Lymphovascular Invasion at the Time of Radical Prostatectomy Adversely Impacts Oncological Outcomes
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Population
2.2. Selection Criteria
2.3. Staging and Follow-Up Data Collection
2.4. Surgical Procedure
2.5. Tissue Processing
2.6. Outcomes
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
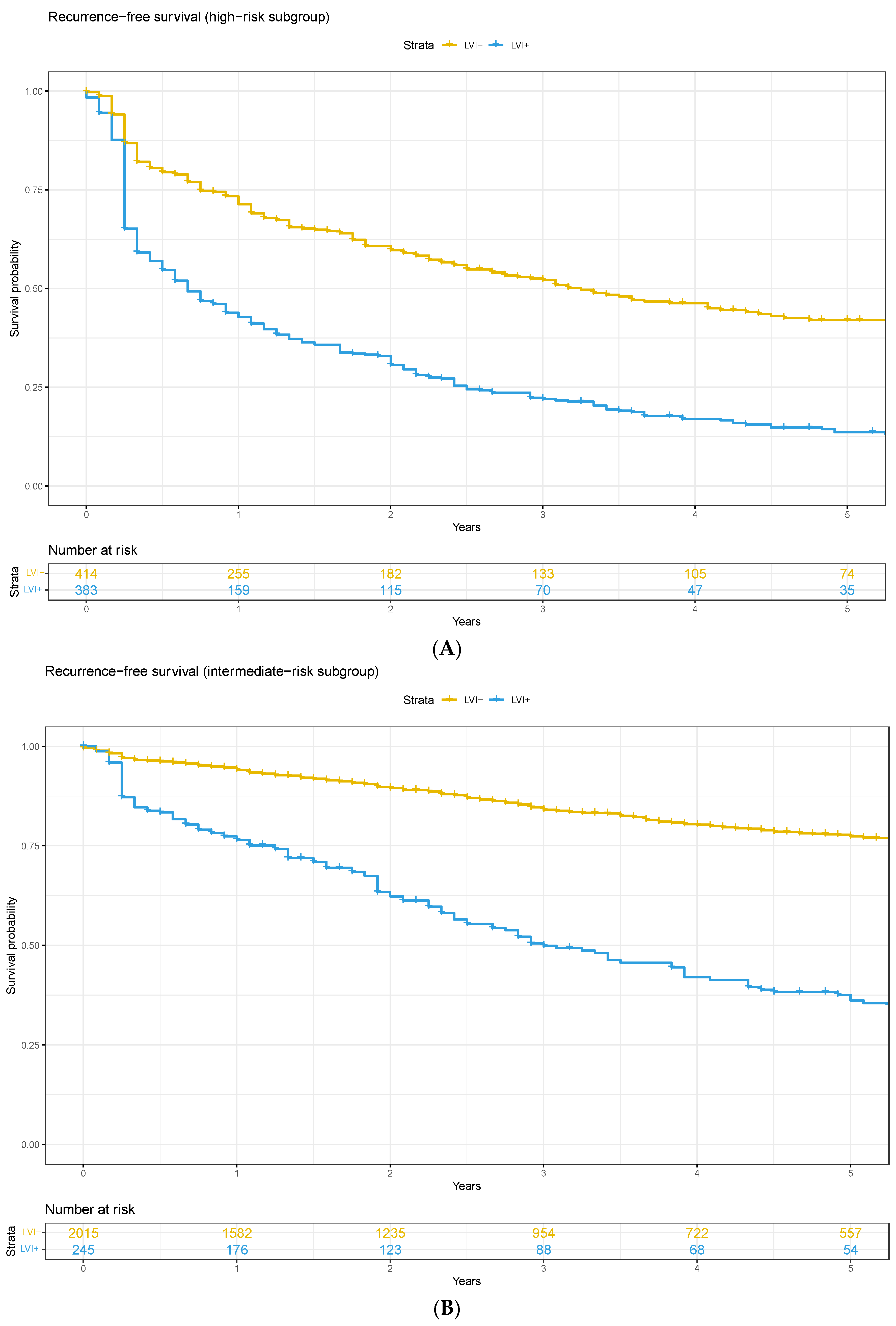
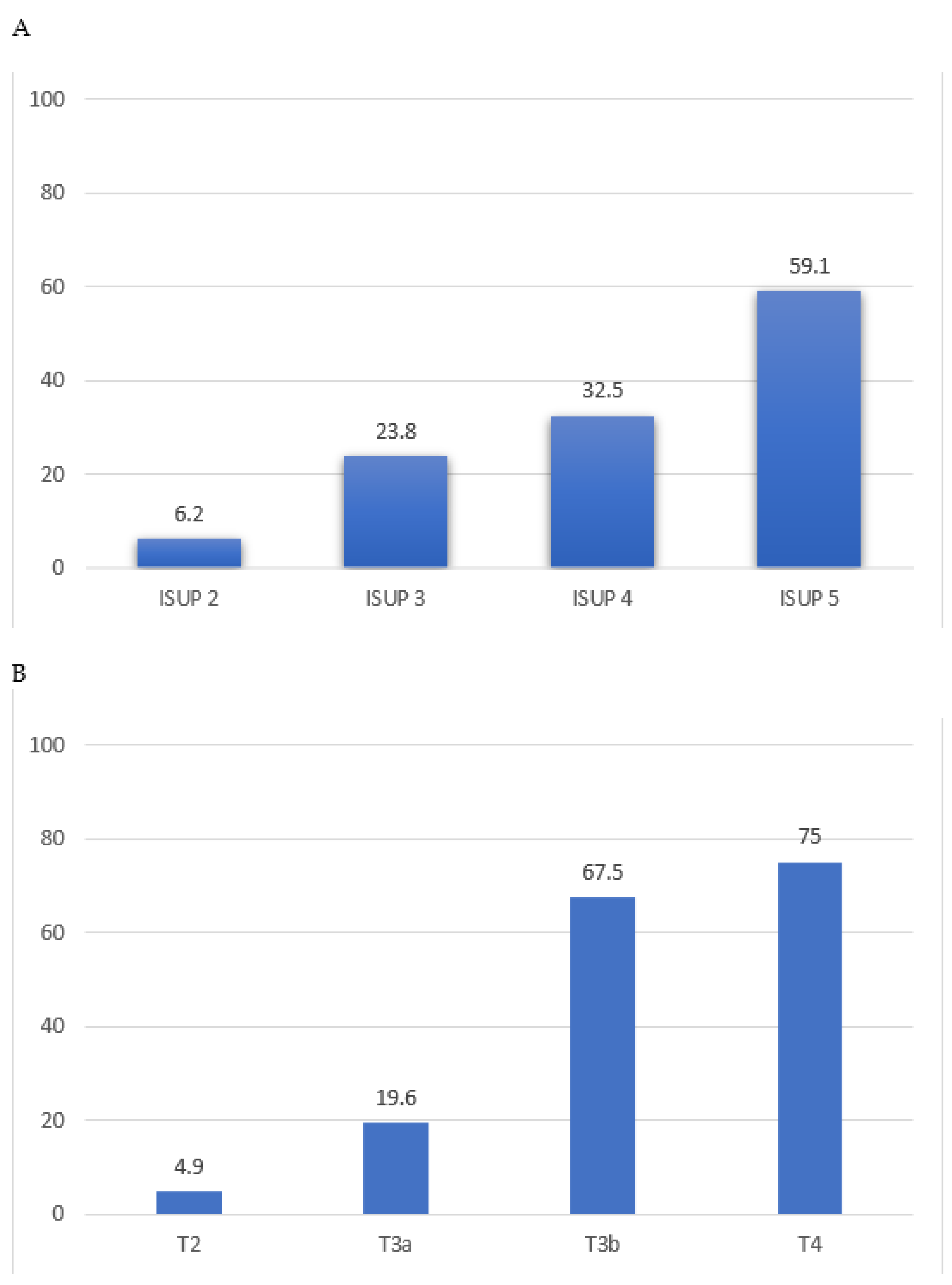
3.1. High-Risk Pathology vs. Lymphovascular Invasion
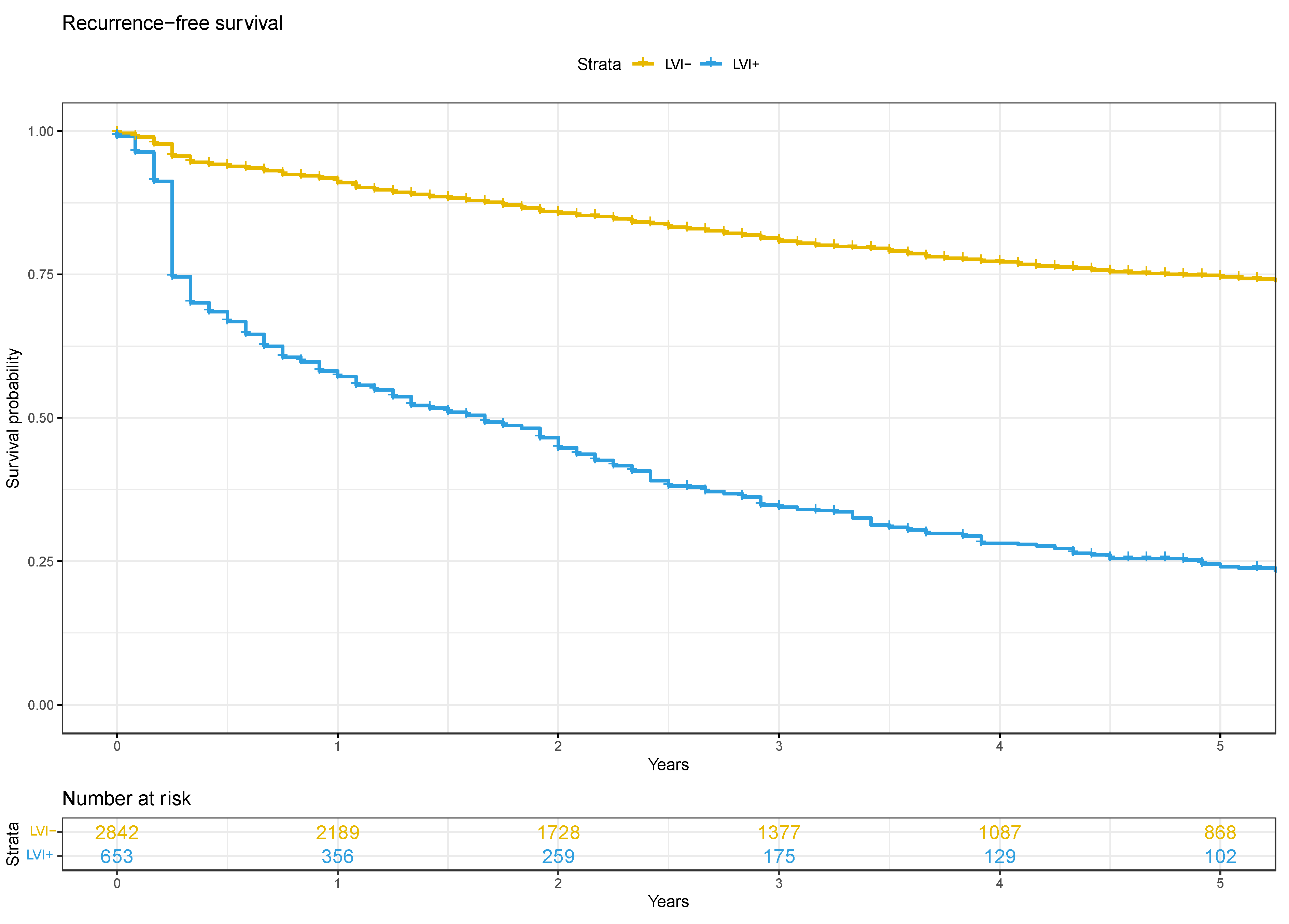
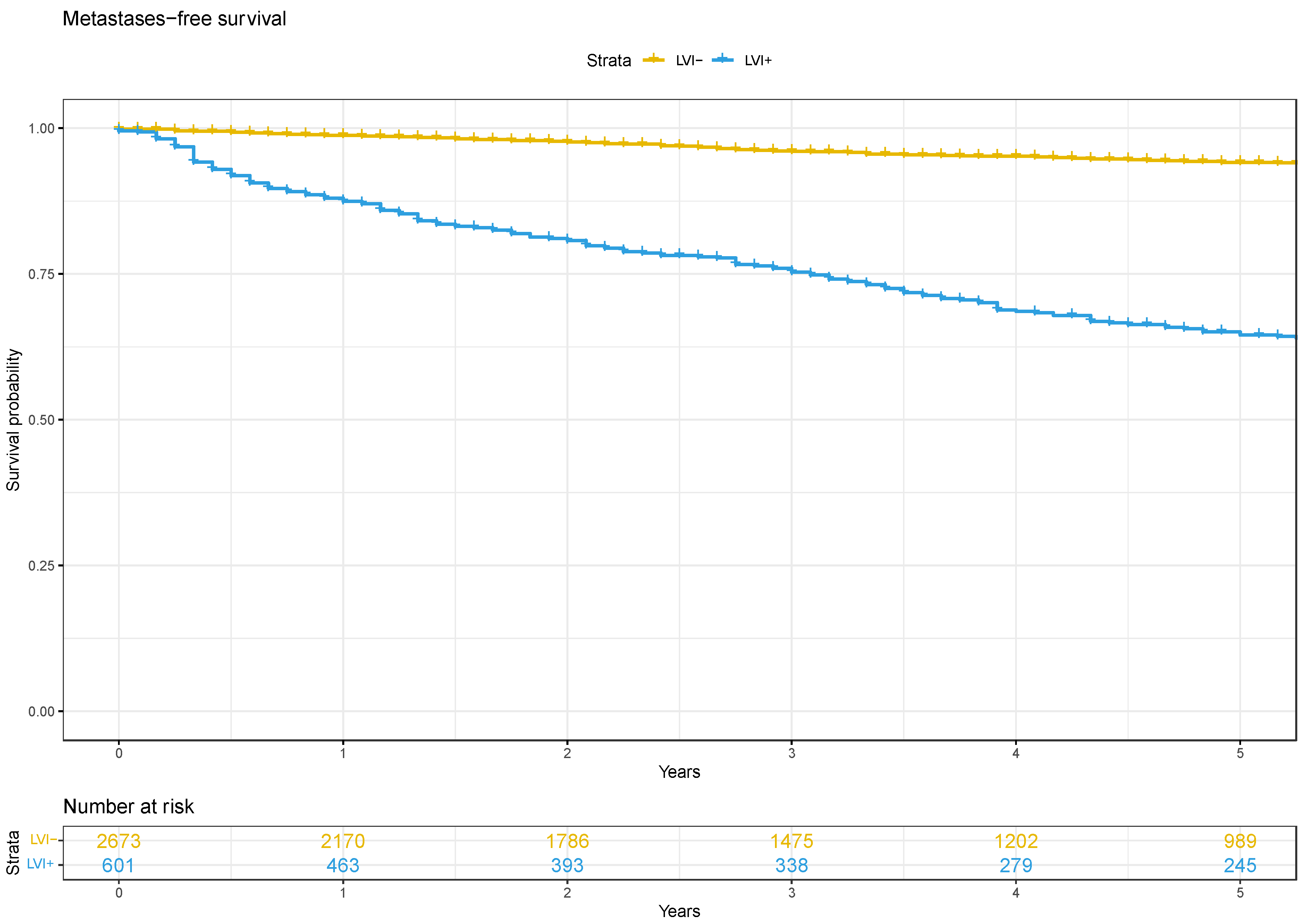
3.2. Oncological Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B

References
- Fujimoto, N.; Dieterich, L.C. Mechanisms and Clinical Significance of Tumor Lymphatic Invasion. Cells 2021, 10, 2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakha, E.A.; Martin, S.; Lee, A.H.S.; Morgan, D.; Pharoah, P.D.P.; Hodi, Z.; MacMillan, D.; Ellis, I.O. The prognostic significance of lymphovascular invasion in invasive breast carcinoma. Cancer 2012, 118, 3670–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidenreich, A.; Paffenholz, P.; Nestler, T.; Pfister, D. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Testis Cancer: Important Take Home Messages. Eur. Urol. Focus 2019, 5, 742–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwer, O.R.; Albersen, M.; Parnham, A.; Protzel, C.; Pettaway, C.A.; Ayres, B.; Antunes-Lopes, T.; Barreto, L.; Campi, R.; Crook, J.; et al. European Association of Urology-American Society of Clinical Oncology Collaborative Guideline on Penile Cancer: 2023 Update. Eur. Urol. 2023, 83, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Jones, T.D.; Lin, H.; Eble, J.N.; Zeng, G.; Carr, M.D.; Koch, M.O. Lymphovascular invasion is an independent prognostic factor in prostatic adenocarcinoma. J. Urol. 2005, 174, 2181–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shariat, S.F.; Khoddami, S.M.; Saboorian, H.; Koeneman, K.S.; Sagalowsky, A.I.; Cadeddu, J.A.; McConnell, J.D.; Holmes, M.N.; Roehrborn, C.G. Lymphovascular invasion is a pathological feature of biologically aggressive disease in patients treated with radical prostatectomy. J. Urol. 2004, 171, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeb, S.; Roehl, K.A.; Yu, X.; Antenor, J.A.; Han, M.; Gashti, S.N.; Yang, X.J.; Catalona, W.J. Lymphovascular invasion in radical prostatectomy specimens: Prediction of adverse pathologic features and biochemical progression. Urology 2006, 68, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, D.S.; Shariat, S.F.; Lowrance, W.T.; Maschino, A.C.; Savage, C.J.; Cronin, A.M.; Scardino, P.T.; Eastham, J.A. Prognostic significance of lymphovascular invasion in radical prostatectomy specimens. BJU Int. 2011, 108, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.G.; Bae, J.; Yi, J.S.; Hwang, I.S.; Lee, S.E.; Lee, E. Perineural invasion is a prognostic factor for biochemical failure after radical prostatectomy. Int. J. Urol. 2009, 16, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.T.; Lee, S.; Yun, C.J.; Jeon, B.J.; Kim, J.M.; Ha, H.K.; Lee, W.; Chung, M.K. Prediction of perineural invasion and its prognostic value in patients with prostate cancer. Korean J. Urol. 2010, 51, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhang, L.; Wu, B.; Zha, Z.; Zhao, H.; Jun, Y.; Jiang, Y. The impact of lymphovascular invasion in patients with prostate cancer following radical prostatectomy and its association with their clinicopathological features: An updated PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e13537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furrer, M.A.; Grueter, T.; Bosshard, P.; Vartolomei, M.D.; Kiss, B.; Thalmann, G.N.; Roth, B. Routine Preoperative Bone Scintigraphy Has Limited Impact on the Management of Patients with Invasive Bladder Cancer. Eur. Urol. Focus 2021, 7, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottet, N.; van den Bergh, R.C.N.; Briers, E.; Van den Broeck, T.; Cumberbatch, M.G.; De Santis, M.; Fanti, S.; Fossati, N.; Gandaglia, G.; Gillessen, S.; et al. EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer-2020 Update. Part 1: Screening, Diagnosis, and Local Treatment with Curative Intent. Eur. Urol. 2021, 79, 243–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furrer, M.A.; Sathianathen, N.; Gahl, B.; Corcoran, N.M.; Soliman, C.; Rodriguez Calero, J.A.; Ineichen, G.B.; Gahl, M.; Kiss, B.; Thalmann, G.N. Oncological outcomes after attempted nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy (NSRP) in patients with high-risk prostate cancer are comparable to standard non-NSRP: A longitudinal long-term propensity-matched single-centre study. BJU Int. 2023. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furrer, M.A.; Abgottspon, J.; Huber, M.; Engel, D.; Löffel, L.M.; Beilstein, C.M.; Burkhard, F.C.; Wuethrich, P.Y. Perioperative continuation of aspirin, oral anticoagulants or bridging with therapeutic low-molecular-weight heparin does not increase intraoperative blood loss and blood transfusion rate in cystectomy patients: An observational cohort study. BJU Int. 2022, 129, 512–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwin, J.C.; Mirmilstein, G.; Pedersen, J.; Lawrentschuk, N.; Bolton, D.; Mills, J. Tumor volume in radical prostatectomy specimens assessed by digital image analysis software correlates with other prognostic factors. J. Urol. 2010, 183, 1808–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, A.J.; Kattan, M.W.; Eastham, J.A.; Dotan, Z.A.; Bianco, F.J., Jr.; Lilja, H.; Scardino, P.T. Defining biochemical recurrence of prostate cancer after radical prostatectomy: A proposal for a standardized definition. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 3973–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Oh, J.J.; Lee, S.; Hong, S.K.; Lee, S.E.; Byun, S.-S. Perineural Invasion and Lymphovascular Invasion are Associated with Increased Risk of Biochemical Recurrence in Patients Undergoing Radical Prostatectomy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 2699–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, M.; Kaufmann, O.; Hammermann, F.; Loy, V.; Siegsmund, M. Prognostic impact of lymphovascular invasion in radical prostatectomy specimens. BJU Int. 2007, 99, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakic, N.; Jamil, M.; Keeley, J.; Sood, A.; Vetterlein, M.; Dalela, D.; Arora, S.; Modonutti, D.; Bronkema, C.; Novara, G.; et al. Evaluation of lymphovascular invasion as a prognostic predictor of overall survival after radical prostatectomy. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 39, 495.e1–495.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneebone, A.; Fraser-Browne, C.; Duchesne, G.M.; Fisher, R.; Frydenberg, M.; Herschtal, A.; Williams, S.G.; Brown, C.; Delprado, W.; Haworth, A.; et al. Adjuvant radiotherapy versus early salvage radiotherapy following radical prostatectomy (TROG 08.03/ANZUP RAVES): A randomised, controlled, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, C.C.; Clarke, N.W.; Cook, A.D.; Kynaston, H.G.; Petersen, P.M.; Catton, C.; Cross, W.; Logue, J.; Parulekar, W.; Payne, H.; et al. Timing of radiotherapy after radical prostatectomy (RADICALS-RT): A randomised, controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 1413–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vale, C.L.; Fisher, D.; Kneebone, A.; Parker, C.; Pearse, M.; Richaud, P.; Sargos, P.; Sydes, M.R.; Brawley, C.; Brihoum, M.; et al. Adjuvant or early salvage radiotherapy for the treatment of localised and locally advanced prostate cancer: A prospectively planned systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregate data. Lancet 2020, 396, 1422–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilki, D.; Chen, M.-H.; Wu, J.; Huland, H.; Graefen, M.; Wiegel, T.; Böhmer, D.; Mohamad, O.; Cowan, J.E.; Feng, F.Y.; et al. Adjuvant Versus Early Salvage Radiation Therapy for Men at High Risk for Recurrence Following Radical Prostatectomy for Prostate Cancer and the Risk of Death. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 2284–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilki, D.; Chen, M.H.; Wu, J.; Huland, H.; Graefen, M.; D’Amico, A.V. Adjuvant Versus Early Salvage Radiation Therapy After Radical Prostatectomy for pN1 Prostate Cancer and the Risk of Death. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2186–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attard, G.; Murphy, L.; Clarke, N.W.; Cross, W.; Jones, R.J.; Parker, C.C.; Gillessen, S.; Cook, A.; Brawley, C.; Amos, C.L.; et al. Abiraterone acetate and prednisolone with or without enzalutamide for high-risk non-metastatic prostate cancer: A meta-analysis of primary results from two randomised controlled phase 3 trials of the STAMPEDE platform protocol. Lancet 2022, 399, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aning, J.J.; Reilly, G.S.; Fowler, S.; Challacombe, B.; McGrath, J.S.; Sooriakumaran, P. Perioperative and oncological outcomes of radical prostatectomy for high-risk prostate cancer in the UK: An analysis of surgeon-reported data. BJU Int. 2019, 124, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.U.; Nam, T.K.; Song, J.Y.; Yoon, M.S.; Ahn, S.J.; Chung, W.K.; Cho, I.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Cho, S.H.; Jung, S.I.; et al. Prognostic significance of lymphovascular invasion in patients with prostate cancer treated with postoperative radiotherapy. Radiat. Oncol. J. 2019, 37, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryvenko, O.N.; Epstein, J.I. Histologic criteria and pitfalls in the diagnosis of lymphovascular invasion in radical prostatectomy specimens. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2012, 36, 1865–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiabovitch, E.; Hovens, C.M.; Peters, J.S.; Costello, A.J.; Battye, S.; Norden, S.; Ryan, A.; Corcoran, N.M. Routinely reported ‘equivocal’ lymphovascular invasion in prostatectomy specimens is associated with adverse outcomes. BJU Int. 2017, 119, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, B.E.; York, M.E.; Petrovics, G.; Kohaar, I.; Chesnut, G.T. Biomarkers of Aggressive Prostate Cancer at Diagnosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggener, S.E.; Rumble, R.B.; Armstrong, A.J.; Morgan, T.M.; Crispino, T.; Cornford, P.; Kwast, T.v.d.; Grignon, D.J.; Rai, A.J.; Agarwal, N.; et al. Molecular Biomarkers in Localized Prostate Cancer: ASCO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1474–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Lymphovascular Invasion-Negative (n = 2842) | Lymphovascular Invasion-Positive (n = 653) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), median (IQR) | 63 (58–68) | 65 (60–69) | <0.01 |
| PSA (ng/mL), median (IQR) | 7 (5–10) | 12 (7–20) | <0.01 |
| ISUP, n (%) | <0.01 | ||
| 1 | 545 (19%) | 63 (9.7%) | |
| 2 | 1415 (50%) | 127 (19%) | |
| 3 | 603 (21%) | 162 (25%) | |
| 4 | 152 (5.4%) | 81 (12%) | |
| 5 | 119 (4.2%) | 219 (34%) | |
| Pathological T stage 3–4, n (%) | 128 (4.5%) | 312 (48%) | <0.01 |
| Tumour volume (cc), median (IQR) | 3 (1–8) | 12 (6–28) | <0.01 |
| PSM, n (%) | 744 (26%) | 338 (52%) | <0.01 |
| PLND, n (%) | 1037 (64%) | 422 (84%) | <0.01 |
| N+, n (%) | 45 (4.9%) | 247 (62%) | <0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sathianathen, N.J.; Furrer, M.A.; Mulholland, C.J.; Katsios, A.; Soliman, C.; Lawrentschuk, N.; Peters, J.S.; Zargar, H.; Costello, A.J.; Hovens, C.M.; et al. Lymphovascular Invasion at the Time of Radical Prostatectomy Adversely Impacts Oncological Outcomes. Cancers 2024, 16, 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010123
Sathianathen NJ, Furrer MA, Mulholland CJ, Katsios A, Soliman C, Lawrentschuk N, Peters JS, Zargar H, Costello AJ, Hovens CM, et al. Lymphovascular Invasion at the Time of Radical Prostatectomy Adversely Impacts Oncological Outcomes. Cancers. 2024; 16(1):123. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010123
Chicago/Turabian StyleSathianathen, Niranjan J., Marc A. Furrer, Clancy J. Mulholland, Andreas Katsios, Christopher Soliman, Nathan Lawrentschuk, Justin S. Peters, Homi Zargar, Anthony J. Costello, Christopher M. Hovens, and et al. 2024. "Lymphovascular Invasion at the Time of Radical Prostatectomy Adversely Impacts Oncological Outcomes" Cancers 16, no. 1: 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010123
APA StyleSathianathen, N. J., Furrer, M. A., Mulholland, C. J., Katsios, A., Soliman, C., Lawrentschuk, N., Peters, J. S., Zargar, H., Costello, A. J., Hovens, C. M., Bishop, C., Rao, R., Tong, R., Steiner, D., Moon, D., Thomas, B. C., Dundee, P., Calero, J. A. R., Thalmann, G. N., & Corcoran, N. M. (2024). Lymphovascular Invasion at the Time of Radical Prostatectomy Adversely Impacts Oncological Outcomes. Cancers, 16(1), 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010123







