Genetic Polymorphisms of the Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase Gene in Relation to Prostate Tumorigenesis, Aggressiveness and Mortality: A Cross-Ancestry Analysis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Outcome Phenotype Ascertainment
2.3. SNPs Selection and Genotyping
2.4. Phasing, Imputation and Quality Control
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Associations between TERT SNPs and PCa Risk
3.3. Associations between TERT SNPs and Aggressive PCa Risk
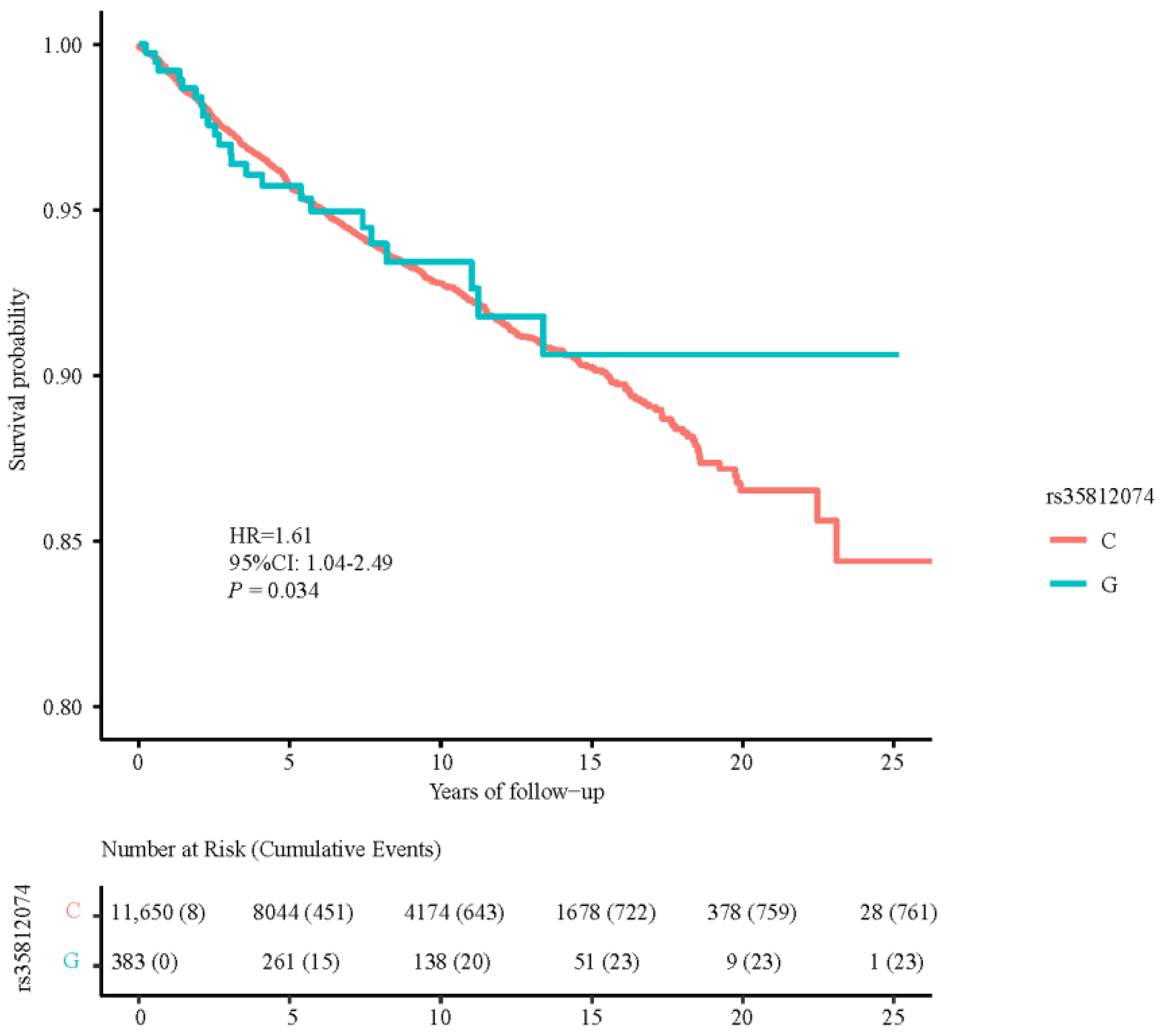
3.4. Associations between TERT SNPs and PCa Death
3.5. Gene-Based Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyba, T.; Randi, G.; Bray, F.; Martos, C.; Giusti, F.; Nicholson, N.; Gavin, A.; Flego, M.; Neamtiu, L.; Dimitrova, N.; et al. The European cancer burden in 2020: Incidence and mortality estimates for 40 countries and 25 major cancers. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 157, 308–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, C.; Dong, X.; Li, H.; Cao, M.; Sun, D.; He, S.; Yang, F.; Yan, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, N.; et al. Cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: Profiles, trends, and determinants. Chin. Med. J. 2022, 135, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, C.B.; Villeponteau, B. Telomeres and telomerase in aging and cancer. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1995, 5, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yin, Z.; Wu, W.; Li, X.; Zhou, B. Genetic variants in TERT-CLPTM1L genetic region associated with several types of cancer: A meta-analysis. Gene 2013, 526, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, M.; Parikh, H.; Jia, J.; Chung, C.C.; Sampson, J.N.; Hoskins, J.W.; Hutchinson, A.; Burdette, L.; et al. Imputation and subset-based association analysis across different cancer types identifies multiple independent risk loci in the TERT-CLPTM1L region on chromosome 5p15.33. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 6616–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Yu, H.; Sun, J.; Qi, J.; Liu, Q.; Li, R.; Zheng, S.L.; Xu, J.; Kang, J. Association of genetic polymorphisms in the telomerase reverse transcriptase gene with prostate cancer aggressiveness. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudlow, C.; Gallacher, J.; Allen, N.; Beral, V.; Burton, P.; Danesh, J.; Downey, P.; Elliott, P.; Green, J.; Landray, M.; et al. UK biobank: An open access resource for identifying the causes of a wide range of complex diseases of middle and old age. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Mo, Z.; Ye, D.; Wang, M.; Liu, F.; Jin, G.; Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Shao, Q.; Chen, Z.; et al. Genome-wide association study in Chinese men identifies two new prostate cancer risk loci at 9q31.2 and 19q13.4. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1231–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Huang, D.; Jiang, G.; Chen, S.; Ruan, X.; Chen, H.; Huang, J.; Liu, A.; Zhang, W.; Lin, X.; et al. Genome-Wide 3’-UTR Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Association Study Identifies Significant Prostate Cancer Risk-Associated Functional Loci at 8p21.2 in Chinese Population. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2201420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bycroft, C.; Freeman, C.; Petkova, D.; Band, G.; Elliott, L.T.; Sharp, K.; Motyer, A.; Vukcevic, D.; Delaneau, O.; O’Connell, J.; et al. The UK Biobank resource with deep phenotyping and genomic data. Nature 2018, 562, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Forer, L.; Schonherr, S.; Sidore, C.; Locke, A.E.; Kwong, A.; Vrieze, S.I.; Chew, E.Y.; Levy, S.; McGue, M.; et al. Next-generation genotype imputation service and methods. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1284–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Leeuw, C.A.; Mooij, J.M.; Heskes, T.; Posthuma, D. MAGMA: Generalized gene-set analysis of GWAS data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.S.; He, W.M.; Ji, J.J.; Zhang, C.; Guo, Y.; Yang, T.L. LDBlockShow: A fast and convenient tool for visualizing linkage disequilibrium and haplotype blocks based on variant call format files. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kote-Jarai, Z.; Saunders, E.J.; Leongamornlert, D.A.; Tymrakiewicz, M.; Dadaev, T.; Jugurnauth-Little, S.; Ross-Adams, H.; Al Olama, A.A.; Benlloch, S.; Halim, S.; et al. Fine-mapping identifies multiple prostate cancer risk loci at 5p15, one of which associates with TERT expression. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 2520–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Majumdar, A.; Wang, L.; Kar, S.; Brown, K.M.; Feng, H.; Turman, C.; Dennis, J.; Easton, D.; Michailidou, K.; et al. Large-scale cross-cancer fine-mapping of the 5p15.33 region reveals multiple independent signals. HGG Adv. 2021, 2, 100041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojesen, S.E.; Pooley, K.A.; Johnatty, S.E.; Beesley, J.; Michailidou, K.; Tyrer, J.P.; Edwards, S.L.; Pickett, H.A.; Shen, H.C.; Smart, C.E.; et al. Multiple independent variants at the TERT locus are associated with telomere length and risks of breast and ovarian cancer. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaid, D.J.; McDonnell, S.K.; FitzGerald, L.M.; DeRycke, L.; Fogarty, Z.; Giles, G.G.; MacInnis, R.J.; Southey, M.C.; Nguyen-Dumont, T.; Cancel-Tassin, G.; et al. Two-stage Study of Familial Prostate Cancer by Whole-exome Sequencing and Custom Capture Identifies 10 Novel Genes Associated with the Risk of Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2021, 79, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, A.A.G.; Atkins, J.R.; Penha, R.C.C.; Smith-Byrne, K.; Gaborieau, V.; Voegele, C.; Abedi-Ardekani, B.; Milojevic, M.; Olaso, R.; Meyer, V.; et al. Genetic Analysis of Lung Cancer and the Germline Impact on Somatic Mutation Burden. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2022, 114, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorev, M.; Carmel, L. The function of introns. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.; Tyekucheva, S.; King, D.C.; Hardison, R.C.; Miller, W.; Chiaromonte, F. ESPERR: Learning strong and weak signals in genomic sequence alignments to identify functional elements. Genome Res. 2006, 16, 1596–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xu, X.; Fang, J.; Wang, L.; Mu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Yao, Z.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Z. Rs2853677 modulates Snail1 binding to the TERT enhancer and affects lung adenocarcinoma susceptibility. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 37825–37838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, M.; Shi, M.; An, C.; Yang, W.; Nie, X.; Zhang, J.; Lv, Z.; Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Du, Z.; et al. Functional evaluation of TERT-CLPTM1L genetic variants associated with susceptibility of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhang, Q.; Hao, J.; Xie, Q.; Xu, B.; Zhang, P.; Lu, H.; Huang, Q.; Yang, T.; Wei, G.H.; et al. Large Multicohort Study Reveals a Prostate Cancer Susceptibility Allele at 5p15 Regulating TERT via Androgen Signaling-Orchestrated Chromatin Binding of E2F1 and MYC. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 754206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsson, J.; Besenbacher, S.; Sulem, P.; Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Olafsson, I.; Arinbjarnarson, S.; Agnarsson, B.A.; Benediktsdottir, K.R.; Isaksson, H.J.; Kostic, J.P.; et al. Genetic correction of PSA values using sequence variants associated with PSA levels. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 62ra92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Xian, Y.; Tian, T.; Zhuang, X.; Chu, M. New evidence of TERT rs2736098 polymorphism and cancer risk: An updated meta-analysis. J. BUON 2016, 21, 491–497. [Google Scholar]
- Wysoczanska, B.; Dratwa, M.; Gebura, K.; Mizgala, J.; Mazur, G.; Wrobel, T.; Bogunia-Kubik, K. Variability within the human TERT gene, telomere length and predisposition to chronic lymphocytic leukemia. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 4309–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, X.; Huang, D.; Huang, J.; Xu, D.; Na, R. Application of European-specific polygenic risk scores for predicting prostate cancer risk in different ancestry populations. Prostate 2023, 83, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, D.; Darst, B.; Moss, L.; Saunders, E.; Sheng, X.; Chou, A.; Schumacher, F.; Olama, A.; Benlloch, S.; Dadaev, T.; et al. Trans-ancestry genome-wide association meta-analysis of prostate cancer identifies new susceptibility loci and informs genetic risk prediction. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cases | Controls | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| European | |||
| N | 14,550 | 195,144 | |
| Age, years (mean ± SD) | 62.1 ± 5.5 | 56.6 ± 8.1 | <0.001 |
| Family history | 12.4% | 8.8% | <0.001 |
| CCI (median, IQR) | 2.0 (0.0–3.0) | 0.0 (0.0–1.0) | <0.001 |
| Chinese | |||
| N | 4438 | 4435 | |
| Age, years (mean ± SD) | 70.3 ± 8.0 | 64.5 ± 9.1 | <0.001 |
| Family history | 4.2% | 3.0% | 0.110 |
| PSA value, ng/mL (median, IQR) | 21.8 (11.0–71) | 9.8 (6.6–14.6) | <0.001 |
| PSA category | <0.001 | ||
| <1 ng/mL | 1.1% | 1.6% | |
| 1–4 ng/mL | 1.9% | 5.4% | |
| 4–10 ng/mL | 18.8% | 46.6% | |
| 10–20 ng/mL | 26.1% | 33.6% | |
| >20 ng/mL | 52.1% | 12.8% | |
| Gleason score (median, IQR) | 7.0 (7.0–8.0) | ||
| GS category | |||
| 2–5 | 2.1% | ||
| 6–7 | 60.3% | ||
| 8–10 | 37.6% |
| SNP ID | Position * | Location | Alleles # | EAF | OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs144704378 † | 1259489 | Intron 12 | T/C | 0.049 | 1.14 (1.07–1.21) | 1.60 × 10−5 |
| rs35311994 † | 1260514 | Intron 12 | T/C | 0.029 | 1.22 (1.14–1.32) | 1.18 × 10−7 |
| rs34194491 † | 1267213 | Intron 9 | C/T | 0.025 | 1.22 (1.12–1.32) | 2.50 × 10−6 |
| rs144020096 † | 1278447 | Intron 6 | C/A | 0.989 | 1.30 (1.12–1.50) | 4.12 × 10−4 |
| rs10069690 | 1279790 | Intron 4 | C/T | 0.743 | 1.12 (1.09–1.16) | 2.58 × 10−13 |
| rs10054203 | 1279964 | Intron 4 | G/C | 0.606 | 1.08 (1.05–1.11) | 1.52 × 10−8 |
| rs2242652 | 1280028 | Intron 4 | G/A | 0.810 | 1.16 (1.12–1.20) | 4.12 × 10−16 |
| rs4975538 | 1280830 | Intron 3 | G/C | 0.648 | 1.09 (1.06–1.12) | 1.57 × 10−9 |
| rs7726159 | 1282319 | Intron 3 | C/A | 0.676 | 1.12 (1.09–1.15) | 3.16 × 10−14 |
| rs7725218 | 1282414 | Intron 3 | G/A | 0.666 | 1.12 (1.09–1.15) | 1.34 × 10−14 |
| rs72709458 | 1283755 | Intron 2 | C/T | 0.799 | 1.15 (1.11–1.19) | 1.57 × 10−14 |
| rs4449583 | 1284135 | Intron 2 | C/T | 0.678 | 1.12 (1.09–1.15) | 7.73 × 10−14 |
| rs7705526 | 1285974 | Intron 2 | C/A | 0.680 | 1.06 (1.03–1.09) | 8.62 × 10−5 |
| rs7710703 † | 1287505 | Intron 2 | C/T | 0.874 | 1.10 (1.06–1.15) | 4.30 × 10−6 |
| rs74682426 | 1289975 | Intron 2 | C/A | 0.867 | 1.15 (1.11–1.20) | 1.04 × 10−11 |
| rs2736098 | 1294086 | Exon 2 | T/C | 0.280 | 1.10 (1.07–1.14) | 2.60 × 10−11 |
| rs2853669 | 1295349 | Promoter | G/A | 0.314 | 1.09 (1.06–1.12) | 7.41 × 10−10 |
| rs7712562 | 1296072 | Promoter | G/A | 0.862 | 1.16 (1.11–1.20) | 1.17 × 10−12 |
| rs2736109 | 1296759 | Promoter | T/C | 0.407 | 1.06 (1.03–1.09) | 2.52 × 10−5 |
| SNP ID | Position * | Location | Alleles # | EAF | OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs2736100 | 1286516 | Intron 2 | A/C | 0.540748 | 1.49 (1.31–1.71) † | 2.91 × 10−9 |
| rs2853677 | 1287194 | Intron 2 | A/G | 0.549014 | 1.74 (1.52–1.98) † | 3.52 × 10−16 |
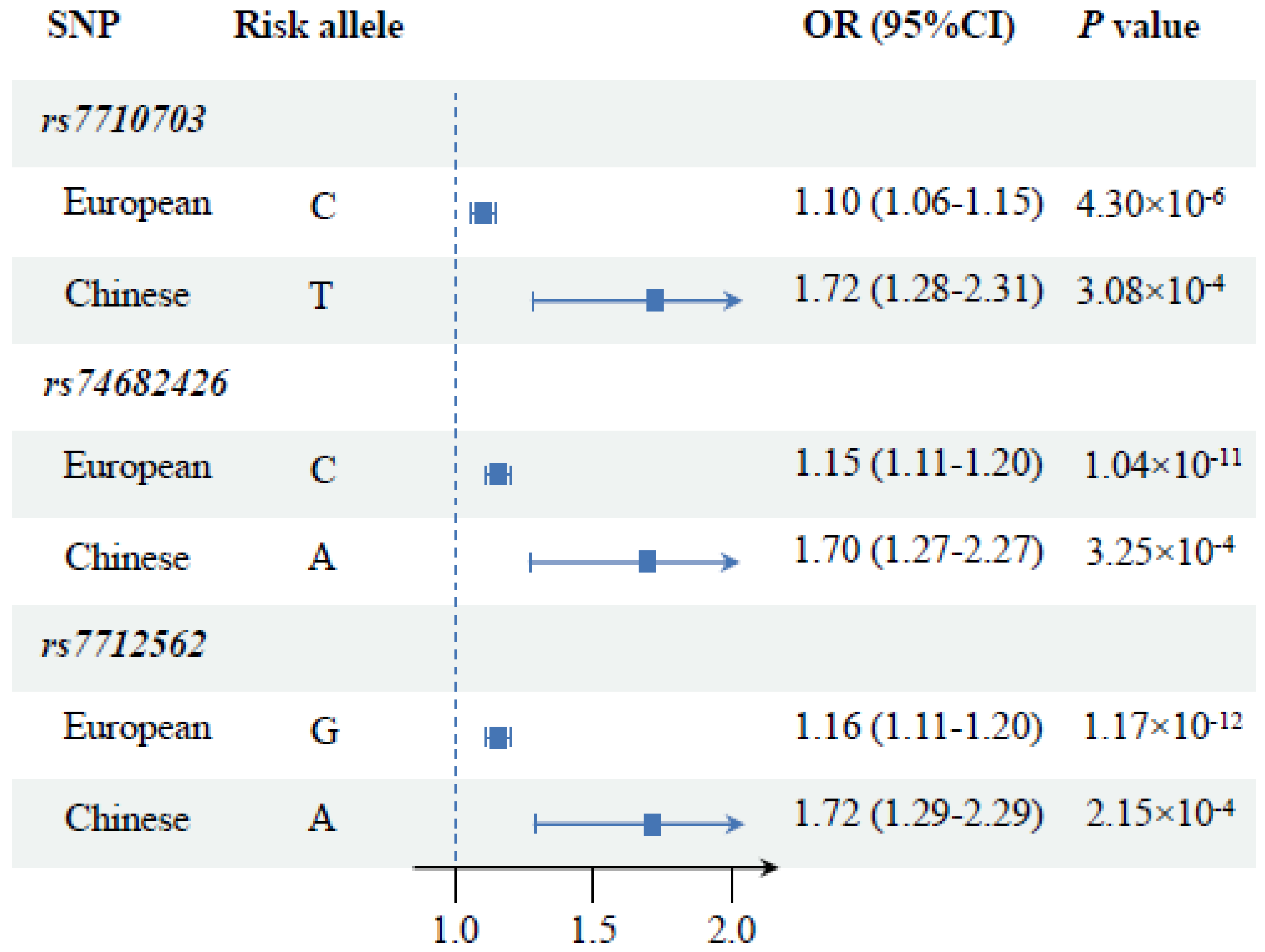
| rs7710703 ‡ | 1287505 | Intron 2 | T/C | 0.898 | 1.72 (1.28–2.31) | 3.08 × 10−4 |
| rs11291391 ‡ | 1287612 | Intron 2 | CA/C | 0.860 | 1.73 (1.34–2.25) | 3.04 × 10−5 |
| rs2853676 | 1288547 | Intron 2 | T/C | 0.818 | 1.53 (1.22–1.92) | 2.67 × 10−4 |
| rs74682426 | 1289975 | Intron 2 | A/C | 0.893 | 1.70 (1.27–2.27) | 3.25 × 10−4 |
| rs7712562 | 1296072 | Promoter | A/G | 0.890 | 1.72 (1.29–2.29) | 2.15 × 10−4 |
| Gene | Chr | Start | Stop | nSNPs | Z stat | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| European ancestry | |||||||
| PCa | TERT | 5 | 1253282 | 1295178 | 56 | 7.78 | 3.66 × 10−15 |
| PCa mortality | TERT | 5 | 1253282 | 1295178 | 55 | 0.95 | 0.171 |
| Chinese ancestry | |||||||
| PCa | TERT | 5 | 1253282 | 1295178 | 79 | 1.72 | 0.043 |
| Aggressive PCa | TERT | 5 | 1253282 | 1295178 | 54 | 2.54 | 0.006 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhan, Y.; Ruan, X.; Liu, J.; Huang, D.; Huang, J.; Huang, J.; Chun, T.T.S.; Ng, A.T.-L.; Wu, Y.; Wei, G.; et al. Genetic Polymorphisms of the Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase Gene in Relation to Prostate Tumorigenesis, Aggressiveness and Mortality: A Cross-Ancestry Analysis. Cancers 2023, 15, 2650. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092650
Zhan Y, Ruan X, Liu J, Huang D, Huang J, Huang J, Chun TTS, Ng AT-L, Wu Y, Wei G, et al. Genetic Polymorphisms of the Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase Gene in Relation to Prostate Tumorigenesis, Aggressiveness and Mortality: A Cross-Ancestry Analysis. Cancers. 2023; 15(9):2650. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092650
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhan, Yongle, Xiaohao Ruan, Jiacheng Liu, Da Huang, Jingyi Huang, Jinlun Huang, Tsun Tsun Stacia Chun, Ada Tsui-Lin Ng, Yishuo Wu, Gonghong Wei, and et al. 2023. "Genetic Polymorphisms of the Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase Gene in Relation to Prostate Tumorigenesis, Aggressiveness and Mortality: A Cross-Ancestry Analysis" Cancers 15, no. 9: 2650. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092650
APA StyleZhan, Y., Ruan, X., Liu, J., Huang, D., Huang, J., Huang, J., Chun, T. T. S., Ng, A. T.-L., Wu, Y., Wei, G., Jiang, H., Xu, D., & Na, R. (2023). Genetic Polymorphisms of the Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase Gene in Relation to Prostate Tumorigenesis, Aggressiveness and Mortality: A Cross-Ancestry Analysis. Cancers, 15(9), 2650. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092650








