Diagnostic Value of FDG PET/CT in Surveillance after Curative Resection of Breast Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
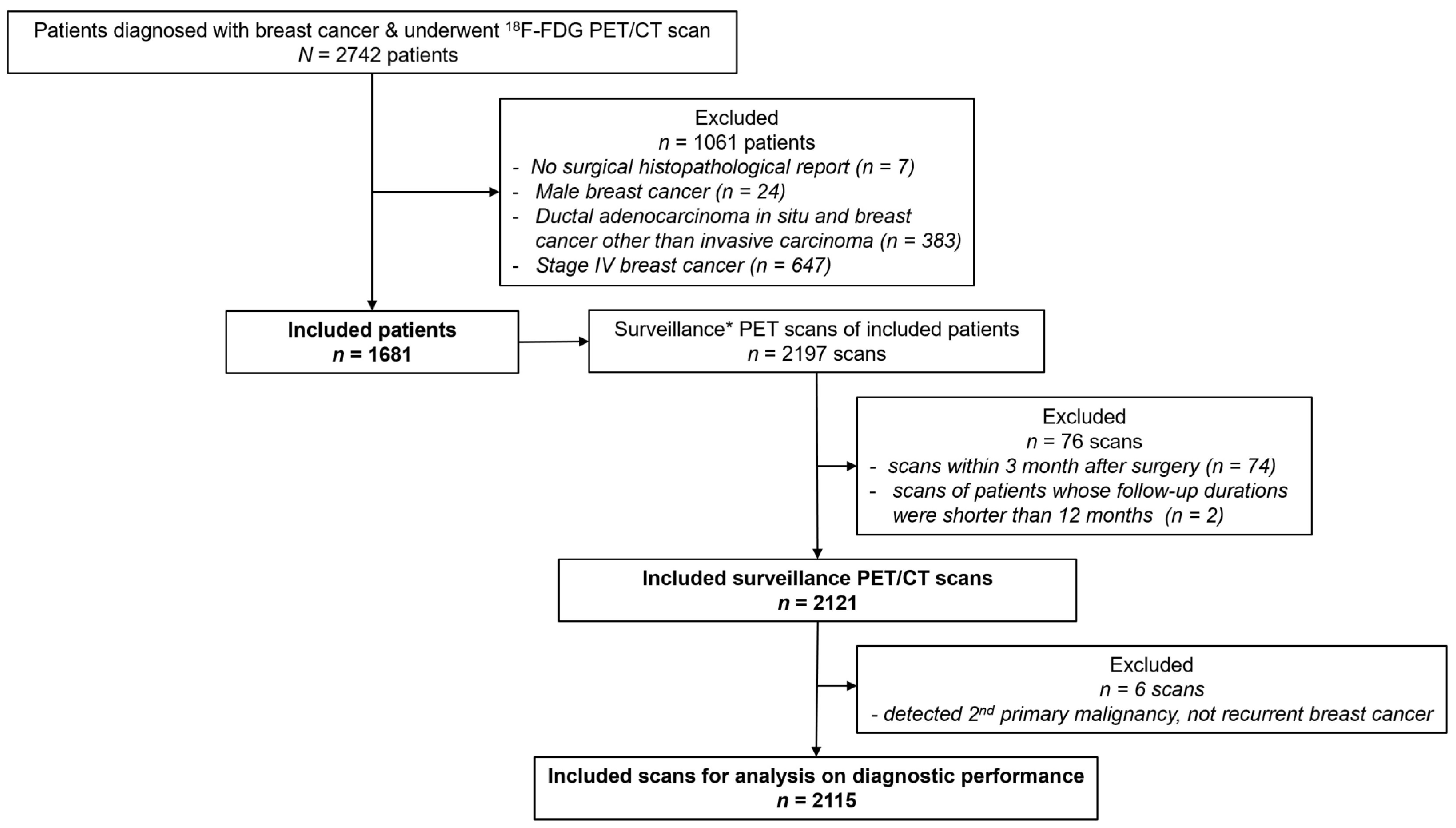
2.1. Study Cohort
2.2. Medical Report Review
2.3. Image Acquisition and Analyses
2.4. Diagnostic Performance Analyses
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Study Population
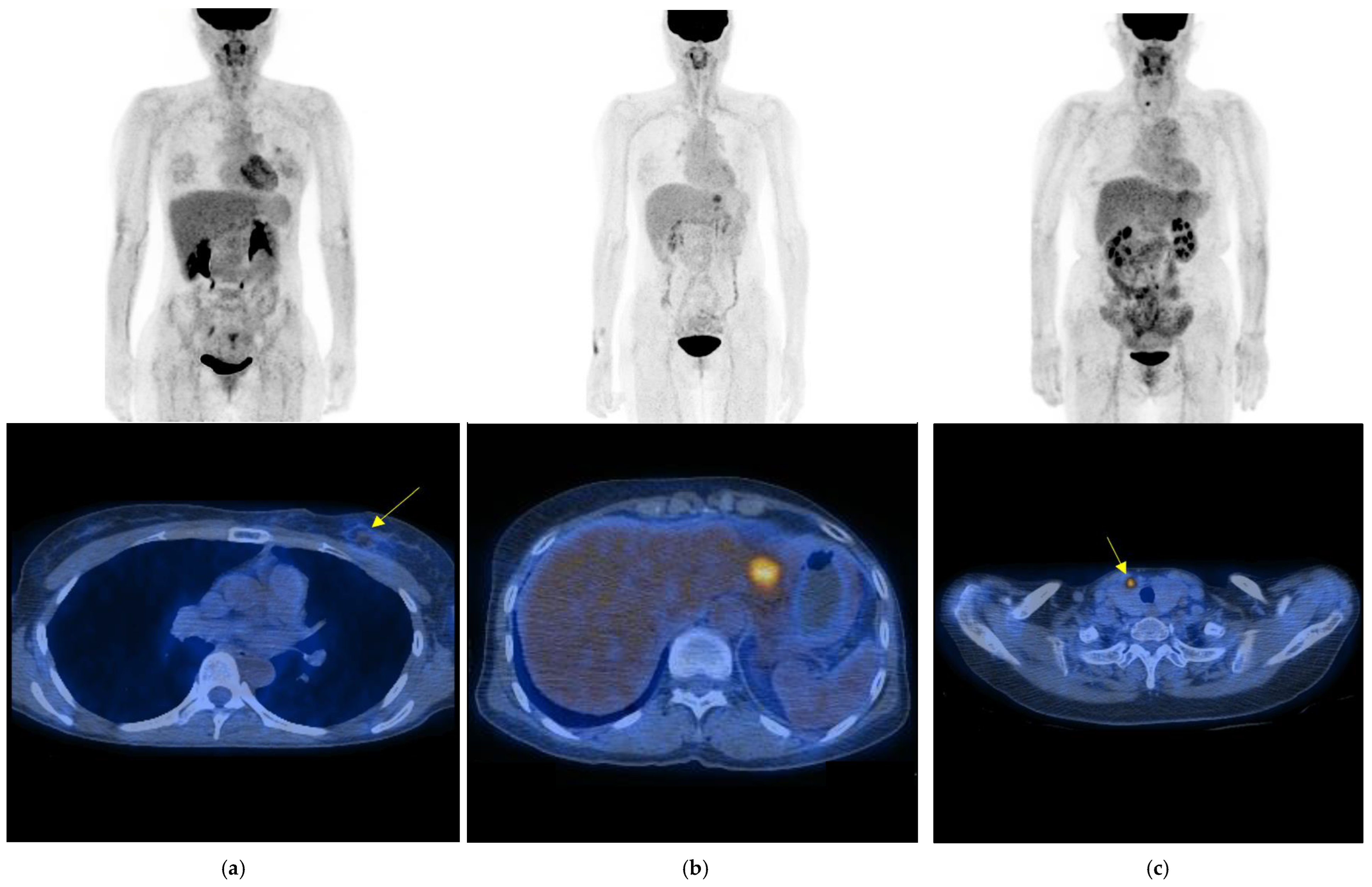
3.2. Diagnostic Findings and Results of Surveillance FDG PET/CT
3.3. Diagnostic Performance of Surveillance FDG PET/CT According to Several Clinical Variables
3.4. Impact of Surveillance FDG PET/CT on Patient Management
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bick, U.; Helbich, T.H. Follow-Up of Patients with Breast Cancer: Imaging of Local Recurrence and Distant Metastases. In Diseases of the Chest, Breast, Heart and Vessels 2019-2022: Diagnostic and Interventional Imaging [Internet]; Hodler, J., Kubik-Huch, R.A., von Schulthess, G.K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Chapter 14. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, J.H.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, E.-K.; Moon, H.J. Imaging Surveillance of Patients with Breast Cancer after Primary Treatment: Current Recommendations. Korean J. Radiol. 2015, 16, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, N.Y.; Yoo, I.R.; Kang, B.J.; Kim, S.H.; Chae, B.J.; Seo, Y.Y. Clinical significance of FDG-PET/CT at the postoperative surveillance in the breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer 2016, 23, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghipour, M.; Sheikhbahaei, S.; Trahan, T.J.; Subramaniam, R.M. Value of fourth and subsequent post-therapy follow-up 18F-FDG PET/CT scans in patients with breast cancer. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2016, 37, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Wang, L.; Jiang, X.; She, W.; He, L.; Hu, G. Diagnostic efficacy of 18F-FDG-PET or PET/CT in breast cancer with suspected recurrence: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2016, 37, 1180–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.I. Radiological Justification for and Optimization of Nuclear Medicine Practices in Korea. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2016, 31 (Suppl. S1), S59–S68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC). AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Breat Cancer, 8th Edition. AJCC Website. Available online: https://cancerstaging.org (accessed on 30 June 2021).
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN). NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: Breast cancer—Version 5.2021. NCCN Website. Available online: www.nccn.org (accessed on 30 June 2021).
- Kim, Y.K.; Lee, K.S.; Kim, B.T.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, H.; Kwon, O.J.; Shim, Y.M.; Yi, C.A.; Kim, H.Y.; Chung, M.J. Mediastinal nodal staging of nonsmall cell lung cancer using integrated 18F-FDG PET/CT in a tuberculosis-endemic country: Diagnostic efficacy in 674 patients. Cancer 2007, 109, 1068–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.; Davey Smith, G. Sifting the evidence-what’s wrong with significance tests? BMJ Clin. Res. Ed. 2001, 322, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houssami, N.; Ciatto, S. Mammographic surveillance in women with a personal history of breast cancer: How accurate? How effective? Breast 2010, 19, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obdeijn, I.-M.; Winter-Warnars, G.A.O.; Mann, R.; Hooning, M.J.; Hunink, M.G.M.; Tilanus-Linthorst, M.M.A. Should we screen BRCA1 mutation carriers only with MRI? A multicenter study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 144, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.H.; Han, B.-K.; Choe, Y.H.; Nam, S.-J.; Park, W.; Im, Y.-H. Ultrasonographic Detection of Occult Cancer in Patients After Surgical Therapy for Breast Cancer. J. Ultrasound Med. 2005, 24, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, Y.J.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, E.-K.; Moon, H.J.; Kim, S.-I.; Park, B.-W. Value of Ultrasound for Postoperative Surveillance of Asian Patients with History of Breast Cancer Surgery: A Single-Center Study. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20, 3461–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kang, B.J.; Kim, S.H. Usefulness of postoperative surveillance MR for women after breast-conservation therapy: Focusing on MR features of early and late recurrent breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aukema, T.; Rutgers, E.; Vogel, W.; Teertstra, H.; Oldenburg, H.; Peeters, M.V.; Wesseling, J.; Russell, N.; Olmos, R.V. The role of FDG PET/CT in patients with locoregional breast cancer recurrence: A comparison to conventional imaging techniques. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 36, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.Y.; Lee, K.S.; Kwon, O.J.; Shim, Y.M.; Baek, C.-H.; Park, K.; Kim, B.-T. Improved Detection of Second Primary Cancer Using Integrated [18F] Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography and Computed Tomography for Initial Tumor Staging. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 7654–7659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Hyun, S.H.; Moon, S.H.; Lee, K.S.; Sun, J.-M.; Oh, D.; Ahn, Y.C.; Zo, J.I.; Shim, Y.M.; Choi, J.Y. Diagnostic value of surveillance 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT for detecting recurrent esophageal carcinoma after curative treatment. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 46, 1850–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | No. of Patients |
|---|---|
| Included female patients with breast cancer | 1681 |
| Age at diagnosis (year) | |
| <40 | 309 |
| 40~50 | 765 |
| 51~60 | 454 |
| >60 | 153 |
| Mean age (SD): 48 (9) | |
| Primary tumor location | |
| Right breast | 642 |
| Left breast | 552 |
| Bilateral breast | 487 |
| Clinical prognostic stage (AJCC 8th ed.) | |
| Stage I | 767 |
| Stage II | 397 |
| Stage III | 517 |
| Protocol of curative treatment | |
| NAC + Surgery | 4 |
| NAC + Surgery + AC | 16 |
| NAC + Surgery + RT | 94 |
| NAC + Surgery + CCRT | 150 |
| Surgery | 20 |
| Surgery + AC | 249 |
| Surgery + RT | 53 |
| Surgery + CCRT | 1095 |
| Type of surgery | |
| Breast-conserving surgery | 608 |
| Mastectomy | 1073 |
| Number of surveillance PET/CT scan(s) | |
| 1 | 1290 |
| 2 | 353 |
| 3 | 30 |
| 4 | 7 |
| 7 | 1 |
| Type of Positive Scans | Local–Regional Recurrence | Distant Recurrence | 2nd Primary Malignancy | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Local, Contralateral *. | Regional Lymph Node | Bone | Thoracic † | Multiorgan | Others ‡ | Thyroid | Others § | ||
| Ipsilateral | Contralateral | ||||||||
| True Positive (74/105, 70.5%) | 3, 1 | 10 | 4 | 20 | 17 | 9 | 4 | 4 | 2 |
| False Positive (31/105, 29.5%) | 2, 1 | 11 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Parameter | All Scans | Interval from Last Treatment * | Prognostic Stage (AJCC 8th) | Option of NAC | Response to NAC | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Within 2 | 2~4 | Beyond 4 | Stage I | Stage II | Stage III | NAC + Surgery | Surgery | No | Partial | Complete | ||
| 2115 Scans | 729 Scans | 818 Scans | 574 Scans | 903 Scans | 486 Scans | 732 Scans | 345 Scans | 1776 Scans | 73 Scans | 221 Scans | 51 Scans | |
| No. of positive scans (%) | 99 (4.7%) | 42 (5.8%) | 34 (4.2%) | 23 (4.0%) | 23 (2.5%) | 15 (3.1%) | 61 (8.3%) | 29 (8.4%) | 70 (3.9%) | 5 (6.8%) | 19 (8.6%) | 1 (2.0%) |
| Sensitivity (%) (No. of scans) | 100 (68/68) | 100 (28/28) | 100 (26/26) | 100 (14/14) | 100 (13/13) | 100 (12/12) | 100 (43/43) | 100 (19/19) | 100 (49/49) | 100 (3 /3) | 100 (11/11) | 100 (1/1) |
| Specificity (%) (No. of scans) | 98.5 (2016/2047) | 98.0 (685/699) | 99.0 (782/790) | 98.4 (549/558) | 98.9 (878/888) | 99.4 (469/472) | 97.4 (669/687) | 96.9 (314/324) | 98.8 (1702/1723) | 97.1 (66/68) | 96.1 (198/206) | 100 (50/50) |
| PPV (%) (No. of scans) | 69 (68/99) | 67 (28/42) | 79 (26/33) | 61 (14/23) | 57 (13/23) | 80 (12/15) | 70 (43/61) | 66 (19/29) | 70 (49/70) | 60 (3/5) | 58 (11/19) | 100 (1/1) |
| NPV (%) (No. of scans) | 100 (2016/2016) | 100 (685/685) | 100 (782/782) | 100 (549/549) | 100 (878/878) | 100 (469/469) | 100 (669/669) | 100 (314/314) | 100 (1702/1702) | 100 (66/66) | 100 (198/198) | 100 (50/50) |
| Accuracy (%) (No. of scans) | 98.5 (2084/2115) | 98.1 (713/727) | 99.0 (808/816) | 98.4 (563/572) | 98.9 (891/901) | 99.4 (481/484) | 97.5 (712/730) | 97.1 (333/343) | 98.8 (1751/1772) | 97.2 (69/71) | 96.3 (209/217) | 100 (51/51) |
| No. of true-positive scans | 68 | 28 | 26 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 43 | 19 | 49 | 3 | 11 | 1 |
| No. of false-positive scans | 31 | 14 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 3 | 18 | 10 | 21 | 2 | 8 | 0 |
| No. of true-negative scans | 2016 | 685 | 782 | 549 | 878 | 469 | 669 | 314 | 1702 | 66 | 198 | 50 |
| No. of false-negative scans | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.; Choi, J.Y.; Park, Y.H.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, S.W.; Nam, S.J.; Cho, Y.S. Diagnostic Value of FDG PET/CT in Surveillance after Curative Resection of Breast Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 2646. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092646
Lee H, Choi JY, Park YH, Lee JE, Kim SW, Nam SJ, Cho YS. Diagnostic Value of FDG PET/CT in Surveillance after Curative Resection of Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2023; 15(9):2646. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092646
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hwanhee, Joon Young Choi, Yeon Hee Park, Jeong Eon Lee, Seok Won Kim, Seok Jin Nam, and Young Seok Cho. 2023. "Diagnostic Value of FDG PET/CT in Surveillance after Curative Resection of Breast Cancer" Cancers 15, no. 9: 2646. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092646
APA StyleLee, H., Choi, J. Y., Park, Y. H., Lee, J. E., Kim, S. W., Nam, S. J., & Cho, Y. S. (2023). Diagnostic Value of FDG PET/CT in Surveillance after Curative Resection of Breast Cancer. Cancers, 15(9), 2646. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092646






