Proton Pencil Beam Scanning Facilitates the Safe Treatment of Extended Radiation Targets for Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Report from the Proton Collaborative Group Registry
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Cohort and Eligibility
2.2. Toxicity Assessment and Follow-Up
2.3. Comparative Volumetric Arc Therapy (VMAT) Plan
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographics
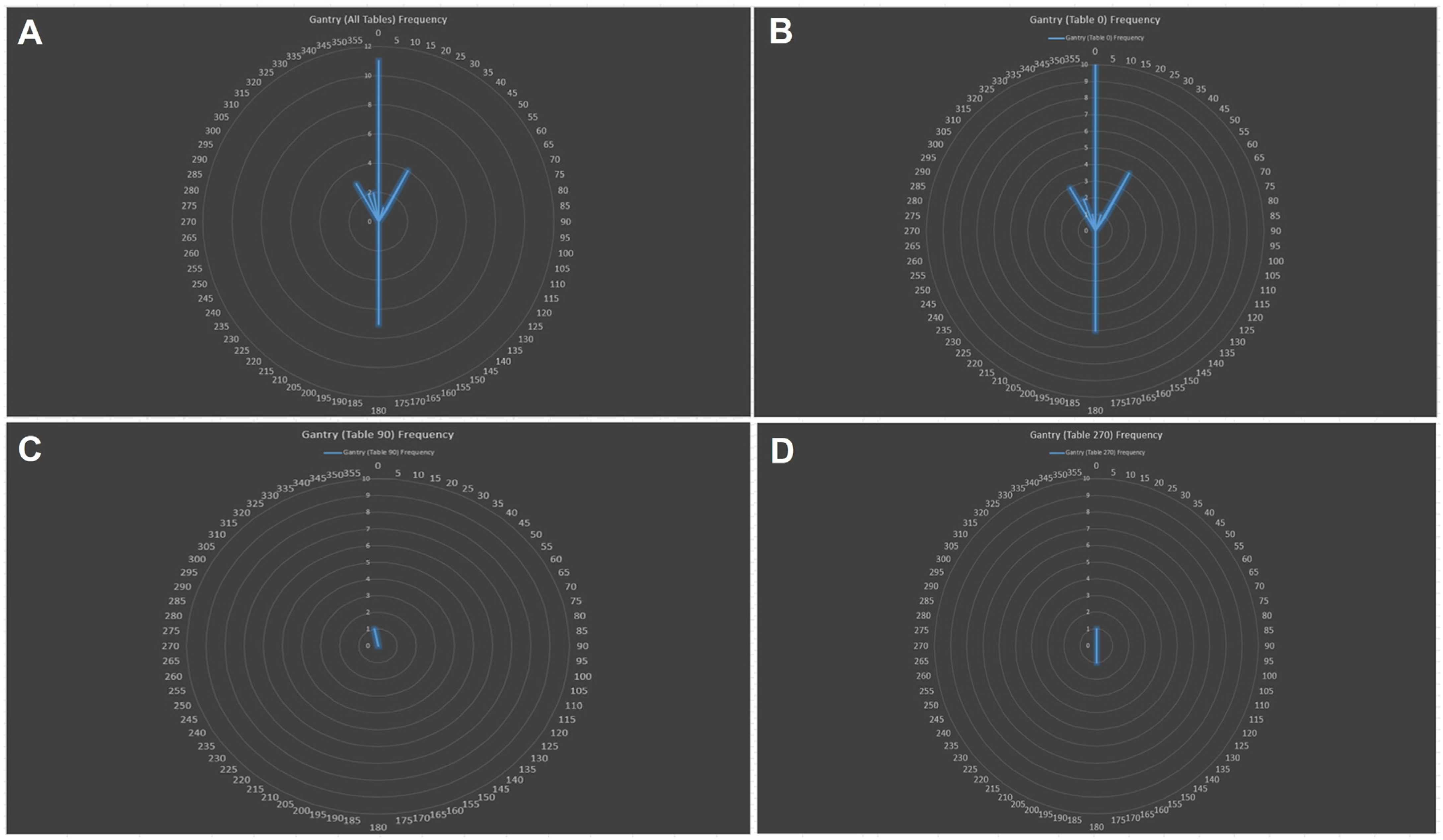
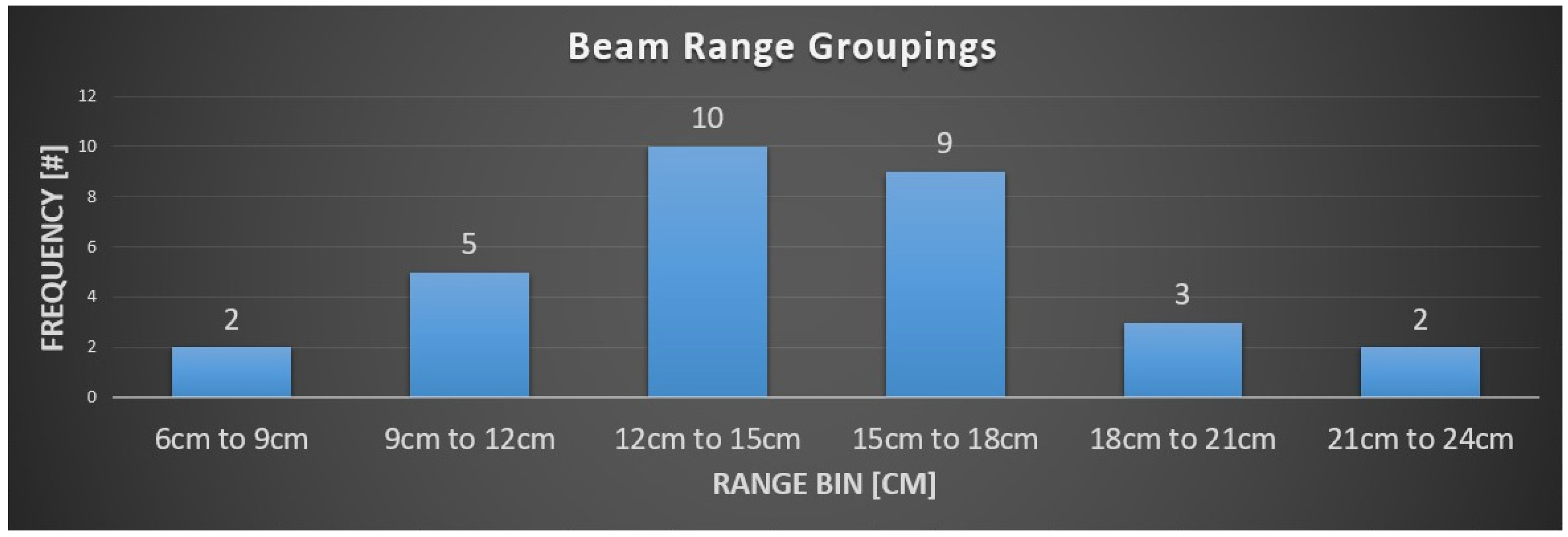
3.2. PBS Proton Therapy Characteristics
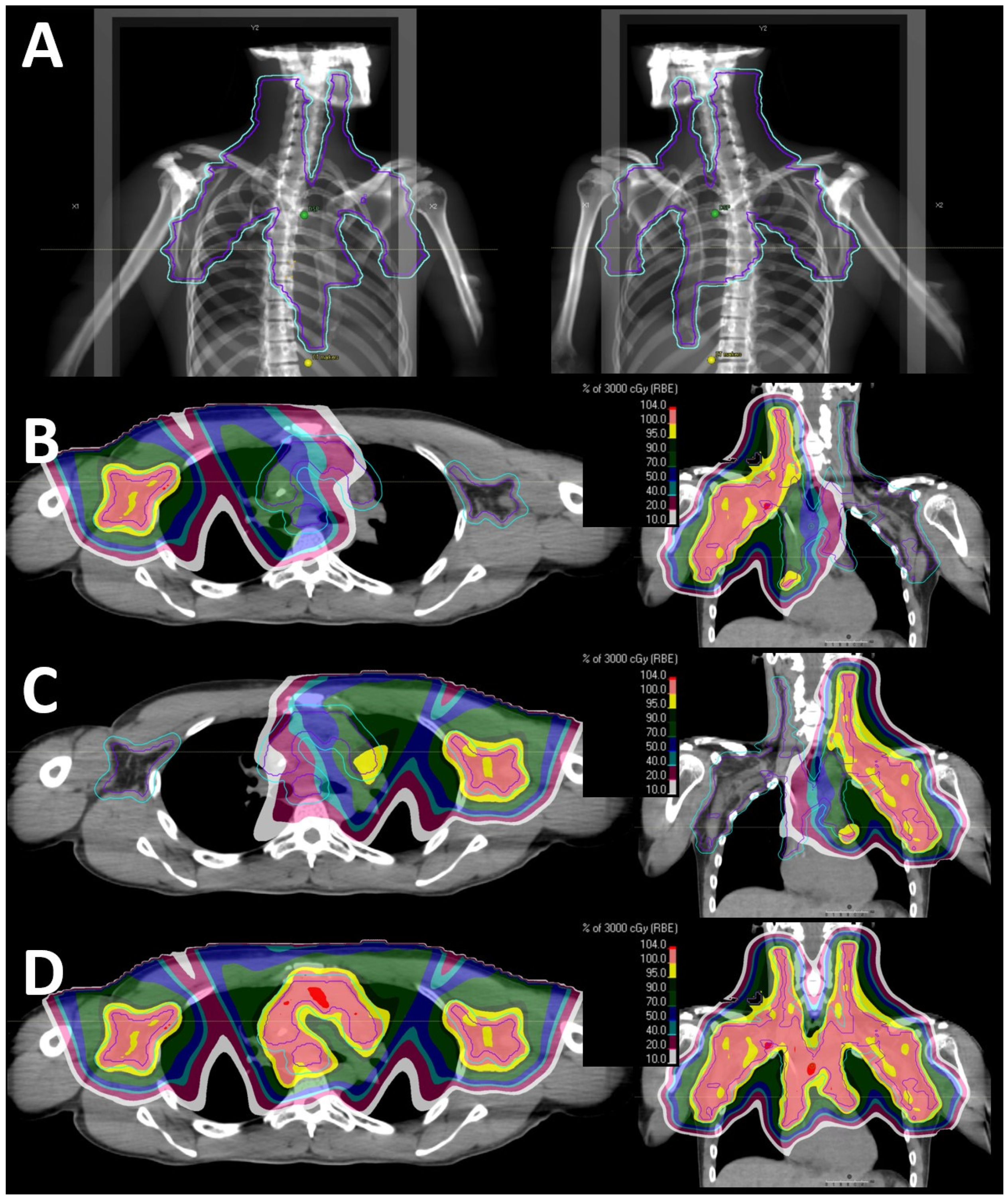
3.3. Dosimetry and Comparative Plans
3.4. Toxicity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Patel, C.G.; Peterson, J.; Aznar, M.; Tseng, Y.D.; Lester, S.; Pafundi, D.; Flampouri, S.; Mohindra, P.; Parikh, R.R.; Mailhot Vega, R.; et al. Systematic Review for Deep Inspiration Breath Hold in Proton Therapy for Mediastinal Lymphoma: A PTCOG Lymphoma Subcommittee Report and Recommendations. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 177, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, Y.D.; Cutter, D.J.; Plastaras, J.P.; Parikh, R.R.; Cahlon, O.; Chuong, M.D.; Dedeckova, K.; Khan, M.K.; Lin, S.Y.; McGee, L.A.; et al. Evidence-Based Review on the Use of Proton Therapy in Lymphoma From the Particle Therapy Cooperative Group (PTCOG) Lymphoma Subcommittee. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 99, 825–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ntentas, G.; Dedeckova, K.; Andrlik, M.; Aznar, M.C.; Shakir, R.; Ramroth, J.; Begum, R.; Kubeš, J.; Darby, S.C.; Mikhaeel, N.G.; et al. Proton Therapy in Supradiaphragmatic Lymphoma: Predicting Treatment-Related Mortality to Help Optimize Patient Selection. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 112, 913–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabaja, B.S.; Hoppe, B.S.; Plastaras, J.P.; Newhauser, W.; Rosolova, K.; Flampouri, S.; Mohan, R.; Mikhaeel, N.G.; Kirova, Y.; Specht, L.; et al. Proton Therapy for Adults with Mediastinal Lymphomas: The International Lymphoma Radiation Oncology Group Guidelines. Blood 2018, 132, 1635–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, M.P.; Girinsky, T.; Federico, M.; Reman, O.; Fortpied, C.; Gotti, M.; Casasnovas, O.; Brice, P.; van der Maazen, R.; Re, A.; et al. Early Positron Emission Tomography Response-Adapted Treatment in Stage I and II Hodgkin Lymphoma: Final Results of the Randomized EORTC/LYSA/FIL H10 Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1786–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radford, J.; Illidge, T.; Counsell, N.; Hancock, B.; Pettengell, R.; Johnson, P.; Wimperis, J.; Culligan, D.; Popova, B.; Smith, P.; et al. Results of a Trial of PET-Directed Therapy for Early-Stage Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1598–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoker, J.B.; Grant, J.; Zhu, X.R.; Pidikiti, R.; Mahajan, A.; Grosshans, D.R. Intensity Modulated Proton Therapy for Craniospinal Irradiation: Organ-at-Risk Exposure and a Low-Gradient Junctioning Technique. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 90, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Ding, X.; Kirk, M.; Liu, H.; Zhai, H.; Hill-Kayser, C.E.; Lustig, R.A.; Tochner, Z.; Both, S.; McDonough, J. Supine Craniospinal Irradiation Using a Proton Pencil Beam Scanning Technique without Match Line Changes for Field Junctions. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 90, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, Y.D.; Pankuch, M.; Mohindra, P.; McGee, L.; Rossi, C.; Flampouri, S.; Hajj, C.; Molitoris, J.K.; Chang, J.H.; Tsai, H.; et al. Selection of Mediastinal Lymphoma Patients for Proton Therapy within the Proton Collaborative Group Registry Concordance with the ILROG Guidelines. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 44, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Cancer Institute. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v5.0; US Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2017.
- Voong, K.R.; McSpadden, K.; Pinnix, C.C.; Shihadeh, F.; Reed, V.; Salehpour, M.R.; Arzu, I.; Wang, H.; Hodgson, D.; Garcia, J.; et al. Dosimetric Advantages of a “ Butterfly” Technique for Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy for Young Female Patients with Mediastinal Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, L.B.; Gospodarowicz, M.; Curtis, R.E.; Clarke, E.A.; Andersson, M.; Glimelius, B.; Joensuu, T.; Lynch, C.F.; Van Leeuwen, F.E.; Holowaty, E.; et al. Lung Cancer Following Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy for Hodgkin’s Disease. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2002, 94, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Nimwegen, F.A.; Schaapveld, M.; Cutter, D.J.; Janus, C.P.M.; Krol, A.D.G.; Hauptmann, M.; Kooijman, K.; Roesink, J.; Van Der Maazen, R.; Darby, S.C.; et al. Radiation Dose-Response Relationship for Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in Survivors of Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, A.M.; Dosoretz, A.P.; Mauch, P.M.; Chen, Y.H.; Fisher, D.C.; Lacasce, A.S.; Freedman, A.S.; Silver, B.; Ng, A.K. Predictive Factors for Radiation Pneumonitis in Hodgkin Lymphoma Patients Receiving Combined-Modality Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 83, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinnix, C.C.; Smith, G.L.; Milgrom, S.; Osborne, E.M.; Reddy, J.P.; Akhtari, M.; Reed, V.; Arzu, I.; Allen, P.K.; Wogan, C.F.; et al. Predictors of Radiation Pneumonitis in Patients Receiving Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy for Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 92, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, Y.D.; Hoppe, B.S.; Dedeckova, K.; Patel, C.G.; Hill-Kayser, C.E.; Miller, D.M.; Maity, A.; Mendenhall, N.P.; Mailhot Vega, R.B.; Yock, T.I.; et al. Risk of Pneumonitis and Outcomes After Mediastinal Proton Therapy for Relapsed/Refractory Lymphoma: A PTCOG and PCG Collaboration. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021, 109, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdes, G.; Scholey, J.; Nano, T.F.; Gennatas, E.D.; Mohindra, P.; Mohammed, N.; Zeng, J.; Kotecha, R.; Rosen, L.R.; Chang, J.; et al. Predicting the Effect of Proton Beam Therapy Technology on Pulmonary Toxicities for Patients with Locally Advanced Lung Cancer Enrolled in the Proton Collaborative Group Prospective Clinical Trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2024, 119, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, Y.D.; Maes, S.M.; Kicska, G.; Sponsellor, P.; Traneus, E.; Wong, T.; Stewart, R.D.; Saini, J. Comparative Photon and Proton Dosimetry for Patients with Mediastinal Lymphoma in the Era of Monte Carlo Treatment Planning and Variable Relative Biological Effectiveness. Radiat Oncol. 2019, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | All Patients (n = 12) | One Isocenter (n = 10) | >One Isocenter (n = 2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neck Involvement | 8 (66.7%) | 6 (60%) | 2 (100%) |
| Unilateral | 2 (16.7%) | 2 (20%) | 0 |
| Bilateral | 6 (50%) | 4 (40%) | 2 (100%) |
| Mediastinum Involvement | 12 (100%) | 10 (100%) | 2 (100%) |
| Upper | 1 (8.3%) | 1 (10%) | 0 |
| Middle | 3 (25%) | 3 (30%) | 0 |
| Lower | 8 (66.7%) | 6 (60%) | 2 (100%) |
| Axilla | 12 (100%) | 10 (100%) | 2 (100%) |
| Unilateral | 7 (58%) | 7 (70%) | 0 |
| Bilateral | 5 (42%) | 3 (30%) | 2 (100%) |
| Internal Mammary Lymph Node Involvement | 2 (16.7%) | 1 (10%) | 1 (50%) |
| Hila/Hilum Involvement | 1 (8.3%) | 1 (10%) | 0 |
| Largest CTV/ITV Dimension (Median, Range) | |||
| Left/right | 22.75 (15.9–38.7) | 21.6 (15.9–38.7) | 32.2 (31.4–33) |
| Superior/inferior | 22.2 (13.6–36.3) | 19.35 (13.6–29) | 34.05 (31.8–36.3) |
| PTV (Median, Range) | |||
| Volume (cc) | 1197.84 (257.44–1834.54) | 1162.12 (257.44–1834.54) | 1454.61 (1117.92–1791.3) |
| DVH Parameter (Median, Range) | Photon | Proton |
|---|---|---|
| Heart | ||
| Mean (Gy (RBE)) | 13.59 (2.77–24.88) | 9.03 (2.36–12.85) |
| V5 | 58.68% (9.62–94.53) | 43% (9.48–65.06) |
| V10 | 48.67% (6.07–85.02) | 35.19% (7.18–54.97) |
| V15 | 43.51% (4.31–75.38) | 29.50% (5.63–46.42) |
| V20 | 34.76% (2.94–66.46) | 23.33% (4.57–35.55) |
| V30 | 7.04% (0–46) | 6.06% (0–21.17) |
| Lung | ||
| Mean (Gy (RBE)) | 10.7 (6.56–18.57) | 7.55 (4.07–13.63) |
| V5 | 54.61% (35.96–91.95) | 41.25% (26.37–56.63) |
| V10 | 39.58% (25.33–64.2) | 30.42% (15.95–44.4) |
| V15 | 33.49% (18.45–54.43) | 21.48% (8.64–37.81) |
| V20 | 24.81% (4.00–47.47) | 15.11% (3.55–32.31) |
| V30 | 4.51% (0–28.07) | 2.43% (0–20.31) |
| Thyroid | ||
| Mean (Gy (RBE)) | 28.54 (1.59–32.21) | 26.42 (17–31.92) |
| V5 | 100% (0–100) | 99.10% (0–100) |
| V10 | 100% (0–100) | 94.24% (0–100) |
| V15 | 98.36% (0–100) | 90.39% (0–100) |
| V20 | 99.41% (0–123.03) | 83.4% (0–100) |
| V25 | 88.09% (0–100) | 71.35% (0–100) |
| V30 | 50.34% (0–98.48) | 41.43% (0–99.85) |
| Breast * | ||
| Mean (Gy (RBE)) | 3.47(1.49–9.68) | 3.15 (1.13–6.86) |
| V4 | 20.94% (10.67–47.12) | 23.41% (10.56–33.39) |
| V5 | 18.27% (9.38–45.15) | 21.97% (9.72–31.96) |
| V10 | 11.11% (4.3–36.89) | 16.04% (3.15–26.66) |
| V15 | 7.4% (1.81–27.85) | 5.11% (0.66–22.79) |
| V20 | 5.26% (0.02–22.4) | 2.88% (0.01–19) |
| V25 | 3.29% (0–16.81) | 1.4% (0–12.69) |
| V30 | 0.41% (0–7.31) | 0.43% (0–2.44) |
| ITV/CTV | ||
| Volume (cc) | 634.68 (131.7–1074.23) | 634.68 (131.7–1074.23) |
| Mean (Gy (RBE)) | 31.65 (21.74–46.52) | 31.26 (21.38–45.71) |
| Mean (as % of prescription) | 100% (100–103.5) | 102% (101.3–106.5) |
| D(98%) (as % of prescription) | 96.6% (94.4–100) | 100% (98.4–100.7) |
| D(99%) (as % of prescription) | 95.9% (93.3–99.7) | 99.2% (97–100.5) |
| D(99.9%) (as % of prescription) | 93.9% (87–98.8%) | 97.7% (89.5–100) |
| PTV | ||
| Volume (cc) | 1197.84 (257.44–2834.54) | 1197.84 (257.44–2834.54) |
| Mean (Gy (RBE)) | 31.31 (21.37–46.01) | 31.07 (21.14–45.54) |
| Mean (as % of prescription) | 99% (98.3–101.3) | 101% (100–104) |
| D(98%) (as % of prescription) | 91.1% (76.4–97.7) | 93.45% (82.5–98.9) |
| D(99%) (as % of prescription) | 88.3% (65.6–96.5) | 91.3% (76.5–97.8) |
| D(99.9%) (as % of prescription) | 75.77% (34.7–89.6) | 80.6% (56.8–95) |
| Heterogeneity Index | ||
| (D (2%) − D (98%))/D (50%) | 0.14 (0.07–0.32) | 0.11 (0.05–0.25) |
| Conformity Index ** | 1.44 (1.05–1.75) | 1.09 (1.01–1.43) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ebadi, M.; Pankuch, M.; Boyer, S.; Chang, J.; Stevens, C.; Hall, M.D.; Hasan, S.; Bates, J.E.; Flampouri, S.; Kole, A.J.; et al. Proton Pencil Beam Scanning Facilitates the Safe Treatment of Extended Radiation Targets for Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Report from the Proton Collaborative Group Registry. Cancers 2024, 16, 2736. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16152736
Ebadi M, Pankuch M, Boyer S, Chang J, Stevens C, Hall MD, Hasan S, Bates JE, Flampouri S, Kole AJ, et al. Proton Pencil Beam Scanning Facilitates the Safe Treatment of Extended Radiation Targets for Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Report from the Proton Collaborative Group Registry. Cancers. 2024; 16(15):2736. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16152736
Chicago/Turabian StyleEbadi, Maryam, Mark Pankuch, Sean Boyer, John Chang, Craig Stevens, Matthew D. Hall, Shaakir Hasan, James E. Bates, Stella Flampouri, Adam J. Kole, and et al. 2024. "Proton Pencil Beam Scanning Facilitates the Safe Treatment of Extended Radiation Targets for Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Report from the Proton Collaborative Group Registry" Cancers 16, no. 15: 2736. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16152736
APA StyleEbadi, M., Pankuch, M., Boyer, S., Chang, J., Stevens, C., Hall, M. D., Hasan, S., Bates, J. E., Flampouri, S., Kole, A. J., Mohindra, P., Rossi, C., Sanghvi, P., McGee, L., Rana, Z., & Tseng, Y. D. (2024). Proton Pencil Beam Scanning Facilitates the Safe Treatment of Extended Radiation Targets for Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Report from the Proton Collaborative Group Registry. Cancers, 16(15), 2736. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16152736






