Pre-Op Hydronephrosis Predicts Outcomes in Patients Receiving Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Witjes, J.A.; Bruins, H.M.; Cathomas, R.; Comperat, E.M.; Cowan, N.C.; Gakis, G.; Hernandez, V.; Linares Espinos, E.; Lorch, A.; Neuzillet, Y.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Muscle-invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer: Summary of the 2020 Guidelines. Eur. Urol. 2021, 79, 82–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, H.R.; Santos, P.B.; de Oliveira, M.C.; Muller, S. Is robotic-assisted radical cystectomy (RARC) with intracorporeal diversion becoming the new gold standard of care? World J. Urol. 2016, 34, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parekh, D.J.; Reis, I.M.; Castle, E.P.; Gonzalgo, M.L.; Woods, M.E.; Svatek, R.S.; Weizer, A.Z.; Konety, B.R.; Tollefson, M.; Krupski, T.L.; et al. Robot-assisted radical cystectomy versus open radical cystectomy in patients with bladder cancer (RAZOR): An open-label, randomised, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 2525–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Challacombe, B.J.; Bochner, B.H.; Dasgupta, P.; Gill, I.; Guru, K.; Herr, H.; Mottrie, A.; Pruthi, R.; Redorta, J.P.; Wiklund, P. The role of laparoscopic and robotic cystectomy in the management of muscle-invasive bladder cancer with special emphasis on cancer control and complications. Eur. Urol. 2011, 60, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochner, B.H.; Dalbagni, G.; Marzouk, K.H.; Sjoberg, D.D.; Lee, J.; Donat, S.M.; Coleman, J.A.; Vickers, A.; Herr, H.W.; Laudone, V.P. Randomized Trial Comparing Open Radical Cystectomy and Robot-assisted Laparoscopic Radical Cystectomy: Oncologic Outcomes. Eur. Urol. 2018, 74, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartsch, G.C.; Kuefer, R.; Gschwend, J.E.; de Petriconi, R.; Hautmann, R.E.; Volkmer, B.G. Hydronephrosis as a prognostic marker in bladder cancer in a cystectomy-only series. Eur. Urol. 2007, 51, 690–697; discussion 697–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.J.; Byun, S.S.; Jeong, C.W.; Kwak, C.; Kim, H.H.; Ku, J.H. Association Between Preoperative Hydronephrosis and Prognosis After Radical Cystectomy Among Patients With Bladder Cancer: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitropoulos, D.; Artibani, W.; Graefen, M.; Remzi, M.; Roupret, M.; Truss, M.; European Association of Urology Guidelines, P. Reporting and grading of complications after urologic surgical procedures: An ad hoc EAU guidelines panel assessment and recommendations. Eur. Urol. 2012, 61, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assel, M.; Sjoberg, D.; Elders, A.; Wang, X.; Huo, D.; Botchway, A.; Delfino, K.; Fan, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Koyama, T.; et al. Guidelines for reporting of statistics for clinical research in urology. BJU Int. 2019, 123, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montironi, R.; Lopez-Beltran, A. The 2004 WHO classification of bladder tumors: A summary and commentary. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2005, 13, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babyak, M.A. What you see may not be what you get: A brief, nontechnical introduction to overfitting in regression-type models. Psychosom. Med. 2004, 66, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Pang, C.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, X. Prognostic value of preoperative hydronephrosis in patients with bladder cancer undergoing radical cystectomy: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resorlu, B.; Baltaci, S.; Resorlu, M.; Ergun, G.; Abdulmajeed, M.; Haliloglu, A.H.; Gogus, C.; Beduk, Y. Prognostic significance of hydronephrosis in bladder cancer treated by radical cystectomy. Urol. Int. 2009, 83, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.Y.; Wang, S.Z.; Chen, J.X.; Chen, L.W.; Xiao, J. The prognostic value of hydronephrosis in bladder cancer treated by radical cystectomy. Urologia 2011, 78, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martini, T.; Aziz, A.; Roghmann, F.; Rink, M.; Chun, F.K.; Fisch, M.; Trojan, L.; Hakenberg, O.W.; Zastrow, S.; Wirth, M.P.; et al. Prediction of Locally Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder Using Clinical Parameters before Radical Cystectomy—A Prospective Multicenter Study. Urol. Int. 2016, 96, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aglamis, E.; Toktas, G.; Unluer, E.; Tasdemir, C.; Ceylan, C. Prognostic factors in radical cystectomy affecting survival. Arch. Med. Sci. 2012, 8, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Zhan, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Fu, S.; Ding, M.; Luan, T.; Wei, H.; Yang, C. The Influence of Preoperative Hydronephrosis on the Prognosis after Radical Cystectomy among Patients with Different Pathological Stages of Bladder Cancer. Urol. Int. 2023, 107, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thotakura, R.; Anjum, F. Hydronephrosis and Hydroureter; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Gu, X.; Zuo, Z.; Tian, G.; Liu, J. Prognostic value of circulating tumor cells in patients with bladder cancer: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Msaouel, P.; Koutsilieris, M. Diagnostic value of circulating tumor cell detection in bladder and urothelial cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Fan, W.; Deng, Q.; Tang, S.; Wang, P.; Xu, P.; Wang, J.; Yu, M. The prognostic and diagnostic value of circulating tumor cells in bladder cancer and upper tract urothelial carcinoma: A meta-analysis of 30 published studies. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 59527–59538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillenwater, J.Y.; Westervelt, F.B., Jr.; Vaughan, E.D., Jr.; Howards, S.S. Renal function after release of chronic unilateral hydronephrosis in man. Kidney Int. 1975, 7, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wiesner, C.; Pfitzenmaier, J.; Faldum, A.; Gillitzer, R.; Melchior, S.W.; Thuroff, J.W. Lymph node metastases in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer are correlated with the number of transurethral resections and tumour upstaging at radical cystectomy. BJU Int. 2005, 95, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stimson, C.J.; Cookson, M.S.; Barocas, D.A.; Clark, P.E.; Humphrey, J.E.; Patel, S.G.; Smith, J.A., Jr.; Chang, S.S. Preoperative hydronephrosis predicts extravesical and node positive disease in patients undergoing cystectomy for bladder cancer. J. Urol. 2010, 183, 1732–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojadinovic, M.M.; Prelevic, R.I. External validation of existing nomograms predicting lymph node metastases in cystectomized patients. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 20, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuck, G.; da Cunha, I.W.; da Costa, W.H.; Pinto, C.A.L.; Sacomani, C.A.R.; da Fonseca, F.P.; Guimarães, G.C. Diagnosis of micrometastasis in muscle invasive bladder cancer through immunohistochemistry analysis: Is there indication for routine evaluation? Appl. Cancer Res. 2016, 36, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.T.; Lam, W.W.; Yu, M.Y.; Cheung, T.H.; Metreweli, C. Comparison of dynamic helical CT and dynamic MR imaging in the evaluation of pelvic lymph nodes in cervical carcinoma. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2000, 175, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Hussein, A.A.; Ma, Y.; Azabdaftari, G.; Ahmed, Y.; Wong, L.P.; Hu, Q.; Luo, W.; Cranwell, V.N.; Bunch, B.L.; et al. Accurate Quantification of Residual Cancer Cells in Pelvic Washing Reveals Association with Cancer Recurrence Following Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy. J. Urol. 2019, 201, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshabrawy, A.; Wang, H.; Dursun, F.; Kaushik, D.; Liss, M.; Svatek, R.S.; Mansour, A.M. Diffusion of robot-assisted radical cystectomy: Nationwide trends, predictors, and association with continent urinary diversion. Arab. J. Urol. 2022, 20, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| No Hydronephrosis | Hydronephrosis | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | %/SD | N | %/SD | ||
| Number of patients, % | 429 | 80.0% | 107 | 20.0% | |
| Mean age, SD | 66.2 | 9.7 | 66.9 | 11.1 | 0.52 |
| Gender (male to female) | 369:60 | 89:18 | 0.46 | ||
| Smoking history, % | 220 | 51.3% | 50 | 46.7% | 0.34 |
| Diabetes mellitus, % | 96 | 22.4% | 24 | 22.4% | 0.94 |
| Preoperative renal impairment, % | 32 | 7.5% | 28 | 26.2% | <0.001 |
| History of abdominal surgery, % | 10 | 2.3% | 3 | 2.8% | 0.549 |
| History of pelvic radiotherapy, % | 12 | 4.2% | 4 | 2.1% | 0.78 |
| ASA, % | 0.86 | ||||
| 1 | 96 | 22.4% | 26 | 24.3% | |
| 2 | 278 | 64.8% | 65 | 60.7% | |
| 3+ | 55 | 12.8% | 16 | 15.0% | |
| Neoadjuvant chemotherapy, % | 132 | 30.8% | 24 | 22.4% | 0.085 |
| Intracorporeal urinary reconstruction, % | 234 | 48.9% | 61 | 57.0% | 0.68 |
| Lymph node dissection performed, % | 421 | 98.1% | 107 | 100% | 0.16 |
| High grade histology, % | 310 | 72.3% | 72 | 67.3% | 0.58 |
| pT stage, % | 0.004 | ||||
| T0 | 22 | 5.1% | 3 | 2.8% | |
| Ta/is | 106 | 42.7% | 17 | 15.9% | |
| 1 | 79 | 18.4% | 11 | 10.3% | |
| 2 | 88 | 20.5% | 24 | 22.4% | |
| 3 | 101 | 23.5% | 39 | 36.4% | |
| 4 | 33 | 7.7% | 13 | 12.2% | |
| pN+, % | 76 | 17.7% | 26 | 24.3% | 0.114 |
| HR | 95% CI | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pathological upstaging | 1.699 | 1.096 | 2.631 | 0.018 |
| Nodal upstaging | 1.500 | 0.857 | 2.627 | 0.16 |
| Hospital stays above median | 0.940 | 0.614 | 1.44 | 0.78 |
| Blood loss above median | 1.371 | 0.896 | 2.096 | 0.15 |
| Console time above median | 1.033 | 0.676 | 1.579 | 0.88 |
| 30-days readmission | 2.692 | 1.702 | 4.256 | <0.001 |
| All grade complications | 1.401 | 0.896 | 2.191 | 0.14 |
| Severe complications (Clavien Dindo ≥ 3) | 2.095 | 1.242 | 3.532 | 0.006 |
| (a) Entire Cohort | ||||||||
| Disease-Free Survival | Overall Survival | |||||||
| Effect Size | 95% CI | p Value | Effect Size | 95% CI | p Value | |||
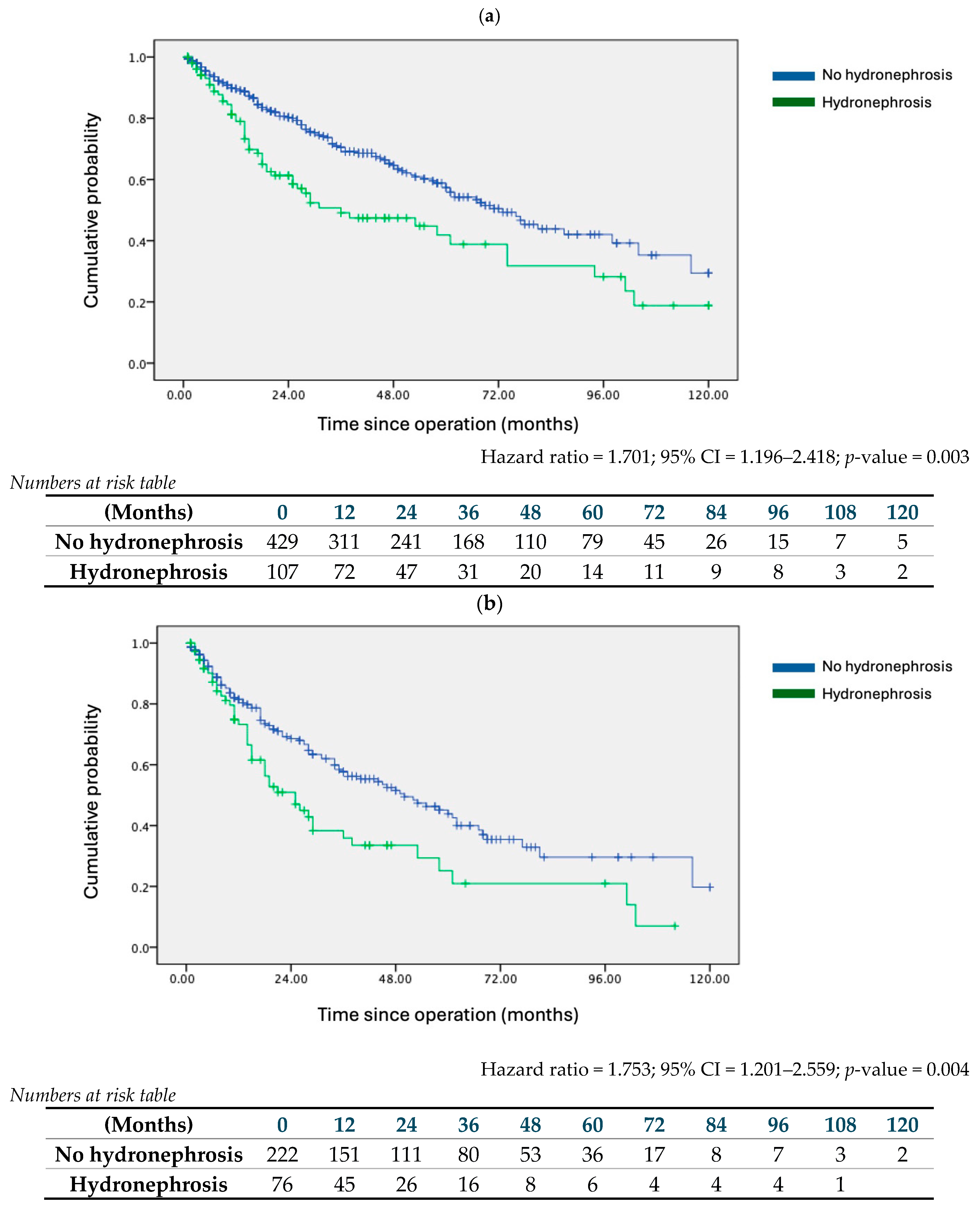
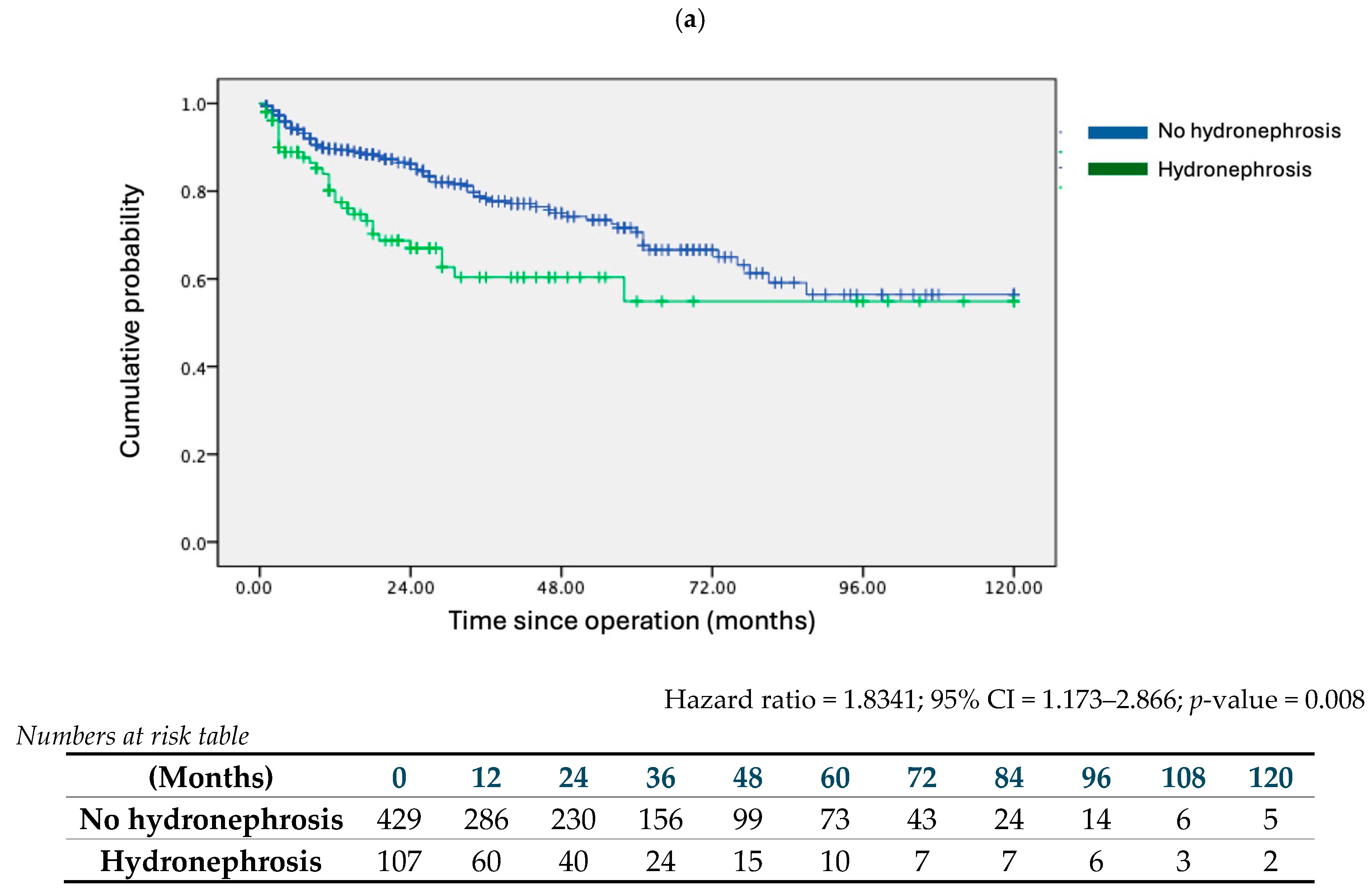
| Hydronephrosis | 1.701 | 1.196 | 2.418 | 0.003 | 1.834 | 1.173 | 2.866 | 0.008 |
| Clear surgical margin | 1.216 | 0.85 | 1.739 | 0.284 | 0.698 | 0.425 | 1.149 | 0.158 |
| Adjuvant therapy | 2.145 | 1.492 | 3.085 | <0.001 | 1.954 | 1.221 | 3.126 | 0.005 |
| pN+ status | 1.49 | 1.01 | 2.198 | 0.044 | 1.243 | 0.752 | 2.056 | 0.396 |
| High grade tumour | 1.757 | 1.061 | 2.912 | 0.029 | 2.419 | 1.197 | 4.885 | 0.014 |
| pT stage | 1.191 | 1.047 | 1.355 | 0.008 | 1.151 | 0.976 | 1.357 | 0.095 |
| (b) pT2+ Stage or above Subgroup | ||||||||
| Disease-Free Survival | Overall Survival | |||||||
| Effect Size | 95% CI | p Value | Effect Size | 95% CI | p Value | |||
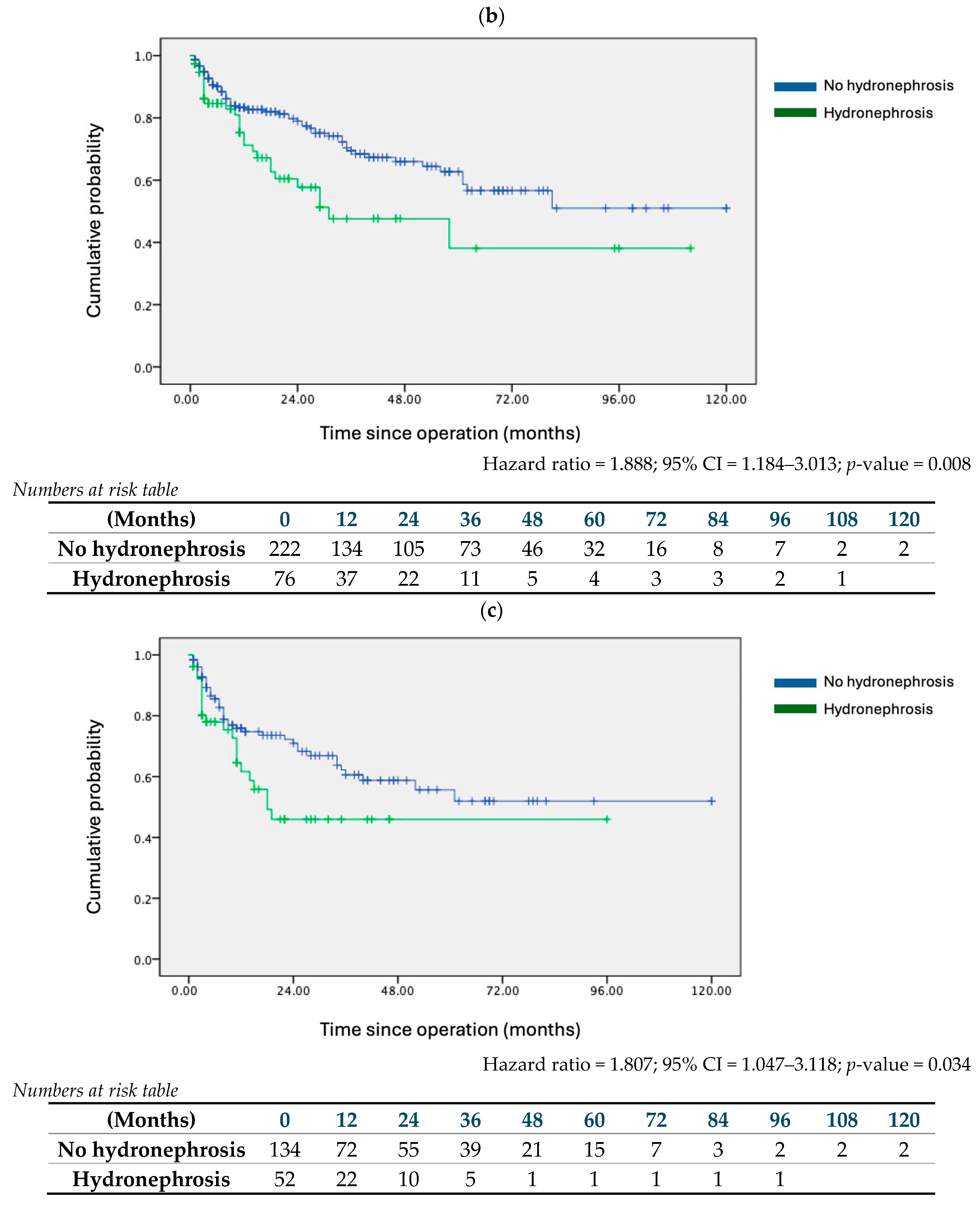
| Hydronephrosis | 1.753 | 1.201 | 2.559 | 0.004 | 1.888 | 1.184 | 3.013 | 0.008 |
| Clear surgical margin | 1.286 | 0.876 | 1.889 | 0.2 | 0.713 | 0.416 | 1.22 | 0.216 |
| Adjuvant therapy | 1.411 | 0.946 | 2.105 | 0.091 | 1.402 | 0.85 | 2.313 | 0.185 |
| pN+ status | 1.222 | 0.813 | 1.835 | 0.335 | 0.999 | 0.601 | 1.66 | 0.996 |
| High grade tumour | 0.554 | 0.278 | 1.104 | 0.093 | 0.626 | 0.27 | 1.454 | 0.276 |
| pT stage | pT2 as reference | pT2 as reference | ||||||
| pT3 | 1.586 | 1.014 | 2.483 | 0.044 | 2.054 | 1.18 | 3.577 | 0.011 |
| pT4 | 2.905 | 1.665 | 5.066 | <0.001 | 2.882 | 1.386 | 5.991 | 0.005 |
| (c) pT3+ Stage or above Subgroup | ||||||||
| Disease-Free Survival | Overall Survival | |||||||
| Effect Size | 95% CI | p value | Effect Size | 95% CI | p Value | |||
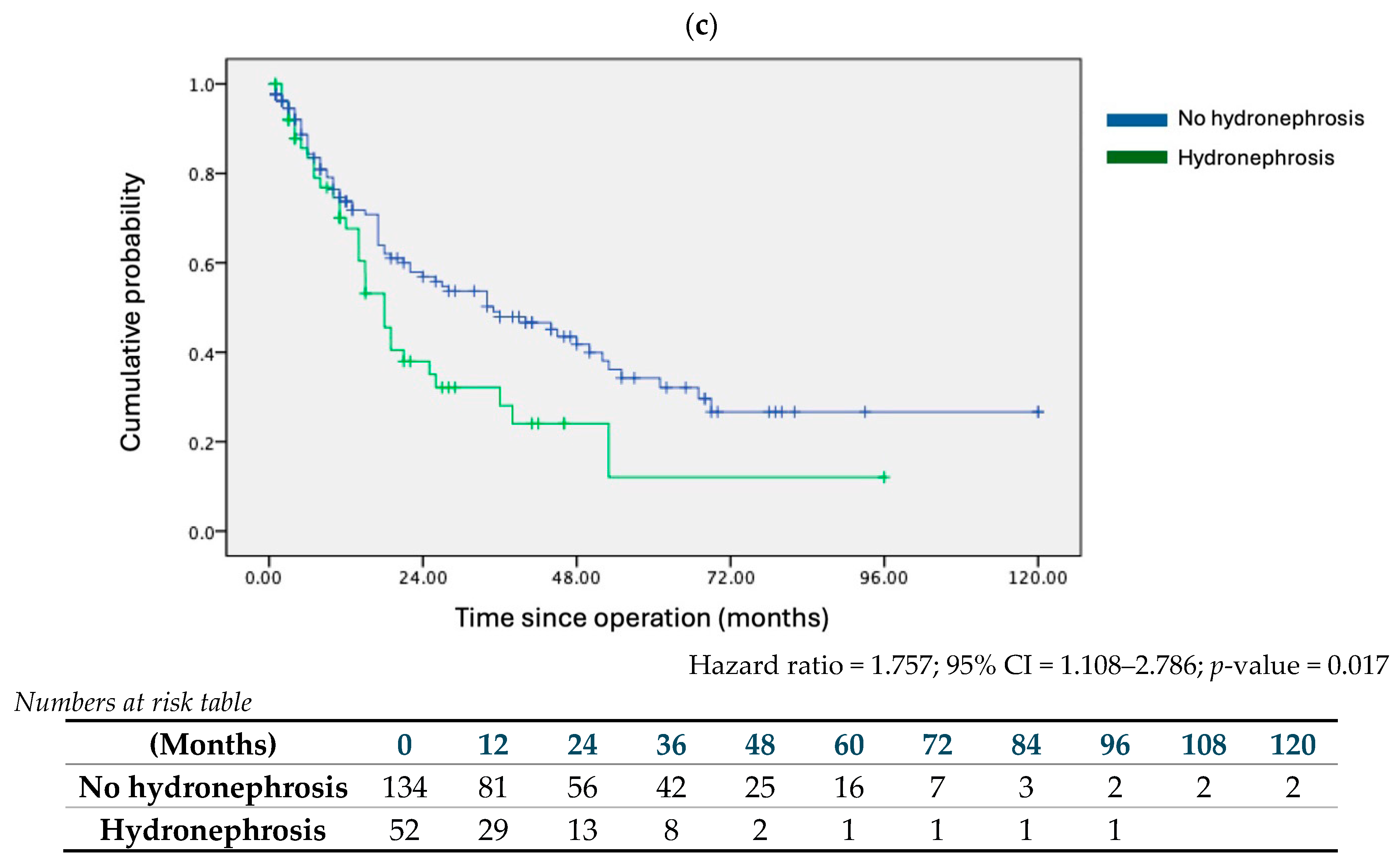
| Hydronephrosis | 1.757 | 1.108 | 2.786 | 0.017 | 1.807 | 1.047 | 3.118 | 0.034 |
| Clear surgical margin | 1.014 | 0.651 | 1.579 | 0.951 | 0.581 | 0.312 | 1.083 | 0.087 |
| Adjuvant therapy | 1.141 | 0.724 | 1.798 | 0.57 | 1.33 | 0.763 | 2.32 | 0.315 |
| pN+ status | 1.122 | 0.72 | 1.749 | 0.61 | 0.849 | 0.488 | 1.476 | 0.561 |
| High grade tumour | 0.68 | 0.269 | 1.72 | 0.415 | 0.69 | 0.246 | 1.935 | 0.481 |
| pT stage | pT3 as reference | pT3 as reference | ||||||
| pT4 | 1.784 | 1.132 | 2.812 | 0.013 | 1.305 | 0.71 | 2.402 | 0.392 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wong, C.H.-M.; Ko, I.C.-H.; Leung, D.K.-W.; Kang, S.H.; Kitamura, K.; Horie, S.; Muto, S.; Ohyama, C.; Hatakeyama, S.; Patel, M.; et al. Pre-Op Hydronephrosis Predicts Outcomes in Patients Receiving Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy. Cancers 2024, 16, 2826. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162826
Wong CH-M, Ko IC-H, Leung DK-W, Kang SH, Kitamura K, Horie S, Muto S, Ohyama C, Hatakeyama S, Patel M, et al. Pre-Op Hydronephrosis Predicts Outcomes in Patients Receiving Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy. Cancers. 2024; 16(16):2826. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162826
Chicago/Turabian StyleWong, Chris Ho-Ming, Ivan Ching-Ho Ko, David Ka-Wai Leung, Seok Ho Kang, Kousuke Kitamura, Shigeo Horie, Satoru Muto, Chikara Ohyama, Shingo Hatakeyama, Manish Patel, and et al. 2024. "Pre-Op Hydronephrosis Predicts Outcomes in Patients Receiving Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy" Cancers 16, no. 16: 2826. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162826
APA StyleWong, C. H.-M., Ko, I. C.-H., Leung, D. K.-W., Kang, S. H., Kitamura, K., Horie, S., Muto, S., Ohyama, C., Hatakeyama, S., Patel, M., Yang, C.-K., Kijvikai, K., Lee, J. Y., Chen, H.-G., Zhang, R.-Y., Lin, T.-X., Lee, L. S., Teoh, J. Y.-C., & Chan, E. (2024). Pre-Op Hydronephrosis Predicts Outcomes in Patients Receiving Robot-Assisted Radical Cystectomy. Cancers, 16(16), 2826. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162826









