Diagnostic Bioliquid Markers for Pancreatic Cancer: What We Have vs. What We Need
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Biomarkers Currently Used for PDAC in the Clinic
Reasons for the Insufficiency of Current Clinical Biomarkers for Decreasing Pancreatic Cancer Mortality
3. Newly Identified or Reported Biomarkers for Pancreatic Cancer
3.1. Diagnostic Biomarkers at Early Stages of Clinical Trails
3.2. Combination of Clinical Biomarkers
3.3. Reported Diagnostic Biomarkers That May Move to Future Clinical Trials
4. Biomarkers for Pancreatic Cancer Precursors
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bengtsson, A.; Andersson, R.; Ansari, D. The actual 5-year survivors of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma based on real-world data. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, H.E.; Gupta, S.; Kang, J.Y.; Quinn, M.J.; Maxwell, J.D.; Mudan, S.; Majeed, A. Pancreatic cancer in England and Wales 1975-2000: Patterns and trends in incidence, survival and mortality. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 23, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, E.; Grant, R.N. Cancer statistics, 1970. CA Cancer J. Clin. 1970, 20, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochefort, P.; Lardy-Cleaud, A.; Sarabi, M.; Desseigne, F.; Cattey-Javouhey, A.; de la Fouchardiere, C. Long-Term Survivors in Metastatic Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: A Retrospective and Matched Pair Analysis. Oncologist 2019, 24, 1543–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renz, B.W.; Boeck, S.; Roeder, F.; Trumm, C.; Heinemann, V.; Werner, J. Oligometastatic Disease in Pancreatic Cancer—How to Proceed? Visc. Med. 2017, 33, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts and Figures; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Takikawa, T.; Kiruta, K.; Hamada, S.; Kume, K.; Miura, S.; Yoshida, N.; Tanaka, Y.; Matsumoto, R.; Ikeda, M.; Kataoka, F.; et al. Clinical features and prognostic impact of asymptomatic pancreatic cancer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.J.; Yoon, W.; Lee, A.; Han, Y.; Byun, Y.; Kang, J.S.; Kim, H.; Kwon, W.; Suh, Y.A.; Kim, Y.; et al. Diagnostic model for pancreatic cancer using a multi-biomarker panel. Ann. Surg. Treat. Res. 2021, 100, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, A.; Ohmori, K.; Takahashi, N.; Tsuyuoka, K.; Yago, A.; Zenita, K.; Hasegawa, A.; Kannagi, R. Adhesion of human cancer cells to vascular endothelium mediated by a carbohydrate antigen, sialyl Lewis A. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1991, 179, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kang, K.N.; Shin, Y.S.; Byun, Y.; Han, Y.; Kwon, W.; Kim, C.W.; Jang, J.Y. Biomarker Panel for the Diagnosis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, D.; El-Maraghi, R.H.; Hammel, P.; Heinemann, V.; Kunzmann, V.; Sastre, J.; Scheithauer, W.; Siena, S.; Tabernero, J.; Teixeira, L.; et al. nab-Paclitaxel plus gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer: Long-term survival from a phase III trial. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107, dju413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarantis, P.; Koustas, E.; Papadimitropoulou, A.; Papavassiliou, A.G.; Karamouzis, M.V. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Treatment hurdles, tumor microenvironment and immunotherapy. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2020, 12, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahrmann, J.F.; Schmidt, C.M.; Mao, X.; Irajizad, E.; Loftus, M.; Zhang, J.; Patel, N.; Vykoukal, J.; Dennison, J.B.; Long, J.P.; et al. Lead-Time Trajectory of CA19-9 as an Anchor Marker for Pancreatic Cancer Early Detection. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1373–1383.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engle, D.D.; Tiriac, H.; Rivera, K.D.; Pommier, A.; Whalen, S.; Oni, T.E.; Alagesan, B.; Lee, E.J.; Yao, M.A.; Lucito, M.S.; et al. The glycanCA19-9 promotes pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer in mice. Science 2019, 364, 1156–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Liu, C.; Guo, M.; Cheng, H.; Lu, Y.; Jin, K.; Liu, L.; Long, J.; Xu, J.; Lu, R.; et al. Potential Biomarkers in Lewis Negative Patients With Pancreatic Cancer. Ann. Surg. 2017, 265, 800–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Deng, S.; Jin, K.; Gong, Y.; Cheng, H.; Fan, Z.; Qian, Y.; Huang, Q.; Ni, Q.; Luo, G.; et al. Lewis antigen-negative pancreatic cancer: An aggressive subgroup. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 56, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Sokoll, L.J.; Pasay, J.J.; Rubin, A.L.; Li, H.; Bach, D.M.; Chan, D.W.; Zhang, Z. Identification of Serum Biomarker Panels for the Early Detection of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019, 28, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, A.Z.; Mulhollad, E.J.; Cole, G.; McCarthy, H.O. MicroRNAs in Pancreatic Cancer: Biomarkers, prognostic, and therapeutic modulators. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
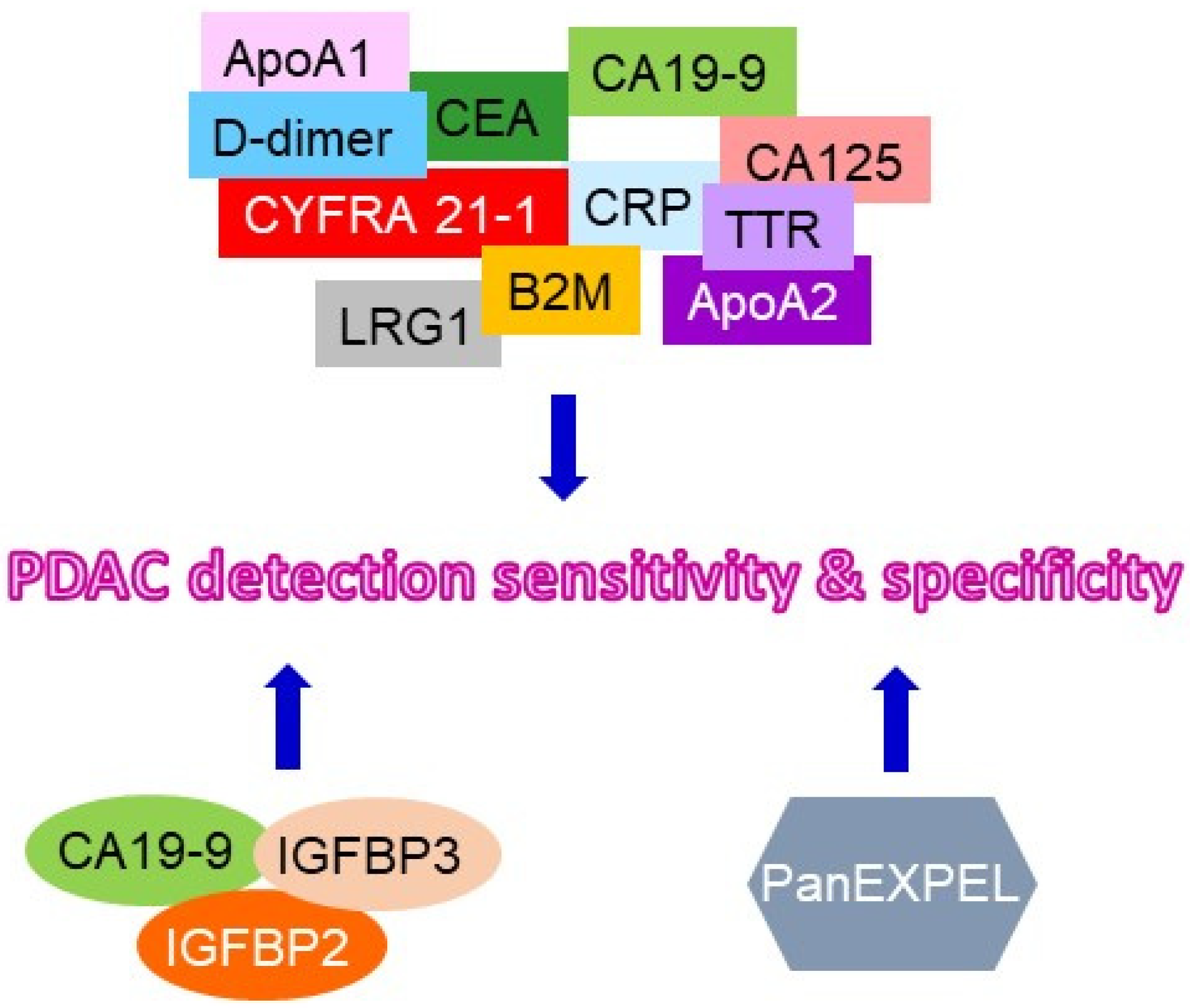
- Yoneyama, T.; Ohtsuki, S.; Honda, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Iwasaki, M.; Uchida, Y.; Okusaka, T.; Nakamori, S.; Shimahara, M.; Ueno, T.; et al. Identification of IGFBP2 and IGFBP3 As Compensatory Biomarkers for CA19-9 in Early-Stage Pancreatic Cancer Using a Combination of Antibody-Based and LC-MS/MS-Based Proteomics. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Z.; Liu, D.; Zhao, Y.X.; Wang, H.T.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Y. Diagnostic performance of serum macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 in pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis and meta-regression analysis. DNA Cell Biol. 2014, 33, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagayoshi, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Matsuoka, K.; Ohtsuka, T.; Mori, Y.; Kono, H.; Aso, T.; Ideno, N.; Takahata, S.; Ryo, A.; et al. Profiling of autoantibodies in sera of pancreatic cancer patients. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21 (Suppl. 3), S459–S465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Abraham, S.; McKenzie, J.A.G.; Jeffs, N.; Swire, M.; Tripathi, V.B.; Luhmann, U.F.O.; Lange, C.A.K.; Zhai, Z.; Arthur, H.M.; et al. LRG1 promotes angiogenesis by modulating endothelial TGF-β signalling. Nature 2013, 499, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leisner, T.M.; Freeman, T.C.; Black, J.L.; Parise, L.V. CIB1: A small protein with big ambitions. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 2640–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, M.U.; Naik, U.P. Calcium- and integrin-binding protein 1 regulates microtubule organization and centrosome segregation through polo like kinase 3 during cell cycle progression. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 43, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Peng, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, H.; Lu, C.; Liu, L.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y. The Emerging Roles of CIB1 in Cancer. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godmann, M.; Lambrot, R.; Kimmins, S. The dynamic epigenetic program in male germ cells: Its role in spermatogenesis, testis cancer, and its response to the environment. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2009, 72, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.M.; Song, M.H.; Kim, M.J.; Daudi, S.; Miliotto, A.; Old, L.; Odunsi, K.; Lee, S.Y. A novel cancer/testis antigen KP-OVA-52 identified by SEREX in human ovarian cancer is regulated by DNA methylation. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankratz, N.; Beecham, G.W.; DeStefano, A.L.; Dawson, T.M.; Doheny, K.F.; Factor, S.A.; Hamza, T.H.; Hung, A.Y.; Hyman, B.T.; Ivinson, A.J.; et al. Meta-analysis of Parkinson’s disease: Identification of a novel locus, RIT2. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Tian, H.; Qi, J.; Li, M.; Fu, C.; We, F.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, D.; Zhao, W.; et al. Macrophage inhibitory cytokine 1 (MIC-1/GDF15) as a novel diagnostic serum biomarker in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Pan, B.; Song, F.; Ma, J.; Zeraatkar, D.; Zhou, J.; Tian, J. Comparing the diagnostic accuracy of five common tumour biomarkers and CA19-9 for pancreatic cancer: A protocol for a network meta-analysis of diagnostic test accuracy. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e018175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Bamlet, W.R.; Oberg, A.L.; Chaffee, K.G.; Donahue, G.; Cao, X.J.; Chari, S.; Garcia, B.A.; Petersen, G.M.; Zaret, K.S. Detection of early pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with thrombospondin-2 and CA19-9 blood markers. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaah5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souche, R.; Tosato, G.; Riviere, B.; Valats, J.C.; Debourdeau, A.; Flori, N.; Pourquier, D.; Fabre, J.M.; Assenat, E.; Colinge, J.; et al. Detection of soluble biomarkers of pancreatic cancer in endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration samples. Endoscopy 2022, 54, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, S.A.; Luecke, L.B.; Kahlert, C.; Fernandez, A.F.; Gammon, S.T.; Kaye, J.; LeBleu, V.S.; Mittendorf, E.A.; Weitz, J.; Rahbari, N.; et al. Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer. Nature 2015, 523, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, S.; Sadakari, Y.; Ohtsuka, T.; Okayama, T.; Nakashima, Y.; Gotoh, Y.; Saeki, K.; Mori, Y.; Nakata, K.; Miyasaka, Y.; et al. Pancreatic Juice Exosomal MicroRNAs as Biomarkers for Detection of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 2104–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, K.; Lin, Q.; Li, L.; Bai, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, H.; Kong, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, H.; He, F.; et al. Prometastatic secretome trafficking via exosomes initiates pancreatic cancer pulmonary metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2020, 481, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, K.E.; Zeleniak, A.E.; Fishel, M.L.; Wu, J.; Littlepage, L.E.; Hill, R. Cancer-associated fibroblast exosomes regulate survival and proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogene 2017, 36, 1770–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Hernandez, J.M.; Doussot, A.; Bojmar, L.; Zambirinis, C.P.; Costa-Silva, B.; van Beek, E.J.A.H.; Mark, M.T.; Molina, H.; Askan, G.; et al. Extracellular matrix proteins and carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecules characterize pancreatic duct fluid exosomes in patients with pancreatic cancer. HPB 2018, 20, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Wang, M.; McElyea, S.D.; Sherman, S.; House, M.; Korc, M. A microRNA signature in circulating exosomes is superior to exosomal glypican-1 levels for diagnosing pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017, 393, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Liu, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, L.; Dong, Z. Downregulation of miR-124 predicts poor prognosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 73, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimori, M.; Sugimori, K.; Tsuchiya, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Tsuyuki, S.; Kaneta, Y.; Hirotani, A.; Sanga, K.; Tozuka, Y.; Komiyama, S.; et al. Quantitative monitoring of circulating tumor DNA in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer undergoing chemotherapy. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guven, D.C.; Sahin, T.K.; Yildirim, H.C.; Aktepe, O.H.; Dizdar, O.; Yalcin, S. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) and prognosis in pancreatic cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2021, 168, 103528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrasz, D.; Wang-Renault, S.; Taieb, J.; Dahan, L.; Postel, M.; Durand-Labrunie, J.; Le Malicot, K.; Mulot, C.; Rinaldi, Y.; Phelip, J.M.; et al. Prognostic value of circulating tumour DNA in metastatic pancreatic cancer patients: Post-hoc analyses of two clinical trials. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 126, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.D.; Javed, A.A.; Thoburn, C.; Wong, F.; Tie, J.; Gibbs, P.; Schmidt, C.M.; Yip-Schneider, M.T.; Allen, P.J.; Schattner, M.; et al. Combined circulating tumor DNA and protein biomarkers-based liquid biopsy for the earlier detection of pancreatic cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10202–10207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, G.D.; Ning, Y.; Ku, C.J.; Phillips, T.; McCarthy, E.; Ellison, C.K.; Bergamaschi, A.; Collin, F.; Lioyd, P.; Scott, A.; et al. Detection of early stage pancreatic cancer using 5-hydroxymethylcytosine signatures in circulating cell free DNA. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.A.; Rashid, S.; Singh, N.; Rashid, S.; Singh, V.; Gunjan, D.; Das, P.; Dash, N.R.; Pandey, R.M.; Chauhan, S.S.; et al. Panel of serum miRNAs as potential non-invasive biomarkers for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, D.K.; Korc, M.; Petersen, G.M.; Eibl, G.; Li, D.; Rickels, M.R.; Chari, S.T.; Abbruzzese, J.L. Diabetes, Pancreatogenic Diabetes, and Pancreatic Cancer. Diabetes 2017, 66, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, A.E.; Hernandez, Y.G.; Frucht, H.; Lucas, A.L. Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: Risk factors, screening, and early detection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 11182–11198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahn, S.; Zimmermann, V.; Viol, F.; Knaack, H.; Stemmer, K.; Peters, L.; Lenk, L.; Ungefroren, H.; Saur, D.; Schaefer, H.; et al. Diabetes as risk factor for pancreatic cancer: Hyperglycemia promotes epithelial-mesenchymal-transition and stem cell properties in pancreatic ductal epithelial cells. Cancer Lett. 2018, 415, 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimondi, S.; Lowenfels, A.B.; Morselli-Labate, A.M.; Maisonneuve, P.; Pezzilli, R. Pancreatic cancer in chronic pancreatitis; aetiology, incidence, and early detection. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 24, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimondi, S.; Maisonneuve, P.; Lowenfels, A.B. Epidemiology of pancreatic cancer: An overview. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 6, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schawkat, K.; Manning, M.A.; Glickman, J.N.; Mortele, K.J. Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarinoma and Its Variants: Pearls and Perils. Radiographics 2020, 40, 1219–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazio, E.N.; Young, C.C.; Toma, J.; Levy, M.; Berger, K.R.; Johnson, C.L.; Mehmood, R.; Swan, P.; Chu, A.; Cregan, S.P.; et al. Activating transcription factor 3 promotes loss of the acinar cell phenotype in response to cerulein-induced pancreatitis in mice. Mol. Biol. Cell 2017, 28, 2347–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Lahmy, R.; Riha, C.; Yang, C.; Jakubison, B.L.; van Niekerk, J.; Staub, C.; Wu, Y.; Gates, K.; Dong, D.S.; et al. The basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor E47 reprograms human pancreatic cancer cells to a quiescent acinar state with reduced tumorigenic potential. Pancreas 2015, 44, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, W.; Zilch, O.; Koska, C.; Lindinger, G.; Deecke, L. Negative cortical DC shifts preceding and accompanying simple and complex sequential movements. Exp. Brain. Res. 1989, 74, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prevot, P.P.; Simion, A.; Girmont, A.; Colletti, M.; Khalaileh, A.; Van den Steen, G.; Sempoux, C.; Xu, X.; Roelants, V.; Hald, J.; et al. Role of the ductal transcription factors HNF6 and Sox9 in pancreatic acinar-to-ductal metaplasia. Gut 2012, 61, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaik, A.P.; Jamil, K. A study on the ALAD gene polymorphisms associated with lead exposure. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2008, 24, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, G.Y.; Doeppler, H.; Necela, B.; Krishna, M.; Crawford, H.C.; Raimondo, M.; Storz, P. Macrophage-secreted cytokines drive pancreatic acinar-to-ductal metaplasia through NF-kappaB and MMPs. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 202, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Zogopoulos, G.; Shao, Q.; Dong, K.; Lv, F.; Nwilati, K.; Gui, X.Y.; Cuggia, A.; Liu, J.L.; et al. Reg proteins promote acinar-to-ductal metaplasia and act as novel diagnostic and prognostic markers in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 77838–77853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, G.Y.; Doeppler, H.; Necela, B.; Endenfield, B.; Zhang, L.; Dawson, D.W.; Storz, P. Mutant KRAS-induced expression of ICAM-1 in pancreatic acinar cells causes attraction of macrophages to expedite the formation of precancerous lesions. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.H.; Jung, K.H.; Lee, J.E.; Son, M.K.; Fang, Z.; Park, J.H.; Kim, S.J.; Lim, J.H.; Hong, S.S. ANGPTL4 accelerates KRAS(G12D)-Induced acinar to ductal metaplasia and pancreatic carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2021, 519, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koliwad, S.K.; Gray, N.E.; Wang, J.C. Angiopoietin-like 4 (Angptl4): A glucocorticoid-dependent gatekeeper of fatty acid flux during fasting. Adipocyte 2012, 1, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makohon-Moore, A.P.; Matsukuma, K.; Zhang, M.; Reiter, J.G.; Gerold, J.M.; Jiao, Y.; Sikkema, L.; Attiyeh, M.A.; Yachida, S.; Sandone, C.; et al. Precancerous neoplastic cells can move through the pancreatic ductal system. Nature 2018, 561, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, H.N.; Jun, S.; Oh, A.Y.; Srivastava, M.; Lee, S.; Taniguchi, C.M.; Zhang, S.; Lee, W.S.; Chen, J.; Park, B.J.; et al. Identification of KIAA1199 as a Biomarker for Pancreatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.S.; Ciprani, D.; O’Shea, A.; Liss, A.S.; Yang, R.; Fletcher-Mercaldo, S.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Fernandez-Del Castillo, C.; Weissleder, R. Extracellular Vesicle Analysis Allows for Identification of Invasive IPMN. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1345–1358.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Biomarkers | FDA Approval | Disease | Specificity | Sensitivity | Fluid Type | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA19-9 | Yes | Pancreatic Cancer (Symptomatic) | 79% | 80% | Blood/serum | [12] |
| CA19-9 | Yes | Pancreatic Cancer (Asymptomatic) | ND* | 13% | Blood/serum | [9,12,14] |
| CA19-9 | Yes | PDAC (Symptomatic) | ND* | 43% | Blood/serum | [18,21] |
| CA125 + CEA | No | PDAC | ND* | 74% | Blood/serum | [16] |
| CA125 | No | PDAC | ND* | 51% | Blood/serum | [16] |
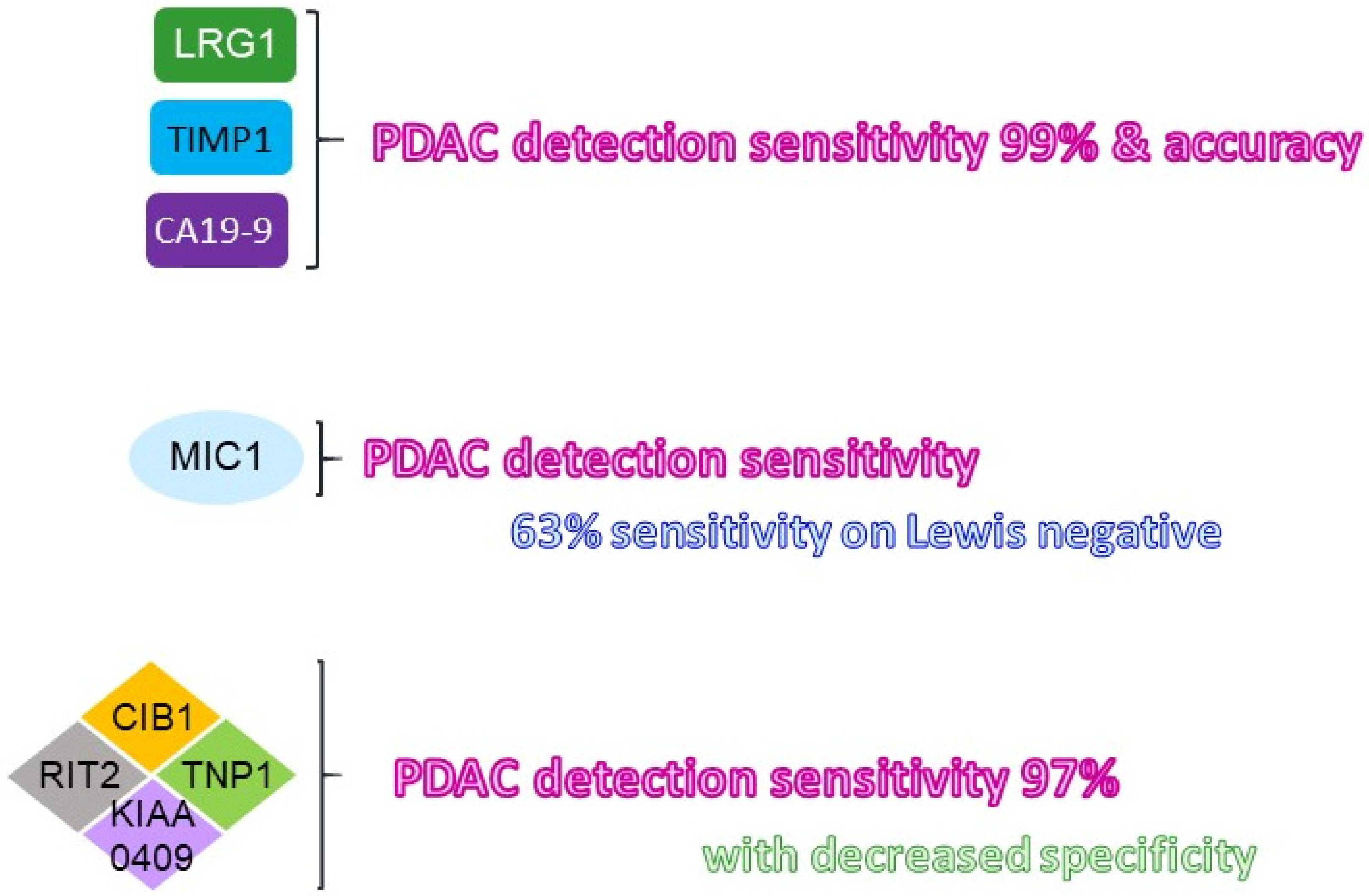
| LRG1 + TIMP1 + CA19-9 | No | PDAC | >99% | ND* | Blood/serum | [14] |
| KIAA0409 + RIT2 + TNP1 + CIB1 | No | PDAC | 35% | 97% | Blood/serum | [22] |
| CIB1 | No | PDAC | 70% | 76% | Blood/serum | [22] |
| MIC-1 | No | PDAC (Symptomatic) | ND* | 65% | Blood/serum | [18,21] |
| MIC-1 | No | PDAC (Asymptomatic) | ND* | 63% | Blood/serum | [21] |
| MIC-1 + CA19-9 | No | PDAC | ND* | 78% | Blood/serum | [30] |
| ApoA1 + CA-125 + CA19-9 + CEA + CA19-9 + D-Dimer + CYFRA 21-1 + TTR + ApoA2 + B2M + LRG1 | No | PDAC | ND* | ND* | Blood/plasma | [11] |
| Circulating tumor DNA: Kras mutation + CA19-9 + CEA + HGF + OPN | No | PDAC | ND* | 64% | Blood/plasma | [44] |
| Kras mutation + 5 hydroxymethylcytosine modification in GATA4, GATA6, YAP1, TEAD1 | No | PDAC | ND* | ND* | Blood/plasma | [45] |
| Circulating tumor cells | No | PDAC | ND* | ND* | Blood/serum | [34,35,36] |
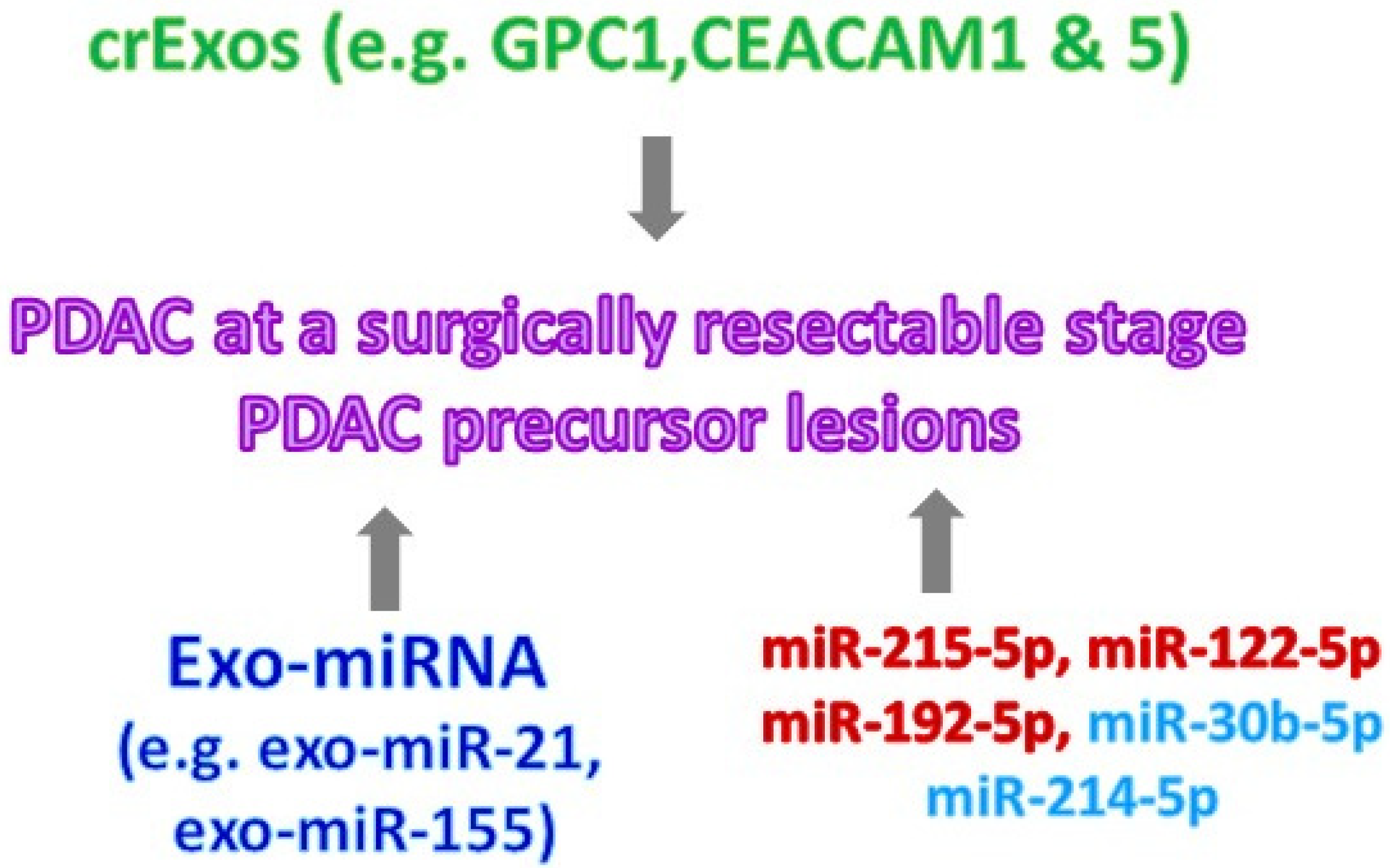
| Circulating tumor RNA: miR-215-5p, miR-122-5p, miR-192-5p, miR-181a-2-3p, miR-30b-5p, miR-216b-5p, miR-320b and miR-214-5p | No | PDAC and its precursor lesions | ND* | ND* | Blood/serum | [41] |
| Cancer exosomes: GPC1 and Exo-miRNA | No | PDAC and its precursor lesions | ND* | ND* | Pancreatic juice | [35] |
| CEACAM1 and 5 | PDAC and its precursor lesions | ND* | ND* | Pancreatic juice | [38] | |
| Migratory PanIN cells | No | PDAC precursor lesions | ND* | ND* | NA# | [58] |
| TNF | No | Early event to initiate PDAC | ND* | ND* | NA | [53,55] |
| RANTES | No | Early event to initiate PDAC | ND* | ND* | NA | [53,55] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liou, G.-Y.; Byrd, C.J. Diagnostic Bioliquid Markers for Pancreatic Cancer: What We Have vs. What We Need. Cancers 2023, 15, 2446. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092446
Liou G-Y, Byrd CJ. Diagnostic Bioliquid Markers for Pancreatic Cancer: What We Have vs. What We Need. Cancers. 2023; 15(9):2446. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092446
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiou, Geou-Yarh, and Crystal J. Byrd. 2023. "Diagnostic Bioliquid Markers for Pancreatic Cancer: What We Have vs. What We Need" Cancers 15, no. 9: 2446. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092446
APA StyleLiou, G.-Y., & Byrd, C. J. (2023). Diagnostic Bioliquid Markers for Pancreatic Cancer: What We Have vs. What We Need. Cancers, 15(9), 2446. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092446







