Insights into Gold Nanoparticles Possibilities for Diagnosis and Treatment of the Head and Neck Upper Aerodigestive Tract Cancers
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Gold Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications
3.2. Gold Nanoparticles for Diagnostic Proposals
3.3. Gold Nanoparticles for Tumor Treatment
3.4. Implication for Practice
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shah, J.P.; Johnson, N.W. Oral and Oropharyngeal Cancer, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 9781498700085. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, L.Q.M. Head and Neck Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geraldo, J.M.; Scalzo, S.; Reis, D.S.; Leão, T.L.; Guatimosim, S.; Ladeira, L.O.; Andrade, L.M. HDR brachytherapy decreases proliferation rate and cellular progression of a radioresistant human squamous cell carcinoma in vitro. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2017, 93, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feofanova, N.; Geraldo, J.M.; Andrade, L.M.D. Radiation Oncology in Vitro: Trends to Improve Radiotherapy through Molecular Targets. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 461687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, L.M.; Geraldo, J.M.; Gonçalves, O.X.; Leite, M.T.T.; Catarina, A.M.; Guimarães, M.M.; Leme, A.F.P.; Yokoo, S.; Machado, C.R.; Rajão, M.A.; et al. Nucleoplasmic calcium buffering sensitizes human squamous cell carcinoma to anticancer therapy. J. Cancer Sci. Ther. 2012, 4, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byeon, H.K.; Ku, M.; Yang, J. Beyond EGFR inhibition: Multilateral combat strategies to stop the progression of head and neck cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaraghuli, M.M. Al Biotherapeutic Antibodies for the Treatment of Head and Neck Cancer: Current Approaches and Future Considerations of Photothermal Therapies. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 559596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versiani, A.F.; Martins, E.M.N.; Andrade, L.M.; Cox, L.; Pereira, G.C.; Barbosa-Stancioli, E.F.; Nogueira, M.L.; Ladeira, L.O.; da Fonseca, F.G. Nanosensors based on LSPR are able to serologically differentiate dengue from Zika infections. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastav, A.M.; Cvelbar, U.; Abdulhalim, I. A comprehensive review on plasmonic-based biosensors used in viral diagnostics. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, L.M.; Cox, L.; Versiani, A.F.; Da Fonseca, F.G. A growing world of small things: A brief review on the nanostructured vaccines. Future Virol. 2017, 12, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, W.; Sun, M.; Choi, W.J.; Kim, J.-Y.; Hao, C.; Li, S.; Qu, A.; Lu, M.; et al. Enantiomer-dependent immunological response to chiral nanoparticles. Nature 2022, 601, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.U.; Novosad, V.; Rozhkova, E.A.; Wali, H.; Ali, A.; Fateh, A.A.; Neogi, P.B.; Neogi, A.; Wang, Z. Gold Nanoparticles-enabled Efficient Dual Delivery of Anticancer Therapeutics to HeLa Cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Lin, M.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, W. Gold nanoparticle-enhanced detection of dna hybridization by a block copolymer-templating fiber-optic localized surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mereuta, L.; Asandei, A.; Dragomir, I.S.; Bucataru, I.C.; Park, J.; Seo, C.H.; Park, Y.; Luchian, T. Sequence-specific detection of single-stranded DNA with a gold nanoparticle-protein nanopore approach. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versiani, A.F.; Andrade, L.M.; Martins, E.M.N.; Scalzo, S.; Geraldo, J.M.; Chaves, C.R.; Ferreira, D.C.; Ladeira, M.; Guatimosim, S.; Ladeira, L.O.; et al. Gold nanoparticles and their applications in biomedicine. Future Virol. 2016, 11, 293–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastinehad, A.R.; Anastos, H.; Wajswol, E.; Winoker, J.S.; Sfakianos, J.P.; Doppalapudi, S.K.; Carrick, M.R.; Knauer, C.J.; Taouli, B.; Lewis, S.C.; et al. Gold nanoshell-localized photothermal ablation of prostate tumors in a clinical pilot device study. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 18590–18596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, G.L.; Teixeira, F.M.F.; Ferreira, G.S.C.; Versiani, A.F.; Andrade, L.M.; Ladeira, L.O.; Fonseca, F.G.; Ramirez, J.C. Computational Guided Method Applied to LSPR-Based Biosensor for Specific Detection of the Four-Serotypes of Dengue Virus in Seropositive Patients. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2022, 2100157, 2100157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Wang, D. Gold Nanoparticles in Cancer Theranostics. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 647905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niaz, S.; Forbes, B.; Raimi-Abraham, B.T. Exploiting Endocytosis for Non-Spherical Nanoparticle Cellular Uptake. Nanomanufacturing 2022, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contini, C.; Hindley, J.W.; Macdonald, T.J.; Barritt, J.D.; Ces, O.; Quirke, N. Size dependency of gold nanoparticles interacting with model membranes. Commun. Chem. 2020, 3, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa De Almeida, M.; Susnik, E.; Drasler, B.; Taladriz-Blanco, P.; Petri-Fink, A.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B. Understanding nanoparticle endocytosis to improve targeting strategies in nanomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 5397–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Pandit, S.; Mokkapati, V.R.S.S.; Garg, A.; Ravikumar, V.; Mijakovic, I. Gold nanoparticles in diagnostics and therapeutics for human cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.J.; Zhang, X.Q.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, G. Nanotechnology: A promising method for oral cancer detection and diagnosis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Fang, M.; Zhu, J.; Dong, H.; Cao, J.; Yan, L.; Leonard, F.; Oppel, F.; Sudhoff, H.; Kaufmann, A.M.; et al. Insights into nanomedicine for immunotherapeutics in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 2506–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Yan, B.; Li, Y.; Tan, Y.; Luo, X.; Wang, M. Surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy of blood serum based on gold nanoparticles for tumor stages detection and histologic grades classification of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 4977–4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Yan, B.; Xue, L.; Li, Y.; Luo, X.; Ji, P. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of blood serum based on gold nanoparticles for the diagnosis of the oral squamous cell carcinoma. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lu, G. Applications of Gold Nanoparticles in Cancer Imaging and Treatment. In Noble and Precious Metals—Properties, Nanoscale Effects and Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- Barnoy, E.A.; Motiei, M.; Tzror, C.; Rahimipour, S.; Popovtzer, R.; Fixler, D. Biological Logic Gate Using Gold Nanoparticles and Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 6527–6536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, D.S.; de Oliveira, V.L.; Silva, M.L.; Paniago, R.M.; Ladeira, L.O.; Andrade, L.M. Gold nanoparticles enhance fluorescence signals by flow cytometry at low antibody concentrations. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 1414–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombé, C.; Le Guével, X.; Martin-Serrano, A.; Henry, M.; Porret, E.; Comby-Zerbino, C.; Antoine, R.; Atallah, I.; Busser, B.; Coll, J.L.; et al. Gold nanoclusters as a contrast agent for image-guided surgery of head and neck tumors. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2019, 20, 102011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khademi, S.; Sarkar, S.; Shakeri-Zadeh, A.; Attaran, N.; Kharrazi, S.; Ay, M.R.; Azimian, H.; Ghadiri, H. Targeted gold nanoparticles enable molecular CT imaging of head and neck cancer: An in vivo study. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 114, 105554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez Jimenez, A.M.; Rodrigo, M.A.M.; Milosavljevic, V.; Krizkova, S.; Kopel, P.; Heger, Z.; Adam, V. Gold nanoparticles-modified nanomaghemite and quantum dots-based hybridization assay for detection of HPV. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 240, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, K.; Pickwell-Macpherson, E. Gold nanoparticle enhanced detection of EGFR with a terahertz metamaterial biosensor. Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibuyi, N.R.S.; Moabelo, K.L.; Fadaka, A.O.; Meyer, S.; Onani, M.O.; Madiehe, A.M.; Meyer, M. Multifunctional Gold Nanoparticles for Improved Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications: A Review. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teraoka, S.; Kakei, Y.; Akashi, M.; Iwata, E.; Hasegawa, T. Gold nanoparticles enhance X-ray irradiation-induced apoptosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in vitro. Biomed. Rep. 2018, 9, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidi, E.S.; Dreifuss, T.; Motiei, M.; Shai, E.; Bragilovski, D.; Lubimov, L.; Kindler, M.J.J.; Popovtzer, A.; Don, J.; Popovtzer, R. Cisplatin-conjugated gold nanoparticles as a theranostic agent for head and neck cancer. Head Neck 2018, 40, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashin, M.; Kakei, Y.; Teraoka, S.; Hasegawa, T.; Yamaguchi, A.; Fukuoka, T.; Sasaki, R.; Akashi, M. Gold Nanoparticles Enhance EGFR Inhibition and Irradiation Effects in Head and Neck Squamous Carcinoma Cells. Biomed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1281645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazkani, I.; Motiei, M.; Betzer, O.; Sadan, T.; Bragilovski, D.; Lubimov, L.; Mizrachi, A.; Hadar, T.; Levi, M.; Ben-Aharon, I.; et al. Can molecular profiling enhance radiotherapy? Impact of personalized targeted gold nanoparticles on radiosensitivity and imaging of adenoid cystic carcinoma. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3962–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolo, O.; Lincoln, J.D.; Melong, N.; Orr, B.C.; Fernandez, N.R.; Borsavage, J.; Berman, J.N.; Robar, J.; Ha, M.N. Radiation dose enhancement using gold nanoparticles with a diamond linear accelerator target: A multiple cell type analysis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cong, L.; He, J.; Wang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Yang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, S.; He, X. Photothermal treatment with EGFRmAb–AuNPs induces apoptosis in hypopharyngeal carcinoma cells via PI3K/AKT/mTOR and DNA damage response pathways. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2018, 50, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egnuni, T.; Ingram, N.; Mirza, I.; Coletta, P.L.; McLaughlan, J.R. Evaluation of the targeting and therapeutic efficiency of anti-egfr functionalised nanoparticles in head and neck cancer cells for use in nir-ii optical window. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.D.; Lee, J.; Lee, M.; Choi, K.M.; Park, M.W. Real-time phase-contrast imaging of photothermal treatment of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: An in vitro study of macrophages as a vector for the delivery of gold nanoshells. J. Biomed. Opt. 2021, 17, 128003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katrina, A.; Santi, M.; Voliani, V. Combined chemo-photothermal treatment of three-dimensional head and neck squamous cell carcinomas by gold nano-architectures. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 582, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.H.; Lee, Y.K.; Park, I.S.; Park, I.K.; Hong, S.M.; Kwon, S.Y.; Choi, Y.H.; Madsen, S.J.; Hirschberg, H.; Hong, S.J. Biomimetic Gold Nanoshell-Loaded Macrophage for Photothermal Biomedicine. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 5869235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir Duman, F.; Demir Duman, F.; Sebek, M.; Sebek, M.; Thanh, N.T.K.; Thanh, N.T.K.; Loizidou, M.; Shakib, K.; MacRobert, A.J. Enhanced photodynamic therapy and fluorescence imaging using gold nanorods for porphyrin delivery in a novel: In vitro squamous cell carcinoma 3D model. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 5131–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, Y.F.; Qin, J.J.; Li, Z.; Ge, Q.; Zeng, W.H. Enhanced anti-tumor efficacy of 5-aminolevulinic acid-gold nanoparticles-mediated photodynamic therapy in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma cells. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2020, 53, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, L.M.; Martins, E.M.N.; Versiani, A.F.; Reis, D.S.; da Fonseca, F.G.; Souza, I.P.D.; Paniago, R.M.; Pereira-Maia, E.; Ladeira, L.O. The physicochemical and biological characterization of a 24-month-stored nanocomplex based on gold nanoparticles conjugated with cetuximab demonstrated long-term stability, EGFR affinity and cancer cell death due to apoptosis. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 107, 110203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.H.; Kim, M.S.; Song, H.S.; Yoo, S.H.; Sai, S.; Chung, K.; Sung, J.; Jeong, Y.K.; Jo, Y.H.; Yoon, M. Gold nanoparticles as a potent radiosensitizer in neutron therapy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 112390–112400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhussan, A.; Bozdoğan, E.P.D.; Chithrani, D.B. Combining gold nanoparticles with other radiosensitizing agents for unlocking the full potential of cancer radiotherapy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromma, K.; Chithrani, D.B. Advances in gold nanoparticle-based combined cancer therapy. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, S.; Connolly, C.; Schettino, G.; Butterworth, K.T.; Prise, K.M. Biological mechanisms of gold nanoparticle radiosensitization. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Fu, S.; Wu, J. Gold nanoparticles as radiosensitizers in cancer radiotherapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 9407–9430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vines, J.B.; Yoon, J.H.; Ryu, N.E.; Lim, D.J.; Park, H. Gold nanoparticles for photothermal cancer therapy. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Li, J.; Mei, Y.; Yin, Y.; Wang, W. Multifunctional inorganic nanomaterials for cancer photoimmunotherapy. Cancer Commun. 2022, 42, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, D.C.; Monteiro, C.S.; Chaves, C.R.; Sáfar, G.A.M.; Moreira, R.L.; Pinheiro, M.V.B.; Martins, D.C.S.; Ladeira, L.O.; Krambrock, K. Hybrid systems based on gold nanostructures and porphyrins as promising photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 150, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, B.; Shen, Y.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Huan, X.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, W. Thermo-responsive polymer encapsulated gold nanorods for single continuous wave laser-induced photodynamic/photothermal tumour therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, H.F.; Lou, P.J. Immune checkpoint inhibitors for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Current landscape and future directions. Head Neck 2019, 41, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damasio, M.P.S.; Nascimento, C.S.; Andrade, L.M.; de Oliveira, V.L.; Calzavara-silva, C.E. The role of T-cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: From immunity to immunotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1021609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.S.; Liu, S.J.; Zhang, Y.R.; Chu, X.D.; Lin, Z.-B.; Zhao, Z.; Qiu, S.H.; Guo, Y.G.; Ding, H.; Pan, Y.L.; et al. The Application of and Strategy for Gold Nanoparticles in Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 687399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Santos, H.A. Smart Nanoparticle-Based Platforms for Regulating Tumor Microenvironment and Cancer Immunotherapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 2202063, 2202063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, A.; Khan, T.; Omri, A. Design and encapsulation of immunomodulators onto gold nanoparticles in cancer immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Pulido, G.; Medina, D.I.; Barani, M.; Rahdar, A.; Sargazi, G.; Baino, F.; Pandey, S. Nanomaterials for the diagnosis and treatment of head and neck cancers: A review. Materials 2021, 14, 3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagrino, T.R.S.; Godoy, A.P.; Barbosa, J.M.; Lima, A.G.T.; Sousa, N.C.O.; Pedrotti, J.J.; Garcia, P.S.; Paniago, R.M.; Andrade, L.M.; Domingues, S.H.; et al. Multifunctional Hybrid MoS2-PEGylated/Au Nanostructures with Potential Theranostic Applications in Biomedicine. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madni, A.; Rehman, S.; Sultan, H.; Khan, M.M.; Ahmad, F.; Raza, M.R.; Rai, N.; Parveen, F. Mechanistic Approaches of Internalization, Subcellular Trafficking, and Cytotoxicity of Nanoparticles for Targeting the Small Intestine. AAPS PharmSciTech 2021, 22, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnovale, C.; Bryant, G.; Shukla, R.; Bansal, V. Identifying Trends in Gold Nanoparticle Toxicity and Uptake: Size, Shape, Capping Ligand, and Biological Corona. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, L.; Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y.; Hieawy, A.; Liu, H.; Ma, J. Advances in nanomaterials for the diagnosis and treatment of head and neck cancers: A review. Bioact. Mater. 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, G.P.F.; Ferraz, F.S.; Andrade, L.M.; Costa, G.M.J. Male reproductive toxicity of inorganic nanoparticles in rodent models: A systematic review. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 363, 110023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kus-liśkiewicz, M.; Fickers, P.; Ben Tahar, I. Biocompatibility and cytotoxicity of gold nanoparticles: Recent advances in methodologies and regulations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottardo, S.; Crutzen, H.; Jantunen, P.; Gottardo, S.; Alessandrelli, M.; Atluri, R.; Barberio, G.; Bergonzo, P.; Bleeker, E.; Andy, M.; et al. The NANoREG Toolbox; European Commission Joint Research Centre: Brussels, Belgium, 2017; ISBN 9789279702730. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, N.; Thakur, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Das, J.; Sil, P.C. Nanoparticles as Smart Carriers for Enhanced Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 597806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa, P.; Corvo, M.L.; Ferreira-Silva, M.; Martins, P.; Carvalheiro, M.C.; Costa, P.M.; Martins, C.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Baptista, P.V.; Fernandes, A.R. Targeting cancer resistance via multifunctional gold nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumthekar, P.; Ko, C.H.; Paunesku, T.; Dixit, K.; Sonabend, A.M.; Bloch, O.; Tate, M.; Schwartz, M.; Zuckerman, L.; Lezon, R.; et al. A first-in-human phase 0 clinical study of RNA interference-based spherical nucleic acids in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabb3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumthekar, P. A Phase 0 First-in-Human Study Using NU-0129: A Spherical Nucleic Acid (SNA) Gold Nanoparticle Targeting BCL2L12 in Recurrent Glioblastoma Multiforme or Gliosarcoma Patients. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT03020017 (accessed on 22 November 2021).
- Farag, A.F. Gold Nanoparticles as Novel Biomarkers for Cancer Stem Cells in Salivary Gland Tumours: A Diagnostic and Prognostic Accuracy Study. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04907422 (accessed on 8 April 2022).
- Liu, H. Study of the Exhaled Breath and Salivary Metabolites of Patients with Malignant or Benign Gastric Lesions. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01420588 (accessed on 8 April 2022).
- Jendrzej, S.; Gökce, B.; Epple, M.; Barcikowski, S. How Size Determines the Value of Gold: Economic Aspects of Wet Chemical and Laser-Based Metal Colloid Synthesis. ChemPhysChem 2017, 18, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viegas, C.; Pereira, D.S.M.; Fonte, P. Insights into Nanomedicine for Head and Neck Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment. Materials 2022, 15, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Wang, Y.; Song, Z.; Feng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, D.; Feng, L. The basic properties of gold nanoparticles and their applications in tumor diagnosis and treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuemann, J.; Bagley, A.F.; Berbeco, R.; Bromma, K.; Butterworth, K.T.; Byrne, H.L.; Chithrani, B.D.; Cho, S.H.; Cook, J.R.; Favaudon, V.; et al. Roadmap for metal nanoparticles in radiation therapy: Current status, translational challenges, and future directions. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 21RM02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
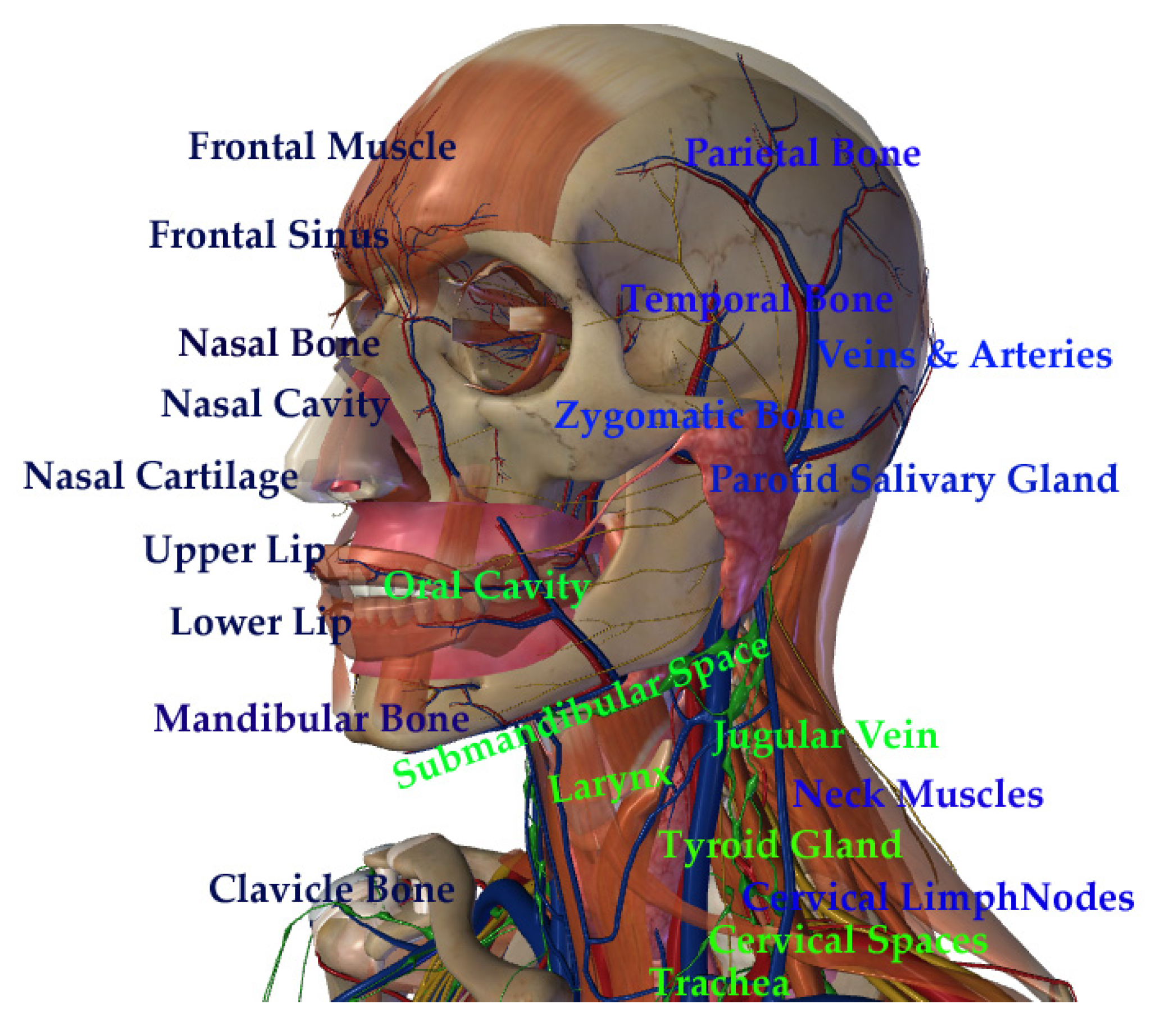
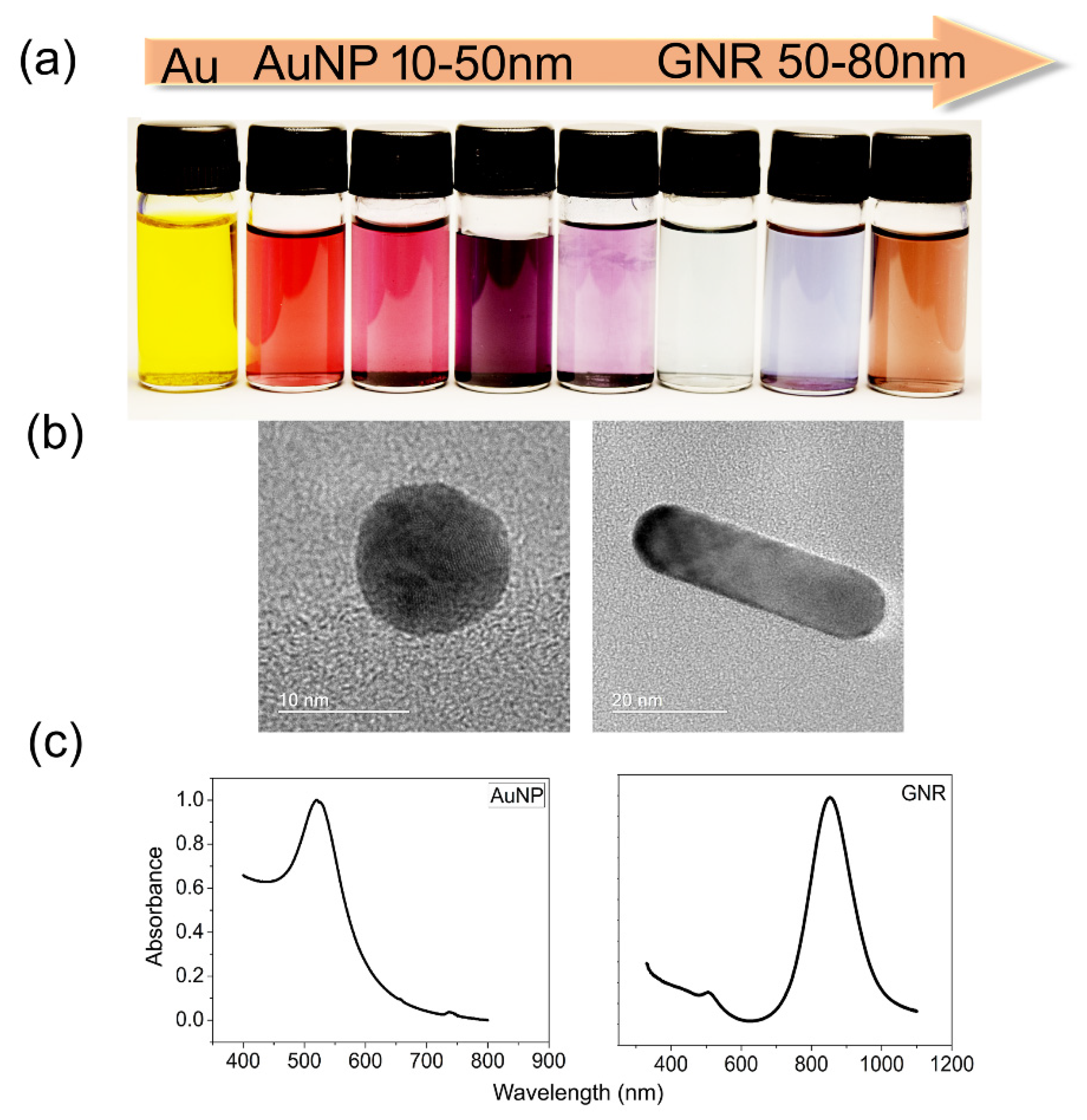

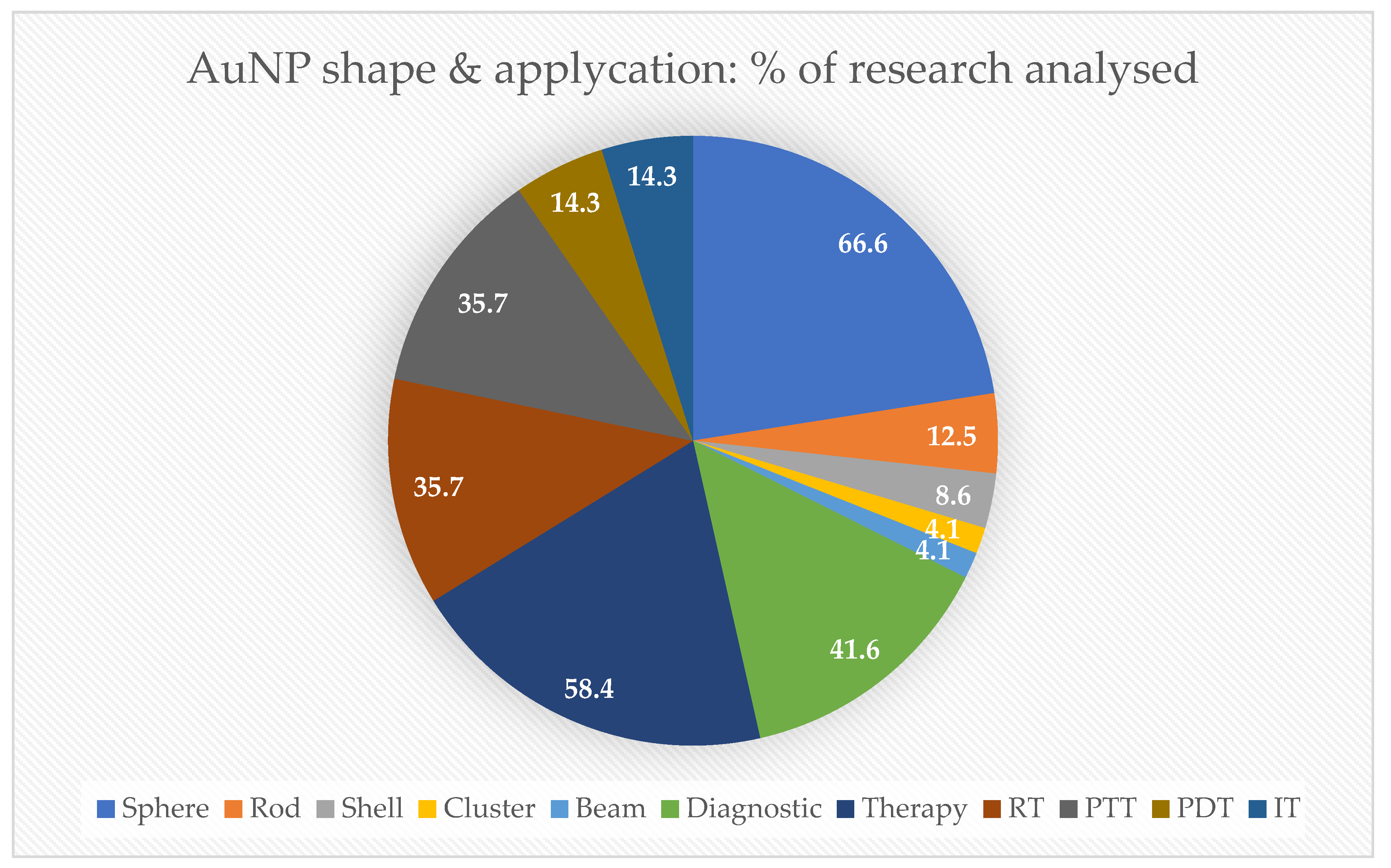
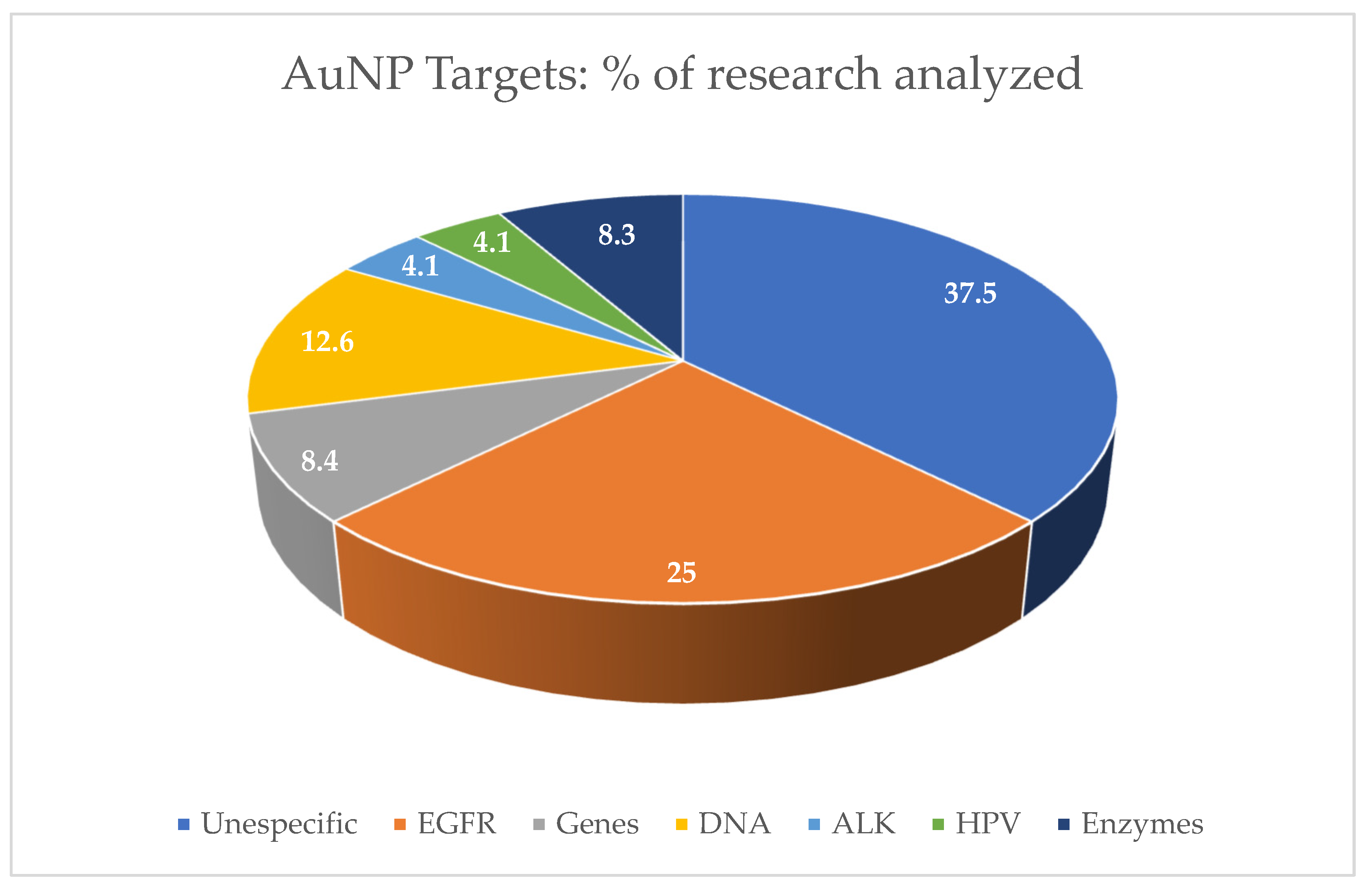
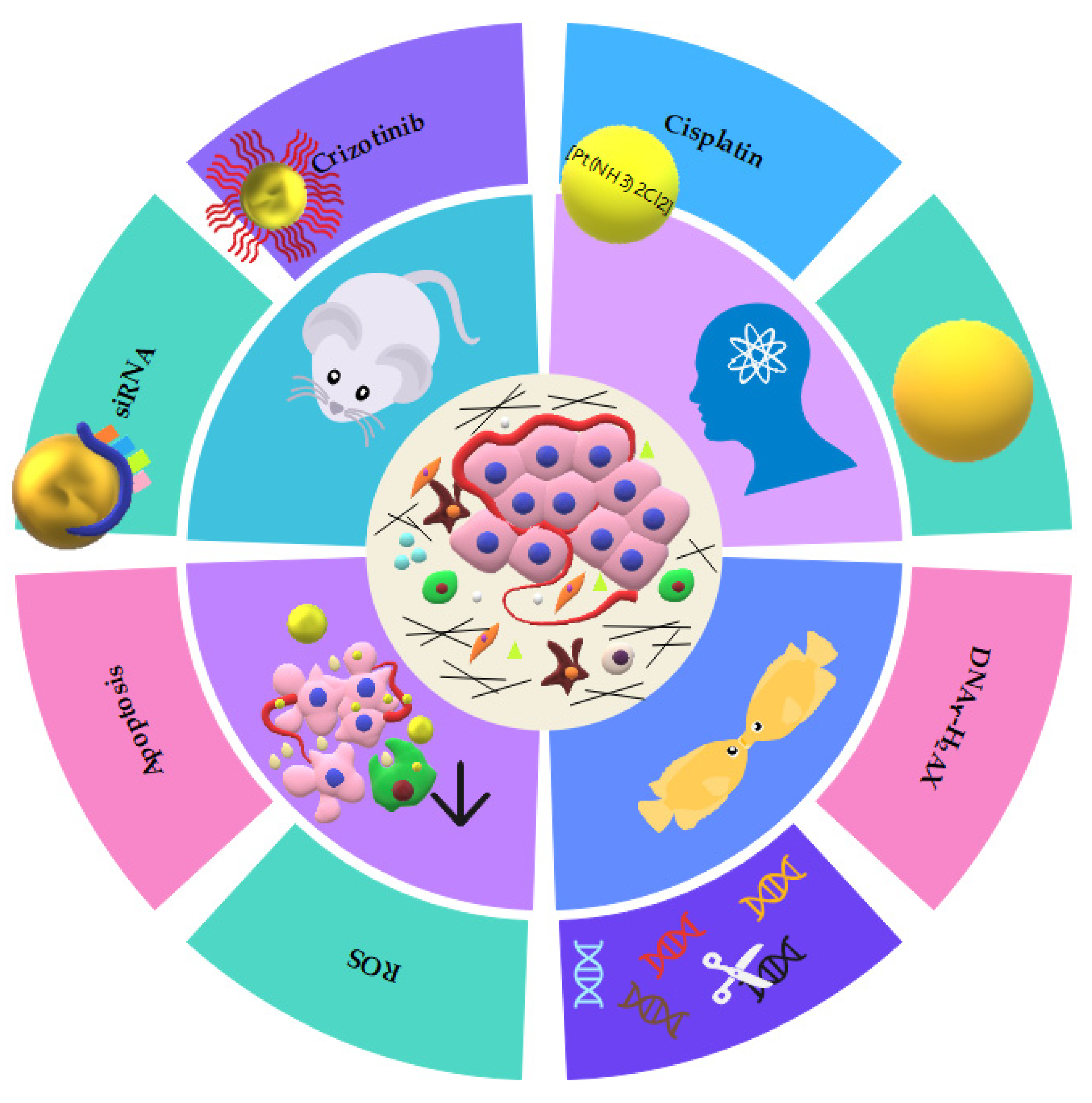
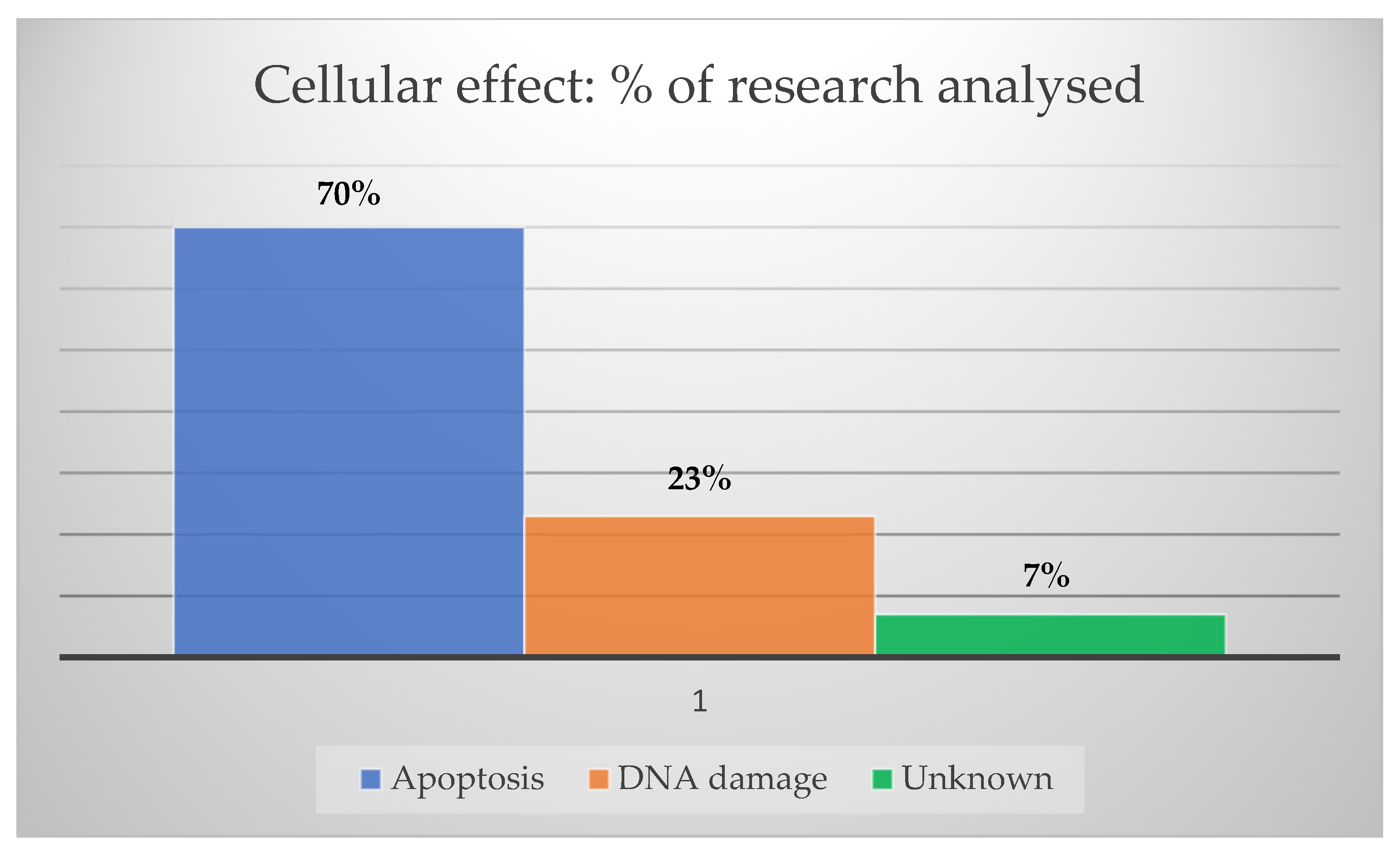

| Nanoparticle Features | Purpose | Target | Study Design | Tumor Death | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sphere-shaped (~20 nm). | Diagnostic | Nucleic acids and proteins | Human blood samples from patients with mucoepidermoid carcinoma, oral squamous cell carcinoma, and normal individuals. | _ | [25] |
| Bean-shaped (55 nm). | Diagnostic | Nucleic acids and proteins | Human blood samples from patients with mucoepidermoid carcinoma, oral squamous cell carcinoma, and normal individuals. | _ | [26] |
| Sphere-shaped (~20 nm) coated with Oregon Green 488-X. | Diagnostic | Trypsin | In vitro using healthy male Balb/C mice organs for FLIM image acquisition and measurement. | _ | [29] |
| Sphere-shaped (~20 nm) coated with Cetuximab. | Diagnostic | EGFR | In vitro fluorescence enhancement using human squamous cell carcinoma A431 cell line. | _ | [30] |
| Nanoclusters (1.4 nm to 10.5 nm). | Diagnostic | Tumor cells | In vitro using female athymic NMRI nude mice for orthotopic implantation of the HNC cell lines CAL-33 and SQ20B and fluorescence contrast image acquisition. | _ | [31] |
| Sphere-shaped (~15 nm). | Diagnostic | Tumor cells | In vitro using male nude mice for xenograft implantation of nasopharyngeal adenocarcinoma KB cell line. | _ | [32] |
| Sphere-shaped (5 nm, 15 nm, and 25 nm). | Diagnostic | EGFR | Samples of EGFR antibodies were deposited in a bow-tie device for plasmonic resonance signal biosensing at a frequency of tHz. | _ | [34] |
| Sphere-shaped (~10 nm). | Diagnostic | HPV | Samples from patients with HPV+ oropharyngeal cancer were exposed to nanoparticles to detect the E-6 HPV-16 oncogene. | _ | [33] |
| Sphere-shaped (~5 nm). | Therapy—ionizing radiation | Tumor cells | In vitro using human tongue squamous cell carcinoma cell line HSC-3. | Apoptosis | [36] |
| Sphere-shaped (~20 nm) coated with glucose and Cisplatin. | Therapy—ionizing radiation | DNA | In vitro xenograft nude mice model using A431 cell line. | DNA ϒ- H2AX | [37] |
| Sphere-shaped (~60 nm) coated with AG1478. | Therapy—ionizing radiation | EGFR | In vitro using human tongue squamous cell carcinoma cell line HSC3. | Apoptosis | [38] |
| Sphere-shaped (~20 nm) coated with Crizotinib. | Therapy—ionizing radiation | ALK | In vitro xenograft mice model using ACC sample collected from a patient donor. | DNA ϒ- H2AX | [39] |
| Sphere-shaped (~15 nm). | Therapy—ionizing radiation | Tumor cells | In vitro using FaDu, HSC-3, Detroit-562 cell lines and in vivo using zebrafish xenotransplantation. | DNA ϒ- H2AX | [40] |
| Rod-shaped (12 nm × 50 nm) coated with EGFR-mAb. | Therapy—hyperthermia | PI3K/AKT/mTOR | In vitro using human larynx squamous cell carcinoma FaDu cell line. | Apoptosis | [41] |
| Rod-shaped (10 nm × 67 nm) coated with Cetuximab and EGFR-hIgG1. | Therapy—hyperthermia | EGFR | In vitro using human squamous cell carcinoma CAL-27 cell line. | Apoptosis | [42] |
| Nanoshell (14 nm) and silica core (157 nm). | Therapy—hyperthermia | Tumor cells | In vitro using macrophages and human squamous pharyngeal SNU-1041 cell line. | Unknown | [43] |
| Rhomboid (~98 nm). | Therapy—hyperthermia | Tumor cells | In vitro using human squamous cell carcinoma SCC-25 (HPV-negative) and UPCI: SCC-154 (HPV-positive) cell lines. | Apoptosis | [44] |
| Nanoshell (~152 nm) coated with PEG. | Therapy—hyperthermia | Tumor cells | In vitro using human larynx squamous cell carcinoma FaDu cell line. | Apoptosis | [45] |
|
Rod-shaped (~148 nm) Coupled with TMPyP. | Therapy—photodynamic | Tumor cells | In vitro using human squamous cell carcinoma A431 cell line. | Apoptosis | [46] |
| Sphere-shaped (~18 nm) coated with 5-aminolevulinic acid. | Therapy—photodynamic | Cytoplasm | In vitro using human larynx squamous cell carcinoma FaDu cell line. | Apoptosis | [47] |
|
Sphere-shaped (~20 nm) coated with Cetuximab. | Immunotherapy | EGFR | In vitro using human squamous cell carcinoma A431 cell line. | Apoptosis | [48] |
| * Study Phase | Title | Study Design | Study Accession NTC Number |
|---|---|---|---|
Early Phase 1 | A Phase 0 First-In-Human Study Using NU-0129: A Spherical Nucleic Acid (SNA) Gold Nanoparticle Targeting BCL2L12 in Recurrent Glioblastoma Multiforme or Gliosarcoma Patients | Gold nanoparticles were coated with NU-0129 and arranged in spherical nucleic acids. This platform was infused in patients with glioblastoma multiforme or gliosarcoma. The purpose of this research study was to evaluate the safety of the platform. The nucleic acid component can target a gene called Bcl2L12, which is present in glioblastoma multiforme and is associated with tumor growth. Eight patients were enrolled and received NU-0129 IV over 20–50 min and underwent standard-of-care tumor resection within 8–48 h. | NCT03020017 Northwestern University [73,74] |
Early Phase 1 | Gold Nanoparticles as Novel Biomarkers for Cancer Stem Cells in Salivary Gland Tumors: A Diagnostic and Prognostic Accuracy Study | Gold nanoparticles were conjugated with the protein-coding gene molecule CD24. This study aimed to introduce a novel diagnostic and prognostic approach in the early detection of cancer stem cells in salivary gland tumors using gold nanoparticles conjugated to CD24 (CD24-gold nanocomposite). Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma of salivary glands and pleomorphic adenoma of salivary glands were tested. This approach was designed for cancer diagnostics through RT-qPCR, and sixty patients were enrolled. | NCT04907422 October 6 University [75] |
Early Phase 1 | Study of the Exhaled Breath and Salivary Metabolites of Patients with Malignant or Benign Gastric Lesions |
The study aimed to test a novel method in oncology based on breath analysis and saliva with a nanosensor array for identifying gastric diseases. Alveolar exhaled breath samples collected from volunteers referred for upper endoscopy or surgery were analyzed using a custom-designed array of chemical nanosensors based on organically functionalized gold nanoparticles. The chemical composition of the breath samples was studied using gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (GC-MS). One thousand patients were enrolled. | NCT01420588 Anhui Medical University [76] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andrade, L.M.; Costa, G.M.J. Insights into Gold Nanoparticles Possibilities for Diagnosis and Treatment of the Head and Neck Upper Aerodigestive Tract Cancers. Cancers 2023, 15, 2080. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072080
Andrade LM, Costa GMJ. Insights into Gold Nanoparticles Possibilities for Diagnosis and Treatment of the Head and Neck Upper Aerodigestive Tract Cancers. Cancers. 2023; 15(7):2080. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072080
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndrade, Lídia M., and Guilherme M. J. Costa. 2023. "Insights into Gold Nanoparticles Possibilities for Diagnosis and Treatment of the Head and Neck Upper Aerodigestive Tract Cancers" Cancers 15, no. 7: 2080. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072080
APA StyleAndrade, L. M., & Costa, G. M. J. (2023). Insights into Gold Nanoparticles Possibilities for Diagnosis and Treatment of the Head and Neck Upper Aerodigestive Tract Cancers. Cancers, 15(7), 2080. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072080






