CBCT-to-CT Translation Using Registration-Based Generative Adversarial Networks in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Radiotherapy
1.2. CBCT Image Quality Improvement
1.3. CT Synthesis Using Deep Learning
1.4. Study Objectives
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Dataset
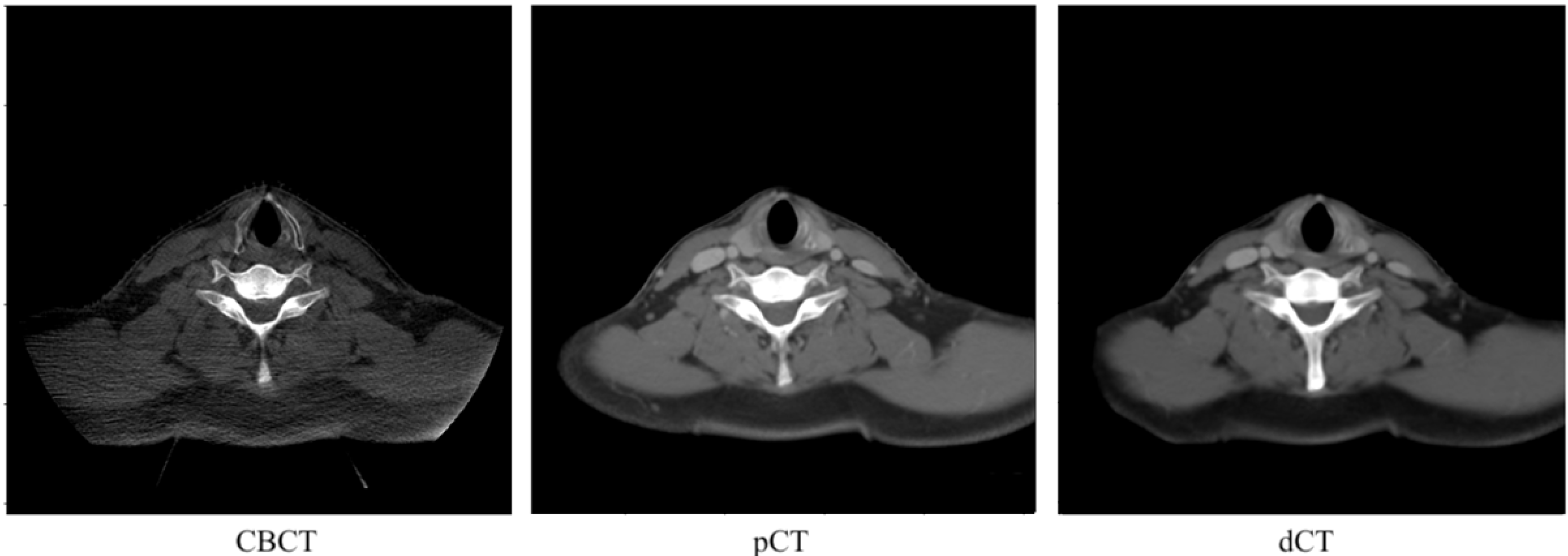
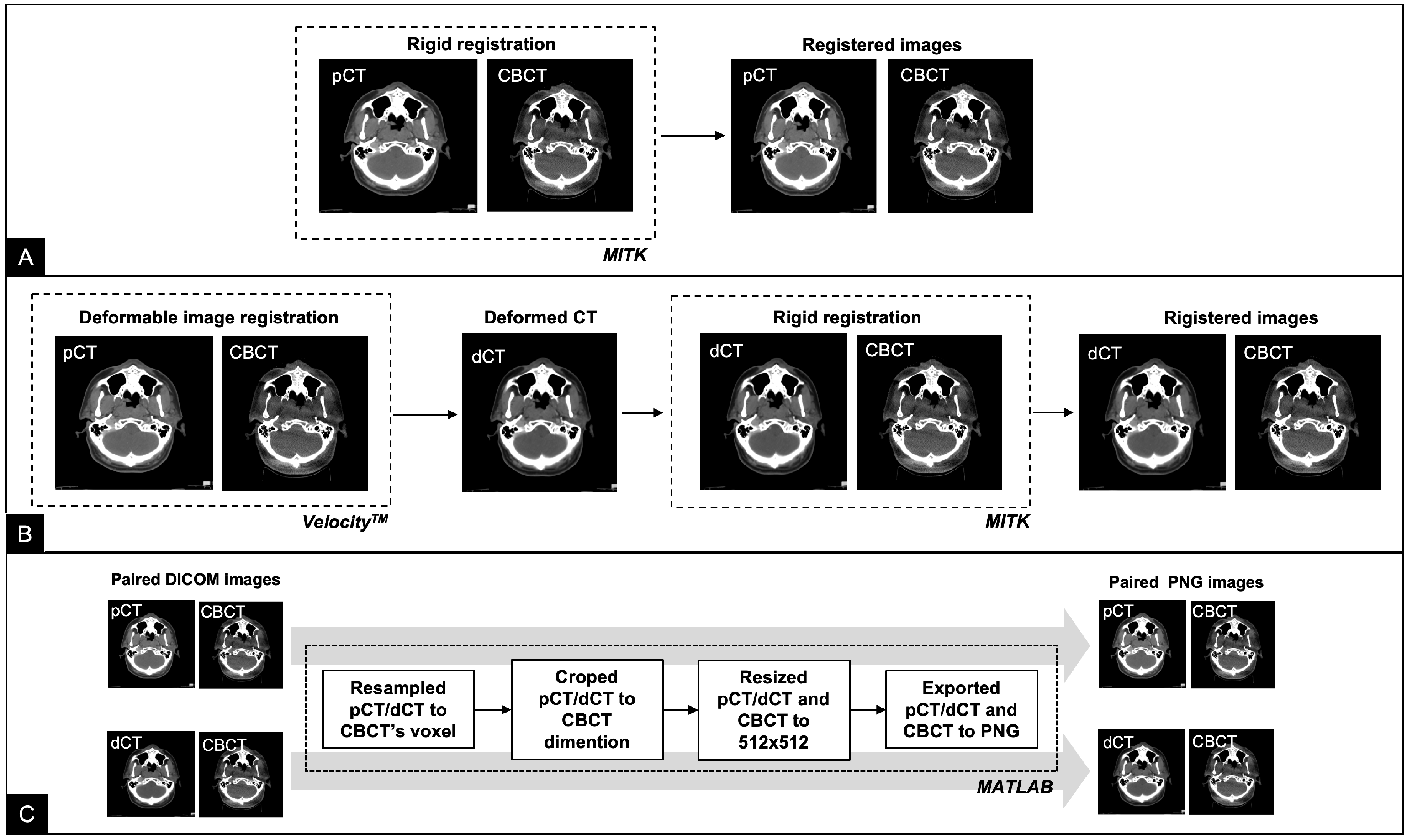
2.2. Data Preparation
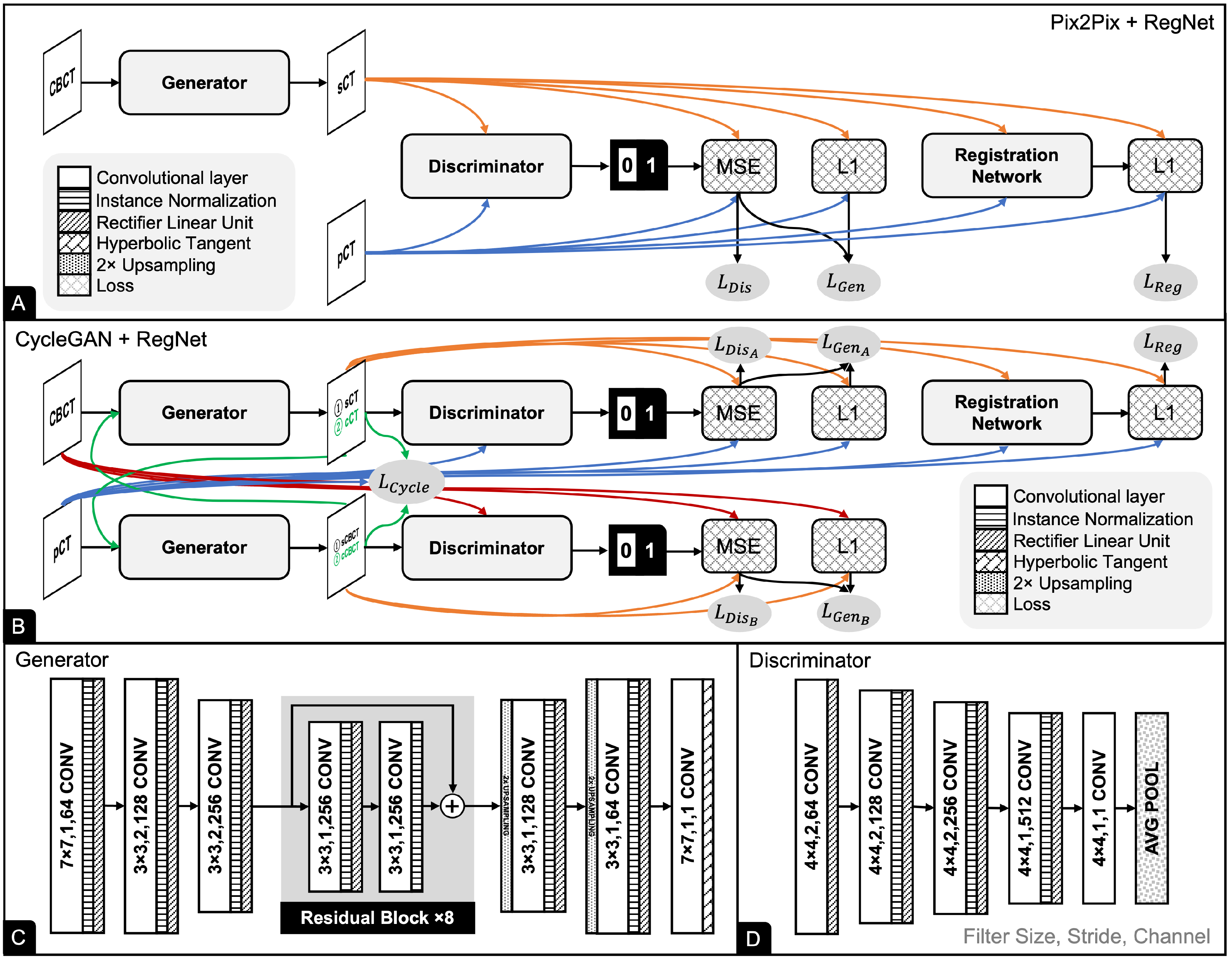
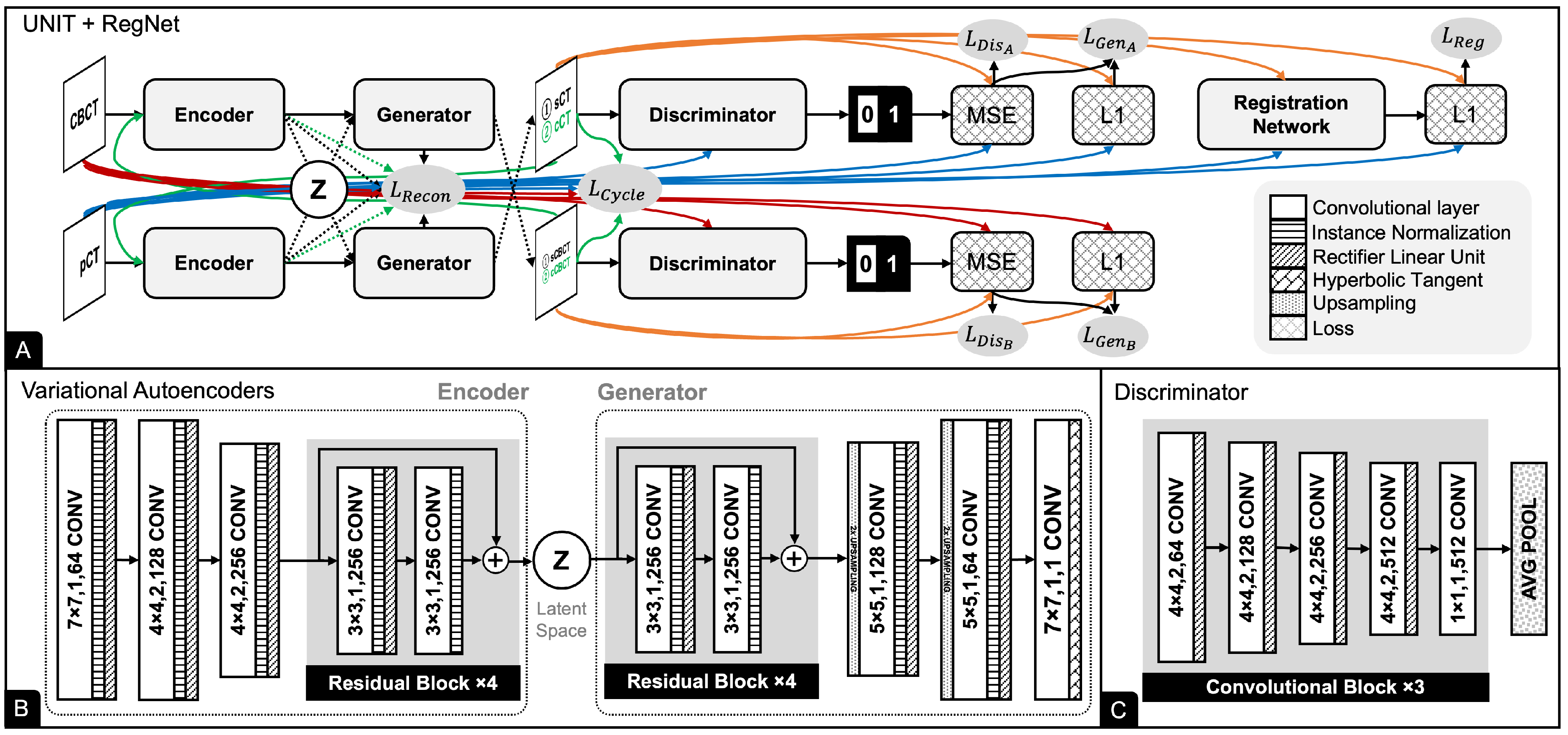
2.3. Registration Network
2.4. Pix2Pix
2.5. CycleGAN
2.6. UNIT
2.7. Network Training
2.8. Evaluation Procedures
3. Results
3.1. Image Quality Evaluation with Quantitative Metrics
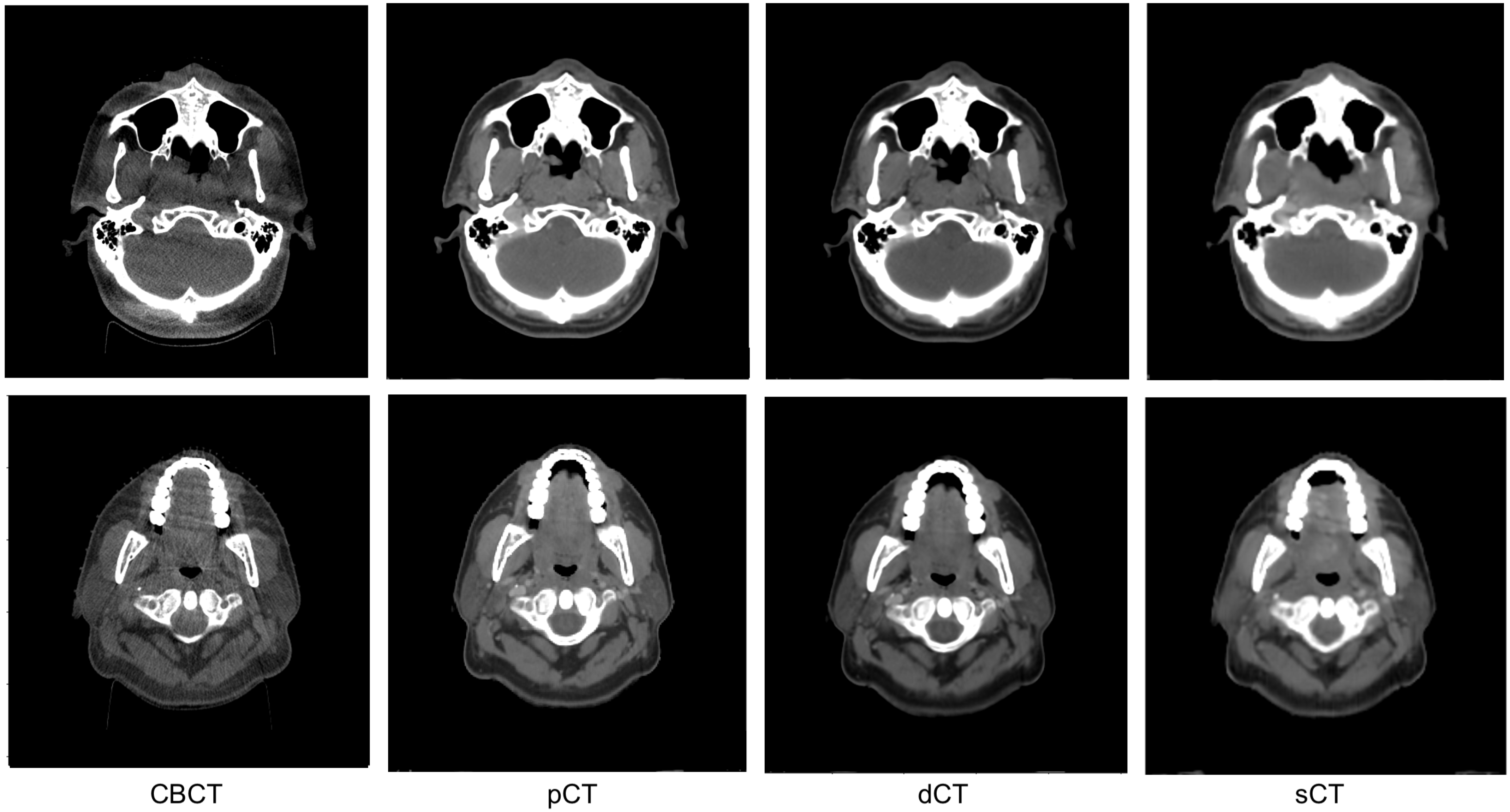
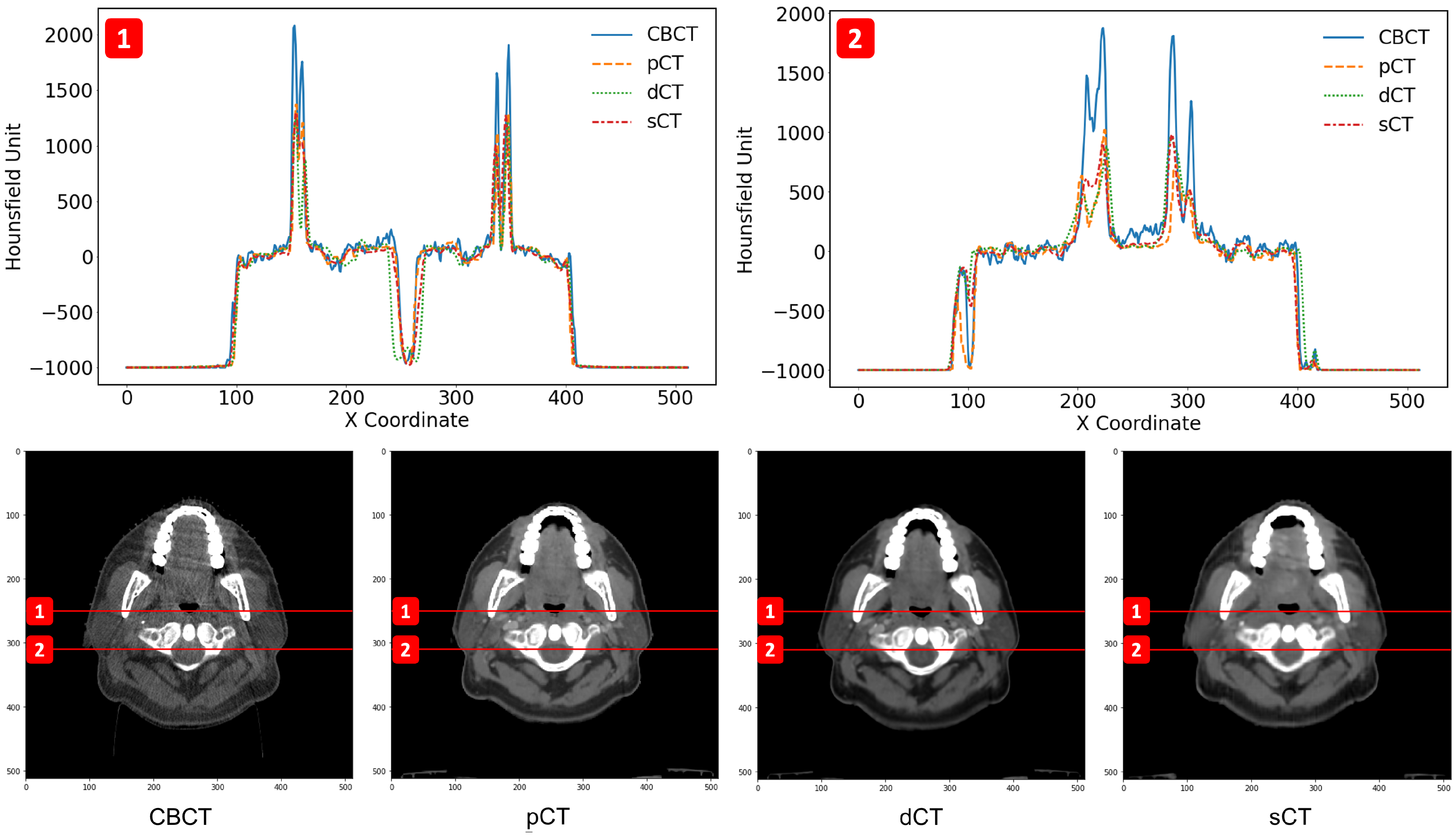
3.2. Image Quality Evaluation in Preserving Anatomy
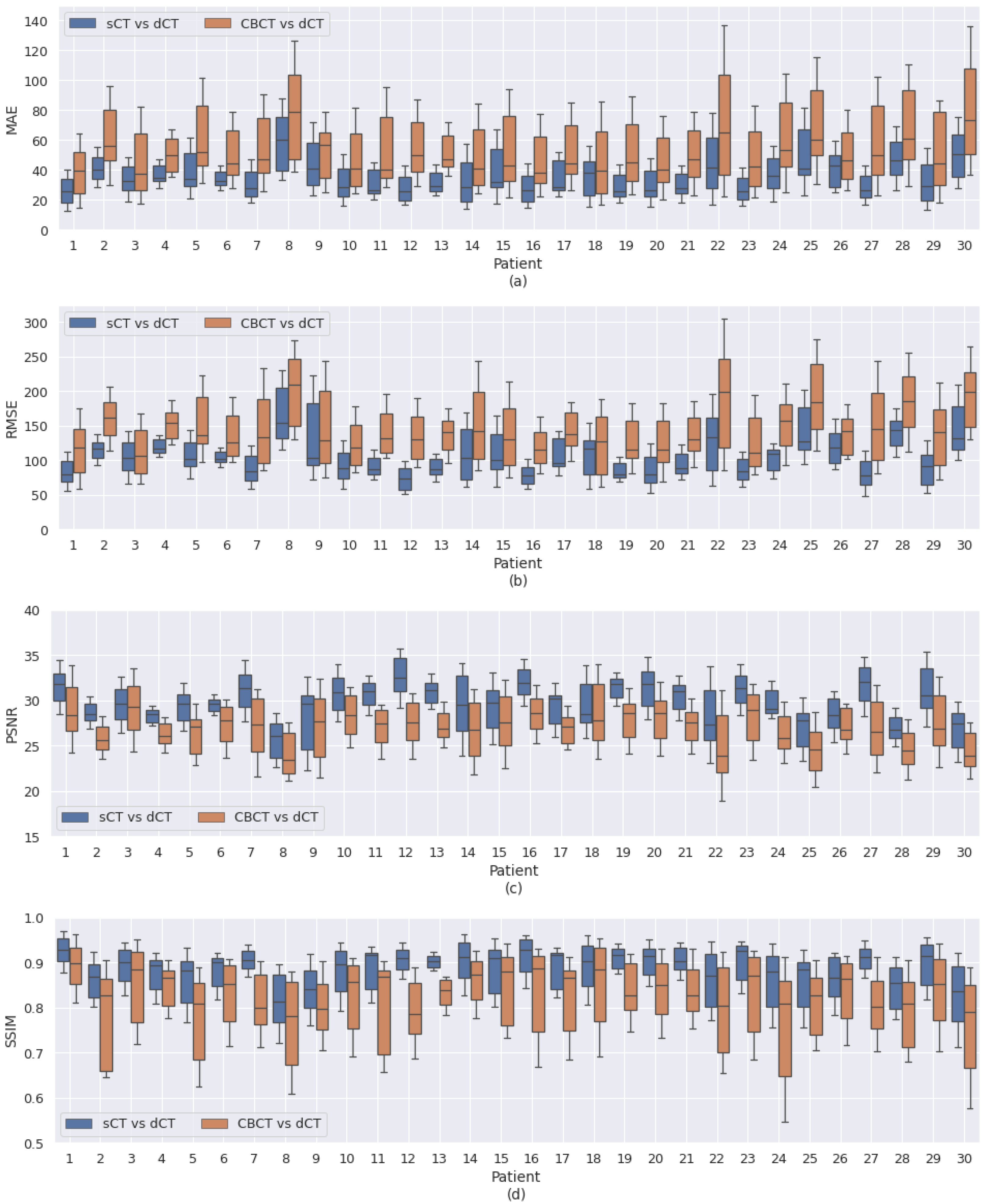
3.3. Patient-Specific Differences
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podgorsak, E.B. (Ed.) Radiation Oncology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Alterio, D.; Marvaso, G.; Ferrari, A.; Volpe, S.; Orecchia, R.; Jereczek-Fossa, B.A. Modern radiotherapy for head and neck cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2019, 46, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, R.; Grosshans, D. Proton therapy–present and future. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 109, 26–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonke, J.J.; Aznar, M.; Rasch, C. Adaptive radiotherapy for anatomical changes. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 29, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewan, A.; Sharma, S.; Dewan, A.; Srivastava, H.; Rawat, S.; Kakria, A.; Mishra, M.; Suresh, T.; Mehrotra, K. Impact of adaptive radiotherapy on locally advanced head and neck Cancer-a Dosimetric and volumetric study. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 17, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.M.; Daly, M.E.; Cui, J.; Mathai, M.; Benedict, S.; Purdy, J.A. Clinical outcomes among patients with head and neck cancer treated by intensity-modulated radiotherapy with and without adaptive replanning. Head Neck 2014, 36, 1541–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Vicini, F.; Wong, J.; Martinez, A. Adaptive radiation therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 1997, 42, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, C.L.; Steenbakkers, R.J.; Langendijk, J.A.; Sijtsema, N.M. Identifying patients who may benefit from adaptive radiotherapy: Does the literature on anatomic and dosimetric changes in head and neck organs at risk during radiotherapy provide information to help? Radiother. Oncol. 2015, 115, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutic, S.; Palta, J.R.; Butker, E.K.; Das, I.J.; Huq, M.S.; Loo, L.N.D.; Salter, B.J.; McCollough, C.H.; Dyk, J.V. Quality assurance for computed-tomography simulators and the computed-tomography-simulation process: Report of the AAPM Radiation Therapy Committee Task Group No. 66. Med. Phys. 2003, 30, 2762–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, S.; Kataria, T. Image Guidance in Radiation Therapy: Techniques and Applications. Radiol. Res. Pract. 2014, 2014, 705604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, K.; Mohammadi, M.; Shepherd, J. Applications of linac-mounted kilovoltage Cone-beam Computed Tomography in modern radiation therapy: A review. Pol. J. Radiol. 2014, 79, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poludniowski, G.G.; Evans, P.M.; Webb, S. Cone Beam Computed Tomography Number Errors and Consequences for Radiotherapy Planning: An Investigation of Correction Methods. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 84, e109–e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurz, C.; Nijhuis, R.; Reiner, M.; Ganswindt, U.; Thieke, C.; Belka, C.; Parodi, K.; Landry, G. Feasibility of automated proton therapy plan adaptation for head and neck tumors using cone beam CT images. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thing, R.S.; Bernchou, U.; Hansen, O.; Brink, C. Accuracy of dose calculation based on artefact corrected Cone Beam CT images of lung cancer patients. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 1, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, K.; Kadoya, N.; Kato, T.; Endo, H.; Komori, S.; Abe, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Wada, H.; Kikuchi, Y.; Takai, Y.; et al. Feasibility of CBCT-based proton dose calculation using a histogram-matching algorithm in proton beam therapy. Phys. Med. 2017, 33, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peroni, M.; Ciardo, D.; Spadea, M.F.; Riboldi, M.; Comi, S.; Alterio, D.; Baroni, G.; Orecchia, R. Automatic Segmentation and Online virtualCT in Head-and-Neck Adaptive Radiation Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 84, e427–e433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veiga, C.; Alshaikhi, J.; Amos, R.; Lourenço, A.M.; Modat, M.; Ourselin, S.; Royle, G.; McClelland, J.R. Cone-Beam Computed Tomography and Deformable Registration-Based “Dose of the Day” Calculations for Adaptive Proton Therapy. Int. J. Part. Ther. 2015, 2, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacometti, V.; King, R.B.; Agnew, C.E.; Irvine, D.M.; Jain, S.; Hounsell, A.R.; McGarry, C.K. An evaluation of techniques for dose calculation on cone beam computed tomography. Br. J. Radiol. 2019, 92, 20180383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, C.; Dedes, G.; Resch, A.; Reiner, M.; Ganswindt, U.; Nijhuis, R.; Thieke, C.; Belka, C.; Parodi, K.; Landry, G. Comparing cone-beam CT intensity correction methods for dose recalculation in adaptive intensity-modulated photon and proton therapy for head and neck cancer. Acta Oncol. 2015, 54, 1651–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Park, Y.K.; Sharp, G.; Busse, P.; Winey, B. Water equivalent path length calculations using scatter-corrected head and neck CBCT images to evaluate patients for adaptive proton therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 62, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurz, C.; Kamp, F.; Park, Y.K.; Zöllner, C.; Rit, S.; Hansen, D.; Podesta, M.; Sharp, G.C.; Li, M.; Reiner, M.; et al. Investigating deformable image registration and scatter correction for CBCT-based dose calculation in adaptive IMPT. Med. Phys. 2016, 43, 5635–5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalonde, A.; Winey, B.; Verburg, J.; Paganetti, H.; Sharp, G.C. Evaluation of CBCT scatter correction using deep convolutional neural networks for head and neck adaptive proton therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 245022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Shen, D.; Zhou, L. Medical Image Synthesis via Deep Learning. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1213, 23–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.04597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Chen, L.; Nguyen, D.; Zhou, Z.; Gu, X.; Yang, M.; Wang, J.; Jiang, S. Generating synthesized computed tomography (CT) from cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) using CycleGAN for adaptive radiation therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2019, 64, 125002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yue, N.; Su, M.Y.; Liu, B.; Ding, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Kuang, Y.; Nie, K. Improving CBCT quality to CT level using deep learning with generative adversarial network. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 2816–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maspero, M.; Houweling, A.C.; Savenije, M.H.F.; van Heijst, T.C.F.; Verhoeff, J.J.C.; Kotte, A.N.T.J.; van den Berg, C.A.T. A single neural network for cone-beam computed tomography-based radiotherapy of head-and-neck, lung and breast cancer. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 14, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kida, S.; Kaji, S.; Nawa, K.; Imae, T.; Nakamoto, T.; Ozaki, S.; Ohta, T.; Nozawa, Y.; Nakagawa, K. Visual enhancement of Cone-beam CT by use of CycleGAN. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, 998–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckl, M.; Hoppen, L.; Sarria, G.R.; Boda-Heggemann, J.; Simeonova-Chergou, A.; Steil, V.; Giordano, F.A.; Fleckenstein, J. Evaluation of a cycle-generative adversarial network-based cone-beam CT to synthetic CT conversion algorithm for adaptive radiation therapy. Phys. Med. 2020, 80, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, P.; Xu, K.; Wang, T.; Zheng, Q.; Yang, H.; Baydoun, A.; Zhu, J.; Traughber, B.; Muzic, R.F. Estimating CT from MR Abdominal Images Using Novel Generative Adversarial Networks. J. Grid Comput. 2020, 18, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, N.; Dyer, B.; Rao, S.; Chen, Q.; Benedict, S.; Shang, L.; Kang, Y.; Qi, J.; Rong, Y. Convolutional neural network enhancement of fast-scan low-dose cone-beam CT images for head and neck radiotherapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 035003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arar, M.; Ginger, Y.; Danon, D.; Leizerson, I.; Bermano, A.; Cohen-Or, D. Unsupervised Multi-Modal Image Registration via Geometry Preserving Image-to-Image Translation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.08073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Lian, C.; Huang, D.; Li, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, Q. Breaking the Dilemma of Medical Image-to-image Translation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.06465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, N.; Zhao, Z.; Fan, X.; Chang, E.I.C.; Xu, Y. MRI Cross-Modality Image-to-Image Translation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wei, J.; Li, R. Unsupervised Multi-Modal Medical Image Registration via Discriminator-Free Image-to-Image Translation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.13656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, G.; Zhao, A.; Sabuncu, M.R.; Guttag, J.; Dalca, A.V. VoxelMorph: A Learning Framework for Deformable Medical Image Registration. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 38, 1788–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.07004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation using Cycle-Consistent Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.10593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Ding, Y.; Shi, J.; Hao, X.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Wu, Y.; An, H.; Jiang, M.; Wei, W.; et al. Cone beam CT (CBCT) based synthetic CT generation using deep learning methods for dose calculation of nasopharyngeal carcinoma radiotherapy. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 20, 15330338211062415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lei, Y.; Wang, T.; Fu, Y.; Tang, X.; Curran, W.J.; Liu, T.; Patel, P.; Yang, X. CBCT-based synthetic CT generation using deep-attention cycleGAN for pancreatic adaptive radiotherapy. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, 2472–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kida, S.; Kaji, S.; Nawa, K.; Imae, T.; Nakamoto, T.; Ozaki, S.; Ohta, T.; Nozawa, Y.; Nakagawa, K. Cone-beam CT to planning CT synthesis using generative adversarial networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.05773. [Google Scholar]
- Hay, L.K.; Paterson, C.; McLoone, P.; Miguel-Chumacero, E.; Valentine, R.; Currie, S.; Grose, D.; Schipani, S.; Wilson, C.; Nixon, I.; et al. Analysis of dose using CBCT and synthetic CT during head and neck radiotherapy: A single centre feasibility study. Tech. Innov. Patient Support Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 14, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Characteristics | All | Training | Validation | Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients (N) | 146 | 95 | 21 | 30 |
| Sex (N) | ||||
| − Male | 108 | 68 | 18 | 22 |
| − Female | 38 | 27 | 3 | 8 |
| Age (Mean ± SD [Range]) | 54.3 ± 15.2 | 53.3 ± 15.1 | 58.4 ± 15.3 | 54.7 ± 15.4 |
| [11–89] | [11–87] | [23–85] | [22–89] | |
| Body Mass Index (Mean ± SD [Range]) | 21.7 ± 4.4 | 22.2 ± 4.3 | 20.2 ± 3.9 | 21.1 ± 4.8 |
| [12.7–37.9] | [12.7–34.0] | [13.9–30.5] | [15.6–37.9] | |
| Diagnosis site (N) | ||||
| − Oral cavity | 41 | 25 | 8 | 8 |
| − Nasopharynx | 49 | 41 | 5 | 3 |
| − Oropharynx | 15 | 6 | 3 | 6 |
| − Hypopharynx | 5 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| − Larynx | 10 | 4 | 1 | 5 |
| − Nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses | 18 | 9 | 3 | 6 |
| − Salivary gland | 3 | 3 | - | - |
| − Others | 5 | 5 | - | - |
| Pathology results (N) | ||||
| − Squamous cell carcinoma | 132 | 81 | 21 | 30 |
| − Others | 14 | 14 | − | − |
| TNM classification | ||||
| − Primary tumours | ||||
| ∘ T1 | 14 | 11 | 2 | 1 |
| ∘ T2 | 28 | 19 | 4 | 5 |
| ∘ T3 | 46 | 27 | 7 | 12 |
| ∘ T4 | 58 | 38 | 8 | 12 |
| − Regional lymph nodes | ||||
| ∘ N0 | 30 | 21 | 1 | 8 |
| ∘ N1 | 21 | 15 | 3 | 3 |
| ∘ N2 | 65 | 38 | 12 | 15 |
| ∘ N3 | 30 | 21 | 5 | 4 |
| − Metastasis | ||||
| ∘ M0 | 146 | 95 | 21 | 30 |
| ∘ M1 | − | − | − | − |
| Treatment | ||||
| − Concurrent chemoradiotherapy | 108 | 59 | 20 | 29 |
| − Post-operative radiotherapy | 26 | 26 | - | - |
| − Definitive radiotherapy | 12 | 10 | 1 | 1 |
| Period between pCT and CBCT in days | 16.7 ± 5.4 | 16.7± 5.4 | 16.3 ± 5.1 | 16.8 ± 5.8 |
| (Mean ± SD [Range]) | [4–31] | [4–31] | [7–30] | [5–29] |
| Comparison | MAE | RMSE | PSNR | SSIM |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBCT vs. pCT | 58.16 ± 25.17 | 160.40 ± 46.08 | 26.06 ± 2.44 | 0.8152 ± 0.0859 |
| CBCT vs. dCT | 55.78 ± 26.15 | 148.32 ± 51.36 | 26.89 ± 2.93 | 0.8168 ± 0.0876 |
| pCT vs. dCT | 35.84 ± 16.21 | 118.94 ± 39.30 | 28.76 ± 2.80 | 0.8938 ± 0.0483 |
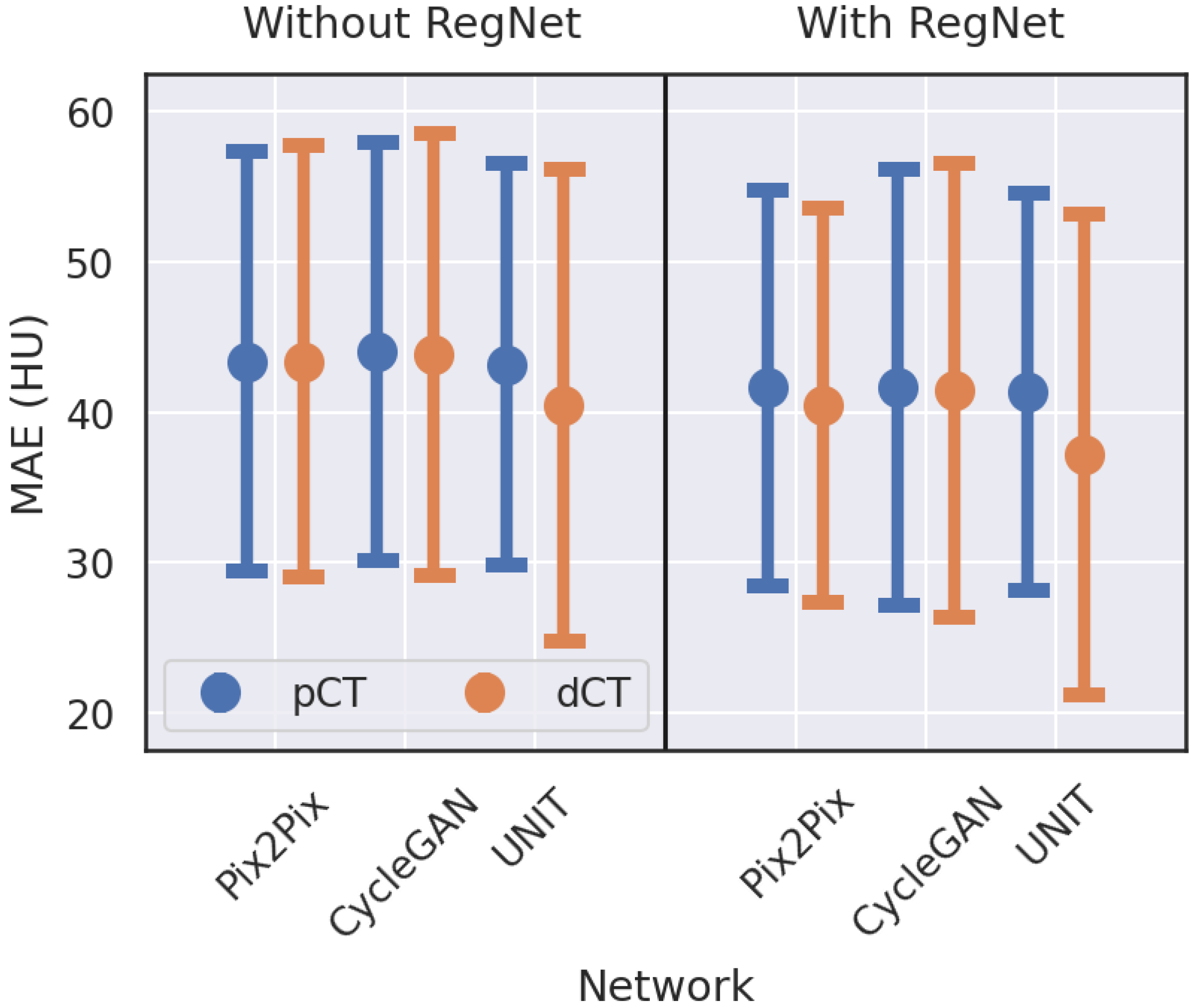
| Model | Target | RegNet | MAE | RMSE | PSNR | SSIM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pix2Pix | pCT | No | 43.39 ± 14.43 | 134.33 ± 31.40 | 27.48 ± 1.99 | 0.8479 ± 0.0542 |
| pCT | Yes | 41.62 ± 13.69 | 132.00 ± 34.96 | 27.71 ± 2.32 | 0.8578 ± 0.0513 | |
| dCT | No | 43.34 ± 14.81 | 133.32 ± 33.68 | 27.60 ± 2.23 | 0.8566 ± 0.0515 | |
| dCT | Yes | 40.46 ± 13.55 | 124.07 ± 31.22 | 28.20 ± 2.12 | 0.8635 ± 0.0467 | |
| CycleGAN | pCT | No | ||||
| pCT | Yes | |||||
| dCT | No | 43.87 ± 15.23 | 139.85 ± 35.30 | 27.18 ± 2.20 | 0.8527 ± 0.0473 | |
| dCT | Yes | 41.44 ± 15.53 | 124.67 ± 34.43 | 28.22 ± 2.38 | 0.8597 ± 0.0591 | |
| UNIT | pCT | No | ||||
| pCT | Yes | |||||
| dCT | No | 40.46 ± 16.21 | 119.45 ± 37.28 | 28.67 ± 2.62 | 0.8630 ± 0.0527 | |
| dCT | Yes | 37.21 ± 16.51 | 108.86 ± 38.13 | 29.55 ± 2.82 | 0.8791 ± 0.0547 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suwanraksa, C.; Bridhikitti, J.; Liamsuwan, T.; Chaichulee, S. CBCT-to-CT Translation Using Registration-Based Generative Adversarial Networks in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072017
Suwanraksa C, Bridhikitti J, Liamsuwan T, Chaichulee S. CBCT-to-CT Translation Using Registration-Based Generative Adversarial Networks in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers. 2023; 15(7):2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072017
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuwanraksa, Chitchaya, Jidapa Bridhikitti, Thiansin Liamsuwan, and Sitthichok Chaichulee. 2023. "CBCT-to-CT Translation Using Registration-Based Generative Adversarial Networks in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer" Cancers 15, no. 7: 2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072017
APA StyleSuwanraksa, C., Bridhikitti, J., Liamsuwan, T., & Chaichulee, S. (2023). CBCT-to-CT Translation Using Registration-Based Generative Adversarial Networks in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers, 15(7), 2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072017






