Glycemic Burden and Clinical Outcomes of Early Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Curative Treatment
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Participants, and Variables
2.2. Glycemic Burden Assessment
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
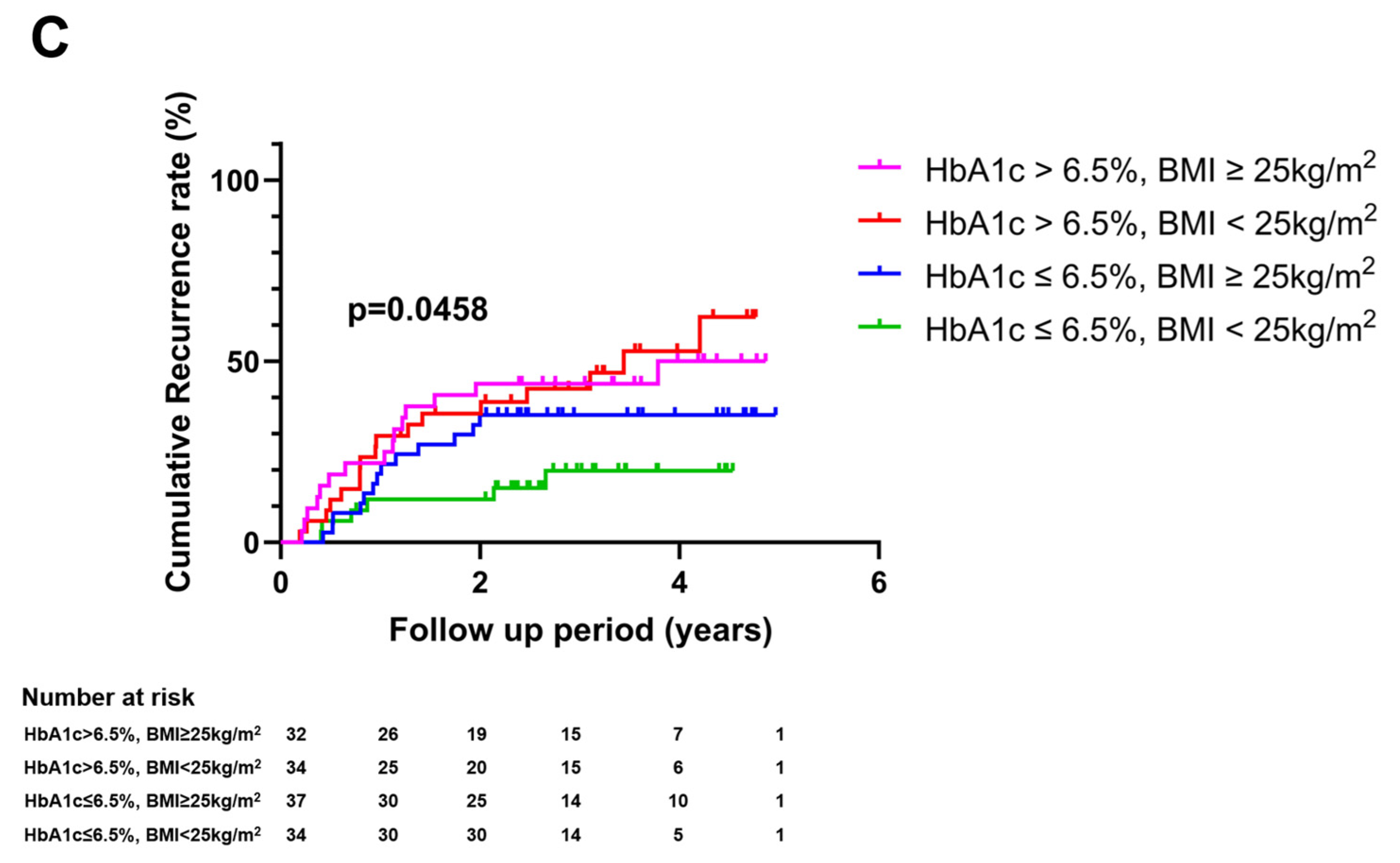
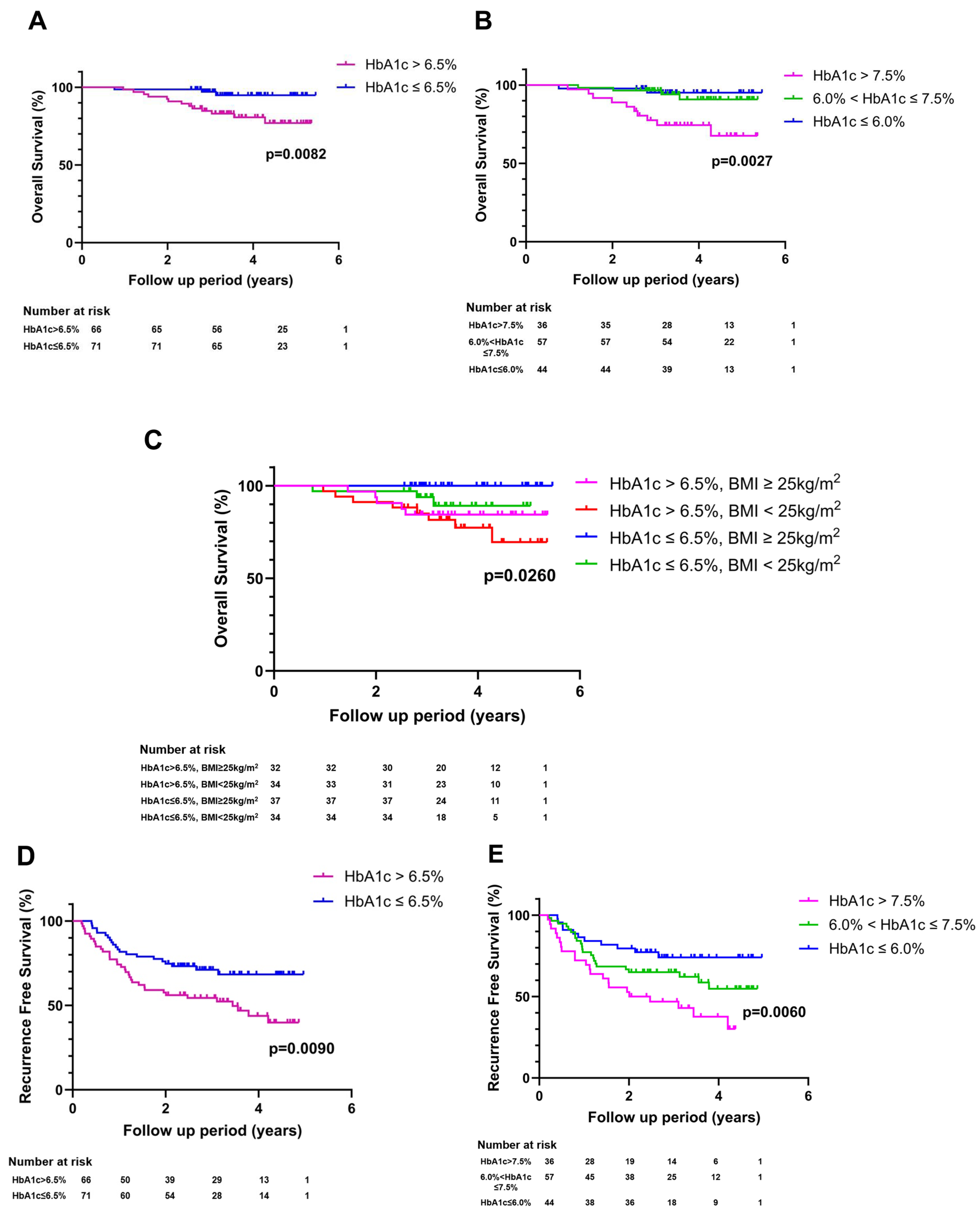
3.2. Impact of Glycemic Burden on HCC Recurrence
3.3. Impact of Glycemic Burden on HCC Mortality and Recurrence-Free Survival
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| RFA | Radiofrequency ablation |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| HbA1c | Hemoglobin A1c |
| BCLC | Barcelona clinic liver cancer |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| AFP | Alpha fetoprotein |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| aHR | Adjusted hazard ratio |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| IGF-1 | Insulin-like growth factor-1 |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| mTOR | Mammalian target of rapamycin |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MEK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omata, M.; Cheng, A.L.; Kokudo, N.; Kudo, M.; Lee, J.M.; Jia, J.; Tateishi, R.; Han, K.H.; Chawla, Y.K.; Shiina, S.; et al. Asia-Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: A 2017 update. Hepatol. Int. 2017, 11, 317–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reig, M.; Forner, A.; Rimola, J.; Ferrer-Fàbrega, J.; Burrel, M.; Garcia-Criado, Á.; Kelley, R.K.; Galle, P.R.; Mazzaferro, V.; Salem, R.; et al. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korean Liver Cancer Association (KLCA) and National Cancer Center (NCC) Korea. 2022 KLCA-NCC Korea practice guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2022, 28, 583–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kang, W.; Sinn, D.H.; Gwak, G.Y.; Paik, Y.H.; Choi, M.S.; Lee, J.H.; Koh, K.C.; Paik, S.W. Substantial risk of recurrence even after 5 recurrence-free years in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2020, 26, 516–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizian, P.; Jibara, G.; Shrager, B.; Schwartz, M.; Roayaie, S. Recurrence of hepatocellular cancer after resection: Patterns, treatments, and prognosis. Ann. Surg. 2015, 261, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranchart, H.; Chirica, M.; Sepulveda, A.; Massault, P.P.; Conti, F.; Scatton, O.; Soubrane, O. Long-term outcomes following aggressive management of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after upfront liver resection. World. J. Surg. 2012, 36, 2684–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lim, Y.S.; Yeon, J.E.; Song, T.J.; Yu, S.J.; Gwak, G.Y.; Kim, K.M.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.W.; et al. Sustained efficacy of adjuvant immunotherapy with cytokine-induced killer cells for hepatocellular carcinoma: An extended 5-year follow-up. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2019, 68, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero, A.; Toubert, C.; Bedoya, J.U.; Assenat, E.; Guiu, B.; Panaro, F.; Bardol, T.; Cassese, G. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence after liver surgery and thermal ablations: State of the art and future perspectives. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2024, 13, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaire, M.; Nault, J.C. Type 2 diabetes-associated hepatocellular carcinoma: A molecular profile. Clin. Liver. Dis. 2016, 8, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Targher, G. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: Spotlight on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, H.; Gao, P. Diabetes Mellitus is a Risk Factor for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection in China. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 6729–6734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.K.; Das, B.K.; Choudhary, S.; Gupta, D.; Patil, U.K. Diabetes and hepatocellular carcinoma: A pathophysiological link and pharmacological management. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 991–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Gong, G.; Ben, Q.; Qiu, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, L. Increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Int. J. Cancer. 2012, 130, 1639–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.S.; Va, P.; Bray, F.; Gao, S.; Gao, J.; Li, H.L.; Xiang, Y.B. The role of pre-existing diabetes mellitus on hepatocellular carcinoma occurrence and prognosis: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, W.P.; Wang, R.; Jin, A.; Yu, M.C.; Yuan, J.M. Diabetes mellitus and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: Findings from the Singapore Chinese Health Study. Br. J. Cancer. 2013, 108, 1182–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Targher, G.; Corey, K.E.; Byrne, C.D.; Roden, M. The complex link between NAFLD and type 2 diabetes mellitus—Mechanisms and treatments. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caturano, A.; Acierno, C.; Nevola, R.; Pafundi, P.C.; Galiero, R.; Rinaldi, L.; Salvatore, T.; Adinolfi, L.E.; Sasso, F.C. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: From Pathogenesis to Clinical Impact. Processes 2021, 9, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Hao, J. The effect of metformin usage on survival outcomes for hepatocellular carcinoma patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus after curative therapy. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1060768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatsuka, T.; Tateishi, R. Development and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with diabetes. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; Chai, Z.T.; Feng, J.K.; Zhu, H.M.; Zhang, F.; Hu, Y.R.; Zhong, C.Q.; Chen, Z.H.; Wang, K.; Shi, J.; et al. Association of type 2 diabetes mellitus with incidences of microvascular invasion and survival outcomes in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma after liver resection: A multicenter study. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 48, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, N.; Midorikawa, Y.; Higaki, T.; Nakayama, H.; Tsuji, S.; Matsuoka, S.; Ishihara, H.; Moriyama, M.; Takayama, T. Diabetes mellitus not an unfavorable factor on the prognosis of hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2018, 48, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Yokohama, K.; Ohama, H.; Tsuchimoto, Y.; Asai, A.; Fukunishi, S.; Kimura, F.; Higuchi, K.; Uchiyama, K. Diabetes mellitus does not influence results of hepatectomy in hepatocellular carcinoma: Case control study. Contemp. Oncol. 2020, 24, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevola, R.; Ruocco, R.; Criscuolo, L.; Villani, A.; Alfano, M.; Beccia, D.; Imbriani, S.; Claar, E.; Cozzolino, D.; Sasso, F.C.; et al. Predictors of early and late hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence. World. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 1243–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Z.F.; Xu, H.; Xu, Y.Y.; Wang, Z.N.; Zhao, T.T.; Song, Y.X.; Xu, H.M. Diabetes mellitus and the risk of gastric cancer: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 44881–44892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhong, L.; Xu, B.; Chen, M.; Huang, H. Diabetes mellitus and the risk of ovarian cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort and case-control studies. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e040137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrelli, F.; Ghidini, M.; Rausa, E.; Ghidini, A.; Cabiddu, M.; Borgonovo, K.; Ghilardi, M.; Parati, M.C.; Pietrantonio, F.; Sganzerla, P.; et al. Survival of Colorectal Cancer Patients With Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis. Can. J. Diabetes 2021, 45, 186–197.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Z.H.; Luther, Y.; Xiong, G.H.; Ni, Y.L.; Yun, F.; Chen, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Kuang, Y.M.; Zhu, Y.C. Association between diabetes mellitus and lung cancer: Meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 50, e13332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.J.; Shan, S.B.; Zhou, Y.H.; Zhong, L.Y. Diabetes mellitus and the risk of gastrointestinal cancer in women compared with men: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Serag, H.B.; Hampel, H.; Javadi, F. The association between diabetes and hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review of epidemiologic evidence. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneda, K.; Uenishi, T.; Takemura, S.; Shinkawa, H.; Urata, Y.; Sakae, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Kubo, S. The influence of postoperative glycemic control on recurrence after curative resection in diabetics with hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 105, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Y.; Lu, C.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Ye, S.; Wu, S.; Huang, J.; Bu, S.; Wang, F. IGF-1 contributes to liver cancer development in diabetes patients by promoting autophagy. Ann. Hepatol. 2022, 27, 100697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.S.; Scherer, P.E. Obesity, Diabetes, and Increased Cancer Progression. Diabetes Metab. J. 2021, 45, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; Kobara, H.; Oura, K.; Masaki, T. Mechanisms Underlying Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2021, 8, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abera, R.G.; Demesse, E.S.; Boko, W.D. Evaluation of glycemic control and related factors among outpatients with type 2 diabetes at Tikur Anbessa Specialized Hospital, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: A cross-sectional study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2022, 22, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caballero, A.E.; Nordstrom, B.L.; Liao, B.; Fan, L.; Zhang, N.; Fraeman, K.H.; Perez-Nieves, M. Individualized HbA1c target selection and achievement in the Multinational Observational Study Assessing Insulin Use (MOSA1c) type 2 diabetes study. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2021, 35, 108011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowker, S.L.; Majumdar, S.R.; Veugelers, P.; Johnson, J.A. Increased cancer-related mortality for patients with type 2 diabetes who use sulfonylureas or insulin. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.H.; Lin, J.W.; Wu, L.C.; Lai, M.S.; Chuang, L.M. Oral insulin secretagogues, insulin, and cancer risk in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E1170–E1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Singh, P.P.; Singh, A.G.; Murad, M.H.; Sanchez, W. Anti-diabetic medications and the risk of hepatocellular cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.Y.; Zhu, G.Q.; Liu, T.; Zheng, J.N.; Cheng, Z.; Zou, T.T.; Braddock, M.; Fu, S.W.; Zheng, M.H. Systematic Review with Network Meta-Analysis: Antidiabetic Medication and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variables | Low Glycemic Burden HbA1c ≤ 6.5% (N = 71) | High Glycemic Burden HbA1c > 6.5% (N = 66) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 62.0 (55.0–66.0) | 64.0 (56.7–69.2) | 0.18 |
| Male | 58 (81.7) | 56 (84.8) | 0.65 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 25.3 (22.6–27.9) | 24.9 (23.4–26.3) | 0.57 |
| Hypertension | 38 (53.5) | 34 (51.5) | 0.86 |
| Dyslipidemia | 35 (49.3) | 42 (63.6) | 0.12 |
| Etiological liver disease | 0.032 | ||
| HBV | 49 (69.0) | 31 (47.0) | |
| HCV | 3 (4.2) | 5 (7.6) | |
| Others | 19 (26.8) | 30 (45.4) | |
| Child–Pugh score | 0.46 | ||
| 5 | 48 (67.6) | 33 (50.0) | |
| 6–9 | 10 (14.1) | 10 (15.2) | |
| Total bilirubin, mg/dL | 0.7 (0.6–1.1) | 0.6 (0.5–1.0) | 0.23 |
| Albumin, g/dL | 4.5 (4.3–4.7) | 4.3 (4.0–4.7) | 0.19 |
| AST, IU/L | 30 (24–50) | 34 (27–47) | 0.22 |
| ALT, IU/L | 29 (20–41) | 32 (21–50) | 0.19 |
| Prothrombin Time, INR | 1.01 (0.97–1.06) | 1.04 (0.97–1.11) | 0.11 |
| Platelet count (×103/μL) | 164 (123–206) | 157 (108–219) | 0.71 |
| Tumor number | 0.35 | ||
| Solitary | 67 (94.4) | 59 (89.4) | |
| Multiple | 4 (5.6) | 7 (10.6) | |
| Tumor diameter, cm | 3.0 ± 2.5 | 3.8 ± 3.0 | 0.08 |
| Alpha fetoprotein, ng/mL | 5.50 (2.30–17.7) | 5.05 (2.95–35.6) | 0.52 |
| Treatment modality | 0.34 | ||
| Ablation | 23 (32.4) | 16 (24.2) | |
| Resection | 48 (67.6) | 50 (75.8) |
| Variables | Unadjusted HR (95%CI) | p-Value | * Adjusted HR (95%CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HbA1c ≤ 6.5% | Reference | Reference | ||
| HbA1c > 6.5% | 2.05 (1.18–3.69) | 0.013 | 2.66 (1.26–5.78) | 0.011 |
| HbA1c ≤ 6.0% | Reference | Reference | ||
| HbA1c 6.0–7.5% | 1.64 (0.79–3.65) | 0.20 | 2.00 (0.78–5.55) | 0.15 |
| HbA1c > 7.5% | 3.17 (1.53–7.03) | 0.002 | 6.05 (2.31–17.5) | 0.001 |
| Variables | Unadjusted HR (95%CI) | p-Value | * Adjusted HR (95%CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HbA1c ≤ 6.5% | Reference | Reference | ||
| HbA1c > 6.5% | 1.61 (0.92–2.89) | 0.10 | 2.33 (1.10–5.08) | 0.029 |
| HbA1c ≤ 6.0% | Reference | Reference | ||
| HbA1c 6.0–7.5% | 1.41 (0.67–3.14) | 0.37 | 2.36 (0.89–6.86) | 0.095 |
| HbA1c > 7.5% | 2.54 (1.22–5.64) | 0.015 | 6.22 (2.36–18.1) | 0.0004 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.J.; Choi, M.S.; Song, B.G.; Kang, W.S.; Gwak, G.Y.; Goh, M.J.; Paik, Y.H.; Lee, J.H.; Sinn, D.H. Glycemic Burden and Clinical Outcomes of Early Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Curative Treatment. Cancers 2024, 16, 2652. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16152652
Lee HJ, Choi MS, Song BG, Kang WS, Gwak GY, Goh MJ, Paik YH, Lee JH, Sinn DH. Glycemic Burden and Clinical Outcomes of Early Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Curative Treatment. Cancers. 2024; 16(15):2652. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16152652
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hyun Joo, Moon Seok Choi, Byeong Geun Song, Won Seok Kang, Geum Youn Gwak, Myung Ji Goh, Yong Han Paik, Joon Hyeok Lee, and Dong Hyun Sinn. 2024. "Glycemic Burden and Clinical Outcomes of Early Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Curative Treatment" Cancers 16, no. 15: 2652. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16152652
APA StyleLee, H. J., Choi, M. S., Song, B. G., Kang, W. S., Gwak, G. Y., Goh, M. J., Paik, Y. H., Lee, J. H., & Sinn, D. H. (2024). Glycemic Burden and Clinical Outcomes of Early Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Curative Treatment. Cancers, 16(15), 2652. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16152652






