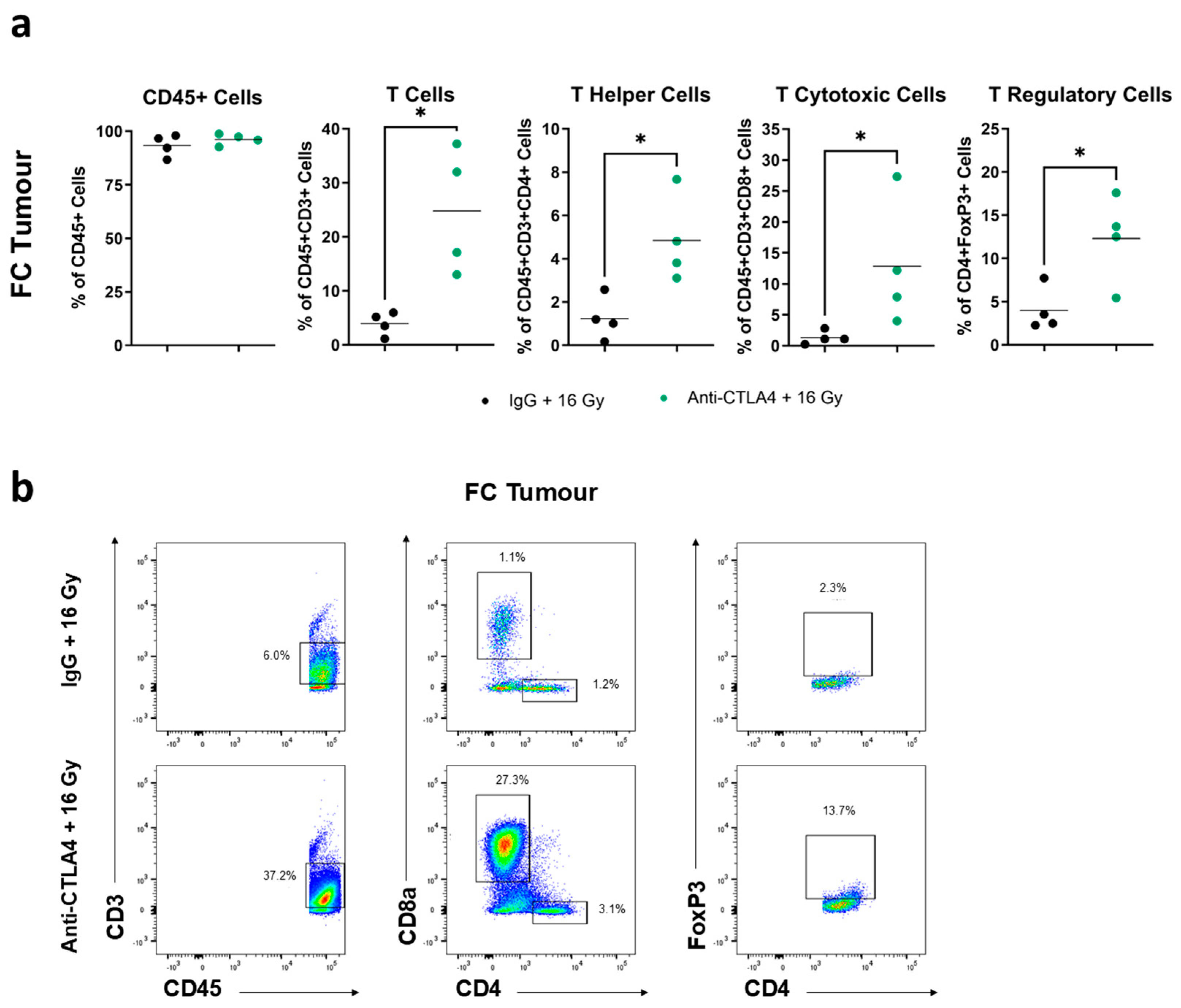
3.6. Treatment with 16 Gy + Anti-CTLA4 Promoted T-Cell Activation in Tumors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Canadian Cancer Society. Prostate Cancer Statistics. Available online: https://cancer.ca/en/cancer-information/cancer-types/prostate/statistics#:~:text=It%20is%20estimated%20that%20about,30%20will%20die%20from%20it (accessed on 3 September 2023).
- American Cancer Society. Key Statistics for Prostate Cancer. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/prostate-cancer/about/key-statistics.html (accessed on 3 September 2023).
- Van Hemelrijck, M.; Folkvaljon, Y.; Adolfsson, J.; Akre, O.; Holmberg, L.; Garmo, H.; Stattin, P. Causes of death in men with localized prostate cancer: A nationwide, population-based study. BJU Int. 2016, 117, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.J.; Autio, K.A.; Roach, M.; Scher, H.I. High-risk prostate cancer-classification and therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, A.J.; Scardino, P.T.; Bianco, F.J.; DiBlasio, C.J.; Fearn, P.A.; Eastham, J.A. Morbidity and functional outcomes of salvage radical prostatectomy for locally recurrent prostate cancer after radiation therapy. J. Urol. 2004, 172 Pt 1, 2239–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishan, A.U.; Chu, F.I.; King, C.R.; Seiferheld, W.; Spratt, D.E.; Tran, P.; Wang, X.; Pugh, S.E.; Sandler, K.A.; Bolla, M.; et al. Local Failure and Survival after Definitive Radiotherapy for Aggressive Prostate Cancer: An Individual Patient-level Meta-analysis of Six Randomized Trials. Eur. Urol. 2020, 77, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuks, Z.; Leibel, S.A.; Wallner, K.E.; Begg, C.B.; Fair, W.R.; Anderson, L.L.; Hilaris, B.S.; Whitmore, W.F. The effect of local control on metastatic dissemination in carcinoma of the prostate: Long-term results in patients treated with 125I implantation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1991, 21, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, F.; Lipton, A.; Cook, R.; Chen, Y.M.; Smith, M.; Coleman, R. Pathologic fractures correlate with reduced survival in patients with malignant bone disease. Cancer 2007, 110, 1860–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, K.; Muders, M.; Zhang, H.; Tindall, D.J. Mechanism of lymph node metastasis in prostate cancer. Future Oncol. 2010, 6, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bono, J.S.; Logothetis, C.J.; Molina, A.; Fizazi, K.; North, S.; Chu, L.; Chi, K.N.; Jones, R.J.; Goodman, O.B.; Saad, F.; et al. Abiraterone and increased survival in metastatic prostate cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1995–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, L.J. Enzalutamide: A Review in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Drugs 2018, 78, 1913–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haj-Hamed, M.; Karivedu, V.; Sidana, A. Salvage treatment for radio-recurrent prostate cancer: A review of literature with focus on recent advancements in image-guided focal salvage therapies. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2019, 51, 1101–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corkum, M.T.; Morton, G.; Loblaw, D.A.; Tseng, C.L.; Murgic, J.; Ravi, A.; Davidson, M.T.M.; Wronski, M.; Haider, M.; Chung, H.T. A Prospective Study of Magnetic Resonance Imaging-guided Focal Salvage High-dose-Rate Brachytherapy for Radiorecurrent Prostate Cancer: Updated Results of 30 Patients. Pr. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 12, e531–e537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corkum, M.T.; Buyyounouski, M.K.; Chang, A.J.; Chung, H.T.; Chung, P.; Cox, B.W.; Crook, J.M.; Davis, B.J.; Frank, S.J.; Henriquez, I.; et al. Salvage prostate brachytherapy in radiorecurrent prostate cancer: An international Delphi consensus study. Radiother. Oncol. 2023, 184, 109672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murgic, J.; Morton, G.; Loblaw, A.; D’Alimonte, L.; Ravi, A.; Wronski, M.; Davidson, M.; Haider, M.; Commisso, K.; Zhang, L.; et al. Focal Salvage High Dose-Rate Brachytherapy for Locally Recurrent Prostate Cancer after Primary Radiation Therapy Failure: Results from a Prospective Clinical Trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 102, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiravand, Y.; Khodadadi, F.; Kashani, S.M.A.; Hosseini-Fard, S.R.; Hosseini, S.; Sadeghirad, H.; Ladwa, R.; O’Byrne, K.; Kulasinghe, A. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 3044–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchbinder, E.I.; Desai, A. CTLA-4 and PD-1 Pathways: Similarities, Differences, and Implications of Their Inhibition. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 39, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, I.; Song, L.; Wang, B.Y.; Rezazadeh Kalebasty, A.; Uchio, E.; Zi, X. Prostate cancer immunotherapy: A review of recent advancements with novel treatment methods and efficacy. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Urol. 2022, 10, 210–233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Venkatachalam, S.; McFarland, T.R.; Agarwal, N.; Swami, U. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Tong, D. Immunotherapy in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: A meta-analysis of data from 7 phase III studies and 3 phase II studies. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 11, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonarakis, E.S.; Piulats, J.M.; Gross-Goupil, M.; Goh, J.; Ojamaa, K.; Hoimes, C.J.; Vaishampayan, U.; Berger, R.; Sezer, A.; Alanko, T.; et al. Pembrolizumab for Treatment-Refractory Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Multicohort, Open-Label Phase II KEYNOTE-199 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Pachynski, R.K.; Narayan, V.; Fléchon, A.; Gravis, G.; Galsky, M.D.; Mahammedi, H.; Patnaik, A.; Subudhi, S.K.; Ciprotti, M.; et al. Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Preliminary Analysis of Patients in the CheckMate 650 Trial. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 489–499.E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute. Pembrolizumab. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/drugs/pembrolizumab (accessed on 5 September 2023).
- Mulvey, A.; Muggeo-Bertin, E.; Berthold, D.R.; Herrera, F.G. Overcoming Immune Resistance with Radiation Therapy in Prostate Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 859785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fizazi, K.; Drake, C.G.; Beer, T.M.; Kwon, E.D.; Scher, H.I.; Gerritsen, W.R.; Bossi, A.; den Eertwegh, A.J.M.V.; Krainer, M.; Houede, N.; et al. Final Analysis of the Ipilimumab Versus Placebo Following Radiotherapy Phase III Trial in Postdocetaxel Metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer Identifies an Excess of Long-term Survivors. Eur. Urol. 2020, 78, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keam, S.P.; Halse, H.; Nguyen, T.; Wang, M.; Van Kooten Losio, N.; Mitchell, C.; Caramia, F.; Byrne, D.J.; Haupt, S.; Ryland, G.; et al. High dose-rate brachytherapy of localized prostate cancer converts tumors from cold to hot. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philipson, R.G.; Romero, T.; Wong, J.K.; Stish, B.J.; Dess, R.T.; Spratt, D.E.; Pilar, A.; Reddy, C.; Wedde, T.B.; Lilleby, W.A.; et al. Patterns of Clinical Progression in Radiorecurrent High-risk Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2021, 80, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, L.C.; Morton, G.C. High dose-rate brachytherapy in the treatment of prostate cancer. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2018, 7, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, L.C.; Ravi, A.; Chung, H.; Tseng, C.L.; Wronski, M.; Paudel, M.; McGuffin, M.; Cheung, P.; Loblaw, A.; Morton, G. Pattern of relapse and dose received by the recurrent intraprostatic nodule in low- to intermediate-risk prostate cancer treated with single fraction 19Gy high-dose-rate brachytherapy. Brachytherapy 2018, 17, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa, R.J.M.; Loblaw, A. Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy: Hitting Harder, Faster, and Smarter in High-Risk Prostate Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 889132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haughey, C.M.; Mukherjee, D.; Steele, R.E.; Popple, A.; Dura-Perez, L.; Pickard, A.; Patel, M.; Jain, S.; Mullan, P.B.; Williams, R.; et al. Investigating Radiotherapy Response in a Novel Syngeneic Model of Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brummel, K.; Eerkens, A.L.; de Bruyn, M.; Nijman, H.W. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes: From prognosis to treatment selection. Br. J. Cancer 2023, 128, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, A.; Nguyen, N.P. Mechanistic rationales for combining immunotherapy with radiotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1125905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theelen, W.S.M.E.; Peulen, H.M.U.; Lalezari, F.; van der Noort, V.; de Vries, J.F.; Aerts, J.G.J.V.; Dumoulin, D.W.; Bahce, I.; Niemeijer, A.N.; de Langen, A.J.; et al. Effect of Pembrolizumab after Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy vs Pembrolizumab Alone on Tumor Response in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Results of the PEMBRO-RT Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonia, S.J.; Villegas, A.; Daniel, D.; Vicente, D.; Murakami, S.; Hui, R.; Yokoi, T.; Chiappori, A.; Lee, K.H.; de Wit, M.; et al. Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitmanee, P.; Tsang, Y.; Tharmalingam, H.; Hamada, M.; Alonzi, R.; Ostler, P.; Hughes, R.; Lowe, G.; Hoskin, P. Single-Dose Focal Salvage High Dose Rate Brachytherapy for Locally Recurrent Prostate Cancer. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 32, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koukourakis, M.I.; Giatromanolaki, A. Tumor draining lymph nodes, immune response, and radiotherapy: Towards a revisal of therapeutic principles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2022, 1877, 188704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, D.; Yu, J. Radiotherapy combined with immunotherapy: The dawn of cancer treatment. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Attwood, K.; Bshara, W.; Mohler, J.L.; Guru, K.; Xu, B.; Kalinski, P.; Chatta, G. High intratumoral CD8. Prostate 2021, 81, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhani, N.; Tardiel-Cyril, D.R.; Davtyan, A.; Generali, D.; Roudi, R.; Li, Y. CTLA-4 in Regulatory T Cells for Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Z. PD-1/PD-L1 Checkpoint Inhibitors in Tumor Immunotherapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 731798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latchman, Y.; Wood, C.R.; Chernova, T.; Chaudhary, D.; Borde, M.; Chernova, I.; Iwai, Y.; Long, A.J.; Brown, J.A.; Nunes, R.; et al. PD-L2 is a second ligand for PD-1 and inhibits T cell activation. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, R.E.; Richardson, E.K.; Toh, H.C. Revisiting the role of CD4. Cancer Gene Ther. 2021, 28, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, S.; Rakshit, S.; Sarkar, K. The Role of STAT1 in T Helper Cell Differentiation during Breast Cancer Progression. J. Breast Cancer 2021, 24, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.J.; Lee, J.B.; Park, S.H.; Chang, J.; Lee, C.W. T-bet expression is regulated by EGR1-mediated signaling in activated T cells. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 131, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malek, T.R.; Castro, I. Interleukin-2 receptor signaling: At the interface between tolerance and immunity. Immunity 2010, 33, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Weyden, C.A.; Pileri, S.A.; Feldman, A.L.; Whisstock, J.; Prince, H.M. Understanding CD30 biology and therapeutic targeting: A historical perspective providing insight into future directions. Blood Cancer J. 2017, 7, e603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikenheiser, D.J.; Stumhofer, J.S. ICOS Co-Stimulation: Friend or Foe? Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Eeckhout, B.; Tavernier, J.; Gerlo, S. Interleukin-1 as Innate Mediator of T Cell Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 621931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macian, F. NFAT proteins: Key regulators of T-cell development and function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, R.; Burn, T.N.; Gandolfo, L.C.; Devi, S.; Park, S.L.; Obers, A.; Evrard, M.; Christo, S.N.; Buquicchio, F.A.; Lareau, C.A.; et al. Runx3 drives a CD8. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 1236–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Kong, L.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Oh, S.; Jo, S.; Jang, I.; Kim, T.D. The Role of IL-7 and IL-7R in Cancer Pathophysiology and Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messal, N.; Serriari, N.E.; Pastor, S.; Nunès, J.A.; Olive, D. PD-L2 is expressed on activated human T cells and regulates their function. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 48, 2214–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Subudhi, S.K.; Blando, J.; Scutti, J.; Vence, L.; Wargo, J.; Allison, J.P.; Ribas, A.; Sharma, P. Anti-CTLA-4 Immunotherapy Does Not Deplete FOXP3. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 1233–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Quezada, S.A.; Sepulveda, M.A.; Sharma, P.; Allison, J.P. Engagement of the ICOS pathway markedly enhances efficacy of CTLA-4 blockade in cancer immunotherapy. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurwitz, A.A.; Foster, B.A.; Kwon, E.D.; Truong, T.; Choi, E.M.; Greenberg, N.M.; Burg, M.B.; Allison, J.P. Combination immunotherapy of primary prostate cancer in a transgenic mouse model using CTLA-4 blockade. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 2444–2448. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wada, S.; Jackson, C.M.; Yoshimura, K.; Yen, H.R.; Getnet, D.; Harris, T.J.; Goldberg, M.V.; Bruno, T.C.; Grosso, J.F.; Durham, N.; et al. Sequencing CTLA-4 blockade with cell-based immunotherapy for prostate cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.; Hsu, C.C.; Chen, W.M.; Chen, B.P.C.; Han, C.; Story, M.; Aguilera, T.; Pop, L.M.; Hannan, R.; Fu, Y.X.; et al. Personalized Ultrafractionated Stereotactic Adaptive Radiotherapy (PULSAR) in Preclinical Models Enhances Single-Agent Immune Checkpoint Blockade. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 110, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, C.W.; Sherer, M.V.; Zamarin, D.; Sharabi, A.B.; Dyer, B.A.; Mell, L.K.; Mayadev, J.S. Immunotherapy and radiation therapy sequencing: State of the data on timing, efficacy, and safety. Cancer 2021, 127, 1553–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, T.J.; Hipkiss, E.L.; Borzillary, S.; Wada, S.; Grosso, J.F.; Yen, H.R.; Getnet, D.; Bruno, T.C.; Goldberg, M.V.; Pardoll, D.M.; et al. Radiotherapy augments the immune response to prostate cancer in a time-dependent manner. Prostate 2008, 68, 1319–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalina, J.L.; Neilson, D.S.; Comber, A.P.; Rauw, J.M.; Alexander, A.S.; Vergidis, J.; Lum, J.J. Immune Modulation by Androgen Deprivation and Radiation Therapy: Implications for Prostate Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancers 2017, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, M.D.; McNeel, D.G. Prostate cancer patients on androgen deprivation therapy develop persistent changes in adaptive immune responses. Hum. Immunol. 2010, 71, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Gong, L.; Huang, X.; White, S.D.; Chung, H.T.; Vesprini, D.; Petchiny, T.N.; Fokas, E.; He, H.; Kerbel, R.S.; et al. Potentiating Salvage Radiotherapy in Radiorecurrent Prostate Cancer Through Anti-CTLA4 Therapy: Implications from a Syngeneic Model. Cancers 2024, 16, 2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162839
Wang H, Gong L, Huang X, White SD, Chung HT, Vesprini D, Petchiny TN, Fokas E, He H, Kerbel RS, et al. Potentiating Salvage Radiotherapy in Radiorecurrent Prostate Cancer Through Anti-CTLA4 Therapy: Implications from a Syngeneic Model. Cancers. 2024; 16(16):2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162839
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hanzhi, Linsey Gong, Xiaoyong Huang, Stephanie D. White, Hans T. Chung, Danny Vesprini, Tera N. Petchiny, Emmanouil Fokas, Hansen He, Robert S. Kerbel, and et al. 2024. "Potentiating Salvage Radiotherapy in Radiorecurrent Prostate Cancer Through Anti-CTLA4 Therapy: Implications from a Syngeneic Model" Cancers 16, no. 16: 2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162839
APA StyleWang, H., Gong, L., Huang, X., White, S. D., Chung, H. T., Vesprini, D., Petchiny, T. N., Fokas, E., He, H., Kerbel, R. S., & Liu, S. K. (2024). Potentiating Salvage Radiotherapy in Radiorecurrent Prostate Cancer Through Anti-CTLA4 Therapy: Implications from a Syngeneic Model. Cancers, 16(16), 2839. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162839




