4-[(5-Methyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)amino]-2H-phenyl-1-phthalazinone Inhibits MCPyV T Antigen Expression in Merkel Cell Carcinoma Independent of Aurora Kinase A
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Vectors and Lentiviral Infection
2.4. Screen for Compounds Repressing NCCR-Dependent Transcription
2.5. Immunoblotting
2.6. Real-Time PCR
2.7. EdU Incorporation Assay
2.8. Animal Experiments
2.9. GSK3 Kinase Assay
2.10. Phospho-Histone H3 Flow Cytometry
2.11. Statistics
3. Results
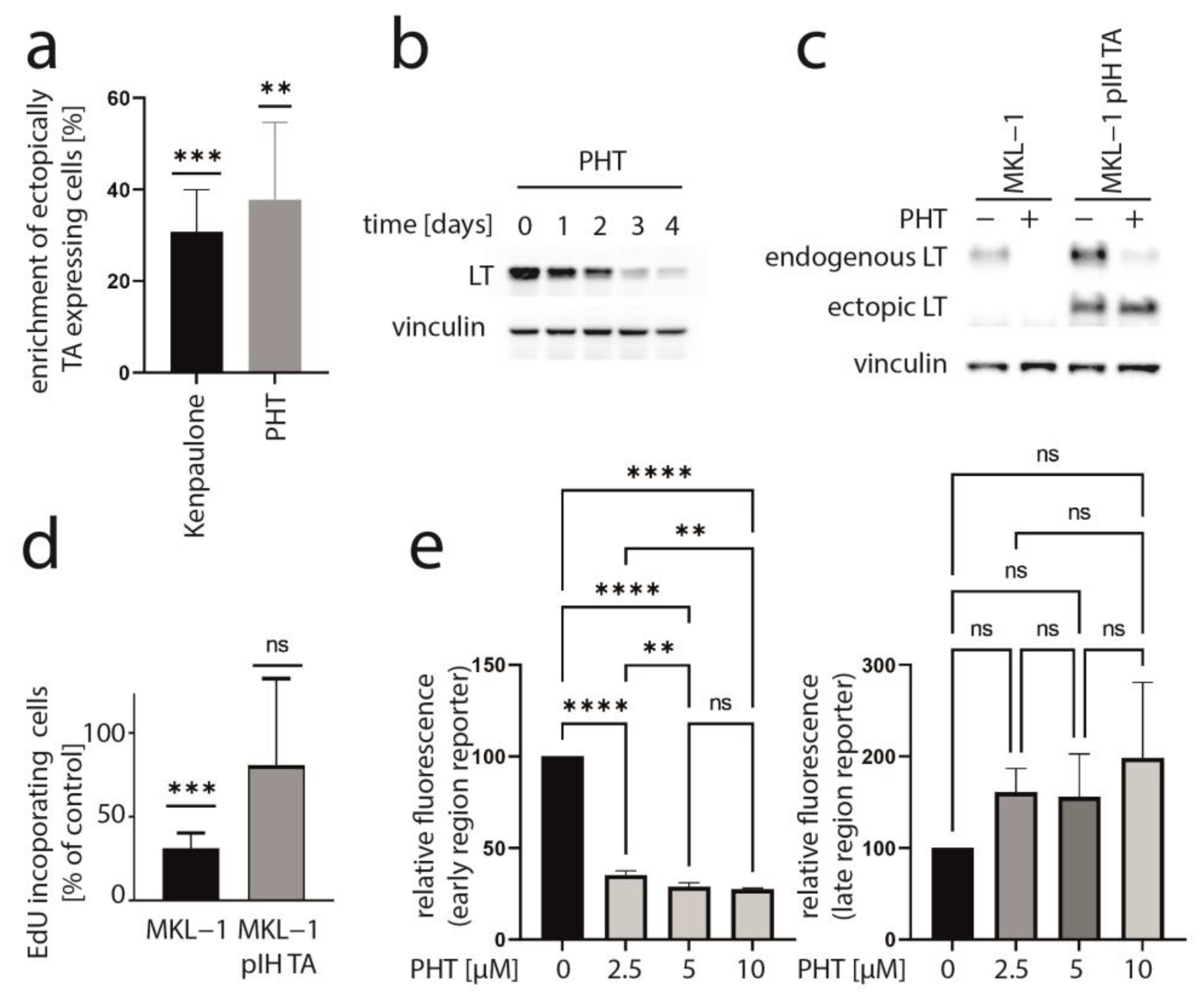
3.1. Screening for Kinase Inhibitors Targeting TA Expression
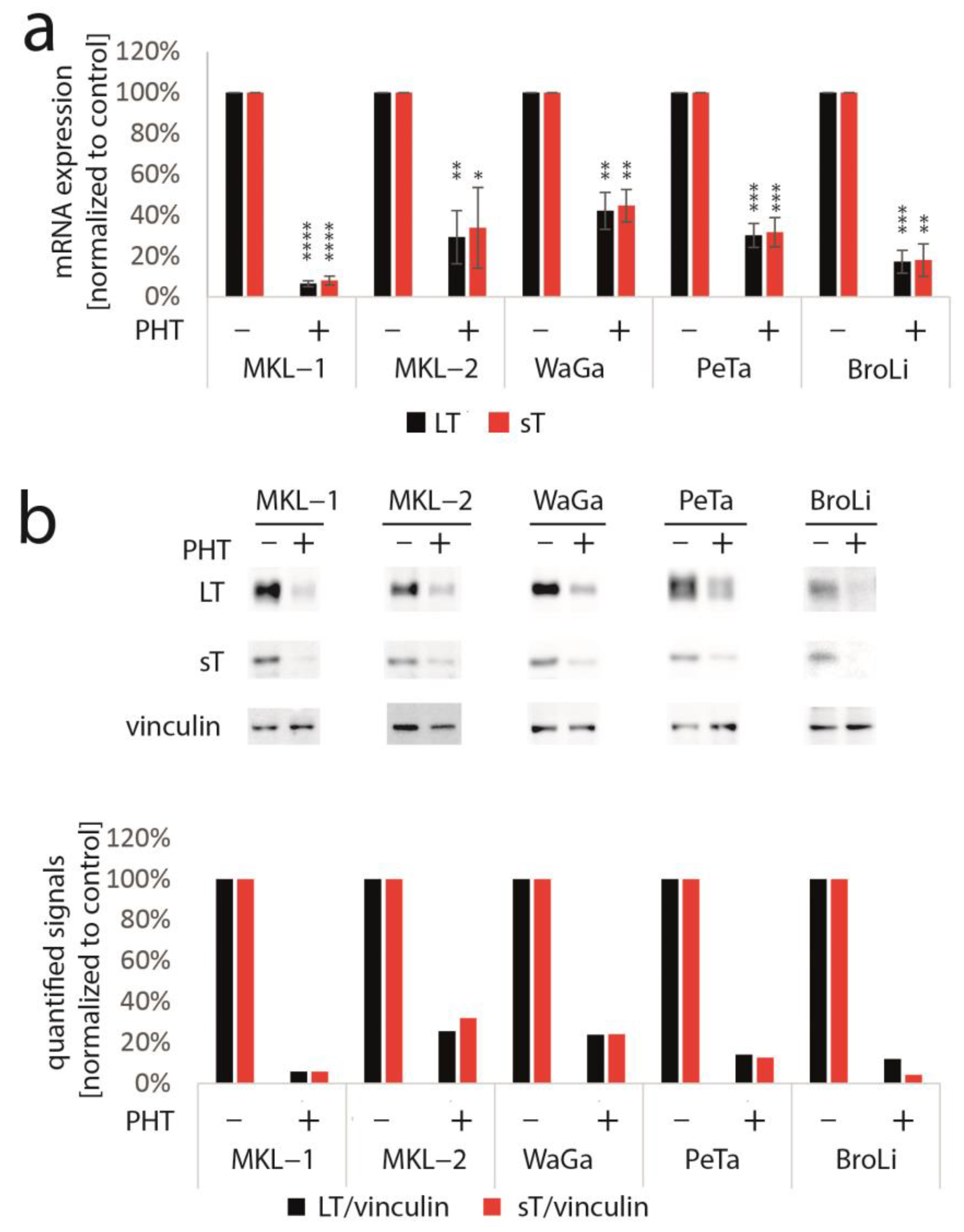
3.2. PHT Represses MCC Growth by Repressing MCPyV-TA Expression
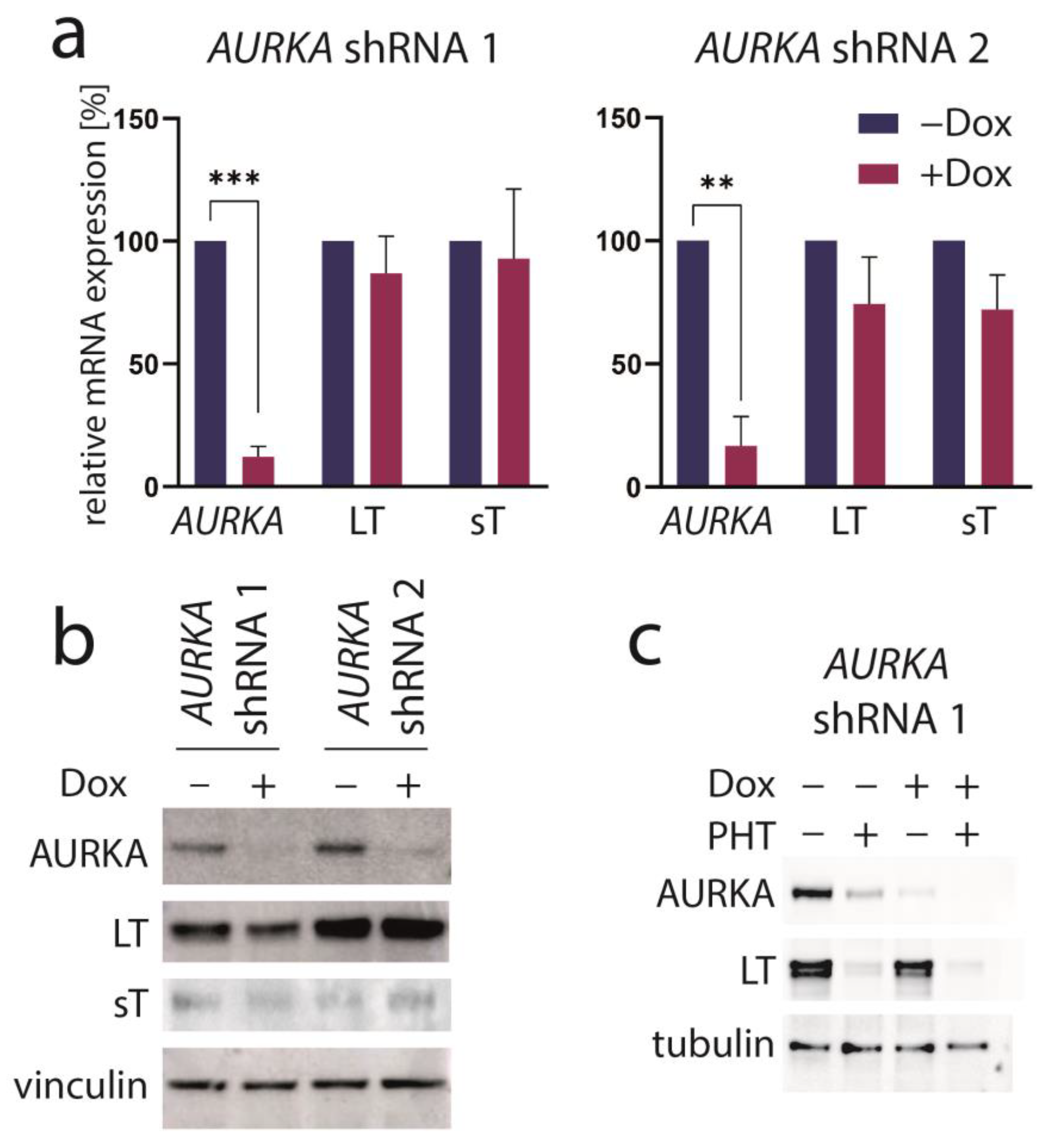
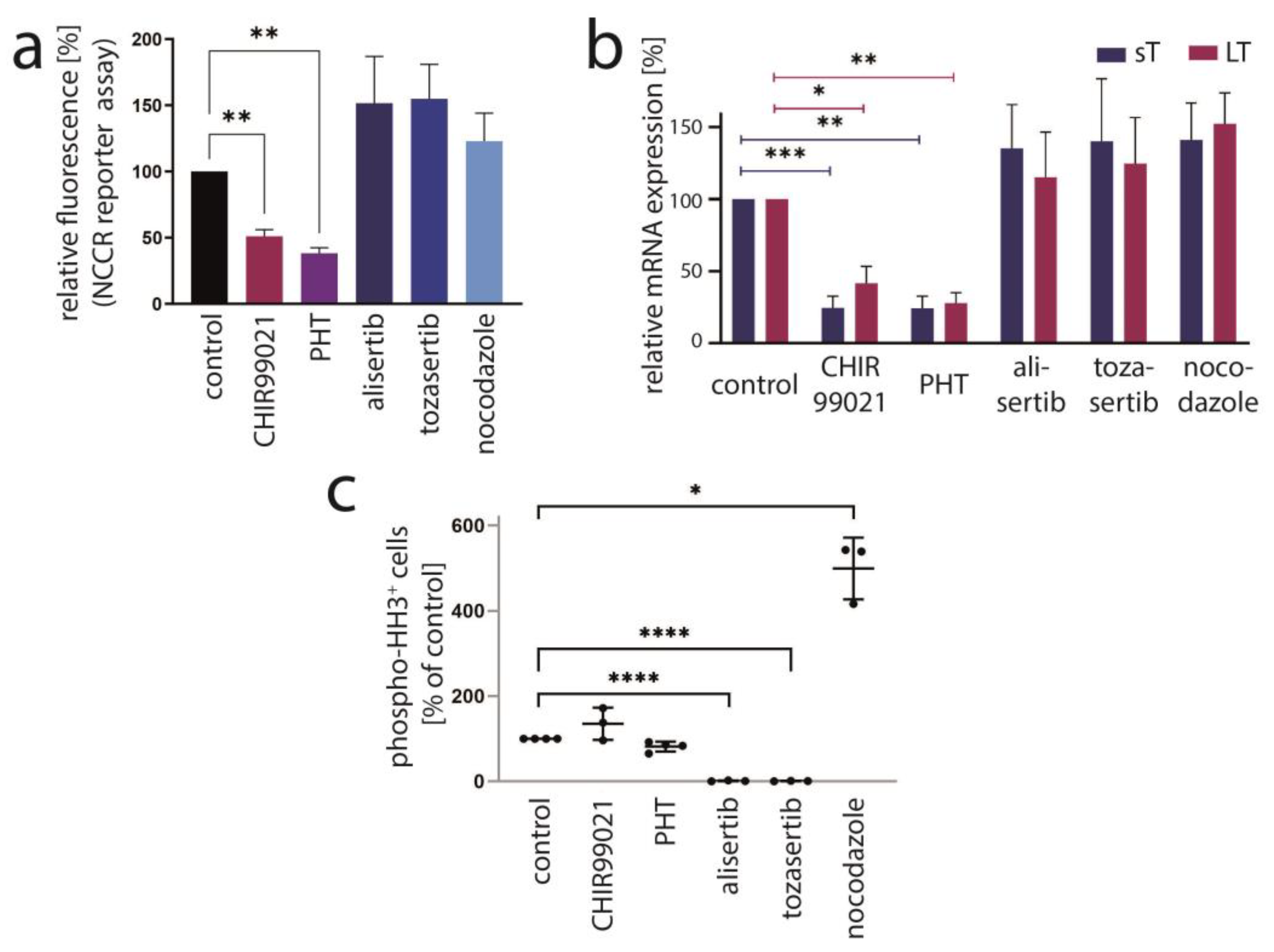
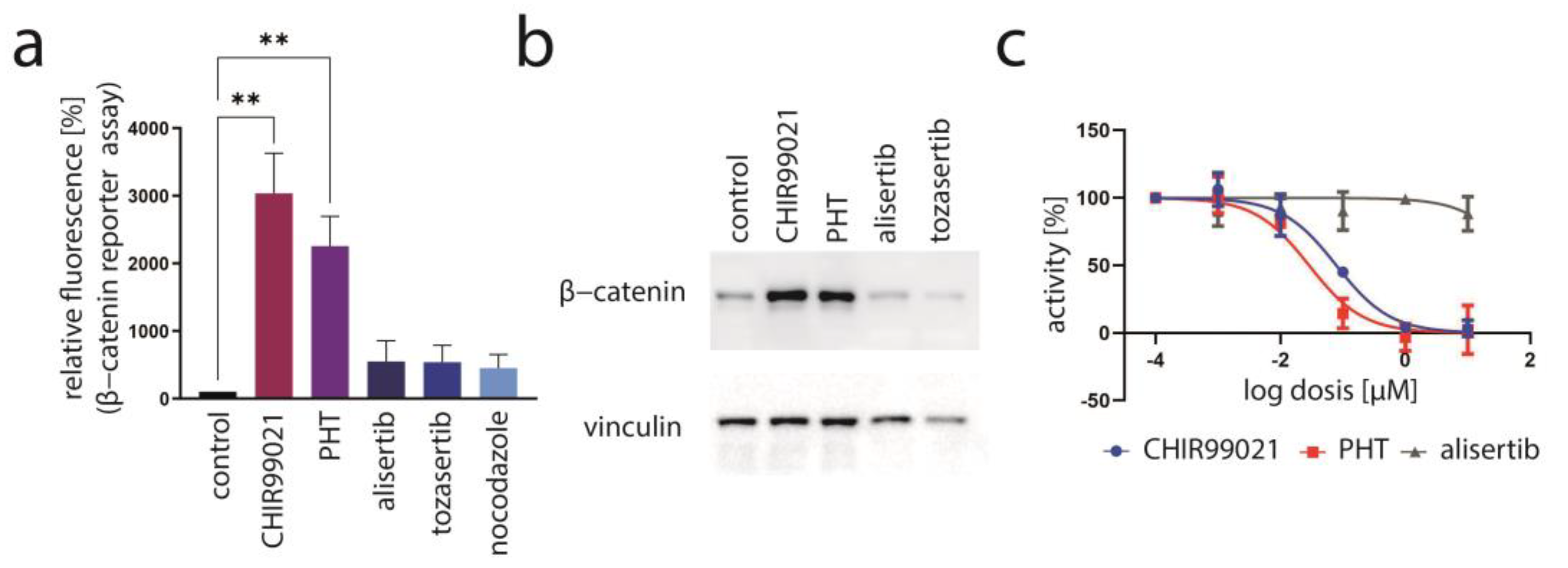
3.3. Aurora Kinase A Is Not the Crucial Target of PHT Mediating TA Repression
3.4. PHT Is a GSK3 Inhibitor
3.5. Inhibition of MCC Tumor Growth In Vivo by PHT
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller, R.W.; Rabkin, C.S. Merkel cell carcinoma and melanoma: Etiological similarities and differences. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 1999, 8, 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald, T.L.; Dennis, S.; Kachare, S.D.; Vohra, N.A.; Wong, J.H.; Zervos, E.E. Dramatic Increase in the Incidence and Mortality from Merkel Cell Carcinoma in the United States. Am. Surg. 2015, 81, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Shuda, M.; Chang, Y.; Moore, P.S. Clonal Integration of a Polyomavirus in Human Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Science 2008, 319, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nirenberg, A.; Steinman, H.; Dixon, J.; Dixon, A. Merkel cell carcinoma update: The case for two tumours. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietropaolo, V.; Prezioso, C.; Moens, U. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus and Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaegen, M.E.; Harms, P.W.; Van Goor, J.J.; Arche, J.; Patrick, M.T.; Wilbert, D.; Zabawa, H.; Grachtchouk, M.; Liu, C.J.; Hu, K.; et al. Direct cellular reprogramming enables development of viral T antigen-driven Merkel cell carcinoma in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e152069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuda, M.; Kwun, H.J.; Feng, H.C.; Chang, Y.; Moore, P.S. Human Merkel cell polyomavirus small T antigen is an oncoprotein targeting the 4E-BP1 translation regulator. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3623–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, R.; Shuda, M.; Weinkam, R.; Schrama, D.; Feng, H.; Chang, Y.; Moore, P.S.; Becker, J.C. Merkel cell polyomavirus-infected Merkel cell carcinoma cells require expression of viral T antigens. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 7064–7072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuda, M.; Feng, H.; Kwun, H.J.; Rosen, S.T.; Gjoerup, O.; Moore, P.S.; Chang, Y. T antigen mutations are a human tumor-specific signature for Merkel cell polyomavirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16272–16277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrama, D.; Sarosi, E.-M.; Adam, C.; Ritter, C.; Kaemmerer, U.; Klopocki, E.; König, E.-M.; Utikal, J.; Becker, J.C.; Houben, R. Characterization of six Merkel cell polyomavirus-positive Merkel cell carcinoma cell lines: Integration pattern suggest that large T antigen truncating events occur before or during integration. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIlroy, D.; Halary, F.; Bressollette-Bodin, C. Intra-patient viral evolution in polyomavirus-related diseases. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2019, 374, 20180301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurgeon, M.E.; Cheng, J.; Ward-Shaw, E.; Dick, F.A.; DeCaprio, J.A.; Lambert, P.F. Merkel cell polyomavirus large T antigen binding to pRb promotes skin hyperplasia and tumor development. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesbacher, S.; Pfitzer, L.; Wiedorfer, K.; Angermeyer, S.; Borst, A.; Haferkamp, S.; Scholz, C.J.; Wobser, M.; Schrama, D.; Houben, R. RB1 is the crucial target of the Merkel cell polyomavirus Large T antigen in Merkel cell carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 32956–32968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, J.C.; Stang, A.; Hausen, A.Z.; Fischer, N.; DeCaprio, J.A.; Tothill, R.W.; Lyngaa, R.; Hansen, U.K.; Ritter, C.; Nghiem, P.; et al. Epidemiology, biology and therapy of Merkel cell carcinoma: Conclusions from the EU project IMMOMEC. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2018, 67, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Park, D.E.; Berrios, C.; White, E.A.; Arora, R.; Yoon, R.; Branigan, T.; Xiao, T.; Westerling, T.; Federation, A.; et al. Merkel cell polyomavirus recruits MYCL to the EP400 complex to promote oncogenesis. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.E.; Cheng, J.; Berrios, C.; Montero, J.; Cortes-Cros, M.; Ferretti, S.; Arora, R.; Tillgren, M.L.; Gokhale, P.C.; DeCaprio, J.A. Dual inhibition of MDM2 and MDM4 in virus-positive Merkel cell carcinoma enhances the p53 response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.C.; Klaeger, S.; Le, P.M.; Korthauer, K.; Cheng, J.; Ananthapadmanabhan, V.; Frost, T.C.; Stevens, J.D.; Wong, A.Y.; Iorgulescu, J.B.; et al. Reversal of viral and epigenetic HLA class I repression in Merkel cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e151666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Jia, Y.; Shen, S.; Kim, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, E.; Brownell, I.; Cho-Vega, J.H.; Lewis, C.; Homsi, J.; et al. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Small T Antigen Activates Noncanonical NF-kappaB Signaling to Promote Tumorigenesis. Mol. Cancer Res. 2020, 18, 1623–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwun, H.-J.; Shuda, M.; Feng, H.; Camacho, C.-J.; Moore, P.-S.; Chang, Y. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Small T Antigen Controls Viral Replication and Oncoprotein Expression by Targeting the Cellular Ubiquitin Ligase SCFFbw7. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassler, N.M.; Merrill, D.; Bichakjian, C.K.; Brownell, I. Merkel Cell Carcinoma Therapeutic Update. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2016, 17, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemos, B.D.; Storer, B.E.; Iyer, J.G.; Phillips, J.L.; Bichakjian, C.K.; Fang, L.C.; Johnson, T.M.; Liegeois-Kwon, N.J.; Otley, C.C.; Paulson, K.G.; et al. Pathologic nodal evaluation improves prognostic accuracy in Merkel cell carcinoma: Analysis of 5823 cases as the basis of the first consensus staging system. J. Am. Acad. Derm. 2010, 63, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, S.; Storer, B.E.; Iyer, J.G.; Moshiri, A.; Parvathaneni, U.; Byrd, D.; Sober, A.J.; Sondak, V.K.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Nghiem, P. Adjuvant Radiation Therapy and Chemotherapy in Merkel Cell Carcinoma: Survival Analyses of 6908 Cases From the National Cancer Data Base. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 108, djw042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nghiem, P.T.; Bhatia, S.; Lipson, E.J.; Kudchadkar, R.R.; Miller, N.J.; Annamalai, L.; Berry, S.; Chartash, E.K.; Daud, A.; Fling, S.P.; et al. PD-1 Blockade with Pembrolizumab in Advanced Merkel-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2542–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, H.L.; Russell, J.; Hamid, O.; Bhatia, S.; Terheyden, P.; D’Angelo, S.P.; Shih, K.C.; Lebbe, C.; Linette, G.P.; Milella, M.; et al. Avelumab in patients with chemotherapy-refractory metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma: A multicentre, single-group, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet. Oncol. 2016, 17, 1374–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nghiem, P.; Bhatia, S.; Lipson, E.J.; Sharfman, W.H.; Kudchadkar, R.R.; Brohl, A.S.; Friedlander, P.A.; Daud, A.; Kluger, H.M.; Reddy, S.A.; et al. Durable Tumor Regression and Overall Survival in Patients With Advanced Merkel Cell Carcinoma Receiving Pembrolizumab as First-Line Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, S.P.; Russell, J.; Lebbé, C.; Chmielowski, B.; Gambichler, T.; Grob, J.-J.; Kiecker, F.; Rabinowits, G.; Terheyden, P.; Zwiener, I.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of First-line Avelumab Treatment in Patients With Stage IV Metastatic Merkel Cell Carcinoma: A Preplanned Interim Analysis of a Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, e180077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nghiem, P.; Bhatia, S.; Lipson, E.J.; Sharfman, W.H.; Kudchadkar, R.R.; Brohl, A.S.; Friedlander, P.A.; Daud, A.; Kluger, H.M.; Reddy, S.A.; et al. Three-year survival, correlates and salvage therapies in patients receiving first-line pembrolizumab for advanced Merkel cell carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prime, M.E.; Courtney, S.M.; Brookfield, F.A.; Marston, R.W.; Walker, V.; Warne, J.; Boyd, A.E.; Kairies, N.A.; von der Saal, W.; Limberg, A.; et al. Phthalazinone pyrazoles as potent, selective, and orally bioavailable inhibitors of Aurora-A kinase. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, R.; Dreher, C.; Angermeyer, S.; Borst, A.; Utikal, J.; Haferkamp, S.; Peitsch, W.K.; Schrama, D.; Hesbacher, S. Mechanisms of p53 restriction in Merkel cell carcinoma cells are independent of the Merkel cell polyoma virus T antigens. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 2453–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, S.T.; Gould, V.E.; Salwen, H.R.; Herst, C.V.; Le Beau, M.M.; Lee, I.; Bauer, K.; Marder, R.J.; Andersen, R.; Kies, M.S.; et al. Establishment and characterization of a neuroendocrine skin carcinoma cell line. Lab. Investig. J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 1987, 56, 302–312. [Google Scholar]
- Sarma, B.; Willmes, C.; Angerer, L.; Adam, C.; Becker, J.C.; Kervarrec, T.; Schrama, D.; Houben, R. Artesunate Affects T Antigen Expression and Survival of Virus-Positive Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, R.; Adam, C.; Baeurle, A.; Hesbacher, S.; Grimm, J.; Angermeyer, S.; Henzel, K.; Hauser, S.; Elling, R.; Brocker, E.B.; et al. An intact retinoblastoma protein-binding site in Merkel cell polyomavirus large T antigen is required for promoting growth of Merkel cell carcinoma cells. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, R.; Hesbacher, S.; Sarma, B.; Schulte, C.; Sarosi, E.M.; Popp, S.; Adam, C.; Kervarrec, T.; Schrama, D. Inhibition of T-antigen expression promoting glycogen synthase kinase 3 impairs merkel cell carcinoma cell growth. Cancer Lett. 2022, 524, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastrana, D.V.; Tolstov, Y.L.; Becker, J.C.; Moore, P.S.; Chang, Y.; Buck, C.B. Quantitation of human seroresponsiveness to merkel cell polyomavirus. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sells, T.B.; Chau, R.; Ecsedy, J.A.; Gershman, R.E.; Hoar, K.; Huck, J.; Janowick, D.A.; Kadambi, V.J.; LeRoy, P.J.; Stirling, M.; et al. MLN8054 and Alisertib (MLN8237): Discovery of Selective Oral Aurora A Inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyler, R.K.; Shpiro, N.; Marquez, R.; Eyers, P.A. VX-680 Inhibits Aurora A and Aurora B Kinase Activity in Human Cells. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 2846–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Parameswaran, J.; Sandoval-Schaefer, T.; Eoh, K.J.; Yang, D.-H.; Zhu, F.; Mehra, R.; Sharma, R.; Gaffney, S.G.; Perry, E.B.; et al. Combined Aurora Kinase A (AURKA) and WEE1 Inhibition Demonstrates Synergistic Antitumor Effect in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3430–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, W.; Wei, L.; Jin, J.; Tang, K.; Li, C.; Teh, B.T.; Chen, X. The effect of Aurora kinases on cell proliferation, cell cycle regulation and metastasis in renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 2139–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; He, X. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: New (and old) players and new insights. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2008, 20, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, C.; Baeurle, A.; Brodsky, J.L.; Wipf, P.; Schrama, D.; Becker, J.C.; Houben, R. The HSP70 modulator MAL3-101 inhibits Merkel cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, R.; Huang, C.; Liu, K.; Li, X.; Dong, Z. Targeting AURKA in Cancer: Molecular mechanisms and opportunities for Cancer therapy. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, P.K.; Yang, E.J.; Shi, C.; Ren, G.; Tao, S.; Shim, J.S. Aurora kinase A, a synthetic lethal target for precision cancer medicine. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 835–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.W.; Song, C.W.; Kim, D.S.; Yoon, S.; Park, H.J. Phthalazinone Pyrazole Enhances the Hepatic Functions of Human Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Hepatocyte-Like Cells via Suppression of the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Stem Cell Rev. 2018, 14, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beurel, E.; Grieco, S.F.; Jope, R.S. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3): Regulation, actions, and diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 148, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurty, R.; Maly, D.J. Biochemical mechanisms of resistance to small-molecule protein kinase inhibitors. ACS Chem. Biol. 2010, 5, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haferkamp, S.; Borst, A.; Adam, C.; Becker, T.M.; Motschenbacher, S.; Windhovel, S.; Hufnagel, A.L.; Houben, R.; Meierjohann, S. Vemurafenib induces senescence features in melanoma cells. J. Investig. Derm. 2013, 133, 1601–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, D.; Mukherjee, S.; Song, I.H.; Nimse, S.B. GSK-3 Inhibitors: A New Class of Drugs for Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment. Curr. Drug Targets 2021, 22, 1725–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muneer, A. Wnt and GSK3 Signaling Pathways in Bipolar Disorder: Clinical and Therapeutic Implications. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2017, 15, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivani, G.; Sharvirala, R.; Veerareddy, P.R.; Pal, D.; Kiran, G. GSK-3 Inhibitors as New Leads to Treat Type-II Diabetes. Curr. Drug Targets 2021, 22, 1555–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandar, C.C.; Sen, D.; Maity, A. Anti-inflammatory Potential of GSK-3 Inhibitors. Curr. Drug Targets 2021, 22, 1464–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domoto, T.; Uehara, M.; Bolidong, D.; Minamoto, T. Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β in Cancer Biology and Treatment. Cells 2020, 9, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuenzi, B.M.; Remsing Rix, L.L.; Kinose, F.; Kroeger, J.L.; Lancet, J.E.; Padron, E.; Rix, U. Off-target based drug repurposing opportunities for tivantinib in acute myeloid leukemia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Houben, R.; Alimova, P.; Sarma, B.; Hesbacher, S.; Schulte, C.; Sarosi, E.-M.; Adam, C.; Kervarrec, T.; Schrama, D. 4-[(5-Methyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)amino]-2H-phenyl-1-phthalazinone Inhibits MCPyV T Antigen Expression in Merkel Cell Carcinoma Independent of Aurora Kinase A. Cancers 2023, 15, 2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092542
Houben R, Alimova P, Sarma B, Hesbacher S, Schulte C, Sarosi E-M, Adam C, Kervarrec T, Schrama D. 4-[(5-Methyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)amino]-2H-phenyl-1-phthalazinone Inhibits MCPyV T Antigen Expression in Merkel Cell Carcinoma Independent of Aurora Kinase A. Cancers. 2023; 15(9):2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092542
Chicago/Turabian StyleHouben, Roland, Pamela Alimova, Bhavishya Sarma, Sonja Hesbacher, Carolin Schulte, Eva-Maria Sarosi, Christian Adam, Thibault Kervarrec, and David Schrama. 2023. "4-[(5-Methyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)amino]-2H-phenyl-1-phthalazinone Inhibits MCPyV T Antigen Expression in Merkel Cell Carcinoma Independent of Aurora Kinase A" Cancers 15, no. 9: 2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092542
APA StyleHouben, R., Alimova, P., Sarma, B., Hesbacher, S., Schulte, C., Sarosi, E.-M., Adam, C., Kervarrec, T., & Schrama, D. (2023). 4-[(5-Methyl-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)amino]-2H-phenyl-1-phthalazinone Inhibits MCPyV T Antigen Expression in Merkel Cell Carcinoma Independent of Aurora Kinase A. Cancers, 15(9), 2542. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092542





