Cancer Risk in Patients Treated with the JAK Inhibitor Tofacitinib: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
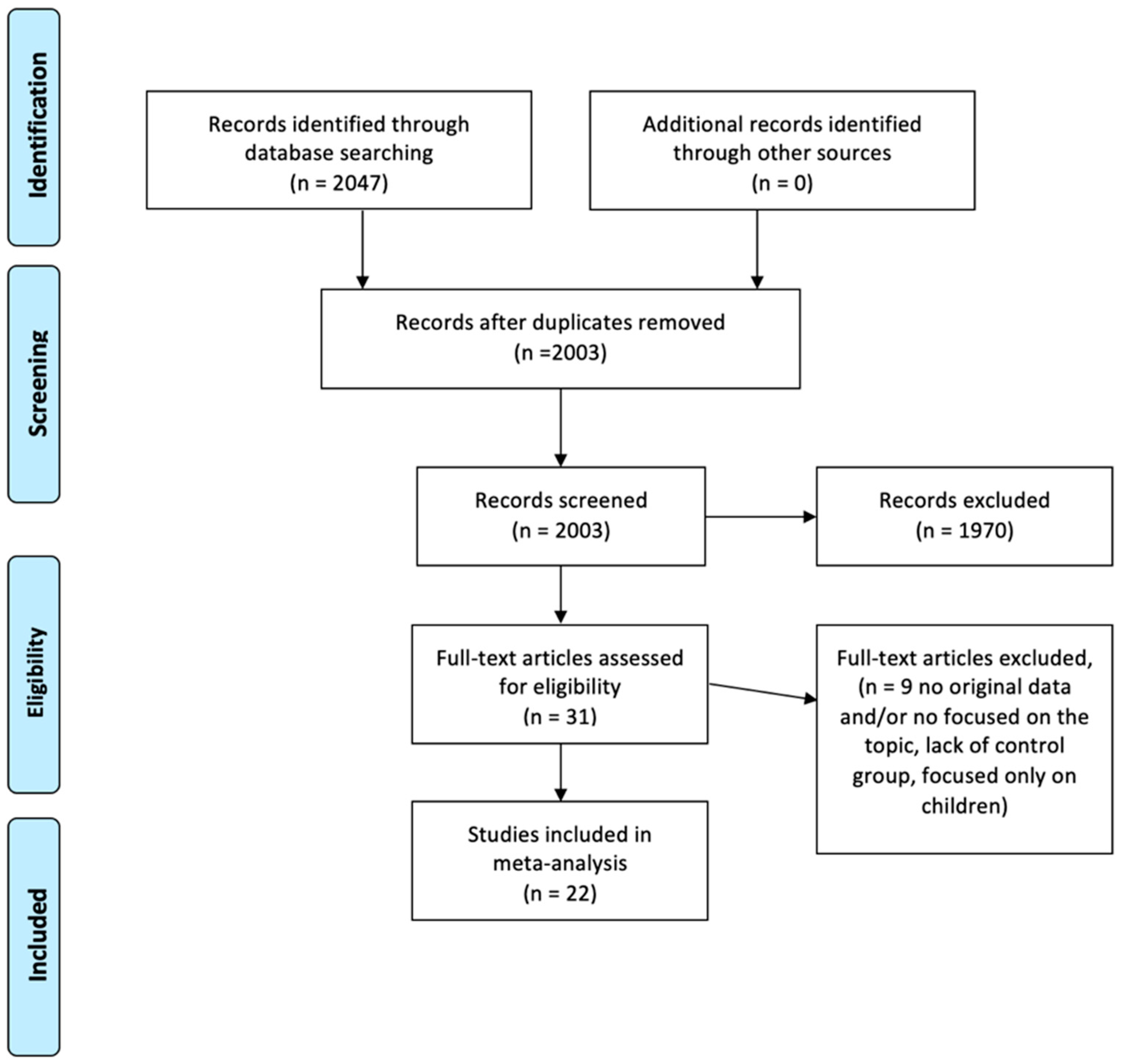
2.1. Bibliographic Research and Article Selection
2.2. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.3. Meta-Analyses
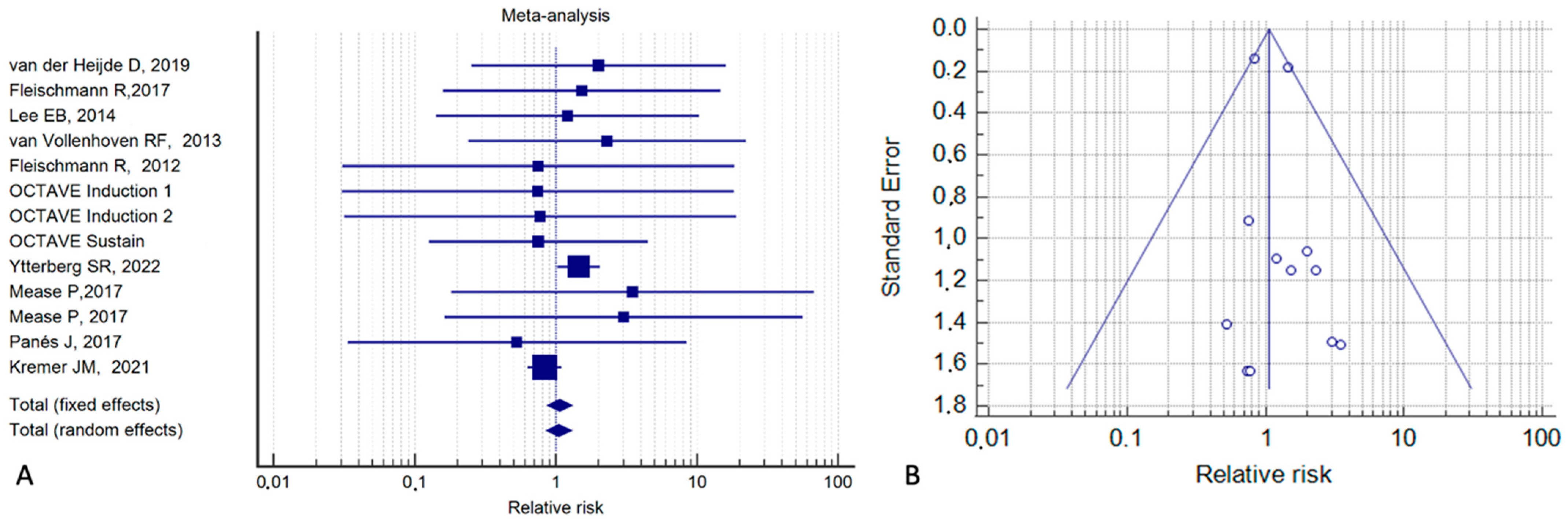
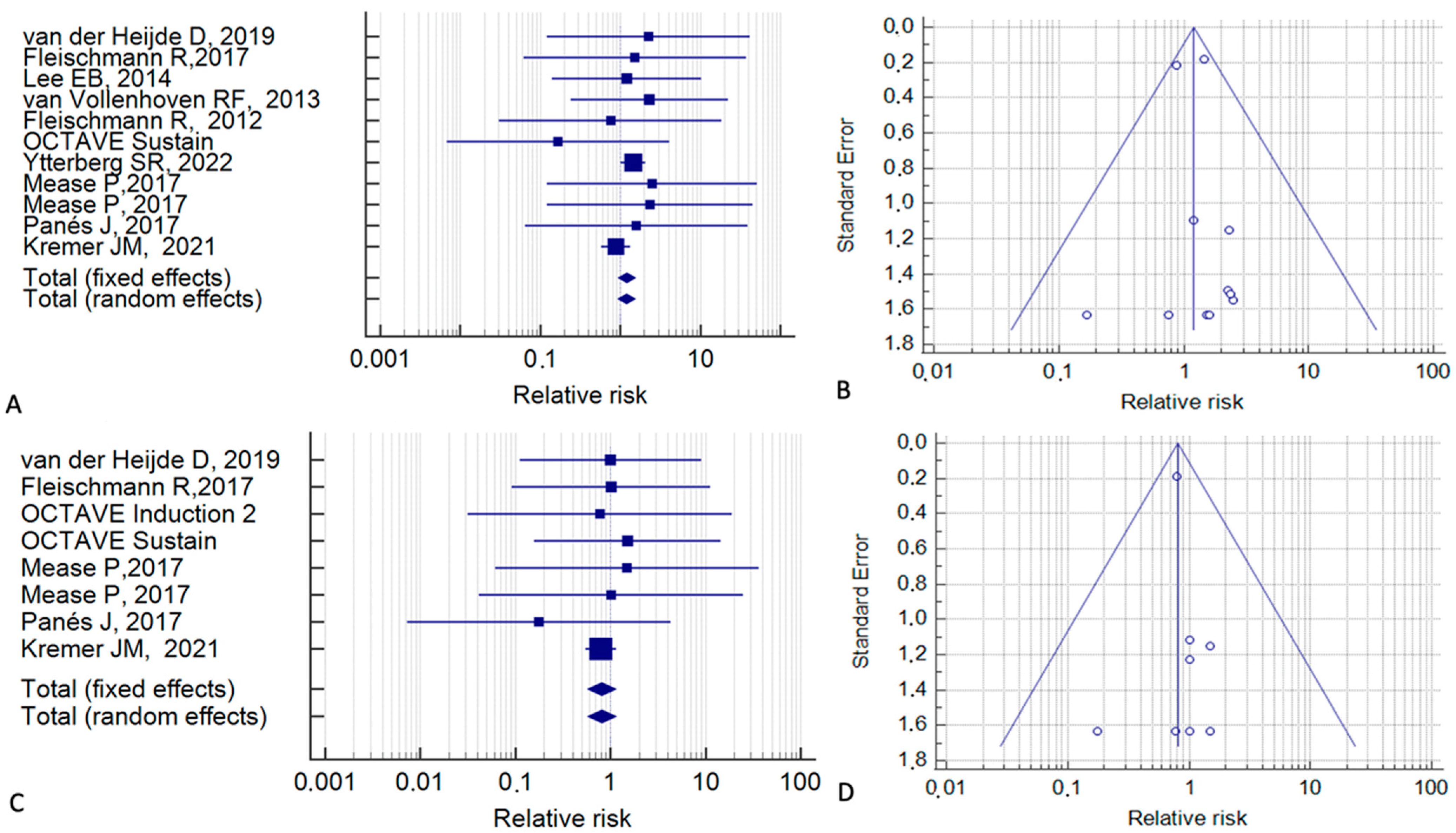
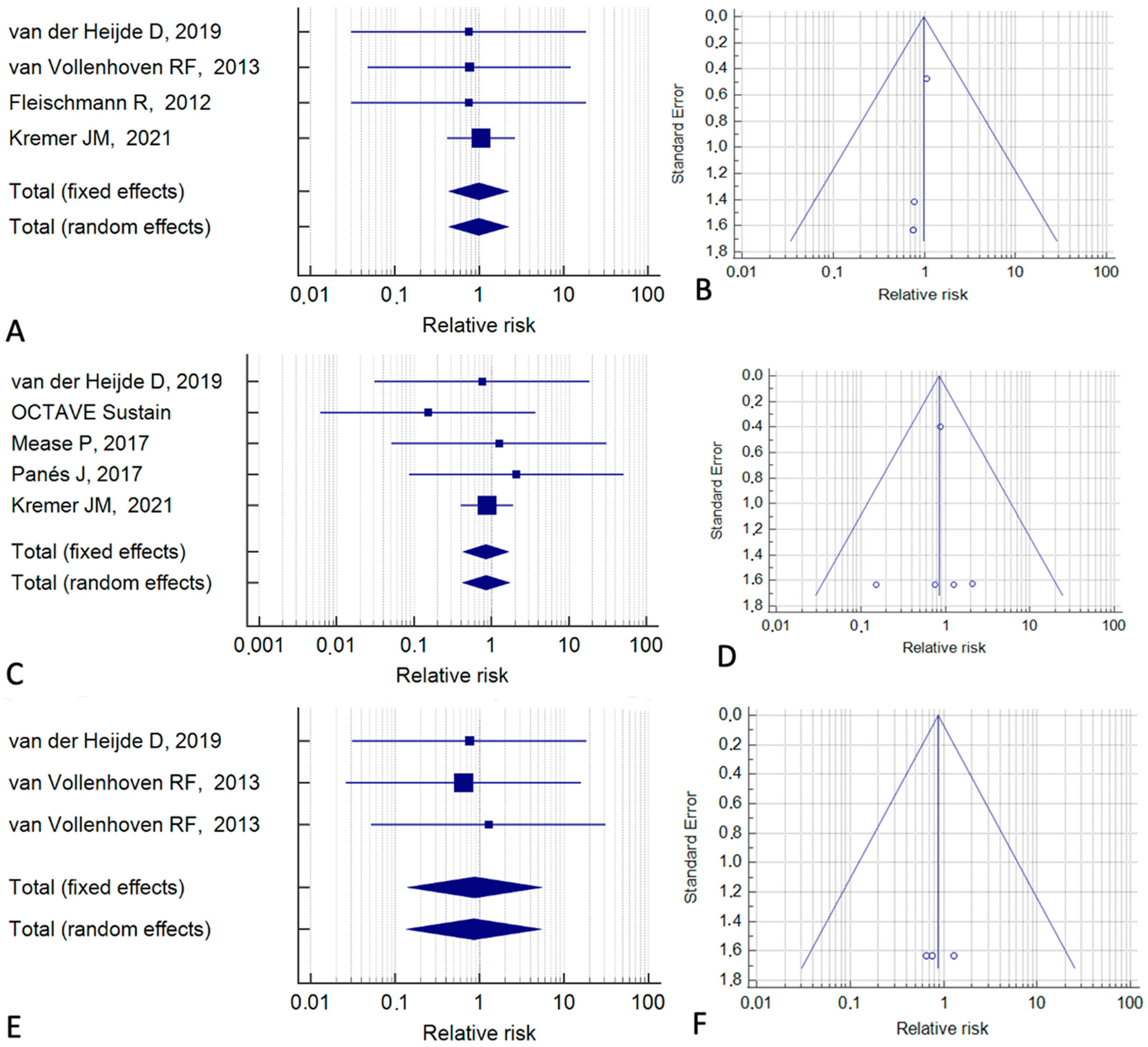
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Honap, S.; Cookson, H.; Sharma, E.; Samaan, M.A.; Irving, P.M. Tofacitinib for the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis, Alopecia Universalis, and Atopic Dermatitis: One Drug, Three Diseases. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2021, 27, E13–E14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Jiang, M.; Sun, M.-J. Tofacitinib as Induction and Maintenance Therapy for Ulcerative Colitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlman, H.; Mavers, M.; Ruderman, E.M. Intracellular signal pathways: Potential for therapies. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2009, 11, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seavey, M.M.; Dobrzanski, P. The many faces of Janus kinase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeshi, K.; Ruscher, R.; Hunter, L.; Daly, N.L.; Loukas, A.; Wangchuk, P. Revisiting Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Pathology, Treatments, Challenges and Emerging Therapeutics Including Drug Leads from Natural Products. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofacitinib: Approved for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/110353 (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Available online: https://www.pfizermedicalinformation.com/en-us/xeljanz/indications-usage (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Zand, M.S. Tofacitinab in renal transplantation. Transplant. Rev. 2013, 27, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, K.; Roongta, R.; Dey, S.; Dey, S.; Mondal, S.; Sinhamahapatra, P.; Ghosh, P.; Ghosh, B. Refractory Takayasu arteritis with recurrent Pyoderma gangrenosum: A therapeutic challenge with case-based review. Clin. Rheumatol. 2023, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orfaly, V.E.; Kovalenko, I.; Tolkachjov, S.N.; Ortega-Loayza, A.G.; Nunley, J.R. Tofacitinib for the treatment of refractory Pyoderma gangrenosum. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 46, 1082–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olavarría, P.S.; Iturria, S.R.; Castillejo, Ó.N. Tofacitinib, a useful option for the treatment of Pyoderma gangrenosum in an ulcerative colitis patient. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2021, 113, 733–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedano, R.; Jairath, V. Tofacitinib for the Treatment of Three Immune-mediated Conditions in One Patient: Ulcerative Colitis, Pyoderma Gangrenosum, and Alopecia Areata. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2021, 27, E65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalles, C.; Lepelley, M.; Mouret, S.; Charles, J.; Leccia, M.T.; Trabelsi, S. Skin cancers under Janus kinase inhibitors: A World Health Organization drug safety database analysis. Therapie 2022, 77, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.; Xue, X.; Shannon, J. Characteristics of adverse event reporting of Xeljanz/Xeljanz XR, Olumiant, and Rinvoq to the US Food and Drug Administration. J. Manag. Care Spec. Pharm. 2022, 28, 1046–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ytterberg, S.R.; Bhatt, D.L.; Mikuls, T.R.; Koch, G.G.; Fleischmann, R.; Rivas, J.L.; Germino, R.; Menon, S.; Sun, Y.; Wang, C.; et al. Cardiovascular and Cancer Risk with Tofacitinib in Rheumatoid Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA. FDA Approves Boxed Warning about Increased Risk of Blood Clots and Death with Higher Dose of Arthritis and Ulcerative Colitis Medicine Tofacitinib (Xeljanz, Xeljanz XR). Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/fda-drug-safety-podcasts/fda-approves-boxed-warning-about-increased-risk-blood-clots-and-death-higher-dose-arthritis-and (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Curtis, J.R.; Yamaoka, K.; Chen, Y.H.; Bhatt, D.L.; Gunay, L.M.; Sugiyama, N.; Connell, C.A.; Wang, C.; Wu, J.; Menon, S.; et al. Malignancy risk with tofacitinib versus TNF inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis: Results from the open-label, randomised controlled ORAL Surveillance trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 82, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosrow-Khavar, F.; Desai, R.J.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.B.; Kim, S.C. Tofacitinib and Risk of Malignancy: Results From the Safety of Tofacitinib in Routine Care Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (STAR-RA) Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 1648–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Sutton, A.J.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Terrin, N.; Jones, D.R.; Lau, J.; Carpenter, J.; Rücker, G.; Harbord, R.M.; Schmid, C.H.; et al. Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta-analyses of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Heijde, D.; Strand, V.; Tanaka, Y.; Keystone, E.; Kremer, J.; Zerbini, C.A.F.; Cardiel, M.H.; Cohen, S.; Nash, P.; Song, Y.W.; et al. Tofacitinib in Combination with Methotrexate in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis: Clinical Efficacy, Radiographic, and Safety Outcomes from a Twenty-Four-Month, Phase III Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 878–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischmann, R.; Mysler, E.; Hall, S.; Kivitz, A.J.; Moots, R.J.; Luo, Z.; DeMasi, R.; Soma, K.; Zhang, R.; Takiya, L.; et al. Efficacy and safety of tofacitinib monotherapy, tofacitinib with methotrexate, and adalimumab with methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (ORAL Strategy): A phase 3b/4, double-blind, head-to-head, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.B.; Fleischmann, R.; Hall, S.; Wilkinson, B.; Bradley, J.D.; Gruben, D.; Koncz, T.; Krishnaswami, S.; Wallenstein, G.V.; Zang, C.; et al. Tofacitinib versus methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2377–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremer, J.; Li, Z.G.; Hall, S.; Fleischmann, R.; Genovese, M.; Martin-Mola, E.; Isaacs, J.D.; Gruben, D.; Wallenstein, G.; Krishnaswami, S.; et al. Tofacitinib in combination with nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2013, 159, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Fleischmann, R.; Cohen, S.; Lee, E.B.; García Meijide, J.A.; Wagner, S.; Forejtova, S.; Zwillich, S.H.; Gruben, D.; Koncz, T.; et al. Tofacitinib or adalimumab versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischmann, R.; Kremer, J.; Cush, J.; Schulze-Koops, H.; Connell, C.A.; Bradley, J.D.; Gruben, D.; Wallenstein, G.V.; Zwillich, S.H.; Kanik, K.S. Placebo-controlled trial of tofacitinib monotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischmann, R.; Cutolo, M.; Genovese, M.C.; Lee, E.B.; Kanik, K.S.; Sadis, S.; Connell, C.A.; Gruben, D.; Krishnaswami, S.; Wallenstein, G.; et al. Phase IIb dose-ranging study of the oral JAK inhibitor tofacitinib (CP-690,550) or adalimumab monotherapy versus placebo in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis with an inadequate response to disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Takeuchi, T.; Yamanaka, H.; Nakamura, H.; Toyoizumi, S.; Zwillich, S. Efficacy and safety of tofacitinib as monotherapy in Japanese patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: A 12-week, randomized, phase 2 study. Mod. Rheumatol. 2015, 25, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremer, J.M.; Cohen, S.; Wilkinson, B.E.; Connell, C.A.; French, J.L.; Gomez-Reino, J.; Gruben, D.; Kanik, K.S.; Krishnaswami, S.; Pascual-Ramos, V.; et al. A phase IIb dose-ranging study of the oral JAK inhibitor tofacitinib (CP-690,550) versus placebo in combination with background methotrexate in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to methotrexate alone. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 970–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Nakamura, H.; Toyoizumi, S.; Zwillich, S.H. Phase II study of tofacitinib (CP-690,550) combined with methotrexate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to methotrexate. Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63, 1150–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremer, J.M.; Bloom, B.J.; Breedveld, F.C.; Coombs, J.H.; Fletcher, M.P.; Gruben, D.; Krishnaswami, S.; Burgos-Vargas, R.; Wilkinson, B.; Zerbini, C.A.F.; et al. The safety and efficacy of a JAK inhibitor in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: Results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled phase IIa trial of three dosage levels of CP-690,550 versus placebo. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1895–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straatmijer, T.; Biemans, V.B.C.; Visschedijk, M.; Hoentjen, F.; de Vries, A.; van Bodegraven, A.A.; Bodelier, A.; de Boer, N.K.H.; Dijkstra, G.; Festen, N.; et al. Superior Effectiveness of Tofacitinib Compared to Vedolizumab in Anti-TNF-experienced Ulcerative Colitis Patients: A Nationwide Dutch Registry Study. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, H.K.; Zhang, H.S.; Yu, J.; Kang, E.A.; Park, J.; Park, S.J.; Park, J.J.; Kim, T.I.; Kim, W.H.; Cheon, J.H. Comparative effectiveness of second-line biological therapies for ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease in patients with prior failure of anti-tumour necrosis factor treatment. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022, 22, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, R.S.; Mitri, J.; Goodrick, H.; Allegretti, J.R. Real-World Comparison of Tofacitinib vs. Ustekinumab Among Bio-Exposed Patients With Ulcerative Colitis: A Propensity Score Analysis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2021, 27, 1694–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandborn, W.J.; Ghosh, S.; Panes, J.; Vranic, I.; Su, C.; Rousell, S.; Niezychowski, W. Tofacitinib, an oral Janus kinase inhibitor, in active ulcerative colitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 16, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mease, P.; Hall, S.; FitzGerald, O.; van der Heijde, D.; Merola, J.F.; Avila-Zapata, F.; Cieślak, D.; Graham, D.; Wang, C.; Menon, S.; et al. Tofacitinib or Adalimumab versus Placebo for Psoriatic Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1537–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panés, J.; Sandborn, W.J.; Schreiber, S.; Sands, B.E.; Vermeire, S.; D’Haens, G.; Panaccione, R.; Higgins, P.D.R.; Colombel, J.F.; Feagan, B.G.; et al. Tofacitinib for induction and maintenance therapy of Crohn’s disease: Results of two phase IIb randomised placebo-controlled trials. Gut 2017, 66, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deodhar, A.; Sliwinska-Stanczyk, P.; Xu, H.; Baraliakos, X.; Gensler, L.S.; Fleishaker, D.; Wang, L.; Wu, J.; Menon, S.; Wang, C.; et al. Tofacitinib for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis: A phase III, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Heijde, D.; Deodhar, A.; Wei, J.C.; Drescher, E.; Fleishaker, D.; Hendrikx, T.; Li, D.; Menon, S.; Kanik, K.S. Tofacitinib in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: A phase II, 16-week, randomised, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1340–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremer, J.M.; Bingham, C.O.; Cappelli, L.C.; Greenberg, J.D.; Madsen, A.M.; Geier, J.; Rivas, J.L.; Onofrei, A.M.; Barr, C.J.; Pappas, D.A.; et al. Postapproval Comparative Safety Study of Tofacitinib and Biological Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs: 5-Year Results from a United States-Based Rheumatoid Arthritis Registry. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2021, 3, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, K.; Laila, D.; Nandagudi, A.; Bharadwaj, A. Long-term outcomes in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Review of data from the “Basildon Inflammatory Arthritis Cohort”. Rheumatol. Adv. Pract. 2022, 6, rkac075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T.M.; Yang, Y.; Roul, P.; Sauer, B.C.; Cannon, G.W.; Kunkel, G.; Michaud, K.; Baker, J.F.; Mikuls, T.R.; England, B.R. A Narrowing Mortality Gap: Temporal Trends of Cause-Specific Mortality in a National, Matched Cohort Study in U.S. Veterans with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; You, Z.; Tu, H.; He, P.; Li, J.; Gao, R.; Liu, Z.; Xi, Z.; Li, Z.; et al. Cancer risks in rheumatoid arthritis patients who received immunosuppressive therapies: Will immunosuppressants work? Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1050876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
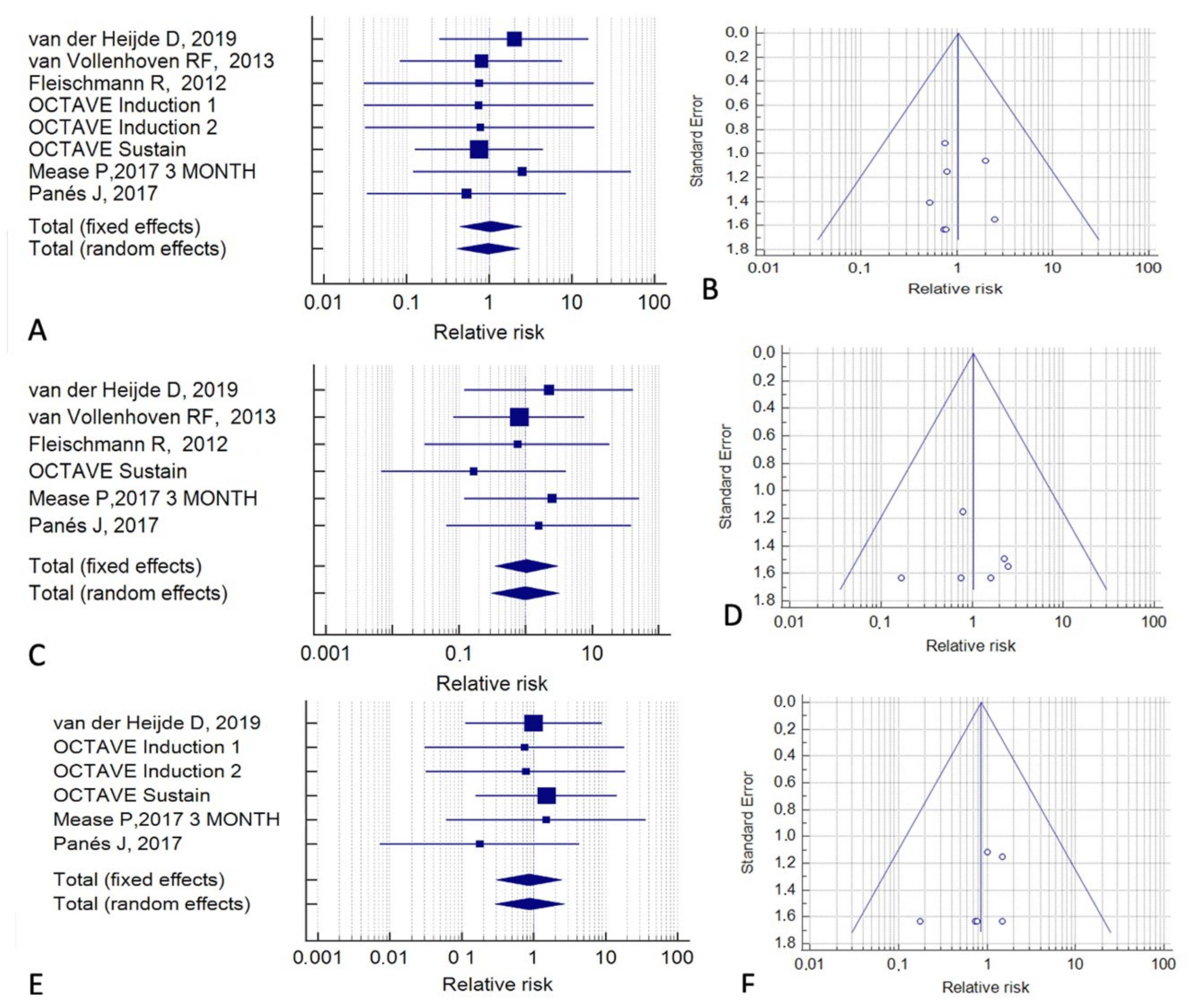
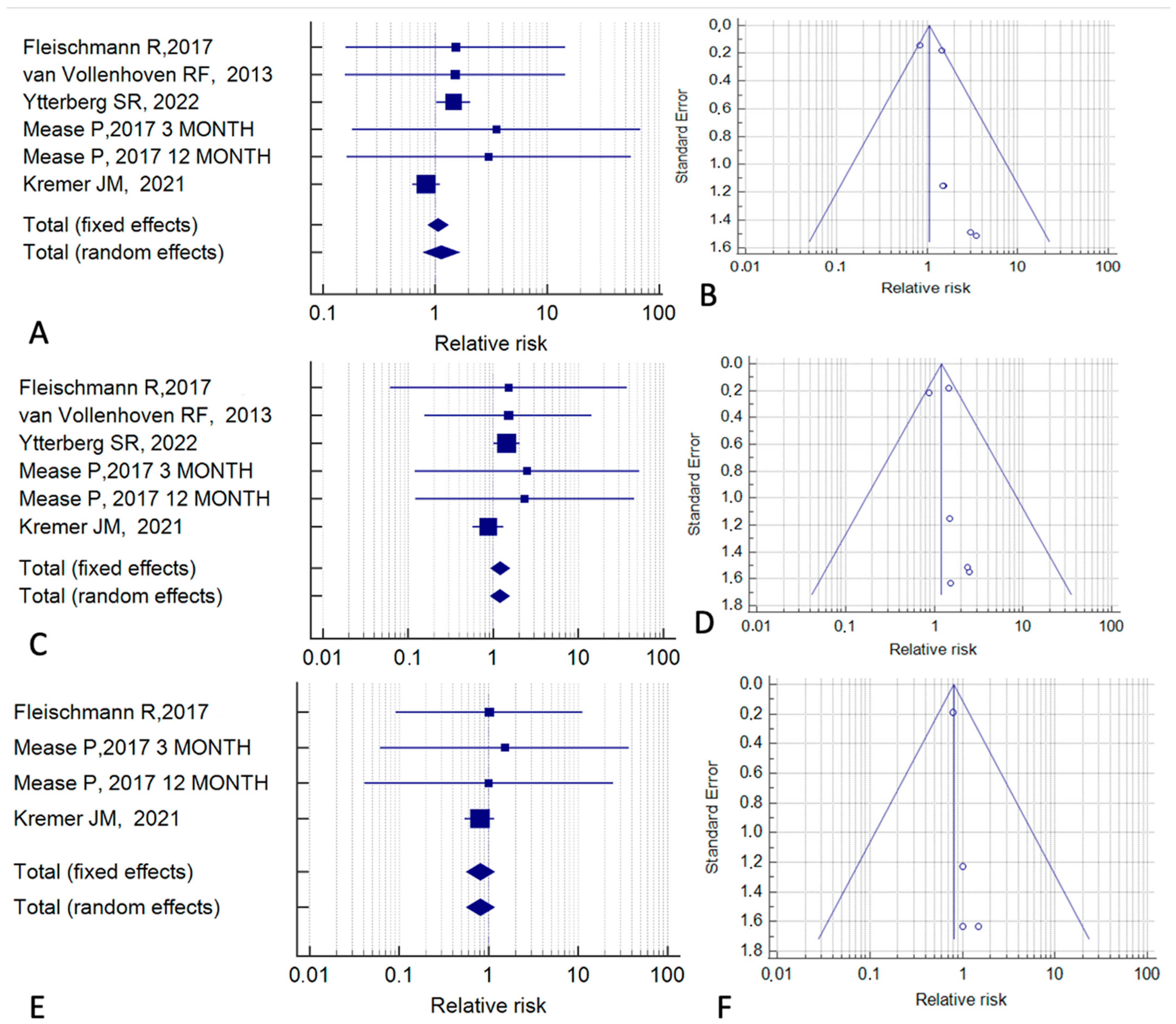
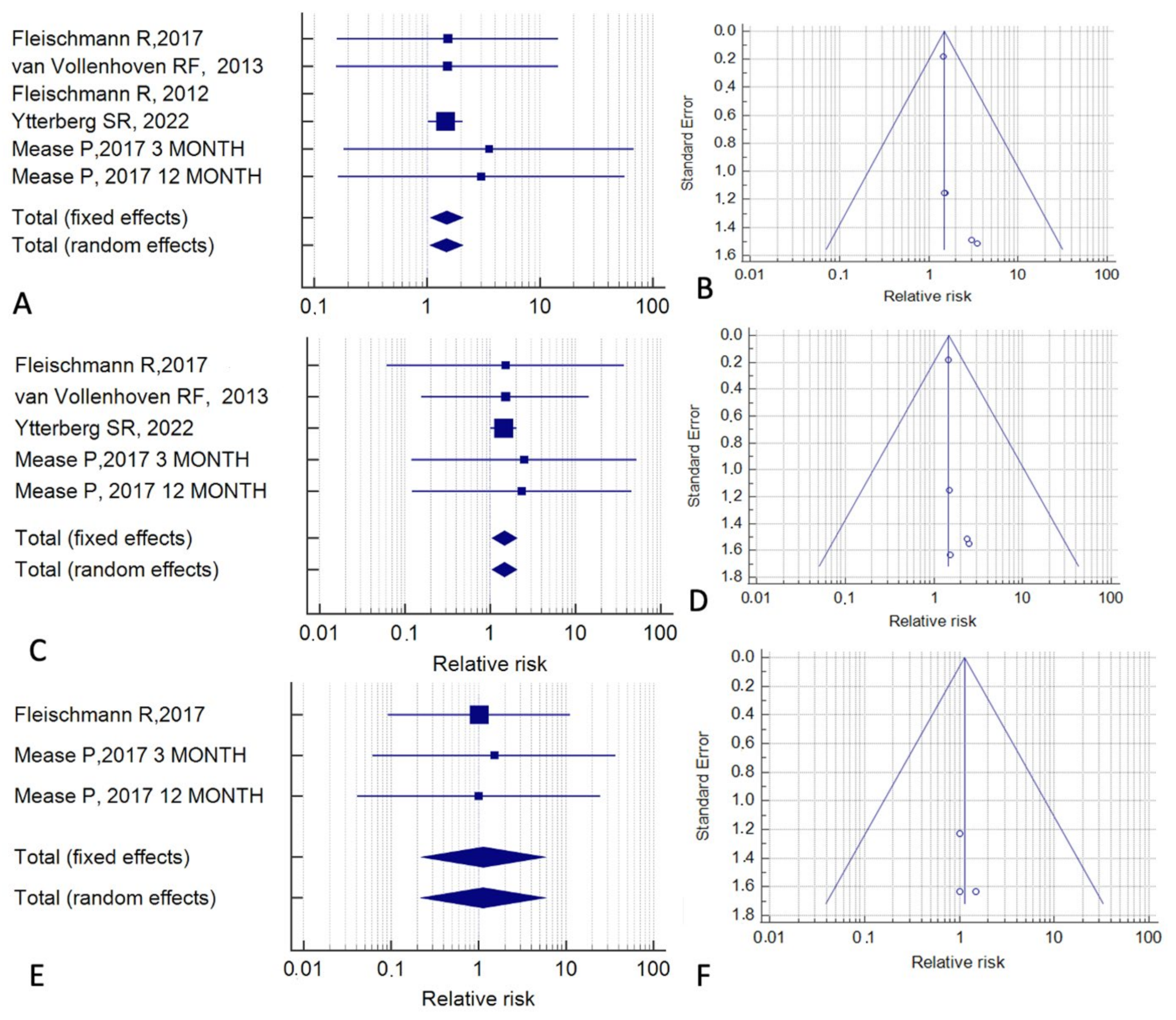
| Reference | Study Type | Cases (n) | Controls (n) | Follow-Up (months) | Tofacitinib Indication | Control Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| van der Heijde et al., 2019 [20] | Phase III trial | 637 | 160 | 6 | RA | Placebo |
| Fleischmann et al., 2017 [21] | Phase IIIb/IV trial | 760 | 386 | 12 | RA | Adalimumab |
| Lee et al., 2014 [22] | Phase III trial | 770 | 186 | 24 | RA | Methotrexate |
| Kremer et al., 2013 [23] | Phase III trial | 636 | 159 | 6 | RA | Placebo |
| van Vollenhoven et al., 2012 [24] | Phase III trial | 405 | 312 | 6 | RA | Placebo and adalimumab |
| Fleischmann et al., 2012 [25] | Phase III trial | 488 | 122 | 3 | RA | Placebo |
| Fleischmann et al., 2012 [26] | Phase Iib trial | 272 | 112 | 3 | RA | Placebo and adalimumab |
| Tanaka et al., 2015 [27] | Phase II trial | 265 | 53 | 3 | RA | Placebo |
| Kremer et al., 2012 [28] | Phase Iia trial | 440 | 69 | 6 | RA | Placebo |
| Tanaka et al., 2011 [29] | Phase II trial | 108 | 28 | 3 | RA | Placebo |
| Kremer et al., 2009 [30] | Phase Iia trial | 199 | 65 | 2 | RA | Placebo |
| Straatmijer et al., 2023 [31] | Observational study | 152 | 150 | 12 | UC | Vedolizumab |
| Hyun et al., 2022 [32] | Observational study | 13 | 37 | 12 | UC | Vedolizumab and Ustekinumab |
| Dalal et al., 2021 [33] | Observational study | 45 | 36 | 13.6 | UC | Ustekinumab |
| Sandborn et al., 2017 [2] | Phase III trials | UC | Placebo | |||
| OCTAVE Induction 1 | 492 | 122 | 2 | |||
| OCTAVE Induction 2 | 435 | 112 | 2 | |||
| OCTAVE Sustain | 395 | 198 | 13 | |||
| Sandborn et al., 2012 [34] | Phase III trial | 146 | 48 | 3 | UC | Placebo |
| Ytterberg et al., 2022 [15] | Phase IV trial | 2911 | 1451 | 38.5 | RA | Anti-TNF drugs |
| Mease et al., 2017 [35] | Phase III trial | PsA | Placebo and adalimumab | |||
| Part A | 211 | 105 | 3 | |||
| Part B | 316 | 106 | 12 | |||
| Panés et al., 2017 [36] | Phase II trials | CD | Placebo | |||
| Induction study | 172 | 91 | 2 | |||
| Maintenance study | 121 | 59 | 5 | |||
| Deodhar et al., 2021 [37] | Phase II trial | 133 | 136 | 4 | AS | Placebo |
| van der Heijde et al., 2017 [38] | Phase II trial | 156 | 51 | 4 | AS | Placebo |
| Kremer et al., 2021 [39] | Observational study | 1999 | 6354 | 12 | RA | Biological drugs |
| Reference | Selection | Comparability | Exposure | NOS Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| van der Heijde et al., 2019 [20] | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 |
| Fleischmann et al., 2017 [21] | 3 | 2 | 4 | 9 |
| Lee et al., 2014 [22] | 3 | 2 | 4 | 9 |
| Kremer et al., 2014 [23] | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 |
| van Vollenhoven et al., 2012 [24] | 3 | 1 | 3 | 7 |
| Fleischmann et al., 2012 [25] | 4 | 2 | 2 | 8 |
| Fleischmann et al., 2012 [26] | 4 | 2 | 4 | 10 |
| Tanaka et al., 2015 [27] | 3 | 1 | 3 | 7 |
| Kremer et al., 2012 [28] | 4 | 2 | 4 | 10 |
| Tanaka et al., 2011 [29] | 4 | 2 | 2 | 8 |
| Kremer et al., 2009 [30] | 4 | 2 | 4 | 10 |
| Straatmijer et al., 2023 [31] | 3 | 2 | 3 | 8 |
| Hyun et al., 2022 [32] | 3 | 0 | 3 | 6 |
| Dalal et al., 2021 [33] | 3 | 0 | 3 | 6 |
| Sandborn et al., 2017 [2] | 4 | 1 | 4 | 9 |
| Sandborn et al., 2012 [34] | 4 | 2 | 4 | 10 |
| Ytterberg et al., 2022 [15] | 4 | 2 | 4 | 10 |
| Mease et al., 2017 [35] | 4 | 2 | 4 | 10 |
| Panés et al., 2017 [36] | 3 | 2 | 3 | 8 |
| Deodhar et al., 2021 [37] | 2 | 2 | 3 | 7 |
| van der Heijde et al., 2017 [38] | 3 | 2 | 3 | 8 |
| Kremer et al., 2021 [39] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 |
| Reference | Tofacitinib Treatment | Placebo or Active Control Treatment | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Follow-Up (Person-mo.) | Cancer (excl. NMSC) | NMSC | Total Cancer | Follow-Up (Person-mo.) | Cancer (excl. NMSC) | NMSC | Total Cancer | |
| van der Heijde et al. [20] | 3822 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 960 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Fleischmann et al. [21] | 9120 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4632 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Lee et al. [22] | 18,480 | 5 | 0 | 5 | 4464 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Kremer et al. [23] | 3816 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 954 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| van Vollenhoven et al. [24] | 2430 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 1872 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Fleischmann et al. [25] | 1464 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 366 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Fleischmann et al. [26] | 816 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 336 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Tanaka et al. [27] | 795 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 159 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Kremer et al. [28] | 2640 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 414 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Tanaka et al. [29] | 324 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 84 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Kremer et al. [30] | 398 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 130 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Straatmijer et al. [31] | 1824 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1800 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Hyun et al. [32] | 156 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 444 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Dalal et al. [33] | 612 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 490 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| OCTAVE Induction 1 [2] | 984 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 244 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| OCTAVE Induction 2 [2] | 870 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 224 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| OCTAVE Sustain [2] | 5135 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 2574 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Sandborn et al. [34] | 438 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 144 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ytterberg et al. [15] | 112,074 | 122 | 0 | 122 | 55,864 | 42 | 0 | 42 |
| Mease et al. [35] Part A | 633 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 315 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Mease et al. [35] Part B | 3792 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 1272 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Panés et al. [36] Induction | 344 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 182 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Panés et al. [36] Maintenance | 605 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 295 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Deodhar et al. [37] | 532 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 544 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| van der Heijde et al. [38] | 624 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 204 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Kremer et al. [39] | 23,988 | 28 | 34 | 62 | 76,248 | 101 | 136 | 237 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bezzio, C.; Vernero, M.; Ribaldone, D.G.; Alimenti, E.; Manes, G.; Saibeni, S. Cancer Risk in Patients Treated with the JAK Inhibitor Tofacitinib: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2023, 15, 2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082197
Bezzio C, Vernero M, Ribaldone DG, Alimenti E, Manes G, Saibeni S. Cancer Risk in Patients Treated with the JAK Inhibitor Tofacitinib: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2023; 15(8):2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082197
Chicago/Turabian StyleBezzio, Cristina, Marta Vernero, Davide Giuseppe Ribaldone, Eleonora Alimenti, Gianpiero Manes, and Simone Saibeni. 2023. "Cancer Risk in Patients Treated with the JAK Inhibitor Tofacitinib: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Cancers 15, no. 8: 2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082197
APA StyleBezzio, C., Vernero, M., Ribaldone, D. G., Alimenti, E., Manes, G., & Saibeni, S. (2023). Cancer Risk in Patients Treated with the JAK Inhibitor Tofacitinib: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 15(8), 2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082197








