Outcomes of Radical Hysterectomy for Early-Stage Cervical Carcinoma, with or without Prior Cervical Excision Procedure
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
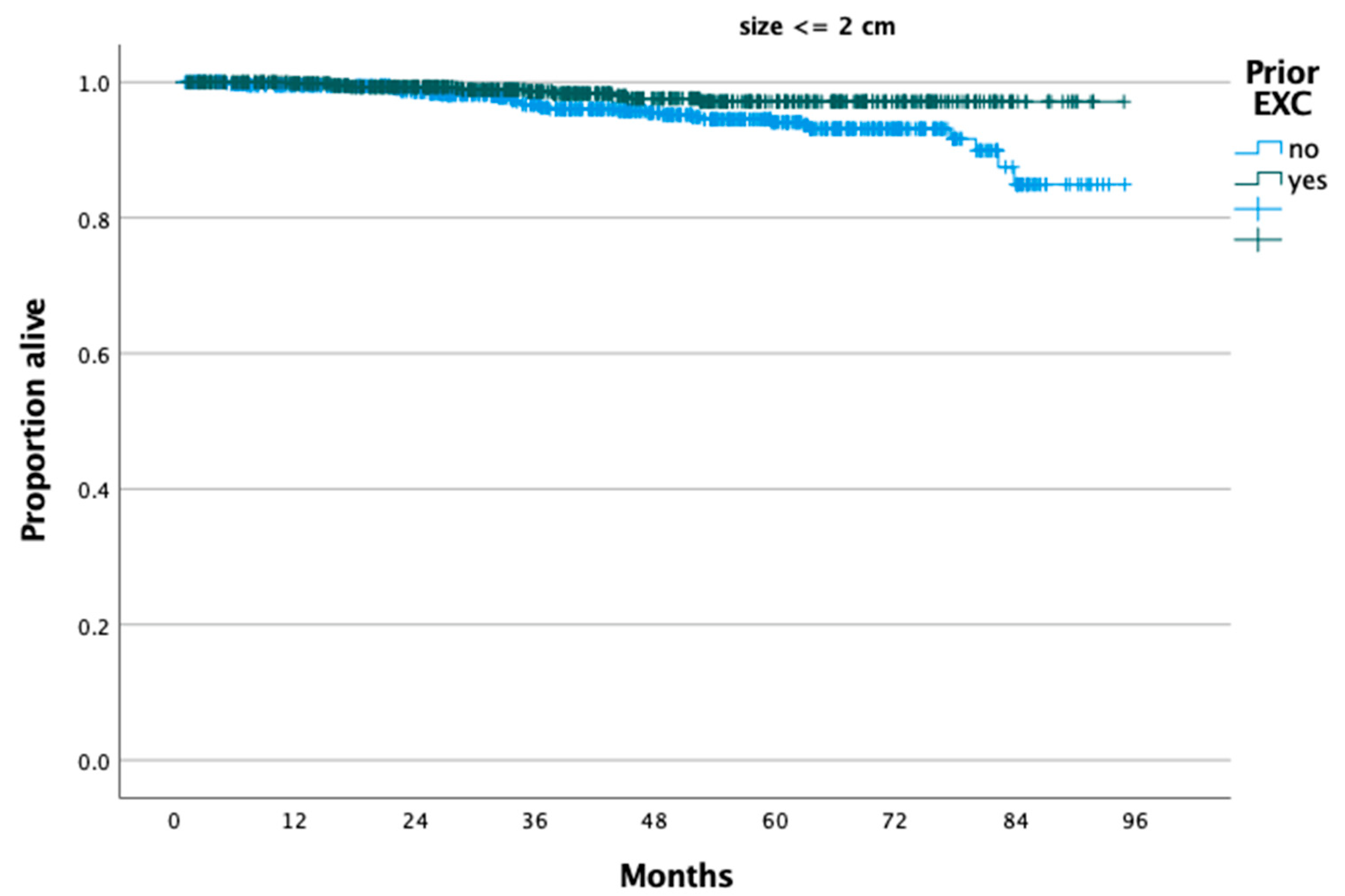
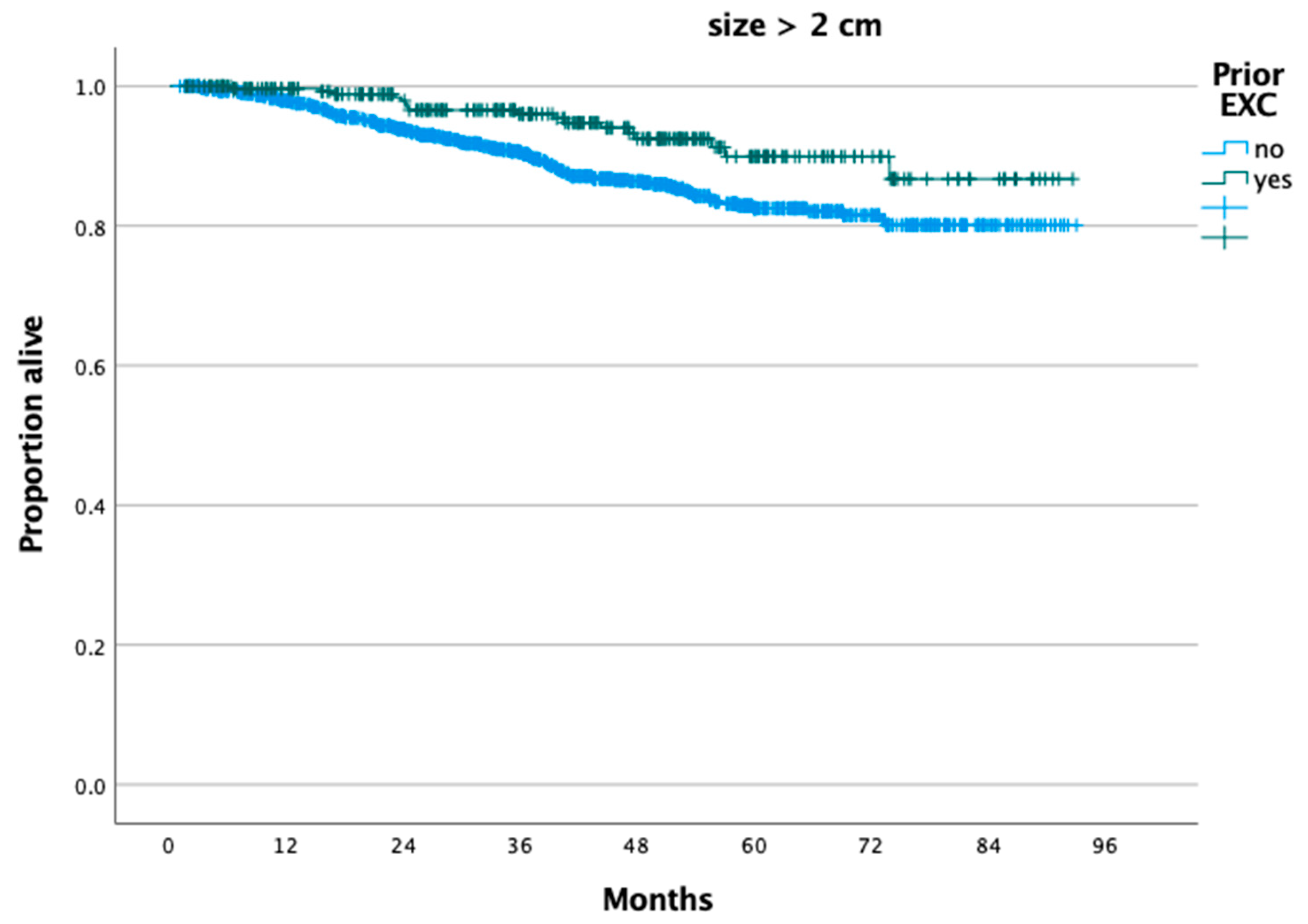
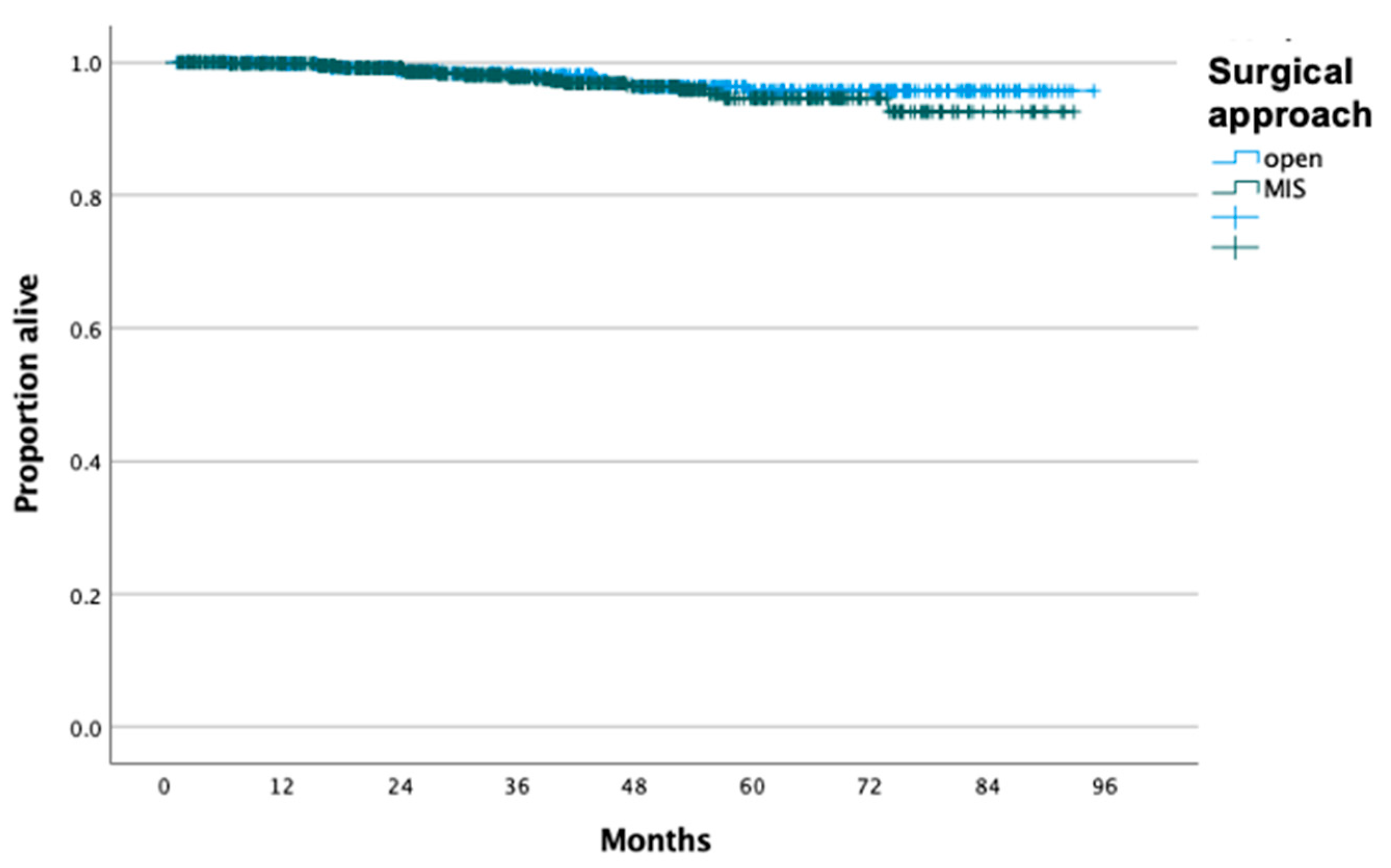
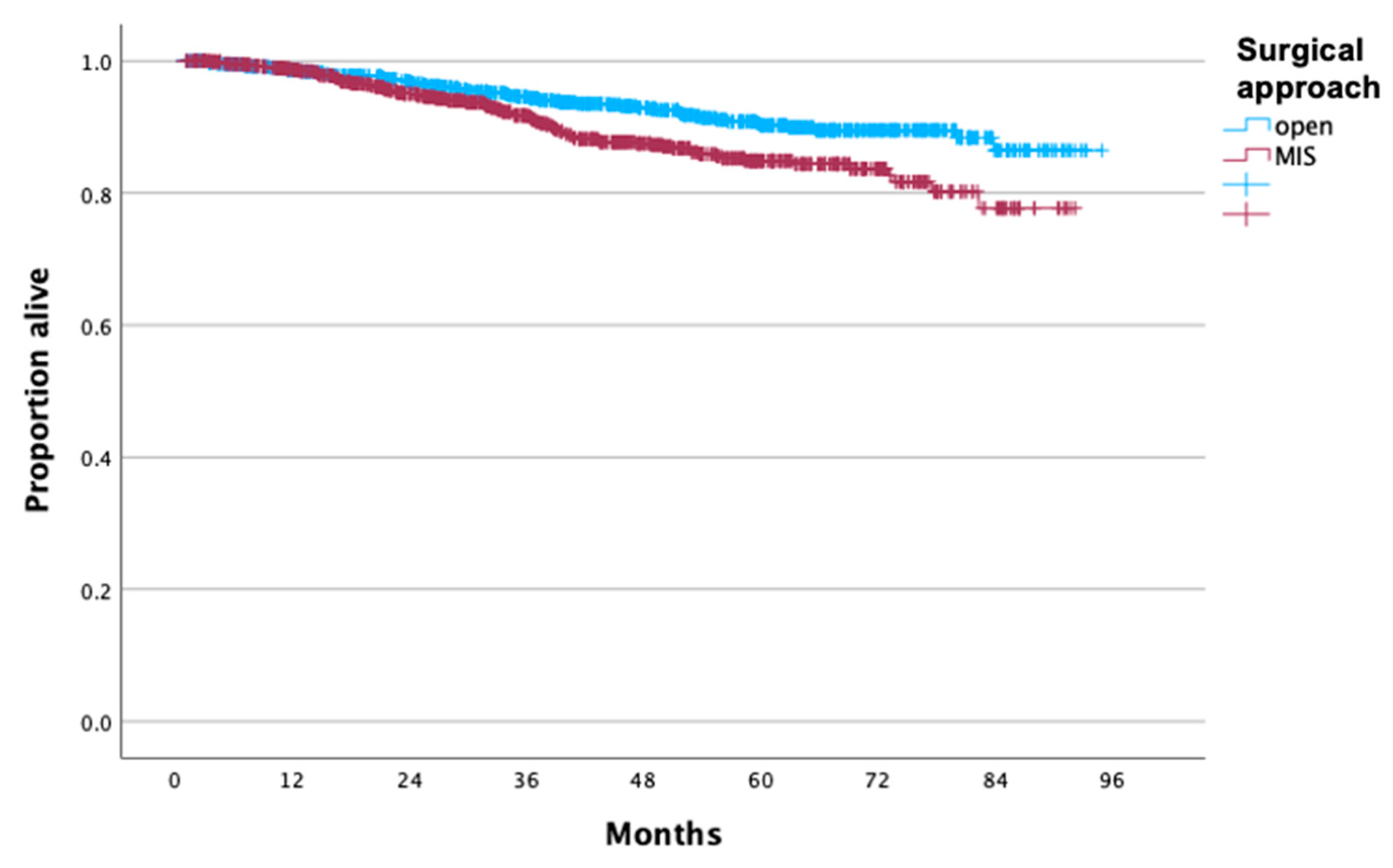
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arbyn, M.; Weiderpass, E.; Bruni, L.; de Sanjosé, S.; Saraiya, M.; Ferlay, J.; Bray, F. Estimates of incidence and mortality of cervical cancer in 2018: A worldwide analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e191–e203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, W.J.; Abu-Rustum, N.R.; Bean, S.; Bradley, K.; Campos, S.M.; Cho, K.R.; Chon, H.S.; Chu, C.; Clark, R.; Cohn, D.; et al. Cervical Cancer, Version 3.2019, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2019, 17, 64–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melamed, A.; Ramirez, P.T. Changing treatment landscape for early cervical cancer: Outcomes reported with minimally invasive surgery compared with an open approach. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 32, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, P.T.; Frumovitz, M.; Pareja, R.; Lopez, A.; Vieira, M.; Ribeiro, M.; Buda, A.; Yan, X.; Shuzhong, Y.; Chetty, N.; et al. Minimally Invasive versus Abdominal Radical Hysterectomy for Cervical Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1895–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitecki, R.; Ramirez, P.T.; Frumovitz, M.; Krause, K.J.; Tergas, A.I.; Wright, J.D.; Rauh-Hain, J.A.; Melamed, A. Survival After Minimally Invasive vs. Open Radical Hysterectomy for Early-Stage Cervical Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melamed, A.; Margul, D.J.; Chen, L.; Keating, N.L.; Del Carmen, M.G.; Yang, J.; Seagle, B.L.; Alexander, A.; Barber, E.L.; Rice, L.W.; et al. Survival after Minimally Invasive Radical Hysterectomy for Early-Stage Cervical Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1905–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greggi, S.; Casella, G.; Scala, F.; Falcone, F.; Visconti, S.; Scaffa, C. Surgical Management of Early Cervical Cancer: When Is Laparoscopic Appropriate? Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 22, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizzarri, N.; Pedone Anchora, L.; Kucukmetin, A.; Ratnavelu, N.; Korompelis, P.; Carbone, V.; Fedele, C.; Bruno, M.; Vizzielli, G.; Gallotta, V.; et al. Protective Role of Conization Before Radical Hysterectomy in Early-Stage Cervical Cancer: A Propensity-Score Matching Study. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casarin, J.; Bogani, G.; Papadia, A.; Ditto, A.; Pinelli, C.; Garzon, S.; Donadello, N.; Laganà, A.S.; Cromi, A.; Mueller, M.; et al. Preoperative Conization and Risk of Recurrence in Patients Undergoing Laparoscopic Radical Hysterectomy for Early Stage Cervical Cancer: A Multicenter Study. J. Minim. Invasive Gynecol. 2021, 28, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoit, L.; Koual, M.; Nguyen-Xuan, H.T.; Balaya, V.; Nos, C.; Montero-Macías, R.; Bats, A.S. Does a pre-operative conization improve disease-free survival in early-stage cervical cancer? Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2021, 303, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.I.; Cho, J.H.; Seol, A.; Kim, Y.I.; Lee, M.; Kim, H.S.; Chung, H.H.; Kim, J.W.; Park, N.H.; Song, Y.S. Comparison of survival outcomes between minimally invasive surgery and conventional open surgery for radical hysterectomy as primary treatment in patients with stage IB1-IIA2 cervical cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2019, 153, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chacon, E.; Manzour, N.; Zanagnolo, V.; Querleu, D.; Núñez-Córdoba, J.M.; Martin-Calvo, N.; Căpîlna, M.E.; Fagotti, A.; Kucukmetin, A.; Mom, C.; et al. SUCCOR cone study: Conization before radical hysterectomy. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2022, 32, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uppal, S.; Gehrig, P.A.; Peng, K.; Bixel, K.L.; Matsuo, K.; Vetter, M.H.; Davidson, B.A.; Cisa, M.P.; Lees, B.F.; Brunette, L.L.; et al. Recurrence Rates in Patients With Cervical Cancer Treated With Abdominal Versus Minimally Invasive Radical Hysterectomy: A Multi-Institutional Retrospective Review Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1030–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.I.; Nam, S.H.; Hwangbo, S.; Kim, Y.; Cho, H.W.; Suh, D.H.; Song, J.Y.; Kim, J.W.; Choi, C.H.; Kim, D.Y.; et al. Conization before radical hysterectomy in patients with early-stage cervical cancer: A Korean multicenter study (COBRA-R). Gynecol. Oncol. 2023, 173, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, J.; Li, C.; Hua, K. Association of preoperative conization with recurrences after laparoscopic radical hysterectomy for FIGO 2018 stage IB1 cervical cancer. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2023, 307, 1901–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Gong, X.; Li, P.; Ouyang, X.; Chang, X.; Tang, J. Preoperative Conization May Have a Positive Impact on Survival in Early-Stage Cervical Cancer: A Propensity-Matched Study. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2021, 44, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klapdor, R.; Hertel, H.; Delebinski, L.; Hillemanns, P. Association of preoperative cone biopsy with recurrences after radical hysterectomy. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2022, 305, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gennari, P.; Tchaikovski, S.; Mészáros, J.; Gerken, M.; Klinkhammer-Schalke, M.; Toth, G.; Ortmann, O.; Eggemann, H.; Ignatov, A. Protective effect of preoperative conization in patients undergoing surgical treatment for early-stage cervical cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2022, 166, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, A.; Chen, H. Effect of preoperative cervical conization before hysterectomy on survival and recurrence of patients with cervical cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gynecol. Oncol. 2023, 174, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samlal, R.A.; van der Velden, J.; Schilthuis, M.S.; Ten Kate, F.J.; Hart, A.A.; Lammes, F.B. Influence of diagnostic conization on surgical morbidity and survival in patients undergoing radical hysterectomy for stage IB and IIA cervical carcinoma. Eur. J. Gynaecol. Oncol. 1997, 18, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lerro, C.C.; Robbins, A.S.; Phillips, J.L.; Stewart, A.K. Comparison of cases captured in the national cancer data base with those in population-based central cancer registries. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20, 1759–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoegl, J.; Viveros-Carreño, D.; Palacios, T.; Gallego-Ardila, A.; Rauh-Hain, J.A.; Estrada, E.E.; Noll, F.; Krause, K.; Baiocchi, G.; Minig, L.; et al. Peritoneal carcinomatosis after minimally invasive surgery versus open radical hysterectomy: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2022, 32, 1497–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.L.; Li, R.Z.; Feng, B.J.; Lu, Y.H.; Wang, L.F.; Wang, Z.Y.; Pei, K.G.; Sun, L.F.; Li, R. Survival after minimally invasive radical hysterectomy with protective colpotomy for early-stage cervical cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2024, 50, 108240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.Z.; Sun, L.F.; Li, R.; Wang, H.J. Survival after minimally invasive radical hysterectomy without using uterine manipulator for early-stage cervical cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2023, 130, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubrey, C.; Pond, G.R.; Helpman, L.; Vicus, D.; Elit, L.; Plante, M.; Lau, S.; Kwon, J.S.; Altman, A.D.; Willows, K.; et al. Oncologic Outcomes of Surgically Treated Cervical Cancer with No Residual Disease on Hysterectomy Specimen: A 4C (Canadian Cervical Cancer Collaborative) Working Group Study. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 1977–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.S.; Min, J.S.; Song, K.H.; Choi, C.H.; Kim, T.J.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, B.G.; Lee, Y.Y. The Role of Conization before Radical Hysterectomy in Cervical Cancer including High Risk Factors of Recurrence: Propensity Score Matching. Cancers 2022, 14, 3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sert, B.M.; Kristensen, G.B.; Kleppe, A.; Dørum, A. Long-term oncological outcomes and recurrence patterns in early-stage cervical cancer treated with minimally invasive versus abdominal radical hysterectomy: The Norwegian Radium Hospital experience. Gynecol. Oncol. 2021, 162, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, P.; Frumovitz, M.; Pareja, R.; Isla, D.; Robledo, K.; Asher, R.; Gebski, V.; Behan, V.; Lopez, A.; Ribeiro, R.; et al. Open vs. Minimally Invasive Radical Hysterectomy in Early Cervical Cancer: LACC Trial Final Analysis (LBA 10). Gynecol. Oncol. 2022; 166, (Suppl. S1), S53–S54. [Google Scholar]
- Plante, M.; Kwon, J.S.; Ferguson, S.; Samouëlian, V.; Ferron, G.; Maulard, A.; de Kroon, C.; Van Driel, W.; Tidy, J.; Williamson, K.; et al. Simple versus Radical Hysterectomy in Women with Low-Risk Cervical Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahner, S.; Trillsch, F.; Kwon, J.; Ferguson, S.E.; Bessette, P.; Ferron, G.; Maulard, A.; De Kroon, C.D.; Van Driel, W.J.; Tidy, J.; et al. 738 Surgical approach, preoperative LEEP/cone biopsy and patterns of recurrence and death in low-risk cervical cancer—analysis of the international CCTG CX.5/SHAPE phase III trial. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2024, 34, A1. [Google Scholar]
- Nasioudis, D.; Ramirez, P.T. Is prior conization the way forward to determine surgical approach? The answer is not so simple! Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2022, 32, 125–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falconer, H.; Palsdottir, K.; Stalberg, K.; Dahm-Kähler, P.; Ottander, U.; Lundin, E.S.; Wijk, L.; Kimmig, R.; Jensen, P.T.; Zahl Eriksson, A.G.; et al. Robot-assisted approach to cervical cancer (RACC): An international multi-center, open-label randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2019, 29, 1072–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bixel, K.L.; Leitao, M.M.; Chase, D.M.; Quick, A.; Lim, P.C.; Eskander, R.N.; Gotlieb, W.H.; LoCoco, S.; Martino, M.A.; McCormick, C.; et al. ROCC/GOG-3043: A randomized non-inferiority trial of robotic versus open radical hysterectomy for early-stage cervical cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, TPS5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No Prior EXC | Prior EXC | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 0.013 | ||
| ≤50 | 1356 (68.2%) | 848 (72.4%) | |
| >50 | 632 (31.8%) | 323 (27.6%) | |
| Race | 0.20 | ||
| White | 1611 (81%) | 969 (82.7%) | |
| Black | 209 (10.5%) | 100 (8.5%) | |
| Other/Unknown | 168 (8.5%) | 102 (8.7%) | |
| Comorbidities | 0.064 | ||
| No | 1726 (86.8%) | 1043 (89.1%) | |
| Yes | 262 (13.2%) | 128 (10.9%) | |
| Insurance | 0.001 | ||
| Private | 1160 (58.4%) | 768 (65.6%) | |
| Government | 656 (33%) | 327 (27.9%) | |
| Uninsured/Unknown | 172 (8.6%) | 76 (6.5%) | |
| Mode of surgery | <0.001 | ||
| Open | 931 (46.8%) | 462 (39.5%) | |
| MIS | 1057 (53.2%) | 709 (60.5%) | |
| Tumor size | <0.001 | ||
| ≤2 cm | 747 (37.6%) | 703 (60%) | |
| >2 cm | 1114 (56%) | 401 (25.7%) | |
| Unknown | 127 (6.4%) | 167 (14.3%) | |
| Radiotherapy | <0.001 | ||
| Yes | 552 (27.8%) | 181 (15.5%) | |
| No | 1420 (71.4%) | 980 (83.7%) | |
| Unknown | 16 (0.8%) | 10 (0.8%) | |
| Histology | 0.047 | ||
| Squamous | 1164 (58.6%) | 688 (58.8%) | |
| Adenosquamous | 121 (6.1%) | 48 (4.1%) | |
| Adenocarcinoma | 703 (35.4%) | 435 (37.1%) | |
| LVSI | 0.014 | ||
| No | 1129 (56.8%) | 723 (61.7%) | |
| Yes | 693 (34.9%) | 350 (29.9%) | |
| Unknown | 166 (8.3%) | 98 (8.4%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nasioudis, D.; Labban, N.; Gysler, S.; Ko, E.M.; Giuntoli, R.L., II; Kim, S.H.; Latif, N.A. Outcomes of Radical Hysterectomy for Early-Stage Cervical Carcinoma, with or without Prior Cervical Excision Procedure. Cancers 2024, 16, 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16112051
Nasioudis D, Labban N, Gysler S, Ko EM, Giuntoli RL II, Kim SH, Latif NA. Outcomes of Radical Hysterectomy for Early-Stage Cervical Carcinoma, with or without Prior Cervical Excision Procedure. Cancers. 2024; 16(11):2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16112051
Chicago/Turabian StyleNasioudis, Dimitrios, Nayla Labban, Stefan Gysler, Emily M. Ko, Robert L. Giuntoli, II, Sarah H. Kim, and Nawar A. Latif. 2024. "Outcomes of Radical Hysterectomy for Early-Stage Cervical Carcinoma, with or without Prior Cervical Excision Procedure" Cancers 16, no. 11: 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16112051
APA StyleNasioudis, D., Labban, N., Gysler, S., Ko, E. M., Giuntoli, R. L., II, Kim, S. H., & Latif, N. A. (2024). Outcomes of Radical Hysterectomy for Early-Stage Cervical Carcinoma, with or without Prior Cervical Excision Procedure. Cancers, 16(11), 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16112051





