Artificial Intelligence in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pancreatic Cystic Lesions and Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
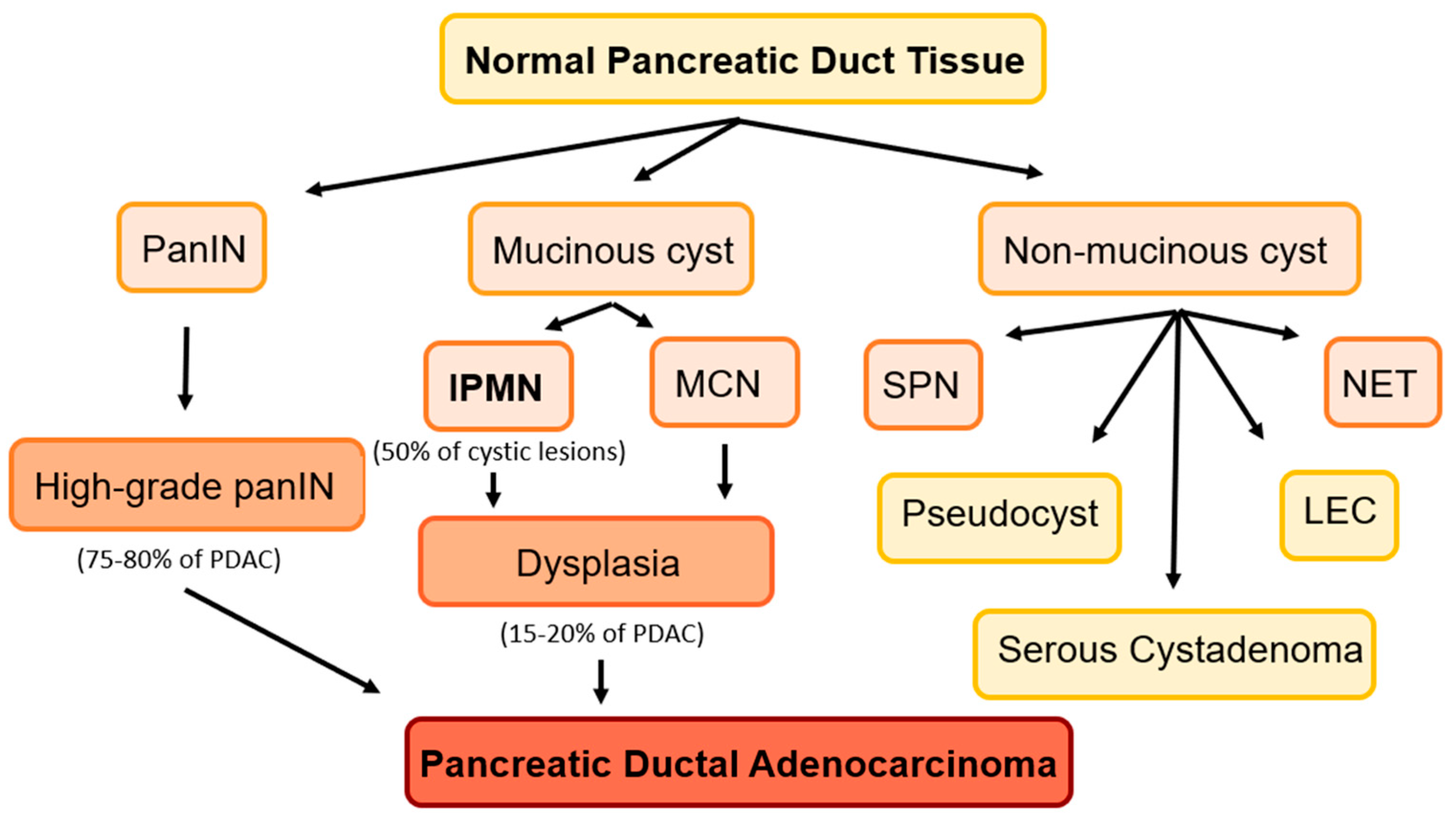
1. Introduction
1.1. Challenges in Predicting Progression to PDAC
1.2. Artificial Intelligence
2. Methods
3. Results
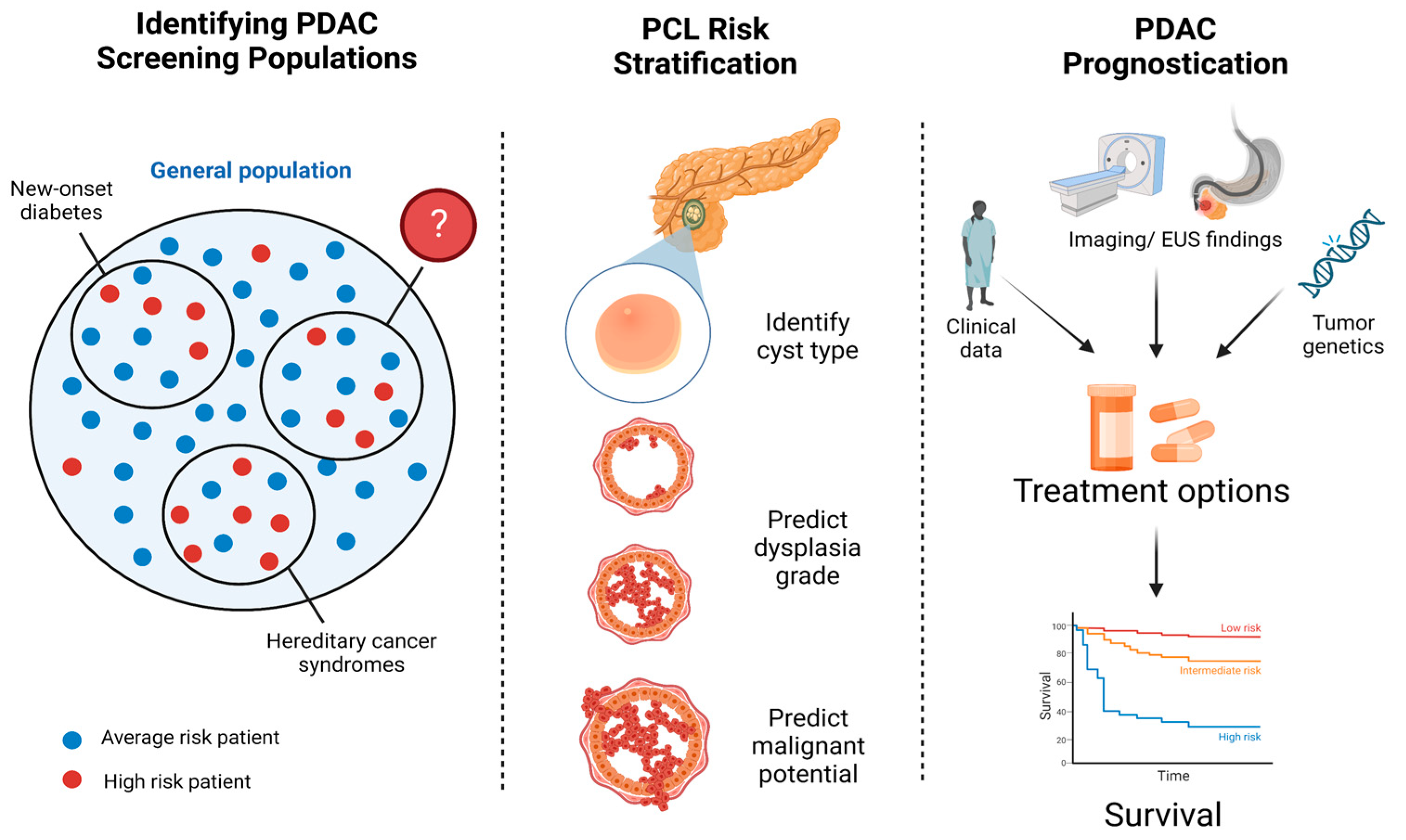
3.1. Developing a Screening Strategy
3.1.1. Models Incorporating Clinical Data
3.1.2. Models Incorporating Genomics and Radiomics
3.2. Detection and Risk Stratification of Pancreatic Cystic Lesions
3.2.1. Cross-Sectional Imaging in IPMNs
3.2.2. Cross-Sectional Imaging in PCLs
3.2.3. EUS-Guided Diagnostics
| Study | Sample Size | Model | Task | Accuracy | Comparisons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schultz, 2022 [23] | 43 | CNN | Low- vs. high-grade IPMN dysplasia | Accuracy 99.6% | Higher accuracy than AGA, ACG, Fukuoka guidelines |
| Kuwahara, 2019 [62] | 50 | Deep learning | Evaluate malignant potential in IPMN images | Sensitivity 95.7%, Specificity 96.2%, Accuracy 94.0% | Human interpretation, 56% accuracy |
| Nguon, 2021 [63] | 109 | CNN | Differentiate between MCNs and SCAs | Accuracy 83% | |
| Machicado, 2021 [76] | 35 | CNN | Low- vs. high-grade BD-IPMN dysplasia | Accuracy 82% | Higher accuracy than AGA and Fukuoka guidelines |
3.2.4. Limitations and Future Directions
3.2.5. Radiomics in Detection of PDAC
3.3. AI in Pancreatic Cancer Prognostication
3.3.1. Treatment Selection
3.3.2. Survival Prediction
4. Discussion
Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahib, L.; Smith, B.D.; Aizenberg, R.; Rosenzweig, A.B.; Fleshman, J.M.; Matrisian, L.M. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: The unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2913–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckler, M.; Michalski, C.W.; Schaefle, S.; Kaiser, J.; Büchler, M.W.; Hackert, T. The Sendai and Fukuoka consensus criteria for the management of branch duct IPMN-A meta-analysis on their accuracy. Pancreatology 2017, 17, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagami, R.; Sato, T.; Mizukami, K.; Motomura, M.; Okamoto, K.; Fukuchi, S.; Otsuka, Y.; Abe, T.; Ono, H.; Mori, K.; et al. Diagnostic Strategy of Early Stage Pancreatic Cancer via Clinical Predictor Assessment: Clinical Indicators, Risk Factors and Imaging Findings. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, F.; Davis, A.M.; Chapman, C.G. Pancreatic Cysts-An Overview and Summary of Society Guidelines, 2021. JAMA 2021, 325, 391–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Fernandez-Del Castillo, C.; Kamisawa, T.; Jang, J.Y.; Levy, P.; Ohtsuka, T.; Salvia, R.; Shimizu, Y.; Tada, M.; Wolfgang, C.L. Revisions of international consensus Fukuoka guidelines for the management of IPMN of the pancreas. Pancreatology 2017, 17, 738–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrejevic-Blant, S.; Kosmahl, M.; Sipos, B.; Kloppel, G. Pancreatic intraductal papillary-mucinous neoplasms: A new and evolving entity. Virchows Arch. 2007, 451, 863–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jais, B.; Rebours, V.; Malleo, G.; Salvia, R.; Fontana, M.; Maggino, L.; Bassi, C.; Manfredi, R.; Moran, R.; Lennon, A.M.; et al. Serous cystic neoplasm of the pancreas: A multinational study of 2622 patients under the auspices of the International Association of Pancreatology and European Pancreatic Club (European Study Group on Cystic Tumors of the Pancreas). Gut 2016, 65, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerboni, G.; Signoretti, M.; Crippa, S.; Falconi, M.; Arcidiacono, P.G.; Capurso, G. Systematic review and meta-analysis: Prevalence of incidentally detected pancreatic cystic lesions in asymptomatic individuals. Pancreatology 2019, 19, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacevic, B.; Klausen, P.; Rift, C.V.; Toxværd, A.; Grossjohann, H.; Karstensen, J.G.; Brink, L.; Hassan, H.; Kalaitzakis, E.; Storkholm, J. Clinical impact of endoscopic ultrasound-guided through-the-needle microbiopsy in patients with pancreatic cysts. Endoscopy 2021, 53, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, R.; Thosani, N.; Annangi, S.; Guha, S.; Bhutani, M.S. Diagnostic yield of EUS-FNA-based cytology distinguishing malignant and benign IPMNs: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pancreatology 2014, 14, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsangkar, N.P.; Morales-Oyarvide, V.; Thayer, S.P.; Ferrone, C.R.; Wargo, J.A.; Warshaw, A.L.; Fernandez-del Castillo, C. 851 resected cystic tumors of the pancreas: A 33-year experience at the Massachusetts General Hospital. Surgery 2012, 152, S4–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaujoux, S.; Brennan, M.F.; Gonen, M.; D’Angelica, M.I.; DeMatteo, R.; Fong, Y.; Schattner, M.; DiMaio, C.; Janakos, M.; Jarnagin, W.R.; et al. Cystic lesions of the pancreas: Changes in the presentation and management of 1,424 patients at a single institution over a 15-year time period. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2011, 212, 590–600, discussion 600–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiman, J.M.; Hwang, J.H.; Moayyedi, P. American gastroenterological association technical review on the diagnosis and management of asymptomatic neoplastic pancreatic cysts. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 824–848.e822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahora, K.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Brugge, W.; Thayer, S.P.; Ferrone, C.R.; Sahani, D.; Pitman, M.B.; Warshaw, A.L.; Lillemoe, K.D.; Fernandez-del Castillo, C.F. Branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: Does cyst size change the tip of the scale? A critical analysis of the revised international consensus guidelines in a large single-institutional series. Ann. Surg. 2013, 258, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharib, J.M.; Fonseca, A.L.; Swords, D.S.; Jaradeh, K.; Bracci, P.M.; Firpo, M.A.; Hatcher, S.; Scaife, C.L.; Wang, H.; Kim, G.E. Surgical overtreatment of pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: Do the 2017 International Consensus Guidelines improve clinical decision making? Surgery 2018, 164, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchegiani, G.; Pollini, T.; Andrianello, S.; Tomasoni, G.; Biancotto, M.; Javed, A.A.; Kinny-Köster, B.; Amini, N.; Han, Y.; Kim, H. Progression vs cyst stability of branch-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms after observation and surgery. JAMA Surg. 2021, 156, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas as the main focus for early detection of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 2018, 47, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, D.; Heilmaier, M.; Phillip, V.; Treiber, M.; Mayr, U.; Lahmer, T.; Mueller, J.; Demir, I.E.; Friess, H.; Reichert, M.; et al. Accurate prediction of histological grading of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasia using deep learning. Endoscopy 2023. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, S.; Jin, Y.; Zhou, L.; Sun, S.; Xu, X.; Li, S.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y. Assessment of performance of the machine learning-based breast cancer risk prediction models: A systematic review. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2022, 8, e35750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDowell, A.; Kang, J.; Yang, J.; Jung, J.; Oh, Y.M.; Kym, S.M.; Shin, T.S.; Kim, T.B.; Jee, Y.K.; Kim, Y.K. Machine-learning algorithms for asthma, COPD, and lung cancer risk assessment using circulating microbial extracellular vesicle data and their application to assess dietary effects. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 1586–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzano, L.; Darwich, A.S.; Tendler, S.; Dan, A.; Lewensohn, R.; De Petris, L.; Raghothama, J.; Meijer, S. A novel analytical framework for risk stratification of real-world data using machine learning: A small cell lung cancer study. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2022, 15, 2437–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, L.A.; Chazard, E.; Poncelet, E.; Serb, T.; Rusu, A.; Pauwels, X.; Parsy, C.; Poclet, T.; Cauliez, H.; Engelaere, C.; et al. Impact of artificial intelligence in breast cancer screening with mammography. Breast Cancer 2022, 29, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Shen, G.; Zhou, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Ma, X. Artificial Intelligence in Cervical Cancer Screening and Diagnosis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 851367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritzen, A.D.; Rodriguez-Ruiz, A.; von Euler-Chelpin, M.C.; Lynge, E.; Vejborg, I.; Nielsen, M.; Karssemeijer, N.; Lillholm, M. An Artificial Intelligence-based Mammography Screening Protocol for Breast Cancer: Outcome and Radiologist Workload. Radiology 2022, 304, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Tang, R.S.Y.; Lam, T.Y.T.; Zhao, G.; Lau, J.Y.W.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Rong, L.; Xu, W.; Li, X.; et al. Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Colonoscopy for Colorectal Cancer Screening: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegelmayer, S.; Graf, M.; Makowski, M.; Gawlitza, J.; Gassert, F. Cost-Effectiveness of Artificial Intelligence Support in Computed Tomography-Based Lung Cancer Screening. Cancers 2022, 14, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, H.; Pamarthy, R.; Vallabhaneni, M.; Sarfraz, S.; Ali, H.; Rafique, H. Pancreatic cancer incidence trends in the United States from 2000–2017: Analysis of Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) database. F1000Res 2021, 10, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Domchek, S.M.; Kochman, M.L.; Katona, B.W. Reaching beyond family history as inclusion criteria for pancreatic cancer surveillance in high-risk populations. Genes Cancer 2022, 13, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuigan, A.; Kelly, P.; Turkington, R.C.; Jones, C.; Coleman, H.G.; McCain, R.S. Pancreatic cancer: A review of clinical diagnosis, epidemiology, treatment and outcomes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 4846–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirkus, J.; Ead, A.S.; Mackenzie, G.G. Impact of dietary fat composition and quantity in pancreatic carcinogenesis: Recent advances and controversies. Nutr. Res. 2021, 88, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, A.; Goldstein, J.; Margalit, O.; Shacham-Shmueli, E.; Lawrence, Y.R.; Yang, Y.X.; Reiss, K.A.; Golan, T.; Mamtani, R.; Halpern, N.; et al. Assessing the effects of beta-blockers on pancreatic cancer risk: A nested case-control study. Pharm. Drug Saf. 2020, 29, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panthangi, V.; Cyril Kurupp, A.R.; Raju, A.; Luthra, G.; Shahbaz, M.; Almatooq, H.; Foucambert, P.; Esbrand, F.D.; Zafar, S.; Khan, S. Association Between Helicobacter pylori Infection and the Risk of Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review Based on Observational Studies. Cureus 2022, 14, e28543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canto, M.I.; Hruban, R.H.; Fishman, E.K.; Kamel, I.R.; Schulick, R.; Zhang, Z.; Topazian, M.; Takahashi, N.; Fletcher, J.; Petersen, G.; et al. Frequent detection of pancreatic lesions in asymptomatic high-risk individuals. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 796–804, quiz e714-795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, A.; Rachet, B.; Bonaventure, A.; Pereira, S.P.; Woods, L.M. Can we screen for pancreatic cancer? Identifying a sub-population of patients at high risk of subsequent diagnosis using machine learning techniques applied to primary care data. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0251876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulin, K.; Gastaldi, G.; Serratrice, J.; Baroz, F. [Diabetes and pancreatic cancer—When diabetes indicates a pancreatic cancer]. Rev. Med. Suisse 2022, 18, 1994–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, N.; Wang, Z.; Liu, C. Hyperglycemia Promotes Pancreatic Cancer Initiation and Progression by Activating the Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 2592–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Z.; Zong, L.; Ma, Q. Hyperglycemia Promotes the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Pancreatic Cancer via Hydrogen Peroxide. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 5190314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Hu, Y.; Scelo, G.; Myrskyla, M.; Martikainen, P. Pre-existing psychological disorders, diabetes, and pancreatic cancer: A population-based study of 38,952 Finns. Cancer Epidemiol. 2022, 82, 102307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, R.P.; Nagpal, S.J.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Chari, S.T. New insights into pancreatic cancer-induced paraneoplastic diabetes. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kandlakunta, H.; Nagpal, S.J.S.; Feng, Z.; Hoos, W.; Petersen, G.M.; Chari, S.T. Model to Determine Risk of Pancreatic Cancer in Patients With New-Onset Diabetes. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 730–739.E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Butler, R.K.; Lustigova, E.; Chari, S.T.; Maitra, A.; Rinaudo, J.A.; Wu, B.U. Risk Prediction of Pancreatic Cancer in Patients With Recent-onset Hyperglycemia: A Machine-learning Approach. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2023, 57, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.F.; Ye, Z.; Qin, Y.; Xu, X.W.; Yu, X.J.; Zhuo, Q.F.; Ji, S.R. Mutations in key driver genes of pancreatic cancer: Molecularly targeted therapies and other clinical implications. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2021, 42, 1725–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, A.P.; Wolpin, B.M.; Risch, H.A.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.Z.; Mocci, E.; Zhang, M.; Canzian, F.; Childs, E.J.; Hoskins, J.W.; Jermusyk, A.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies five new susceptibility loci for pancreatic cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.Y.; Chen, H.T.; Na, R.; Jiang, D.K.; Lin, X.L.; Yang, F.; Jin, C.; Fu, D.L.; Xu, J.F. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms based genetic risk score in the prediction of pancreatic cancer risk. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 3076–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, A.P.; Lindstrom, S.; Mendelsohn, J.B.; Steplowski, E.; Arslan, A.A.; Bueno-de-Mesquita, H.B.; Fuchs, C.S.; Gallinger, S.; Gross, M.; Helzlsouer, K.; et al. An absolute risk model to identify individuals at elevated risk for pancreatic cancer in the general population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, T.A.; Gaddam, S.; Wachsman, A.M.; Wang, L.; Azab, L.; Asadpour, V.; Chen, W.; Xie, Y.; Wu, B.; Pandol, S.J.; et al. Predicting pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma using artificial intelligence analysis of pre-diagnostic computed tomography images. Cancer Biomark. 2022, 33, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elta, G.H.; Enestvedt, B.K.; Sauer, B.G.; Lennon, A.M. ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis and Management of Pancreatic Cysts. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 464–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, N.O.; Al Qadhi, H.; Al Wahibi, K. Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm of Pancreas. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 7, 160–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, S.; Solis, L.; Parra, E.R.; Uraoka, N.; Jiang, M.; Wang, H.; Rodriguez-Canales, J.; Wistuba, I.; Maitra, A.; Sen, S.; et al. A Functional Spatial Analysis Platform for Discovery of Immunological Interactions Predictive of Low-Grade to High-Grade Transition of Pancreatic Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms. Cancer Inf. 2018, 17, 1176935118782880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, M.F.; Kluger, M.D.; Su, G.H.; Chabot, J.A.; Yang, C.-Y.; Lou, W.; Valente, R.; Del Chiaro, M.; Shyr, Y.-M.; Wang, S.-E.; et al. Validation of a nomogram to predict the risk of cancer in patients with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm and main duct dilatation of 10 mm or less. Br. J. Surg. 2020, 107, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, X.; Liu, F.; Li, J.; Cao, K.; Wang, T.; Zhang, H.; Li, Q.; Meng, Y.; Yu, J.; Feng, X.; et al. Computed tomography nomogram to predict a high-risk intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. Abdom. Radiol. 2021, 46, 5218–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Permuth, J.B.; Choi, J.; Balarunathan, Y.; Kim, J.; Chen, D.T.; Chen, L.; Orcutt, S.; Doepker, M.P.; Gage, K.; Zhang, G.; et al. Combining radiomic features with a miRNA classifier may improve prediction of malignant pathology for pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 85785–85797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanania, A.N.; Bantis, L.E.; Feng, Z.; Wang, H.; Tamm, E.P.; Katz, M.H.; Maitra, A.; Koay, E.J. Quantitative imaging to evaluate malignant potential of IPMNs. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 85776–85784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, J.; Midya, A.; Gazit, L.; Attiyeh, M.; Langdon-Embry, L.; Allen, P.J.; Do, R.K.G.; Simpson, A.L. CT radiomics to predict high-risk intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. Med. Phys. 2018, 45, 5019–5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral, J.E.; Hussein, S.; Kandel, P.; Bolan, C.W.; Bagci, U.; Wallace, M.B. Deep Learning to Classify Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Pancreas 2019, 48, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.C.; Park, S.; Soleimani, S.; Fouladi, D.F.; Shayesteh, S.; He, J.; Javed, A.A.; Wolfgang, C.L.; Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W.; et al. Classification of pancreatic cystic neoplasms using radiomic feature analysis is equivalent to an experienced academic radiologist: A step toward computer-augmented diagnostics for radiologists. Abdom. Radiol. 2022, 47, 4139–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Tian, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ruan, S.; Shao, J.; Zhang, X.; Huang, D.; et al. Classification prediction of pancreatic cystic neoplasms based on radiomics deep learning models. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuyama, T.; Ohno, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Ikedo, M.; Yui, M.; Furuta, M.; Fujisawa, R.; Hanamatsu, S.; Nagata, H.; Ueda, T.; et al. Comparison of utility of deep learning reconstruction on 3D MRCPs obtained with three different k-space data acquisitions in patients with IPMN. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 6658–6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, R.; Bird, K.; Cheung, P.Y.; Decker, J.H.; Flory, M.N.; Goff, D.; Morimoto, L.N.; Shon, A.; Wentland, A.L.; Rubin, D.L.; et al. Automated Identification and Measurement Extraction of Pancreatic Cystic Lesions from Free-Text Radiology Reports Using Natural Language Processing. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2022, 4, e210092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilas-Boas, F.; Ribeiro, T.; Afonso, J.; Cardoso, H.; Lopes, S.; Moutinho-Ribeiro, P.; Ferreira, J.; Mascarenhas-Saraiva, M.; Macedo, G. Deep Learning for Automatic Differentiation of Mucinous versus Non-Mucinous Pancreatic Cystic Lesions: A Pilot Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwahara, T.; Hara, K.; Mizuno, N.; Okuno, N.; Matsumoto, S.; Obata, M.; Kurita, Y.; Koda, H.; Toriyama, K.; Onishi, S.; et al. Usefulness of Deep Learning Analysis for the Diagnosis of Malignancy in Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasms of the Pancreas. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, e00045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguon, L.S.; Seo, K.; Lim, J.H.; Song, T.J.; Cho, S.H.; Park, J.S.; Park, S. Deep Learning-Based Differentiation between Mucinous Cystic Neoplasm and Serous Cystic Neoplasm in the Pancreas Using Endoscopic Ultrasonography. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiesslich, R.; Burg, J.; Vieth, M.; Gnaendiger, J.; Enders, M.; Delaney, P.; Polglase, A.; McLaren, W.; Janell, D.; Thomas, S.; et al. Confocal laser endoscopy for diagnosing intraepithelial neoplasias and colorectal cancer in vivo. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, S.G.; Swanson, B.; Hart, P.A.; El-Dika, S.; Walker, J.P.; McCarthy, S.T.; Malli, A.; Shah, Z.K.; Conwell, D.L. Validation of diagnostic characteristics of needle based confocal laser endomicroscopy in differentiation of pancreatic cystic lesions. Endosc. Int. Open 2016, 4, E1124–E1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, S.G.; Swanson, B.; Conwell, D.L.; Muscarella, P., 2nd. In vivo and ex vivo needle-based confocal endomicroscopy of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 82, 571–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamboj, A.K.; Dewitt, J.M.; Modi, R.M.; Conwell, D.L.; Krishna, S.G. Confocal Endomicroscopy Characteristics of Different Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm Subtypes. JOP J. Pancreas 2017, 18, 198–202. [Google Scholar]
- Konda, V.J.; Meining, A.; Jamil, L.H.; Giovannini, M.; Hwang, J.H.; Wallace, M.B.; Chang, K.J.; Siddiqui, U.D.; Hart, J.; Lo, S.K.; et al. A pilot study of in vivo identification of pancreatic cystic neoplasms with needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy under endosonographic guidance. Endoscopy 2013, 45, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, Y.; Iwashita, T.; Park, D.H.; Samarasena, J.B.; Lee, J.G.; Chang, K.J. Diagnosis of pancreatic cysts: EUS-guided, through-the-needle confocal laser-induced endomicroscopy and cystoscopy trial: DETECT study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 81, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoleon, B.; Lemaistre, A.I.; Pujol, B.; Caillol, F.; Lucidarme, D.; Bourdariat, R.; Morellon-Mialhe, B.; Fumex, F.; Lefort, C.; Lepilliez, V.; et al. A novel approach to the diagnosis of pancreatic serous cystadenoma: Needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy. Endoscopy 2015, 47, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoleon, B.; Lemaistre, A.I.; Pujol, B.; Caillol, F.; Lucidarme, D.; Bourdariat, R.; Morellon-Mialhe, B.; Fumex, F.; Lefort, C.; Lepilliez, V.; et al. In vivo characterization of pancreatic cystic lesions by needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy (nCLE): Proposition of a comprehensive nCLE classification confirmed by an external retrospective evaluation. Surg. Endosc. 2016, 30, 2603–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napoleon, B.; Palazzo, M.; Lemaistre, A.I.; Caillol, F.; Palazzo, L.; Aubert, A.; Buscail, L.; Maire, F.; Morellon, B.M.; Pujol, B.; et al. Needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy of pancreatic cystic lesions: A prospective multicenter validation study in patients with definite diagnosis. Endoscopy 2019, 51, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishna, S.G.; Hart, P.A.; Malli, A.; Kruger, A.J.; McCarthy, S.T.; El-Dika, S.; Walker, J.P.; Dillhoff, M.E.; Manilchuk, A.; Schmidt, C.R.; et al. Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy Increases Accuracy of Differentiation of Pancreatic Cystic Lesions. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Off. Clin. Pract. J. Am. Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2020, 18, 432–440.E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, R.M.; Kamboj, A.K.; Swanson, B.; Conwell, D.L.; Krishna, S.G. Novel technique for diagnosis of mucinous cystic neoplasms: In vivo and ex vivo confocal laser endomicroscopy. VideoGIE 2017, 2, 55–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.; Goel, A. The Risk Factors for Acute Pancreatitis after Endoscopic Ultrasound Guided Biopsy. Korean J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 72, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machicado, J.D.; Chao, W.L.; Carlyn, D.E.; Pan, T.Y.; Poland, S.; Alexander, V.L.; Maloof, T.G.; Dubay, K.; Ueltschi, O.; Middendorf, D.M.; et al. High performance in risk stratification of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms by confocal laser endomicroscopy image analysis with convolutional neural networks (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 94, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriegsmann, M.; Kriegsmann, K.; Steinbuss, G.; Zgorzelski, C.; Kraft, A.; Gaida, M.M. Deep Learning in Pancreatic Tissue: Identification of Anatomical Structures, Pancreatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia, and Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, B.; Chen, M.; Ratnakumar, P.; Alemu, E.; Logan, A.; Linton-Reid, K.; Tong, D.; Senthivel, N.; Bhamani, A.; Bloch, S.; et al. A radiomics-based decision support tool improves lung cancer diagnosis in combination with the Herder score in large lung nodules. EBioMedicine 2022, 86, 104344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, W.C.; Hsu, M.H.; Cai, Z.X.; Chen, C.M. Developing an AI-assisted clinical decision support system to enhance in-patient holistic health care. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0276501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastrup, N.; Bjerregaard, H.H.; Laursen, M.; Valentin, J.B.; Johnsen, S.P.; Jensen, C.E. An AI-based patient-specific clinical decision support system for OA patients choosing surgery or not: Study protocol for a single-centre, parallel-group, non-inferiority randomised controlled trial. Trials 2023, 24, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niranjan, K.; Shankar Kumar, S.; Vedanth, S.; Chitrakala, D.S. An Explainable AI driven Decision Support System for COVID-19 Diagnosis using Fused Classification and Segmentation. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 218, 1915–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiang, T.; Garwood, E.; Debenedectis, C.M. Artificial intelligence-based decision support system (AI-DSS) implementation in radiology residency: Introducing residents to AI in the clinical setting. Clin. Imaging 2022, 92, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarnowska, K.A.; Dispoto, B.C.; Conragan, J. Explainable AI-based clinical decision support system for hearing disorders. AMIA Jt. Summits Transl. Sci. Proc. 2021, 2021, 595–604. [Google Scholar]
- Tutun, S.; Johnson, M.E.; Ahmed, A.; Albizri, A.; Irgil, S.; Yesilkaya, I.; Ucar, E.N.; Sengun, T.; Harfouche, A. An AI-based Decision Support System for Predicting Mental Health Disorders. Inf. Syst. Front. 2022, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Yixing, Y.; Jia, D.; Ling, Y. Application of mammography-based radiomics signature for preoperative prediction of triple-negative breast cancer. BMC Med. Imaging 2022, 22, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Lou, X.; Kong, N.; Xu, M.; Gao, C. Can quantitative peritumoral CT radiomics features predict the prognosis of patients with non-small cell lung cancer? A systematic review. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 33, 2105–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baysal, B.; Baysal, H.; Eser, M.B.; Dogan, M.B.; Alimoglu, O. Radiomics Features Based on MRI-ADC Maps of Patients with Breast Cancer: Relationship with Lesion Size, Features Stability, and Model Accuracy. Medeni. Med. J. 2022, 37, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi, G.; Abbasian Ardakani, A.; Ghafoori, M.; Babapour Mofrad, F.; Saligheh Rad, H. Radiomics-based machine-learning method to diagnose prostate cancer using mp-MRI: A comparison between conventional and fused models. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2023, 36, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Chen, Y.; Yue, X.; Ma, C.; Liu, X.; Yang, P.; Lu, J. Deep pancreas segmentation with uncertain regions of shadowed sets. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 68, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, K.; Xue, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhu, X.; Li, Q.; Gong, W.; Liang, T.; Duan, S. Fully end-to-end deep-learning-based diagnosis of pancreatic tumors. Theranostics 2021, 11, 1982–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhou, Y.; Asadpour, V.; Parker, R.A.; Puttock, E.J.; Lustigova, E.; Wu, B.U. Quantitative Radiomic Features from Computed Tomography Can Predict Pancreatic Cancer up to 36 Months before Diagnosis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2022, 14, e00548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein-Brill, A.; Amar-Farkash, S.; Lawrence, G.; Collisson, E.A.; Aran, D. Comparison of FOLFIRINOX vs Gemcitabine Plus Nab-Paclitaxel as First-Line Chemotherapy for Metastatic Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2216199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conroy, T.; Castan, F.; Lopez, A.; Turpin, A.; Ben Abdelghani, M.; Wei, A.C.; Mitry, E.; Biagi, J.J.; Evesque, L.; Artru, P.; et al. Five-Year Outcomes of FOLFIRINOX vs Gemcitabine as Adjuvant Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 1571–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.; Chawla, A.; O’Reilly, E.M. Pancreatic Cancer: A Review. JAMA 2021, 326, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Ding, Y.; Yu, Y.; Liu, K.; Rao, S.; Ge, Y.; Zeng, M. Whole-tumour evaluation with MRI and radiomics features to predict the efficacy of S-1 for adjuvant chemotherapy in postoperative pancreatic cancer patients: A pilot study. BMC Med. Imaging 2021, 21, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwatate, Y.; Hoshino, I.; Yokota, H.; Ishige, F.; Itami, M.; Mori, Y.; Chiba, S.; Arimitsu, H.; Yanagibashi, H.; Nagase, H.; et al. Radiogenomics for predicting p53 status, PD-L1 expression, and prognosis with machine learning in pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 123, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.L.; Liu, L.; Qi, Z.H.; Xu, H.X.; Wang, W.Q.; Wu, C.T.; Zhang, S.R.; Xu, J.Z.; Ni, Q.X.; Yu, X.J. The clinicopathological and prognostic significance of PD-L1 expression in pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2018, 17, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, P.C.; Frey, M.C.; Ruzza, C.M.; Nickel, F.; Jost, C.; Gwerder, C.; Hackert, T.; Z’Graggen, K.; Kessler, U. Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Pancreatic Cancer: An Appraisal of the Current High-Level Evidence. Pharmacology 2021, 106, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, T.; Ban, D.; Nishino, J.; Watanabe, S.; Maekawa, A.; Ishikawa, Y.; Akahoshi, K.; Ogawa, K.; Ono, H.; Kudo, A.; et al. Prediction of early recurrence of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma after resection. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, X. Comparative Recurrence Analysis of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma after Resection. J. Oncol. 2021, 2021, 3809095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Roessel, S.; Kasumova, G.G.; Verheij, J.; Najarian, R.M.; Maggino, L.; de Pastena, M.; Malleo, G.; Marchegiani, G.; Salvia, R.; Ng, S.C.; et al. International Validation of the Eighth Edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) TNM Staging System in Patients With Resected Pancreatic Cancer. JAMA Surg. 2018, 153, e183617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, N.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Lee, W.; Fang, Y.; Han, X.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, L.; Nuerxiati, A.; Yin, H.; et al. Comparison of prognostic prediction between nomogram based on lymph node ratio and AJCC 8th staging system for patients with resected pancreatic head carcinoma: A SEER analysis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Zhang, J.; Han, Y.; Wang, X.; Ye, X.; Meng, Y.; Parwani, A.; Han, Z.; Feng, Q.; Huang, K. Integrative analysis of histopathological images and genomic data predicts clear cell renal cell carcinoma prognosis. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e91–e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ge, D.; Gu, J.; Xu, F.; Zhu, Q.; Lu, C. A large cohort study identifying a novel prognosis prediction model for lung adenocarcinoma through machine learning strategies. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Park, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; Jun, E.; Song, K.B.; Hwang, D.W.; Lee, J.H.; Lim, K.; Kim, N.; Lee, S.S.; et al. Preoperative data-based deep learning model for predicting postoperative survival in pancreatic cancer patients. Int. J. Surg. 2022, 105, 106851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaissis, G.; Ziegelmayer, S.; Lohofer, F.; Algul, H.; Eiber, M.; Weichert, W.; Schmid, R.; Friess, H.; Rummeny, E.; Ankerst, D.; et al. A machine learning model for the prediction of survival and tumor subtype in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma from preoperative diffusion-weighted imaging. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2019, 3, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.K.; Kim, H.; Son, D.S.; Kim, N.K.D.; Sung, Y.K.; Cho, M.; Lee, C.; Noh, D.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, K.T.; et al. Accurate Prognosis Prediction of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Using Integrated Clinico-Genomic Data of Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Biopsy. Cancers 2021, 13, 2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study | Sample Size | Data | Best-Performing Model | Task | AUC | Comparisons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Permuth, 2016 [53] | 38 | CT texture analysis + genomics | Logistic regression | Distinguish malignant from benign IPMNs | 0.92 | N/A |
| Hanania, 2016 [54] | 53 | CT imaging (texture, shape, intensity) | Logistic regression | IPMN high- vs. low-grade dysplasia | 0.96 | Lower false positive rate than Fukuoka |
| Chakraborty, 2018 [55] | 103 | CT imaging features | Random forest | High- vs. low-risk BD-IPMN | 0.77 | N/A |
| Corral, 2019 [56] | 139 | MRI imaging features | CNN | Identify high-grade dysplasia or cancer in IPMNs | 0.78 | Accuracy was comparable to AGA/Fukuoka |
| Chu, 2022 [57] | 214 | CT radiomics features | Random forest | Classify mucinous and non-mucinous cysts | 0.94 | Accuracy was comparable to radiologist |
| Liang, 2022 [58] | 193 | CT + clinical data | Fused radiomics-DL | Differentiate MCN from IPMN | 0.973 | N/A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, J.; Chao, W.-L.; Culp, S.; Krishna, S.G. Artificial Intelligence in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pancreatic Cystic Lesions and Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 2410. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092410
Jiang J, Chao W-L, Culp S, Krishna SG. Artificial Intelligence in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pancreatic Cystic Lesions and Adenocarcinoma. Cancers. 2023; 15(9):2410. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092410
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Joanna, Wei-Lun Chao, Stacey Culp, and Somashekar G. Krishna. 2023. "Artificial Intelligence in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pancreatic Cystic Lesions and Adenocarcinoma" Cancers 15, no. 9: 2410. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092410
APA StyleJiang, J., Chao, W.-L., Culp, S., & Krishna, S. G. (2023). Artificial Intelligence in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pancreatic Cystic Lesions and Adenocarcinoma. Cancers, 15(9), 2410. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092410







