Immunotherapy for Peritoneal Carcinomatosis: Challenges and Prospective Outcomes
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
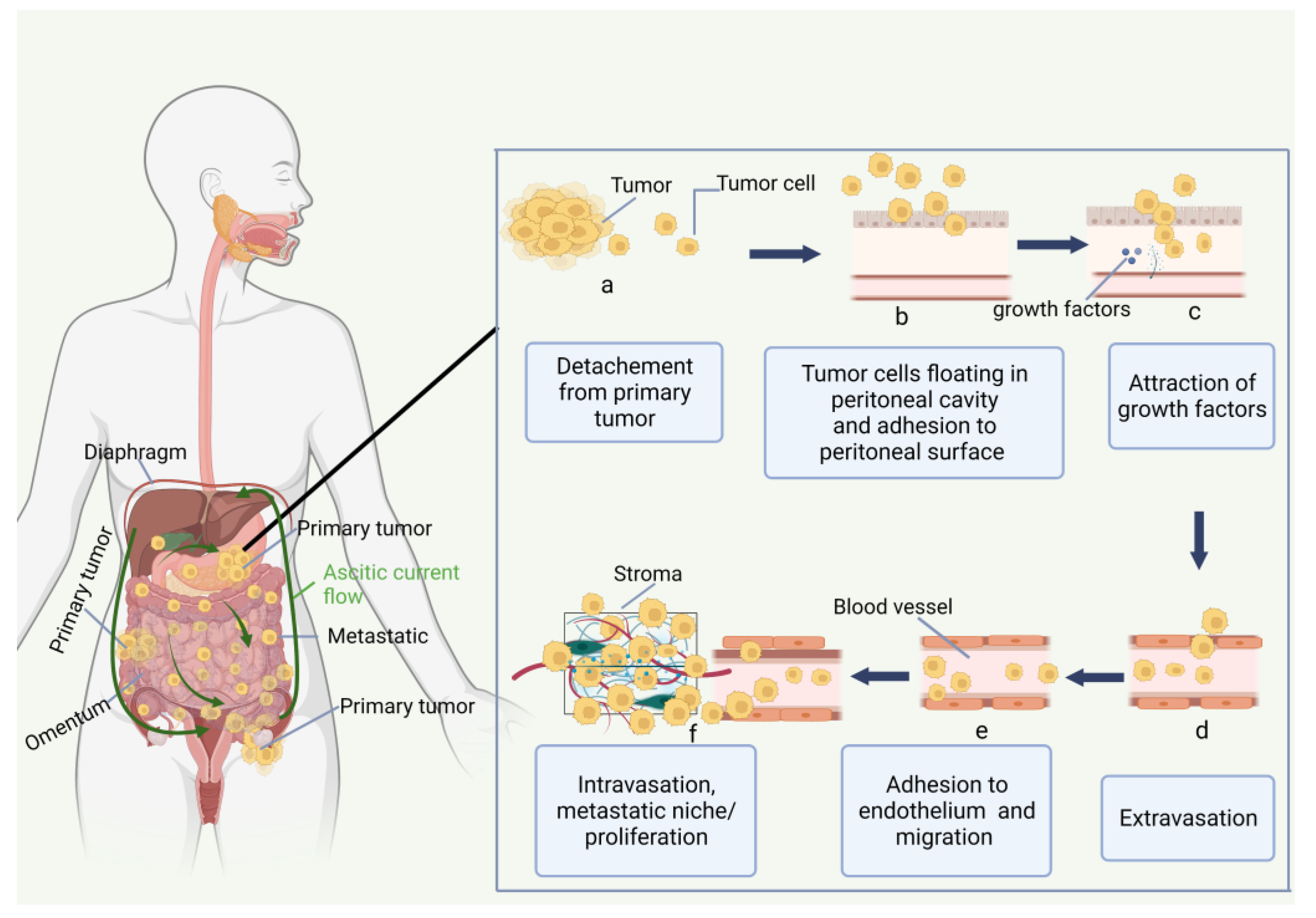
2. Peritoneal Carcinomatosis
2.1. Peritoneum and Peritoneal Carcinomatosis
2.2. Immune Environment of Peritoneal Carcinomatosis
3. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
4. Monoclonal Antibodies
4.1. MOC31PE Immunotoxin
4.2. Catumaxomab
5. Cancer Vaccines for Peritoneal Metastasis
6. CAR-T Cell Therapy for Peritoneal Carcinomatosis
6.1. Basic of CAR-T Cells
6.2. Administration Route of CAR-T for Peritoneal Carcinomas
6.3. CAR-T Cell Studies for Peritoneal Carcinomatosis
7. Comparison of Emerging Theories and Therapeutic Approaches for the PC Therapy
7.1. Immunotherapy Compared to Cytotoxic Chemotherapy in Peritoneal Carcinomatosis
7.2. Emerging Theories and Therapeutic Approaches of Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Peritoneal Carcinomatosis
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Willaims, S.C.P. Peritoneal Carcinomatosis: Cause, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Available online: https://www.webmd.com/cancer/what-is-peritoneal-carcinomatosis (accessed on 9 July 2022).
- Coccolini, F.; Gheza, F.; Lotti, M.; Virzì, S.; Iusco, D.; Ghermandi, C.; Melotti, R.; Baiocchi, G.; Giulini, S.M.; Ansaloni, L.; et al. Peritoneal Carcinomatosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 6979–6994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullen, J.R.W.; Selleck, M.; Wall, N.R.; Senthil, M. Peritoneal Carcinomatosis: Limits of Diagnosis and the Case for Liquid Biopsy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 43481–43490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shariat-Madar, B.; Jayakrishnan, T.T.; Gamblin, T.C.; Turaga, K.K. Surgical Management of Bowel Obstruction in Patients with Peritoneal Carcinomatosis. J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 110, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, R.L.; LeDuc, R.J. Small Intestinal Obstruction from Peritoneal Carcinomatosis. Am. J. Surg. 1973, 125, 316–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, D.Z.; Lang, N.P.; Thompson, C.; Osteen, P.K.; Westbrook, K.C. Peritoneal Carcinomatosis in Nongynecologic Malignancy. A Prospective Study of Prognostic Factors. Cancer 1989, 63, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerscher, A.G.; Chua, T.C.; Gasser, M.; Maeder, U.; Kunzmann, V.; Isbert, C.; Germer, C.T.; Pelz, J.O.W. Impact of Peritoneal Carcinomatosis in the Disease History of Colorectal Cancer Management: A Longitudinal Experience of 2406 Patients over Two Decades. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 1432–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonemura, Y.; Bandou, E.; Kinoshita, K.; Kawamura, T.; Takahashi, S.; Endou, Y.; Sasaki, T. Effective Therapy for Peritoneal Dissemination in Gastric Cancer. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2003, 12, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomassen, I.; Bernards, N.; van Gestel, Y.R.; Creemers, G.-J.; Jacobs, E.M.; Lemmens, V.E.; de Hingh, I.H. Chemotherapy as Palliative Treatment for Peritoneal Carcinomatosis of Gastric Origin. Acta. Oncol. 2014, 53, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugarbaker, P.H.; Jablonski, K.A. Prognostic Features of 51 Colorectal and 130 Appendiceal Cancer Patients with Peritoneal Carcinomatosis Treated by Cytoreductive Surgery and Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy. Ann. Surg. 1995, 221, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahteme, H.; Hansson, J.; Berglund, A.; Påhlman, L.; Glimelius, B.; Nygren, P.; Graf, W. Improved Survival in Patients with Peritoneal Metastases from Colorectal Cancer: A Preliminary Study. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 90, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verwaal, V.; van Ruth, S.; de Bree, E.; van Sloothen, G.; van Tinteren, H.; Boot, H.; Zoetmulder, F. Randomized Trial of Cytoreduction and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy versus Systemic Chemotherapy and Palliative Surgery in Patients with Peritoneal Carcinomatosis of Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 3737–3743. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/14551293/ (accessed on 14 July 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Oudheusden, T.R.; Nienhuijs, S.W.; Luyer, M.D.; Nieuwenhuijzen, G.A.; Lemmens, V.E.; Rutten, H.J.; de Hingh, I.H. Incidence and Treatment of Recurrent Disease after Cytoreductive Surgery and Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy for Peritoneally Metastasized Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 41, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karunasena, E.; Sham, J.; McMahon, K.W.; Ahuja, N. Genomics of Peritoneal Malignancies. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 27, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavin, T.; Neuhausen, S.L.; Rybak, C.; Solomon, I.; Nehoray, B.; Blazer, K.; Niell-Swiller, M.; Adamson, A.W.; Yuan, Y.-C.; Yang, K.; et al. Genetic Gastric Cancer Susceptibility in the International Clinical Cancer Genomics Community Research Network. Cancer Genet. 2017, 216–217, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Ajani, J.; Song, S. Molecular Biology and Immunology of Gastric Cancer Peritoneal Metastasis. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ströhlein, M.; Heiss, M.; Jauch, K.-W. The Current Status of Immunotherapy in Peritoneal Carcinomatosis. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2016, 16, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, M.; Kodera, Y. Molecular Mechanisms of Peritoneal Dissemination in Gastric Cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 6829–6840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugarbaker, E.V. Cancer Metastasis: A Product of Tumor-Host Interactions. Curr. Probl. Cancer 1979, 3, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikuła-Pietrasik, J.; Uruski, P.; Tykarski, A.; Książek, K. The Peritoneal “Soil” for a Cancerous “Seed”: A Comprehensive Review of the Pathogenesis of Intraperitoneal Cancer Metastases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 509–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ji, Z.; Li, Y. Peritoneal Carcinomatosis Diagnosis and Treatment in China: Focusing on Training and Collaboration. Indian J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 10, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, B.; Arvieux, C.; Glehen, O.; Beaujard, A.C.; Rivoire, M.; Baulieux, J.; Fontaumard, E.; Brachet, A.; Caillot, J.L.; Faure, J.L.; et al. Peritoneal Carcinomatosis from Non-Gynecologic Malignancies: Results of the EVOCAPE 1 Multicentric Prospective Study. Cancer 2000, 88, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, C.S.; You, B.; Decullier, E.; Vaudoyer, D.; Lorimier, G.; Abboud, K.; Bereder, J.-M.; Arvieux, C.; Boschetti, G.; Glehen, O.; et al. Patients with Peritoneal Carcinomatosis from Gastric Cancer Treated with Cytoreductive Surgery and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy: Is Cure a Possibility? Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 1971–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verwaal, V.J.; Bruin, S.; Boot, H.; van Slooten, G.; van Tinteren, H. 8-Year Follow-up of Randomized Trial: Cytoreduction and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy versus Systemic Chemotherapy in Patients with Peritoneal Carcinomatosis of Colorectal Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 15, 2426–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Yan, T.D.; Black, D.; Morris, D.L. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cytoreductive Surgery with Perioperative Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy for Peritoneal Carcinomatosis of Colorectal Origin. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2009, 16, 2152–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubicka, U.; Olszewski, W.L.; Tarnowski, W.; Bielecki, K.; Ziółkowska, A.; Wierzbicki, Z. Normal Human Immune Peritoneal Cells: Subpopulations and Functional Characteristics. Scand. J. Immunol. 1996, 44, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, V.; Abbaszadegan, M.R.; Memar, B.; Motie, M.R.; Asadi, M.; Mahmoudian, R.A.; Gholamin, M. Induction of T Cell-Mediated Immune Response by Dendritic Cells Pulsed with MRNA of Sphere-Forming Cells Isolated from Patients with Gastric Cancer. Life Sci. 2019, 219, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Räihä, M.R.; Puolakkainen, P.A. Tumor-Associated Macrophages (TAMs) as Biomarkers for Gastric Cancer: A Review. Chronic. Dis. Transl. Med. 2018, 4, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Yashiro, M.; Sunami, T.; Sakate, Y.; Kosaka, K.; Hirakawa, K. ICAM-2 Gene Therapy for Peritoneal Dissemination of Scirrhous Gastric Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 4885–4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimori, D.; Kinoshita, J.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Gunjigake, K.; Ohama, T.; Sato, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Tsukamoto, T.; Nomura, S.; et al. Established Fibrous Peritoneal Metastasis in an Immunocompetent Mouse Model Similar to Clinical Immune Microenvironment of Gastric Cancer. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, K.; Dong, X.; Estrella, J.S.; Correa, A.M.; Xu, Y.; Hofstetter, W.L.; Sudo, K.; Onodera, H.; Suzuki, K.; Suzuki, A.; et al. Tumor-Associated Macrophage Infiltration Is Highly Associated with PD-L1 Expression in Gastric Adenocarcinoma. Gastric Cancer 2018, 21, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Hu, S.; Wu, Y.; Li, S.; He, C.; Xing, X.; Wang, Y.; Du, X. Accumulation and Suppressive Function of Regulatory T Cells in Malignant Ascites: Reducing their Suppressive Function using Arsenic Trioxide in Vitro. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 5384–5390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Kwon, W.S.; Park, S.; Jo, E.; Lim, S.J.; Lee, C.-K.; Lee, J.B.; Jung, M.; Kim, H.S.; Beom, S.-H.; et al. Comprehensive Immune Profiling and Immune-Monitoring using Body Fluid of Patients with Metastatic Gastric Cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, B.; Kim, C.; Kim, J.-H.; Kwon, W.S.; Lee, W.S.; Kim, J.M.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Park, K.H.; Kim, T.S.; et al. Genetic Alterations and their Clinical Implications in Gastric Cancer Peritoneal Carcinomatosis Revealed by Whole-Exome Sequencing of Malignant Ascites. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 8055–8066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasada, T.; Kimura, M.; Yoshida, Y.; Kanai, M.; Takabayashi, A. CD4+CD25+ Regulatory T Cells in Patients with Gastrointestinal Malignancies: Possible Involvement of Regulatory T Cells in Disease Progression. Cancer 2003, 98, 1089–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, J.; Suzuki, H.; Fuchino, R.; Yamasaki, A.; Nagai, S.; Yanai, K.; Koga, K.; Nakamura, M.; Tanaka, M.; Morisaki, T.; et al. The Contribution of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor to the Induction of Regulatory T-Cells in Malignant Effusions. Antcancer Res. 2009, 29, 881–888. [Google Scholar]
- Ribas, A.; Wolchok, J.D. Cancer Immunotherapy Using Checkpoint Blockade. Science 2018, 359, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodi, F.S.; O’Day, S.J.; McDermott, D.F.; Weber, R.W.; Sosman, J.A.; Haanen, J.B.; Gonzalez, R.; Robert, C.; Schadendorf, D.; Hassel, J.C.; et al. Improved Survival with Ipilimumab in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, N.; Kennedy, J. A Review of Cancer Immunotherapy Toxicity: Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. J. Med. Toxicol. 2021, 17, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Li, W.; Yoshiya, S.; Xu, Y.; Hata, M.; El-Darawish, Y.; Markova, T.; Yamanishi, K.; Yamanishi, H.; Tahara, H.; et al. Augmentation of Immune Checkpoint Cancer Immunotherapy with IL18. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2969–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, D.K.A.; Gwee, Y.X.; Sundar, R. Resistance to Systemic Immune Checkpoint Inhibition in the Peritoneal Niche. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e004749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonneville, R.; Krook, M.A.; Kautto, E.A.; Miya, J.; Wing, M.R.; Chen, H.-Z.; Reeser, J.W.; Yu, L.; Roychowdhury, S. Landscape of Microsatellite Instability Across 39 Cancer Types. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2017, 2017, PO.17.00073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casak, S.J.; Marcus, L.; Fashoyin-Aje, L.; Mushti, S.L.; Cheng, J.; Shen, Y.-L.; Pierce, W.F.; Her, L.; Goldberg, K.B.; Theoret, M.R.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Pembrolizumab for the First-Line Treatment of Patients with MSI-H/DMMR Advanced Unresectable or Metastatic Colorectal Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 4680–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marabelle, A.; Le, D.T.; Ascierto, P.A.; Di Giacomo, A.M.; De Jesus-Acosta, A.; Delord, J.-P.; Geva, R.; Gottfried, M.; Penel, N.; Hansen, A.R.; et al. Efficacy of Pembrolizumab in Patients with Noncolorectal High Microsatellite Instability/Mismatch Repair-Deficient Cancer: Results from the Phase II KEYNOTE-158 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Kim, W.; Han, Y.; Kim, J.; Chon, H. Cancer Immunotherapy with STING Agonist and PD-1 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Effectively Suppresses Peritoneal Carcinomatosis of Colon Cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, iv35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, Y.; Futoh, Y.; Miyato, H.; Ohzawa, H.; Yamaguchi, H.; Saito, S.; Kurashina, K.; Hosoya, Y.; Lefor, A.K.; Sata, N.; et al. Effect of Systemic or Intraperitoneal Administration of Anti-PD-1 Antibody for Peritoneal Metastases from Gastric Cancer. Vivo 2022, 36, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Lee, W.S.; Kim, C.W.; Lee, S.J.; Yang, H.; Kong, S.J.; Ning, J.; Yang, K.-M.; Kang, B.; Kim, W.R.; et al. Oncolytic Vaccinia Virus Reinvigorates Peritoneal Immunity and Cooperates with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor to Suppress Peritoneal Carcinomatosis in Colon Cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Zhao, L.; Li, W.; Fan, K.; Qian, W.; Hou, S.; Wang, H.; Dai, M.; Hellstrom, I.; Hellstrom, K.E.; et al. Combinatorial PD-1 Blockade and CD137 Activation Has Therapeutic Efficacy in Murine Cancer Models and Synergizes with Cisplatin. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, X.; Cheng, D.; Xia, Z.; Luan, M.; Zhang, S. PD-1 Blockade and OX40 Triggering Synergistically Protects against Tumor Growth in a Murine Model of Ovarian Cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Xu, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, R.; Ji, H.; Wang, X. Combined PD-1 Blockade and GITR Triggering Induce a Potent Antitumor Immunity in Murine Cancer Models and Synergizes with Chemotherapeutic Drugs. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Fushida, S.; Yamamoto, Y.; Tsukada, T.; Kinoshita, J.; Oyama, K.; Miyashita, T.; Tajima, H.; Ninomiya, I.; Munesue, S.; et al. Tumor-Associated Macrophages of the M2 Phenotype Contribute to Progression in Gastric Cancer with Peritoneal Dissemination. Gastric Cancer 2016, 19, 1052–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Kinoshita, J.; Yamaguchi, T.; Aoki, T.; Saito, H.; Hamabe-Horiike, T.; Harada, S.; Nomura, S.; Inaki, N.; Fushida, S. Crosstalk between Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and Immune Cells in Peritoneal Metastasis: Inhibition in the Migration of M2 Macrophages and Mast Cells by Tranilast. Gastric Cancer 2022, 25, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fucà, G.; Cohen, R.; Lonardi, S.; Shitara, K.; Elez, M.E.; Fakih, M.; Chao, J.; Klempner, S.J.; Emmett, M.; Jayachandran, P.; et al. Ascites and Resistance to Immune Checkpoint Inhibition in DMMR/MSI-H Metastatic Colorectal and Gastric Cancers. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e004001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, Q.L.; Mas, L.; Hollebecque, A.; Tougeron, D.; de la Fouchardière, C.; Pudlarz, T.; Alouani, E.; Guimbaud, R.; Taieb, J.; André, T.; et al. Treatments after Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Patients with DMMR/MSI Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barraud, S.; Tougeron, D.; Villeneuve, L.; Eveno, C.; Bayle, A.; Parc, Y.; Pocard, M.; André, T.; Cohen, R. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Patients with Isolated Peritoneal Carcinomatosis from DMMR/MSI-H Colorectal Cancer, a BIG-RENAPE Collaboration. Dig. Liver Dis. 2022, ahead of print. [CrossRef]
- Origuchi, M.; Korth, C.; Li, Z.; Braendle, E.E. A Phase Ib/II, Multicenter, Open-Label Study of DSP-7888 Dosing Emulsion in Combination with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (CPI) Nivolumab or Pembrolizumab in Adult Patients (Pts) with Advanced Solid Tumors, Including Platinum-Resistant Ovarian Cancer (PROC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, TPS6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldbrügge, L.; Gronau, F.; Brandl, A.; Auer, T.A.; Oeff, A.; Thuss-Patience, P.; Pratschke, J.; Rau, B. Systemic Chemotherapy Including Ramucirumab in Combination with Pressurized Intra-Peritoneal Aerosol Chemotherapy is a Safe Treatment Option for Peritoneal Metastasis of Gastric Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 610572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razenberg, L.G.E.M.; van Gestel, Y.R.B.M.; Lemmens, V.E.P.P.; de Hingh, I.H.J.T.; Creemers, G.-J. Bevacizumab in Addition to Palliative Chemotherapy for Patients With Peritoneal Carcinomatosis of Colorectal Origin: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. Clin. Color. Cancer 2016, 15, e41–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellone, S.; Siegel, E.R.; Cocco, E.; Cargnelutti, M.; Silasi, D.-A.; Azodi, M.; Schwartz, P.E.; Rutherford, T.J.; Pecorelli, S.; Santin, A.D. Overexpression of Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule in Primary, Metastatic, and Recurrent/Chemotherapy-Resistant Epithelial Ovarian Cancer: Implications for Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule-Specific Immunotherapy. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2009, 19, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köbel, M.; Kalloger, S.E.; Boyd, N.; McKinney, S.; Mehl, E.; Palmer, C.; Leung, S.; Bowen, N.J.; Ionescu, D.N.; Rajput, A.; et al. Ovarian Carcinoma Subtypes are Different Diseases: Implications for Biomarker Studies. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, Y.; Engebraaten, O.; Fodstad, Ø. Synergistic Anti-Cancer Effects of Immunotoxin and Cyclosporin in Vitro and in Vivo. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 101, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, Y.; Juell, S.; Fodstad, Ø. Downregulation of the Antiapoptotic MCL-1 Protein and Apoptosis in MA-11 Breast Cancer Cells Induced by an Anti-Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Pseudomonas Exotoxin a Immunotoxin. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 112, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, Y.; Engebraaten, O.; Juell, S.; Aamdal, S.; Brunsvig, P.; Fodstad, Ø.; Dueland, S. Phase I Trial of EpCAM-Targeting Immunotoxin MOC31PE, Alone and in Combination with Cyclosporin. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 1548–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiiger, M.T.; Bideli, H.; Fodstad, O.; Flatmark, K.; Andersson, Y. The MOC31PE Immunotoxin Reduces Cell Migration and Induces Gene Expression and Cell Death in Ovarian Cancer Cells. J. Ovarian Res. 2014, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frøysnes, I.S.; Andersson, Y.; Larsen, S.G.; Davidson, B.; Øien, J.-M.T.; Olsen, K.H.; Giercksky, K.-E.; Julsrud, L.; Fodstad, Ø.; Dueland, S.; et al. Novel Treatment with Intraperitoneal MOC31PE Immunotoxin in Colorectal Peritoneal Metastasis: Results From the ImmunoPeCa Phase 1 Trial. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 24, 1916–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatmark, K.; Guldvik, I.J.; Svensson, H.; Fleten, K.G.; Flørenes, V.A.; Reed, W.; Giercksky, K.-E.; Fodstad, Ø.; Andersson, Y. Immunotoxin Targeting EpCAM Effectively Inhibits Peritoneal Tumor Growth in Experimental Models of Mucinous Peritoneal Surface Malignancies. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 133, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frøysnes, I.S.; Andersson, Y.; Larsen, S.G.; Davidson, B.; Øien, J.-M.T.; Julsrud, L.; Fodstad, Ø.; Dueland, S.; Flatmark, K. ImmunoPeCa Trial: Long-Term Outcome Following Intraperitoneal MOC31PE Immunotoxin Treatment in Colorectal Peritoneal Metastasis. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 47, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, Y.; Haavardtun, S.I.; Davidson, B.; Dørum, A.; Fleten, K.G.; Fodstad, Ø.; Flatmark, K. MOC31PE Immunotoxin—Targeting Peritoneal Metastasis from Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 61800–61809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorgersen, E.B.; Asvall, J.; Frøysnes, I.S.; Schjalm, C.; Larsen, S.G.; Dueland, S.; Andersson, Y.; Fodstad, Ø.; Mollnes, T.E.; Flatmark, K. Increased Local Inflammatory Response to MOC31PE Immunotoxin After Cytoreductive Surgery and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 28, 5252–5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ströhlein, M.A.; Heiss, M.M. Intraperitoneal Immunotherapy to Prevent Peritoneal Carcinomatosis in Patients with Advanced Gastrointestinal Malignancies. J. Surg. Oncol. 2009, 100, 329–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, M.; Schoberth, A.; Ruf, P.; Hess, J.; Hennig, M.; Schmalfeldt, B.; Wimberger, P.; Ströhlein, M.; Theissen, B.; Heiss, M.M.; et al. Immunomonitoring Results of a Phase II/III Study of Malignant Ascites Patients Treated with the Trifunctional Antibody Catumaxomab (Anti-EpCAM × Anti-CD3). Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ströhlein, M.A.; Heiss, M.M. Immunotherapy of Peritoneal Carcinomatosis. Cancer Treat. Res. 2007, 134, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelius, D.; Ruf, P.; Gruber, P.; Plöscher, M.; Liedtke, R.; Gansberger, E.; Hess, J.; Wasiliu, M.; Lindhofer, H. Structural and Functional Characterization of the Trifunctional Antibody Catumaxomab. MAbs 2010, 2, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seimetz, D. Novel Monoclonal Antibodies for Cancer Treatment: The Trifunctional Antibody Catumaxomab (Removab®). J. Cancer 2011, 2, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiss, M.M.; Murawa, P.; Koralewski, P.; Kutarska, E.; Kolesnik, O.O.; Ivanchenko, V.V.; Dudnichenko, A.S.; Aleknaviciene, B.; Razbadauskas, A.; Gore, M.; et al. The Trifunctional Antibody Catumaxomab for the Treatment of Malignant Ascites Due to Epithelial Cancer: Results of a Prospective Randomized Phase II/III Trial. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 2209–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiss, M.M.; Ströhlein, M.A.; Jäger, M.; Kimmig, R.; Burges, A.; Schoberth, A.; Jauch, K.-W.; Schildberg, F.-W.; Lindhofer, H. Immunotherapy of Malignant Ascites with Trifunctional Antibodies. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 117, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thadi, A.; Khalili, M.; Morano, W.F.; Richard, S.D.; Katz, S.C.; Bowne, W.B. Early Investigations and Recent Advances in Intraperitoneal Immunotherapy for Peritoneal Metastasis. Vaccines 2018, 6, 54, Erratum in Vaccines 2019, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezan, A.; Hohla, F.; Meissnitzer, T.; Greil, R. Systemic Effect of Catumaxomab in a Patient with Metastasized Colorectal Cancer: A Case Report. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ströhlein, M.A.; Siegel, R.; Jäger, M.; Lindhofer, H.; Jauch, K.-W.; Heiss, M.M. Induction of Anti-Tumor Immunity by Trifunctional Antibodies in Patients with Peritoneal Carcinomatosis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 28, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokemeyer, C.; Stein, A.; Ridwelski, K.; Atanackovic, D.; Arnold, D.; Wöll, E.; Ulrich, A.; Fischer, R.; Krüger, C.; Schuhmacher, C. A Phase II Study of Catumaxomab Administered Intra- and Postoperatively as Part of a Multimodal Approach in Primarily Resectable Gastric Cancer. Gastric Cancer 2015, 18, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, A.; Stienen, S.; Zhu, M.; Li, H.; Yuraszeck, T.; Gibbs, J.; Heath, T.; Loberg, R.; Kasichayanula, S. Clinical Pharmacology and Translational Aspects of Bispecific Antibodies. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2017, 10, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burges, A.; Wimberger, P.; Kümper, C.; Gorbounova, V.; Sommer, H.; Schmalfeldt, B.; Pfisterer, J.; Lichinitser, M.; Makhson, A.; Moiseyenko, V.; et al. Effective Relief of Malignant Ascites in Patients with Advanced Ovarian Cancer by a Trifunctional Anti-EpCAM × Anti-CD3 Antibody: A Phase I/II Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 3899–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackey, J.R.; Venner, P.M. Malignant Ascites: Demographics, Therapeutic Efficacy and Predictors of Survival. Can. J. Oncol. 1996, 6, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wimberger, P.; Gilet, H.; Gonschior, A.-K.; Heiss, M.M.; Moehler, M.; Oskay-Oezcelik, G.; Al-Batran, S.-E.; Schmalfeldt, B.; Schmittel, A.; Schulze, E.; et al. Deterioration in Quality of Life (QoL) in Patients with Malignant Ascites: Results from a Phase II/III Study Comparing Paracentesis plus Catumaxomab with Paracentesis Alone. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 1979–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knödler, M.; Körfer, J.; Kunzmann, V.; Trojan, J.; Daum, S.; Schenk, M.; Kullmann, F.; Schroll, S.; Behringer, D.; Stahl, M.; et al. Randomised Phase II Trial to Investigate Catumaxomab (Anti-EpCAM × Anti-CD3) for Treatment of Peritoneal Carcinomatosis in Patients with Gastric Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 119, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingsworth, R.E.; Jansen, K. Turning the Corner on Therapeutic Cancer Vaccines. NPJ Vaccines 2019, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, D.T.; Pardoll, D.M.; Jaffee, E.M. Cellular Vaccine Approaches. Cancer J. 2010, 16, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, K.; Freeman, D.J.; Kelly, B.; Harper, J.; Soria, J.-C. Optimizing Oncolytic Virotherapy in Cancer Treatment. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2019, 18, 689–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osipov, A.; Murphy, A.; Zheng, L. From Immune Checkpoints to Vaccines: The Past, Present and Future of Cancer Immunotherapy. Adv. Cancer Res. 2019, 143, 63–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczorek, M.; Abualrous, E.T.; Sticht, J.; Álvaro-Benito, M.; Stolzenberg, S.; Noé, F.; Freund, C. Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) Class I and MHC Class II Proteins: Conformational Plasticity in Antigen Presentation. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slingluff, C.L. The Present and Future of Peptide Vaccines for Cancer: Single or Multiple, Long or Short, Alone or in Combination? Cancer J. 2011, 17, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Miao, L.; Sui, J.; Hao, Y.; Huang, G. Nanoparticle Cancer Vaccines: Design Considerations and Recent Advances. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 15, 576–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.-Q.; Cai, K.; Hu, J.-H.; Jiang, L.-W.; Gao, Y.-R.; Zhao, H.; Jia, S.-C. The Clinical Effects of Dendritic Cell Vaccines Combined with Cytokine-Induced Killer Cells Intraperitoneal Injected on Patients with Malignant Ascites. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 4272–4281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Geller, M.A.; Knorr, D.A.; Hermanson, D.A.; Pribyl, L.; Bendzick, L.; McCullar, V.; Miller, J.S.; Kaufman, D.S. Intraperitoneal Delivery of Human Natural Killer Cells for Treatment of Ovarian Cancer in a Mouse Xenograft Model. Cytotherapy 2013, 15, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denman, C.J.; Senyukov, V.V.; Somanchi, S.S.; Phatarpekar, P.V.; Kopp, L.M.; Johnson, J.L.; Singh, H.; Hurton, L.; Maiti, S.N.; Huls, M.H.; et al. Membrane-Bound IL-21 Promotes Sustained Ex Vivo Proliferation of Human Natural Killer Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyer, J.L.; Pandey, V.; Igarashi, R.Y.; Somanchi, S.S.; Zakari, A.; Solh, M.; Lee, D.A.; Altomare, D.A.; Copik, A.J. Natural Killer Cells Stimulated with PM21 Particles Expand and Biodistribute in Vivo: Clinical Implications for Cancer Treatment. Cytotherapy 2016, 18, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangisetty, S.L.; Miner, T.J. Malignant Ascites: A Review of Prognostic Factors, Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Measures. World J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2012, 4, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzanski, M.J.; Rewers-Felkins, K.A.; Quinlin, I.S.; Samad, K.A.; Phillips, C.A.; Robinson, W.; Dobrzanski, D.J.; Wright, S.E. Autologous MUC1-Specific Th1 Effector Cell Immunotherapy Induces Differential Levels of Systemic TReg Cell Subpopulations That Result in Increased Ovarian Cancer Patient Survival. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 133, 333–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, H.; Li, L.; Ma, Y.; Ni, J.; Li, Y. The Role of Tumour-Associated MUC1 in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Metastasis and Progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2013, 32, 535–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkayyal, A.A.; Tai, L.-H.; Kennedy, M.A.; de Souza, C.T.; Zhang, J.; Lefebvre, C.; Sahi, S.; Ananth, A.A.; Mahmoud, A.B.; Makrigiannis, A.P.; et al. NK-Cell Recruitment Is Necessary for Eradication of Peritoneal Carcinomatosis with an IL12-Expressing Maraba Virus Cellular Vaccine. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2017, 5, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Luo, M.; Wei, X.-W.; Ma, C.-C.; Yang, Y.-H.; Shao, B.; Liu, Y.-T.; Liu, T.; Ren, J.; Liu, L.; et al. A Folate Receptor-Targeted Lipoplex Delivering Interleukin-15 Gene for Colon Cancer Immunotherapy. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 52207–52217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujar, S.; Marcato, P.; Pan, D.; Lee, P.W. Reovirus Virotherapy Overrides Tumor Antigen Presentation Evasion and Promotes Protective Antitumor Immunity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 2924–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujar, S.; Dielschneider, R.; Clements, D.; Helson, E.; Shmulevitz, M.; Marcato, P.; Pan, D.; Pan, L.-Z.; Ahn, D.-G.; Alawadhi, A.; et al. Multifaceted Therapeutic Targeting of Ovarian Peritoneal Carcinomatosis through Virus-Induced Immunomodulation. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clements, D.; Helson, E.; Gujar, S.A.; Lee, P.W. Reovirus in Cancer Therapy: An Evidence-Based Review. Oncol. Virother. 2014, 3, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauer, U.M.; Schell, M.; Beil, J.; Berchtold, S.; Koppenhöfer, U.; Glatzle, J.; Königsrainer, A.; Möhle, R.; Nann, D.; Fend, F.; et al. Phase I Study of Oncolytic Vaccinia Virus GL-ONC1 in Patients with Peritoneal Carcinomatosis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 4388–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardwick, N.R.; Carroll, M.; Kaltcheva, T.; Qian, D.; Lim, D.; Leong, L.; Chu, P.; Kim, J.; Chao, J.; Fakih, M.; et al. P53MVA Therapy in Patients with Refractory Gastrointestinal Malignancies Elevates P53-Specific CD8+ T-Cell Responses. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 4459–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardwick, N.; Chung, V.; Cristea, M.; Ellenhorn, J.D.; Diamond, D.J. Overcoming Immunosuppression to Enhance a P53MVA Vaccine. Oncoimmunology 2014, 3, e958949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chianese-Bullock, K.A.; Irvin, W.P.; Petroni, G.R.; Murphy, C.; Smolkin, M.; Olson, W.C.; Coleman, E.; Boerner, S.A.; Nail, C.J.; Neese, P.Y.; et al. A Multipeptide Vaccine Is Safe and Elicits T-Cell Responses in Participants with Advanced Stage Ovarian Cancer. J. Immunother. 2008, 31, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, G.; Waks, T.; Eshhar, Z. Expression of Immunoglobulin-T-Cell Receptor Chimeric Molecules as Functional Receptors with Antibody-Type Specificity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 10024–10028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newick, K.; O’Brien, S.; Moon, E.; Albelda, S.M. CAR T Cell Therapy for Solid Tumors. Annu. Rev. Med. 2017, 68, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadelain, M.; Brentjens, R.; Rivière, I. The Basic Principles of Chimeric Antigen Receptor Design. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Wang, Y.; Lu, X.; Han, W. Chimeric Antigen Receptors Modified T-Cells for Cancer Therapy. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 108, djv439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kershaw, M.H.; Westwood, J.A.; Darcy, P.K. Gene-Engineered T Cells for Cancer Therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chmielewski, M.; Hombach, A.A.; Abken, H. Antigen-Specific T-Cell Activation Independently of the MHC: Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Redirected T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, J.; Schüßler-Lenz, M.; Bondanza, A.; Buchholz, C.J. Clinical Development of CAR T Cells-Challenges and Opportunities in Translating Innovative Treatment Concepts. EMBO Mol. Med. 2017, 9, 1183–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Gong, J.; Li, J.; Liu, D.; Qin, Y.; Ge, S.; Zhang, M.; Peng, Z.; Zhou, J.; Cao, Y.; et al. Claudin18.2-Specific CAR T Cells in Gastrointestinal Cancers: Phase 1 Trial Interim Results. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.C.; Abramson, J.S. Patient Selection for Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-Cell Therapy for Aggressive B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas. Leuk. Lymphoma 2020, 61, 2561–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramson, J.S. Anti-CD19 CAR T-Cell Therapy for B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2020, 34, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastoupil, L.J.; Jain, M.D.; Feng, L.; Spiegel, J.Y.; Ghobadi, A.; Lin, Y.; Dahiya, S.; Lunning, M.; Lekakis, L.; Reagan, P.; et al. Standard-of-Care Axicabtagene Ciloleucel for Relapsed or Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Results From the US Lymphoma CAR T Consortium. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3119–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, M.; Sharif, S.; Simmonds, M.; Claxton, L.; Hodgson, R. Tisagenlecleucel for the Treatment of Relapsed or Refractory B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia in People Aged up to 25 Years: An Evidence Review Group Perspective of a NICE Single Technology Appraisal. Pharmacoeconomics 2019, 37, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, S.C.; Point, G.R.; Cunetta, M.; Thorn, M.; Guha, P.; Espat, N.J.; Boutros, C.; Hanna, N.; Junghans, R.P. Regional CAR-T Cell Infusions for Peritoneal Carcinomatosis Are Superior to Systemic Delivery. Cancer Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murad, J.P.; Kozlowska, A.K.; Lee, H.J.; Ramamurthy, M.; Chang, W.-C.; Yazaki, P.; Colcher, D.; Shively, J.; Cristea, M.; Forman, S.J.; et al. Effective Targeting of TAG72+ Peritoneal Ovarian Tumors via Regional Delivery of CAR-Engineered T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, W.X.; Li, Z.; Chi, Z.; Du, S.-H.; Chen, C.; Tay, J.C.K.; Toh, H.C.; Connolly, J.E.; Xu, X.H.; Wang, S. Intraperitoneal Immunotherapy with T Cells Stably and Transiently Expressing Anti-EpCAM CAR in Xenograft Models of Peritoneal Carcinomatosis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 13545–13559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Olmo, D.; Villarejo Campos, P.; Barambio, J.; Gomez-Heras, S.G.; Vega-Clemente, L.; Olmedillas-Lopez, S.; Guadalajara, H.; Garcia-Arranz, M. Intraperitoneal Collagenase as a Novel Therapeutic Approach in an Experimental Model of Colorectal Peritoneal Carcinomatosis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benmebarek, M.-R.; Karches, C.H.; Cadilha, B.L.; Lesch, S.; Endres, S.; Kobold, S. Killing Mechanisms of Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Zhao, R.; Wu, D.; Zheng, D.; Wu, Z.; Shi, J.; Wei, X.; Wu, Q.; Long, Y.; Lin, S.; et al. Mesothelin Is a Target of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells for Treating Gastric Cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, G.; Li, J.; Lv, X.; Shi, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, S.; Yan, P.; Wang, S.; et al. Antitumor Effects and Persistence of a Novel HER2 CAR T Cells Directed to Gastric Cancer in Preclinical Models. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 106–119. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, M.; Yang, Y.; McCloskey, J.E.; Zaman, M.; Vedvyas, Y.; Zhang, X.; Stefanova, D.; Gray, K.D.; Min, I.M.; Zarnegar, R.; et al. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy Targeting ICAM-1 in Gastric Cancer. Mol. Ther. Oncol. 2020, 18, 587–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, S.C.; Burga, R.A.; McCormack, E.; Wang, L.J.; Mooring, W.; Point, G.R.; Khare, P.D.; Thorn, M.; Ma, Q.; Stainken, B.F.; et al. Phase I Hepatic Immunotherapy for Metastases Study of Intra-Arterial Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified T-Cell Therapy for CEA+ Liver Metastases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3149–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkhurst, M.R.; Yang, J.C.; Langan, R.C.; Dudley, M.E.; Nathan, D.-A.N.; Feldman, S.A.; Davis, J.L.; Morgan, R.A.; Merino, M.J.; Sherry, R.M.; et al. T Cells Targeting Carcinoembryonic Antigen Can Mediate Regression of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer but Induce Severe Transient Colitis. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayne, L.; Beatty, G.; Jhala, N.; Clark, C.; Rhim, A.; Stanger, B.; Vonderheide, R. Tumor-Derived Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor Regulates Myeloid Inflammation and T Cell Immunity in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 822–835. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22698406/ (accessed on 15 July 2022). [CrossRef]
- Dilek, N.; Vuillefroy de Silly, R.; Blancho, G.; Vanhove, B. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells: Mechanisms of Action and Recent Advances in Their Role in Transplant Tolerance. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pylayeva-Gupta, Y.; Lee, K.E.; Hajdu, C.H.; Miller, G.; Bar-Sagi, D. Oncogenic Kras-Induced GM-CSF Production Promotes the Development of Pancreatic Neoplasia. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 836–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledermann, J.A.; Canevari, S.; Thigpen, T. Targeting the Folate Receptor: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches to Personalize Cancer Treatments. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 2034–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, D.-G.; Ye, Q.; Carpenito, C.; Poussin, M.; Wang, L.-P.; Ji, C.; Figini, M.; June, C.H.; Coukos, G.; Powell, D.J. In Vivo Persistence, Tumor Localization, and Antitumor Activity of CAR-Engineered T Cells Is Enhanced by Costimulatory Signaling through CD137 (4-1BB). Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 4617–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, W.A.; June, C.H. The Principles of Engineering Immune Cells to Treat Cancer. Cell 2017, 168, 724–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawalekar, O.U.; O’Connor, R.S.; Fraietta, J.A.; Guo, L.; McGettigan, S.E.; Posey, A.D.; Patel, P.R.; Guedan, S.; Scholler, J.; Keith, B.; et al. Distinct Signaling of Coreceptors Regulates Specific Metabolism Pathways and Impacts Memory Development in CAR T Cells. Immunity 2016, 44, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, Y.; Hasegawa, K.; Matsushita, H.; Fujieda, N.; Sato, S.; Miyagi, E.; Kakimi, K.; Fujiwara, K. Expression of Multiple Immune Checkpoint Molecules on T Cells in Malignant Ascites from Epithelial Ovarian Carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 6457–6468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiko, K.; Mandai, M.; Hamanishi, J.; Yoshioka, Y.; Matsumura, N.; Baba, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Murakami, R.; Yamamoto, A.; Kharma, B.; et al. PD-L1 on Tumor Cells Is Induced in Ascites and Promotes Peritoneal Dissemination of Ovarian Cancer through CTL Dysfunction. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 1363–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koneru, M.; Purdon, T.; Spriggs, D.; Koneru, S.; Brentjens, R. IL-12 Secreting Tumor-Targeted Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells Eradicate Ovarian Tumors in Vivo. Oncoimmunology 2015, 4, e994446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Brown, C.E.; Ostberg, J.R.; Priceman, S.J.; Chang, W.-C.; Weng, L.; Lin, P.; Wakabayashi, M.T.; Jensen, M.C.; Forman, S.J. L1 Cell Adhesion Molecule-Specific Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Redirected Human T Cells Exhibit Specific and Efficient Antitumor Activity against Human Ovarian Cancer in Mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daponte, A.; Kostopoulou, E.; Kollia, P.; Papamichali, R.; Vanakara, P.; Hadjichristodoulou, C.; Nakou, M.; Samara, S.; Koukoulis, G.; Messinis, I.E. L1 (CAM) (CD171) in Ovarian Serous Neoplasms. Eur. J. Gynaecol. Oncol. 2008, 29, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.J.; Dougan, M.; Jailkhani, N.; Ingram, J.; Fang, T.; Kummer, L.; Momin, N.; Pishesha, N.; Rickelt, S.; Hynes, R.O.; et al. Nanobody-Based CAR T Cells That Target the Tumor Microenvironment Inhibit the Growth of Solid Tumors in Immunocompetent Mice. Biol. Sci. 2019, 116, 7624–7631. Available online: https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.1817147116#supplementary-materials (accessed on 15 July 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, D.; Li, D.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Y.; Liao, X.; Li, X.; Alexander, P.B.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.-J. Potential Lung Attack and Lethality Generated by EpCAM-Specific CAR-T Cells in Immunocompetent Mouse Models. Oncoimmunology 2020, 9, 1806009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Garcia, A.; Lynn, R.C.; Poussin, M.; Eiva, M.A.; Shaw, L.C.; O’Connor, R.S.; Minutolo, N.G.; Casado-Medrano, V.; Lopez, G.; Matsuyama, T.; et al. CAR-T Cell-Mediated Depletion of Immunosuppressive Tumor-Associated Macrophages Promotes Endogenous Antitumor Immunity and Augments Adoptive Immunotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Wei, F.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yu, B.; Huang, Z. Delivery of CD47 Blocker SIRPα-Fc by CAR-T Cells Enhances Antitumor Efficacy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e003737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janjigian, Y.Y.; Shitara, K.; Moehler, M.; Garrido, M.; Salman, P.; Shen, L.; Wyrwicz, L.; Yamaguchi, K.; Skoczylas, T.; Campos Bragagnoli, A.; et al. First-Line Nivolumab plus Chemotherapy versus Chemotherapy Alone for Advanced Gastric, Gastro-Oesophageal Junction, and Oesophageal Adenocarcinoma (CheckMate 649): A Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shariati, M.; Willaert, W.; Ceelen, W.; De Smedt, S.C.; Remaut, K. Aerosolization of Nanotherapeutics as a Newly Emerging Treatment Regimen for Peritoneal Carcinomatosis. Cancers 2019, 11, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Qiu, M.; Wang, T.; Li, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, T.; Liu, P.; Wang, Q.; Qian, Z.R.; Zhu, C.; et al. Carrier-Free Multifunctional Nanomedicine for Intraperitoneal Disseminated Ovarian Cancer Therapy. J. Nanobiotechnology 2022, 20, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, B.; He, Z.; Tu, B.; Zhao, P.; Wang, H.; Asrorov, A.; Muhitdinov, B.; Jiang, J.; Huang, Y. Nanotherapeutic Macrophage-Based Immunotherapy for the Peritoneal Carcinomatosis of Lung Cancer. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 2304–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.; Guo, F.; Yu, Z.; Liu, P.; Dong, S.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, Y.; Kong, X.; Li, T.; Luo, Y.; et al. Engineered Apoptosis-Bioinspired Nanoparticles Initiate Immune Cascade for Cancer Immunotherapy of Malignant Ascites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 10371–10382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Identifier | Trial Phase | Treatment | Cancer Condition | Administration Route | Study Status | Start-Completion Date | Autor and Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT03311334 | I II | Nivolumab Pembrolizumab (Anti-PD-1) DSP-7888 Dosing Emulsion | Primary Peritoneal Cancer Cancer metastases in the peritoneum | Intradermally | Completed | December 2017–November 2022 | United States |
| NCT04442126 | I, II | NM21-1480 (Anti-PDL-1/Anti-4-1BB/Anti-has Tri-Specific Antibody) | Advanced solid tumors. | Intravenously | Recruiting | August 2020–January 2025 | United States |
| NCT03249142 | I, II | Durvalumab (Anti-PD) Tremelimumab (CTLA-4) chemotherapy | Ovarian Cancer primary peritoneal or fallopian tube adenocarcinoma | Intravenously | Active, not recruiting | October 2017–April 2023 | France |
| NCT05538091 | II | Atezolizumab (Anti-PD-L1) Vismodegib | Ovarian, Fallopian Tube, and Primary Peritoneal Cancer | Intravenously | Not yet recruiting | October 2022–October 2026 | United States |
| NCT02725489 | II | Durvalumab (Anti-PD-L1) Vigil | Gynecologic cancer Breast Cancer Primary Peritoneal Carcinoma | Intravenously | Complete | Jun 2016–December 2020 | United States |
| NCT02728830 | Early Phase I | Pembrolizumab (Anti-PD-L1) | Gynecologic Cancers of Mullerian Origin | Intravenously | Active, not recruiting | Jun 2016–December 2021 | United States |
| NCT03598270 | III | Atezolizumab (Anti-PD-L1) Niraparib platinum-based doublet chemotherapy | Ovarian Cancer | Intravenously | Active, not recruiting | November 2018–January 2025 | Belgium |
| NCT05065021 | II | Dostarlimab (Anti-PD-L1) Niraparib Bevacizumab Paclitaxel | Ovarian Cancer Fallopian Tube Cancer Primary Peritoneal Cancer | Intravenously | Not yet recruiting | Jun 2022–Jun 2025 | Canada |
| NCT04739800 | II | Durvalumab (Anti-PD-L1) Cediranib olaparib | Ovarian Cancer Fallopian Tube Cancer Primary Peritoneal Cancer | Intravenously | Recruiting | April 2021–December 2023 | United States |
| NCT02963831 | I, II | Durvalumab (Anti-PD-L1) ONCOS-102 Cyclophosphamide | Colorectal Cancer Ovarian Cancer Appendiceal Cancer Biological: ONCOS-102 | Intravenously | Completed | September 2017–Jun 2022 | United States |
| NCT02659384 | II | Atezolizumab (Anti-PD-L1) Bevacizumab acetylsalicylic acid | Ovarian Neoplasms Fallopian Tube or Primary Peritoneal Adenocarcinoma | Intravenously | Active, not recruiting | December 2016–February 2023 | France and Netherlands |
| NCT02399371 | II | Pembrolizumab (Anti-PD-L1) | Malignant Mesothelioma | Intravenously | Active, not recruiting | March 2015–March 2024 | United States |
| NCT03363867 | II | Atezolizumab (Anti-PD-L1) Bevacizumab Cobimetinib | Ovarian Cancer Fallopian Tube Cancer Primary Peritoneal Cancer | Intravenously | Recruiting | July 2018– February 2024 | Australia |
| NCT04611126 | I, II | Ipilimumab (anti-CTLA-4) Nivolumab (Anti-PD-1) Relatlimab Cyclophosphamide Fludarabine Phosphate | Ovarian Cancer Fallopian Tube Cancer Primary Peritoneal Cancer | Intravenously | Recruiting | April 2021–December 2023 | Denmark |
| NCT02834013 | II | Ipilimumab (anti-CTLA-4) Nivolumab (Anti-PD-1) | Peritoneal Mesothelioma Primary Peritoneal High Grade Serous Adenocarcinoma | Intravenously | Recruiting | January 2017–October 2023 | United States |
| NCT03872947 | I | Nivolumab/Pembrolizumab (Anti-PD-1) TRK-950 | Solid Tumor Malignancy | Intravenously | Recruiting | April 2019–August 2024 | United States |
| NCT03029598 | I, II | Pembrolizumab (Anti-PD-1) Carboplatin | Recurrent Fallopian Tube Carcinoma Recurrent ovarian Carcinoma Recurrent Primary Peritoneal Carcinoma | Intravenously | Completed Has Results | March 2017–December 2021 | United States |
| NCT05030246 | II | Toripalimab (Anti-PD-1) Surufatinib | Refractory Metastatic Digestive System Carcinoma Primary Peritoneal Cancer | Intravenously | Recruiting | July 2021–July 2023 | China |
| NCT04387227 | II | Pembrolizumab (Anti-PD-1) Carboplatin | Recurrent Fallopian Tube Carcinoma Recurrent Ovarian Carcinoma Recurrent Primary Peritoneal Carcinoma | Intravenously | Recruiting | March 2021–April 2025 | United States |
| NCT05648487 | II | Sintilimab (anti-PD-1) Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC) | Gastric Cancer | Intravenously | Not yet recruiting | January 2023–December 2027 | China |
| NCT05446298 | II | Pembrolizumab (anti-PD-1) ONC-392 (Anti-CTLA-4) | Ovarian Cancer High Grade Serous Adenocarcinoma of Ovary Primary Peritoneal Carcinoma Fallopian Tube Cancer | Intravenously | Recruiting | December 2022–June 2026 | United States |
| NCT05271318 | I | Pembrolizumab (anti-PD-1) TILT-123 | Ovarian Carcinoma Fallopian Tube Carcinoma Primary Peritoneal Carcinoma | Intravenously | Recruiting | May 2022–March 2026 | United States |
| NCT05581719 | I, II | Nivolumab (Anti-PD-1) Allocetra-OTS | Solid Tumor Malignancy | Intravenously | Recruiting | October 2022–June 2024 | Israel |
| NCT04042116 | I, II | Nivolumab (Anti-PD-1) Lucitanib | Advanced Solid Tumor Gynecologic Cancer | Intravenously | Active, not recruiting | July 2019–January 2024 | United States |
| NCT02571725 | I, II | Tremelimumab (anti-CTLA-4) Olaparib | Ovarian Cancer Fallopian Tube Cancer Primary Peritoneal Cancer | Intravenously | Active, not recruiting | February 2016–July 2027 | United States |
| NCT04034927 | II | Tremelimumab (anti-CTLA-4) Olaparib | Ovarian Cancer Fallopian Tube Cancer Primary Peritoneal Cancer | Intravenously | Active, not recruiting | October 2019–December 2022 | United States |
| Identifier | Trial Phase | Target | Cancer Condition | Administration Route | Start-Completion Date | Study Status | Outcomes | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOC31PE Immunotoxin (antibody MOC31) | ||||||||
| NCT02219893 | I & II | EpCAM | Colorectal Neoplasms | Intraperitoneal | August 2014–30 May 2017 | Completed | No results | Norway |
| Catumaxomab | ||||||||
| NCT00189345 | II | EpCAM, Anti-CD3 | Ovarian Cancer | Intraperitoneal | May 2004–October 2005 | Completed | No results | Germany |
| NCT00377429 | II | EpCAM Anti-CD3 | Ovarian Cancer | Intraperitoneal | September 2006–February 2008 | Completed Has Results |
| United States |
| NCT01784900 | II | EpCAM, Anti-CD3 | Gastric Cancer | Intraperitoneal | November 2012–January 2016 | Terminated | No results | France |
| NCT01504256 | II | Anti-EpCAM Anti-CD3 | Gastric Cancer | Intraperitoneal | October 2011–July 2017 | completed | No results | Germany |
| NCT00326885 | II | Anti-EpCAM, Anti-CD3 | Ovarian cancer | Intraperitoneal | June 2006–August 2010 | Completed Has Results | Catumaxomab extended PuFI and TTPu, im-proved ascites symptoms, and exhibited an acceptable safety profile | United States |
| NCT04222114 | III | Anti-EpCAM, Anti-CD3 | Gastric Cancer | Intraperitoneal | 6 October 2020–31 August 2023 | Recruiting | No results | China |
| NCT01246440 | II | Anti-EpCAM, Anti-CD3 | Ovarian cancer | Intraperitoneal | June 2010–December 2014 | Completed | No results | Spain |
| Identifier | Trial Phase | Treatment | Cancer Condition | Administration Route | Study Status | Outcomes | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02151448 | I, II | Dendritic cell vaccine (αDC1 Vaccine) | Pancreas cancer | Intranodal and intradermal | Completed Has results | Well-tolerated Not acceptable for CRS/HIPEC for peritoneal metastases. | United States |
| NCT02275039 | I | p53MVA vaccine | Ovarian cancer Fallopian Tube Primary Peritoneal Cancers | Intravenously | Completed | No results | United States |
| NCT00478452 | I | Dendritic cell vaccine | Ovarian cancer | Intradermal | Completed | No results | United States |
| NCT00803569 | I | ALVAC(2)-NY-ESO-1(M)/TRICOM | Ovarian cancer Fallopian Tube Primary Peritoneal Cancers | Subcutaneous | Completed Has results | NY-ESO-1 produces significant immune responses in cancer patients but has limited objective clinical responses to NY-ESO-1 expressing tumors | United States |
| NCT00112957 | II | rV-NY-ESO-1 vaccine | Ovarian cancer Fallopian Tube Cancer Primary Peritoneal Cavity Cancer | Intradermal | Completed Has results | PFS was 21 months and OS 48 months. Vaccinated CD8+ T cells lysed NY-ESO-1-expressing tumors. | United States |
| NCT01673217 | I | NY-ESO-1 peptide vaccine | Ovarian Fallopian Tube Cancer Primary Peritoneal Cavity Cancer | Subcutaneously | Completed | No results | United States |
| NCT03029403 | II | DPX-Survivac | Ovarian cancer | Subcutaneously | Recruiting | No results | Canada |
| NCT03113487 | II | P53MVA vaccine | Ovarian cancer | subcutaneously | Active, not recruiting | No results | United States |
| NCT03206047 | I, II | DEC-205/NY-ESO-1 Fusion Protein CDX-1401 | Ovarian cancer | Intravenously | Active, not recruiting | No results | United States |
| NCT02111941 | Early Phase 1 | Multi-epitope Folate Receptor Alpha-loaded Dendritic Cell Vaccine | Ovarian cancer | Intradermally | Active, not recruiting | No results | United States |
| NCT01606241 | I | Multi-epitope Folate Receptor Alpha Peptide Vaccine | Ovarian cancer Breast Cancer | Intradermally (ID) | Completed | No results | United States |
| NCT02166905 | I, II | DEC-205/NY-ESO-1 Fusion Protein CDX-1401 | Ovarian cancer Fallopian Tube Carcinoma | Intravenously | Completed | No results | United States |
| NCT03332576 | I | DPX-Survivac | Ovarian cancer Fallopian Tube Carcinoma | Subcutaneously | Completed | No results | Canada |
| NCT00616941 | I | NY-ESO-1 OLP4 Montanide Poly-ICLC | Ovarian cancer Fallopian Tube Carcinoma | Subcutaneously | Completed Has results | Montanide and poly-ICLC induced NY-ESO-1-specific Th1 cells by OLP vaccination. | United States |
| NCT00437502 | I | tumor peptide vaccine | Ovarian cancer | Intradermally subcutaneously | Completed | No results | United States |
| NCT01536054 | I | ALVAC (2)-NY-ESO-1 (M)/TRICOM vaccine | Ovarian cancer Fallopian Tube Carcinoma Primary Peritoneal Cavity Cancer | Subcutaneously | Completed | No results | United States |
| NCT00857545 | II | Polyvalent Antigen-KLH Conjugate Vaccine | Ovarian cancer Fallopian Tube Carcinoma Primary Peritoneal Cavity Cancer | Subcutaneously | Completed Has results | Vaccine+OPT-821 was slightly immunogenic and did not prolong PFS or OS | United States |
| NCT00408590 | I | carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)-expressing measles virus (MV-CEA) and oncolytic measles virus encoding thyroidal sodium iodide symporter (MV-NIS) | Ovarian cancer Primary Peritoneal Cavity Cancer | Intraperitoneally | Completed Has results | no dose-limiting toxicity, treatment-induced immunosuppression Survival rates averaged 12.15 months. | United States |
| NCT01416038 | I | DPX-Survivac | Ovarian cancer Fallopian Tube Carcinoma Primary Peritoneal Cavity Cancer | Subcutaneously. | Completed | No results | United States |
| NCT00683241 | I | DCVac-L | Ovarian cancer | Intradermally | Completed | No results | United States |
| NCT00437502 | I | tumor peptide vaccine | Ovarian cancer | Intradermally Subcutaneously | Completed | No results | United States |
| NCT01248273 | I | Globo-H-GM2-sTn-TF-Tn-KLH conjugate, plus the immunological adjuvant QS-21 | Ovarian cancer Fallopian Tube Carcinoma | Subcutaneously | Completed | No results | United States |
| NCT02151448 | I, II | DC vaccine | Appendiceal Cancer, colorectal cancer Pancreas cancer | Intradermally | Completed | No results | United States |
| NCT01580696 | I, II | E39 peptide (100 mcg)/GM-CSF vaccine plus E39 booster | Ovarian cancer Fallopian Tube Carcinoma | Intradermally | Completed | No results | United States |
| NCT00006041 | I | MUC1-KLH conjugate vaccine | Ovarian cancer Fallopian Tube Carcinoma | Subcutaneously | Completed | No results | United States |
| NCT00091273 | I | ovarian cancer peptide vaccine tetanus toxoid helper peptide | Ovarian cancer | Subcutaneously Intradermally | Completed | No results | United States |
| NCT00066729 | I | NY-ESO-1 peptide vaccine | Ovarian cancer Fallopian Tube Carcinoma | Subcutaneously | Completed Has results | Low toxicity and promotes T-cell immunity in NY-ESO-1 positive and negative tumor patients. | United States |
| NCT00058435 | I | MOAB ACA125 | Ovarian cancer Fallopian Tube Carcinoma Peritoneal Cancer | Intramuscularly, Subcutaneously | Completed | No results | United States |
| NCT00478387 | Killed Influenza Vaccine | Ovarian Cancer Fallopian Tube, and Primary Peritoneal Cancer | Intramuscular | Completed | No results | United States | |
| NCT00799110 | II | Dendritic Cell/Tumor Fusion Vaccine | Ovarian cancer Fallopian Tube Carcinoma | Subcutaneously | Active, not recruiting | No results | United States |
| NCT01132014 | Early Phase 1 | OC-DC, | Ovarian cancer | Intranodally | Completed | No results | United States |
| NCT02785250 | I, II | DPX-Survivac | Ovarian cancer Fallopian Tube Carcinoma | Subcutaneously | Active, not recruiting | No results | United States |
| NCT00398138 | I | WT-1 analog peptide vaccine | Primary Peritoneal Cavity Cancer | Subcutaneously | Completed Has Results | No serious adverse effects were observed. polyvalent WT1 peptide vaccination can be safely provided to individuals with an immunological response. | United States |
| NCT02737787 | I | WT1 Vaccine Nivolumab NY-ESO-1 Vaccine | Ovarian Cancer Fallopian Tube Primary Peritoneal Cancer | Intravenously | Active, not recruiting | No results | United States |
| NCT03311334 | I, II | DSP-7888 Dosing Emulsion with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Nivolumab or Pembrolizumab | Renal Cell Carcinoma Urothelial Carcinoma Primary Peritoneal Cancer Ovarian Cancer Fallopian Tube Cancer | Intradermally | Completed | No results | United States |
| NCT03735589 | I II | Alpha-type-1 Polarized Dendritic Cells Autologous Natural Killer Cell-like CTLs | Fallopian Tube Cancer Ovarian Cancer Primary Peritoneal Cancer | Intraperitoneal Intradermally | Not yet recruiting | No results | United States |
| Identifier | Trial Phase | Target Antigen | Cancer Condition | Administration Route | Start-Completion Date | Study Status | Autor and Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT03563326 | I | EpCAM | Cancer Gastric with peritoneal metastasis9 | Intraperitoneal | August 2018– December 2022 | Recruiting | China |
| NCT03054298 | I | huCART-meso cells | Ovarian Cancer Peritoneal Carcinoma Fallopian Tube Cancer Mesotheliomas Pleural Mesothelioma Peritoneum | Intravenous or local delivery | April 2017 –March 2025 | Recruiting | United States |
| NCT04684459 | I | HER2 and PD-L1 | Peritoneal Carcinoma Metastatic | Intraperitoneal | March 2021– January 2024 | Active, not recruiting | China |
| NCT05477927 | I | VEGFR1 and PD-L1 | Ovarian cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, gastric cancer, with peritoneal metastasis, etc. | Intrapleural or intraperitoneal | August 2022–December 2024 | Active, not recruiting | China |
| NCT03907527 | I | MUC16 | Ovarian Cancer Fallopian Tube Cancer Primary peritoneal Carcinoma | Intraperitoneal and intravenously | April 2019–November 2028 | Recruiting | United States |
| NCT03585764 | I | Folate receptor-α (FRα) | Ovarian Cancer Fallopian Tube Cancer Primary peritoneal Carcinoma | Intraperitoneal | October 2018–October 2041 | Recruiting | United States |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ornella, M.S.C.; Badrinath, N.; Kim, K.-A.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, E.; Hwang, T.-H.; Kim, J.-J. Immunotherapy for Peritoneal Carcinomatosis: Challenges and Prospective Outcomes. Cancers 2023, 15, 2383. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082383
Ornella MSC, Badrinath N, Kim K-A, Kim JH, Cho E, Hwang T-H, Kim J-J. Immunotherapy for Peritoneal Carcinomatosis: Challenges and Prospective Outcomes. Cancers. 2023; 15(8):2383. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082383
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrnella, Mefotse Saha Cyrelle, Narayanasamy Badrinath, Kyeong-Ae Kim, Jung Hee Kim, Euna Cho, Tae-Ho Hwang, and Jae-Joon Kim. 2023. "Immunotherapy for Peritoneal Carcinomatosis: Challenges and Prospective Outcomes" Cancers 15, no. 8: 2383. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082383
APA StyleOrnella, M. S. C., Badrinath, N., Kim, K.-A., Kim, J. H., Cho, E., Hwang, T.-H., & Kim, J.-J. (2023). Immunotherapy for Peritoneal Carcinomatosis: Challenges and Prospective Outcomes. Cancers, 15(8), 2383. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082383






